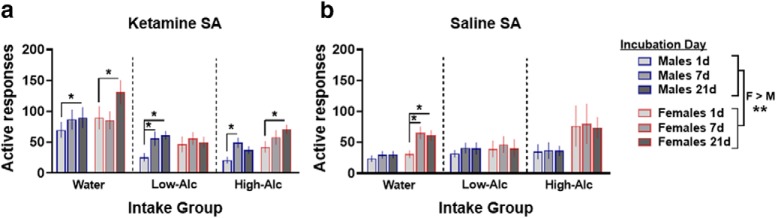
Figure 4.
Incubation of ketamine craving develops in all groups except low-alcohol intake female rats. a, b, Active responses during 2 h FR1 sessions 1, 7, and 21 d into the ketamine abstinence period in male and female rats. Drug-paired cues were identical, but active responses yielded no drug infusion. Female rats displayed increased levels of active responding compared with males, regardless of ketamine or saline self-administration. a, In male rats, active responses within the ketamine groups (water, n = 11; low-Alc, n = 8; high-Alc, n = 8) increased over the 21 d period. In female rats, those that self-administered ketamine (water, n = 11; low-Alc, n = 7; high-Alc, n = 7) that were considered water- and high-alcohol intake rats increased responding over time; however, low-alcohol intake female rats did not. b, In male rats, intake did not affect active responding in the saline groups (water, n = 11; low-Alc, n = 8; high-Alc, n = 7). Water-intake female rats that self-administered saline increased responding over time while the alcohol groups did not (water, n = 9; low-Alc, n = 8; high-Alc, n = 7). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM active responses.