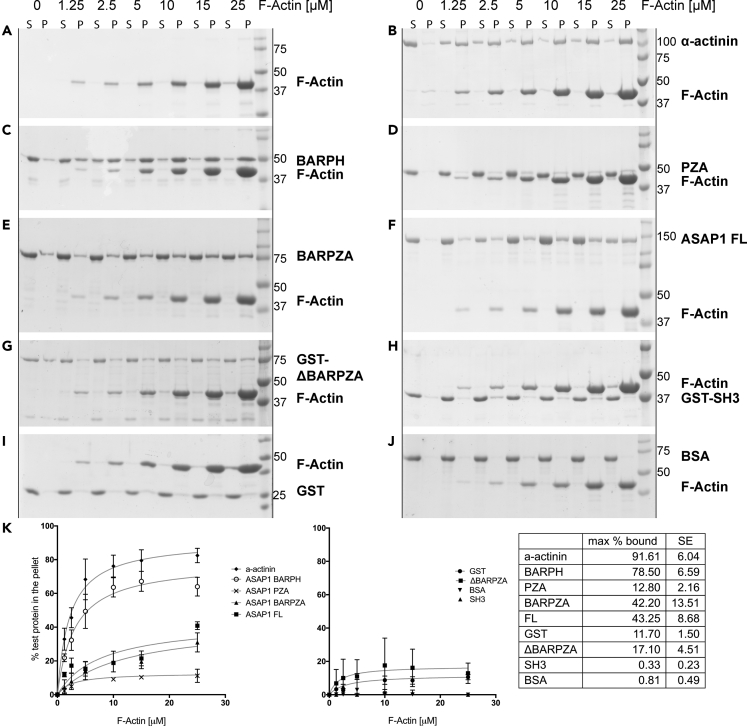
Figure 3.
ASAP1 Binds Directly to Actin Filaments through Its N-BAR Domain
(A–J) Purified recombinant ASAP1 full-length and domain fragments (2 μM) were subjected to high-speed co-sedimentation assay with the indicated concentrations (0–25 μM) of rabbit muscle F-actin. Actin filaments and filament-bound proteins (P, pellet) were separated from residual globular actin and unbound proteins (S, supernatant), resolved on single percentage (10 or 12%) SDS-PAGE, and stained with GelCode Blue. Co-sedimentation with BSA and GST (negative controls) and α-actinin (positive control) was performed in the same fashion. F-actin was titrated into solutions containing (A) no additional proteins, (B) α-actinin, (C) ASAP1 BAR-PH, (D) PZA, (E) BARPZA, (F) full-length ASAP1, (G) GST-ΔBARPZA, (H) GST-SH3, (I) GST, and (J) BSA. Gels are representative of at least three independent experiments.
(K) Summary of quantification of binding for 3 experiments. The extent of binding to actin was calculated as the percentage of total protein in the pellet, e.g., ASAP1 in P/(ASAP1 in P + ASAP1 in S) × 100%, and plotted against the concentration of actin. Data from three independent experiments were combined, and each point on the graph is a mean ± SEM. Table (right) summarizes the estimated % maximum bound of each test protein with standard error (SE) at saturating actin concentration.