Figure 19.
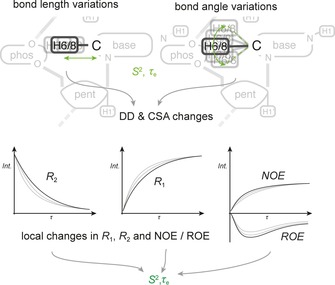
Principle of fast exchange. Geometrical changes within a molecule, such as bond length variations or bond angle variations, as illustrated in the top panel, lead to changes of DD and CSA interactions. Since these DD and CSA interactions are some of the most significant drivers for relaxation mechanisms, a change of these interactions faster than the tumbling rate of the molecule will lead to a direct influence of local relaxation rates. In practice, site specific R 1, R 2 and other geometry dependent observables such as NOE transfer rates are determined throughout the molecule.
