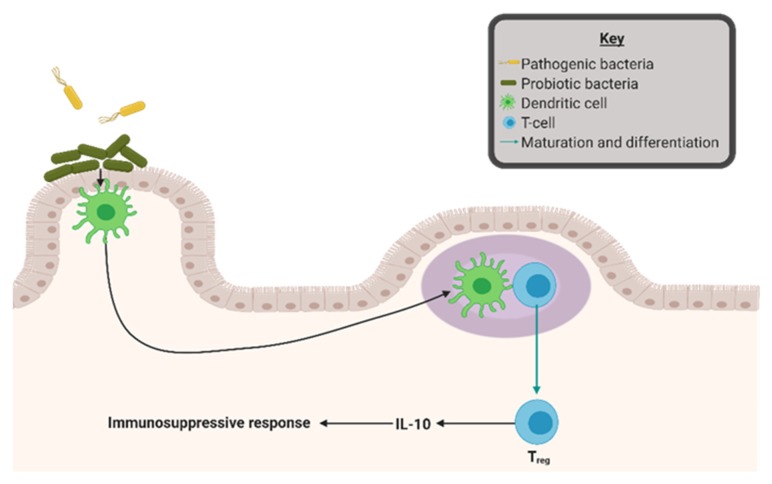
Figure 3.
Probiotic interactions in the gut can modify inflammation. Probiotic bacterial species adheres to the gut lining, strengthening the gut epithelial barrier, and allows for competitive inhibition of pathogenic microorganisms. Additionally, probiotic bacteria produce anti-microbial substances promoting anti-inflammatory response in the gut-associated lymphoid tissue. Figure was created with BioRender.com.