This systematic review and meta-analysis assesses the association of marijuana use with the development of cancer in adults with at least 1 joint-year exposure (equivalent to 1 joint per day for 1 year).
Key Points
Question
What is the association between marijuana use and cancer development in adults with at least 1 joint-year exposure (equivalent to 1 joint per day for 1 year)?
Findings
This systematic review and meta-analysis identified 25 English-language studies assessing marijuana use and the risk for developing lung, head and neck, urogenital, and other cancers. In meta-analyses, regular marijuana use was associated with development of testicular germ cell tumors, although the strength of evidence was low; evidence regarding other cancers was insufficient.
Meaning
Sustained marijuana use may increase the risk for testicular cancer, but overall, the association of marijuana use and cancer development remains unclear.
Abstract
Importance
Marijuana use is common and growing in the United States amid a trend toward legalization. Exposure to tobacco smoke is a well-described preventable cause of many cancers; the association of marijuana use with the development of cancer is not clear.
Objective
To assess the association of marijuana use with cancer development.
Data Sources
A search of PubMed, Embase, PsycINFO, MEDLINE, and the Cochrane Library was conducted on June 11, 2018, and updated on April 30, 2019. A systematic review and meta-analysis of studies published from January 1, 1973, to April 30, 2019, and references of included studies were performed, with data analyzed from January 2 through October 4, 2019.
Study Selection
English-language studies involving adult marijuana users and reporting cancer development. The search strategy contained the following 2 concepts linked together with the AND operator: marijuana OR marihuana OR tetrahydrocannabinol OR cannabinoid OR cannabis; AND cancer OR malignancy OR carcinoma OR tumor OR neoplasm.
Data Extraction and Synthesis
Two reviewers independently reviewed titles, abstracts, and full-text articles; 3 reviewers independently assessed study characteristics and graded evidence strength by consensus.
Main Outcomes and Measures
Rates of cancer in marijuana users, with ever use defined as at least 1 joint-year exposure (equivalent to 1 joint per day for 1 year), compared with nonusers. Meta-analysis was conducted if there were at least 2 studies of the same design addressing the same cancer without high risk of bias when heterogeneity was low to moderate for the following 4 cancers: lung, head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, oral squamous cell carcinoma, and testicular germ cell tumor (TGCT), with comparisons expressed as odds ratios (ORs) with 95% CIs.
Results
Twenty-five English-language studies (19 case-control, 5 cohort, and 1 cross-sectional) were included; few studies (n = 2) were at low risk of bias. In pooled analysis of case-control studies, ever use of marijuana was not associated with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma or oral cancer. In pooled analysis of 3 case-control studies, more than 10 years of marijuana use (joint-years not reported) was associated with TGCT (OR, 1.36; 95% CI, 1.03-1.81; P = .03; I2 = 0%) and nonseminoma TGCT (OR, 1.85; 95% CI, 1.10-3.11; P = .04; I2 = 0%). Evaluations of ever use generally found no association with cancers, but exposure levels were low and poorly defined. Findings for lung cancer were mixed, confounded by few marijuana-only smokers, poor exposure assessment, and inadequate adjustment; meta-analysis was not performed for several outcomes.
Conclusions and Relevance
Low-strength evidence suggests that smoking marijuana is associated with developing TGCT; its association with other cancers and the consequences of higher levels of use are unclear. Long-term studies in marijuana-only smokers would improve understanding of marijuana’s association with lung, oral, and other cancers.
Trial Registration
PROSPERO identifier: CRD42018102457
Introduction
Marijuana is the most widely used illicit substance in the United States, with almost half of adults reporting lifetime use.1 Rates are increasing,2 with use among young adults (age range, 18-29 years) doubling from 10.5% in 2002 to 21.2% in 2014. Smoking remains the main route of marijuana exposure.3,4
Marijuana smoke and tobacco smoke share carcinogens, including toxic gases, reactive oxygen species, and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, such as benzo[α]pyrene and phenols,5 which are 20 times higher in unfiltered marijuana than in cigarette smoke.6 The larger the puff volume, the greater the depth of inhalation,7 and longer breath-holding time with marijuana compared with cigarette smoking leads to higher tar and carbon monoxide exposure.8 Furthermore, marijuana use is associated with histopathologic bronchial inflammatory changes comparable to changes observed with smoking tobacco.9 Given that cancer is the second leading cause of death in the United States10 and smoking remains the largest preventable cause of cancer death (responsible for 28.6% of all cancer deaths in 2014),11 similar toxic effects of marijuana smoke and tobacco smoke may have important health implications.
Aside from shared properties with tobacco, marijuana use may alter cancer risk through other mechanisms. Tetrahydrocannabinol, the primary psychoactive ingredient in marijuana, may have adverse immunomodulatory effects8,9 associated with cancer. Two proto-oncogenes are overexpressed in the bronchial epithelium of marijuana-only smokers, with a higher frequency of gene expression compared with tobacco-only smokers.8,12 In contrast, cannabinoids, including tetrahydrocannabinol, can inhibit proliferation of some cancer cell types, impede angiogenesis in vitro, and reduce cancer growth in some animal models.13,14 The net association of marijuana use with developing cancer is unclear.
The increasing prevalence of marijuana use, particularly among young adults, raises concerns regarding whether using marijuana increases the risk for developing cancer. Despite increasing social acceptance of marijuana use, there remains a dearth of information on the association between marijuana consumption and health, including its association with incident cancer. We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis to improve the understanding of the association of marijuana use with developing cancers.
Methods
This systematic review and meta-analysis was consistent with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses (PRISMA) statement.15 The protocol was registered at PROSPERO at the start of our investigation.
Data Sources and Searches
A systematic literature review was performed using studies found in a search of several online databases (PubMed, Embase, PsycINFO, MEDLINE, and the Cochrane Library), as well as references of the included studies. The search was conducted on June 11, 2018, and was updated on April 30, 2019. The studies were published from January 1, 1973, to June 11, 2018. We chose 1973 as the start date because Oregon decriminalized possession of marijuana in that year.16 For PubMed, Embase, MEDLINE, and the Cochrane Library, we used both controlled vocabulary and text words for synonymous terminology within titles and abstracts in the development of search strategies. In PsycINFO, we used text word searching of titles and abstracts. The search strategy contained the following 2 concepts linked together with the AND operator17: marijuana OR marihuana OR tetrahydrocannabinol OR cannabinoid OR cannabis; AND cancer OR malignancy OR carcinoma OR tumor OR neoplasm (eAppendix 1 in the Supplement). We combined search results using a bibliographic management tool (EndNote, version X9; Clarivate Analytics) and used the method by Bramer et al18 to eliminate duplicates.
Study Selection
Two of us (M.G. and B.B.) independently screened all titles and abstracts for inclusion. We included studies published in English involving participants 18 years or older with at least 1 joint-year exposure (equivalent of 1 joint per day for 1 year) or more cumulative use (defined as ever use) of marijuana and reporting on the development of cancer. We excluded review articles, commentaries, case reports, case series, editorial articles, in vitro and animal studies, studies that did not primarily evaluate marijuana exposure or include information on cancer outcomes, studies that reported only outcomes after short-term exposure in a laboratory setting, and studies that included fewer than 10 marijuana users (eAppendix 5 in the Supplement). The same 2 reviewers (M.G. and B.B.) independently reviewed all full-text articles using predetermined inclusion and exclusion criteria. Additional articles were identified through author tracking of first and last authors and reference tracking. Disagreements regarding publication inclusion were resolved by discussion or referral to a third reviewer (D.K.) (eAppendix 2 in the Supplement).
Data Extraction and Quality Assessment
For each included study, 2 of us (M.G. and B.B.) independently collected information on outcomes by cancer type (lung, head and neck, urogenital, and other cancers). They also extracted data on study design (eg, case-control vs cohort), study population, participant age, exposure route, marijuana use intensity and duration, percentage of marijuana-only smokers, confounders (eg, tobacco or alcohol use and occupational exposure), and funding source. Risk of bias (ROB) in individual studies was assessed independently by 3 of us (M.G., S.K., and D.K.) at both study and outcome levels using the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale for outcomes in observational studies.19 Disagreements were resolved by consensus. Studies were rated as having low ROB if they provided detail on exposure assignment (eg, marijuana-only smokers vs marijuana and tobacco smokers), had robust assessment and adjustment for key confounders, had sufficient follow-up for outcomes to occur, and quantified marijuana use in terms of joint-years of exposure (when presented) or years of use.
Statistical Analysis
Data were analyzed from January 2 through October 4, 2019. The meta-analysis was performed if there were at least 2 studies of the same design (eg, case-control) addressing the same cancer without high ROB when heterogeneity was low to moderate for the following 4 specific cancers: lung cancer, head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC), oral squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), and testicular germ cell tumor (TGCT). We extracted binary outcome odds ratios (ORs) or calculated them (with 95% CIs) when adequate data were provided. Narrative synthesis was performed when meta-analysis was not possible. We pooled data using a random-effects model. We used the method by Paule and Mandel20 to estimate τ2 and the method by Hartung and Knapp21 to adjust for small sample sizes. For meta-analyses with at least 2 studies, we performed the test for funnel plot asymmetry based on weighted linear regression using the efficient score and score variance described by Higgins et al22 and by Harbord et al.23 Statistical analysis was done using R statistical software (package “meta,” version 1.1.453; R Project for Statistical Computing). Heterogeneity was evaluated using forest plots and the I2 statistic; I2 values of 25%, 50%, and 75% were considered evidence of low, moderate, and high heterogeneity, respectively.23 Tests were 2-tailed and P < .05 was considered statistically significant. Three of us (M.G., S.K., and D.K.) discussed the overall strength of evidence for each outcome and graded it as insufficient, low, moderate, or high based on methods outlined by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality.24
Results
Literature Search
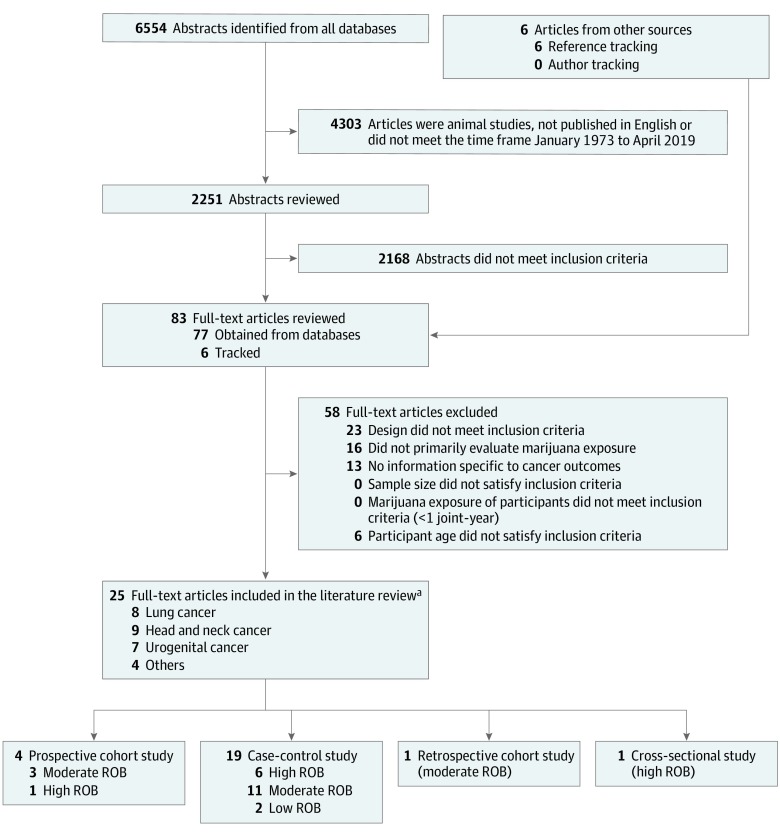
Initial searches across databases identified 6554 abstracts; 25 studies ultimately met the inclusion criteria (Figure 1), including 19 case-control studies, 4 prospective cohort studies, 1 retrospective cohort study, and 1 cross-sectional study. Eight studies addressed risk of lung cancer, 9 addressed head and neck cancers, 7 addressed urogenital cancers, and 4 addressed other cancers (eAppendix 3 in the Supplement). All 25 included articles are described in eTable 1, eTable 2, eTable 3, eTable 4, eAppendix 4, eTable 5, and eTable 6 in the Supplement.
Figure 1. PRISMA Diagram of Evidence Search and Selection.
The flow of articles in the systematic review is shown. PRISMA indicates Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses; ROB, risk of bias.
aThe number of full texts included in the literature review exceeds 25 because some studies were assigned to more than 1 outcome label and are counted twice.
Study Characteristics
Most studies were conducted in the United States (n = 16 [published 1993-2015]), followed by Europe (n = 3), northern Africa (n = 3), New Zealand (n = 2), and 1 from multiple countries. Methods of quantifying marijuana use varied (eg, frequency vs duration vs total joint-years). Two articles did not report the specific route of marijuana administration (eg, edible or smoked). Among those specifying exposure route (n = 23 [92%]), smoking predominated. We identified 19 distinct outcomes, of which 2 had sufficient supporting data from 2 or more studies and could be pooled in a meta-analysis. eAppendix 4, eTable 4 and eTable 5 in the Supplement describe ROB assessments for all included studies.
Lung Cancer
Eight studies25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32 (1 prospective cohort, 1 retrospective cohort, 1 cross-sectional, and 5 case-control studies) examined the association between marijuana use and the development of lung cancer (Table 1 and eTable 1 in the Supplement). These studies were published between 1997 and 2015; the smallest was a case-control study with 33 lung cancer cases, and the largest was a prospective cohort study with 49 321 male participants. Three studies were undertaken in the United States, 2 in northern Africa, 1 in Sweden, 1 in New Zealand, and 1 in multiple countries. All studies had a moderate to high ROB and were generally limited by the small number of marijuana-only smokers (ie, most marijuana users also used tobacco), minimal exposure to marijuana, poorly described use assessment, and inadequate adjustment for confounders (Table 1). There were 405 individuals across case-control studies with more than 10 joint-years of marijuana use.
Table 1. Studies of Marijuana Use and Lung Cancer.
| Source | Population or Data Source | Study Design | Sample Size | Adjusted Risk for Lung Cancer With Marijuana Use | Risk of Bias | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Callaghan et al,25 2013 | Swedish population based | Prospective cohort | 49 321 Men | HR, 2.12 (95% CI, 1.08-4.14) with >50 lifetime episodes | High | 1-Time use assessment, no results for marijuana-only smokers, 40-y follow-up period |
| Sidney et al,26 1997 | Kaiser Permanente, California | Retrospective cohort | 64 855 | RR, 0.9 (95% CI, 0.5-1.7) in men; RR, 1.1 (95% CI, 0.5-2.6) in women | Moderate | Minimal exposure, no results for marijuana-only smokers, short follow-up period of 8.6 y |
| Han et al,32 2010 | National US sample | Cross-sectional | 29 195 | OR, 7.87 (95% CI, 1.28-48.40) with ≥11 y of marijuana use | High | Unclear marijuana use assessment, no results for marijuana-only smokers, inadequate adjustment |
| Zhang et al,29 2015 | Multiple countries (United States, Canada, United Kingdom, and New Zealand) | Case-control | 2159 Cases | OR, 0.54 (95% CI, 0.12-2.55) with ≥10 joint-years | High | Limited number of marijuana-only smokers (2 cases and 20 controls), inadequate adjustment |
| Aldington et al,27 2008 | New Zealand registry | Case-control | 79 Cases | RR, 5.7 (95% CI, 1.5-21.6) with >10.5 joint-years | Moderate | Small sample of heavy users, no results for marijuana-only smokers |
| Hashibe et al,28 2006 | Los Angeles, California | Case-control | 33 Cases | OR, 0.63 (95% CI, 0.32-1.2) with ≥60 joint-years | Moderate | Young participants, no results for marijuana-only smokers |
| Berthiller et al,30 2008 | Tunisia, Morocco, and Algeria | Case-control | 430 Cases | OR, 2.3 (95% CI, 1.5-3.6) | High | Inadequate adjustment for confounders, unusual exposure form, no dose-response association seen |
| Voirin et al,31 2006 | Tunisia | Case-control | 149 Cases | OR, 4.1 (95% CI, 1.9-9.0) | High | Inadequate adjustment for confounders, unusual exposure form, no dose-response association seen |
Abbreviations: HR, hazard ratio; OR, odds ratio; RR, risk ratio.
Study results were mixed, and we were unable to pool data for this outcome. In general, studies were limited by low levels of marijuana exposure, little information about marijuana-only smokers, and other methodological flaws. Therefore, we concluded that evidence of the association between marijuana use and incident lung cancer was insufficient (Table 2).
Table 2. Strength of Evidence of Association of Marijuana Use and Each Type of Cancer.
| Outcome | Study Type | Evidence Strength | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lung cancer | 1 Prospective study29 (high ROB), 1 retrospective observational cohort26 (moderate ROB), 5 case-control studies (2 moderate27,28 and 3 high29,30,31 ROB), and 1 cross-sectional study32 (high ROB) | Insufficient | 1 Prospective study found an increased risk of lung cancer during a long period of follow-up; however, the study was limited by 1-time assessment of marijuana exposure and minimal exposure to marijuana. The retrospective study reported no association between marijuana use and an increased risk of lung cancer; however, the study was limited by minimal exposure to marijuana and the young age of participants. The case-control studies were limited by inadequate marijuana exposure, lack of information on the median marijuana exposure, limited results on marijuana-only smokers, and many other methodological flaws, with mixed findings. The cross-sectional study reported association between marijuana use and an increased risk of lung cancer; however, it was limited by unclear definitions in the marijuana assessment and no reported results on marijuana-only smokers. |
| HNSCC | 4 Case-control studies (1 low33 and 3 moderate34,35,36 ROB) | Low | All studies rated as low or moderate ROB. Pooled data demonstrated that marijuana use exceeding 8 joint-years was associated with an increased risk of HNSCC. |
| Nasopharyngeal carcinoma | 1 Case-control study37 (moderate ROB) | Insufficient | 1 Case-control study demonstrated marijuana use was associated with increased risk of nasopharyngeal carcinoma; however, this study was limited by lack of reporting of the median marijuana exposure, inconsistent adjustment for important confounders, and potential bias in the selection of cases and controls |
| Oral cancer | 4 Case-control studies (2 moderate28,38 and 2 high39,40 ROB) | Insufficient | Pooled data from moderate ROB studies demonstrated ever use of marijuana was not associated with an increased risk of oral cancer |
| Laryngeal cancer | 1 Case-control study28 (moderate ROB) | Insufficient | 1 Case-control study demonstrated marijuana use was not associated with increased risk of laryngeal cancer. However, results were not reported on marijuana-only smokers, and it was limited by a small sample of heavy marijuana users. The study did not report average marijuana exposure. |
| Pharyngeal cancer | 1 Case-control study28 (moderate ROB) | Insufficient | 1 Case-control study demonstrated marijuana use was not associated with increased risk of pharyngeal cancer. However, there were no results on marijuana-only smokers and no report of average marijuana exposure, and the study was limited by a small sample of heavy marijuana users. |
| Esophageal cancer | 1 Case-control study28 (moderate ROB) | Insufficient | 1 Case-control study demonstrated marijuana use was not associated with increased risk of esophageal cancer. However, results were not reported on marijuana-only smokers, the sample of heavy marijuana users was low, and average marijuana exposure was not reported. |
| Bladder cancer | 1 Prospective cohort41 (moderate ROB) | Insufficient | 1 Prospective study did not find association between marijuana use and increased risk of bladder cancer. The study was limited by inadequate adjustment for key confounders and 1-time assessment of marijuana exposure. The study did not report average marijuana exposure. |
| TGCT | 3 Case-control studies42,43,44 (3 moderate ROB) | Low | Pooled data demonstrated more than a 10-y use of marijuana was associated with an increased risk of TGCT and nonseminoma TGCT. |
| Transitional cell carcinoma | 1 Case-control study45 (low ROB) | Insufficient | 1 Case-control study demonstrated marijuana use was associated with increased risk of transitional cell carcinoma. There were adequate marijuana exposure assessments and adjustment for confounders. The study was limited by few marijuana-only smokers. |
| Prostate cancer | 1 Retrospective observational cohort26 (moderate ROB) | Insufficient | 1 Retrospective study found association between marijuana use and increased risk of prostate cancer. The study was limited by lack of adjustment for key confounders, inadequate marijuana exposure, and no quantification of marijuana exposure. |
| Cervical cancer | 1 Retrospective observational cohort26 (moderate ROB) | Insufficient | 1 Retrospective study found association between marijuana use and increased risk of cervical cancer. The study was limited by lack of adjustment for key confounders, inadequate marijuana exposure, and no quantification of use. |
| Penile cancer | 1 Case-control study46 (moderate ROB) | Insufficient | 1 Case-control study did not demonstrate marijuana use was associated with increased risk of penile cancer. However, results were not reported on marijuana-only smokers, and it was limited by no quantification of use. |
| Kaposi sarcoma | 1 Prospective cohort47 (moderate ROB) | Insufficient | 1 Prospective study found association between weekly or more frequent use of marijuana and increased risk of Kaposi sarcoma. The study was limited by minimal marijuana exposure, young age of participants, and inadequate description of quantification of marijuana use. |
| Malignant primary adult-onset glioma | 1 Prospective cohort48 (moderate ROB) | Insufficient | 1 Prospective study found association between marijuana use and increased risk of malignant primary adult-onset glioma, but the study was limited by no quantification of marijuana use and no description of data collection. |
| Non-Hodgkin lymphoma | 1 Case-control study49 (high ROB) | Insufficient | 1 Case-control study did not demonstrate marijuana use was associated with increased risk of non-Hodgkin lymphoma. The study was limited by lack of information on dose and duration of use, inadequate marijuana exposure, and adjustment for key confounders. |
| Colorectal cancer | 1 Retrospective observational cohort26 (moderate ROB) | Insufficient | 1 Retrospective study did not find association between marijuana use and increased risk of colorectal cancer. The study was limited by lack of adjustment for key confounders, inadequate marijuana exposure, and no quantification of marijuana use. |
| Melanoma | 1 Retrospective observational cohort26 (moderate ROB) | Insufficient | 1 Retrospective study did not find association between marijuana use and increased risk of melanoma cancer. The study was limited by lack of adjustment for key confounders, inadequate marijuana exposure, and no quantification of marijuana use. |
| Breast cancer | 1 Retrospective observational cohort26 (moderate ROB) | Insufficient | 1 Retrospective study did not find association between marijuana use and increased risk of breast cancer. The study was limited by lack of adjustment for key confounders, inadequate marijuana exposure, and no quantification of marijuana use. |
Abbreviations: HNSCC, head and neck squamous cell carcinoma; ROB, risk of bias; TGCT, testicular germ cell tumor.
Head and Neck Cancer
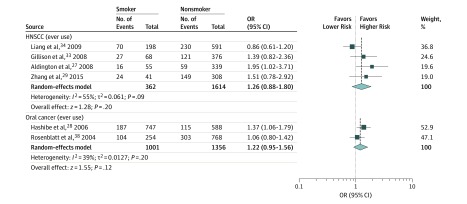
Nine case-control studies investigated the association of marijuana exposure with the development of head and neck cancers, including HNSCC, nasopharyngeal carcinoma, oral cancer, laryngeal cancer, pharyngeal cancer, and esophageal cancer; 1 of these studies evaluated multiple cancers28 (eTable 2 in the Supplement). Only 1 was rated as having a low ROB,33 and the number of cases ranged from 53 to 636. Four case-control studies (1 with low ROB33 and 3 with moderate ROB34,35,36) examined the association between marijuana use and HNSCC. All had sufficient supporting data for meta-analysis. Compared with nonsmokers, ever users of marijuana had similar risk of HNSCC (OR, 1.26; 95% CI, 0.88-1.80; P = .09; I2 = 55%) (Figure 2). The test for funnel plot asymmetry showed evidence of asymmetry (P = .045), with a bias coefficient of 3.48 (eFigure 1 in the Supplement). Findings among heavier users were mixed across studies (eTable 2 in the Supplement).
Figure 2. Association Between Marijuana Use and Risk of Developing Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma (HNSCC) and Oral Cancer in Case-Control Studies.
Included are 4 studies27,29,33,34 for HNSCC and 2 studies28,38 for oral cancer. The size of the boxes represents the weight of each study, and the diamond represents the overall effect. OR indicates odds ratio.
Four other case-control studies (2 with a moderate ROB28,38 and 2 with a high ROB39,40) evaluated marijuana exposure and risk of oral cancer. Pooled data from the 2 studies with moderate ROB28,38 revealed no association between ever use and oral cancer (OR, 1.22; 95% CI, 0.95-1.56; P = .12; I2 = 39%) (Figure 2); heterogeneity was moderate, and there was no evidence of funnel plot asymmetry (eFigure 1 in the Supplement). The 2 studies with a high ROB39,40 reported no association between marijuana use and the risk of oral SCC, but interpretability is limited by poor quantification of marijuana use and inadequate adjustment for confounders.
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma was examined in a 2004 case-control study with a moderate ROB37; a second population-based case-control study with a moderate ROB28 evaluated laryngeal, pharyngeal, and esophageal cancers. The study37 of nasopharyngeal carcinoma, which was performed in northern Africa and included 636 cases, found a higher risk of nasopharyngeal carcinoma with both ever marijuana consumption and lifetime high-dose marijuana smoking (≥2000 times; OR, 2.62; 95% CI, 1.00-6.86), after adjusting for tobacco and baseline variables. The study was limited by potential selection bias, inconsistent adjustment, and no reported results on marijuana-only smokers. The case-control study,28 which was based in Los Angeles, California, found no association of at least 30 joint-years of use with laryngeal, pharyngeal, or esophageal cancers, but it included too few such marijuana users (<10 users with ≥30 joint-years) to draw reliable conclusions (eTable 2 in the Supplement).
Urogenital Cancer
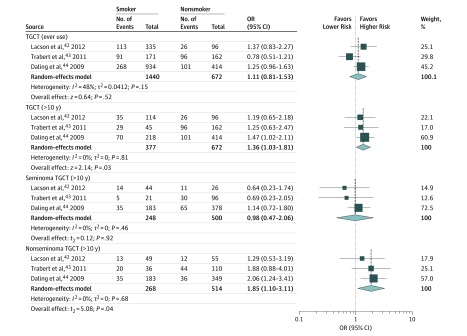
The association between marijuana use and developing urogenital cancer was evaluated in 1 prospective study,41 a retrospective study,26 and 5 case-control studies42,43,44,45,46 published between 1993 and 2015. Three case-control studies42,43,44 (with moderate ROB) assessed the association of marijuana use with TGCT; all of the studies included young participants and had a mean follow-up period of 6.6 years. In a pooled analysis (low heterogeneity), development of TGCT was not associated with ever use compared with never use (OR, 1.11; 95% CI, 0.81-1.53; P = .52; I2 = 48%), but it was associated with more than 10 years of marijuana use (OR, 1.36; 95% CI, 1.03-1.81; P = .03; I2 = 0%) (Figure 3). Subanalysis by histological type showed association of more than 10 years of marijuana use with the development of nonseminoma TGCT (OR, 1.85; 95% CI, 1.10-3.11; P = .04; I2 = 0%) but not seminoma TGCT (OR, 0.98; 95% CI, 0.47-2.06; P = .92; I2 = 0%) (Figure 3). There was no significant evidence of funnel plot asymmetry for TGCT (ever use) (P = .75), TGCT (>10 years) (P = .20), and seminoma TGCT (P = .09) (eFigure 2, eFigure 3, and eFigure 4 in the Supplement).
Figure 3. Association Between Marijuana Use and Risk of Developing Testicular Germ Cell Tumor (TGCT) in Case-Control Studies.
Included are 3 studies.42,43,44 The size of the boxes represents the weight of each study, and the diamond represents the overall effect. OR indicates odds ratio.
Other urogenital cancers were addressed in US-based single studies26,41,45,46 (eTable 3 in the Supplement). A prospective study41 (with moderate ROB) found that marijuana-only ever use was associated with a lower risk of bladder cancer (adjusted hazard ratio, 0.55; 95% CI, 0.31-1.00; P = .048), but the study was limited by inadequate adjustment for confounders. In a small study with low ROB,45 marijuana-only smoking was associated with transitional cell carcinoma (adjusted OR, 3.3), but there were only 10 marijuana-only smokers. Other studies with a moderate ROB found that marijuana use was associated with risk for prostate cancer (risk ratio [RR], 3.1; 95% CI, 1.0-9.5) and cervical cancer (RR, 1.4; 95% CI, 1.0-2.1)26 and was not associated with penile cancer,46 but study design issues limit reliability.
Other Cancers
Four studies26,47,48,49 addressed marijuana use and the development of other cancers; all were performed in the United States (eTable 4 in the Supplement). A large, prospective study48 found an association between the development of malignant primary adult-onset glioma and weekly (n = 6002; RR, 3.2; 95% CI, 1.1-9.2) and monthly (n = 4699; RR, 3.6; 95% CI, 1.3-10.2) marijuana smoking compared with nonuse. Other studies found no association between marijuana ever use and breast cancer, colorectal cancer, and melanoma26 and non-Hodgkin lymphoma49; however, methodological concerns limit interpretation. Finally, a prospective study47 found that marijuana use among HIV-infected white men was associated with risk for developing Kaposi sarcoma (hazard ratio, 1.52; 95% CI, 0.99-2.32) in the 5-year lagged analysis. However, the study did not quantify exposure or report separately for marijuana-only smokers.
Strength of Evidence
Low-strength evidence suggests that chronically smoking marijuana is associated with development of TGCT. Evidence on the association between marijuana use and other cancer types and evidence of the consequences of higher levels of use are insufficient (Table 2).
Discussion
Although much is known about the association between tobacco smoke and cancer, less is known about the association between marijuana smoke and cancer. Both contain particulate matter and carcinogens. With increasing marijuana use and the high number of cancer-related deaths, understanding the association between marijuana use and cancer incidence is important. Low-strength evidence in the present systematic review and meta-analysis suggests that more than 10 years of marijuana use (joint-years were not reported) is associated with the development of TGCT. There was insufficient evidence to support an association between ever having used marijuana and other types of cancer. Available studies were limited by a small number of participants with high levels of use, poor use quantification, confounding related to cigarette smoking, and other methodological problems.
Our study contributes to the literature on the association between marijuana use and multiple cancers that has been examined individually in prior systematic reviews. Two systematic reviews50,51 examined the association between smoking marijuana and lung cancer. The first study50 offered evidence of biological plausibility (ie, molecular, cytomorphologic, and histopathologic changes); the second study51 noted pulmonary toxic effects and mixed evidence of an association with lung cancer but did not pool data to estimate an overall association. We found 1 meta-analysis52 examining the association of smoking marijuana with the development of head and neck cancer; it found no association but was limited by meta-analytic inconsistencies, pooling head and neck cancer subtypes in 1 plot and not addressing variable marijuana use, which may undermine its conclusions. Three other systematic reviews53,54,55 found an association between marijuana smoking and increased risk of TGCT but reported conflicting data on the association with other urogenital cancers. The present study confirms these findings and builds on the existing literature by assessing ROB, pooling data when feasible, and providing a clear picture of the gaps in evidence by rating the strength of the overall evidence.
Our systematic review and meta-analysis found insufficient evidence on the association between marijuana use and the development of lung cancer. There are biological reasons for concern about marijuana use and lung cancer. Several reports have documented changes in the bronchial epithelium of marijuana smokers that are similar to metaplastic premalignant alterations observed among tobacco smokers.12,50,56 Furthermore, histopathologic and molecular alterations and premalignant changes found in marijuana users,12,57,58 including mitotic figures, squamous cell metaplasia, and cell disorganization, suggest increased risk for respiratory neoplasm. In addition, marijuana joints with similar weight as tobacco cigarettes have higher tar burden, which may increase the carcinogenic risk.8,59,60,61 However, the difference in per weight tar burden is counterbalanced by the usual practice of smoking far fewer marijuana joints than tobacco cigarettes per day. Furthermore, lung cancer risk increases with both the number of daily cigarettes and the lifetime duration of smoking,62 with an increased risk only among those with high exposure. For example, a 40-year-old smoker of 1 pack per day (14 600 cigarettes) has a lung cancer risk approximately 20 times that of a nonsmoker. Our systematic review and meta-analysis included few marijuana smokers with similarly high exposure levels: there were 405 individuals across case-control lung cancer studies with more than 10 joint-years of use (3650 joints). Hence, low exposure burden, young participant age, and inadequate follow-up time in included studies may prevent detection of an association. Longitudinal cohorts with older populations of heavier marijuana users may be necessary to clarify the association of marijuana use with developing lung cancer.
Our findings are notable in a time of increasing marijuana use in the United States,2,3,63 with novel drug delivery methods, including vaping and edibles, becoming more popular, particularly in states that have legalized recreational use4 and among adolescents.64,65 However, most of the studies included in the present systematic review and meta-analysis are not recent, and smoking was the near-universal form of exposure. Vaped marijuana is believed to have fewer long-term toxic effects than smoked marijuana,66 but evidence is lacking. Although levels of tar are lower with marijuana use through vaping compared with smoking, vaporized marijuana can contain toxic levels of ammonia and heavy metals that may be associated with cancer, possibly cancers unrelated to smoking.67,68,69 Furthermore, with legalization may come heavier and more long-term use that may confer a higher risk for cancer. Misinformation may constitute an additional threat to public health; cannabis is being increasingly marketed as a potential cure for cancer in the absence of evidence,70 with enormous engagement in this misinformation on social media, particularly in states that have legalized recreational use.71 As marijuana smoking and other forms of marijuana use increase and evolve, it will be critical to develop a better understanding of the association of these different use behaviors with the development of cancers and other chronic conditions and to ensure accurate messaging to the public.
Limitations
This systematic review and meta-analysis has limitations. Non–English-language articles were excluded; therefore, we may have overlooked relevant studies. Study populations were young, and few studies measured longitudinal exposure. The included studies were often limited by selection bias, recall bias, small sample of marijuana-only smokers, reporting of outcomes on marijuana users and tobacco users combined, and inadequate follow-up for the development of cancer. In addition, despite clear methodological differences across studies, we pooled some data. Although we used a conservative approach, these pooled estimates provide only a rough approximation of the association. Most studies poorly assessed exposure, and some studies did not report details on exposure, preventing meta-analysis for several outcomes. Understanding of the long-term health consequences of marijuana use could be improved by standardizing assessment tools to quantify use, including studies with larger samples of marijuana-only smokers, performing subanalysis based on form of use, and having longer follow-up times.
Conclusions
Low-strength evidence suggests that smoking marijuana is associated with the development of TGCT; evidence of an association between marijuana use and incident lung cancer is of poor quality and inconclusive. Similarly, evidence regarding other cancer types is insufficient and is limited by low exposure and duration of follow-up. Increasing rates of marijuana use and evolution in delivery routes raise concerns about long-term consequences. Large-scale longitudinal studies with representative samples of marijuana-only smokers are needed to better understand the association of marijuana use with the development of lung, oral, and other cancers. In the meantime, clinicians should discuss marijuana use with patients to raise awareness of the lack of clarity on potential clinically important harms and to debunk beliefs in unproven benefits.
eAppendix 1. Search Strategies
eAppendix 2. Study Selection
eAppendix 3. Flow of Papers in the Review and Risk of Bias
eTable 1. Studies That Examined Exposure to Marijuana and Development of Lung Cancer
eTable 2. Studies That Examined Exposure to Marijuana and Development of Head and Neck Cancer
eTable 3. Studies That Examined Exposure to Marijuana and Development of Urogenital Cancer
eTable 4. Studies That Examined Exposure to Marijuana and Development of Other Cancers
eAppendix 4. Quality Assessment Criteria and Risk of Bias Assessment
eTable 5. Risk of Bias Assessment in Cohort and Cross-sectional Studies
eTable 6. Risk of Bias Assessment in Case-Control Studies
eFigure 1. Funnel Plot: Head and Neck Squamous Cell Cancer Case-Control Studies
eFigure 2. Funnel Plot: Testicular Germ Cell Tumor Case-Control Studies
eFigure 3. Funnel Plot: Testicular Germ Cell Tumor Case-Control Studies (>10 Years Use)
eFigure 4. Funnel Plot: Testicular Germ Cell Tumor Case-Control Studies (Seminoma)
eReferences.
eAppendix 5. List of Excluded Studies
References
- 1.Results from the 2017. National Survey on Drug Use and Health: detailed tables. https://www.samhsa.gov/data/sites/default/files/cbhsq-reports/NSDUHDetailedTabs2017/NSDUHDetailedTabs2017.htm. Accessed October 17, 2019.
- 2.National Institutes of Health Prevalence of marijuana use among U.S. adults doubles over past decade [press release]. https://www.nih.gov/news-events/news-releases/prevalence-marijuana-use-among-us-adults-doubles-over-past-decade. Published October 21, 2015. Accessed October 17, 2019.
- 3.Azofeifa A, Mattson ME, Schauer G, McAfee T, Grant A, Lyerla R. National estimates of marijuana use and related indicators: National Survey on Drug Use and Health, United States, 2002-2014. MMWR Surveill Summ. 2016;65(11):-. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.ss6511a1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Steigerwald S, Wong PO, Cohen BE, et al. Smoking, vaping, and use of edibles and other forms of marijuana among US adults. Ann Intern Med. 2018;169(12):890-892. doi: 10.7326/M18-1681 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Hoffmann D, Brunnemann KD, Gori GB, et al. On the carcinogenicity of marijuana smoke In: Runeckles VC, ed. Recent Advances in Phytochemistry. Boston, MA: Springer-Verlag; 1975:63-81. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-0823-2_3 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Moir D, Rickert WS, Levasseur G, et al. A comparison of mainstream and sidestream marijuana and tobacco cigarette smoke produced under two machine smoking conditions. Chem Res Toxicol. 2008;21(2):494-502. doi: 10.1021/tx700275p [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Wu TC, Tashkin DP, Djahed B, Rose JE. Pulmonary hazards of smoking marijuana as compared with tobacco. N Engl J Med. 1988;318(6):347-351. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198802113180603 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Tashkin DP, Gliederer F, Rose J, et al. Tar, CO and Δ9-THC delivery from the 1st and 2nd halves of a marijuana cigarette. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1991;40(3):657-661. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(91)90378-F [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Tashkin DP, Baldwin GC, Sarafian T, Dubinett S, Roth MD. Respiratory and immunologic consequences of marijuana smoking. J Clin Pharmacol. 2002;42(S1):71S-81S. doi: 10.1002/j.1552-4604.2002.tb06006.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Heron M. Deaths: leading causes for 2016. https://stacks.cdc.gov/view/cdc/57988. Published July 26, 2018. Accessed October 17, 2019.
- 11.Lortet-Tieulent J, Goding Sauer A, Siegel RL, et al. State-level cancer mortality attributable to cigarette smoking in the United States. JAMA Intern Med. 2016;176(12):1792-1798. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2016.6530 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Barsky SH, Roth MD, Kleerup EC, Simmons M, Tashkin DP. Histopathologic and molecular alterations in bronchial epithelium in habitual smokers of marijuana, cocaine, and/or tobacco. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1998;90(16):1198-1205. doi: 10.1093/jnci/90.16.1198 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Śledziński P, Zeyland J, Słomski R, Nowak A. The current state and future perspectives of cannabinoids in cancer biology. Cancer Med. 2018;7(3):765-775. doi: 10.1002/cam4.1312 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Pellati F, Borgonetti V, Brighenti V, Biagi M, Benvenuti S, Corsi L. Cannabis sativa L. and nonpsychoactive cannabinoids: their chemistry and role against oxidative stress, inflammation, and cancer. Biomed Res Int. 2018;2018:1691428. doi: 10.1155/2018/1691428 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG; PRISMA Group . Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Ann Intern Med. 2009;151(4):264-269, W64. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-151-4-200908180-00135 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Blachly PH. Effects of decriminalization of marijuana in Oregon. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1976;282:405-415. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1976.tb49913.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.IMS Institute for Healthcare Informatics Global use of medicines: outlook through 2017. http://www.quotidianosanita.it/allegati/allegato1501906.pdf. Published November 2013. Accessed October 17, 2019.
- 18.Bramer WM, Giustini D, de Jonge GB, Holland L, Bekhuis T. De-duplication of database search results for systematic reviews in EndNote [published correction appears in J Med Libr Assoc. 2017;105(1):111]. J Med Libr Assoc. 2016;104(3):240-243. doi: 10.3163/1536-5050.104.3.014 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Wells GA, Shea B, O’Connell D, et al. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. http://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp. Published 2014. Accessed September 29, 2017.
- 20.Paule RC, Mandel J. Consensus values and weighting factors. J Res Natl Bur Stand. 1982;87:377-385. doi: 10.6028/jres.087.022 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Hartung J, Knapp G. A refined method for the meta-analysis of controlled clinical trials with binary outcome. Stat Med. 2001;20(24):3875-3889. doi: 10.1002/sim.1009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ. 2003;327(7414):557-560. doi: 10.1136/bmj.327.7414.557 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Harbord RM, Egger M, Sterne JA. A modified test for small-study effects in meta-analyses of controlled trials with binary endpoints. Stat Med. 2006;25(20):3443-3457. doi: 10.1002/sim.2380 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Berkman ND, Lohr KN, Ansari M, et al. Grading the strength of a body of evidence when assessing health care interventions for the Effective Health Care Program of the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality: an update. Methods guide for comparative effectiveness reviews (prepared by the RTI-UNC Evidence-based Practice Center under contract 290-2007-10056-I). AHRQ publication 13(14)-EHC130-EF. Rockville, MD: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality; November 2013. https://effectivehealthcare.ahrq.gov/sites/default/files/pdf/methods-guidance-grading-evidence_methods.pdf. Accessed October 17, 2019.
- 25.Callaghan RC, Allebeck P, Sidorchuk A. Marijuana use and risk of lung cancer: a 40-year cohort study. Cancer Causes Control. 2013;24(10):1811-1820. doi: 10.1007/s10552-013-0259-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Sidney S, Quesenberry CP Jr, Friedman GD, Tekawa IS. Marijuana use and cancer incidence (California, United States). Cancer Causes Control. 1997;8(5):722-728. doi: 10.1023/A:1018427320658 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Aldington S, Harwood M, Cox B, et al. ; Cannabis and Respiratory Disease Research Group . Cannabis use and risk of lung cancer: a case-control study. Eur Respir J. 2008;31(2):280-286. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00065707 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Hashibe M, Morgenstern H, Cui Y, et al. Marijuana use and the risk of lung and upper aerodigestive tract cancers: results of a population-based case-control study. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2006;15(10):1829-1834. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-06-0330 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Zhang LR, Morgenstern H, Greenland S, et al. ; Cannabis and Respiratory Disease Research Group of New Zealand . Cannabis smoking and lung cancer risk: pooled analysis in the International Lung Cancer Consortium. Int J Cancer. 2015;136(4):894-903. doi: 10.1002/ijc.29036 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Berthiller J, Straif K, Boniol M, et al. Cannabis smoking and risk of lung cancer in men: a pooled analysis of three studies in Maghreb. J Thorac Oncol. 2008;3(12):1398-1403. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e31818ddcde [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Voirin N, Berthiller J, Benhaïm-Luzon V, et al. Risk of lung cancer and past use of cannabis in Tunisia. J Thorac Oncol. 2006;1(6):577-579. doi: 10.1097/01243894-200607000-00013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Han B, Gfroerer JC, Colliver JD. Associations between duration of illicit drug use and health conditions: results from the 2005-2007 National Surveys on Drug Use and Health. Ann Epidemiol. 2010;20(4):289-297. doi: 10.1016/j.annepidem.2010.01.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Gillison ML, D’Souza G, Westra W, et al. Distinct risk factor profiles for human papillomavirus type 16–positive and human papillomavirus type 16–negative head and neck cancers. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2008;100(6):407-420. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djn025 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Liang C, McClean MD, Marsit C, et al. A population-based case-control study of marijuana use and head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2009;2(8):759-768. doi: 10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-09-0048 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Aldington S, Harwood M, Cox B, et al. ; Cannabis and Respiratory Disease Research Group . Cannabis use and cancer of the head and neck: case-control study. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2008;138(3):374-380. doi: 10.1016/j.otohns.2007.12.002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Zhang ZF, Morgenstern H, Spitz MR, et al. Marijuana use and increased risk of squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 1999;8(12):1071-1078. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Feng BJ, Khyatti M, Ben-Ayoub W, et al. Cannabis, tobacco and domestic fumes intake are associated with nasopharyngeal carcinoma in North Africa. Br J Cancer. 2009;101(7):1207-1212. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6605281 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Rosenblatt KA, Daling JR, Chen C, Sherman KJ, Schwartz SM. Marijuana use and risk of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2004;64(11):4049-4054. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-03-3425 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Llewellyn CD, Johnson NW, Warnakulasuriya KAAS. Risk factors for oral cancer in newly diagnosed patients aged 45 years and younger: a case-control study in Southern England. J Oral Pathol Med. 2004;33(9):525-532. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0714.2004.00222.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Llewellyn CD, Linklater K, Bell J, Johnson NW, Warnakulasuriya S. An analysis of risk factors for oral cancer in young people: a case-control study. Oral Oncol. 2004;40(3):304-313. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2003.08.015 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Thomas AA, Wallner LP, Quinn VP, et al. Association between cannabis use and the risk of bladder cancer: results from the California Men’s Health Study. Urology. 2015;85(2):388-392. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2014.08.060 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Lacson JCA, Carroll JD, Tuazon E, Castelao EJ, Bernstein L, Cortessis VK. Population-based case-control study of recreational drug use and testis cancer risk confirms an association between marijuana use and nonseminoma risk. Cancer. 2012;118(21):5374-5383. doi: 10.1002/cncr.27554 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Trabert B, Sigurdson AJ, Sweeney AM, Strom SS, McGlynn KA. Marijuana use and testicular germ cell tumors. Cancer. 2011;117(4):848-853. doi: 10.1002/cncr.25499 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Daling JR, Doody DR, Sun X, et al. Association of marijuana use and the incidence of testicular germ cell tumors. Cancer. 2009;115(6):1215-1223. doi: 10.1002/cncr.24159 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Chacko JA, Heiner JG, Siu W, Macy M, Terris MK. Association between marijuana use and transitional cell carcinoma. Urology. 2006;67(1):100-104. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2005.07.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Maden C, Sherman KJ, Beckmann AM, et al. History of circumcision, medical conditions, and sexual activity and risk of penile cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1993;85(1):19-24. doi: 10.1093/jnci/85.1.19 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Chao C, Jacobson LP, Jenkins FJ, et al. Recreational drug use and risk of Kaposi’s sarcoma in HIV- and HHV-8–coinfected homosexual men. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2009;25(2):149-156. doi: 10.1089/aid.2008.0196 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Efird JT, Friedman GD, Sidney S, et al. The risk for malignant primary adult-onset glioma in a large, multiethnic, managed-care cohort: cigarette smoking and other lifestyle behaviors. J Neurooncol. 2004;68(1):57-69. doi: 10.1023/B:NEON.0000024746.87666.ed [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Holly EA, Lele C, Bracci PM, McGrath MS. Case-control study of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma among women and heterosexual men in the San Francisco Bay Area, California. Am J Epidemiol. 1999;150(4):375-389. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a010017 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Mehra R, Moore BA, Crothers K, Tetrault J, Fiellin DA. The association between marijuana smoking and lung cancer: a systematic review. Arch Intern Med. 2006;166(13):1359-1367. doi: 10.1001/archinte.166.13.1359 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Martinasek MP, McGrogan JB, Maysonet A. A systematic review of the respiratory effects of inhalational marijuana. Respir Care. 2016;61(11):1543-1551. doi: 10.4187/respcare.04846 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.de Carvalho MFF, Dourado MR, Fernandes IB, Araújo CT, Mesquita AT, Ramos-Jorge ML. Head and neck cancer among marijuana users: a meta-analysis of matched case-control studies. Arch Oral Biol. 2015;60(12):1750-1755. doi: 10.1016/j.archoralbio.2015.09.009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Gurney J, Shaw C, Stanley J, Signal V, Sarfati D. Cannabis exposure and risk of testicular cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Cancer. 2015;15(1):897. doi: 10.1186/s12885-015-1905-6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Gandhi S, Vasisth G, Kapoor A. Systematic review of the potential role of cannabinoids as antiproliferative agents for urological cancers. Can Urol Assoc J. 2017;11(3-4):E138-E142. doi: 10.5489/cuaj.4371 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Rajanahally S, Raheem O, Rogers M, et al. The relationship between cannabis and male infertility, sexual health, and neoplasm: a systematic review. Andrology. 2019;7(2):139-147. doi: 10.1111/andr.12585 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Sarafian TA, Magallanes JAM, Shau H, Tashkin D, Roth MD. Oxidative stress produced by marijuana smoke: an adverse effect enhanced by cannabinoids. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1999;20(6):1286-1293. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb.20.6.3424 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Roth MD, Arora A, Barsky SH, Kleerup EC, Simmons M, Tashkin DP. Airway inflammation in young marijuana and tobacco smokers. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998;157(3, pt 1):928-937. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.157.3.9701026 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Fligiel SE, Roth MD, Kleerup EC, Barsky SH, Simmons MS, Tashkin DP. Tracheobronchial histopathology in habitual smokers of cocaine, marijuana, and/or tobacco. Chest. 1997;112(2):319-326. doi: 10.1378/chest.112.2.319 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Kaufman DW, Palmer JR, Rosenberg L, Stolley P, Warshauer E, Shapiro S. Tar content of cigarettes in relation to lung cancer. Am J Epidemiol. 1989;129(4):703-711. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a115185 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Yoshie Y, Ohshima H. Synergistic induction of DNA strand breakage by cigarette tar and nitric oxide. Carcinogenesis. 1997;18(7):1359-1363. doi: 10.1093/carcin/18.7.1359 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Zang EA, Wynder EL. Cumulative tar exposure: a new index for estimating lung cancer risk among cigarette smokers. Cancer. 1992;70(1):69-76. doi: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Mattson ME, Pollack ES, Cullen JW. What are the odds that smoking will kill you? Am J Public Health. 1987;77(4):425-431. doi: 10.2105/AJPH.77.4.425 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Abuhasira R, Shbiro L, Landschaft Y. Medical use of cannabis and cannabinoids containing products: regulations in Europe and North America. Eur J Intern Med. 2018;49:2-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ejim.2018.01.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Trivers KF, Phillips E, Gentzke AS, Tynan MA, Neff LJ. Prevalence of cannabis use in electronic cigarettes among US youth. JAMA Pediatr. 2018;172(11):1097-1099. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2018.1920 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Borodovsky JT, Lee DC, Crosier BS, Gabrielli JL, Sargent JD, Budney AJ. U.S. cannabis legalization and use of vaping and edible products among youth. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2017;177:299-306. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2017.02.017 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Budney AJ, Sargent JD, Lee DC. Vaping cannabis (marijuana): parallel concerns to e-cigs? Addiction. 2015;110(11):1699-1704. doi: 10.1111/add.13036 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Eng CH, Yu K, Lucas J, White E, Abraham RT. Ammonia derived from glutaminolysis is a diffusible regulator of autophagy. Sci Signal. 2010;3(119):ra31. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2000911 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Bloor RN, Wang TS, Španěl P, Smith D. Ammonia release from heated “street” cannabis leaf and its potential toxic effects on cannabis users. Addiction. 2008;103(10):1671-1677. doi: 10.1111/j.1360-0443.2008.02281.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Spinelli JB, Yoon H, Ringel AE, Jeanfavre S, Clish CB, Haigis MC. Metabolic recycling of ammonia via glutamate dehydrogenase supports breast cancer biomass. Science. 2017;358(6365):941-946. doi: 10.1126/science.aam9305 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.FDA warns companies marketing unproven products, derived from marijuana, that claim to treat or cure cancer [press release]. https://www.fda.gov/newsevents/newsroom/pressannouncements/ucm583295.htm. Published November 1, 2017. Accessed October 17, 2019.
- 71.Shi S, Brant AR, Sabolch A, Pollom E. False news of a cannabis cancer cure. Cureus. 2019;11(1):e3918. doi: 10.7759/cureus.3918 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
eAppendix 1. Search Strategies
eAppendix 2. Study Selection
eAppendix 3. Flow of Papers in the Review and Risk of Bias
eTable 1. Studies That Examined Exposure to Marijuana and Development of Lung Cancer
eTable 2. Studies That Examined Exposure to Marijuana and Development of Head and Neck Cancer
eTable 3. Studies That Examined Exposure to Marijuana and Development of Urogenital Cancer
eTable 4. Studies That Examined Exposure to Marijuana and Development of Other Cancers
eAppendix 4. Quality Assessment Criteria and Risk of Bias Assessment
eTable 5. Risk of Bias Assessment in Cohort and Cross-sectional Studies
eTable 6. Risk of Bias Assessment in Case-Control Studies
eFigure 1. Funnel Plot: Head and Neck Squamous Cell Cancer Case-Control Studies
eFigure 2. Funnel Plot: Testicular Germ Cell Tumor Case-Control Studies
eFigure 3. Funnel Plot: Testicular Germ Cell Tumor Case-Control Studies (>10 Years Use)
eFigure 4. Funnel Plot: Testicular Germ Cell Tumor Case-Control Studies (Seminoma)
eReferences.
eAppendix 5. List of Excluded Studies