Abstract
There is an urgent need for new effective antifungal agents suitable for the treatment of superficial skin infections, since acquired resistance of fungi to currently available agents is increasing. The antifungal activity of mono-floral Agastache honey and commercially available honeys were tested against dermatophytes (T. mentagrophytes and T. rubrum) and C. albicans (ATCC 10231 and a clinical isolate) by agar well diffusion and micro-dilution (AWD and MD). In AWD and MD assays, Agastache honey was effective at 40% concentration against dermatophytes (zone diameter, 19.5–20 mm) and C. albicans with the same MIC and MFC values indicating fungicidal activity. Tea tree honey was effective at 80% concentration (zone diameter, 14 mm) against dermatophytes and at 40% concentration against T. mentagrophytes and C. albicans. Manuka was effective at 80% concentration only against T. mentagrophytes (zone diameter, 12 mm) and at 40% against T. rubrum and C. albicans with fungistatic activity. Similar to the AWD results, Jelly bush, Super Manuka, and Jarrah showed no activity against dermatophytes but showed some activity against C. albicans. Headspace volatiles of six honeys were isolated by SPME and identified by GC-MS. The characteristic chemical markers for each honey were as follows: Agastache- Phenol, 2,4-bis(1,1-dimethylethyl) and Estragole; Manuka and Tea-tree- Acetanisole and Methyl 3,5-dimethoxybenzoate; Jelly bush- Linalool and Nonanal; Super Manuka- Methyl 3,5-dimethoxybenzoate and Nonanal; Jarrah- Isophorone and Nonanoic acid. Overall, analysis of the bioactive compound content and antifungal activity of Agastache honey indicated possible use as an antifungal agent for management of superficial fungal infections.
Subject terms: Antifungal agents, Fungi
Introduction
The health benefits of honey have been known for centuries and have recently gained acceptance in the modern medicine. Recently, honey has been reported to possess many biological properties including antimicrobial, antibiofilm, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and wound healing activities1–4. Furthermore, medical-grade honey has been used in wound dressing with the successful reduction of wound size5. An increase in resistance to currently available antifungal agents for skin-infections caused by C. albicans and the dermatophytes has also been reported6,7. Hence, development of new antifungal agents is important.
Honey is a viscous functional food which comprises 81% sugar, 17% water and 2% of other compounds. These compounds include non-volatile products such as enzymes, phenolic compounds and flavonoids as well as volatile compounds, all of which influence the pharmacological properties of honey. The antimicrobial activity of honey is chiefly due to hydrogen peroxide, the osmotic effect, pH and various phenolic compounds8,9. Larsen and White, (1995) reported that all 38 clinical isolates of Candida spp. examined were inhibited by hydrogen peroxide at pH 4 and pH 7 confirming the role of hydrogen peroxide10. Similar results were obtained by Carter et al.11. However, in addition to hydrogen peroxide, chemical compounds (volatile and semi-volatile) in honey play significant role in exerting biological activity12.
Volatile organic compounds of honey, responsible for its flavour and aroma, are mainly sourced from plant nectar. The volatile compound profile of any honey is specific to the plant species and geographical origin of the honey12. More than 600 volatile compounds have been isolated from honey. These compounds originate from different biosynthetic pathways and belong to different chemical families13. The composition and concentration of these compounds may vary to some extent between batches due to seasonal variation, even if the honey is sourced from a single flower (mono-floral honey). However, the composition of volatile compounds of mono-floral honeys is generally specific and characteristic of honey type whereas the composition of poly-floral honeys is more variable.
Honey contains the three categories of volatile compounds: terpenes, norisoprenoids and benzene derivatives14. Terpenes contain a chain of isoprene and can be categorized as monoterpenes, sesquiterpenes, diterpenes, triterpenes or tetraterpenes. The most common monoterpenes identified are linalool and its derivatives, β-terpineol, dihydrocitronellol, β-citronellol, citronellal, geranyl acetone, limonene, β-pinene, tetrahydrogeraniol, cavacrol, p-cymene, 1,8-cineol, camphor, isoborneol and p-cymenol12,15,16. Most of these compounds show activity against bacteria, viruses and fungi17. Norisoprenoids include α-isophorone, β-isophorone, β-damascenone and 4-oxoisophorone18. These compounds have radical scavenging capacity19. Benzene derivatives such as benzene acetaldehyde, benzaldehyde, and benzene ethanol are also present in honey20. Benzene derivatives identified in New Zealand Manuka and Kanuka honey include methyl 4, hydroxy-3, 5-dimethoxy benzoate and methyl 3, 4, 5-trimethoxy benzoate21.
The method used to extract volatiles can also determine the range of compounds identified. Methods of extraction include ultrasonic solvent extraction (USE), hydro-distillation (HD), liquid-liquid extraction (LLE), simultaneous steam distillation extraction (SDE), and solid phase extraction (SPE) with the help of solvents and heat. To eliminate the effects of toxic solvents, the preferred method of extraction is head space (HS) Solid Phase Micro-extraction (HS-SPME)22. The benefits of HS-SPME compared to other methods include short sample preparation time and ability to quantify a large number of molecules in a short space of time. Moreover, the fibres used for the extraction of volatiles are selective23. This method has been utilized to nominate specific chemical markers in honey from various parts of the globe. Some of the reported markers for honey are listed in Table 1.
Table 1.
Chemical markers assigned to honeys.
| Method Employed | Honey type | Floral Marker | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| HS-SPME GC-MS | Acacia honey | Cis-linalool oxide and heptanal | 70 |
| HS-SPME GC-MS | Chestnut honey | 2-aminoacetophenone, 1-phenylethanol | 71 |
| HS-SPME GC-MS | Lime-tree honey | Carvacrol and p-cymene | 72 |
| HS-SPME GC-MS | Eucalyptus honey | 2-hydroxy-5-methyl-3-hexanone, 3-hydroxy-5-methyl-2-hexanone | 62 |
| HS-SPME GC-MS | Citrus honey | limonyl alcohol, sinensal isomers, and α-4-dimethyl-3-cyclohexene-1-acetaldehyde | 63 |
| HS-SPME GC-MS | Ulmo honey | 4-vinylanisole, benzylaldehyde, ethyl benzoate, ethyl anisate, lyrame, linalool and damascenone | 56 |
Honeys with potent antibacterial activity may not necessarily have antifungal activity, for instance; Manuka honey has good antibacterial activity but weak activity against C. albicans and dermatophytes24. Therefore, it becomes necessary to test the efficacy of honeys known to have antimicrobial activity against common dermatophytes and C. albicans. Recently, we produced mono-floral honey from Agastache rugosa (Lamiaceae family) grown under controlled conditions and characterised its physicochemical properties and antioxidant capacities, antimicrobial activity and bioactive compounds3,25. A. rugosa (Lamiaceae family), a medicinal plant is commonly known as Korean Mint, is widely grown in the fields of Korea, China, and Japan. In traditional Chinese medicine, its leaves have been used to treat cholera, vomiting and miasma and have been reported to have antimicrobial, antifungal, antitumor and cytotoxic activities26–28. In addition to its use in traditional medicines, it is used as wild vegetable and cultivated commercially for use as a flavouring agent29. Hence, we hypothesize that at least some of the products derived from this plant have antifungal activity.
The aims of the present study were to (i) assess the antifungal activity of Agastache honey and important commercial honeys derived from Leptospermum species (New-Zealand Manuka honey, Australian Tea tree honey, Jelly bush honey, and Super manuka honey) and Australian Jarrah honey, (ii) Characterize the volatile compounds present in Agastache honey and flowers (containing nectar) (iii) Compare the volatile compound profile of Agastache honey with that of important commercial honeys (iv) Identify compounds in Agastache honey and other honeys with possible antifungal activity.
Results
Agar well diffusion assay (T. mentagrophytes and T. rubrum)
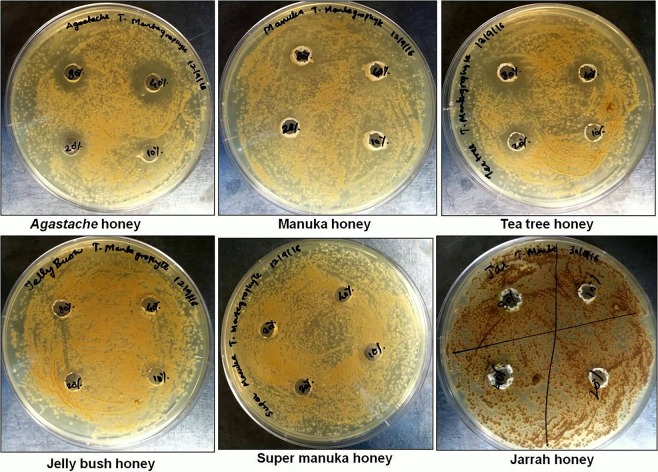
The antifungal activity of Agastache honey, Leptospermum-origin honeys and Jarrah honey was tested against T. mentagrophytes and T. rubrum by the well-diffusion assay. Table 2 shows the inhibition zone sizes produced by honey samples tested at different concentrations (80–10%). Agastache honey exhibited strong antifungal activity against both the isolates. The zone of inhibition of honey at various concentrations for Agastache honey against T. mentagrophytes ranged from 20 mm to 10 mm and against T. rubrum ranged from 19.5 to 12 mm. Manuka exhibited weak activity against T. mentagrophytes but showed no activity against T. rubrum. Tea tree honey exhibited moderate activity against both isolates with zones ranging from 11–14 mm against T. mentagrophytes and 12–14 mm against T. rubrum. Jelly bush, Super Manuka and Jarrah honey showed no activity against either isolate. The images depicting the zone of inhibition for honeys against both isolates are given below in Figs. 1 and 2.
Table 2.
Antifungal activity of honey at different concentrations, hydrogen peroxide content and major volatile compounds of honeys.
| Honey type | Honey source (species) | Agar well diffusion (zone size in mm) | Micro-dilution (MIC, % honey) | Hydrogen peroxide | Major volatile compounds | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trichophyton mentagrophytes | Trichophyton rubrum | Trichophyton mentagrophytes | Trichophyton rubrum | Candida albicans ATCC-10231 | Candida albicans clinical isolate | (µM) at 40% honey conc. | |||||||||
| 80% | 40% | 20% | 10% | 80% | 40% | 20% | 10% | ||||||||
| Agastache | Agastache Rugosa | 15 ± 0.5 | 20 ± 0.5 | 10 ± 0.3 | 0 | 16 ± 0.3 | 19.5 ± 0.4 | 12 ± 0.3 | 0 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 5.13 ± 2 | Phenol, 2,4-bis(1,1-dimethylethyl), Estragole and Nonanoic acid, ethyl ester |
| Manuka | Leptospermum scoparium | 12 ± 0.7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 0.04 ± 0.5 | Acetanisole, and Methyl 3,5-dimethoxybenzoate |
| Tea Tree | Leptospermum lanigerum & Leptospermum scoparium | 14 ± 0.5 | 12 ± 0.3 | 11 ± 0 | 0 | 14 ± 0.3 | 12 ± 0.4 | 0 | 0 | 40 | 0 | 40 | 40 | 155 ± 5.7 | Acetanisole, and Methyl 3,5-dimethoxybenzoate |
| Jelly Bush | Leptospermum polygalifolium | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 40 | 0 | 13.02 ± 0.5 | Linalool and Nonanal |
| Super Manuka | Leptospermum polygalifolium | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 41.30 ± 0.5 | Methyl 3,5-dimethoxybenzoate and Nonanal |
| Jarrah | Eucalyptus marginata | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 40 | 0 | 115 ± 9.1 | Isophorone and Nonanoic acid |
The antifungal activity of honey was assessed against dermatophytes and C. albicans. The hydrogen peroxide content of honeys was determined at a concentration of 40%. Data represent the mean of triplicate readings ± standard deviations (SD).
Figure 1.
Antifungal activity of honey against T. mentagrophytes determined by agar well diffusion. Honeys were tested in the range of 80–10% (w/v). Agastache honey exhibited the largest zone of inhibition at 40% concentration (20 mm) followed by tea-tree honey and Manuka honey at 80% concentration (14 mm and 12 mm, respectively).
Figure 2.
Antifungal activity of honey against T. rubrum determined by agar well diffusion. Honeys were tested in the range of 80–10% (w/v). Agastache honey exhibited the largest zone of inhibition at 40% concentration (19.5 mm) followed by tea-tree honey at 80% honey (14 mm).
Broth micro-dilution assay
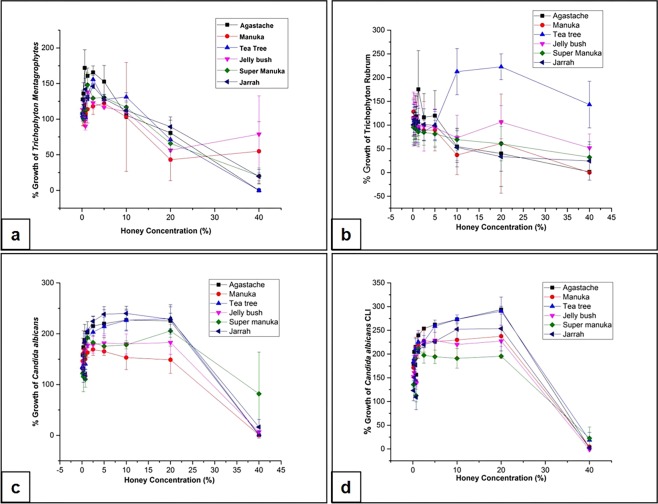
All honeys showed some antifungal activity in the broth dilution assay. The activity of six honeys against four fungal strains including clinical isolates varied, depending on the species and strain and the type of honey (Fig. 3a–d). In general, all honeys were more effective against C. albicans than against the two dermatophytes. The dermatophytes grew in the presence of lower concentrations of all honeys, as did T. rubrum in the presence of tea tree honey. However, at 40% honey concentration, all strains with the exception of T. rubrum/tea tree honey, showed some inhibition. Agastache honey was consistent in inhibiting growth of dermatophytes and yeasts at this honey concentration. The MIC and MFC values were the same for all the strains/isolates, indicating the fungicidal activity of honey. Among Leptospermum origin honeys, Manuka honey (40%) was effective against T. rubrum and C. albicans but only partially effective (45% inhibition) against T. mentagrophytes. Manuka honey showed only fungistatic activity. Tea tree honey (40%) inhibited the growth of T. mentagrophytes and C. albicans and exhibited fungicidal activity but was partially (50% inhibition) effective against T. rubrum and C. albicans clinical isolates. Other honeys such as Jelly bush (<50% inhibition), Super Manuka (60–70% inhibition), and Jarrah (75–80% inhibition) showed variable activity against dermatophytes whilst, Jelly bush and Jarrah showed only fungistatic against C. albicans clinical isolate.
Figure 3.
Antifungal activity of honeys measured by broth dilution. The graph shows the amount of growth (%) after exposure to honey at concentrations ranging from 0% to 40%. Agastache (square, black); Manuka (circle, red); Tea-tree (upwards triangle, blue); Jelly bush (downwards triangle, pink); Super Manuka (diamond, green); Jarrah (left triangle, navy) against T. mentagrophytes (a), T. rubrum (b), C. albicans ATCC 10231 (c) and a clinical isolate of C. albicans (d). Each point represents the mean of triplicate readings ± standard deviations (SD).
Statistical analysis showed that interaction between three parameters, honey concentration, honey type and fungal strains were significant and affected the growth of all fungal isolates/strains and the C. albicans reference strain (ATCC 10231). The main influence on activity was honey concentration, which explained 33% of the variation, fungal strain/isolate (25% of the variation), while honey concentration and fungal strain/isolate interaction explained 16% of variation (Table 3). The non-parametric Kruskal-Wallis test also showed that honey concentration had a significant effect on fungal growth (p = 0.001).
Table 3.
Analysis of variance (ANOVA) main effect of independent variables: tests of independent variables.
| Source | DF | Adj SS | Adj MS | F-Value | P-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Honey Concentration | 10 | 1261350 | 126135 | 154.60 | 0.001 |
| Honey Type | 6 | 78347 | 15669 | 19.21 | 0.001 |
| Fungal Strain | 4 | 981169 | 327056 | 400.86 | 0.001 |
|
Honey Concentration *Honey Type |
60 | 139183 | 2784 | 3.41 | 0.001 |
|
Honey Concentration *Fungal Strain |
40 | 611643 | 20388 | 24.99 | 0.001 |
| Honey Type*Fungal strain | 24 | 53907 | 3594 | 4.40 | 0.001 |
| Honey Concentration*Honey Type*Fungal strain | 240 | 224330 | 1496 | 1.83 | 0.001 |
| Error | 528 | 430784 | 816 | ||
| Total | 912 | 3780713 | |||
| S | R-sq | R-sq(adj) | R- sq(pred) | ||
| 28.56 | 88.61% | 82.93% | 74.36% |
Hydrogen peroxide concentrations in honeys
H2O2 concentrations ranged from 155 µM to 0.04 µM in the different honeys (Fig. 4). At 40% concentration tea tree honey produced the highest amount of hydrogen peroxide (155 µm), Jarrah and Super Manuka honey produced 115 µm and 41 µm of H2O2 whereas Manuka (0.04 µm), Jelly bush (13 µm) and Agastache (5.13 µm) produced low amounts of hydrogen peroxide.
Figure 4.
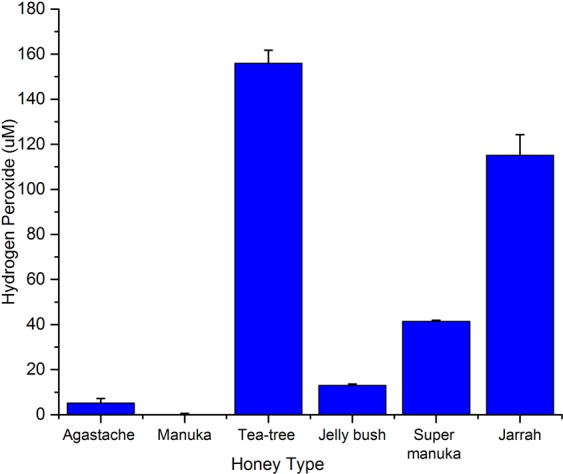
Effect of honey dilutions (40%) on the production of hydrogen peroxide (µM). Data represent the mean of triplicate readings ± standard deviations (SD).
Head space-solid phase microextraction gas chromatography-mass spectroscopy (HS-SPME GC-MS)
The volatile compounds in six honey samples were isolated by SPME and identified by GC-MS. Samples were analysed in three groups namely Agastache honey and Agastache flower, honeys derived from Leptospermum origin, and Jarrah honey. As replicates differed in the number of volatile compounds detected in each replicate, all three replicates were analysed. The number of common compounds found in all three replicates were; 32 in Agastache, 46 in Manuka, 26 in Tea-tree, 38 in Jelly bush, 38 in Super Manuka, 43 in Jarrah honey (Supplementary Tables S1–S6).
Volatile compounds in agastache honey
The important volatile compounds in Agastache honey were (% peak area): Phenol, 2,4-bis(1,1-dimethylethyl) (12.77%), Estragole (12.31%), Nonanoic acid, ethyl ester (7.22%), 2-Propenoic acid, 3-phenyl-, ethyl ester (6.32%), Hexadecanoic acid, ethyl ester (5.68%), Benzaldehyde, 4 methoxy (5.17%), β-Caryophyllene (4.67%), Nonanal (3.19%), and 2H-Benzimidazol-2-one, 1,3-dihydro-5-methyl- (2.34%). All identified volatile compounds are shown in the Fig. 5.
Figure 5.
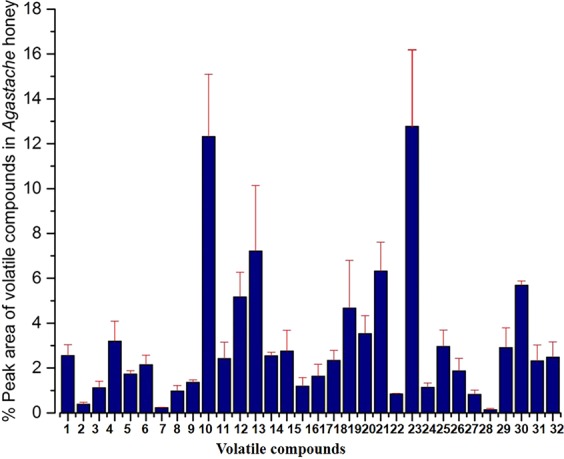
HS-SPME GC-MS volatile compounds identified in Agastache honey. Compounds were identified with GC-MS reference libraries (Adams, Wiley 7th and NIST 2.0) using a 70% similarity match cut-off value. The peak area in the total ion chromatograms was the basis of calculations of concentration of studied compounds. The error bar represents the mean of triplicate readings ± standard deviations (SD). 1-Benzaldehyde, 2-D-Limonene, 3-Benzeneacetaldehyde, 4-Nonanal, 5-Phenylethyl Alcohol, 6-1H-Pyrazole, 4,5-dihydro-5,5-dimethyl-4-isopropylidene-, 7-Cyclopentasiloxane, decamethyl-, 8-4,Ketoisophorone, 9-Octanoic acid, ethyl ester, 10-Estragole, 11-Decanal, 12-Benzaldehyde, 4-methoxy, 13-Nonanoic acid, ethyl ester, 14-Benzene, 1-methoxy-4-propyl, 15-Phenol, 2,3,5-trimethyl-, 16-Nonanoic acid, 17-Propanoic acid, 2-methyl-, 2-ethyl-3-hydroxyhexyl ester, 18-2H-Benzimidazol-2-one, 1,3-dihydro-5-methyl-, 19-β-Caryophyllene, 20-Benzoic acid, 4-methoxy-, ethyl ester, 21-2-Propenoic acid, 3-phenyl-, ethyl ester, 22-Y-cadinene, 23-Phenol, 2,4-bis(1,1-dimethylethyl), 24-Benzoic acid, 3,5-dimethoxy-, methyl ester, 25-Dodecanoic acid, ethyl ester, 26-Y-Eudesmol, 27-Heptadecane, 28-Homosalate, 29-Nonadecane, 30-Hexadecanoic acid, ethyl ester, 31-Heneicosane, 32-9,12-Octadecadienoic acid (Z,Z). Data represent the mean of triplicate readings ± standard deviations (SD).
Volatile compounds derived from honey of Leptospermum origin
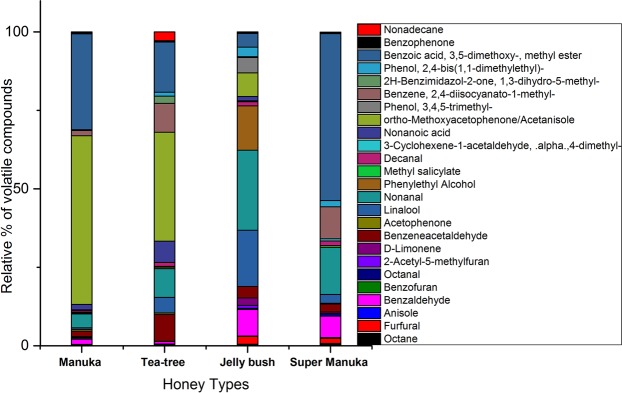
Many common compounds were observed in all honeys as shown in Fig. 6. The major volatile compounds detected in each honey were as follows; Manuka contained Acetanisole/ortho-Methoxyacetophenone (39%), Methyl 3,5-dimethoxybenzoate (26.67%), Anisole (4.34%), Nonanal (3.87%) and Ethanone, 1-(2-hydroxyphenyl) (1.29%), Tea-tree contained Acetanisole (31.3%), Methyl 3,5-dimethoxybenzoate (14.47%), 2,4-Diisosynato-1-methylbenzene (8.31%), Nonanal (8.25%), Benzene acetaldehyde (7.7%), Nonanoic acid (6.12%), Linalool (4.5%) and Nonanol (4.5%), Jelly bush contained Linalool (19.4%), Nonanal (12.4%), Methyl 3,5-dimethoxybenzoate (11.7%), α-Terpineol (9.16%), 3,4,5-trimethylphenol (7.82%), Benzaldehyde (6.75%), p-Cresol (4.34%), and ortho-Methoxyacetophenone (2.93%), Super Manuka contained Methyl 3,5-dimethoxybenzoate (40%), Nonanal (11.3%), 3,4,5-trimethylphenol (8.63%), 2,4-Diisosynato-1-methylbenzene (7.67%), Benzaldehyde (5.12%), 2,3,5-trimethylphenol (4.52%), and Anethole (2.94%).
Figure 6.
Detection of common volatile compounds by HS-SPME GC-MS in Leptospernum-origin honeys (Manuka, Tea-tree, Jelly bush and Super Manuka). Compounds were identified with GC-MS reference libraries (Adams, Wiley 7th and NIST 2.0) using a 70% similarity match cut-off value. The peak area in the total ion chromatograms was the basis of calculations of concentration of studied compounds. The relative % of common volatile compounds were calculated from the total peak area of the volatile compounds.
Of the 80 different species of Leptospermum origin native to Australia, honey was available from the following: Jelly bush, Super Manuka and Tea-tree honeys. Manuka is derived from Leptospermum genus found in New Zealand. The common major compounds were benzaldehyde, benzacetaldehyde, Linalool, Nonanal and Methyl 3, 5-dimethoxybenzoate. Acetanisole was the major marker compound found in Manuka and Tea tree, whilst it was detected in low amounts in Jelly bush and not in Super Manuka honey. Methyl 3,5-dimethoxybenzoate was detected in all honeys at variable percentages and can be described in the descending order as follows: Super Manuka > Manuka > Tea tree > Jelly bush. Linalool was the marker compound found in Jelly bush honey and a minor compound in Tea tree honey but was detected in trace amounts in other honeys. Benzene 2, 4-diisocynato-1-methyl was detected in Tea tree and Super manuka honey only. Nonanal was another common compound detected in all honeys at variable percentages, in the descending order: Jelly bush > Super Manuka > Tea tree > Manuka.
Volatile compounds in Jarrah honey
Jarrah tree (Eucalyptus marginata) is native to Western Australian. The major bioactive compounds in Jarrah honey were Isophorone (40.06%), Nonanoic acid (5.62%), 2, hydroxy 3, 5, 5-trimethyl-2 cyclohexenone (5.12%), and 2,4-Diisosynato-1-methylbenzene (3.75%) as shown in Fig. 7. Isophorone is the chemical marker compound which was identified only in this honey. Another major compound was Nonanoic acid which was also found in Jelly bush and Tea tree honey.
Figure 7.
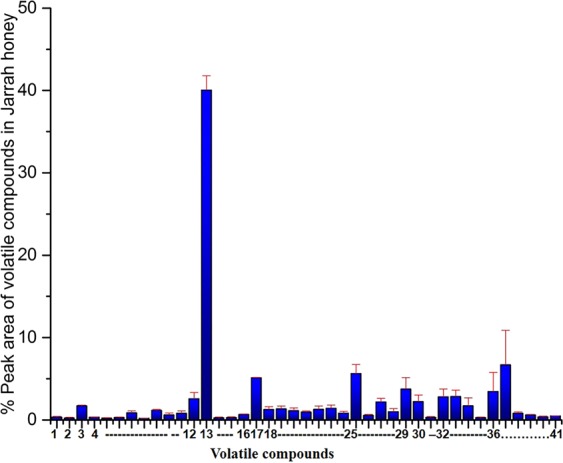
Volatile compounds identified in Jarrah honey by HS-SPME GC-MS. Compounds were identified with GC-MS reference libraries (Adams, Wiley 7th and NIST 2.0) using a 70% similarity match cut-off value. The peak area in the total ion chromatograms was the basis of calculations of concentration of studied compounds. The error bar represents the mean of triplicate readings ± standard deviations (SD). 1-Methane, thiobis-, 2-2-Butanone, 3-hydroxy-, 3-Acetyl valeryl, 4-(Z)-2-(Aminomethylene)-3,3-dimethylbutanenitrile, 5-4-Methyl-2-hexanol, 6-Benzaldehyde, 7-Cymene < Ortho > , 8-3-Cyclohexen-1-one, 3,5,5-trimethyl-, 9-Benzeneacetaldehyde, 10-Cymenene < Para- > , 11-Linalool, 12-Nonanal, 13-Isophorone, 14-Cyclopentasiloxane, decamethyl-, 15-Cyclohexanol, 4-(1-methylethyl), 16-Ethanone, 1-(1,4-dimethyl-3-cyclohexen-1-yl), 17-2-Hydroxy-3,5,5-Trimethyl-2-Cyclohexenone, 18-Octanoic Acid, 19-Terpineol < alpha- > , 20-Benzenemethanol, alpha., alpha, 4-trimethyl, 21-1,3-Cyclohexadiene-1-carboxaldehyde, 2,6,6-trimethyl, 22-Decanal, 23-Furan, 3-phenyl, 24-Cumin aldehyde, 25-Nonanoic acid, 26-Cymen-7-ol < Para- > 27-Thymol 28- Phenol, 2-methyl-5-(1-methylethyl) 29-Benzene, 2,4-diisocyanato-1-methyl, 30-Decanoic acid, 31-2-Propenoic acid, 3-phenyl- 32-2H-Benzimidazol-2-one, 1,3-dihydro-5-methyl- 33-9,9-dimethyl-9,-10-dihydroanthacene, 34-Pentadecane 35-Coumarin, 3,4-dihydro-4,4,7-trimethyl- 36-(+−)-(5,6,7,8-Tetrahydro-4-methyl-1-naphthalenyl)-1-ethanone 37-Benzoic acid, 3,5-dimethoxy-, methyl ester 38-Benzophenone 39-2-Cyclohexen-1-one, 3,5,5-trimethyl-4-(3-oxobutyl)- 40-1,2-Benzenedicarboxylic acid, bis(2-methylpropyl) ester, 41-Homo menthyl salicylate. Data represent the mean of triplicate readings ± standard deviations (SD).
Discussion
The most common dermatophytes causing skin infection in humans are T. mentagrophytes and T. rubrum30. Tinea pedis or athletes foot, tinea cruris or jock itch, tinea corporus or ringworm of the body (face, scalp, nail and hand) are the major infections caused by dermatophytes31. Candidiasis is most commonly caused by C. albicans. Currently, there are many anti-mycotic agents available over the counter and some have become only partially effective7. Moreover, some patients prefer to use natural products instead of commercially available antimycotic agents. Therefore, we evaluated honey as an alternative to available antifungal agents. The antifungal activity was assessed by two methods, agar well diffusion (AWD) and micro-dilution (MD).
Based on the AWD assay, Agastache honey was the most effective honey against T. mentagrophytes and T. rubrum, closely followed by Tea tree honey, with Manuka honey showing some activity. The other honeys examined (Jelly bush, Super Manuka, and Jarrah honeys) showed no activity in the AWD assay (Fig. 1, Table 2). The more sensitive MD assay reflected these results, with only Agastache honey showing inhibition against both dermatophytes at 40% concentration, while Tea tree honey and Manuka were active against T. mentagrophytes and T. rubrum respectively. The other honeys examined were less active or showed no anti-dermatophyte activity; indeed T. rubrum was able to grow in the presence of Tea tree honey (Table 2). The MIC and MFC values of Agastache honey against the two dermatophytes indicated fungicidal activity. Tea tree honey was also fungicidal, but only against T. mentagrophytes. No other honeys displayed fungicidal activity against the dermatophytes. The lower sensitivity of the AWD assay compared with MD could be explained by the need for the active components to diffuse across agar; however, AWD is considered to be an appropriate model to assess agents applied topically32. Furthermore, the observed zones of inhibition of honey at 80% for Agastache honey were smaller than at 40% concentration (Table 2). Generally, the production of hydrogen peroxide increases over the serial dilutions. However, for most of the honeys, accumulation of hydrogen peroxide is maximum at 30–50%33. Therefore, the inhibition size variation may be a result of less hydrogen peroxide production at highest concentration (80%).
In general C. albicans was more susceptible to all honeys than the dermatophytes (Fig. 3c,d), the only exception being Super Manuka honey that showed no activity against either Candida strain (Table 2). Only Tea tree honey showed fungicidal activity against C. albicans. The highest concentration of honey used for MIC determination in the present study was 40%. It is possible that honeys such as Jelly bush, Super Manuka and Jarrah might show activity at higher concentration. Notably, Agastache honey was effective at 40% concentration against both dermatophytes and both strains of C. albicans. The control antifungal, fluconazole failed to inhibit T. mentagrophytes in both assays but strongly inhibited T. rubrum (21 mm), as well as C. albicans, ATCC 10231 and a clinical isolate at a concentration of 128 µg/ml.
The few reports in the literature on antifungal activity of honey against dermatophytes and yeasts partially agree with the findings of the present study. Suhana et al.34 reported that Manuka honey (UMF 10+) has antifungal activity against C. albicans (25% v/v) and dermatophytes (50% v/v), while Brady et al.24 also reported activity of Manuka honey against T. mentagrophytes, although the zone of inhibition (18.4 mm) was wider than found in the current study (12 mm). Koc et al.35 found that fluconazole-resistant C. albicans required 40–80% (MIC values) concentration of Turkish honey (Rhododendron, Orange and Eucalyptus) for inhibition. Another honey, Jujube honey (Zizyphus spina-christi) was active against C. albicans ATCC 10231 at 40% (w/v) (MIC), with the MFC at 50%36. In another study, Carter et al.11 found that Manuka honey was less effective for treatment of fungal skin infections caused by C. albicans and dermatophytes than for bacterial skin infections. This finding was attributed the observation that Manuka honey lacks hydrogen peroxide, which is responsible for the antifungal activities of some honeys11,24. However, our results do not support this view since Agastache honey, which showed the most antifungal activity according to the assays we used, produced lower amounts of H2O2 (5.13 µm) than Jarrah and Super Manuka honeys (115 µm and 41 µm respectively), which displayed weak antifungal activity. On the other hand, Tea tree honey produced the highest amount of H2O2 (155 µM) and showed antifungal activity. These findings clearly indicate that other factors than H2O2 production, for example, volatile and phenolic compounds, contribute to the antifungal activity. In this study, therefore, we have identified volatile compounds in the honeys and their possible relation to the antifungal activity.
This study is the first to investigate and compare the volatile organic compounds of Agastache honey (greenhouse-produced, monofloral) with monofloral tea tree honeys sourced from different regions. The aroma and flavour of honey is influenced by its floral origin as well as honey bee species and processing and storage conditions37. Also, this is the first study to characterize volatile compounds in Agastache honey and compare the profile with data previously reported from our laboratory on the volatile compounds found in Agastache flowers (Yamani et al.)38. The major compounds identified (Fig. 5) in Agastache honey were Phenol, 2,4-bis(1,1-dimethylethyl) (12.77%), Estragole (12.31%), Nonanoic acid, ethyl ester (7.22%), 2-Propenoic acid, 3-phenyl-, ethyl ester (6.32%), Hexadecanoic acid, ethyl ester (5.68%), Benzaldehyde, 4 methoxy (5.17%), β-Caryophyllene (4.67%), Nonanal (3.19%), and 2H-Benzimidazol-2-one, 1,3-dihydro-5-methyl- (2.34%). Limonene was also detected (0.11%), whilst menthone, pulegone, methyl eugenol were detected in trace amounts, although not in all replicates.
In order to investigate the source of the volatile compounds in Agastache honey, we compared the findings of the present study with an earlier study from our laboratory38 which analyzed greenhouse-grown Agastache flowers, leaves and flowers with nectar for the presence of volatile compounds. In that study, the predominant volatile compounds present in were estragole, caryophyllene and D-limonene. Estragole was present in highest percentage in leaves (94.35%), flower (96.74%), and flower with nectar (97.16%). In contrast, our present findings that Agastache honey contained only 12.31% estragole suggests that the nectar contained only a low amount of the compound compared to flower and leaves. However, this needs to be further confirmed by analyzing volatile compounds of nectar separately. Jerković and Marijanović39,40 reported that the volatile compound composition of nectar, honey-sac and Satsuma Mandarin honey were significantly different. The authors suggested these differences could be due to hive conditions and bee-enzyme activity. Other compounds found in the flower nectar, such as Bicyclo undec-4-ene, 4,11,11-trimethyl-8-methylene- an isomer of caryophyllene (4.67%) and D-limonene (0.38%) were detected in Agastache honey confirming that major compounds of nectar were transferred to the honey. Estragole was also detected in Australian Super Manuka honey, but in low amounts (1.92%). Estragole was also identified as the most abundant compound in A. rugosa and A. foeniculum arial parts (18.6% to over 98%)41.
Other major compounds identified only in our Agastache honey could be the result of transformation of plant compounds by the metabolism of a bee, microbial and environmental contaminations12,40. The Agastache honey was produced in the greenhouse to ensure that bees forage onto the single flower species. However, the bees store their food inside the honey-sac, honey could be sourced from other plants before the hive was introduced into the glasshouse. Therefore, some compounds could be introduced from the different plant sources. Moreover, bees interact with plants trichome and carry loads of volatile compounds on the wings and transfer them into the honey. Considering different factors, the above-mentioned compounds were identified in the significant amount in samples, hence they can be nominated as chemical markers of Agastache honey.
The volatile compound profile of Agastache honey identified many antifungal compounds which could be correlated with the activity demonstrated in the present study. These include estragole, the major volatile component, which was effective against Trichophyton species, when used at 1.25 mg/ml concentration in combination with ketoconazole (12.5 µg/ml)42. In addition, phenol-2, 4-bis (1, 1-dimethylethyl) (100 µg/ml) has activity against Aspergillus indicated by reduction in the germ tube length and presence of an inhibition zone in agar dilution studies43. Moreover, 2, 4-di-tert-butylphenol (100 µg/ml) inhibited the growth of fungal cells and biofilm formation of C. albicans44.
Several studies have also reported that oils containing high concentrations of estragole have antifungal activity. For example, croton zehntneri oil, which contains 84.7% estragole produced significant zones of inhibition against fungi (C. albicans and B. dermatitidis)45. The essential oil extracted from Foeniculum vulgare, which contains a major fraction of estragole, demonstrated antifungal activity against C. albicans46. In addition, other components identified in Agastache honey in the present study were reported to have antifungal activity. For example, nonanoic acid, was identified as the antifungal compound in the roots of Hibiscus syriacus which has been used successfully to treat tinea pedis47. Moreover, 2-propenoic acid, 3-phenyl, ethyl ester (ethyl cinnamate) were effective against A. niger and C. albicans than E. coli and S. aureus48. Finally, ethyl cinnamate is also active against C. albicans49.
The study conducted by Kim J. H. reported that several benzaldehydes (such as 2-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzaldehyde, 2-hydroxy-5-methoxybenzaldehyde) have antifungal activity and structure-activity analysis revealed the presence of hydroxyl group increases the antifungal activity50. A promising class of bioactive heterocyclic compounds that exhibit a range of biological activities is benzimidazole. Khabnadideh S. studied the derivatives of benzimidazole (such as 1-Nonyl-1 H-benzo[d]imidazole and 1-Decyl-1 H-benzo[d]imidazole) and evaluated the antifungal activity against C. albicans and dermatophytes51.
As expected, there were differences in the major volatile compounds identified in the different honeys of Leptospernum origin (Table 2, Fig. 6). In agreement with other reports52–54 the major compound identified in Manuka honey was Acetanisole (O-Methoxyacetophenone). This compound was also observed in highest amount in Tea-tree honey (31.3%) but was present in only low amounts in Jelly bush honey and was absent in Super Manuka honey. These findings are consistent with the Leptospermum species origin of the various honeys; since Manuka honey and Tea-tree honey are derived or partially derived from Leptospermum scoparium, while Jelly bush and Super Manuka honeys are derived from Leptospermum polygalifolium.
In the present study, methyl 3,5-dimethoxybenzoate was identified for the first time in all Leptospermum-origin honeys; however, Kirkpatrick et al.55 detected methyl syringate as the characteristic antioxidant in Leptospermum-origin honeys, using GC-MS and HPLC, Methyl 3,5-dimethoxybenzoate could be formed due to a loss of an oxygen atom from methyl syringate. The percentages of this compound among total volatiles in the different honeys was as follows: Manuka (26.67%), Tea tree (14.47%), Jelly bush (11.7%) and Super Manuka (40%). Since Methyl 3,5-dimethoxybenzoate constituted the highest percentage of volatile compounds of Super Manuka honey it could be nominated as a chemical marker of the honey.
Nonanal was identified in all Leptospermum-origin honeys and has not been reported previously in Manuka honey. The concentrations of nonanal in the different honeys of Leptospermum-origin were as follows; Manuka (3.87%), Tea tree (8.25%), Jelly bush (12.4%) and Super Manuka (11.3%). It was reported to be present in Chilean Ulmo honey (7.97%)56. Also, as found in the present study, Jelly bush was reported to contain Cis-linalool and Nonanal52, which were nominated chemical markers for Jelly bush.
Several authors have reported on the anti-Candida albicans and antibacterial activity of compounds of Leptospermum origin that were identified in this study. These include Methyl 3,5-dimethoxybenzoate (Benzoic acid, 3,5-dimethoxy, methyl ester), which has activity against Candida albicans57. Linalool, the major component (54.4%) of the essential oil of Ocimum basilucum, had antimicrobial effects on eight bacteria and three fungi tested, giving inhibition zones ranging from 7 to 19 mm in agar dilution studies58. Acetanisole was found to be antimicrobial59. Nonanal was found to be antimicrobial against P. vulgaris when isolated from the olive oil60. The major compounds of Leptospermum honeys with bioactivity against C. albicans, lacked activity against dermatophytes. A correlation was clearly observed between the presence of antifungal compounds in honey samples and the activity shown in the present study.
The major compounds detected in Jarrah honey were Isophorone (40.06%) and Nonanoic acid (5.62%). Isophorone is an antioxidant19, which has been detected by others in three other Australian Eucalyptus honeys as well as Sunflower honey61. In contrast, Spanish Eucalyptus honeys contained two major chemical marker compounds (2-hydroxy-5-methyl-3-hexanone and 3-hydroxy-5-methyl-2-hexanone), but Isophorone was absent62. In another study, Fir, Thyme and Orange blossom honeys from Greece were reported to have Isophorone in significant amounts. The compound was detected in Spanish Citrus, Rosemary, Eucalyptus, Lavender, Thyme and Heather honeys as reported by63. In addition, Alpha Isophorone was identified in Corsican strawberry-tree honey and defined as a chemical marker for that honey. Jarrah honey is derived from Jarrah tree which belongs to Eucalyptus species. Other countries such as Italy, Spain, Portugal and Israel also produce Eucalyptus honey, but these have different tastes and aromas due to different floral varieties and climate conditions, which affect volatile compound composition. Isophorone has been declared floral marker for Heather honey64 and Ulmo Chilean honey13. Another major compound observed in the present study was Nonanoic acid. This compound was also detected in other Australian Eucalyptus honeys14.
In summary, Agastache honey (40%) exhibited antifungal activity against dermatophytes and C. albicans in both the AWD and MD assays. The activity was fungicidal. Tea-tree showed fungicidal activity against T. mentagrophytes and C. albicans, but activity against T. rubrum was less than activity against the other fungal species tested. Manuka honey was active against C. albicans and showed some activity against dermatophytes. The activity was only fungistatic. Jelly bush, Super Manuka and Jarrah showed no activity against dermatophytes, but Jelly bush and Jarrah showed some activity against C. albicans. The volatile compound of all honeys were analysed by HS-SPME-GC-MS. This is the first time the volatile compounds of Agastache honey have been reported and screened for compounds possibly responsible for antifungal activity. Agastache honey contained several volatile compounds which have been reported to have antifungal activity whereas other honeys contained few antifungal compounds confirming the higher antifungal activity of Agastache honey than other honeys. The source of the volatile compounds were elucidated by detecting same compounds in both honey and flower. The study also identified chemical markers in each honey and identified common compounds in honey samples from different origin, for instance Leptospermum origin honeys contained Methyl 3,5-dimethoxybenzoate and Nonanal at variable percentages (Fig. 6). Based on higher abundance in each honey, the nominated chemical marker for honeys were: Agastache- Phenol-2, 4-bis (1, 1-dimethylethyl), Estragole and Nonanoic acid, ethyl ester; Manuka and Tea tree-ortho-Methoxyacetophenone, and Methyl 3,5-dimethoxybenzoate; Jelly bush-Linalool and Nonanal; Super Manuka-Methyl 3,5-dimethoxybenzoate and Nonanal; Jarrah honey- Isophorone and Nonanoic acid. The present findings that Agastache honey has greater antifungal activity than Leptospermum honeys, suggests that Agastache honey products could be developed for the topical application against skin-infections caused by fungi. However, this needs to be further confirmed by assessing honey in-vivo studies.
Methods
Sample preparation
Mono-floral Agastache honey was produced in a closed glass house as described by Anand et al.3 Other commercial honey samples: Manuka honey (hnz, UMF 22+, Leptospermum scoparium, produced in New Zealand), Tea-tree honey (Miellerie, Leptospermum lanigerum & Leptospermum scoparium, produced in Tasmania, Australia), Jelly bush honey (Australia’s Manuka, 20 + Active, Leptospermum polygalifolium, produced in New South Wales, Australia), Super Manuka honey (Berringa, MGO-400, Leptospermum polygalifolium, produced in Queensland, Australia) and Jarrah honey (Elixir, TA 45 + Eucalyptus marginata, produced in Perth, Australia) were purchased from a local store.
Antifungal activity of honey
Two different methods were used to evaluate antifungal activity of honey: well-diffusion (dermatophytes), broth dilution (dermatophytes and C. albicans). The well-diffusion and micro-broth dilution methods were performed according to the guidelines of National Committee for Clinical Laboratories Standards65 and as described by the Alio S. et al.66.
Inoculum size preparation
A clinical isolate of C. albicans (obtained from nail infection, Dorevitch pathology, Melbourne) and a reference strain of C. albicans (ATCC 10231) were maintained on Sabouraud Dextrose Agar (SDA, Oxoid, Australia) plates at 4 °C and sub-cultured prior to each experiment. C. albicans was suspended in sterile RPMI 1640 (Sigma Chemicals, St Louis, MO) and turbidity was adjusted to 0.5 McFarland, then suspensions were further diluted 1:100. T. mentagrophytes and T. rubrum, obtained from RMIT culture collection, were sub-cultured on SDA plates and incubated at 28 °C for 7 to 15 days. Both isolates sporulated well after this period. Stock conidial suspensions were prepared by covering the fungal colonies with 5 ml of sterile MilliQ water and gently rubbing with the tip of a sterile pipette tip. The suspensions were collected in sterile centrifuge tubes, counted using a haemocytometer. Conidial suspensions were adjusted to the desired density by adding RPMI 1640 medium with 10 g/l glucose (Sigma Chemicals, St Louis, MO) without sodium bicarbonate, to obtain a final concentration of 2 × 104 to 6 × 104 CFU/ml in 0.165 mol/l MOPS buffer (Gibco, Grand Island, NY), pH 7.0. Conidial concentration was verified by plating 10 ul of the adjusted conidial suspensions on SDA plates.
Agar well diffusion assay
The agar well diffusion assay was used to assess the antifungal activity of T. mentagrophytes and T. rubrum. To perform the assay, SDA plates were flooded with 100 µl of RPMI media containing conidial suspensions (2 × 104 to 6 × 104 CFU/ml) of either T. mentagrophytes or T. rubrum and the suspensions were evenly spread. The plates were dried for 20 mins followed by punching four holes (10 mm) with a sterile cork borer at different sites. Diluted honey samples (80%, 40%, 20%, and 10% w/v) were placed in each well. Fluconazole was included as control. Fluconazole was dissolved in water and tested in the range of (128–0.05 ug/ml). Plates were allowed for pre-diffusion for 10–15 min before incubation at 28 °C for 7 days. The growth of dermatophytes was observed each day and diameters of zones of inhibition were recorded after 7 days.
Broth micro-dilution assay
The minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) and minimal fungicidal concentration (MFC) were determined for the honey samples against C. albicans and the two dermatophyte isolates according to the method described in Nature protocol67 with some modifications. The assays were performed in sterile, 96-well, flat-bottom, polystyrene microtiter plates (Corning Coster Ltd., NY). Briefly, C. albicans was streaked onto SDA plates and incubated for 24–48 hrs. Colony suspensions were prepared by touching 3–5 colonies with a sterile loop and transferring the inoculum into sterile 3–5 ml RPMI 1640. Turbidity was adjusted to 0.5 McFarland with sterile RPMI 1640, then suspensions were further diluted 1:100. Honey suspensions at variable concentrations (10%, 20%, 40% and 80%) were prepared in sterile RPMI, filtered through 0.45 µM filters and ten two-fold dilutions were made. Spore suspensions of the two dermatophytes were prepared as described in the previous section. 100 µl volumes of the diluted yeast or spore suspensions were inoculated into wells containing the honey dilutions resulting in the final inocula of ~5 × 105 cfu/ml C. albicans or 2 × 103 to 6 × 103 cfu/ml dermatophyte suspension.
Sterility controls containing media only and growth controls containing yeast/dermatophytes only were included in the assay. Inoculum size was validated by removing 10 µl volumes from the growth control well and performing viable counts. To control for the colour of different honey samples, OD600 measurements were taken at 0 hrs and after 24–48 hrs incubation at 37 °C in the dark. Growth of yeast in the presence of honey was assessed by the following formula: ODhoney treated wells/ODnegative control well × 100, where the control well was assigned 100% growth. To assess fungistatic activity, 10 µl samples from the first 2 wells containing no visible growth were plated onto the SDA plates and incubated for 24 hrs. The fungistatic end point was defined as the highest dilution showing growth inhibition. The fungicidal end point was defined as the highest dilution showing no growth on the inoculated plates. Since the hydrogen peroxide and glucose oxidase are light-sensitive, samples were incubated in the dark. All experiments were performed in triplicate.
Hydrogen peroxide assay
Honey dilution initiates the production of hydrogen-peroxide since the glucose oxidase, an enzyme present in honey, is inactive in undiluted honey. Honeys used in this study were diluted to 40% and the production of hydrogen peroxide were measured as described in the protocol of OxiSelect™ Hydrogen Peroxide Assay Kit (Fluorometric) (catalogue number STA-344, Cell Biolabs, VIC, Australia). The H2O2 concentrations in the samples were calculated from the standard curve obtained by testing H2O2 in the concentration range of 0 µM – 200 µM. A fluorescence micro plate reader (Omega BMG LabTech, Australia) was used with an excitation of 544 nm and an emission of 590 nm. Experiments were performed three times in duplicate.
HS-SPME/GC-MS analysis
Extraction of volatiles
The volatile compounds of honeys were determined according to the method described in Bianchi et al.68 with minor modifications. Briefly, honey samples (4 g) were dissolved in 2 ml of Milli Q water in a 10 ml vial hermetically capped with PTFE/silicon septum (Chromatographic Specialties Inc.). Diluted honey samples were equilibrated for 20 mins using a heating block and volatiles were extracted for 50 min at 60 °C. Samples were agitated by magnetic stirring to accelerate the transfer of analyte from the sample matrix to the coating fibre. An 85-µm polyacrylate (PA) fibre was fitted to the manual sampling fibre holder (Supelco, Bellefonte, PA). The precondition PA fibre (270 °C, 1 h) was inserted into the headspace of the vial containing the sample and vial was placed on the heating blocks. The extraction process was performed in triplicate.
Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry
The extracted volatiles were desorbed by placing the fibre into the gas chromatography injection port for 5 min. The identification of volatile compounds was performed as described by Yamani et al.38 using an Agilent 5973 MSD fitted with a DB-5 MS (5%-phenyl)-methylpolysiloxane fused silica column (Agilent) (30 m × 250 µm i.e. film thickness 0.25 µm). The analytical conditions were as follows; carrier gas helium (He 99.99%), flow rate 1.5 ml/min, split ratio 50:1. Initially, the oven temperature was 40 °C for 3 min, and it was raised later from 40 °C to 250 °C at 6 °C/min, where it was held for 5 min. The temperatures for injection port, transfer line and source temperatures were set at 250 °C, 280 °C, and 230 °C respectively. The samples were scanned in the mass range of 41–415 m/z as per Adams: Essential oil components by Quadrupole GC/MS69.
Spectra were acquired and processed using MSD ChemStation (E02.00.493). Compounds were identified with GC-MS reference libraries (Adams, Wiley 7th and NIST 2.0) using a 70% similarity match cut-off value. The peak area in the total ion chromatograms was the basis of calculations of concentration of studied compounds. The relative abundance was determined by integrating measurements obtained from three replicates.
Statistical analysis
Minitab 18 (MiniTab Inc., PA, USA) was used to compare the fungal growth after treatment with different concentrations of honey. Analysis of variance (ANOVA) was followed by post hoc Tukey test and Kruskal-Wallis (KW) tests. Each experiment was conducted in triplicate and data were calculated from three different experiments. Significance was accepted as p ≤ 0.05.
Supplementary information
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank George Livanos (Kenkay Pharmaceuticals) and David Hobday for their financial contributions to the project. David Hobday helped with production of Agastache honey. We would like to thank Helen Williams for arranging clinical isolates from Dorevitch Pathology, Melbourne. We would like to acknowledge Paul D. Morrison for technical assistance.
Author contributions
N.M., G.L. and E.P. conceptualized the project. S.A., N.M. and E.P. designed the experiments. S.A. performed all experiments. S.A., M.D., N.M. and E.P. analyzed the data. N.M., E.P. and G.L. contributed reagents, materials and analytical tools. S.A. wrote the draft manuscript. M.D., N.M., E.P. and G.L. reviewed and approved the final manuscript.
Competing interests
Author George Livanos was employed by company Kenkay Pharmaceuticals. All other authors declare no competing interests. Kenkay Pharmaceuticals partially funded this work through Australian Research Council’s Linkage Project scheme (Grant number LP120200743).
Footnotes
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Sushil Anand, Email: sush.anand@gmail.com.
Nitin Mantri, Email: nitin.mantri@rmit.edu.au.
Supplementary information
is available for this paper at 10.1038/s41598-019-54679-w.
References
- 1.Sojka Martin, Valachova Ivana, Bucekova Marcela, Majtan Juraj. Antibiofilm efficacy of honey and bee-derived defensin-1 on multispecies wound biofilm. Journal of Medical Microbiology. 2016;65(4):337–344. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.000227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Chakraborti, T., Barman, S. & Mandal, N. C. Original Research Article Evaluation of antibacterial potential of some Indian honey samples against throat and skin infective pathogens. 3, 362–369 (2014).
- 3.Anand, S., Pang, E., Livanos, G. & Mantri, N. Characterization of physico-chemical properties and antioxidant capacities of bioactive honey produced from australian grown agastache rugosa and its correlation with colour and poly-phenol content. Molecules23 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 4.Sell Scott A., Wolfe Patricia S., Spence Andrew J., Rodriguez Isaac A., McCool Jennifer M., Petrella Rebecca L., Garg Koyal, Ericksen Jeffery J., Bowlin Gary L. A Preliminary Study on the Potential of Manuka Honey and Platelet-Rich Plasma in Wound Healing. International Journal of Biomaterials. 2012;2012:1–14. doi: 10.1155/2012/313781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Lund-Nielsen Betina, Adamsen Lis, Kolmos Hans Jørn, Rørth Mikael, Tolver Anders, Gottrup Finn. The effect of honey-coated bandages compared with silver-coated bandages on treatment of malignant wounds-a randomized study. Wound Repair and Regeneration. 2011;19(6):664–670. doi: 10.1111/j.1524-475X.2011.00735.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Fisher Matthew C., Hawkins Nichola J., Sanglard Dominique, Gurr Sarah J. Worldwide emergence of resistance to antifungal drugs challenges human health and food security. Science. 2018;360(6390):739–742. doi: 10.1126/science.aap7999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Fuentefria A.M., Pippi B., Dalla Lana D.F., Donato K.K., de Andrade S.F. Antifungals discovery: an insight into new strategies to combat antifungal resistance. Letters in Applied Microbiology. 2017;66(1):2–13. doi: 10.1111/lam.12820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Kwakman PHS, Zaat SAJ. Antibacterial components of honey. IUBMB Life. 2012;64:48–55. doi: 10.1002/iub.578. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Nguyen Huong, Panyoyai Naksit, Kasapis Stefan, Pang Edwin, Mantri Nitin. Honey and Its Role in Relieving Multiple Facets of Atherosclerosis. Nutrients. 2019;11(1):167. doi: 10.3390/nu11010167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Larsen Bryan, White Sandra. Antifungal Effect of Hydrogen Peroxide on Catalase-Producing Strains of Candida spp. Infectious Diseases in Obstetrics and Gynecology. 1995;3(2):73–78. doi: 10.1155/S1064744995000354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Carter, D. A. et al. Therapeutic manuka honey: No longer so alternative. Frontiers in Microbiology, 10.3389/fmicb.2016.00569 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 12.Manyi-Loh Christy E., Ndip Roland N., Clarke Anna M. Volatile Compounds in Honey: A Review on Their Involvement in Aroma, Botanical Origin Determination and Potential Biomedical Activities. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2011;12(12):9514–9532. doi: 10.3390/ijms12129514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Manyi-Loh Christy E., Ndip Roland N., Clarke Anna M. Volatile Compounds in Honey: A Review on Their Involvement in Aroma, Botanical Origin Determination and Potential Biomedical Activities. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2011;12(12):9514–9532. doi: 10.3390/ijms12129514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Vázquez Lucía Castro, Díaz-Maroto M. Consuelo, Guchu Emilia, Pérez-Coello M. Soledad. Analysis of volatile compounds of eucalyptus honey by solid phase extraction followed by gas chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry. European Food Research and Technology. 2006;224(1):27–31. doi: 10.1007/s00217-006-0284-2. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Castro-Vázquez Lucia, Díaz-Maroto M. Consuelo, Pérez-Coello M. Soledad. Volatile Composition and Contribution to the Aroma of Spanish Honeydew Honeys. Identification of a New Chemical Marker. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 2006;54(13):4809–4813. doi: 10.1021/jf0604384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Peña Rosa M., Barciela Julia, Herrero Carlos, García-Martín Sagrario. Solid-phase microextraction gas chromatography-mass spectrometry determination of monoterpenes in honey. Journal of Separation Science. 2004;27(17-18):1540–1544. doi: 10.1002/jssc.200301705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Inouye S., Takizawa T., Yamaguchi H. Antibacterial activity of essential oils and their major constituents against respiratory tract pathogens by gaseous contact. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy. 2001;47(5):565–573. doi: 10.1093/jac/47.5.565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Bianchi Federica, Careri Maria, Musci Marilena. Volatile norisoprenoids as markers of botanical origin of Sardinian strawberry-tree (Arbutus unedo L.) honey: Characterisation of aroma compounds by dynamic headspace extraction and gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. Food Chemistry. 2005;89(4):527–532. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2004.03.009. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Gómez-Caravaca A.M., Gómez-Romero M., Arráez-Román D., Segura-Carretero A., Fernández-Gutiérrez A. Advances in the analysis of phenolic compounds in products derived from bees. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis. 2006;41(4):1220–1234. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2006.03.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Viuda-Martos Manuel, Ruiz-Navajas Yolanda, Zaldivar-Cruz Juan M., Kuri Victor, Fernández-López Juana, Carbonell-Barrachina Ángel A., Pérez-Álvarez JoséÁ. Aroma profile and physico-chemical properties of artisanal honey from Tabasco, Mexico. International Journal of Food Science & Technology. 2010;45(6):1111–1118. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2621.2010.02243.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Tan Seng To, Holland Patrick T., Wilkins Alistair L., Molan Peter C. Extractives from New Zealand honeys. 1. White clover, manuka and kanuka unifloral honeys. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 1988;36(3):453–460. doi: 10.1021/jf00081a012. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Cuevas-Glory Luis F., Pino Jorge A., Santiago Louis S., Sauri-Duch E. A review of volatile analytical methods for determining the botanical origin of honey. Food Chemistry. 2007;103(3):1032–1043. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2006.07.068. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Pontes M., Marques J.C., Câmara J.S. Screening of volatile composition from Portuguese multifloral honeys using headspace solid-phase microextraction-gas chromatography–quadrupole mass spectrometry. Talanta. 2007;74(1):91–103. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2007.05.037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Brady, N. F., Molan, P. C. & Harfoot, C. G. The sensitivity of dermatophytes to the antimicrobial activity of manuka honey and other honey. Pharm. Sci. 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1996.tb00540.x (1996).
- 25.Anand S, et al. Antimicrobial Activity of Agastache Honey and Characterization of Its Bioactive Compounds in Comparison With Important Commercial Honeys. Frontiers in Microbiology. 2019;10:263. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.00263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Shin S., Kang C.-A. Antifungal activity of the essential oil of Agastache rugosa Kuntze and its synergism with ketoconazole. Letters in Applied Microbiology. 2003;36(2):111–115. doi: 10.1046/j.1472-765X.2003.01271.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Hong Jung-Joo, Choi Jae-Hoon, Oh Sei-Ryang, Lee Hyeong-Kyu, Park Jae-Hak, Lee Kun-Yeong, Kim Jung-Jae, Jeong Tae-Sook, Oh Goo Taeg. Inhibition of cytokine-induced vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 expression; possible mechanism for anti-atherogenic effect of Agastache rugosa. FEBS Letters. 2001;495(3):142–147. doi: 10.1016/S0014-5793(01)02379-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Oh Hwa Min, Kang Young Jin, Kim Sun Hee, Lee Young Soo, Park Min Kyu, Heo Ja Myung, Sun Jin ji, Kim Hyo Jung, Kang Eun Sil, Kim Hye Jung, Seo Han Geuk, Lee Jae Heun, Yun-Choi Hye Sook, Chang Ki Churl. Agastache rugosa leaf extract inhibits the iNOS expression in ROS 17/2.8 cells activated with TNF-α and IL-1β. Archives of Pharmacal Research. 2005;28(3):305–310. doi: 10.1007/BF02977797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Jun H-J, et al. Nutrigenomic analysis of hypolipidemic effects of Agastache rugosa essential oils in HepG2 cells and C57BL/6 mice. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2010;19:219–227. doi: 10.1007/s10068-010-0030-1. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Patton Monica E., Workowski Kimberly A. Principles and Practice of Pediatric Infectious Diseases. 2018. Skin and Mucous Membrane Infections and Inguinal Lymphadenopathy; p. 353-357.e1. [Google Scholar]
- 31.Havlickova Blanka, Czaika Viktor A., Friedrich Markus. Epidemiological trends in skin mycoses worldwide. Mycoses. 2008;51:2–15. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0507.2008.01606.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Brady N, Molan P, Bang L. A survey of non-manuka New Zealand honeys for antibacterial and antifungal activities. Journal of Apicultural Research. 2004;43(2):47–52. doi: 10.1080/00218839.2004.11101109. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Bang Lynne M., Buntting Catherine, Molan Peter. The Effect of Dilution on the Rate of Hydrogen Peroxide Production in Honey and Its Implications for Wound Healing. The Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine. 2003;9(2):267–273. doi: 10.1089/10755530360623383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Suhana, S., Aisyah Sayadi, S. & Mohd Zohdi, R. Antifungal activity of selected Malaysian honeys: a comparison with Manuka honey. Journal of Coastal Life Medicine3 (2015).
- 35.Koc Ayşe Nedret, Silici Sibel, Ercal Bariş Derya, Kasap Filiz, Hörmet-Öz Hatice Tuna, Mavus-Buldu Hikmet. Antifungal Activity of Turkish Honey againstCandidaspp. andTrichosporonspp: anin vitroevaluation. Medical Mycology. 2009;47(7):707–712. doi: 10.3109/13693780802572554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Ansari, M. et al. Effect of Jujube Honey on Candida albicans Growth and Biofilm Formation. Archives of medical research44 (2013). [DOI] [PubMed]
- 37.Pattamayutanon Praetinee, Angeli Sergio, Thakeow Prodpran, Abraham John, Disayathanoowat Terd, Chantawannakul Panuwan. Volatile organic compounds of Thai honeys produced from several floral sources by different honey bee species. PLOS ONE. 2017;12(2):e0172099. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0172099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Yamani, H., Mantri, N., Morrison, P. D. & Pang, E. Analysis of the volatile organic compounds from leaves, flower spikes, and nectar of Australian grown Agastache rugosa. BMC Complement. Altern. Med., 10.1186/1472-6882-14-495 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 39.Jerković Igor, Marijanović Zvonimir. Screening of Volatile Composition ofLavandula hybridaReverchon II Honey Using Headspace Solid-Phase Microextraction and Ultrasonic Solvent Extraction. Chemistry & Biodiversity. 2009;6(3):421–430. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.200800074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Jerković Igor, Prđun Saša, Marijanović Zvonimir, Zekić Marina, Bubalo Dragan, Svečnjak Lidija, Tuberoso Carlo. Traceability of Satsuma Mandarin (Citrus unshiu Marc.) Honey through Nectar/Honey-Sac/Honey Pathways of the Headspace, Volatiles, and Semi-Volatiles: Chemical Markers. Molecules. 2016;21(10):1302. doi: 10.3390/molecules21101302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Zielińska Sylwia, Piątczak Ewelina, Kalemba Danuta, Matkowski Adam. Influence of plant growth regulators on volatiles produced by in vitro grown shoots of Agastache rugosa (Fischer & C.A.Meyer) O. Kuntze. Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture (PCTOC) 2011;107(1):161–167. doi: 10.1007/s11240-011-9954-2. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Shin Seungwon. Essential oil compounds fromAgastache rugosa as antifungal agents againstTrichophyton species. Archives of Pharmacal Research. 2004;27(3):295–299. doi: 10.1007/BF02980063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Rangel-Sánchez Gerardo, Castro-Mercado Elda, García-Pineda Ernesto. Avocado roots treated with salicylic acid produce phenol-2,4-bis (1,1-dimethylethyl), a compound with antifungal activity. Journal of Plant Physiology. 2014;171(3-4):189–198. doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2013.07.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Padmavathi Alwar Ramanujam, Bakkiyaraj Dhamodharan, Thajuddin Nooruddin, Pandian Shunmugiah Karutha. Effect of 2, 4-di-tert-butylphenol on growth and biofilm formation by an opportunistic fungusCandida albicans. Biofouling. 2015;31(7):565–574. doi: 10.1080/08927014.2015.1077383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.ANDRADE THALLITA C.B., LIMA SIDNEY G. DE, FREITAS RIVELILSON M., ROCHA MÁRCIO S., ISLAM TOREQUL, SILVA TERESINHA G. DA, MILITÃO GARDENIA C.G. Isolation, characterization and evaluation of antimicrobial and cytotoxic activity of estragole, obtained from the essential oil of croton zehntneri (euphorbiaceae) Anais da Academia Brasileira de Ciências. 2015;87(1):173–182. doi: 10.1590/0001-3765201520140111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Garzoli Stefania, Božović Mijat, Baldisserotto Anna, Sabatino Manuela, Cesa Stefania, Pepi Federico, Vicentini Chiara Beatrice, Manfredini Stefano, Ragno Rino. Essential oil extraction, chemical analysis and anti-Candidaactivity ofFoeniculum vulgareMiller – new approaches. Natural Product Research. 2017;32(11):1254–1259. doi: 10.1080/14786419.2017.1340291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Jang Yun-Woo, Jung Jin-Young, Lee In-Kyoung, Kang Si-Yong, Yun Bong-Sik. Nonanoic Acid, an Antifungal Compound from Hibiscus syriacus Ggoma. Mycobiology. 2012;40(2):145–146. doi: 10.5941/MYCO.2012.40.2.145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Narasimhan Balasubramanian, Belsare Deepak, Pharande Devayani, Mourya Vishnukant, Dhake Avinash. Esters, amides and substituted derivatives of cinnamic acid: synthesis, antimicrobial activity and QSAR investigations. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 2004;39(10):827–834. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2004.06.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Indupalli, M., Muvva, V., Mangamuri, U., Munaganti, R. K. & Naragani, K. Bioactive compounds from mangrove derived rare actinobacterium Saccharomonospora oceani VJDS-3. 3 Biotech, 10.1007/s13205-018-1093-6 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 50.Kim Jong H, Chan Kathleen L, Mahoney Noreen, Campbell Bruce C. Antifungal activity of redox-active benzaldehydes that target cellular antioxidation. Annals of Clinical Microbiology and Antimicrobials. 2011;10(1):23. doi: 10.1186/1476-0711-10-23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Khabnadideh, S., Rezaei, Z., Pakshir, K., Zomorodian, K. & Ghafari, N. Synthesis and antifungal activity of benzimidazole, benzotriazole and aminothiazole derivatives. Res. Pharm. Sci. (2012). [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 52.Beitlich Nicole, Koelling-Speer Isabelle, Oelschlaegel Stefanie, Speer Karl. Differentiation of Manuka Honey from Kanuka Honey and from Jelly Bush Honey using HS-SPME-GC/MS and UHPLC-PDA-MS/MS. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 2014;62(27):6435–6444. doi: 10.1021/jf501818f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Tan ST, Wilkins AL, Holland PT, McGhie TK. Extractives from New Zealand Honeys. 3. Unifloral Thyme and Willow Honey Constituents. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1990;38:1833–1838. doi: 10.1021/jf00099a010. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Daher Sawsan, Gülaçar Fazil O. Identification of New Aromatic Compounds in the New Zealand Manuka Honey by Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. E-Journal of Chemistry. 2010;7(s1):S7–S14. doi: 10.1155/2010/472769. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Kirkpatrick, G., Nigam, P. & Owusu-Apenten, R. Total Phenols, Antioxidant Capacity and Antibacterial Activity of Manuka Honey Chemical Constituents. Journal of Advances in Biology & Biotechnology15 (2017).
- 56.Acevedo Francisca, Torres Paulina, Oomah B. Dave, de Alencar Severino Matias, Massarioli Adna Prado, Martín-Venegas Raquel, Albarral-Ávila Vicenta, Burgos-Díaz César, Ferrer Ruth, Rubilar Mónica. Volatile and non-volatile/semi-volatile compounds and in vitro bioactive properties of Chilean Ulmo ( Eucryphia cordifolia Cav.) honey. Food Research International. 2017;94:20–28. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2017.01.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.ARAI MASAYOSHI, TOMODA HIROSHI, OKUDA TAKAKO, WANG HAIYAN, TABATA NORIKO, MASUMA ROKURO, YAMAGUCHI YUICHI, OMURA SATOSHI. Funicone-related Compounds, Potentiators of Antifungal Miconazole Activity, Produced by Talaromyces flavus FKI-0076. The Journal of Antibiotics. 2002;55(2):172–180. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.55.172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Duman, A. D. et al. Evaluation of bioactivity of linalool-rich essential oils from Ocimum basilucum and Coriandrum sativum varieties. Nat. Prod. Commun. Commun. 10.1002/vnl (2010). [PubMed]
- 59.BOWLES B.L., SACKITEY S.K., WILLIAMS A.C. INHIBITORY EFFECTS OF FLAVOR COMPOUNDS ON STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS WRRC B124. Journal of Food Safety. 1995;15(4):337–347. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-4565.1995.tb00144.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Kubo Aya, Lunde Christopher S., Kubo Isao. Antimicrobial Activity of the Olive Oil Flavor Compounds. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 1995;43(6):1629–1633. doi: 10.1021/jf00054a040. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Guyot Christine, Scheirman Vincent, Collin Sonia. Floral origin markers of heather honeys: Calluna vulgaris and Erica arborea. Food Chemistry. 1999;64(1):3–11. doi: 10.1016/S0308-8146(98)00122-8. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 62.de la Fuente Esther, Valencia-Barrera Rosa M., Martínez-Castro Isabel, Sanz Jesús. Occurrence of 2-hydroxy-5-methyl-3-hexanone and 3-hydroxy-5-methyl-2-hexanone as indicators of botanic origin in eucalyptus honeys. Food Chemistry. 2007;103(4):1176–1180. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2006.10.020. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Castro-Vázquez L., Díaz-Maroto M.C., González-Viñas M.A., Pérez-Coello M.S. Differentiation of monofloral citrus, rosemary, eucalyptus, lavender, thyme and heather honeys based on volatile composition and sensory descriptive analysis. Food Chemistry. 2009;112(4):1022–1030. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.06.036. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 64.DELAFUENTE E, SANZ M, MARTINEZCASTRO I, SANZ J, RUIZMATUTE A. Volatile and carbohydrate composition of rare unifloral honeys from Spain. Food Chemistry. 2007;105(1):84–93. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2007.03.039. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Clsi. Reference Method for Broth Dilution Antifungal Susceptibility Testing of Filamentous Fungi; Approved Standard — Second Edition. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) (2009).
- 66.Alió S A. B., Mendoza M., Zambrano E. A., Díaz E., Cavallera E. Dermatophytes growth curve andin vitrosusceptibility test: a broth micro-titration method. Medical Mycology. 2005;43(4):319–325. doi: 10.1080/13693780500092947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Wiegand I, Hilpert K, Hancock REW. Agar and broth dilution methods to determine the minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) of antimicrobial substances. Nat. Protoc. 2008;3:163–175. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2007.521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Bianchi F., Mangia A., Mattarozzi M., Musci M. Characterization of the volatile profile of thistle honey using headspace solid-phase microextraction and gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. Food Chemistry. 2011;129(3):1030–1036. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2011.05.070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Adams, R. Identification of Essential Oil Components by Gas Chromatography/Quadrupole Mass Spectroscopy. Carol Stream16 (2005).
- 70.Radovic B.S., Careri M., Mangia A., Musci M., Gerboles M., Anklam E. Contribution of dynamic headspace GC–MS analysis of aroma compounds to authenticity testing of honey. Food Chemistry. 2001;72(4):511–520. doi: 10.1016/S0308-8146(00)00263-6. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Piasenzotto Lara, Gracco Luisa, Conte Lanfranco. Solid phase microextraction (SPME) applied to honey quality control. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture. 2003;83(10):1037–1044. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.1502. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Lušić, D., Koprivnjak, O., Ćurić, D., Sabatini, A. G. & Conte, L. S. Volatile profile of croatian lime tree (Tilia sp.), fir honeydew (Abies alba) and sage (Salvia officinalis) honey. Food Technol. Biotechnol. (2007).
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.