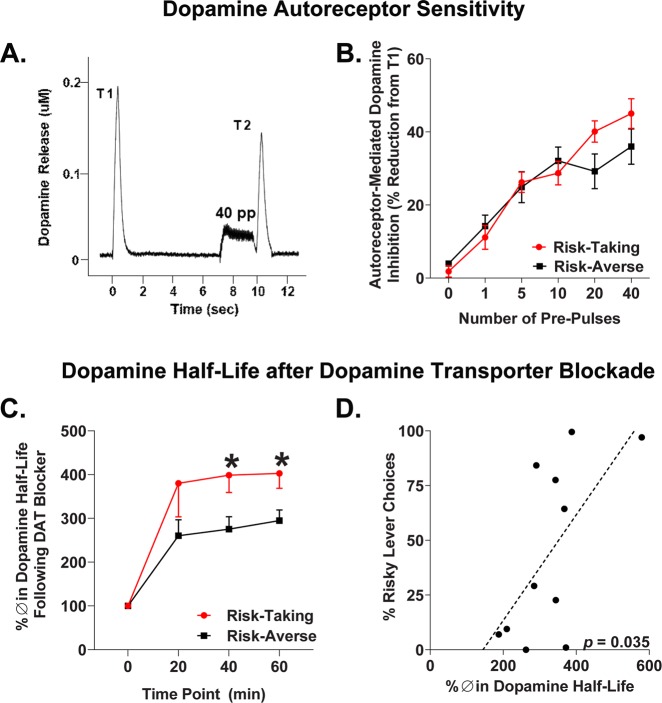
Fig. 4.
Nucleus accumbens shell dopamine autoreceptor function and nomifensine sensitivity. a Representative response depicting autoreceptor-mediated inhibition of dopamine release in terms of change from test stimulation 1 (T1) to test stimulation 2 (T2). Autoreceptor inhibition of dopamine release is evoked by a train of pulses prior to T2 (shown: 40 pulses). b Risk-taking rats express increased autoreceptor sensitivity with higher stimulation parameters, confirmed by a significant risk group × pulse interaction. c Percent change in dopamine half-life following nomifensine treatment during 60 min amperometric recordings for risk-taking and -averse rats. d Correlation between risk preference and average percent change in dopamine half-life across the 20, 40, and 60 min time points. Error bars represent ±SEM. *p < 0.05