In the title compound, the S atom is attached equatorially to the sugar ring. The C—S bond lengths are unequal. In the crystal, a system of three weak hydrogen bonds, sharing an oxygen acceptor, links the molecules to form chains propagating parallel to the b-axis direction.
Keywords: crystal structure, galactose, pyrimidine, weak hydrogen bond
Abstract
In the title compound, C20H26N2O9S, the S atom is attached equatorially to the sugar ring. The C—S bond lengths are unequal, with S—Cs = 1.8018 (13) Å and S—Cp = 1.7662 (13) Å (s = sugar and p = pyrimidyl). In the crystal, a system of three weak hydrogen bonds, sharing an oxygen acceptor, links the molecules to form chains propagating parallel to the b-axis direction.
Chemical context
Nucleosides are building blocks of biological systems and display a wide range of biological activities (Ding et al., 2003 ▸). Pyrimidine nucleoside analogues provide diverse and novel moieties for pharmacological targets, and they play basic and comprehensive roles in the field of medicinal chemistry (Xu et al., 2017 ▸). Different strategies for the synthesis of many pyrimidine nucleoside analogues have been developed to access new and potent pharmacological agents (Cao et al., 2011 ▸). Many such derivatives are manufactured as potential chemotherapeutic agents and have a significant impact on current medicinal research (Ohkubo et al., 2012 ▸). Recently, thioglycosides have proved to be important in the production of medically important carbohydrate compounds, because of their ease of preparation and chemical stability (Gourdain et al., 2011 ▸).
We have recently described the preparation of various pyrimidine and pyridine thioglycosides that displayed antagonistic activity (Hammad et al., 2018 ▸; Elgemeie et al., 2010 ▸). We have also reported the use of dihydropyridine thioglycosides as substrates or inhibitors of protein glycosylation (Scale et al., 1997 ▸; Elgemeie et al., 2015 ▸, 2016 ▸, 2017 ▸) and the use of pyrimidine thioglycosides as antihepatocellular carcinoma agents (Elgemeie & Farag, 2017 ▸). Continuing our efforts to develop simple and cost-effective methodologies for the synthesis of pyrimidine thioglycosides, we report here the one-step synthesis of a pyrimidine-2-thiogalactoside derivative by the reaction of 4,6-dimethylpyrimidine-2(1H)-thione (1) with 2,3,4,6-tetra-O-acetyl-α-d-galactopyranosyl bromide (2). This reaction in NaH/DMF at room temperature gave a product for which two isomeric structures seemed possible, corresponding to two possible modes of glysosylation to give the pyrimidine-N-galactoside (3) or its regioisomer pyrimidine-2-thiogalactoside 4 (see Scheme). Spectroscopic data cannot differentiate between these structures. It has been suggested that 1 reacts with 2 via a simple SN2 reaction to give the β-glycoside product 4 (Davis, 2000 ▸).
Structural commentary
The crystal structure determination indicated unambiguously the formation of the pyrimidine-2-thiogalactoside, 4, as the only product in the solid state.
The molecular structure of 4 is shown in Fig. 1 ▸ (for selected torsion angles, see Table 1 ▸) and the S atom is attached equatorially to the sugar ring. Similar to the structure of a related glucose derivative (Masoud et al., 2017 ▸), the C—S bond lengths are unequal, with S—Cs = 1.8018 (13) Å and S—Cp = 1.7662 (13) Å (s = sugar and p = pyrimidyl). The relative orientation of the pyridyl ring and the sugar moiety is defined by the torsion angles N2—C1—S1—C11 [−7.85 (12)°] and C1—S1—C11—C12 [165.01 (9)°]. All the acetyl groups show extended conformations, with absolute C—O—C—C torsion angles in the range 173–179°.
Figure 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound, 4, in the crystal. Displacement ellipsoids represent 50% probability levels.
Table 1. Selected torsion angles (°).
| S1—C11—C12—C13 | 178.21 (9) | C22—C21—O4—C14 | 177.90 (11) |
| S1—C11—O1—C15 | 171.60 (8) | C24—C23—O5—C16 | 178.85 (13) |
| C18—C17—O2—C12 | 176.21 (11) | C15—C16—O5—C23 | 174.82 (12) |
| C20—C19—O3—C13 | −173.83 (12) |
Supramolecular features
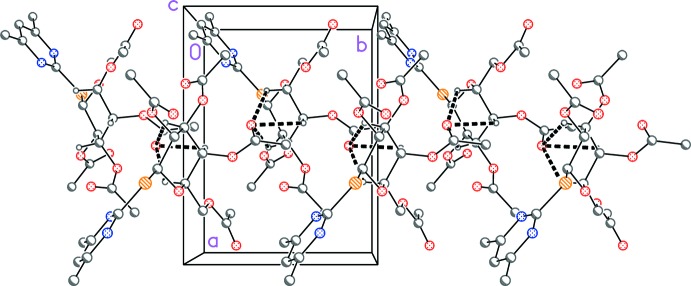
Some short C—H⋯O and C—H⋯S contacts are listed in Table 2 ▸, but these are at best borderline ‘weak’ hydrogen bonds, particularly in view of their narrow angles. The molecular packing is thus rather featureless. However, a motif of three sugar-ring C—H groups (C13—H13, C14—H14 and C15—H15) sharing a common acceptor (O8) can be recognized (Fig. 2 ▸). Neighbouring molecules are connected via the 21 operator, leading to chains of molecules propagating parallel to the b-axis direction.
Table 2. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C7—H7C⋯O9i | 0.98 | 2.57 | 3.495 (2) | 157 |
| C8—H8B⋯O1ii | 0.98 | 2.52 | 3.2499 (18) | 131 |
| C13—H13⋯O8iii | 1.00 | 2.65 | 3.2998 (16) | 123 |
| C14—H14⋯O8iii | 1.00 | 2.53 | 3.0626 (16) | 113 |
| C15—H15⋯O8iii | 1.00 | 2.50 | 3.1759 (16) | 124 |
| C18—H18B⋯S1iv | 0.98 | 2.95 | 3.7876 (19) | 144 |
| C22—H22C⋯O6v | 0.98 | 2.51 | 3.1911 (19) | 127 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii)  ; (iv)
; (iv)  ; (v)
; (v)  .
.
Figure 2.
Packing diagram of 4 projected parallel to the ab plane in the region z ≃ 1. Dashed lines indicate weak C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds. H atoms not involved in this hydrogen bonding system have been omitted.
Database survey
A search of the Cambridge Structural Database (Vwersion 2.0.0; Groom et al., 2016 ▸) for tetraacetyl thioglycosides with an S-bonded heterocycle [linkage S—C(—N)2, restricted to hexoses] gave one hit, a 1,2,4-triazole derivative of tetraacetylglucose (refcode HEKPUL; El Ashry et al., 2018 ▸).
Synthesis and crystallization
To a solution of pyrimidine-2(1H)-thione (1; 1.40 g, 0.01 mol) in dry DMF (20 ml), NaH (15 mmol) was added gradually over a period of 15 min and the solution was stirred at room temperature for another 30 min. A solution of 2,3,4,6-tetra-O-acetyl-α-d-galactopyranosyl bromide (2; 4.52 g, 0.011 mol) in DMF (20 ml) was then added dropwise over a period of 30 min and the reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature until the reaction was judged complete by thin-layer chromatography (3–6 h). The mixture was evaporated under reduced pressure at 333 K and the residue was washed with distilled water to remove potassium bromide. The crude solid was collected by filtration and purified using column chromatography (the solvent system was petroleum ether/ethyl acetate, 3:1 v/v; R F = 0.35); after evaporation of the solvent, this afforded compound 4 as colourless crystals in 85% yield (m.p. 441.2 K). IR (KBr, cm−1): ν 1752 (C=O); 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d 6): δ 2.11 (s, 12H, 4 × OAc), 2.45 (s, 6H, 2CH3), 4.01–4.12 (m, 2H, 2H-6′), 4.35–4.37 (m, 1H, H-5′), 5.21 (t, 1H, J 4′-3′ = 2.6, J 4′-5′ = 2.4 Hz, H-4′), 5.42–5.46 (m, 2H, H-3′, H-2′), 5.98 (d, 1H, J 1′-2′ = 10.65 Hz, H-1′), 7.01 (s, 1H, pyrimidine H-5); 13C NMR: δ 21.43 (4 × OAc), 22.4 (2CH3), 62.13 (C-6′), 68.41 (C-5′), 71.12 (C-4′), 74.43 (C-3′), 77.56 (C-2′), 82.12 (C-1′), 118.41 (C-5), 168.35 (C-4), 170.45 (C-6), 172.78 (4 × C=O). Analysis calculated (%) for C20H26N2O9S: C 51.06, H 5.57, N 5.95, S 6.82; found: C 51.16, H 5.46, N 5.82, S 6.75.
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 3 ▸. Methyl groups were refined as idealized rigid groups allowed to rotate but not tip (C—H = 0.98 Å and H—C—H = 109.5°). Other H atoms were included using a riding model starting from calculated positions (aromatic C—H = 0.95 Å, methylene C—H = 0.99 Å and methine C—H = 1.00 Å).
Table 3. Experimental details.
| Crystal data | |
| Chemical formula | C20H26N2O9S |
| M r | 470.49 |
| Crystal system, space group | Monoclinic, P21 |
| Temperature (K) | 100 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 11.4868 (2), 8.6444 (2), 11.5561 (2) |
| β (°) | 91.3762 (16) |
| V (Å3) | 1147.14 (4) |
| Z | 2 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.19 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.40 × 0.40 × 0.08 |
| Data collection | |
| Diffractometer | Oxford Diffraction Xcalibur Eos |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Rigaku OD, 2015 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.896, 1.000 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 107162, 7825, 7530 |
| R int | 0.034 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.757 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.028, 0.073, 1.04 |
| No. of reflections | 7825 |
| No. of parameters | 295 |
| No. of restraints | 1 |
| H-atom treatment | H-atom parameters constrained |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.34, −0.21 |
| Absolute structure | Flack x determined using 3355 quotients [(I +)−(I −)]/[(I +)+(I −)] (Parsons et al., 2013 ▸) |
| Absolute structure parameter | −0.003 (11) |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901901449X/hb7861sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901901449X/hb7861Isup2.hkl
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
GHE would like to thank the Egyptian Academy of Scientific Research & Technology (ASRT), Jesor program, for awarding a grant.
supplementary crystallographic information
Crystal data
| C20H26N2O9S | F(000) = 496 |
| Mr = 470.49 | Dx = 1.362 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 11.4868 (2) Å | Cell parameters from 34705 reflections |
| b = 8.6444 (2) Å | θ = 2.5–31.9° |
| c = 11.5561 (2) Å | µ = 0.19 mm−1 |
| β = 91.3762 (16)° | T = 100 K |
| V = 1147.14 (4) Å3 | Plate, colourless |
| Z = 2 | 0.40 × 0.40 × 0.08 mm |
Data collection
| Oxford Diffraction Xcalibur Eos diffractometer | 7825 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed X-ray tube | 7530 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Detector resolution: 16.1419 pixels mm-1 | Rint = 0.034 |
| ω–scan | θmax = 32.6°, θmin = 2.5° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Rigaku OD, 2015) | h = −16→17 |
| Tmin = 0.896, Tmax = 1.000 | k = −13→12 |
| 107162 measured reflections | l = −17→17 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.028 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.073 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0448P)2 + 0.1562P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.04 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.003 |
| 7825 reflections | Δρmax = 0.34 e Å−3 |
| 295 parameters | Δρmin = −0.21 e Å−3 |
| 1 restraint | Absolute structure: Flack x determined using 3355 quotients [(I+)-(I-)]/[(I+)+(I-)] (Parsons et al., 2013) |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Absolute structure parameter: −0.003 (11) |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| S1 | 0.31717 (3) | 0.37712 (4) | 0.52391 (3) | 0.01490 (7) | |
| C1 | 0.20586 (11) | 0.24276 (15) | 0.55326 (12) | 0.0142 (2) | |
| N2 | 0.19449 (10) | 0.18868 (14) | 0.65991 (10) | 0.0157 (2) | |
| C3 | 0.10603 (12) | 0.08858 (17) | 0.67531 (12) | 0.0172 (2) | |
| C4 | 0.03201 (12) | 0.04670 (18) | 0.58372 (14) | 0.0206 (3) | |
| H4 | −0.030920 | −0.022627 | 0.594791 | 0.025* | |
| C5 | 0.05295 (11) | 0.10958 (19) | 0.47507 (13) | 0.0199 (3) | |
| N6 | 0.14080 (10) | 0.20913 (15) | 0.45864 (10) | 0.0171 (2) | |
| C7 | 0.09350 (14) | 0.0274 (2) | 0.79576 (14) | 0.0245 (3) | |
| H7A | 0.168605 | −0.013057 | 0.824151 | 0.037* | |
| H7B | 0.035507 | −0.055784 | 0.795217 | 0.037* | |
| H7C | 0.068210 | 0.110957 | 0.846639 | 0.037* | |
| C8 | −0.02150 (15) | 0.0695 (3) | 0.37087 (15) | 0.0321 (4) | |
| H8A | −0.006740 | 0.143333 | 0.308590 | 0.048* | |
| H8B | −0.103788 | 0.074109 | 0.391103 | 0.048* | |
| H8C | −0.002582 | −0.035284 | 0.344863 | 0.048* | |
| C11 | 0.36873 (11) | 0.41461 (15) | 0.66971 (11) | 0.0131 (2) | |
| H11 | 0.375290 | 0.314664 | 0.712943 | 0.016* | |
| C12 | 0.48727 (11) | 0.49574 (15) | 0.67193 (11) | 0.0128 (2) | |
| H12 | 0.483420 | 0.593888 | 0.626193 | 0.015* | |
| C13 | 0.52391 (10) | 0.52856 (15) | 0.79714 (11) | 0.0126 (2) | |
| H13 | 0.543513 | 0.428968 | 0.837101 | 0.015* | |
| C14 | 0.42901 (11) | 0.61209 (15) | 0.86310 (10) | 0.0125 (2) | |
| H14 | 0.450359 | 0.615925 | 0.947450 | 0.015* | |
| C15 | 0.31396 (11) | 0.52721 (16) | 0.84512 (11) | 0.0134 (2) | |
| H15 | 0.320387 | 0.421966 | 0.880626 | 0.016* | |
| C16 | 0.21073 (12) | 0.61091 (19) | 0.89541 (11) | 0.0182 (2) | |
| H16A | 0.199582 | 0.712822 | 0.857662 | 0.022* | |
| H16B | 0.138732 | 0.549329 | 0.883778 | 0.022* | |
| C17 | 0.60600 (13) | 0.42066 (17) | 0.51651 (12) | 0.0189 (3) | |
| C18 | 0.70211 (15) | 0.3144 (2) | 0.48332 (15) | 0.0268 (3) | |
| H18A | 0.701248 | 0.301910 | 0.399020 | 0.040* | |
| H18B | 0.691163 | 0.213438 | 0.520012 | 0.040* | |
| H18C | 0.777016 | 0.358241 | 0.509150 | 0.040* | |
| C19 | 0.70586 (11) | 0.60977 (19) | 0.88007 (12) | 0.0195 (3) | |
| C20 | 0.80074 (13) | 0.7270 (2) | 0.86755 (15) | 0.0289 (3) | |
| H20A | 0.777357 | 0.824463 | 0.903511 | 0.043* | |
| H20B | 0.814694 | 0.744261 | 0.785231 | 0.043* | |
| H20C | 0.872252 | 0.688885 | 0.905729 | 0.043* | |
| C21 | 0.47753 (11) | 0.87850 (18) | 0.87510 (11) | 0.0161 (2) | |
| C22 | 0.46064 (15) | 1.03358 (18) | 0.81936 (13) | 0.0229 (3) | |
| H22A | 0.484169 | 1.114920 | 0.874164 | 0.034* | |
| H22B | 0.378397 | 1.047057 | 0.797118 | 0.034* | |
| H22C | 0.508294 | 1.040209 | 0.750322 | 0.034* | |
| C23 | 0.15859 (13) | 0.71433 (19) | 1.07533 (13) | 0.0219 (3) | |
| C24 | 0.19319 (16) | 0.7243 (3) | 1.20142 (14) | 0.0306 (4) | |
| H24A | 0.135476 | 0.785614 | 1.242427 | 0.046* | |
| H24B | 0.269721 | 0.773711 | 1.209540 | 0.046* | |
| H24C | 0.196923 | 0.619929 | 1.234481 | 0.046* | |
| O1 | 0.28647 (8) | 0.51166 (12) | 0.72429 (8) | 0.01402 (17) | |
| O2 | 0.57416 (8) | 0.39412 (12) | 0.62726 (8) | 0.01502 (18) | |
| O3 | 0.62667 (8) | 0.62251 (13) | 0.79139 (8) | 0.01642 (18) | |
| O4 | 0.41523 (8) | 0.76733 (12) | 0.81822 (8) | 0.01450 (18) | |
| O5 | 0.23709 (9) | 0.63008 (14) | 1.01710 (9) | 0.0198 (2) | |
| O6 | 0.56194 (12) | 0.51912 (15) | 0.45620 (10) | 0.0278 (2) | |
| O7 | 0.69797 (10) | 0.51640 (16) | 0.95647 (10) | 0.0266 (2) | |
| O8 | 0.53897 (9) | 0.85198 (13) | 0.95903 (9) | 0.0201 (2) | |
| O9 | 0.07262 (10) | 0.76925 (17) | 1.03075 (11) | 0.0295 (3) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| S1 | 0.01701 (13) | 0.01501 (14) | 0.01247 (12) | −0.00376 (11) | −0.00397 (9) | −0.00027 (11) |
| C1 | 0.0126 (5) | 0.0123 (6) | 0.0177 (5) | 0.0001 (4) | −0.0024 (4) | −0.0023 (4) |
| N2 | 0.0156 (5) | 0.0138 (5) | 0.0176 (5) | 0.0000 (4) | −0.0019 (4) | 0.0000 (4) |
| C3 | 0.0151 (5) | 0.0148 (6) | 0.0218 (6) | 0.0007 (4) | 0.0013 (4) | 0.0003 (5) |
| C4 | 0.0143 (5) | 0.0210 (7) | 0.0265 (7) | −0.0033 (5) | −0.0001 (5) | −0.0024 (5) |
| C5 | 0.0136 (5) | 0.0224 (7) | 0.0235 (6) | −0.0022 (5) | −0.0030 (5) | −0.0043 (5) |
| N6 | 0.0144 (5) | 0.0191 (6) | 0.0177 (5) | −0.0013 (4) | −0.0037 (4) | −0.0033 (4) |
| C7 | 0.0223 (6) | 0.0257 (8) | 0.0257 (7) | −0.0023 (6) | 0.0014 (5) | 0.0072 (6) |
| C8 | 0.0232 (7) | 0.0468 (11) | 0.0260 (7) | −0.0135 (7) | −0.0066 (6) | −0.0073 (7) |
| C11 | 0.0139 (5) | 0.0129 (6) | 0.0123 (5) | −0.0003 (4) | −0.0036 (4) | −0.0004 (4) |
| C12 | 0.0139 (5) | 0.0126 (6) | 0.0120 (5) | −0.0005 (4) | −0.0026 (4) | −0.0009 (4) |
| C13 | 0.0118 (5) | 0.0136 (6) | 0.0122 (5) | −0.0016 (4) | −0.0029 (4) | −0.0008 (4) |
| C14 | 0.0142 (5) | 0.0118 (5) | 0.0114 (5) | 0.0002 (4) | −0.0031 (4) | 0.0011 (4) |
| C15 | 0.0139 (5) | 0.0149 (6) | 0.0112 (5) | 0.0009 (4) | −0.0027 (4) | 0.0009 (4) |
| C16 | 0.0159 (5) | 0.0242 (7) | 0.0142 (5) | 0.0030 (5) | −0.0017 (4) | −0.0005 (5) |
| C17 | 0.0222 (6) | 0.0199 (7) | 0.0148 (5) | −0.0085 (5) | 0.0028 (4) | −0.0051 (5) |
| C18 | 0.0255 (7) | 0.0288 (8) | 0.0266 (7) | −0.0049 (6) | 0.0080 (6) | −0.0112 (6) |
| C19 | 0.0132 (5) | 0.0263 (7) | 0.0188 (6) | 0.0007 (5) | −0.0036 (4) | −0.0079 (5) |
| C20 | 0.0169 (6) | 0.0392 (10) | 0.0303 (8) | −0.0094 (6) | −0.0020 (5) | −0.0098 (7) |
| C21 | 0.0202 (5) | 0.0137 (6) | 0.0142 (5) | −0.0009 (5) | −0.0014 (4) | −0.0028 (5) |
| C22 | 0.0356 (8) | 0.0137 (6) | 0.0189 (6) | −0.0028 (6) | −0.0062 (5) | 0.0010 (5) |
| C23 | 0.0187 (6) | 0.0250 (7) | 0.0221 (6) | −0.0031 (5) | 0.0056 (5) | −0.0031 (5) |
| C24 | 0.0286 (7) | 0.0445 (11) | 0.0189 (7) | −0.0026 (7) | 0.0045 (6) | −0.0080 (7) |
| O1 | 0.0138 (4) | 0.0156 (4) | 0.0125 (4) | 0.0015 (3) | −0.0042 (3) | −0.0007 (3) |
| O2 | 0.0156 (4) | 0.0163 (5) | 0.0131 (4) | −0.0001 (3) | 0.0001 (3) | −0.0018 (3) |
| O3 | 0.0141 (4) | 0.0201 (5) | 0.0149 (4) | −0.0046 (4) | −0.0029 (3) | −0.0025 (4) |
| O4 | 0.0195 (4) | 0.0108 (4) | 0.0129 (4) | −0.0004 (3) | −0.0055 (3) | 0.0005 (3) |
| O5 | 0.0183 (4) | 0.0270 (6) | 0.0142 (4) | 0.0031 (4) | −0.0005 (3) | −0.0020 (4) |
| O6 | 0.0396 (6) | 0.0273 (6) | 0.0167 (5) | −0.0032 (5) | 0.0034 (4) | 0.0030 (4) |
| O7 | 0.0231 (5) | 0.0330 (7) | 0.0233 (5) | 0.0017 (5) | −0.0102 (4) | 0.0011 (5) |
| O8 | 0.0243 (5) | 0.0184 (5) | 0.0173 (4) | 0.0006 (4) | −0.0076 (4) | −0.0046 (4) |
| O9 | 0.0207 (5) | 0.0371 (7) | 0.0310 (6) | 0.0060 (5) | 0.0038 (4) | −0.0013 (5) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| S1—C1 | 1.7662 (13) | C23—O9 | 1.201 (2) |
| S1—C11 | 1.8018 (13) | C23—O5 | 1.3511 (18) |
| C1—N2 | 1.3275 (18) | C23—C24 | 1.504 (2) |
| C1—N6 | 1.3414 (17) | C4—H4 | 0.9500 |
| N2—C3 | 1.3497 (18) | C7—H7A | 0.9800 |
| C3—C4 | 1.390 (2) | C7—H7B | 0.9800 |
| C3—C7 | 1.499 (2) | C7—H7C | 0.9800 |
| C4—C5 | 1.394 (2) | C8—H8A | 0.9800 |
| C5—N6 | 1.3432 (18) | C8—H8B | 0.9800 |
| C5—C8 | 1.501 (2) | C8—H8C | 0.9800 |
| C11—O1 | 1.4223 (15) | C11—H11 | 1.0000 |
| C11—C12 | 1.5314 (17) | C12—H12 | 1.0000 |
| C12—O2 | 1.4349 (16) | C13—H13 | 1.0000 |
| C12—C13 | 1.5239 (17) | C14—H14 | 1.0000 |
| C13—O3 | 1.4356 (15) | C15—H15 | 1.0000 |
| C13—C14 | 1.5267 (18) | C16—H16A | 0.9900 |
| C14—O4 | 1.4460 (16) | C16—H16B | 0.9900 |
| C14—C15 | 1.5214 (17) | C18—H18A | 0.9800 |
| C15—O1 | 1.4305 (15) | C18—H18B | 0.9800 |
| C15—C16 | 1.5168 (19) | C18—H18C | 0.9800 |
| C16—O5 | 1.4409 (16) | C20—H20A | 0.9800 |
| C17—O6 | 1.204 (2) | C20—H20B | 0.9800 |
| C17—O2 | 1.3591 (16) | C20—H20C | 0.9800 |
| C17—C18 | 1.493 (2) | C22—H22A | 0.9800 |
| C19—O7 | 1.201 (2) | C22—H22B | 0.9800 |
| C19—O3 | 1.3583 (16) | C22—H22C | 0.9800 |
| C19—C20 | 1.498 (2) | C24—H24A | 0.9800 |
| C21—O8 | 1.2077 (16) | C24—H24B | 0.9800 |
| C21—O4 | 1.3584 (16) | C24—H24C | 0.9800 |
| C21—C22 | 1.498 (2) | ||
| C1—S1—C11 | 99.32 (6) | H7A—C7—H7C | 109.5 |
| N2—C1—N6 | 127.96 (13) | H7B—C7—H7C | 109.5 |
| N2—C1—S1 | 119.85 (10) | C5—C8—H8A | 109.5 |
| N6—C1—S1 | 112.19 (10) | C5—C8—H8B | 109.5 |
| C1—N2—C3 | 116.07 (12) | H8A—C8—H8B | 109.5 |
| N2—C3—C4 | 121.02 (13) | C5—C8—H8C | 109.5 |
| N2—C3—C7 | 115.98 (13) | H8A—C8—H8C | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—C7 | 123.00 (13) | H8B—C8—H8C | 109.5 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 117.95 (13) | O1—C11—H11 | 109.3 |
| N6—C5—C4 | 121.56 (13) | C12—C11—H11 | 109.3 |
| N6—C5—C8 | 116.76 (14) | S1—C11—H11 | 109.3 |
| C4—C5—C8 | 121.68 (14) | O2—C12—H12 | 110.6 |
| C1—N6—C5 | 115.43 (12) | C13—C12—H12 | 110.6 |
| O1—C11—C12 | 108.80 (10) | C11—C12—H12 | 110.6 |
| O1—C11—S1 | 108.29 (8) | O3—C13—H13 | 109.4 |
| C12—C11—S1 | 111.73 (9) | C12—C13—H13 | 109.4 |
| O2—C12—C13 | 106.07 (10) | C14—C13—H13 | 109.4 |
| O2—C12—C11 | 109.85 (10) | O4—C14—H14 | 109.9 |
| C13—C12—C11 | 109.05 (10) | C15—C14—H14 | 109.9 |
| O3—C13—C12 | 105.66 (10) | C13—C14—H14 | 109.9 |
| O3—C13—C14 | 110.69 (10) | O1—C15—H15 | 109.1 |
| C12—C13—C14 | 112.20 (10) | C16—C15—H15 | 109.1 |
| O4—C14—C15 | 108.14 (10) | C14—C15—H15 | 109.1 |
| O4—C14—C13 | 109.47 (10) | O5—C16—H16A | 110.5 |
| C15—C14—C13 | 109.39 (10) | C15—C16—H16A | 110.5 |
| O1—C15—C16 | 105.22 (10) | O5—C16—H16B | 110.5 |
| O1—C15—C14 | 110.44 (10) | C15—C16—H16B | 110.5 |
| C16—C15—C14 | 113.71 (11) | H16A—C16—H16B | 108.7 |
| O5—C16—C15 | 106.32 (10) | C17—C18—H18A | 109.5 |
| O6—C17—O2 | 123.07 (14) | C17—C18—H18B | 109.5 |
| O6—C17—C18 | 126.10 (14) | H18A—C18—H18B | 109.5 |
| O2—C17—C18 | 110.82 (13) | C17—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| O7—C19—O3 | 123.23 (13) | H18A—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| O7—C19—C20 | 126.41 (14) | H18B—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| O3—C19—C20 | 110.37 (13) | C19—C20—H20A | 109.5 |
| O8—C21—O4 | 123.04 (13) | C19—C20—H20B | 109.5 |
| O8—C21—C22 | 125.63 (13) | H20A—C20—H20B | 109.5 |
| O4—C21—C22 | 111.33 (11) | C19—C20—H20C | 109.5 |
| O9—C23—O5 | 123.46 (14) | H20A—C20—H20C | 109.5 |
| O9—C23—C24 | 126.07 (15) | H20B—C20—H20C | 109.5 |
| O5—C23—C24 | 110.45 (14) | C21—C22—H22A | 109.5 |
| C11—O1—C15 | 110.79 (9) | C21—C22—H22B | 109.5 |
| C17—O2—C12 | 116.15 (11) | H22A—C22—H22B | 109.5 |
| C19—O3—C13 | 117.11 (11) | C21—C22—H22C | 109.5 |
| C21—O4—C14 | 115.54 (10) | H22A—C22—H22C | 109.5 |
| C23—O5—C16 | 114.90 (11) | H22B—C22—H22C | 109.5 |
| C3—C4—H4 | 121.0 | C23—C24—H24A | 109.5 |
| C5—C4—H4 | 121.0 | C23—C24—H24B | 109.5 |
| C3—C7—H7A | 109.5 | H24A—C24—H24B | 109.5 |
| C3—C7—H7B | 109.5 | C23—C24—H24C | 109.5 |
| H7A—C7—H7B | 109.5 | H24A—C24—H24C | 109.5 |
| C3—C7—H7C | 109.5 | H24B—C24—H24C | 109.5 |
| C11—S1—C1—N2 | −7.85 (12) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | 49.77 (14) |
| C11—S1—C1—N6 | 171.73 (10) | O4—C14—C15—O1 | 63.93 (13) |
| N6—C1—N2—C3 | −0.6 (2) | C13—C14—C15—O1 | −55.22 (14) |
| S1—C1—N2—C3 | 178.90 (10) | O4—C14—C15—C16 | −54.09 (13) |
| C1—N2—C3—C4 | −0.2 (2) | C13—C14—C15—C16 | −173.24 (11) |
| C1—N2—C3—C7 | 179.87 (13) | O1—C15—C16—O5 | −179.18 (11) |
| N2—C3—C4—C5 | 0.9 (2) | C14—C15—C16—O5 | −58.19 (14) |
| C7—C3—C4—C5 | −179.23 (15) | C12—C11—O1—C15 | −66.76 (12) |
| C3—C4—C5—N6 | −0.8 (2) | S1—C11—O1—C15 | 171.60 (8) |
| C3—C4—C5—C8 | 179.22 (15) | C16—C15—O1—C11 | −171.37 (11) |
| N2—C1—N6—C5 | 0.7 (2) | C14—C15—O1—C11 | 65.52 (13) |
| S1—C1—N6—C5 | −178.84 (10) | O6—C17—O2—C12 | −2.78 (19) |
| C4—C5—N6—C1 | 0.1 (2) | C18—C17—O2—C12 | 176.21 (11) |
| C8—C5—N6—C1 | −179.96 (14) | C13—C12—O2—C17 | −140.59 (11) |
| C1—S1—C11—O1 | −75.17 (9) | C11—C12—O2—C17 | 101.70 (12) |
| C1—S1—C11—C12 | 165.01 (9) | O7—C19—O3—C13 | 6.0 (2) |
| O1—C11—C12—O2 | 174.55 (9) | C20—C19—O3—C13 | −173.83 (12) |
| S1—C11—C12—O2 | −65.93 (12) | C12—C13—O3—C19 | −150.10 (11) |
| O1—C11—C12—C13 | 58.70 (13) | C14—C13—O3—C19 | 88.21 (13) |
| S1—C11—C12—C13 | 178.21 (9) | O8—C21—O4—C14 | −1.39 (18) |
| O2—C12—C13—O3 | 69.45 (12) | C22—C21—O4—C14 | 177.90 (11) |
| C11—C12—C13—O3 | −172.30 (10) | C15—C14—O4—C21 | 146.97 (11) |
| O2—C12—C13—C14 | −169.84 (10) | C13—C14—O4—C21 | −93.93 (12) |
| C11—C12—C13—C14 | −51.59 (14) | O9—C23—O5—C16 | 0.4 (2) |
| O3—C13—C14—O4 | 49.20 (13) | C24—C23—O5—C16 | 178.85 (13) |
| C12—C13—C14—O4 | −68.56 (13) | C15—C16—O5—C23 | 174.82 (12) |
| O3—C13—C14—C15 | 167.53 (10) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C7—H7C···O9i | 0.98 | 2.57 | 3.495 (2) | 157 |
| C8—H8B···O1ii | 0.98 | 2.52 | 3.2499 (18) | 131 |
| C13—H13···O8iii | 1.00 | 2.65 | 3.2998 (16) | 123 |
| C14—H14···O8iii | 1.00 | 2.53 | 3.0626 (16) | 113 |
| C15—H15···O8iii | 1.00 | 2.50 | 3.1759 (16) | 124 |
| C18—H18B···S1iv | 0.98 | 2.95 | 3.7876 (19) | 144 |
| C22—H22C···O6v | 0.98 | 2.51 | 3.1911 (19) | 127 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x, y−1/2, −z+2; (ii) −x, y−1/2, −z+1; (iii) −x+1, y−1/2, −z+2; (iv) −x+1, y−1/2, −z+1; (v) −x+1, y+1/2, −z+1.
References
- Cao, S., Okamoto, I., Tsunoda, H., Ohkubo, A., Seio, K. & Sekine, M. (2011). Tetrahedron Lett. 52, 407–410.
- Davis, B. G. (2000). J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1, 14, 2137–2160.
- Ding, Y., Hofstadler, S. A., Swayze, E. E., Risen, L. & Griffey, R. H. (2003). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 42, 3409–3412. [DOI] [PubMed]
- El Ashry El, S. H., Awad, L. F., Al Moaty, M. N. A., Ghabbour, H. A. & Barakwat, A. (2018). J. Mol. Struct. 1152, 87–95.
- Elgemeie, G. H., Abou-Zeid, M., Alsaid, S., Hebishy, A. & Essa, H. (2015). Nucleosides Nucleotides, 34, 659–673. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Elgemeie, G. H., Abu-Zaied, M. A. & Azzam, R. (2016). Nucleosides Nucleotides, 35, 211–222. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Elgemeie, G. H., Abu-Zaied, M. A. & Loutfy, S. A. (2017). Tetrahedron, 73, 5853–5861.
- Elgemeie, G. H. & Farag, A. B. (2017). Nucleosides Nucleotides, 36, 328–342. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Elgemeie, G. H., Mahdy, E. M., Elgawish, M. A., Ahmed, M. M., Shousha, W. G. & Eldin, M. E. (2010). Z. Naturforsch. Teil C, 65, 577–587. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Gourdain, S., Petermann, C., Martinez, A., Harakat, D. & Clivio, P. (2011). J. Org. Chem. 76, 1906–1909. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Groom, C. R., Bruno, I. J., Lightfoot, M. P. & Ward, S. C. (2016). Acta Cryst. B72, 171–179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Hammad, S. F., Masoud, D. M., Elgemeie, G. H. & Jones, P. G. (2018). Acta Cryst. E74, 853–856. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Masoud, D. M., Hammad, S. F., Elgemeie, G. H. & Jones, P. G. (2017). Acta Cryst E73, 1751–1754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Ohkubo, A., Nishino, Y., Ito, Y., Tsunoda, H., Seio, K. & Sekine, M. (2012). Org. Biomol. Chem. 10, 2008–2010. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Parsons, S., Flack, H. D. & Wagner, T. (2013). Acta Cryst. B69, 249–259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Rigaku OD (2015). CrysAlis PRO. Rigaku Oxford Diffraction Ltd, Yarnton, Oxfordshire, England.
- Scale, S., Akhmed, N., Rao, U. S., Paul, K., Lan, L., Dickstein, B., Lee, J., Elgemeie, G. H., Stein, W. D. & Bates, S. E. P. (1997). Mol. Pharmacol. 51, 1024–1033. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Siemens (1994). XP. Siemens Analytical X-ray Instruments, Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Xu, J., Tsanakopoulou, M., Magnani, C. J., Szabla, R., Šponer, J. E., Šponer, J., Góra, R. W. & Sutherland, J. D. (2017). Nat. Chem. 9, 303–309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901901449X/hb7861sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901901449X/hb7861Isup2.hkl
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report