Abstract
Purpose
Left ventricular (LV) wall thickness can be measured at the posterior wall (PW) and the intraventricular septum (IVS) in a parasternal long axis view by transthoracic echocardiography. Thus, there are three methods to calculate relative wall thickness as follows: RWTPW = 2 × PWth/LVDd; RWTIVS + PW = (IVSth + PWth) /LVDd; and RWTIVS = 2 × IVSth/LVDd (IVSth = interventricular septum thickness; LVDd = LV internal dimension at end--diastole; PWth = posterior wall thickness). The aim was to compare the prognostic values of these RWTs in patients with acute decompensated heart failure (ADHF).
Method
This was a single-center, retrospective, observational study at a Japanese community hospital. A total of 389 hospitalized ADHF patients were divided into two groups based on the three median RWT values. The primary outcome was all-cause death. Survival analysis was performed, and Cox proportional hazard models unadjusted and adjusted by Get With The Guideline score were used.
Results
High-RWTPW had poor survival (log-rank, P = 0.009) and was a significant risk (unadjusted HR (95%CI), 1.72 (1.14–2.61), P = 0.01; adjusted HR, 1.95 (1.28–2.98), P = 0.02). High-RWTIVS + PW was not associated with poor survival on survival analysis or the unadjusted Cox model. Only the adjusted Cox model showed that High-RWTIVS + PW was associated with a significant risk of the primary outcome (unadjusted HR (95%CI), 1.45 (0.96–2.17), P = 0.07; adjusted HR, 1.53 (1.01–2.32), P = 0.045). High-RWTIVS did not have significant prognostic value.
Conclusions
When calculating RWT, RWTPW should be recommended for evaluating the mortality risk in ADHF.
Keywords: Concentric left ventricular structure, Relative wall thickness, Acute decompensated heart failure, Transthoracic echocardiography, Prognosis
Introduction
A concentric left ventricular (LV) structure is the result of remodeling that occurs with LV wall thickening relative to the LV cavity to compensate for pressure overload [1, 2]. A concentric LV structure is a risk factor for cardiovascular events in hypertensive patients [3, 4]. Furthermore, we previously reported that a concentric LV structure evaluated by transthoracic echocardiography (TTE) was associated with poor survival in patients with acute decompensated heart failure (ADHF) [5].
Relative wall thickness (RWT) is an index of LV concentricity. RWT is the ratio of LV wall thickness to the LV internal dimension at end diastole (LVDd) [6]. LV wall thickness, which can be measured in a parasternal long-axis view by TTE, is represented by the Interventricular septum wall thickness (IVSth) and the posterior wall thickness (PWth) [6]. Therefore, there are three methods to calculate the RWT: RWTPW = 2 × PWth/LVDd; RWTIVS + PW = (IVSth + PWth) LVDd; and RWTIVS = 2 × IVSth/LVDd. The American Society of Echocardiography (ASE) recommends RWTPW for calculating RWT [6]. However, some studies found that RWTIVS + PW had clinical significance [7, 8]. The difference in clinical significance among the three methods of measuring RWT is unclear.
To compare the clinical significance of RWTPW, RWTIVS + PW, and RWTIVS, the prognostic values of the RWTs were examined and compared in patients with ADHF.
Materials and methods
Participants
This was a single-center, retrospective, observational study conducted at a Japanese community hospital. In total, 426 consecutive patients admitted due to ADHF through the clinic or emergency room were recruited between June 2014 and April 2016 and followed-up from June 2014 to September 2016. A total of 41 patients were excluded for any of the following reasons: no TTE on admission (n = 35); and RWT not measured (n = 6). Finally, 385 patients were eligible for the analysis (Fig. 1). We previously documented the enrolled patients in detail [5].
Fig. 1.
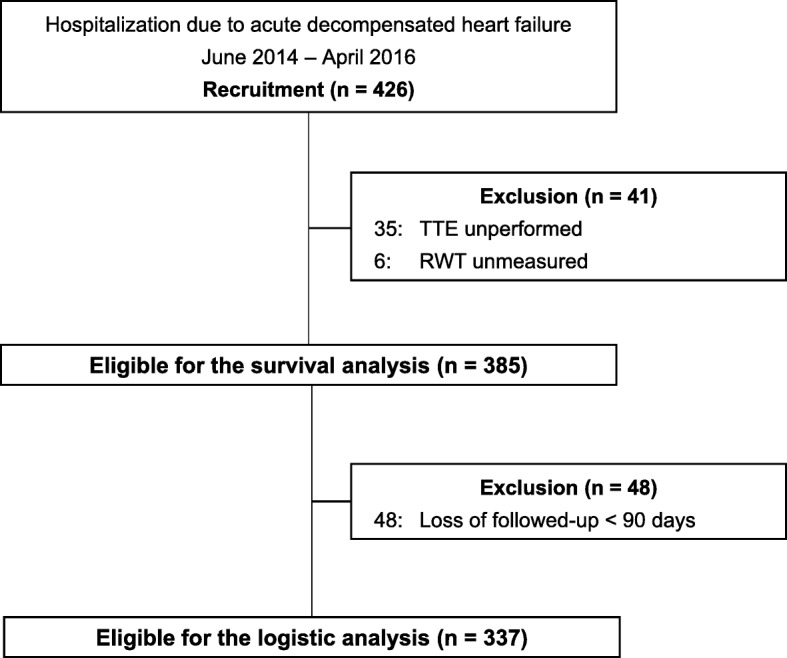
Flowchart of enrollment. RWT, relative wall thickness; TTE, transthoracic echocardiography
The present study followed the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki and the Ethical Guidelines for Medical and Health Research Involving Human Subjects proposed by the Ministry of Health and Welfare in Japan. The institutional ethics committee at Tomishiro Central Hospital approved the present study and waived informed consent because of the observational nature of the study.
Transthoracic echocardiography
Comprehensive TTE (Vivid 7 ultrasound system, GE Vingmed Ultrasound, Horten, Norway) was performed during hospital admission by four medical technicians who had at least 5 years of experience performing TTE. Their measurements followed established and standardized methods recommended by the ASE and the European Society of Cardiology. At least two attending cardiologists certified by the Japanese Circulation Society and an experienced sonographer reviewed the echocardiography reports immediately after comprehensive TTE. LV geometry, including PWth, IVSth, and LVDd, was measured in M-mode in a parasternal long-axis view [6]. All measurements were performed from the leading edge to the leading edge [6]. RWTs were calculated by the three measurement methods and defined as follows: RWTPW = 2 × PWth/LVDd; RWTIVS + PW = (IVSth + PWth)/LVDd; and RWTIVS = 2 × IVSth/LVDd. The patients were divided into two groups based on the median RWTPW (low- and high-RWTPW), median RWTIVS + PW (low- and high-RWTIVS + PW), or median RWTIVS (low- and high-RWTIVS).
Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) was assessed using the biplane Simpson’s method [6]. Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) was defined as an ejection fraction ≥50% [9]. LV mass was computed by the Cube formula [6]. LV end-diastolic volume (LVEDVI) was estimated by the Teichholz equation [10]. Peak transmitral early diastolic wave (E wave) velocity, atrial contraction wave (A wave) velocity, and deceleration time (DCT) were measured by the pulse wave Doppler signals of the mitral inflow in the apical four-chamber view [11]. Valvular diseases were evaluated using a semiquantitative 4-grade scale (none, mild, moderate, and severe) [12].
Data collection
Cardiologists followed the patients at Tomishiro Central Hospital Clinic every 1–3 months after hospital discharge. Medical clerks confirmed the patients’ condition if the patients canceled the appointment.
Patients’ medical charts were reviewed to collect their demographic characteristics and clinical data, including medications, laboratory tests, and hemodynamic data on hospital admission. The primary outcome was all-cause death. Death was confirmed by the medical chart, telephone call with a patient’s family, or obituary in local newspapers.
Statistical analysis
Continuous variables with normal and skewed distributions are presented as means (SD) and medians [25th, 75th percentiles], respectively. Categorical variables are presented as numbers with a percentage.
In two-group comparisons, Student’s t-test and the Mann-Whitney U test were used to compare normally distributed and non-normally distributed continuous variables, respectively. Fisher’s exact test was used for categorical variables.
Survival analysis
During follow-up (235 [92, 425] days), 95/385 (25%) patients died. Survival analysis for all-cause death was performed. Kaplan-Meier curves were stratified by RWTPW, RWTIVS + PW, and RWTIVS. The log-rank test was used to compare survival curves. High-RWTPW, high-RWTIVS + PW, and high-RWTIVS were examined by univariate Cox proportional hazard models and a Cox proportional hazard model adjusted by the Get With The Guideline score (GWTG) [13, 14], an established risk score for mortality in patients with acute heart failure, to obtain hazard ratios (HRs) and 95% confidence intervals (95% CIs).
Logistic regression model for 90-day mortality
A total of 48 patients who were lost to follow-up were excluded to evaluate the risk of 90-day mortality. Logistic regression models were used to obtain the odds ratios (ORs) of 90-day mortality and 95% CIs. High-RWTPW, high-RWTIVS + PW, and high-RWTIVS were examined in univariate logistic regression models and a logistic regression model adjusted by GWTG.
Receiver operating curves for 90-day mortality
Receiver operating curves for 90-day mortality were drawn using RWTPW, RWTIVS + PW, and RWTIVS to obtain c-statistics, and the best RWT cut-off values were determined by the maximum Youden index [15].
Sensitivity analysis of the survival analysis by stratified RWTs by the best cut-off
To confirm the consistency of the survival analysis, the participants were divided based on the best RWT cut-off value derived from the Youden index.
Survival analysis was performed to compare low and high-RWTs. High-RWTPW, high-RWTIVS + PW, and high-RWTIVS were also examined with univariate and adjusted proportional Cox hazard models.
Relationships between RWTs and clinical characteristics
Spearman’s correlation coefficient (ρ) was used to identify significant associations between RWTs and clinical characteristics: age, the natural logarithm of brain natriuretic peptide (logBNP), LVEF, LVEDV, and systolic blood pressure (SBP).
Reliability of measurement of PWth and IVSth
The reliabilities of the TTE measurements of PWth, IVSth, and LVDd were examined in 25 patients whose TTE image quality was good, and all of the patients underwent TTE performed by the same one of four medical technicians. The medical technician and two other examiners re-measured PWth and IVSth in the TTE image stored in the local server on hospital admission, using an off-line image analysis system (Nahri Aqua, Mehergen Group, Fukuoka, Japan). Comparing every two examiners’ measurements, Bland-Altman plots were used to assess the agreement between the measurement by the same examiner and different examiners [16]. The inter-class coefficient (ICC) was computed to assess agreement [17].
The reliabilities of RWTPW, RWTIVS + PW, and RWTIVS were also examined. RWTs were computed using PWth, IVSth, and LVDd measured by three examiners. Bland-Altman plots were drawn, and the ICC and P values were calculated.
Software
The statistical software used was R 3.4.3 (R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Australia). All reported P values are two-tailed, and a P value < 0.05 was considered significant.
Results
Participants
The participants’ median age was 81 years, and there were 181/385 (47%) men in the overall population. Comparing low- and high-RWTPW, high-RWTPW had more elderly patients and more females, whereas in comparisons between low- and high-RWTIVS + PW and between low- and high-RWTIVS, there were no significant differences in baseline characteristics (Table 1).
Table 1.
Demographic data and echocardiographic parameters
| Overall | RWTPWb | RWTIVS + PWb | RWTIVSb | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low | High | P value | Low | High | P value | Low | High | P value | ||
| n = 385 | n = 193 | n = 192 | n = 193 | n = 192 | n = 193 | n = 192 | ||||
| Age, y | 81 [70, 88] | 80 [68, 87] | 83 [73, 89] | 0.021 | 80 [69, 87] | 83 [73, 89] | 0.067 | 80 [69, 87] | 83 [73, 88] | 0.082 |
| Mele, n (%) | 181/385 (47) | 104/193 (54) | 77/192 (40) | 0.008 | 99/193 (51) | 82/192 (43) | 0.1 | 98/193 (51) | 83/192 (43) | 0.15 |
| Height, cm | 154 ± 10 | 156 ± 9.7 | 153 ± 9.9 | 0.002 | 155 ± 10 | 153 ± 10 | 0.048 | 155 ± 10 | 153 ± 10 | 0.15 |
| Body weight., kg | 60 ± 16 | 60 ± 15 | 60 ± 17 | 0.95 | 61 ± 15 | 59 ± 17 | 0.45 | 60 ± 16 | 59 ± 16 | 0.59 |
| Body mass index, kg/m2 | 22.8 ± 4.6 | 22.6 ± 4.5 | 23.0 ± 4.8 | 0.42 | 22.8 ± 4.6 | 22.8 ± 4.7 | 0.99 | 22.9 ± 4.7 | 22.8 ± 4.6 | 0.87 |
| Body surface area, m2 | 1.51 ± 0.22 | 1.53 ± 0.22 | 1.49 ± 0.23 | 0.11 | 1.53 ± 0.22 | 1.50 ± 0.23 | 0.2 | 1.52 ± 0.22 | 1.50 ± 0.22 | 0.3 |
| Get With The Guideline score | 38 ± 7 | 38 ± 6 | 38 ± 8 | 0.99 | 38 ± 7 | 38 ± 8 | 0.55 | 38 ± 7 | 38 ± 8 | 0.86 |
| Hospital stay, days | 13 [8, 20] | 13 [8, 21] | 12 [8, 19] | 0.55 | 13 [8, 21] | 12 [8, 19] | 0.35 | 13 [8, 20] | 12 [8, 19] | 0.76 |
| Past medical history, n (%) | ||||||||||
| Hypertension | 187/385 (49) | 92/193 (48) | 95/192 (50) | 0.76 | 92/193 (48) | 95/192 (50) | 0.76 | 93/193 (48) | 94/192 (49) | 0.92 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 132/385 (34) | 68/193 (35) | 64/192 (33) | 0.75 | 75/193 (39) | 57/192 (30) | 0.068 | 80/193 (42) | 52/192 (27) | 0.004 |
| Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease | 18/385 (4.7) | 7/193 (3.6) | 11/192 (5.7) | 0.35 | 7/193 (3.6) | 11/192 (5.7) | 0.35 | 8/193 (4.1) | 10/192 (5.2) | 0.64 |
| Old myocardial infarction | 62/385 (16) | 37/193 (19) | 25/192 (13) | 0.13 | 35/193 (18) | 27/192 (14) | 0.33 | 34/193 (18) | 28/192 (15) | 0.49 |
| Echocardiographic parameters | ||||||||||
| RWTPWa | 0.36 ± 0.12 | 0.28 ± 0.05 | 0.45 ± 0.12 | < 0.001 | 0.28 ± 0.05 | 0.44 ± 0.12 | < 0.001 | 0.30 ± 0.07 | 0.43 ± 0.13 | < 0.001 |
| RWTIVS + PWa | 0.37 ± 0.13 | 0.29 ± 0.06 | 0.45 ± 0.12 | < 0.001 | 0.28 ± 0.05 | 0.46 ± 0.12 | < 0.001 | 0.29 ± 0.06 | 0.46 ± 0.12 | < 0.001 |
| RWTIVSa | 0.38 ± 0.14 | 0.30 ± 0.09 | 0.46 ± 0.15 | < 0.001 | 0.29 ± 0.06 | 0.48 ± 0.14 | < 0.001 | 0.28 ± 0.06 | 0.48 ± 0.13 | < 0.001 |
| IVSth, mm | 9.4 ± 2.4 | 8.5 ± 2.0 | 10.4 ± 2.4 | < 0.001 | 8.1 ± 1.8 | 10.7 ± 2.2 | < 0.001 | 7.9 ± 1.5 | 11.0 ± 2.1 | < 0.001 |
| PWth, mm | 9.0 ± 2.1 | 7.8 ± 1.3 | 10.3 ± 2.0 | < 0.001 | 8.1 ± 1.4 | 10 ± 2.2 | < 0.001 | 8.3 ± 1.6 | 9.8 ± 2.3 | < 0.001 |
| LVDd, mm | 52 ± 9.7 | 57.1 ± 8.8 | 46.8 ± 7.8 | < 0.001 | 57.7 ± 8.2 | 46.2 ± 7.6 | < 0.001 | 57 ± 8.8 | 46.8 ± 7.8 | < 0.001 |
| LVEF, (%) | 47 ± 17 | 41 ± 16 | 51 ± 16 | < 0.001 | 39 ± 16 | 52 ± 16 | < 0.001 | 40 ± 16 | 51 ± 16 | < 0.001 |
| HFpEF (LVEF ≥ 50%), n (%) | 157/383 (41) | 56/193 (29) | 101/190 (53) | < 0.001 | 47/193 (24) | 110/190 (58) | < 0.001 | 50/193 (26) | 107/190 (56) | < 0.001 |
| LVM, g | 168 [131, 211] | 173 [135, 211] | 164 [132, 208] | 0.51 | 174 [138, 211] | 164 [123, 208] | 0.18 | 170 [135, 207] | 166 [130, 212] | 0.9 |
| LVEDV, mL | 130 [92, 167] | 160 [130, 194] | 102 [79, 126] | < 0.001 | 160 [130, 194] | 97 [74, 124] | < 0.001 | 160 [124, 194] | 102 [79, 130] | < 0.001 |
| LVM/LVEDV | 1.43 ± 0.56 | 1.10 ± 0.23 | 1.75 ± 0.61 | < 0.001 | 1.08 ± 0.20 | 1.77 ± 0.59 | < 0.001 | 1.09 ± 0.21 | 1.76 ± 0.6 | < 0.001 |
| E wave, cm/sec | 97 ± 29 | 97 ± 30 | 97 ± 28 | 0.94 | 95 ± 28 | 99 ± 29 | 0.37 | 98 ± 30 | 96 ± 28 | 0.58 |
| A wave, cm/sec | 76 ± 32 | 70 ± 29 | 82 ± 34 | 0.011 | 73 ± 29 | 79 ± 34 | 0.13 | 74 ± 30 | 77 ± 33 | 0.57 |
| E/A | 1.21 [0.84, 1.83] | 1.29 [0.89, 2.04] | 1.15 [0.82, 1.68] | 0.18 | 1.21 [0.84, 1.84] | 1.21 [0.86, 1.81] | 0.81 | 1.22 [0.84, 1.83] | 1.17 [0.85, 1.83] | 0.6 |
| Deceleration time, ms | 150 [123, 195] | 150 [121, 196] | 150 [128, 192] | 0.49 | 149 [119, 185] | 150 [129, 200] | 0.043 | 147 [118, 181] | 152 [129, 201] | 0.013 |
| Aortic valve stenosis, n (%) | 29/385 (7.5) | 7/193 (3.6) | 22/192 (12) | 0.004 | 8/193 (4.1) | 21/192 (11) | 0.012 | 8/193 (4.1) | 21/192 (11) | 0.012 |
| Aortic valve regurgitation, n (%) | 24/385 (6.2) | 14/193 (7.3) | 10/192 (5.2) | 0.53 | 14/193 (7.3) | 10/192 (5.2) | 0.53 | 11/193 (5.7) | 13/192 (6.8) | 0.68 |
| Mitral valve regurgitation, n (%) | 59/385 (15) | 39/193 (20) | 20/192 (10) | 0.01 | 40/193 (21) | 19/192 (9.9) | 0.004 | 41/193 (21) | 18/192 (9.4) | 0.002 |
| Laboratory data | ||||||||||
| Blood urea nitrogen, mg/dL | 24 [17, 35] | 24 [17, 34] | 24 [17, 36] | 0.77 | 24 [17, 35] | 24 [17, 35] | 0.67 | 24 [17, 36] | 23 [17, 35] | 0.76 |
| Creatinine, mg/dL | 1.14 [0.81, 1.52] | 1.15 [0.83, 1.54] | 1.09 [0.79, 1.51] | 0.31 | 1.18 [0.83, 1.56] | 1.09 [0.79, 1.50] | 0.22 | 1.17 [0.83, 1.55] | 1.07 [0.79, 1.50] | 0.19 |
| Hemoglobin, g/dL | 12.0 ± 2.4 | 12.0 ± 2.4 | 11.9 ± 2.4 | 0.84 | 11.9 ± 2.4 | 12.0 ± 2.4 | 0.78 | 11.9 ± 2.5 | 12 ± 2.3 | 0.68 |
| Brain natriuretic peptide, pg/mL | 666 [427, 1266] | 737 [449, 1376] | 638 [403, 1155] | 0.056 | 765 [472, 1376] | 636 [401, 1092] | 0.026 | 683 [437, 1349] | 645 [413, 1190] | 0.28 |
| Medication, n (%) | ||||||||||
| ACE-I and/or ARB | 124/285 (32) | 71/193 (37) | 53/192 (28) | 0.069 | 67/193 (35) | 57/192 (30) | 0.34 | 66/193 (34) | 58/192 (30) | 0.47 |
| Beta blocker | 153/385 (40) | 78/193 (40) | 75/192 (39) | 0.069 | 75/193 (39) | 78/192 (41) | 0.8 | 74/193 (38) | 79/192 (41) | 0.65 |
| Hemodynamic data | ||||||||||
| Systolic blood pressure, mmHg | 132 ± 26 | 128 ± 24 | 135 ± 29 | 0.006 | 131 ± 24 | 133 ± 29 | 0.35 | 130 ± 24 | 134 ± 29 | 0.13 |
| Diastolic blood pressure, mmHg | 78 ± 21 | 75 ± 19 | 73 ± 17 | 0.009 | 74 ± 18 | 77 ± 21 | 0.17 | 74 ± 18 | 77 ± 21 | 0.1 |
| Heart rate, bpm | 84 ± 21 | 83 ± 21 | 84 ± 21 | 0.81 | 83 ± 19 | 84 ± 22 | 0.64 | 83 ± 19 | 83 ± 22 | 0.78 |
A wave, late mitral valve inflow velocity; ACE-I angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor; ARB angiotensin receptor blocker; E wave, early mitral valve inflow velocity; IVSth interventricular septum thickness; LVEDV left ventricular end diastolic volume; LVDd left ventricular internal dimension at end-diastole; LVEF left ventricular ejection fraction; LVM left ventricular mass; PWth posterior wall thickness; RWT relative wall thickness
aRWT was the ratio of left ventricular wall thickness to LVDd. Left ventricular wall thickness was measured at interventricular septum as IVSth and posterior wall as PWth. Three measurement methods to compute RWT were as follows; RWTPW = 2 × PWth/LVDd, RWTIVS + PW = (PWth + IVSth)/LVDd, and RWTIVS = 2 × IVSth/LVDd
bThe patients were divided into two groups based on the median of RWTPW, RWTIVS + PW, and RWTIVS
Transthoracic echocardiography
The mean RWTPW, RWTIVS + PW, and RWTIVS values in the overall population were 0.36 ± 0.12, 0.37 ± 0.13, and 0.38 ± 0.14, respectively.
On comparing the three RWTs (low- vs. high- RWTPW, RWTIVS + PW, RWTIVS), high-RWTs had thicker IVSth and PWth, smaller LVDd, greater LVEF, smaller LV end-diastolic volume, high LVM/LVEDV, and less severe mitral regurgitation than low-RWTs (Table 1).
Survival analysis
During follow-up (235 [92, 425] days), 95/385 (25%) patients died in the overall population.
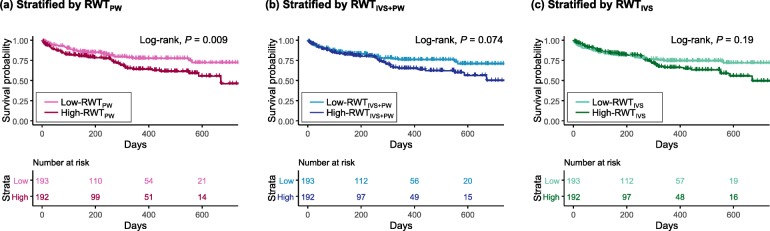
Comparing low- and high-RWTPW, there was a significant difference in the incidence of all-cause death (low 36/193 (19%) vs. high-RWTPW 59/192 (31%), P = 0.007). Kaplan-Meier curves showed that high-RWTPW had worse survival than low-RWTPW (P for log-rank test = 0.009; Fig. 2a).
Fig. 2.
Kaplan-Meier Curves for all-cause death stratified by the RWTs. RWT, relative wall thickness. RWTPW = 2 × PWth/LVDd, RWTIVS + PW = (IVSth + PWth)/LVDd, and RWTIVS = 2 × IVSth/LVDd. The patients were divided into two groups based on the median RWTs
Comparing low- and high-RWTIVS + PW, there was no significant difference in all-cause death (low 40/193 (21%) vs. high-RWTPW 55/192 (29%), P = 0.077) or survival (P for log-rank test = 0.074; Fig. 2b).
In a comparison between low- and high-RWTIVS, there was no significant difference in all-cause death (low 42/193 (22%) vs. high-RWTIVS 53/192 (28%), P incidence = 0.2) or survival (P for log-rank test = 0.19; Fig. 2c).
Cox proportional hazard models for all-cause death
In the unadjusted and adjusted Cox proportional hazard models, high-RWTPW was a significant risk factor for all-cause death (unadjusted Cox model, HR (95% CI), 1.72 (1.41–2.61), P = 0.01; adjusted Cox model, 1.95 (1.28–2.98), P = 0.02; Table 2).
Table 2.
Cox proportional hazard model for evaluate the risk of RWTs for all-cause mortality
| Calculate method and factor | Unadjusted | Adjusted by GWTG | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Event/cases | HR | 95% CI | P value | Event/casesa | HR | 95% CI | P value | |||||
| High- to low-RWTPW | 95/385 | 1.72 | 1.14 | – | 2.61 | 0.01 | 93/380 | 1.95 | 1.28 | – | 2.98 | 0.002 |
| High- to low-RWTIVS + PW | 95/385 | 1.45 | 0.96 | – | 2.17 | 0.075 | 93/380 | 1.53 | 1.01 | – | 2.32 | 0.045 |
| High- to low-RWTIVS | 95/385 | 1.31 | 0.87 | – | 1.96 | 0.19 | 93/380 | 1.36 | 0.9 | – | 2.06 | 0.14 |
CI confidence interval; GWTG Get With The Guideline score; HR hazard ratio; RWT relative wall thickness
a5 cases were removed because of GWTG missing
High-RWTIVS + PW was not a significant risk factor for all-cause death in the unadjusted Cox proportional model (unadjusted Cox model, HR, 1.45 (0.96–2.17), P = 0.075), but it was in the adjusted Cox proportional hazard model (adjusted Cox model, 1.53 (1.01–2.32), P = 0.045; Table 2).
High-RWTIVS was not a significant factor in either the unadjusted or the adjusted Cox proportional hazard model (Table 2).
Logistic regression models for 90-day mortality
The OR of high- to low-RWTPW was significant (univariate, OR, 2.19, 95%CI, 1.15–2.19, P = 0.017; adjusted, OR, 2.26, 95%CI, 1.16–4.4, P = 0.017) on univariate analysis and the adjusted logistic regression model (Table 3). In contrast, the OR of neither high to low-RWTIVS + PW nor RWTIVS was significant on univariate analysis or the adjusted logistic regression models.
Table 3.
Logistic models for evaluating the risk of 90 days mortality
| Calculate method and factor | Unadjusted | Adjusted by GWTG | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Event/cases | OR | 95% CI | P value | Event/cases | OR | 95% CI | P value | |||||
| High- to low-RWTPW | 48/337 | 2.19 | 1.15 | – | 2.19 | 0.017 | 48/337 | 2.26 | 1.16 | – | 4.4 | 0.017 |
| High- to low-RWTIVS + PW | 48/337 | 1.26 | 0.68 | – | 1.26 | 0.46 | 48/337 | 1.19 | 0.63 | – | 2.25 | 0.6 |
| High- to low-RWTIVS | 48/337 | 0.86 | 0.47 | – | 0.86 | 0.64 | 48/337 | 0.8 | 0.42 | – | 1.52 | 0.5 |
CI confidence interval; GWTG Get With The Guideline score, OR odds ratio; RWT relative wall thickness
Receiver operating curves for 90-day mortality
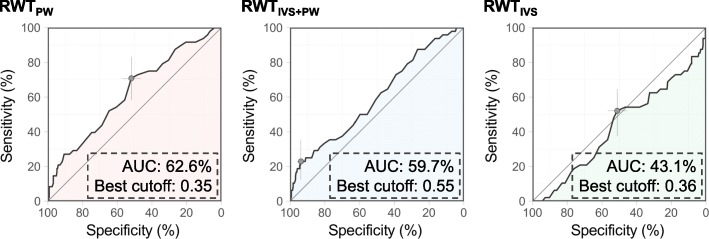
A total of 48 (13%) patients died within 90 days from hospital admission. Figure 3 shows the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves for 90-day mortality using the RWTs. The c-statistic of the ROC curve using RWTPW was 62.6%, and the best cut-off value was 0.35. The c-statistic of the ROC curve using RWTIVS + PW was 59.7%, and the best cut-off value was 0.55. The c-statistic of the ROC curve using RWTIVS was 43.1%, and the best cut-off value was 0.36.
Fig. 3.
Receiver operating curves for 90-day mortality using the RWTs. AUC, area under the curve
Sensitivity analysis of the survival analysis by stratified RWTs by the best cut-off
Additional file 1: Table S1 shows the demographic data and echocardiographic data with stratification by the best RWT cut-off. High-RWTPW had worse survival than low-RWTPW (P for log-rank test = 0.03; Additional file 2: Figure S1a). High-RWTIVS + PW also had a worse prognosis than low-RWTIVS + PW (P for log-rank test < 0.001; Additional file 2: Figure S1b). In contrast, there was no significant difference in survival between low- and high-RWTIVS (P for log-rank test = 0.077; Additional file 2: Figure S1c).
In the unadjusted and adjusted Cox proportional hazard models, high-RWTPW and high-RWTIVS + PW were associated with mortality (high-RWTPW, unadjusted Cox model, HR (95% CI), 1.55 (1.04–2.33), P = 0.033; adjusted Cox model, 1.72 (1.14–2.59), P = 0.01; high-RWTIVS + PW, unadjusted Cox model, HR (95% CI), 3.88 (2.34–6.43), P < 0.001; adjusted Cox model, 3.42 (2.04–5.72), P < 0.001; Additional file 3: Table S2). High-RWTIVS was not a significant risk factor in the unadjusted and adjusted Cox proportional hazard models.
Relationship between RWTs and clinical characteristics
There were significant positive correlations between the three RWTs and age and LVEF, and negative correlations between the RWTs and LogBNP and LVEDV (Table 4). RWTIVS + PW and RWTIVS did not have significant correlations with systolic blood pressure, but RWTPW did (ρ = 0.15, P = 0.004).
Table 4.
Relationship between RWTs and clinical characteristics
| RWTPW | RWTIVS + PW | RWTIVS | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ρ | P value | ρ | P value | ρ | P value | |
| Age, y | 0.15 | 0.003 | 0.17 | 0.003 | 0.17 | 0.001 |
| LogBNP, log (pg/mL) | −0.2 | < 0.001 | −0.15 | 0.003 | −0.11 | 0.039 |
| LVEF, % | 0.42 | < 0.001 | 0.47 | < 0.001 | 0.43 | < 0.001 |
| LVEDV, mL | −0.67 | < 0.001 | −0.74 | < 0.001 | − 0.69 | < 0.001 |
| Systolic blood pressure, mmHg | 0.15 | 0.004 | 0.094 | 0.065 | 0.063 | 0.22 |
LogBNP logarithmed brain natriuretic peptide; LVEDV left ventricular end-diastolic volume; LVEF left ventricular ejection fraction; ρ, Spearman’s correlation coefficient
Reliability of TTE measurement of PWth, IVSth, and LVDd
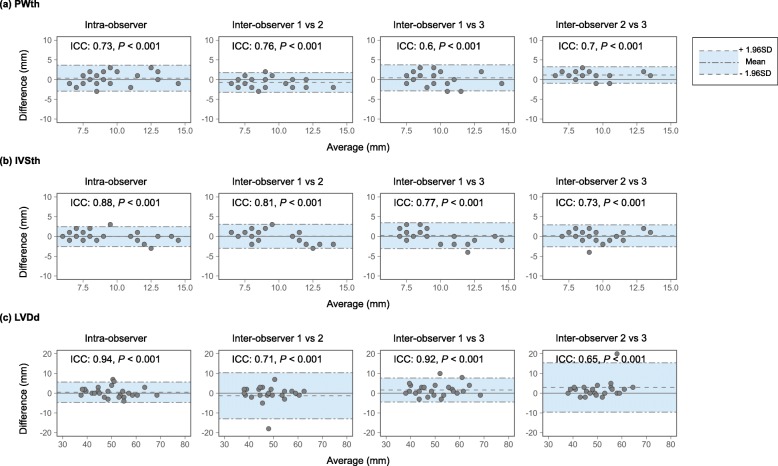
Intra-observer agreement of TTE measurement of PWth was significant (ICC = 0.73, P < 0.001; Fig. 4a). Inter-observer agreements of TTE measurement of PWth were also significant (observer 1 vs. 2, ICC = 0.76, P < 0.001; observer 1 vs. 3, ICC = 0.6, P < 0.001; observer 2 vs. 3, ICC = 0.7, P < 0.001; Fig. 3a). There were no systematic biases in the intra- and inter-observer agreements in PWth measurement (Fig. 4a).
Fig. 4.
Reliability of linear measurements of PWth, IVSth, and LVDd. IVSth, interventricular septum thickness; LVDd, left ventricular internal dimension at end-diastole; PWth, posterior wall thickness; ICC, intraclass correlation coefficient
Intra-observer agreement of TTE measurement of IVSth was significant (ICC = 0.88, P < 0.001; Fig. 4b). Inter-observer agreements of TTE measurement of IVSth were also significant (observer 1 vs. 2, ICC = 0.81, P < 0.001; observer 1 vs. 3, ICC = 0.77, P < 0.001; observer 2 vs. 3, ICC = 0.73, P < 0.001; Fig. 4b). There were no systematic biases in the intra- and inter-observer agreements in IVSth measurement (Fig. 4b).
Intra-observer agreement of TTE measurement of LVDd was significant (ICC = 0.94, P < 0.001; Fig. 4c). Inter-observer agreements of TTE measurement of LVDd were also significant (observer 1 vs. 2, ICC = 0.71, P < 0.001; observer 1 vs. 3, ICC = 0.92, P < 0.001; observer 2 vs. 3, ICC = 0.65, P < 0.001; Fig. 4c). There were no systematic biases in the intra- and inter-observer agreements in LVDd measurement (Fig. 4c).
Reliability of RWTs obtained from TTE measurement
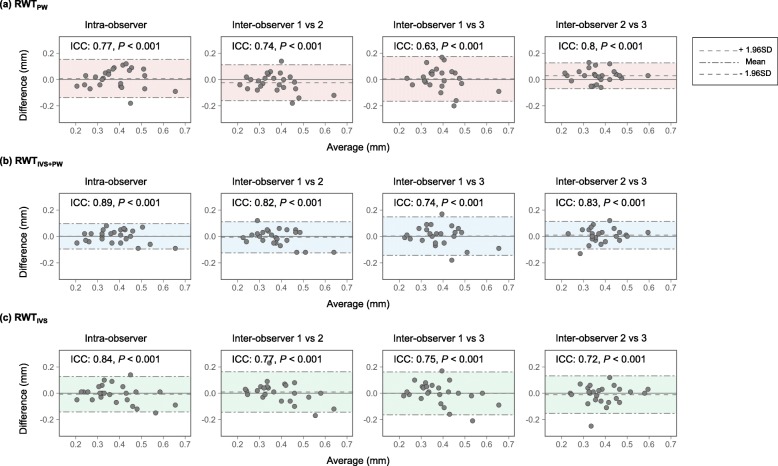
Intra-observer agreement of RWTPW was significant (ICC = 0.77, P < 0.001; Fig. 5a). Inter-observer agreements of RWTPW were significant (observer 1 vs. 2, ICC = 0.74, P < 0.001; observer 1 vs. 3, ICC = 0.63, P < 0.001; observer 2 vs. 3, ICC = 0.8, P < 0.001). There were no systematic biases in the intra- and inter-observer agreements in RWTPW.
Fig. 5.
Reliability of RWTs. RWT, relative wall thickness. RWTPW = 2 × PWth/LVDd, RWTIVS + PW = (IVSth + PWth)/LVDd, and RWTIVS = 2 × IVSth/LVDd in which PWth = posterior wall thickness, IVSth = interventricular septum thickness, and LVDd = left ventricular internal dimension at end-diastole
Intra-observer agreement of RWTIVS + PW was significant (ICC = 0.89, P < 0.001; Fig. 5b). Inter-observer agreements of RWTPW were also significant (observer 1 vs. 2, ICC = 0.82, P < 0.001; observer 1 vs. 3, ICC = 0.74, P < 0.001; observer 2 vs. 3, ICC = 0.83, P < 0.001). There were no systematic biases in the intra- and inter-observer agreements in RWTIVS + PW.
Intra-observer agreement of RWTIVS was significant (ICC = 0.84, P < 0.001; Fig. 5c). Inter-observer agreements of RWTIVS were also significant (observer 1 vs. 2, ICC = 0.77, P < 0.001; observer 1 vs. 3, ICC = 0.75, P < 0.001; observer 2 vs. 3, ICC = 0.72, P < 0.001). There were no systematic biases in the intra- and inter-observer agreements in RWTIVS.
Discussion
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to show the difference in the clinical significance of the three RWTs. The present study demonstrated that, compared to RWTIVS + PW and RWTIVS, RWTPW is the best to stratify the risk for all-cause death in ADHF patients. This may be consistently supported by three findings. First, high-RWTPW had a significantly worse prognosis than low-RWTPW. In contrast, on survival analysis, there was no significant difference between high- and low-RWTIVS + PW or RWTIVS. Second, in the logistic regression model for 90-day mortality, only high-RWTPW was significant among the three RWTs (Table 3). Third, ROC for 90-day all-cause death using RWTPW had the highest c-statistic among the three ROCs.
Explanations of the differences in the prognostic values among the three RWTs
High-RWTPW was associated with a poor prognosis on survival analysis and Cox proportional hazard models (Fig. 2a; Table 2). High-RWTIVS + PW was not associated with poor survival on survival analysis (Fig. 1b), whereas high-RWTIVS + PW was a significant risk only in the Cox proportional hazard model adjusted by GWTG, not in the unadjusted model (Table 2). High-RWTIVS did not show worse survival than low-RWTIVS (Fig. 1c; Table 2). The equations of RWTPW and RWTIVS + PW contain PWth. PWth or the ratio of PWth to LVDd, therefore, may represent the LV remodeling related to a worse prognosis better than IVSth or IVSth to LVDd in patients with ADHF. Patients with high-RWTPW had higher systolic blood pressure than those with low-RWTPW (Table 1), while there was no such difference either between low- and high-RWTIVS + PW or between low- and high-RWTIVS. RWTPW had a positive correlation with systolic blood pressure (Table 4), while either RWTIVS + PW or RWTIVS did not. This may suggest that thickening of PWth, rather than IVSth, is likely to counterbalance pressure overload and may lead to LV diastolic dysfunction leading to a poor prognosis. A higher A wave in high RWTpw patients than in low RWTpw patients may support this assumption (Table 1).
In terms of methodological validity, there were no differences in inter- and intra-observer agreements for each RWT. Given that fairly good reproducibility was observed in all measurements, differences in prognostic values among the three RWTs may not result from technical aspects of TTE.
Paradoxically, high-RWTPW patients had lower BNP than low-RWTPW patients (Table 1). High-RWTPW included 101 (53%) patients with HFpEF. Generally, BNP increases modestly in HFpEF [18]. Furthermore, the prognostic value of BNP has not been confirmed in patients with HFpEF [19]. High RWTPW might be of clinically utility, especially, in patients with HFpEF.
Limitations
The present study had several limitations. The present study did not have pressure data such as LV end-diastolic pressure or pulmonary artery wedge pressure. LV wall thickness was not evaluated by other modalities, such as magnetic resonance imaging or computed tomography. Patients having valvular diseases with various etiologies were included, which might affect the prognostic value of RWTs.
In conclusion, high-RWTPW had a higher systolic pressure and A wave than low-RWTPW. This finding was not observed in the comparison between low- and high-RWTIVS + PW or between low-and high-RWTIVS. PWth may represent pressure overload better than IVSth. When calculating RWT, RWTPW should be recommended for evaluating the mortality risk in ADHF.
Supplementary information
Additional file 1: Table S1. Demographic data and echocardiographic parameters.
Additional file 2: Figure S1. Kaplan-Meier Curves for all-cause mortality stratified by the stratified RWTs by the best cut-off.
Additional file 3: Table S2. Cox proportional hazard model for evaluate the risk of high RWTs for all-cause mortality.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Yoji Takami, Shimon Toma, Chio Iseki, and Kunitoshi Iseki for assistance with data collection and management.
The authors also appreciate the dedicated work of the sonographers, Masako Noborikawa, Naoko Sakugawa, Kazue Kudaka, and Yayoi Taira.
The authors would also like to thank Masanori Kakazu, Masahiro Tamashiro, Toshiya Chinen, Akihiko Yamauchi, Masaki Tabuchi, Hideki Takayasu, and Hideki Sonoi for heart failure patient enrollment and clinical data capture.
Finally, the authors would like to thank Yumi Ikehara and Sachiko Nakaima for manuscript assistance.
Authors’ contributions
SY originated the concept of this study, collected data, and wrote the original manuscript. MA and TA collected the data and discussed the study results. OA took responsibility for conducting the study. MS and SU supervised the study concept and discussed the study results in depth. All authors approved the final manuscript submission.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Availability of data and materials
Not available. We are not allowed the any study data to share by the ethical committee.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The institutional ethics committee at Tomishiro Central Hospital approved the present study and waived informed consent because of the observational nature of the study.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Satoshi Yamaguchi, Email: satoshi-yamaguchi@umin.ac.jp.
Shinichiro Ueda, Email: blessyou@med.u-ryukyu.ac.jp.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information accompanies this paper at 10.1186/s12947-019-0179-6.
References
- 1.Grossman W, Paulus WJ. Myocardial stress and hypertrophy: a complex interface between biophysics and cardiac remodeling. J Clin Invest. 2013;123(9):3701–3703. doi: 10.1172/JCI69830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Gjesdal O, Bluemke DA, Lima JA. Cardiac remodeling at the population level--risk factors, screening, and outcomes. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2011;8(12):673–685. doi: 10.1038/nrcardio.2011.154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Li L, Shigematsu Y, Hamada M, Hiwada K. Relative wall thickness is an independent predictor of left ventricular systolic and diastolic dysfunctions in essential hypertension. Hypertens Res. 2001;24(5):493–499. doi: 10.1291/hypres.24.493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Pierdomenico SD, Lapenna D, Bucci A, Manente BM, Cuccurullo F, Mezzetti A. Prognostic value of left ventricular concentric remodeling in uncomplicated mild hypertension. Am J Hypertens. 2004;17(11 Pt 1):1035–1039. doi: 10.1016/j.amjhyper.2004.06.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Yamaguchi S, Abe M, Arasaki O, Shimabukuro M, Ueda S. The prognostic impact of a concentric left ventricular structure evaluated by transthoracic echocardiography in patients with acute decompensated heart failure: a retrospective study. Int J Cardiol. 2018;287:73–80. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2018.07.097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Lang RM, Badano LP, Mor-Avi V, Afilalo J, Armstrong A, Ernande L, Flachskampf FA, Foster E, Goldstein SA, Kuznetsova T, et al. Recommendations for cardiac chamber quantification by echocardiography in adults: an update from the American Society of Echocardiography and the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2015;28(1):1–39.e14. doi: 10.1016/j.echo.2014.10.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Wang S, Song K, Guo X, Xue H, Wang N, Chen J, Zou Y, Sun K, Wang H, He J, et al. The association of metabolic syndrome with left ventricular mass and geometry in community-based hypertensive patients among Han Chinese. J Res Med Sci. 2015;20(10):963–968. doi: 10.4103/1735-1995.172785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Chahal NS, Lim TK, Jain P, Chambers JC, Kooner JS, Senior R. New insights into the relationship of left ventricular geometry and left ventricular mass with cardiac function: a population study of hypertensive subjects. Eur Heart J. 2010;31(5):588–594. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehp490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Huis AE, de Man FS, van Rossum AC, Handoko ML. How to diagnose heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: the value of invasive stress testing. Netherlands Heart J. 2016;24(4):244–251. doi: 10.1007/s12471-016-0811-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Folland ED, Parisi AF, Moynihan PF, Jones DR, Feldman CL, Tow DE. Assessment of left ventricular ejection fraction and volumes by real-time, two-dimensional echocardiography. A comparison of cineangiographic and radionuclide techniques. Circulation. 1979;60(4):760–766. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.60.4.760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Nagueh SF, Smiseth OA, Appleton CP, Byrd BF, 3rd, Dokainish H, Edvardsen T, Flachskampf FA, Gillebert TC, Klein AL, Lancellotti P, et al. Recommendations for the evaluation of left ventricular diastolic function by echocardiography: an update from the American Society of Echocardiography and the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2016;29(4):277–314. doi: 10.1016/j.echo.2016.01.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Zoghbi WA, Adams D, Bonow RO, Enriquez-Sarano M, Foster E, Grayburn PA, Hahn RT, Han Y, Hung J, Lang RM, et al. Recommendations for noninvasive evaluation of native Valvular regurgitation: a report from the American Society of Echocardiography developed in collaboration with the Society for Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2017;30(4):303–371. doi: 10.1016/j.echo.2017.01.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Peterson PN, Rumsfeld JS, Liang L, Albert NM, Hernandez AF, Peterson ED, Fonarow GC, Masoudi FA. American Heart Association get with the guidelines-heart failure P: a validated risk score for in-hospital mortality in patients with heart failure from the American Heart Association get with the guidelines program. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2010;3(1):25–32. doi: 10.1161/CIRCOUTCOMES.109.854877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Shiraishi Y, Kohsaka S, Abe T, Mizuno A, Goda A, Izumi Y, Yagawa M, Akita K, Sawano M, Inohara T, et al. Validation of the get with the guideline-heart failure risk score in Japanese patients and the potential improvement of its discrimination ability by the inclusion of B-type natriuretic peptide level. Am Heart J. 2016;171(1):33–39. doi: 10.1016/j.ahj.2015.10.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kamarudin AN, Cox T, Kolamunnage-Dona R. Time-dependent ROC curve analysis in medical research: current methods and applications. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2017;17(1):53. doi: 10.1186/s12874-017-0332-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Giavarina D. Understanding bland Altman analysis. Biochem Med (Zagreb) 2015;25(2):141–151. doi: 10.11613/BM.2015.015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Koo TK, Li MY. A guideline of selecting and reporting Intraclass correlation coefficients for reliability research. J Chiropr Med. 2016;15(2):155–163. doi: 10.1016/j.jcm.2016.02.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.van Veldhuisen DJ, Linssen GC, Jaarsma T, van Gilst WH, Hoes AW, Tijssen JG, Paulus WJ, Voors AA, Hillege HL. B-type natriuretic peptide and prognosis in heart failure patients with preserved and reduced ejection fraction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;61(14):1498–1506. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2012.12.044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Kitada S, Kikuchi S, Tsujino T, Masuyama T, Ohte N. The prognostic value of brain natriuretic peptide in patients with heart failure and left ventricular ejection fraction higher than 60%: a sub-analysis of the J-MELODIC study. ESC Heart Fail. 2018;5(1):36–45. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.12206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Additional file 1: Table S1. Demographic data and echocardiographic parameters.
Additional file 2: Figure S1. Kaplan-Meier Curves for all-cause mortality stratified by the stratified RWTs by the best cut-off.
Additional file 3: Table S2. Cox proportional hazard model for evaluate the risk of high RWTs for all-cause mortality.
Data Availability Statement
Not available. We are not allowed the any study data to share by the ethical committee.