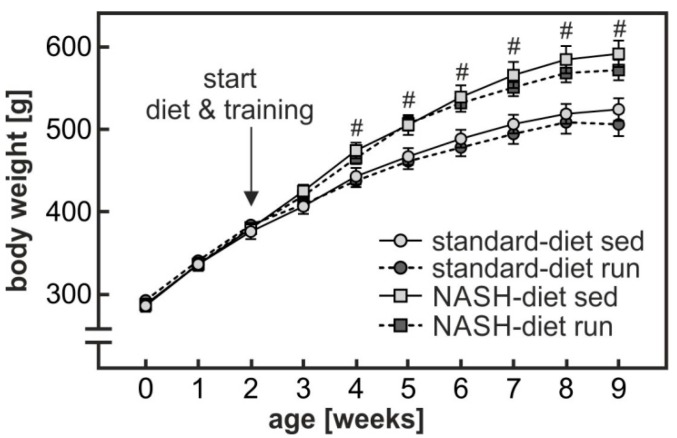
Figure 1.
NASH-diet-dependent increase in body weight gain. After two weeks of adaptation (see Supplementary Figure S1) rats received either a standard chow diet (standard-diet) or a high fat, high cholesterol, high fructose NASH-inducing diet (NASH-diet) for 7 weeks. Both diet groups were subdivided into a sedentary group (sed) and a group subjected to treadmill endurance exercise (run) (see methods section (paragraph 1) and Supplementary Figure S1). Body weight was determined weekly. Values are means ± SEM. Statistics: Multiple Student’s t-test for unpaired samples; #: sedentary or exercised NASH-diet groups versus sedentary or exercised standard-diet groups, p < 0.05.