Abstract
Background
Aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) is a catastrophic disease with devastating consequences, including a high mortality rate and severe disabilities among survivors. Inflammation is induced following SAH, but the exact role and phenotype of innate immune cells remain poorly characterized. We investigated the inflammatory components of the early brain injury in an animal model and in SAH patients.
Method
SAH was induced through injection of blood in the subarachnoid space of C57Bl/6 J wild-type mice. Prospective blood collections were obtained at 12 h, days 1, 2, and 7 to evaluate the systemic inflammatory consequences of SAH by flow cytometry and enzyme-linked immunosorbent-assay (ELISA). Brains were collected, enzymatically digested, or fixed to characterize infiltrating inflammatory cells and neuronal death using flow cytometry and immunofluorescence. Phenotypic evaluation was performed at day 7 using the holding time and footprint tests. We then compared the identified inflammatory proteins to the profiles obtained from the plasma of 13 human SAH patients.
Results
Following SAH, systemic IL-6 levels increased rapidly, whereas IL-10 levels were reduced. Neutrophils were increased both in the brain and in the blood reflecting local and peripheral inflammation following SAH. More intracerebral pro-inflammatory monocytes were found at early time points. Astrocyte and microglia activation were also increased, and mice had severe motor deficits, which were associated with an increase in the percentage of caspase-3-positive apoptotic neurons. Similarly, we found that IL-6 levels in patients were rapidly increased following SAH. ICAM-1, bFGF, IL-7, IL-12p40, and MCP-4 variations over time were different between SAH patients with good versus bad outcomes. Moreover, high levels of Flt-1 and VEGF at admission were associated with worse outcomes.
Conclusion
SAH induces an early intracerebral infiltration and peripheral activation of innate immune cells. Furthermore, microglia and astrocytic activation are present at later time points. Our human and mouse data illustrate that SAH is a systemic inflammatory disease and that immune cells represent potential therapeutic targets to help this population of patients in need of new treatments.
Keywords: Cerebral hemorrhage; Neuroinflammation; Innate immunity; Early brain injury, Neuronal death
Background
Aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) is a catastrophic disease associated with significant mortality and morbidity in patients. Approximately 35% of patients will die during the first 30 days following SAH [1]. Unlike other forms of stroke, SAH affects a predominantly young population (40-60 years) [2]. Given its high mortality and morbidity [3], SAH is a significant cause of premature death and loss of potential life years [4, 5]. Among survivors of the initial bleed, an as-yet-imprecise secondary brain injury is the cause of major morbidity [6]. Historically, this mortality and morbidity were thought to be predominantly related to brain edema and/or arterial vasospasm [2, 7, 8]. However, studies have shown that despite reduction of SAH incidence or targeted therapies, patient outcomes have not change [6]. A recent study from Nassiri et al., through a propensity score-matched analysis from the Clazosentan to Overcome Neurological iSChemia and Infarction OccUring after Subarachnoid hemorrhage (CONSCIOUS) study, showed beneficial effect of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on mortality in SAH patients without any difference on vasospasm and delayed cerebral ischemia (DCI) [9]. It is clear that events in the first 72 h after SAH, the early brain injury (EBI) period, are crucial to the viability of neurons, the loss of which is complicit with the altered functional status of these patients [10]. The exact nature of EBI in SAH is ill-defined, but inflammation following SAH represents a pathway of great interest. Multiple studies have associated high cytokine levels with bad outcomes in SAH patients [6, 10]. Innate cells have been inconsistently involved in the immune response following SAH [11–15]. Altogether, these studies suggest that cellular inflammation is activated during EBI and may be important in DCI. However, there is a gap in the comprehensive appreciation of the role of inflammation in neuronal cell death after SAH. Our objectives were to characterize the inflammatory-like events (referred to as inflammation from hereon) during EBI and the associated neuronal cell death and motor functions in a mouse model of induced SAH by the following [1]: Measuring the blood cytokine response and leukocyte activation, brain monocytes, neutrophil infiltration, and microglia and astrocytic activation at multiple time points following SAH [2]; assess caspase-3 activation and cell death in neurons; and [3] assess motor function. We also compared measures of the blood cytokine response in our murine model of SAH to blood inflammatory protein profiles in adult patients with SAH in a prospectively enrolled cohort from our critical care unit.
Methods
Mouse model of SAH
We used adult male C57BL/6 J wild-type (WT) mice between 10-12 weeks old (n = 125). Mice were housed with water and food ad libitum. We used an adapted SAH model [16] that was approved by the Comité Institutionnel de Protection des Animaux (CIPA) of the Centre de Recherche du Centre Hospitalier de l’Université de Montréal (CRCHUM). In brief, the day before surgery, mice received acetaminophen (160 mg/125 mL H2O) diluted in water. After anesthesia (isofluorane 2%), the head was fixed on a stereotactic frame (Stoelting, Woo Dale, IL). Following incision of the scalp, a 0.8 mm diameter hole was drilled (CircuitMedic, Haverhill, MA) through the skullcap, at 2 mm anterior to the bregma at a 40° angle. To induce SAH in mice (n = 60), 100 μL of isogenic blood from a second mouse (obtained through intracardiac puncture) was injected into the pre-chiasmatic cisternae of the recipient using a 27G spinal needle (Braun medical, Bethlehem, PA). Needle insertion without blood injection served as control (SHAM, n = 59). The normal group (n = 6) were unmanipulated mice. Mice were randomly divided into each group.
Cytokine measurements
The U-Plex technology from Mesoscale Discovery (MSD, Rockville, MD) was used to measure cytokine levels in mouse plasma samples (nSHAM = 19, nSAH = 20). The kit selected (interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6, IL-10, IL-17A, IL-23, and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α) was used per manufacturer’s instructions.
Flow cytometry
Blood cells
Blood was collected by prospective saphenous bleeding (D1 (nSHAM = 35, nSAH = 34, 8 independent experiments) and D2 (nSHAM = nSAH = 19, 4 independent experiments)] or by terminal intracardiac puncture (12 h (nSHAM = nSAH = 8, 2 independent experiments), D1 (nSHAM = 16 nSAH = 18, 4 independent experiments), D2 (nSHAM = 16, nSAH = 15, 4 independant experiments), and D7 (nSHAM = nSAH = 8, 2 independent experiments)) (Fig. 1a), then centrifuged (4000 rotations per minutes (rpm), 15 min, 4 °C) to collect plasma, which was used for cytokine measurements. Red blood cells were eliminated following lysis with Ammonium Chloride Potassium buffer (ACK: 1.5 M NH4Cl, 100 mM KHCO3 and 100 mM ethylenediaminetetraeacetic acid (EDTA)) for 5 min with gentle shaking at 4 °C. Cells were then centrifuged, washed with FACS buffer (phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), 2% fetal bovine serum, 5 mM EDTA) and subjected to staining. Blood was taken from SAH, SHAM, and unmanipulated mice.
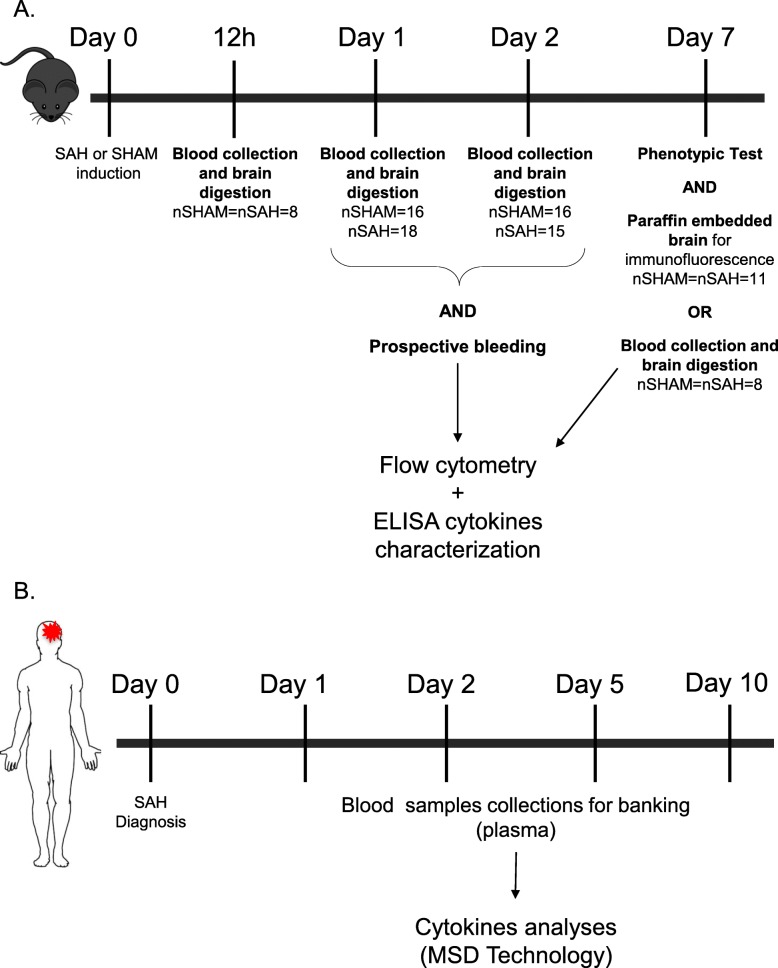
Fig. 1.
Experimental design. a Experimental design for mice experiments. SAH was induced with surgery at D0. At 12 h (nSHAM = nSAH = 8), the mice were sacrificed, and brain and blood were prepared for flow cytometry analyses. At D1 blood was collected by saphenous bleeding for flow cytometry (nSHAM = 35, nSAH = 34) or the mice were sacrificed, and brain and blood were prepared for flow cytometry analyses (nSHAM = 16, nSAH = 18). At D2, blood was collected by saphenous bleeding for flow cytometry (nSHAM = nSAH = 19) or the mice were sacrificed, and brain and blood were prepared for flow cytometry analyses (nSHAM = 16, nSAH = 15). At D7, the phenotypic tests were performed (nSHAM = nSAH = 19) and blood and the brains were conserved, and paraffin embedded for immunofluorescence essays (nSHAM = nSAH = 11) or brains were prepared for flow cytometry (nSHAM = nSAH = 8). b Experimental design for human immunomonitoring. At D0, SAH patients were recruited within the first 48 h. At D0, D1, D2, D5, and D10, blood was collected and centrifuged for banking plasma. Plasma were used for cytokine analyses by MSD technology
Brain cells
At several time points (12 h, D0, D1, D2, and D7) after SAH or SHAM induction or for the unmanipulated group (Fig. 1a), mice were anesthetized, and the vasculature was flushed by intracardiac injection of 25 mL of saline solution (0.9% NaCl). Brains were subsequently harvested, sliced with a scalpel, and enzymatically digested (2 mg/mL of collagenase D and 14 μg/mL of DNase) for 15 min at 37 °C, and finally filtered through a 100 μm mesh. After a wash with Hank’s balanced salt solution (HBSS) (Gibco, Hampton, NH) and centrifugation (1400 rpm, 7 min, 4 °C), the myelin was removed with a 37% Percoll solution (GE Healthcare Bio-science, Uppsala, Sweden; diluted with HBSS) and brain cells were washed with HBSS before staining [17].
Cell staining
Cells were first blocked with purified rat anti-mouse C16/CD32 Fc block (BD Pharmingen, San Jose, CA) for 30 min at 4 °C. After a wash with FACS buffer, cell surface staining was performed at 4 °C for 30 min using the following markers: monoclonal rat anti-mouse CD45 PeCy7 (1/500, eBioscience, San Diego, CA), rat anti-mouse Ly6C BV421 (1/800, BD Horizon, Mississauga, ON, Canada), rat anti-mouse Ly6G FITC (1/1000, BD Pharmingen), and rat anti-mouse CD11b AF700 (1/400, BD Pharmingen). Cell viability was assessed using the Live/Dead Fixable Aqua Dead Cell Stain Kit (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA). Stained cells were acquired on a LSR Fortessa cytometer (BD Immunocytometry Systems, San Jose, CA) and data collection was obtained using the BD FACS Diva software (BD Bioscience, Mississauga, Ontario, Canada). Data analyses were performed using the Flowjo software (v.10.2, flowjo, LLC).
Immunofluorescence analysis
At D7 (Fig. 1a), mice (nSAH = nSHAM = 11, 2 independent experiments and nNormal = 3) were anesthetized and the vasculature was flushed by intracardiac injection of 25 mL of saline solution (0.9% NaCl) and 25 mL of formalin. Formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded brains were sectioned transversally in 6-μm slices and stained manually. After deparaffinization in three successive 5-min baths of xylene, and rehydration in an ethanol gradient (95%, 70%, 30%), antigen retrieval was achieved with an EDTA buffer (1 mM EDTA, 0.05% Tween-20 adjusted to pH 8.0) for 20 min at boiling temperature and then washed for 15 min in running water. Tissues were then permeabilized with 0.25% Triton X-100 in PBS for 30 min at room temperature and washed three times (5 min each) in PBS. The sections were blocked with a BlockAid solution from Life Technologies (Carlsbad, CA) for 1 h at room temperature, washed, and incubated at 4 °C overnight with the following antibodies: mouse monoclonal anti-mouse Neuronal nuclei (NeuN) antibody (Millipore, Billerica, MA) and rabbit anti-mouse cleaved caspase-3 (Asp175) antibody (Cell Signaling, Danvers, MA) or rabbit anti-mouse ionized calcium-binding adapter molecule 1 (Iba-1) antibody (Wako chemicals, Richmond, VA), and mouse monoclonal anti-mouse glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP)-Cy3 antibody (Sigma-Aldrich, Saint-Louis, MO). After washes, sections were incubated for 1 h with their respective secondary antibodies (either anti-rabbit Alexa-647 or anti-mouse Alexa-594) from Life Technologies before counterstaining using ProLong® Gold Antifade Reagent with DAPI (Molecular Probes, Eugene, OR). Substitution of the primary antibody served as negative control. A Zeiss Observer Z1 fluorescent microscope with the AxioVision rel4.8 program (Zeiss, Oberkochen, Germany) was used to read the slides in a blinded fashion. For the astrocytes (GFAP) and microglia (Iba-1) quantification, three pictures (20x) around each ventricle were taken, and the positive pixels were measured using the imageJ software (v 1.6.0). For apoptotic neuron quantification (NeuN and cleaved caspase-3), six random pictures (× 20) were taken throughout the whole section. As suggested in the literature [18], two blinded investigators manually determined co-localized signals and an average was obtained per mice.
Phenotype evaluation
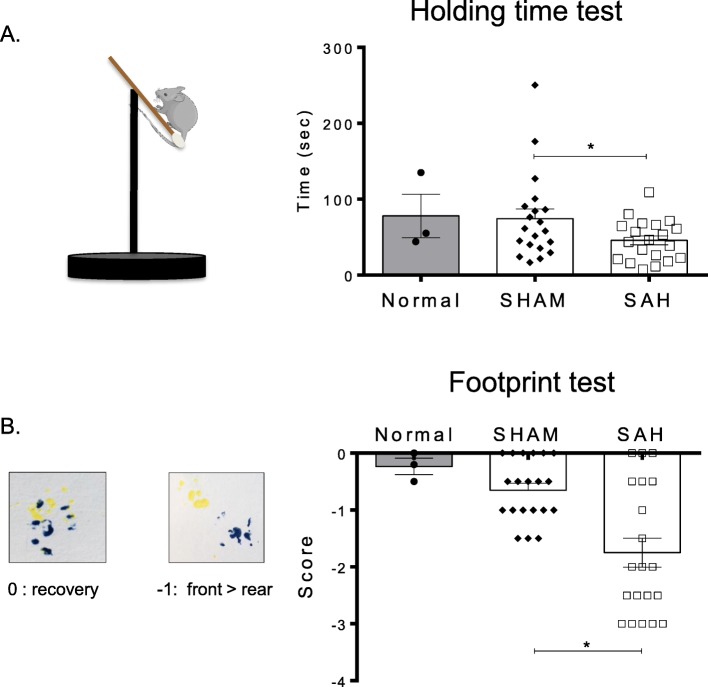
Motor capacities were evaluated at D7 (nSHAM = nSAH = 19, 4 independent experiments and nNormal = 3) (Fig. 1a) in order to confirm SAH induction using two phenotypic tests: the holding time test and the footprint test. The evaluating investigator was blinded to the experimental conditions. The holding time test is adapted from the inverted grid test [19]. Briefly, a cotton-tipped applicator (Fisher scientific, Hampton, NH) was placed and fixed on a pedestal at a 30° angle. Mice were then placed on it and the time during which the mouse stayed suspended was measured. Measures were done in triplicate per mouse to obtain an average time. For the footprint test [20], front and rear paws were respectively colored with yellow and blue nontoxic paint. Animals were then allowed to freely walk on a white paper sheet and only the regions in which the mice walked in a straight line were considered for the gait quantification. Gait pattern was analyzed by a scoring system based on a normal mouse behavior. The score of 0 was given when front and rear paws reached the same level (superposition) while walking. The score of -1 was given when rear paws, left and/or right, were not able to match the position of the front paws (no superposition) while walking, hence reflecting a motor deficit phenotype. Three measurements per paw-side per mouse were obtained.
Human immunomonitoring
We recruited consecutive adult patients who had a diagnosis of SAH in the last 48 h and were admitted to an academic intensive care unit between May 2013 and March 2015. Diagnosis was made by head computed tomography (CT) or the presence of red blood cells and xanthochromia on cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) analysis. Patients with secondary SAH related to trauma, rupture of an arteriovenous malformation or other structural lesions were excluded, as well as patients with significant immunosuppression/cancers/chronic organ failure/chronic viral infection. Written informed consent was obtained from the patient or a legally authorized representative prior to their inclusion in the study. The study was approved by the CHUM ethics committee.
All patients were admitted to a critical care unit and treated as per contemporary clinical guidelines [21]. They received 60 mg per os nimodipine every 4 h and surgical or endovascular treatment was performed as soon as possible. External ventricular drainage (EVD) was inserted as needed, for symptomatic hydrocephalus or intraventricular hemorrhage with reduced level of consciousness. Blood samples were taken at admission and at D1, D2, D5, and D10 (Fig. 1b). Plasma was obtained after centrifugation and frozen until completion of all time points. The V-Plex technology from MSD was used to measure cytokine levels in plasma. The kit selected (c-reactive protein (CRP), Eotaxin, Eotaxin-3, basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF), granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF), intercellular adhesion molecule (ICAM-1), interferon-γ (IFN-γ), IL-10, IL-12/IL-23p40, IL-12p70, IL-13, IL-15, IL-16, IL-17A, IL-1α, IL-1β, IL-2, IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, IL-7, IL-8, interferon-inducible protein (IP)-10, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1), MCP-4, macrophage-derived chemokine (MDC), macrophage inflammatory protein (MIP)-1α, MIP-1β, placental growth factor (PlGF), serum amyloid A (SAA), thymus and activation-regulated chemokine (TARC), tyrosine kinase with immunoglobulin and EGF homology domains (Tie)-2, TNF-α, TNF-β, vascular cell adhesion molecule (VCAM)-1, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-A, VEGF-C, VEGF-D, VEGFR-1/Flt-1)) was used per manufacturer’s instructions. Clinical outcome was evaluated at one year using the modified Rankin Scale (mRS). This mRS is a clinical severity scale based on the patient’s neurological disabilities [22].
Statistical analysis
The results are expressed as mean +/− standard error of the mean (SEM) and were analyzed by Student’s t test (with Bonferroni correction when appropriate). P < 0.05 was deemed to be significant for all tests. For human cytokine analyses, within-group analysis with repeated measure ANOVA was used to confirm significant variation in levels of blood-derived inflammatory factors across time in individual patients. Mean levels of inflammatory mediators stratified by dichotomized outcomes (good [mRS 0–3] or poor [mRS 4–6]) were plotted against time with their 95% confidence interval (CI) using the groupwiseMean function from the rcompanion package in R. Ordinal logistic regressions were used to model the association between each serum-derived inflammatory mediator at admission and clinical outcomes. The roportional odds model was used and was fitted with the “polr” function from the MASS package in R, with 95% CI. All analyses were performed using R version 3.3.1.
Results
SAH induces a peripheral and systemic inflammatory response
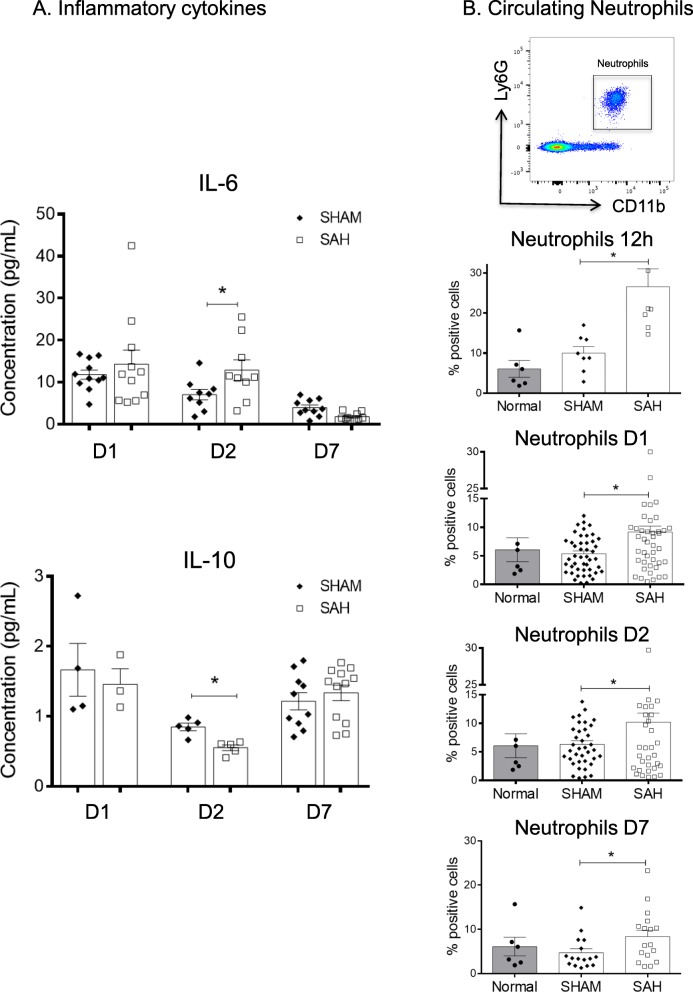
To decipher the early inflammatory innate response present in our model, we first characterized the activation of peripheral cellular inflammation after SAH with prospective blood sample analyses. At 24 h, we observed an increase in pro-inflammatory IL-6 levels and a decrease in anti-inflammatory IL-10 levels. At 48 h, this trend was confirmed by a significant increase in pro-inflammatory IL-6 levels and a significant decrease in anti-inflammatory IL-10 levels (Fig. 2a). According to the published literature [23, 24], the IL-6 and IL-10 values of adult male C57BL/6 J WT are in the expected range of normal mice. However, no variations were observed in levels of IL-17, IL-23, TNF, or IL-1β. SAH also induced a persistent and significant systemic neutrophilia (CD11b+Ly6G+) for all the studied time points (Fig. 2b). The blood monocyte subset populations were not modulated following SAH (data not shown). Our analyses support higher levels of systemic inflammatory mediators in the SAH group when compared with the SHAM group.
Fig. 2.
SAH is linked to a systemic modulation of inflammatory cytokines and neutrophils. a Quantification of IL-6 and IL-10 levels in the plasma at D1 (nSHAM = 4, nSAH = 3), D2 (nSHAM = nSAH = 5) and D7 (nSHAM = 10, nSAH = 12). At D2, we found a significant increase in IL-6 (*p = 0.049) and significant decrease in IL-10 (*p = 0.002) levels in the SAH mice (white squares) compared with SHAM mice (black diamonds). b Representative dot plots and quantification of neutrophil percentages (CD11b+Ly6G+) in the blood. Over time, we observed a sustained increase in neutrophil percentages at 12 h (*p = 0.0035, nSHAM = nSAH = 8), D1 (*p = 0.002, nSHAM = 51, nSAH = 52), D2 (*p = 0.027, nSHAM = 35, nSAH = 34) and D7 (*p = 0.042, nSHAM = nSAH = 19) following SAH (white squares) compared with SHAM (black diamonds). The neutrophil percentages from normal mice (n = 6, black circles) are not different from the SHAM mice
SAH induces early intracerebral innate immune cell recruitment and activation
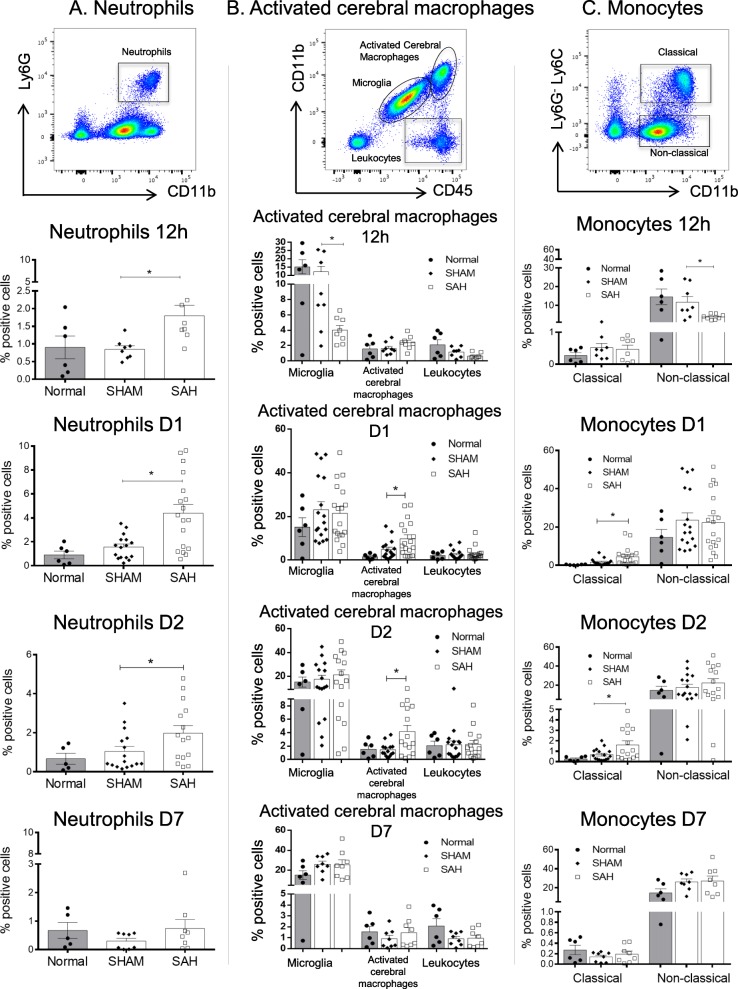
We characterized the brain infiltrating innate immune cells. At 12 h, D1 and D2 after SAH, we highlighted a significant increase in intracerebral neutrophil (CD11b+Ly6G+) proportions compared with the SHAM group (Fig. 3a). However, this difference was not seen at D7 (Fig. 3a). At D1 and D2, a significant increase in intracerebral macrophages and activated microglia (CD45highCD11bhigh) [17] was observed in the SAH group when compared with the SHAM group (Fig. 3b). No difference in resting microglia (CD45lowCD11blow) [17] was detected between the two groups. To further characterize brain innate immune cells, we examined two different monocyte populations: the Ly6G-CD11b+Ly6Clow cells (non-classical or anti-inflammatory monocytes) and Ly6G-CD11b+Ly6Chigh cells (classical or inflammatory monocytes) [25]. Interestingly, we observed a significant early decrease in non-classical monocytes at 12 h associated with an increase in classical monocytes at D1 and D2 in the SAH group compared with the SHAM group (Fig. 3c). Taken all together, these results suggest that brain inflammation following SAH is characterized by microglia and macrophage activation, as well as neutrophils and classical monocyte infiltration.
Fig. 3.
SAH induction was locally associated with activation of microglia and pro-inflammatory monocytes, and neutrophil recruitment. Flow cytometry analyses of brain infiltrating leukocytes. a Representative dot plot for quantification of neutrophil percentages (CD11b+Ly6G+) at 12 h (nSHAM = nSAH = 8), D1 (nSHAM = 16, nSAH = 18), D2 (nSHAM = 16, nSAH = 15) and D7 (nSHAM = nSAH = 8). We observed a significant increase in neutrophils following SAH compared with SHAM at 12 h (*p = 0.0080), D1 (*p = 0,030) and D2 (*p = 0.017). Neutrophils were almost undetectable at D7. Values from the normal group showed no significant differences between normal and SHAM groups. b Representative dot plot and quantification of positive cell percentages of microglia (CD45lowCD11blow), activated microglia and macrophages (CD45highCD11bhigh) and leukocytes (CD45+CD11b-) at 12 h, D1, D2, and D7. We observed a significant decrease in microglia at 12 h (*p = 0.0286) and a significant increase in activated microglia at D1 (*p = 0.031) and D2 (*p = 0.0085) following SAH compared with SHAM. No significant differences were observed for microglia and leukocytes over time using this strategy. No significant differences were observed between normal and SHAM groups. c Representative dot plot and quantification of positive cell percentages for pro-inflammatory (Ly6G-CD11b+Ly6Chigh) and anti-inflammatory (Ly6G-CD11b+Ly6Clow) monocytes at 12 h, D1, D2, and D7. We observed a significant decrease in non-classical monocytes at 12 h (*p = 0.0225) followed by a significant increase in pro-inflammatory monocytes at D1 (*p = 0.049) and D2 (*p = 0.020) following SAH compared with SHAM. Monocytes, either classical or non-classical, were almost undetectable at D7. There was no significant difference between normal and SHAM groups
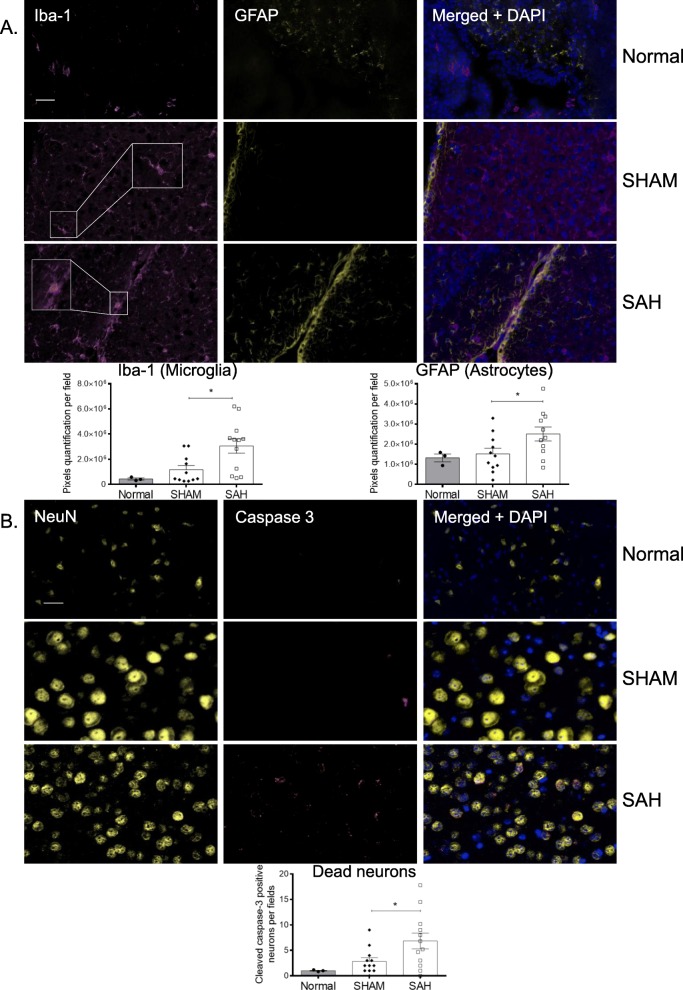
SAH promotes microglia and astrocyte activation and neuron apoptosis
Iba-1 and GFAP immunofluorescence staining to measure microglia and astrocyte activation respectively is a method commonly used in subarachnoid models [26–28]. We found a significant increase in activated cerebral macrophages and astrocytes in the SAH group compared with the SHAM group at D7 (Fig. 4a). Under simple magnification (Fig. 4a), microglia morphology changes were detected between SHAM and SAH with Iba-1 staining. The majority of Iba-1 positive cells in the SHAM group were similar to resting microglia (ramified morphology) whereas the Iba-1 positive cells in the SAH group appeared to have a larger cell body associated with a decrease of ramification similar to the ameboid (activated) microglia [29]. We also found a significant increase in apoptotic neurons, identified by dual positivity for NeuN and cleaved active caspase-3, in SAH mice compared with SHAM at D1 (data not shown) and D7 (Fig. 4b). These results suggest that SAH induced the activation of microglia and astrocytes and neuronal apoptosis.
Fig. 4.
SAH induces a local activation of microglia and astrocytes, and caspase-3-positive apoptotic neurons. Immunofluorescence staining was performed at D7 on brain slides (nSHAM = nSAH = 11). a Representative pictures of activated microglia (Iba-1, pink) and astrocytes (GFAP, yellow) are shown for the different groups (Normal, SHAM, and SAH). Quantification of pixels showed that SAH significantly induced microglia (*p = 0.009) and astrocyte (*p = 0.021) activation compared with control (SHAM). b Representative pictures of neurons (NeuN, yellow) and activated caspase-3 (cleaved caspase-3, red) are shown for the different groups (Normal, SHAM, and SAH). Merged images showing colocalization define apoptotic neurons. Quantification showed that SAH induced a significant increase in neuron death compared with control (*p = 0.010). DAPI was used as a counterstain for nuclei (bar = 50 μm).
Induction of SAH by blood injection induces motor deficits in mice
To validate the efficiency of our mouse model and to confirm that it induces similar signs to what is observed in human patients during DCI, the presence of motor deficits following SAH was confirmed by two complementary phenotypic tests [19, 20]. First, SAH mice had a significant decrease in their holding time as compared with control (SHAM) mice (Fig. 5a). Secondly, we used the footprint test to demonstrate and quantify motor deficits and observed a poorer performance in SAH mice than in SHAM mice on gait analysis (Fig. 5b).
Fig. 5.
SAH induces motor deficiencies. Tests were performed at D7 on SHAM, SAH mice (nSHAM = nSAH = 19) and 3 normal mice. a Holding time test. The SAH group had a significant decrease in its holding capacity compared with the SHAM group (*p = 0.003). b Footprint test. The SAH group showed a significantly deficient gait compared with the SHAM group (*p = 0.001)
Human immunomonitoring in plasma
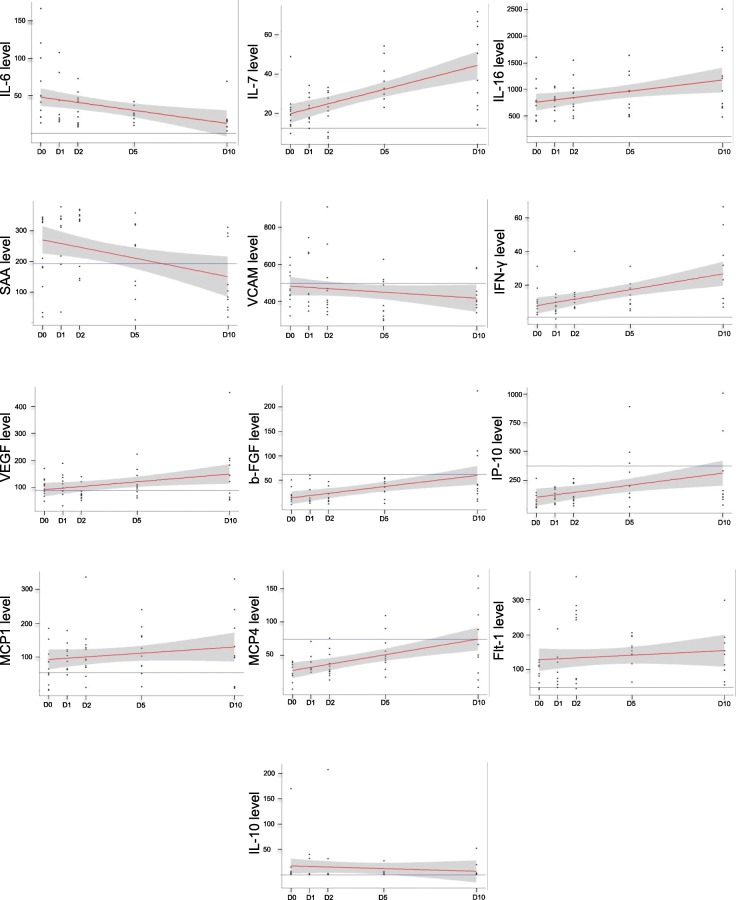
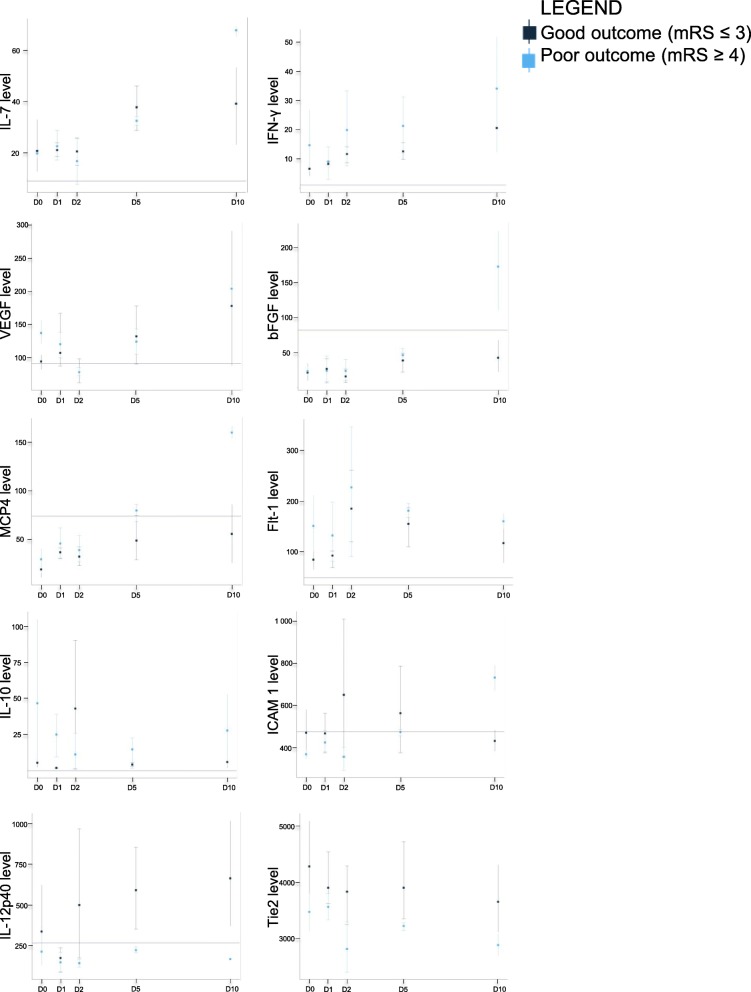
A total of 13 adult patients with SAH were recruited, 86% of which presented with significant brain injury (high-grade SAH with World Federation of Neurological Surgeons (WFNS) grade 4 or 5 at admission) (see Table 1 for patient characteristics). Good neurological outcome was observed in 43% at 12 months (mRS 0–3). Levels of IL-6, IL-7, IL-16, SAA, VCAM-1, IFN-γ, VEGF, bFGF, IP-10, MCP-1, MCP-4, and Flt-1 all varied significantly in time (Fig. 6). The longitudinal variations of inflammatory mediators were markedly different among patients with favorable outcomes compared with those with a worse outcome in regard to ICAM-1, bFGF, IL-7, IL-12p40, and MCP-4 (Fig. 7). Despite the small number of patients, admission levels of blood inflammatory factors showed trends of association with outcome (data not shown). Based on ordinal logistic regression, higher levels of Flt-1 and VEGF at admission were significantly associated with worse outcomes (odds ratio 1.23 [95% C.I. 1.004, 1.586] and 1.70 [95% C.I. 1.05, 3.42] respectively). However, wide confidence intervals with most of the other inflammatory mediators prevented meaningful conclusions.
Table 1.
Characteristics of adult patients with SAH
| Patient | Sex | Age | WFNS grade | Fisher grade | mRS | Comorbidities |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | F | 59 | 4 | 4 | 3 | Arterial hypertension, dyslipidemia, appendectomy, tonsillectomy, smoking |
| 2 | F | 63 | 2 | 4 | 1 | Arterial hypertension |
| 3 | F | 59 | 5 | 4 | 3 | Arterial hypertension, anemia |
| 4 | F | 46 | 4 | 4 | 4 | Multiple sclerosis, substance addiction |
| 5 | M | 51 | 2 | 3 | Smoking | |
| 6 | M | 51 | 3 | 3 | 1 | Smoking |
| 7 | M | 74 | 5 | 3 | Parkinson disease | |
| 8 | M | 55 | 5 | 4 | 5 | Anxiety, depression, chronic alcoholism |
| 9 | M | 63 | 5 | 4 | 3 | Atherosclerotic heart disease, epilepsy, arterial hypertension, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease |
| 10 | F | 62 | 5 | 4 | 4 | Car-pedestrian accident |
| 11 | F | 57 | 5 | 4 | Null | |
| 12 | F | 49 | 4 | 4 | 2 | Arterial hypertension, nephretic colic, smoking |
| 13 | M | 52 | 5 | 4 | 2 | Null |
F female, M male, WFNS World Federation of Neurological Surgeons, mRS modified Rankin Scale
Fig. 6.
Cytokine variation over time by human immunomonitoring. Mean levels and distribution of selected cytokines at D0, D1, D2, D5, and D10, with baseline levels in healthy controls (line parallel to the x axis). We demonstrated a significant variation over time in levels of inflammatory mediators shown in the figure using within-group analysis with repeated measure ANOVA (p value< 0.05)
Fig. 7.
Cytokine variation and outcomes by human immunomonitoring. Group-wise mean levels and distribution of selected cytokines at D0, D1, D2, D5, and D10 stratified by outcomes, 7 patient had good outcomes (good outcome defined as an mRS of 0–3 at 1 year), 3 patients had worse outcomes and 3 patients had unknown outcomes, with baseline levels in healthy controls (line parallel to the x axis). Our observations support a different longitudinal evolution among patients with favorable outcomes compared with those with a worse outcome based on ICAM-1, bFGF, IL-7, IL-12p40, and MCP-4
Discussion
We took advantage of a mouse SAH model that mimics an anterior circulation aneurysm rupture. This model is associated with a prolonged increased in peripheral neutrophil mobilization and a significant increase of IL-6 levels reflecting activation of systemic inflammation. This inflammatory systemic response is translated into an early increase in neutrophil recruitment to the brain (12 h to D2). Following SAH, we also observed an early increase in brain infiltration of innate immune cells. Furthermore, we found an early increase in microglia activation and pro-inflammatory monocyte recruitment within the first 48 h after SAH during the EBI period. Similar to SAH in humans, the presence of apoptotic neurons is associated with motor complications [10] at later time points as confirmed by our two phenotypic tests highlighting motor dysfunctions [30] and muscle weakness [31].
Various events, including brain inflammation as investigated here, occur during EBI and have been implicated in the late increase in neuronal death that is responsible for the development of neurologic symptoms observed in SAH, referred to as DCI [32]. We found significant modulations of IL-6 and IL-10 levels after SAH in our mouse model. In opposition to other studies, we did not find any differences in TNF-α and IL-1β after SAH [33]. In our mice model, the increase of the blood-brain barrier (BBB) permeability [3] following SAH was confirmed indirectly by the significant increase of circulating and brain neutrophils and brain monocytes. Neutrophils have a phagocytic function to eliminate red blood cells [34], but they also release pro-inflammatory factors exacerbating inflammation [35]. The increase of neutrophils in our model and a study that showed that depletion of neutrophils improved survival in rats [36] suggest that they may be important in the neuroinflammation induced after SAH.
In our model, SAH also induced microglia activation, reflecting initiation of cerebral inflammatory events. These results were also observed in other inflammatory models such as spinal cord injury models [37]. Microglial cells play a crucial role in inflammatory processes [38]. Activated microglia can prevent neuronal injury and promote tissue repair, but hyperactivation of microglia can promote cell death and neuronal dysfunctions through high secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6) [39]. The microglia is also the major component of the innate immune system in the brain and is composed of resident macrophages. These macrophages are reprogrammed in response to their microenvironment into several phenotypes ranging from pro-inflammatory to anti-inflammatory macrophages [40]. The intracerebral macrophages are also generated from the differentiation of recruited monocytes into brain macrophages [41]. Our data suggest that SAH induced a significant increase in activated resident microglia and recruited classical monocytes at D1 and D2. Hence, we believe that monocytes are activated and differentiated locally in response to SAH. Astrocyte activation, as observed in our model, is probably a consequence of microglia activation, enhancing neuroinflammation [42]. Moreover, early microglial and astrocyte activation results in macrophage activation through monocyte [43] and neutrophil [34] recruitment, which enters the subarachnoid space early after SAH to activate and maintain local cellular inflammation.
Neuron apoptosis has also been detected after SAH in humans [44] and in animal models [45]. Cleaved caspase-3 is used as a marker of apoptotic cell death because of its effector function [46, 47]. We showed that the induction of SAH caused a significant increase in caspase-3-positive apoptotic neurons. Taken together, our results confirmed that the SAH model induced a motor disturbance associated with late neuronal death, indicating signs of DCI, and reproducing neurological and motor symptoms found in SAH patients.
Our prospective human study revealed that various cytokines, chemokines, and growth factors varied over time. ICAM-1, bFGF, IL-7, IL-12p40, and MCP-4 variations over time were different in SAH patients with good versus bad outcomes. The increased concentration of ICAM-1 within 24 h was already known to be linked with the severity of symptoms in SAH patients [48]. bFGF was implicated in fibrosis, angiopathy, and hyperplasia during late stages in SAH patients [49]. Moreover, high levels of Flt-1 and VEGF at admission were associated with a worse outcome in SAH. Several of these factors are crucial in maintaining BBB integrity. In particular, VEGF increases BBB permeability [50], and mouse experiments have shown that anti-VEGF treatment decreases permeability and severity of symptoms [51, 52], confirming the importance of VEGF on BBB integrity and EBI. In our human samples, SAA varied significantly over time, but was not associated with the prognosis. However, SAA demonstrated a predictive value for detecting patients susceptible to developing a nosocomial infection during their hospitalization [53]. Furthermore, IL-6 is significantly increased over time, but not linked to the severity of SAH. IL-6 is considered a biomarker of vasospasm [54], a finding that was not reproduced in our study. Several markers that varied over time in our study seemed unrelated to DCI, vasospasm, or clinical outcomes in another study [55]. Therefore, further studies are required to better understand the impact of these inflammatory proteins in SAH.
Altogether, these observations suggest that alteration to the BBB may allow innate immune cell recruitment into the brain to promote intracerebral inflammation, leading to neuronal cell death and motor deficits following SAH.
The limitations in our study are primarily linked to our model. Other models exist, such as the endovascular perforation in rats, which reproduces severe SAH. It can generate an important ischemia, but at the expense of mortality [56]. Most other models were developed to study cerebral vasospasm, but have little focus on the alternative pathways of brain injury [57]. In contrast, our model mimics an anterior circulation SAH, which is clinically relevant. Prospective immunomonitoring of circulating leukocytes in SAH patients will lead us to a better understanding of cellular inflammation during EBI and will be assessed in an upcoming study.
Conclusions
In this study, we showed that early infiltration and activation of innate immune cells (neutrophils, classical monocytes, and activated microglia and macrophages) precede late neuronal death and motor deficits associated with SAH. Macrophage reprogramming offers us a new window for pharmacological treatments in SAH. Long-term goals to improve patient outcomes are to modulate microglia activation and macrophage phenotype to decrease neuroinflammation and neuronal cell death, ultimately reducing functional deficits and improving outcomes in SAH patients.
Acknowledgements
TG received a Canderel Scholarship from the Institut de cancer de Montréal. FBM is a recipient of the COPSE scholarship. We acknowledge Jacqueline Chung for manuscript editing. We thank the molecular pathology core facility of the CRCHUM for the paraffin-embedded mouse brain.
Abbreviations
- ACK
Ammonium chloride potassium
- BBB
Blood brain barrier
- bFGF
Basic fibroblast growth factor
- CI
Confidence interval
- CIPA
Comité Institutionnel de Protection des Animaux
- CONSCIOUS
Clazosentan to Overcome Neurological iSChemia and Infarction OccUring after Subarachnoid hemorrhage
- CRCHUM
Centre de Recherche du Centre Hospitalier l’Université de Montréal
- CRP
C-reactive protein
- CSF
Cerebrospinal fluid
- CT
Computed tomography
- D
Day
- DCI
Delayed cerebral ischemia
- EBI
Early brain injury
- EDTA
Ethylenediaminetetraeacetic acid
- EVD
External ventricular drainage
- GFAP
Glial fibrillary acidic protein
- GM-CSF
Granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor
- h
Hours
- HBSS
Hank’s balanced salt solution
- Iba-1
Ionized calcium-binding adapter molecule 1
- ICAM-1
Intercellular adhesion molecule-1
- IFN-γ
Interferon-γ
- IL
Interleukin
- IP
Interferon-inducible protein
- MCP-1
Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1
- MDC
Macrophage-derived chemokine
- MIP
Macrophage inflammatory protein
- mRS
Modified Rankin Scale
- NeuN
Neuronal nuclei
- PBS
Phosphate buffered saline
- PlGF
Placental growth factor
- rpm
Rotation per minutes
- SAA
Serum amyloid A
- SAH
Subarachnoid hemorrhage
- SEM
Standard error of the mean
- TARC
Thymus and activation-regulated chemokine
- Tie
Tyrosine kinase with immunoglobulin and EGF homology domains
- TNF
Tumor necrosis factor
- VCAM
Vascular cell adhesion molecule
- VEGF
Vascular endothelial growth factor
- WFNS
World Federation of Neurological Surgeons
- WT
Wild type
Authors’ contributions
TG, PL, CLF, and J-FC contributed to conception and design, collection and assembly of data, data analysis and interpretation, and manuscript writing. PT, RC, AN, BJ-P, FB-M, EM, SE, RL, and MB contributed to collection, assembly, analysis, and interpretation of the data. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Chaire Claude-Bertrand en Neurochirurgie de l’Université de Montréal.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed in the current study are available from the corresponding author on a reasonable request.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Animal experiments were approved by the Comité Institutionnel de Protection des Animaux (CIPA) of the CRCHUM and CHUM ethics committee.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Typhaine Gris, Email: typhaine.gris@umontreal.ca.
Patrick Laplante, Email: laplantepat@videotron.ca.
Paméla Thebault, Email: pamela.thebault@gmail.com.
Romain Cayrol, Email: romain.cayrol@gmail.com.
Ahmed Najjar, Email: ahmed.najjar@umontreal.ca.
Benjamin Joannette-Pilon, Email: benjamin.joannette-pilon@mail.mcgill.ca.
Frédéric Brillant-Marquis, Email: frederic.brillant-marquis@umontreal.c.
Elsa Magro, Email: elsa.magro@chu-brest.fr.
Shane W. English, Email: senglish@ohri.ca
Réjean Lapointe, Email: rejean.lapointe@umontreal.ca.
Michel Bojanowski, Email: michel.bojanowski.chum@ssss.gouv.qc.ca.
Charles L. Francoeur, Email: charles-langis.francoeur.2@ulaval.ca
Jean-François Cailhier, Email: jf.cailhier@umontreal.ca.
References
- 1.Schertz M, Mehdaoui H, Hamlat A, Piotin M, Banydeen R, Mejdoubi M. Incidence and Mortality of Spontaneous Subarachnoid Hemorrhage in Martinique. PLoS One. 2016;11(5):e0155945. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0155945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Bederson JB, Connolly ES, Jr, Batjer HH, Dacey RG, Dion JE, Diringer MN, et al. Guidelines for the management of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: a statement for healthcare professionals from a special writing group of the Stroke Council. American Heart Association. Stroke. 2009;40(3):994–1025. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.108.191395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Cahill J, Zhang JH. Subarachnoid hemorrhage: is it time for a new direction? Stroke. 2009;40(3 Suppl):S86–S87. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.108.533315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Johnston SC, Selvin S, Gress DR. The burden, trends, and demographics of mortality from subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurology. 1998;50(5):1413–1418. doi: 10.1212/WNL.50.5.1413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Wong GK, Wong R, Mok V, Wong A, Poon WS. Natural history and medical treatment of cognitive dysfunction after spontaneous subarachnoid haemorrhage: review of current literature with respect to aneurysm treatment. J Neurol Sci. 2010;299(1-2):5–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2010.08.059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Macdonald RL. Delayed neurological deterioration after subarachnoid haemorrhage. Nat Rev Neurol. 2014;10(1):44–58. doi: 10.1038/nrneurol.2013.246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Dankbaar JW, Slooter AJ, Rinkel GJ, Schaaf IC. Effect of different components of triple-H therapy on cerebral perfusion in patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage: a systematic review. Crit Care. 2010;14(1):R23. doi: 10.1186/cc8886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Keyrouz SG, Diringer MN. Clinical review: Prevention and therapy of vasospasm in subarachnoid hemorrhage. Crit Care. 2007;11(4):220. doi: 10.1186/cc5958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Nassiri F, Ibrahim GM, Badhiwala JH, Witiw CD, Mansouri A, Alotaibi NM, et al. A Propensity Score-Matched Study of the Use of Non-steroidal Anti-inflammatory Agents Following Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Neurocrit Care. 2016;25(3):351–358. doi: 10.1007/s12028-016-0266-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Sabri M, Lass E, Macdonald RL. Early brain injury: a common mechanism in subarachnoid hemorrhage and global cerebral ischemia. Stroke Res Treat. 2013;2013:394036. doi: 10.1155/2013/394036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Lucke-Wold BP, Logsdon AF, Manoranjan B, Turner RC, McConnell E, Vates GE, et al. Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage and Neuroinflammation: A Comprehensive Review. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(4):497. doi: 10.3390/ijms17040497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Peng J, Wu Y, Tian X, Pang J, Kuai L, Cao F, et al. High-Throughput Sequencing and Co-Expression Network Analysis of lncRNAs and mRNAs in Early Brain Injury Following Experimental Subarachnoid Haemorrhage. Sci Rep. 2017;7:46577. doi: 10.1038/srep46577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Provencio JJ, Altay T, Smithason S, Moore SK, Ransohoff RM. Depletion of Ly6G/C(+) cells ameliorates delayed cerebral vasospasm in subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Neuroimmunol. 2011;232(1-2):94–100. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2010.10.016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Oruckaptan HH, Caner HH, Kilinc K, Ozgen T. No apparent role for neutrophils and neutrophil-derived myeloperoxidase in experimental subarachnoid haemorrhage and vasospasm: a preliminary study. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2000;142(1):83–90. doi: 10.1007/s007010050011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Atangana E, Schneider UC, Blecharz K, Magrini S, Wagner J, Nieminen-Kelha M, et al. Intravascular Inflammation Triggers Intracerebral Activated Microglia and Contributes to Secondary Brain Injury After Experimental Subarachnoid Hemorrhage (eSAH) Transl Stroke Res. 2017;8(2):144–156. doi: 10.1007/s12975-016-0485-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Sabri M, Jeon H, Ai J, Tariq A, Shang X, Chen G, et al. Anterior circulation mouse model of subarachnoid hemorrhage. Brain Res. 2009;1295:179–185. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2009.08.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Legroux L, Pittet CL, Beauseigle D, Deblois G, Prat A, Arbour N. An optimized method to process mouse CNS to simultaneously analyze neural cells and leukocytes by flow cytometry. J Neurosci Methods. 2015;247:23–31. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2015.03.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Sabri M, Kawashima A, Ai J, Macdonald RL. Neuronal and astrocytic apoptosis after subarachnoid hemorrhage: a possible cause for poor prognosis. Brain Res. 2008;1238:163–171. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2008.08.031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Aartsma-Rus A, van Putten M. Assessing functional performance in the mdx mouse model. J Vis Exp. 2014;85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 20.Brooks SP, Trueman RC, Dunnett SB. Assessment of Motor Coordination and Balance in Mice Using the Rotarod, Elevated Bridge, and Footprint Tests. Curr Protoc Mouse Biol. 2012;2(1):37–53. doi: 10.1002/9780470942390.mo110165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Powers WJ, Rabinstein AA, Ackerson T, Adeoye OM, Bambakidis NC, Becker K, et al. 2018 Guidelines for the Early Management of Patients With Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Guideline for Healthcare Professionals From the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2018;49(3):e46–e110. doi: 10.1161/STR.0000000000000158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Banks JL, Marotta CA. Outcomes validity and reliability of the modified Rankin scale: implications for stroke clinical trials: a literature review and synthesis. Stroke. 2007;38(3):1091–1096. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.0000258355.23810.c6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Karatayli E, Hall RA, Weber SN, Dooley S, Lammert F. Effect of alcohol on the interleukin 6-mediated inflammatory response in a new mouse model of acute-on-chronic liver injury. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2019;1865(2):298–307. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2018.11.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Ferreira BL, Ferreira ER, de Brito MV, Salu BR, Oliva MLV, Mortara RA, et al. BALB/c and C57BL/6 Mice Cytokine Responses to Trypanosoma cruzi Infection Are Independent of Parasite Strain Infectivity. Front Microbiol. 2018;9:553. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.00553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Rose S, Misharin A, Perlman H. A novel Ly6C/Ly6G-based strategy to analyze the mouse splenic myeloid compartment. Cytometry A. 2012;81(4):343–350. doi: 10.1002/cyto.a.22012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Gottipati MK, Bekyarova E, Brenner M, Haddon RC, Parpura V. Changes in the morphology and proliferation of astrocytes induced by two modalities of chemically functionalized single-walled carbon nanotubes are differentially mediated by glial fibrillary acidic protein. Nano Lett. 2014;14(7):3720–3727. doi: 10.1021/nl4048114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Ito D, Tanaka K, Suzuki S, Dembo T, Fukuuchi Y. Enhanced expression of Iba1, ionized calcium-binding adapter molecule 1, after transient focal cerebral ischemia in rat brain. Stroke. 2001;32(5):1208–1215. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.32.5.1208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Quick ED, Leser JS, Clarke P, Tyler KL. Activation of intrinsic immune responses and microglial phagocytosis in an ex vivo spinal cord slice culture model of West Nile virus infection. J Virol. 2014;88(22):13005–13014. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01994-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Fernandez-Arjona MDM, Grondona JM, Granados-Duran P, Fernandez-Llebrez P, Lopez-Avalos MD. Microglia Morphological Categorization in a Rat Model of Neuroinflammation by Hierarchical Cluster and Principal Components Analysis. Front Cell Neurosci. 2017;11:235. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2017.00235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Hernandez-Jimenez M, Pena-Martinez C, Godino MDC, Diaz-Guzman J, Moro MA, Lizasoain I. Test repositioning for functional assessment of neurological outcome after experimental stroke in mice. PLoS One. 2017;12(5):e0176770. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0176770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Hoffman E, Winder S. A modified wire hanging apparatus for small animal muscle function testing. PLOS Currents muscular Dystrophy. 2016;Ediction 1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 32.Kaura V, Bonner S. Subarachnoid haemorrhage: early clinical indicators and biomarkers. Anesthesia and critical care. 2012;5.
- 33.Ayer R, Zhang J. Connecting the early brain injury of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage to clinical practice. Turk Neurosurg. 2010;20(2):159–166. doi: 10.5137/1019-5149.JTN.2714-09.0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Chaichana KL, Pradilla G, Huang J, Tamargo RJ. Role of inflammation (leukocyte-endothelial cell interactions) in vasospasm after subarachnoid hemorrhage. World Neurosurg. 2010;73(1):22–41. doi: 10.1016/j.surneu.2009.05.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Kessenbrock K, Frohlich L, Sixt M, Lammermann T, Pfister H, Bateman A, et al. Proteinase 3 and neutrophil elastase enhance inflammation in mice by inactivating antiinflammatory progranulin. J Clin Invest. 2008;118(7):2438–2447. doi: 10.1172/JCI34694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Friedrich V, Flores R, Muller A, Bi W, Peerschke EI, Sehba FA. Reduction of neutrophil activity decreases early microvascular injury after subarachnoid haemorrhage. J Neuroinflammation. 2011;8:103. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-8-103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Dougherty KD, Dreyfus CF, Black IB. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor in astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, and microglia/macrophages after spinal cord injury. Neurobiol Dis. 2000;7(6 Pt B):574–585. doi: 10.1006/nbdi.2000.0318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Mastroeni D, Sekar S, Nolz J, Delvaux E, Lunnon K, Mill J, et al. ANK1 is up-regulated in laser captured microglia in Alzheimer's brain; the importance of addressing cellular heterogeneity. PLoS One. 2017;12(7):e0177814. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0177814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Kumar A, Loane DJ. Neuroinflammation after traumatic brain injury: opportunities for therapeutic intervention. Brain Behav Immun. 2012;26(8):1191–1201. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2012.06.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Novak ML, Koh TJ. Macrophage phenotypes during tissue repair. J Leukoc Biol. 2013;93(6):875–881. doi: 10.1189/jlb.1012512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Mantovani A, Biswas SK, Galdiero MR, Sica A, Locati M. Macrophage plasticity and polarization in tissue repair and remodelling. J Pathol. 2013;229(2):176–185. doi: 10.1002/path.4133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Biswas S, Bachay G, Chu J, Hunter DD, Brunken WJ. Laminin-Dependent Interaction between Astrocytes and Microglia: A Role in Retinal Angiogenesis. Am J Pathol. 2017;187(9):2112–2127. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2017.05.016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Kubota T, Handa Y, Tsuchida A, Kaneko M, Kobayashi H, Kubota T. The kinetics of lymphocyte subsets and macrophages in subarachnoid space after subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats. Stroke. 1993;24(12):1993–2000. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.24.12.1993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Nau R, Haase S, Bunkowski S, Bruck W. Neuronal apoptosis in the dentate gyrus in humans with subarachnoid hemorrhage and cerebral hypoxia. Brain Pathol. 2002;12(3):329–336. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.2002.tb00447.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Prunell GF, Svendgaard NA, Alkass K, Mathiesen T. Inflammation in the brain after experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurosurgery. 2005;56(5):1082–1092. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Li H, Yu JS, Zhang HS, Yang YQ, Huang LT, Zhang DD, et al. Increased Expression of Caspase-12 After Experimental Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Neurochem Res. 2016;41(12):3407–3416. doi: 10.1007/s11064-016-2076-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Liu F, Chen Y, Hu Q, Li B, Tang J, He Y, et al. MFGE8/Integrin beta3 pathway alleviates apoptosis and inflammation in early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats. Exp Neurol. 2015;272:120–127. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2015.04.016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Al-Drawi AS, Wicinski M, Grzesk G, Szadujkis-Szadurska K, Grzesk E, Weclewicz MM, et al. Evaluation of VCAM-1 and ICAM-1 concentration and values of global tests concerning the coagulation system of patients suffering from subarachnoid haemorrage. Ann Agric Environ Med. 2016;23(4):654–659. doi: 10.5604/12321966.1226862. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Ogane K, Wolf EW, Robertson JH. Role of basic fibroblast growth factor in the course of cerebral vasospasm in an experimental model of subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurol Res. 2002;24(4):365–372. doi: 10.1179/016164102101200159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Schoch HJ, Fischer S, Marti HH. Hypoxia-induced vascular endothelial growth factor expression causes vascular leakage in the brain. Brain. 2002;125(Pt 11):2549–2557. doi: 10.1093/brain/awf257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Liu L, Fujimoto M, Kawakita F, Nakano F, Imanaka-Yoshida K, Yoshida T, et al. Anti-Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Treatment Suppresses Early Brain Injury After Subarachnoid Hemorrhage in Mice. Mol Neurobiol. 2016;53(7):4529–4538. doi: 10.1007/s12035-015-9386-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Liu L, Fujimoto M, Kawakita F, Ichikawa N, Suzuki H. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Brain Edema Formation After Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Acta Neurochir Suppl. 2016;121:173–177. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-18497-5_31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Azurmendi L, Degos V, Tiberti N, Kapandji N, Sanchez P, Sarrafzadeh A, et al. Measuring Serum Amyloid A for Infection Prediction in Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. J Proteome Res. 2015;14(9):3948–3956. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.5b00391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Lenski M, Huge V, Briegel J, Tonn JC, Schichor C, Thon N. Interleukin 6 in the Cerebrospinal Fluid as a Biomarker for Onset of Vasospasm and Ventriculitis After Severe Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. World Neurosurg. 2017;99:132–139. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2016.11.131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Rasmussen R, Bache S, Stavngaard T, Moller K. Plasma Levels of IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, ICAM-1, VCAM-1, IFNgamma, and TNFalpha are not Associated with Delayed Cerebral Ischemia, Cerebral Vasospasm, or Clinical Outcome in Patients with Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. World Neurosurg. 2019. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 56.Bederson JB, Germano IM, Guarino L. Cortical blood flow and cerebral perfusion pressure in a new noncraniotomy model of subarachnoid hemorrhage in the rat. Stroke. 1995;26(6):1086–1091. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.26.6.1086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Megyesi JF, Vollrath B, Cook DA, Findlay JM. In vivo animal models of cerebral vasospasm: a review. Neurosurgery. 2000;46(2):448–460. doi: 10.1097/00006123-200002000-00035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed in the current study are available from the corresponding author on a reasonable request.