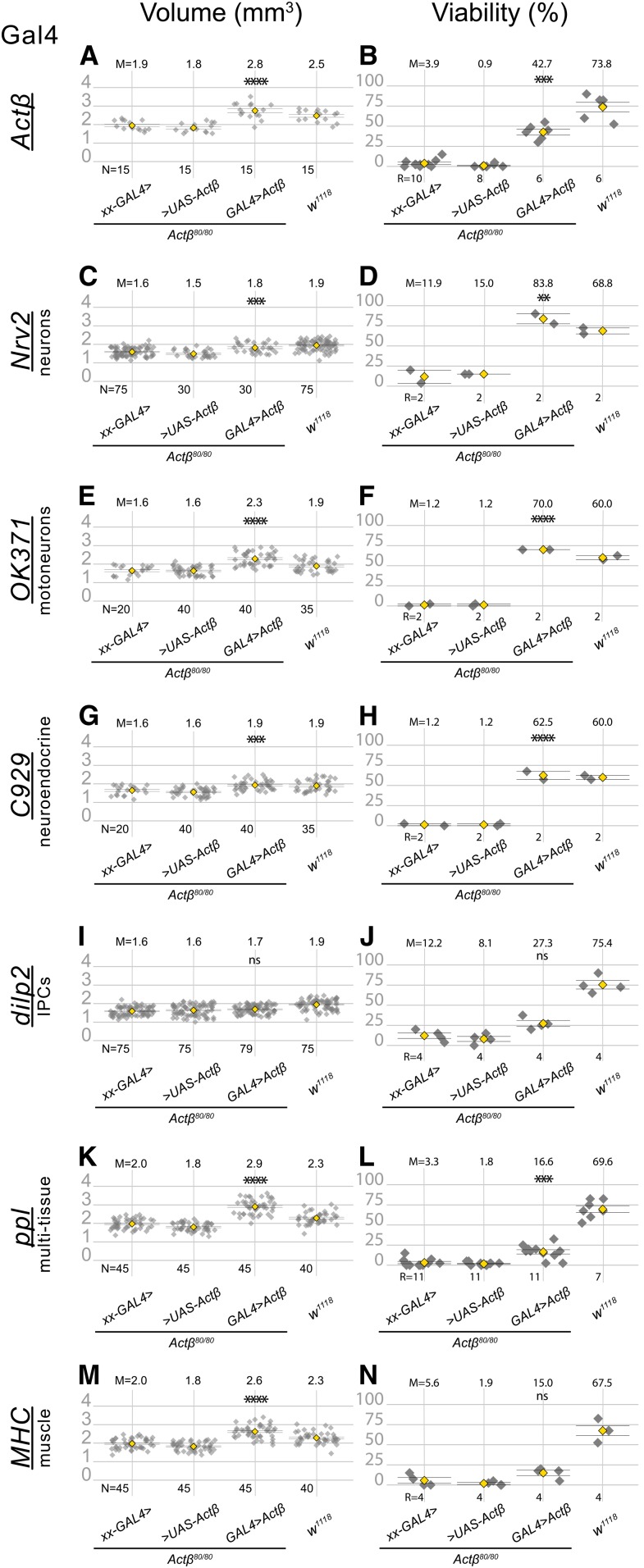
Figure 7.
Expression of Actβ from specific cell types differentially rescues the pupa size (A, C, E, G, I, K and M) and viability (B, D, F, H, J, L and N) phenotypes in Actβ mutants. The first two groups in each panel are controls in which Actβ mutants contain one copy of either the GAL4 driver (indicated on the left side of each panel row) or the UAS Actβ transgene. The third group in each panel is the test cross, and the last group in each panel is the w1118 control. All GAL4 drivers (except dilp2-GAL4) used to overexpress Actβ rescue body size phenotype (A, C, E, G, K, and M). Overexpressing Actβ in neuronal tissues (D, F, and H) completely rescues the adult viability phenotype and partially rescues it when overexpressed in body-wall muscles using MHC-GAL4 (L). ANOVA was used to determine statistical significances between genotypes with one copy of either the Gal4 or UAS transgene in an Actβ80 homozygous background, compared to animals with both Gal4 and UAS transgenes in an Actβ80 homozygous background. w1118 is the wild-type control and was reared side-by-side in each case. M, mean; N, number animals; R, repetition number (10–30 animals per repetition); UAS, upstream activating sequence.