Abstract
Post-transcriptional modifications in mitochondrial tRNAs (mt-tRNAs) play critical roles in mitochondrial protein synthesis, which produces respiratory chain complexes. In this study, we took advantage of mass spectrometric analysis to map 5-methylcytidine (m5C) at positions 48–50 in eight mouse and six human mt-tRNAs. We also confirmed the absence of m5C in mt-tRNAs isolated from Nsun2 knockout (KO) mice, as well as from NSUN2 KO human culture cells. In addition, we successfully reconstituted m5C at positions 48–50 of mt-tRNA in vitro with NSUN2 protein in the presence of S-adenosylmethionine. Although NSUN2 is predominantly localized to the nucleus and introduces m5C into cytoplasmic tRNAs and mRNAs, structured illumination microscopy clearly revealed NSUN2 foci inside mitochondria. These observations provide novel insights into the role of NSUN2 in the physiology and pathology of mitochondrial functions.
INTRODUCTION
The mitochondrion is a eukaryotic organelle that performs aerobic respiration through the electron transport chain and oxidative phosphorylation, thereby generating chemical energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Mitochondria have their own genome (mitochondrial DNA: mt-DNA) and a devoted gene expression system, consisting of transcriptional and translational machinery, that produces 13 subunits of respiratory chain complexes encoded in mt-DNA (1–3).
In mammals, the mitochondrial translational apparatus requires 22 species of mitochondrial (mt-)tRNAs encoded in mt-DNA. Long polycistronic precursor RNAs are transcribed from both strands of mt-DNA and processed into rRNAs, mRNAs and tRNAs. Because mt-tRNAs lie between mRNAs and rRNAs in the precursor RNAs, mt-tRNA processing results in separation of mRNAs and rRNAs (4). During the process of maturation, mt-tRNAs undergo various post-transcriptional modifications (3). We previously identified 15 species of modified nucleosides at 118 positions in all 22 mt-tRNAs of bovine mitochondria (5). mt-tRNAs are more heavily modified than mt-rRNAs, which are modified at only ten positions in the 12S and 16S rRNAs (6). In particular, a wide variety of modifications are present in the anticodon region of tRNAs (3), and these modifications play critical roles in the precise decoding of genetic codes (7).
The functional and physiological importance of mt-tRNA modifications is highlighted by the observation that mt-tRNAs are hypomodified in the cells of patients with mitochondrial diseases (3,8). We previously reported that 5-taurinomethyluridine (τm5U) and its 2-thiouridine derivative (τm5s2U) at the wobble position (position 34) of the anticodon (9) are not formed in mutant mt-tRNAsLeu(UUR) isolated from patients with MELAS (mitochondrial encephalopathy, lactic acidosis and stroke-like syndrome) or in mutant mt-tRNALys isolated from patients with MERRF (myoclonus epilepsy with ragged-red fibers), respectively (3,8). The absence of these taurine modifications results in defective mitochondrial translation, leading to mitochondrial dysfunction. Supporting these findings, several pathogenic mutations associated with mitochondrial disorders have been reported in the human genes MTO1, GTPBP3 and MTU1, which encode enzymes involved in τm5s2U biogenesis (10,11).
5-formylcytidine (f5C), another unique modification found at the wobble position of mt-tRNAMet (12), plays a critical role in deciphering the AUA codon as Met. We reported that NSUN3 (13) and ALKBH1 (14) are responsible for f5C34 biogenesis, and identified two pathogenic point mutations in mt-tRNAMet that impair f5C34 formation (13). N6-threonylcarbamoyladenosine (t6A) occurs at position 37, 3′-adjacent to the anticodon of five mt-tRNA species (5). We also showed that YRDC and OSGEPL1 are responsible for t6A37 formation, and demonstrated that OSGEPL1-knockout cells exhibit mitochondrial dysfunction (15). Moreover, we found that levels of t6A37 are reduced in mutant mt-tRNA isolated from the cells of patients with MERRF-like symptoms (15).
Modifications in the anticodon region of mt-tRNAs are required for mitochondrial translation, and the absence of these modifications has pathological consequences. By contrast, the physiological importance of modifications in the tRNA body region of tRNAs remains elusive. 5-methylcytidine (m5C) is a common modification in tRNA body regions (16). In eukaryotes, m5C is present in a wide variety of RNA species, including tRNA, rRNA, mRNA and viral RNA (17–20) (Figure 1A). m5C is introduced by the NOL1/NOP2/SUN domain (NSUN) family of enzymes, as well as by DNMT2 (21). Cytoplasmic tRNAs (ct-tRNAs) contain m5C at positions 34, 38, 40, 48–50 and 72. m5C38 and m5C72 are introduced by DNMT2 (22) and NSUN6 (23), respectively, whereas m5Cs at the other positions are introduced by NSUN2 (24–27). Loss of m5C in double-knockout mice of Nsun2 and Dnmt2 induces tRNA cleavage mediated by angiogenin to generate 5′ tRNA fragments (28,29) and decreases the steady-state levels of ct-tRNAs (27). In addition, these tRNA fragments inhibit cap-dependent translation (30,31). Loss-of-function mutations in the human NSUN2 gene are associated with autosomal recessive intellectual disabilities such as Dubowitz syndrome (26,32–35), and Nsun2 KO mice exhibit brain-size reduction, weight loss, male infertility and partial alopecia (29,36,37). Despite our knowledge of the importance of m5C in ct-tRNAs, little is known about the biogenesis and function of m5C in mt-tRNAs. In several mt-tRNA species, m5C is present at positions 48–50 in the extra loop (Figure 1B and Supplementary Figure S1) (5,38). We previously speculated that NSUN2 also participates in m5C formation of mt-tRNAs (3), even though NSUN2 is predominantly localized to nucleus (32).
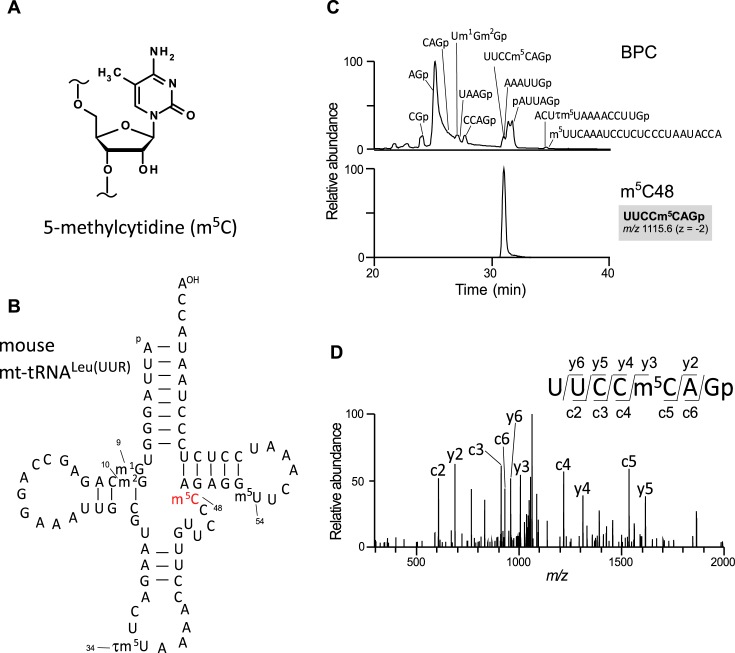
Figure 1.
mt-tRNAs contain m5C in the extra loop. (A) Chemical structure of 5-methylcytidine (m5C). (B) Secondary structure of mouse mitochondrial tRNALeu(UUR) with modified nucleosides: 1-methylguanosine (m1G), N2-methylguanosine (m2G), 5-taurinomehtyluridine (τm5U), 5-methylcytidine (m5C) and 5-methyluridine (m5U). Pseudouridine is not shown. (C) RNA fragment analysis of mouse mt-tRNALeu(UUR) digested with RNase T1. Assigned fragments are indicated on the base peak chromatogram (BPC) in the upper panel. ‘p’ represents a terminal phosphate group. An extracted-ion chromatogram (XIC) for the doubly charged negative ion of an m5C-containing fragment (UUCCm5CAGp m/z 1115.64) is shown in the lower panel. (D) Collision-induced dissociation (CID) spectrum of the m5C-containing fragment shown in (C) used to determine the m5C site. The doubly charged negative ion of the fragment UUCCm5CAGp (m/z 1115.64) was used as the precursor ion. Assigned c- and y-series product ions are indicated in the spectrum.
Here, we report precise mapping of m5C in mt-tRNAs, and present clear evidence that NSUN2 is partially localized to mitochondria and introduces m5C in mt-tRNAs.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Cell culture
HeLa and HEK293T cells, and mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) were cultured at 37°C in an atmosphere containing 5% CO2 in Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium (DMEM, Sigma-Aldrich) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS, Gibco) and 1% penicillin-streptomycin (PS, Fujifilm Wako Pure Chemical Corporation).
Animals
Nsun2 −/− mice (gene trap clone ID 21-B114 in the EGTC database, http://egtc.jp/) (39) were provided by the Center for Animal Resources and Development (CARD) at Kumamoto University. Animals were housed at 25°C with 12 h light and 12 h dark cycles. To generate MEFs, male and female Nsun2+/− mice were mated, and embryos were dissected out at day 14 of gestation. Embryo head and liver were removed for genotyping, the remaining tissues were treated with trypsin for 10 min at 37°C. Primary MEFs were seeded in 10 mm dishes and stored at passage number 2. All animal procedures were approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of Kumamoto University (Approval ID: A29–016R3).
Construction of NSUN2 KO cell lines
Oligonucleotide sequences used for gene editing are listed in Supplementary Table S1. NSUN2 KO HEK293T cell lines were constructed using the CRISPR-Cas9 system as described previously (13,40). In brief, sense and antisense oligonucleotides for a single guide RNA (sgRNA) were cloned into pX330 (Addgene plasmid #42230) (41). HEK293T cells seeded on 24-well plates were co-transfected with 300 ng pX330 containing the sgRNA sequence, 100 ng pEGFP-N1 (Clontech) and 100 ng modified pLL3.7 vector containing a puromycin resistance gene. Transfections were performed using FuGENE HD (Promega). The following day, the cells were sparsely seeded in a 100 mm dish, and transfectants were selected with 1 μg/ml puromycin. Transfection efficiency was assessed by monitoring EGFP fluorescence. A few days after the transfection, several colonies were isolated and grown for an additional week. The sequence of the targeted region in each selected clone was confirmed by direct sequencing of genomic polymerase chain reaction (PCR) products. PCR primer sequences are provided in Supplementary Table S1.
RNA preparation, tRNA isolation and mass spectrometry
Total RNA from culture cells was prepared by a standard acid guanidium-phenol-chloroform (AGPC) method (42). Individual mt-tRNAs were isolated by reciprocal circulation chromatography (RCC) (43). DNA probe sequences complementary to each mt-tRNA are listed in Supplementary Table S1. Capillary LC-nano-ESI-mass spectrometry (RNA-MS) of mt-tRNA fragments digested by RNase T1 was performed as described (5,44).
Northern blotting
Total RNA (2 μg) from mouse liver was separated by 10% denaturing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) and blotted onto a nylon membrane (Amersham Hybond N+; GE Healthcare) using a Transblot Turbo apparatus (Bio-Rad). The blotted RNA was crosslinked to the membrane by two rounds of irradiation with UV light (254 nm, 120 mJ/cm2 for one round; CL-1000, UVP). DNA probes were 5′-phosphorylated with T4 polynucleotide kinase (PNK, Toyobo) and [γ-32P] ATP (PerkinElmer). Northern blotting of tRNAs was performed using PerfectHyb (Toyobo) at 48–55°C with 4 pmol of labeled DNA probes specific to tRNAs and 3 pmol of a labeled DNA probe (mixed with 9 pmol of non-labeled probe) specific for 5S rRNA. The membrane was washed six times with 1 × SSC (150 mM NaCl and 15 mM sodium citrate, adjusted to pH 7.0 with citric acid), and exposed to an imaging plate (BAS-MS2040, Fujifilm). Radioactivity was visualized on an FLA-7000 imaging system (Fujifilm). To quantify the steady-state level of the target tRNA, the radioactivity of the tRNA band was normalized against the 5S rRNA band.
Expression and isolation of NSUN2
Human NSUN2 cDNA was reverse-transcribed from total RNA of HeLa cells, amplified using primers listed in Supplementary Table S1 and cloned into the entry vector pENTR/D-TOPO (Invitrogen). The gene cassette containing the entry clone was then transferred to a modified pDEST12.2 (Invitrogen) harboring a C-terminal FLAG tag.
For transient expression of NSUN2, HEK293T cells (4 × 106) in 100 mm dishes were transfected with 10 μg pDEST12.2-NSUN2-FLAG using Lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen) and cultured for 48–72 h at 37°C in 5% CO2. The cells were suspended with 1 ml of lysis buffer [50 mM HEPES-KOH (pH 7.9), 250 mM KCl, 2 mM MgCl2, 0.5 mM dithiothreitol (DTT), 0.5% Triton X-100, and 1 × Complete ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid-free protease inhibitor cocktail (Roche Life Science)] and lysed by sonication. The lysate was centrifuged twice at 20,000 × g for 20 min at 4°C to remove cell debris. The supernatant was immunoprecipitated with 50 μl of a 50% slurry of anti-FLAG M2 agarose beads (Sigma-Aldrich). The beads were washed three times with lysis buffer, and NSUN2 was eluted from the beads at 4°C for 3 h in elution buffer [150 mM KCl, 10 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0), 20% Glycerol, 0.1 mM DTT and 200 μg/ml DYKDDDDK peptide (Fujifilm Wako Pure Chemical Corporation)]. Isolated NSUN2 was quantified based on the intensity of the corresponding band in an SDS-PAGE gel stained with SYPRO Ruby (Thermo Fisher Scientific), using BSA as a standard.
In vitro m5C formation using NSUN2
Substrate mt-tRNASer(AGY) was transcribed in vitro with T7 RNA polymerase as described (45). Oligonucleotide sequences for preparation of template DNA are listed in Supplementary Table S1. The transcript was run on a 10% denaturing PAGE gel, and the intact tRNA band was excised from the gel, followed by tRNA extraction. In vitro methylation was performed at 37°C for 2 h in 50 μl of a reaction mixture consisting of 20 mM HEPES-KOH (pH 8.0), 5 mM MgCl2, 100 mM KCl, 1 mM DTT, 0.5 μM mt-tRNASer(AGY) transcript, 0.5 μM NSUN2 and 1 mM S-adenosylmethionine (SAM). The tRNA was extracted with phenol and precipitated with ethanol. A 1.5 pmol aliquot of the tRNA was digested with RNase T1 and subjected to LC/MS analysis to detect m5C-containing fragments.
Fluorescence microscopy
HeLa cells grown on poly-L-lysine-coated coverslips were incubated in 5% CO2 at 37°C for 1 h with 5 μM MitoTracker Red CMXRos (Molecular Probes) or 200 nM MitoBright Red (Dojindo) in DMEM. The cells were washed with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), fixed with 3.7% formaldehyde in PBS for 10 min at room temperature, permeabilized with 0.5% Triton X-100 in PBS for 10 min at room temperature, blocked with 2% FBS in PBS for 30 min at room temperature and incubated at room temperature for 1 h with anti-NSUN2 antibody (1:500; Sigma-Aldrich HPA037896) or anti-TFAM antibody (1:500; Abnova E7031) diluted in Can Get Signal solution A (Toyobo). After three washes in PBS, the cells were incubated at room temperature for 1 h with Cy2/Cy3-conjugated anti-mouse or anti-rabbit secondary antibody (1:50; Millipore AP182C). After three washes in PBS, the cells were mounted in 97% 2,2′-thiodiethanol containing 2% 1,4-diazabicyclo[2.2.2]octane. For 5-bromouridine (BrU) labeling, HeLa cells on coverslips were incubated with 2.5 mM BrU for 20 min prior to fixation. Anti-BrU antibody (1:50; Roche 11170376001) and anti-NSUN2 antibody were used to detect BrU-labeled RNA and NSUN2, respectively. Secondary antibodies conjugated with Alexa fluor 555 (1:1000; Invitrogen A-21422) and Alexa fluor 488 (1:1000; Invitrogen A-11008) were subsequently used, respectively. The coverslips were observed using a confocal microscope (FV3000; Olympus) equipped with a 60× oil -immersion objective lens (Olympus, PLAPON 60xOSC2, NA1.40). Images were acquired using the FluoView software (Olympus) and processed using ImageJ (46).
Super-resolution structured illumination microscopy (SR-SIM)
Super-resolution imaging was performed on an ELYRA PS.1 microscope (Carl Zeiss) equipped with a 100× oil -immersion objective lens (Carl Zeiss, alpha Plan-Apochromat 100 × /1.46 Oil DIC M27 ELYRA) and EM-CCD camera (12.1 × 12.1 μm2 field consisting of 256 × 256 pixels) as previously reported (47). To observe mitochondrial foci of NSUN2, 20 Z-series images were obtained at 100 nm intervals with the 561 and 481 nm lasers, and SIM images were calculated using default settings with theoretically predicted point-spread function parameters. For channel alignment, 0.2 μm multicolored beads (TetraSpec Microspheres, Thermo Fisher) immobilized on a sample coverslip were imaged using the same acquisition settings, and the resultant images were used to correct for chromatic shifts between color channels. Images were processed using the ZEN software (Carl Zeiss).
Pulse labeling of mitochondrial protein synthesis
The pulse-labeling experiment was performed essentially as described (13). WT and NSUN2 KO HEK293T cells (2.0 × 106) were cultured at 37°C in 5% CO2 for 10 min in methionine-, glutamine- and cysteine-free DMEM (Gibco) supplemented with 2 mM L-glutamine, 10% FBS and 50 μg/ml emetine (to inhibit cytoplasmic protein synthesis). The cells were then supplemented with 7.4 MBq of [35S] methionine and [35S] cysteine (EXPRE35S35S Protein Labeling Mix, [35S]-, PerkinElmer) and incubated for 1 h to specifically label newly synthesized mitochondrial proteins. Cell lysates (50 μg total proteins) were resolved by tricine–SDS-PAGE (16.5%), and the gel was CBB stained and dried on a gel drier (AE-3750 RapiDry, ATTO). Radiolabeled mitochondrial protein products were visualized using an imaging plate (BAS-MS2040, Fujifilm) on an FLA-7000 imaging system.
Steady-state levels of subunit proteins in respiratory chain complexes
Mitochondria were isolated from WT and NSUN2 KO HEK293T cells (1 × 107) using the Mitochondria Isolation Kit (Miltenyi Biotec). Steady-state levels of subunit proteins of mitochondrial respiratory chain complexes were analyzed by immunoblotting with Total OXPHOS Rodent WB Antibody Cocktail (1:250, ab110413, Abcam) and anti-mt-ND5 antibody (1:100, ab92624, Abcam). HRP-conjugated anti-mouse IgG (1:20,000, 715–035-150, Jackson ImmunoResearch) or HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG (1:20,000, 715-035-152, Jackson ImmunoResearch) was used as the secondary antibody.
Resazurin-based cell proliferation assay
WT, NSUN2 KO and NSUN3 KO HEK293T cells were seeded on 96-well plates (1.0 × 105 cells/well) and cultured in glucose-free DMEM (Gibco) containing 10% FBS, 1% PS, 1 mM sodium pyruvate, and 4% glucose or in glucose-free DMEM (Gibco) containing 10% FBS, 1% PS, 1 mM sodium pyruvate and 4% galactose. On each day, 1/10 volume of 1 mM resazurin solution in PBS was added to each well and incubated for 3 h. Absorbance was measured at 570 and 600 nm on a microplate reader (SpectraMax Paradigm, Molecular Devices). The reduction rate of resazurin was calculated using the following equation:
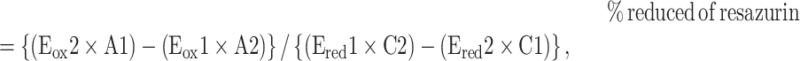 |
where
Eox1 = molar extinction coefficient (E) of oxidized (ox) resazurin at 570 nm = 80 586,
Eox2 = E of oxidized resazurin at 600 nm = 117 216,
Ered1 = E of reduced (red) resazurin at 570 nm = 155 677,
Ered2 = E of reduced resazurin at 600 nm = 14 652,
A1 = absorbance of measured well at 570 nm,
A2 = absorbance of measured well at 600 nm,
C1 = absorbance of blank well (medium and resazurin only) at 570 nm and
C2 = absorbance of blank well at 600 nm.
RESULTS
Mass spectrometric m5C mapping of mouse and human mt-tRNAs
To map m5C, we isolated eight species of mouse mt-tRNAs bearing C at positions 48–50 [for Glu, His, Met, Asn, Leu(UUR), Leu(CUN), Ser(AGY) and Tyr] from mouse liver using RCC (43). Purified tRNAs were digested by RNase T1 and subjected to capillary LC-nano-ESI-mass spectrometry (RNA-MS) to analyze post-transcriptional modifications (15,44,48,49). Each RNA fragment was assigned by comparing observed m/z values with the calculated values (Figure 1C). The sequence of each fragment was further analyzed by collision-induced dissociation (CID) to determine the precise position of each modification (Figure 1D). We mapped m5C at eight positions in the extra loop of the eight tRNA species: at position 48 of five mt-tRNAs [His, Met, Leu(UUR), Asn, and Tyr], and at position 49 of three mt-tRNAs [Glu, Leu(CUN) and Ser(AGY)] (Supplementary Figures S1 and 2).
In a similar manner, we isolated six species of human mt-tRNAs bearing C at positions 48–49 [for Glu, Phe, His, Leu(UUR), Ser(AGY) and Tyr] from HEK293T cells. RNA-MS analyses detected m5C at eight positions in the six tRNA species: at position 48 of five mt-tRNAs [Phe, His, Leu(UUR), Ser(AGY) and Tyr], at position 49 of two mt-tRNAs [Glu and Ser(AGY)], and position 50 of mt-tRNASer(AGY) (Supplementary Figures S1 and 3).
NSUN2 is essential for m5C formation in mammalian mt-tRNA
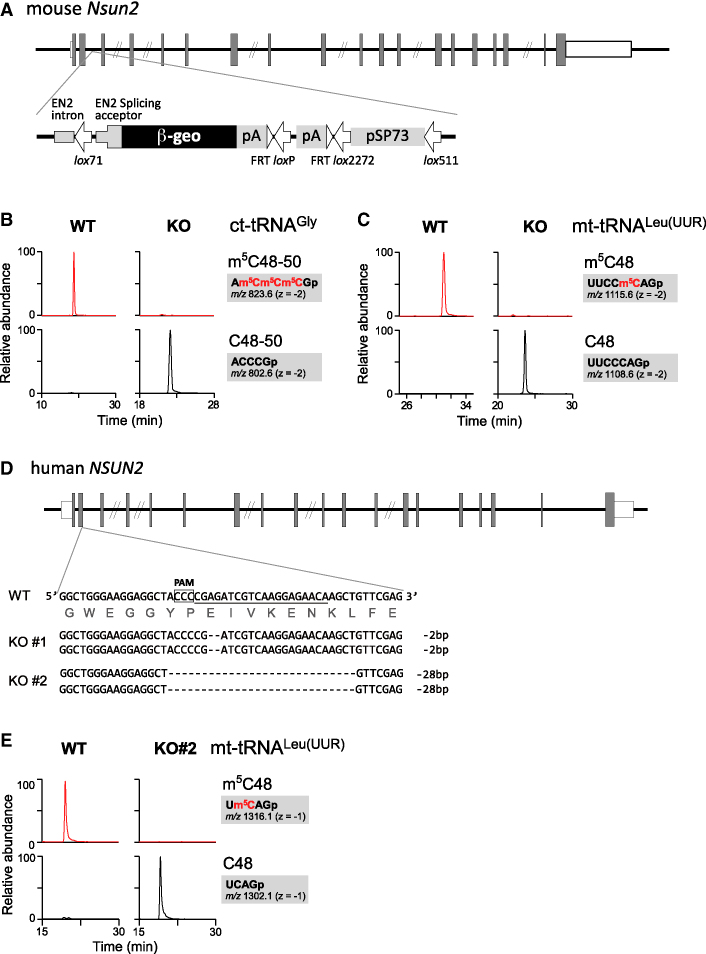
Given that NSUN2 introduces m5C into the extra loop of ct-tRNAs (24–27), we speculated that NSUN2 is also responsible for m5C formation in mammalian mt-tRNAs (3). To test this hypothesis, we analyzed tRNA modification status in an Nsun2-null mouse constructed by gene trapping (Figure 2A). We isolated ct-tRNAs as well as mt-tRNAs from the livers of Nsun2−/− mice, and analyzed m5C48/49/50 state by RNA-MS. As observed previously (27), m5C was not present in ct-tRNAGly isolated from liver from Nsun2−/− mouse (Figure 2B). We also found that m5C was completely absent in eight mt-tRNAs isolated from Nsun2−/− mouse livers (Figure 2C and Supplementary Figure S2).
Figure 2.
NSUN2 is responsible for m5C formation in mt-tRNAs (A) Schematic depiction of the mouse Nsun2 gene with the insertion site of the gene trap cassette containing the β-geo marker. Shaded boxes, open boxes and lines indicate coding regions, untranslated regions of exons and introns, respectively. (B and C) XICs of RNase T1-digested fragments of mouse ct-tRNAGly (B) and mt-tRNALeu(UUR) (C) containing m5C (top) and C (bottom) isolated from WT and Nsun2−/− (KO) mouse liver. (D) Schematic depiction of the human NSUN2 gene with mutation sites introduced by the CRISPR-Cas9 system. The target sequence of the single guide RNA (sgRNA) is underlined. The protospacer adjacent motif (PAM) sequence is boxed. Deletions are represented by dashed lines. (E) XICs of RNase T1-digested fragments of human mt-tRNALeu(UUR) containing m5C (top) and C (bottom) isolated from WT and NSUN2 KO #2 HEK293T cells.
For human culture cells, we knocked out the NSUN2 gene in HEK293T cells using CRISPR/Cas9, yielding two KO cell lines (KO #1 and KO #2) in which both alleles harbored a homozygous frameshift deletion (Figure 2D). We then isolated six mt-tRNAs from NSUN2 KO cells and subjected them to RNA-MS. As expected, no m5C was detected in any of the isolated tRNAs (Figure 2E and Supplementary Figure S3), demonstrating that NSUN2 is required for the formation of m5C in mt-tRNAs.
In vitro reconstitution of m5C in mt-tRNA
We next performed in vitro reconstitution of m5C in mt-tRNA using recombinant NSUN2. For these experiments, human NSUN2 fused with a C-terminal FLAG tag was expressed in HEK293T cells and immunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG antibody. As a substrate, we prepared an in vitro transcript of human mt-tRNASer(AGY), which was incubated with human NSUN2 and SAM. After the reaction, the tRNA substrate was digested with RNase T1 and subjected to RNA-MS. We clearly detected RNA fragments bearing mono-, di- and trimethylations (Figure 3A). CID analysis revealed that trimethylation occurred at cytidines at positions 48–50 (Figure 3B). This result is consistent with our observation that human mt-tRNASer(AGY) had three m5C residues at positions 48–50 (Supplementary Figures S1 and 3).
Figure 3.
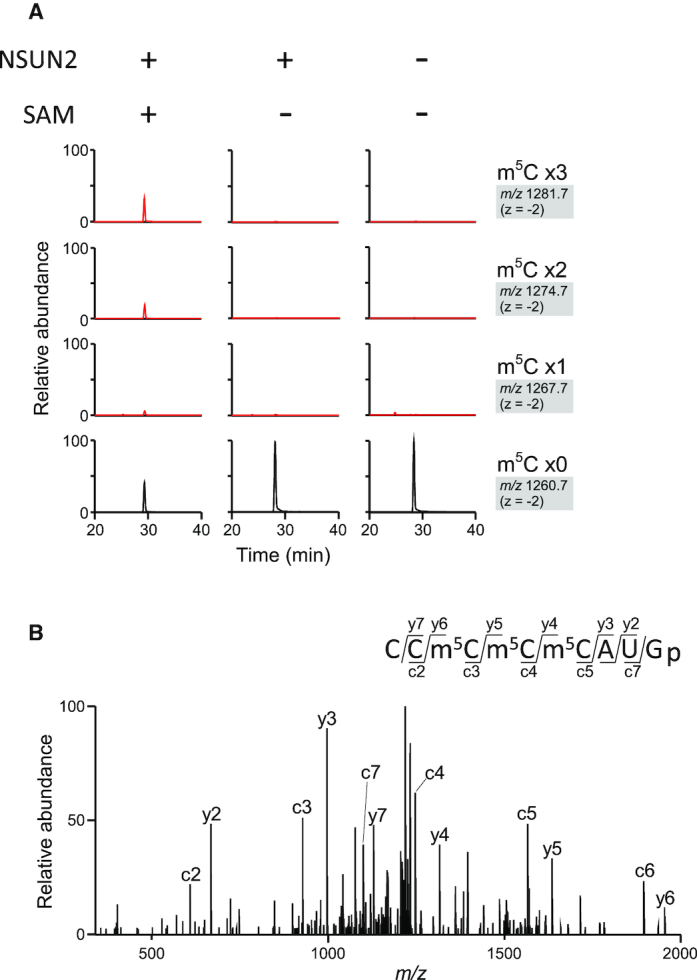
In vitro reconstitution of m5C on mt-tRNA (A) NSUN2-mediated m5C formation on the human mt-tRNASer(AGY) transcript in the presence or absence of recombinant NSUN2 and SAM. XICs of RNase T1-digested fragments (CCCCCAUGp) of human mt-tRNASer (AGY) containing three (top panels), two (second panels), one (third panels) or zero (bottom panels) methyl groups. m/z value with the charge state for each fragment is shown on the right. (B) CID spectrum of the trimethylated fragment in (A). The precursor ion for CID is m/z 1281.69. Assigned c- and y-series product ions are indicated in the spectrum.
Subcellular localization of endogenous NSUN2
NSUN2 is predominantly localized to the nucleus (32). To explore the possibility that some of the enzyme is targeted to mitochondria, we immunostained endogenous NSUN2 in HeLa cells with anti-NSUN2 antibody and visualized the protein by confocal microscopy. Most NSUN2 signal was observed in nucleus (Figure 4A), as reported previously (32), but some of the signal was dispersed in the cytoplasm and overlapped with mitochondria (Figure 4A). We further investigated cytoplasmic NSUN2 signals using super-resolution structured illumination microscopy (SR-SIM) (50). The increase in both the lateral (x-y axis) and axial (z-axis) resolution of SR-SIM enabled visualization of the cytoplasmic NSUN2 signal inside mitochondria (Figure 4B). Furthermore, signals of mitochondrial NSUN2 partially overlapped with those of BrU-labeled RNAs (Figure 4C) which represent newly-synthesized transcripts in mitochondria, whereas mitochondrial NSUN2s were observed as signals that reside next to TFAM-stained signals that co-localize with mt-DNA (51) (Figure 4D). This observation implies that NSUN2-mediated m5C formation takes place co-transcriptionally in the precursor transcripts. Taken together, these observations show that while NSUN2 is predominantly localized to the nucleus, it is also present in mitochondria, consistent with a role in forming m5C formation at positions 48–50 of mt-tRNAs near the site of transcription.
Figure 4.
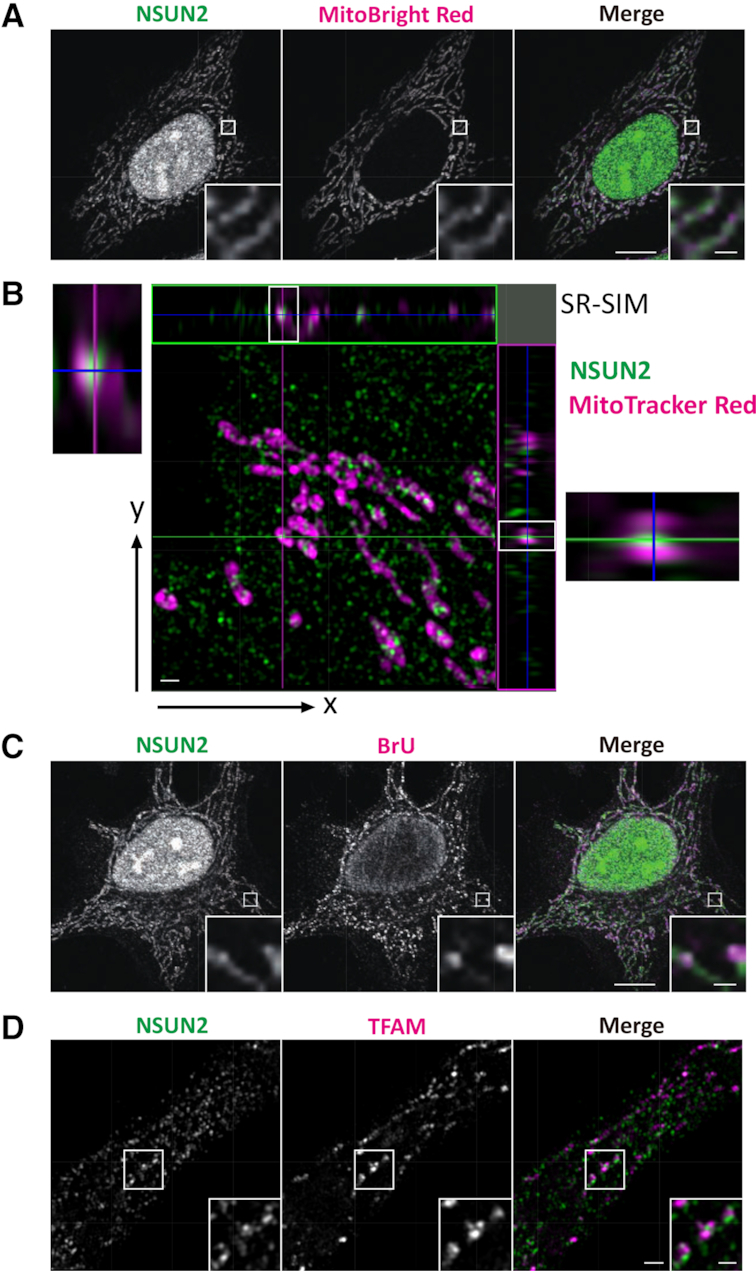
Subcellular localization of endogenous human NSUN2 (A and B) Subcellular localization of human NSUN2 in HeLa cells showing NSUN2 (green) and MitoBright Red (magenta) (A) or MitoTracker Red (magenta) (B). Fluorescence images were obtained by confocal microscopy (A) and super-resolution microscopy (SR-SIM) (B). Scale bars: 10 μm (A), 1 μm (inset of A) and 1 μm (B). (C) Fluorescence images of NSUN2 (green) and BrU (magenta) were obtained by confocal microscopy. Scale bars: main, 10 μm; inset, 1 μm. (D) Fluorescence images of NSUN2 (green) and TFAM (magenta) were obtained by SR-SIM. Scale bars: main, 1 μm; inset, 0.5 μm.
NSUN2 KO has little impact on mitochondrial translation
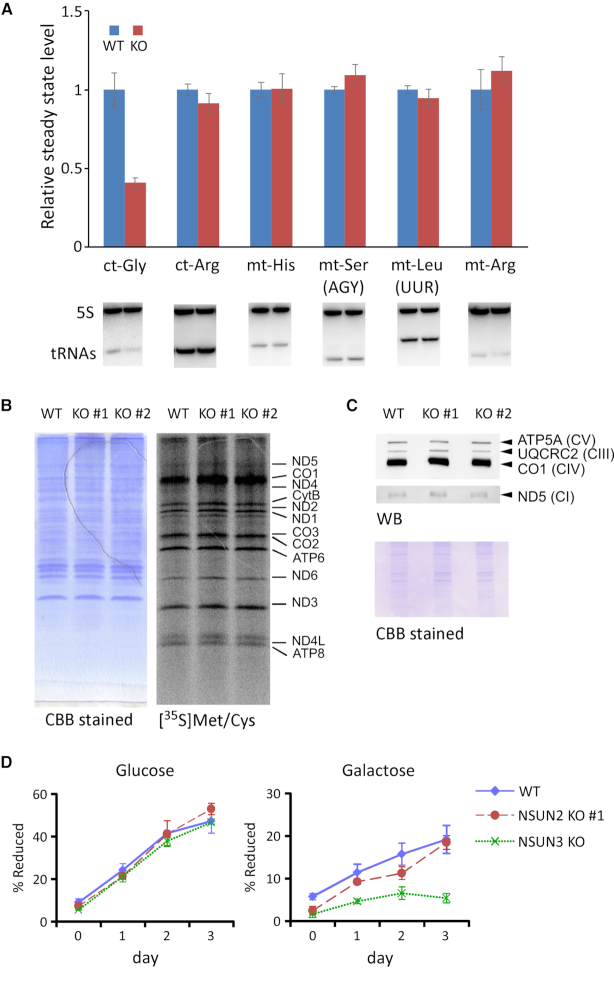
NSUN2-mediated m5C formation stabilizes ct-tRNAs and protein synthesis (27). To determine whether mt-tRNAs are also stabilized by m5C modifications, we measured steady-state levels of mt-tRNAs in Nsun2−/− mouse liver by northern blotting. As reported previously (27), the level of ct-tRNAGly was significantly reduced in Nsun2−/− mouse liver (Figure 5A). By contrast, we observed no significant change in the steady-state levels of mt-tRNAs upon Nsun2−/− mice (Figure 5A). Moreover, we observed no change in the steady-state level of mt-tRNAs in testis (Supplementary Figure S4A) or brain (Supplementary Figure S4B) of Nsun2−/− mice.
Figure 5.
Mitochondrial translation and respiratory activity in NSUN2 KO cells (A) northern blotting of ct-tRNAs and mt-tRNAs in total RNA from WT and Nsun2−/−(KO) mouse liver (lower panels). Bar graph shows relative levels of each tRNA, normalized against 5S rRNA (used as a loading control). Mean ± S.D. was calculated from three biological replicates. (B) Pulse labeling of mitochondrial protein synthesis. WT and NSUN2 KO HEK293T cells were labeled with ([35S] Met/Cys) and chased for 1 h under emetine treatment (right). Total proteins were visualized by CBB staining (left). (C) Steady-state levels of subunit proteins in respiratory chain complexes, as determined by western blotting (top). Loaded proteins were visualized by CBB staining (bottom). (D) Growth curves of WT, NSUN2 KO and NSUN3 KO HEK293T cells cultured in the medium containing glucose (left) or galactose (right) as the primary carbon source. Mean ± S.D. was calculated from three independent cultures.
Next, we performed a pulse-labeling experiment to compare mitochondrial translational activity, and observed no significant difference between WT and NSUN2 KO HEK293T cells (Figure 5B), or WT and Nsun2−/− MEFs (Supplementary Figure S5). We also analyzed steady-state levels of several subunits of the mitochondrial respiratory chain complexes by western blotting, and found no significant change upon NSUN2 KO (Figure 5C). To explore the mitochondria-related phenotypes of NSUN2 KO cells, we compared cell growth in galactose versus glucose (52). As reported previously (13), growth was dramatically slowed in NSUN3 KO cells cultured in galactose medium. NSUN2 KO cells grew well in glucose medium, and slightly slower than WT cells in galactose medium (Figure 5D). But, this is not a significant result. Taken together, these observations indicate that NSUN2 KO has a limited impact on mitochondrial translation and respiratory activity, notwithstanding the absence of m5C modification in mt-tRNAs.
DISCUSSION
In this study, we demonstrated that NSUN2 is partially localized to mitochondria and introduces m5C into the extra loop of mt-tRNAs. RNA-MS detected m5C at eight positions in eight mouse and six human mt-tRNAs. We previously reported m5C at five positions in five bovine mt-tRNAs (5). Among these mammals, m5C is present in three species of mt-tRNAs [for Leu(UUR), Ser(AGY) and Glu], implying that m5C is functionally important in these tRNA species. In terms of the specific positioning of the modification, mt-tRNAsLeu(UUR) and mt-tRNAsGlu have m5C48 and m5C49, respectively. In mt-tRNAsSer(AGY), three m5Cs are present at positions 48–50 in human, whereas in mouse and cow only one m5C is present at position 49. Even if a C is present at positions 48–50, m5C is not always introduced by NSUN2, e.g. C48 in mouse mt-tRNALeu(CUN) remains unmodified. Although NSUN2 is a promiscuous m5C methyltransferase with broad specificity for diverse RNA substrates (16), it does have some substrate and sequence preference. In addition to the extra loop, we found m5C at position 72 in bovine mt-tRNAThr (5), but not in human mt-tRNAThr (15). It still remains unclear whether NSUN2 or other enzyme is responsible for m5C formation at this position.
Using SR-SIM, we clearly detected NSUN2 in mitochondria. In general, mitochondria-localized proteins have a mitochondria-targeting sequence (MTS) in their N-terminal region (53). However, human NSUN2 does not appear to contain an apparent MTS, and it is not described as having a mitochondrial localization in the MitoMiner database (54). Instead, human NSUN2 is predicted by WoLF PSORT to be localized to the nucleus (55). Consistent with this, we observed a strong NSUN2 signal in the nucleus of human cells (Figure 4A), as reported previously (32). However, the observation of clear foci in the mitochondria indicates that NSUN2 does in fact have a weak MTS. In further support of mitochondrial localization, NSUN2 foci co-localized with the signals of BrU-labeled RNA in mitochondria (Figure 4C) and were adjacent to the signal for TFAM (Figure 4D), a transcription factor that covers mt-DNA to form a nucleoid structure. BrU-labeled RNA in mitochondria constitutes mitochondrial RNA granules (MRGs) (56), which are sites for mitochondrial RNA processing and ribosome biogenesis, in close proximity to TFAM-stained nucleoids. Multiple factors for RNA modification and processing are localized to MRGs (57). We speculate that NSUN2 is a novel component of the MRG, where it introduces m5C into mt-tRNAs co-transcriptionally.
m5C stabilizes the RNA structure via base-pairing, base-stacking, and metal binding (58–60). Indeed, the m5C49 on the edge of the T-stem promotes Mg2+-dependent folding of tRNA (61). In canonical tRNAs, the D-loop/T-loop and D-arm/extra loop interactions are critical for the folding of tRNA into an L-shape structure (62). The D-arm/extra loop interaction is composed of a C13–G22–m7G46 base triple and a G15–C48 pair. G15 pairs with C48 in a reverse Watson-Crick geometry called a Levitt pair (62,63). A structural hallmark of animal mt-tRNAs is the absence of the canonical D-loop/T-loop interaction (3,64,65); instead, the D-arm and extra loop interactions, including the G15–C48 Levitt pair, are conserved in most mt-tRNAs and play critical roles in tRNA folding and stability (3,66). In the crystal structure of tRNAs (67), m5C48 may strengthen the stacking interaction with a nucleobase at position 21 in the D-arm, stabilizing the mt-tRNA core structure, although the functional importance of this methylation remains to be determined.
Loss-of-function mutations in human NSUN2 gene result in intellectual disability (26,32–35). Nsun2 KO mice show tissue-specific phenotypes (29,36,37). Some of these phenotypes link to human mitochondrial diseases bearing pathogenic mutations in MT-ATP6 encoded in mt-DNA (68–70), or in nuclear-encoded mitochondrial proteins that regulate translation including KARS (70) and Guf1 (71), indicating that a part of NSUN2-associated phenotypes might originate from reduced mitochondrial function caused by hypomodification of mt-tRNAs. However, it is also possible to consider some indirect effects caused by hypomodification of cytoplasmic tRNAs.
Despite our efforts to identify a functional role of m5C in mt-tRNAs, we could not demonstrate any effects of this modification on mt-tRNA stability or mitochondrial protein synthesis. Further investigations will be necessary to elucidate the biological roles of m5C in mt-tRNAs under environmental stress conditions or in specific physiological contexts in various tissues and cells.
Supplementary Material
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We are grateful to the members of the Suzuki lab, especially Hiroyoshi Iwata, Yuriko Sakaguchi, Kenjyo Miyauchi, Huan Lin and Takayuki Ohira for technical support and fruitful discussion. We also thank Drs N. Mizushima and I. Koyama-Honda (University of Tokyo) for their kind assistance with microscopic analysis. Radioisotope experiments were carried out with the support of the Isotope Science Center, The University of Tokyo.
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA
Supplementary Data are available at NAR Online.
FUNDING
Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology of Japan (MEXT) Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Priority Areas; Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) [26113003, 26220205, 18H05272 to Ts.S., 26702035, 18H02094 to Ta.S.]. Funding for open access charge: JSPS; Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology of Japan (MEXT) Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Priority Areas.
Conflict of interest statement. None declared.
This paper is linked to: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkz559.
REFERENCES
- 1. D'Souza A.R., Minczuk M.. Mitochondrial transcription and translation: overview. Essays Biochem. 2018; 62:309–320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Hallberg B.M., Larsson N.G.. Making proteins in the powerhouse. Cell Metab. 2014; 20:226–240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Suzuki T., Nagao A., Suzuki T.. Human mitochondrial tRNAs: biogenesis, function, structural aspects, and diseases. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2011; 45:299–329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Ojala D., Montoya J., Attardi G.. tRNA punctuation model of RNA processing in human mitochondria. Nature. 1981; 290:470–474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Suzuki T., Suzuki T.. A complete landscape of post-transcriptional modifications in mammalian mitochondrial tRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014; 42:7346–7357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Bohnsack M.T., Sloan K.E.. The mitochondrial epitranscriptome: the roles of RNA modifications in mitochondrial translation and human disease. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2018; 75:241–260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Suzuki T. Grosjean H. Biosynthesis and function of tRNA wobble modifications. Fine-Tuning of RNA Functions by Modification and Editing. 2005; NY: Springer; 24–69. [Google Scholar]
- 8. Suzuki T., Nagao A., Suzuki T.. Human mitochondrial diseases caused by lack of taurine modification in mitochondrial tRNAs. Wiley Interdiscip. Revi. RNA. 2011; 2:376–386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Suzuki T., Suzuki T., Wada T., Saigo K., Watanabe K.. Taurine as a constituent of mitochondrial tRNAs: new insights into the functions of taurine and human mitochondrial diseases. EMBO J. 2002; 21:6581–6589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Asano K., Suzuki T., Saito A., Wei F.Y., Ikeuchi Y., Numata T., Tanaka R., Yamane Y., Yamamoto T., Goto T. et al.. Metabolic and chemical regulation of tRNA modification associated with taurine deficiency and human disease. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018; 46:1565–1583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Umeda N., Suzuki T., Yukawa M., Ohya Y., Shindo H., Watanabe K., Suzuki T.. Mitochondria-specific RNA-modifying enzymes responsible for the biosynthesis of the wobble base in mitochondrial tRNAs. Implications for the molecular pathogenesis of human mitochondrial diseases. J. Biol. Chem. 2005; 280:1613–1624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Moriya J., Yokogawa T., Wakita K., Ueda T., Nishikawa K., Crain P.F., Hashizume T., Pomerantz S.C., McCloskey J.A., Kawai G. et al.. A novel modified nucleoside found at the first position of the anticodon of methionine tRNA from bovine liver mitochondria. Biochemistry. 1994; 33:2234–2239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Nakano S., Suzuki T., Kawarada L., Iwata H., Asano K., Suzuki T.. NSUN3 methylase initiates 5-formylcytidine biogenesis in human mitochondrial tRNA(Met). Nat. Chem. Biol. 2016; 12:546–551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Kawarada L., Suzuki T., Ohira T., Hirata S., Miyauchi K., Suzuki T.. ALKBH1 is an RNA dioxygenase responsible for cytoplasmic and mitochondrial tRNA modifications. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017; 45:7401–7415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Lin H., Miyauchi K., Harada T., Okita R., Takeshita E., Komaki H., Fujioka K., Yagasaki H., Goto Y.I., Yanaka K. et al.. CO2-sensitive tRNA modification associated with human mitochondrial disease. Nat. Commun. 2018; 9:1875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Motorin Y., Lyko F., Helm M.. 5-methylcytosine in RNA: detection, enzymatic formation and biological functions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010; 38:1415–1430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Squires J.E., Patel H.R., Nousch M., Sibbritt T., Humphreys D.T., Parker B.J., Suter C.M., Preiss T.. Widespread occurrence of 5-methylcytosine in human coding and non-coding RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012; 40:5023–5033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Dubin D.T., Taylor R.H.. The methylation state of poly A-containing messenger RNA from cultured hamster cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1975; 2:1653–1668. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Dubin D.T., Stollar V.. Methylation of Sindbis virus ‘26S’ messenger RNA. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1975; 66:1373–1379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Shafik A., Schumann U., Evers M., Sibbritt T., Preiss T.. The emerging epitranscriptomics of long noncoding RNAs. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2016; 1859:59–70. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Bohnsack K.E., Hobartner C., Bohnsack M.T.. Eukaryotic 5-methylcytosine (m(5)C) RNA methyltransferases: mechanisms, cellular functions, and links to disease. Genes. 2019; 10:102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Goll M.G., Kirpekar F., Maggert K.A., Yoder J.A., Hsieh C.L., Zhang X., Golic K.G., Jacobsen S.E., Bestor T.H.. Methylation of tRNAAsp by the DNA methyltransferase homolog Dnmt2. Science. 2006; 311:395–398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Haag S., Warda A.S., Kretschmer J., Gunnigmann M.A., Hobartner C., Bohnsack M.T.. NSUN6 is a human RNA methyltransferase that catalyzes formation of m5C72 in specific tRNAs. RNA. 2015; 21:1532–1543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Motorin Y., Grosjean H.. Multisite-specific tRNA:m5C-methyltransferase (Trm4) in yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae: identification of the gene and substrate specificity of the enzyme. RNA. 1999; 5:1105–1118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Brzezicha B., Schmidt M., Makalowska I., Jarmolowski A., Pienkowska J., Szweykowska-Kulinska Z.. Identification of human tRNA:m5C methyltransferase catalysing intron-dependent m5C formation in the first position of the anticodon of the pre-tRNA Leu (CAA). Nucleic Acids Res. 2006; 34:6034–6043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Martinez F.J., Lee J.H., Lee J.E., Blanco S., Nickerson E., Gabriel S., Frye M., Al-Gazali L., Gleeson J.G.. Whole exome sequencing identifies a splicing mutation in NSUN2 as a cause of a Dubowitz-like syndrome. J. Med. Genet. 2012; 49:380–385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Tuorto F., Liebers R., Musch T., Schaefer M., Hofmann S., Kellner S., Frye M., Helm M., Stoecklin G., Lyko F.. RNA cytosine methylation by Dnmt2 and NSun2 promotes tRNA stability and protein synthesis. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2012; 19:900–905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Schaefer M., Pollex T., Hanna K., Tuorto F., Meusburger M., Helm M., Lyko F.. RNA methylation by Dnmt2 protects transfer RNAs against stress-induced cleavage. Genes Dev. 2010; 24:1590–1595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Blanco S., Dietmann S., Flores J.V., Hussain S., Kutter C., Humphreys P., Lukk M., Lombard P., Treps L., Popis M. et al.. Aberrant methylation of tRNAs links cellular stress to neuro-developmental disorders. EMBO J. 2014; 33:2020–2039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Blanco S., Bandiera R., Popis M., Hussain S., Lombard P., Aleksic J., Sajini A., Tanna H., Cortes-Garrido R., Gkatza N. et al.. Stem cell function and stress response are controlled by protein synthesis. Nature. 2016; 534:335–340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Ivanov P., Emara M.M., Villen J., Gygi S.P., Anderson P.. Angiogenin-induced tRNA fragments inhibit translation initiation. Mol. Cell. 2011; 43:613–623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Khan M.A., Rafiq M.A., Noor A., Hussain S., Flores J.V., Rupp V., Vincent A.K., Malli R., Ali G., Khan F.S. et al.. Mutation in NSUN2, which encodes an RNA methyltransferase, causes autosomal-recessive intellectual disability. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2012; 90:856–863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Abbasi-Moheb L., Mertel S., Gonsior M., Nouri-Vahid L., Kahrizi K., Cirak S., Wieczorek D., Motazacker M.M., Esmaeeli-Nieh S., Cremer K. et al.. Mutations in NSUN2 cause autosomal-recessive intellectual disability. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2012; 90:847–855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Fahiminiya S., Almuriekhi M., Nawaz Z., Staffa A., Lepage P., Ali R., Hashim L., Schwartzentruber J., Abu Khadija K., Zaineddin S. et al.. Whole exome sequencing unravels disease-causing genes in consanguineous families in Qatar. Clin. Genet. 2014; 86:134–141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Komara M., Al-Shamsi A.M., Ben-Salem S., Ali B.R., Al-Gazali L.. A novel single-nucleotide deletion (c.1020delA) in NSUN2 causes intellectual disability in an Emirati child. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2015; 57:393–399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Blanco S., Kurowski A., Nichols J., Watt F.M., Benitah S.A., Frye M.. The RNA-methyltransferase Misu (NSun2) poises epidermal stem cells to differentiate. PLos Genet. 2011; 7:e1002403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Hussain S., Tuorto F., Menon S., Blanco S., Cox C., Flores J.V., Watt S., Kudo N.R., Lyko F., Frye M.. The mouse cytosine-5 RNA methyltransferase NSun2 is a component of the chromatoid body and required for testis differentiation. Mol. Cell Biol. 2013; 33:1561–1570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Van Haute L., Dietmann S., Kremer L., Hussain S., Pearce S.F., Powell C.A., Rorbach J., Lantaff R., Blanco S., Sauer S. et al.. Deficient methylation and formylation of mt-tRNA(Met) wobble cytosine in a patient carrying mutations in NSUN3. Nat. Commun. 2016; 7:12039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Araki M., Nakahara M., Muta M., Itou M., Yanai C., Yamazoe F., Miyake M., Morita A., Araki M., Okamoto Y. et al.. Database for exchangeable gene trap clones: pathway and gene ontology analysis of exchangeable gene trap clone mouse lines. Dev. Growth Differ. 2014; 56:161–174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Pyzocha N.K., Ran F.A., Hsu P.D., Zhang F.. RNA-guided genome editing of mammalian cells. Methods Mol. Biol. 2014; 1114:269–277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Cong L., Ran F.A., Cox D., Lin S., Barretto R., Habib N., Hsu P.D., Wu X., Jiang W., Marraffini L.A. et al.. Multiplex genome engineering using CRISPR/Cas systems. Science. 2013; 339:819–823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Chomczynski P., Sacchi N.. The single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction: twenty-something years on. Nat. Protoc. 2006; 1:581–585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Miyauchi K., Ohara T., Suzuki T.. Automated parallel isolation of multiple species of non-coding RNAs by the reciprocal circulating chromatography method. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007; 35:e24. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Suzuki T., Ikeuchi Y., Noma A., Suzuki T., Sakaguchi Y.. Mass spectrometric identification and characterization of RNA-modifying enzymes. Methods Enzymol. 2007; 425:211–229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Sampson J.R., Uhlenbeck O.C.. Biochemical and physical characterization of an unmodified yeast phenylalanine transfer RNA transcribed in vitro. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 1988; 85:1033–1037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Schneider C.A., Rasband W.S., Eliceiri K.W.. NIH image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods. 2012; 9:671–675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. West J.A., Mito M., Kurosaka S., Takumi T., Tanegashima C., Chujo T., Yanaka K., Kingston R.E., Hirose T., Bond C. et al.. Structural, super-resolution microscopy analysis of paraspeckle nuclear body organization. J. Cell Biol. 2016; 214:817–830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Akichika S., Hirano S., Shichino Y., Suzuki T., Nishimasu H., Ishitani R., Sugita A., Hirose Y., Iwasaki S., Nureki O. et al.. Cap-specific terminal N (6)-methylation of RNA by an RNA polymerase II-associated methyltransferase. Science. 2019; 363:eaav0080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Taniguchi T., Miyauchi K., Sakaguchi Y., Yamashita S., Soma A., Tomita K., Suzuki T.. Acetate-dependent tRNA acetylation required for decoding fidelity in protein synthesis. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2018; 14:1010–1020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Gustafsson M.G. Surpassing the lateral resolution limit by a factor of two using structured illumination microscopy. J. Microsc. 2000; 198:82–87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Brown T.A., Tkachuk A.N., Shtengel G., Kopek B.G., Bogenhagen D.F., Hess H.F., Clayton D.A.. Superresolution fluorescence imaging of mitochondrial nucleoids reveals their spatial range, limits, and membrane interaction. Mol. Cell Biol. 2011; 31:4994–5010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52. Robinson B.H., Petrova-Benedict R., Buncic J.R., Wallace D.C.. Nonviability of cells with oxidative defects in galactose medium: a screening test for affected patient fibroblasts. Biochem. Med. Metab. Biol. 1992; 48:122–126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53. Roise D., Schatz G.. Mitochondrial presequences. J. Biol. Chem. 1988; 263:4509–4511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54. Smith A.C., Robinson A.J.. MitoMiner v4.0: an updated database of mitochondrial localization evidence, phenotypes and diseases. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018; 47:D1225–D1228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55. Horton P., Park K.J., Obayashi T., Fujita N., Harada H., Adams-Collier C.J., Nakai K.. WoLF PSORT: protein localization predictor. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007; 35:W585–W587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56. Jourdain A.A., Boehm E., Maundrell K., Martinou J.C.. Mitochondrial RNA granules: compartmentalizing mitochondrial gene expression. J. Cell Biol. 2016; 212:611–614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57. Pearce S.F., Rebelo-Guiomar P., D'Souza A.R., Powell C.A., Van Haute L., Minczuk M.. Regulation of mammalian mitochondrial gene expression: recent advances. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2017; 42:625–639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58. Chawla M., Oliva R., Bujnicki J.M., Cavallo L.. An atlas of RNA base pairs involving modified nucleobases with optimal geometries and accurate energies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015; 43:6714–6729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59. Sowers L.C., Shaw B.R., Sedwick W.D.. Base stacking and molecular polarizability: effect of a methyl group in the 5-position of pyrimidines. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1987; 148:790–794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60. Chen Y., Sierzputowska-Gracz H., Guenther R., Everett K., Agris P.F.. 5-Methylcytidine is required for cooperative binding of Mg2+ and a conformational transition at the anticodon stem-loop of yeast phenylalanine tRNA. Biochemistry. 1993; 32:10249–10253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61. Nobles K.N., Yarian C.S., Liu G., Guenther R.H., Agris P.F.. Highly conserved modified nucleosides influence Mg2+-dependent tRNA folding. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002; 30:4751–4760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62. Kim S.H., Quigley G.J., Suddath F.L., McPherson A., Sneden D., Kim J.J., Weinzierl J., Rich A.. Three-dimensional structure of yeast phenylalanine transfer RNA: folding of the polynucleotide chain. Science. 1973; 179:285–288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63. Levitt M. Detailed molecular model for transfer ribonucleic acid. Nature. 1969; 224:759–763. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64. Wakita K., Watanabe Y., Yokogawa T., Kumazawa Y., Nakamura S., Ueda T., Watanabe K., Nishikawa K.. Higher-order structure of bovine mitochondrial tRNA(Phe) lacking the ‘conserved’ GG and T psi CG sequences as inferred by enzymatic and chemical probing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994; 22:347–353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65. Messmer M., Putz J., Suzuki T., Suzuki T., Sauter C., Sissler M., Catherine F.. Tertiary network in mammalian mitochondrial tRNAAsp revealed by solution probing and phylogeny. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009; 37:6881–6895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66. Giege R., Juhling F., Putz J., Stadler P., Sauter C., Florentz C.. Structure of transfer RNAs: similarity and variability. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA. 2012; 3:37–61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67. Tsunoda M., Kusakabe Y., Tanaka N., Ohno S., Nakamura M., Senda T., Moriguchi T., Asai N., Sekine M., Yokogawa T. et al.. Structural basis for recognition of cognate tRNA by tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase from three kingdoms. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007; 35:4289–4300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68. Lopez-Gallardo E., Emperador S., Solano A., Llobet L., Martin-Navarro A., Lopez-Perez M.J., Briones P., Pineda M., Artuch R., Barraquer E. et al.. Expanding the clinical phenotypes of MT-ATP6 mutations. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2014; 23:6191–6200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69. Jackson C.B., Hahn D., Schroter B., Richter U., Battersby B.J., Schmitt-Mechelke T., Marttinen P., Nuoffer J.M., Schaller A.. A novel mitochondrial ATP6 frameshift mutation causing isolated complex V deficiency, ataxia and encephalomyopathy. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2017; 60:345–351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70. Boonsawat P., Joset P., Steindl K., Oneda B., Gogoll L., Azzarello-Burri S., Sheth F., Datar C., Verma I.C., Puri R.D. et al.. Elucidation of the phenotypic spectrum and genetic landscape in primary and secondary microcephaly. Genet. Med. 2019; doi:10.1038/s41436-019-0464-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71. Gao Y., Bai X., Zhang D., Han C., Yuan J., Liu W., Cao X., Chen Z., Shangguan F., Zhu Z. et al.. Mammalian elongation factor 4 regulates mitochondrial translation essential for spermatogenesis. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2016; 23:441–449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.