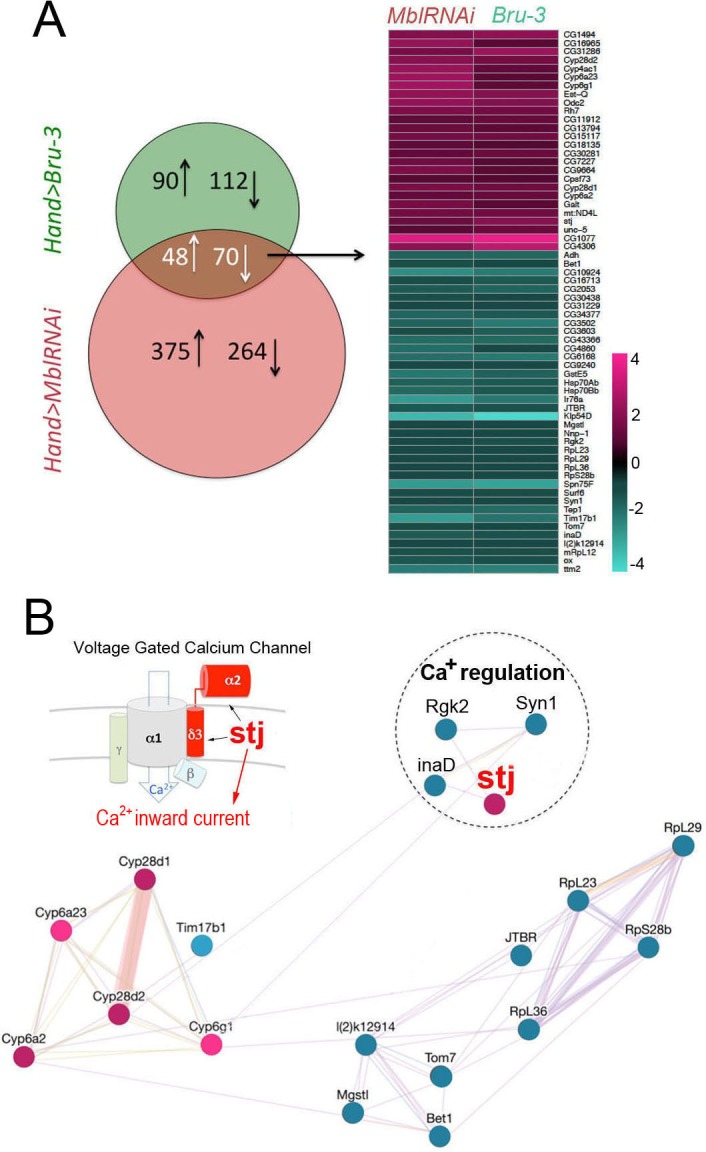
Figure 3. Heart-specific transcriptional profiling of DM1 flies identifies deregulation of genes controlling cellular calcium level.
(A) Venn diagrams of genes deregulated in Hand>UPRT;MblRNAi and in Hand>UPRT;Bru-3 contexts (FC > 1.7) followed by heatmap of commonly deregulated genes. (B) Genemania interaction network of conserved candidates including stj, Rgk2, Syn1 and inaD known to be involved in Ca2 regulation. A scheme presenting the structure of the voltage-gated calcium channel and its regulatory component Stj/α2δ3 is included. Color code in genemania network represents up and down regulation according to the heatmap. Cyan/Blue intensity code indicates fold change of genes expression in the heatmap.