Abstract
Background
Few empirical studies support a bio-psycho-social conceptualization of frailty. In addition to physical frailty (PF), we explored mental (MF) and social (SF) frailty and studied the associations between multidimensional frailty and various adverse health outcomes.
Methods
Cross-sectional and longitudinal analyses were conducted using data from a population-based cohort (SLAS-1) of 2387 community-dwelling Singaporean Chinese older adults. Outcomes examined were functional and severe disability, nursing home referral and mortality. PF was defined by shrinking, weakness, slowness, exhaustion and physical inactivity, 1–2 = pre-frail, 3–5 = frail; MF was defined by ≥1 of cognitive impairment, low mood and poor self-reported health; SF was defined by ≥2 of living alone, no education, no confidant, infrequent social contact or help, infrequent social activities, financial difficulty and living in low-end public housing.
Results
The prevalence of any frailty dimension was 63.0%, dominated by PF (26.2%) and multidimensional frailty (24.2%); 7.0% had all three frailty dimensions. With a few exceptions, frailty dimensions share similar associations with many socio-demographic, lifestyle, health and behavioral factors. Each frailty dimension varied in showing independent associations with functional (Odds Ratios [ORs] = 1.3–1.8) and severe disability prevalence at baseline (ORs = 2.2–7.3), incident functional disability (ORs = 1.1–1.5), nursing home referral (ORs = 1.5–3.4) and mortality (Hazard Ratios = 1.3–1.5) after adjusting for age, gender, medical comorbidity and the two other frailty dimensions. The addition of MF and SF to PF incrementally increased risk estimates by more than 2 folds.
Conclusions
This study highlights the relevance and utility of PF, MF and SF individually and together. Multidimensional frailty can better inform policies and promote the use of targeted multi-domain interventions tailored to older adults’ frailty statuses.
Keywords: Frailty, Multidimensional frailty, Disability, Nursing home referral, Mortality
Background
The multidimensional nature of frailty has been increasingly recognized [1]. However, there remains a dichotomy of frailty definitions in terms of a multidimensional versus a uni-dimensional conceptualization in research and clinical practice. The multidimensional approach to frailty is reflected in instruments such as the (cumulated deficits) Frailty Index [2], which provides a global measure of frailty, and other scales such as the Tilburg Frailty Indicator (TFI) [3, 4] and Edmonton Frail Scale (EFS) [5, 6], which consider physical, psychological and social dimensions of frailty. These multidimensional frailty measures have been evaluated for their construct and predictive validity, have shown good psychometric properties and predicted various adverse health outcomes [3, 7]. Yet, with the exception of the TFI, literature regarding the differential effects of the distinct frailty dimensions within these scales remains obscure [4, 8].
There exist few empirical studies investigating the relationships between each frailty dimension, especially with regards to their independent and relative contributions in predicting functional disability, hospitalization and other adverse health outcomes. Prior studies suggest that physical, mental and social frailty have different associations with known risk factors and predictors [4, 9]. There is little evidence on whether the addition of qualitatively different frailty dimensions to physical frailty can better predict adverse health outcomes. In addition, while the prevalence of these frailty dimensions individually and in combination have been previously described, variations of these estimates in other populations have not been reported partly due to differing frailty operationalization across studies [10]. In line with the World Health Organization’s 2017 global strategy and action plan on ageing and health [11], knowledge regarding a broader conception of frailty beyond physical frailty can aid public health systems in offering tailored policies and interventions to frail older adults. For instance, older adults with physical and mental frailty can benefit from appropriate exercise and cognitive stimulation programs and activities while those with mental and social frailty can benefit from additional cognitive stimulation and appropriate psychosocial support.
In view of this literature gap, we defined three distinct frailty dimensions – physical frailty (PF) [12], mental frailty (MF) [13] and social frailty (SF) [14, 15] – and conducted secondary cross-sectional and longitudinal analyses using data from community-dwelling older adults in the first cohort of the Singapore Longitudinal Aging Studies (SLAS-1). We estimated the individual and combined prevalence of these frailty dimensions, their differential associations with socio-demographic and health-related factors and their independent abilities to predict functional and severe disability, nursing home referral and mortality. We also examined the hypothesis that the addition of MF and SF to PF increases the ability to predict the aforementioned health outcomes.
Methods
Participants
Data was obtained from SLAS-1, a population-based longitudinal study investigating aging and health of community-dwelling older Singaporeans aged 55 and above. Individuals with severe physical or mental disabilities were excluded from this study. Detailed methodology is available in a previous publication [16]. The study was approved by the National University of Singapore Institutional Review Board and written informed consent was obtained from all participants.
From a total of 2804 older adults who were recruited at baseline (2003–2005), cross-sectional analyses were conducted using data from 2387 Chinese participants with complete baseline data on designated variables of interest. Longitudinal analyses for functional disability were performed on 1174 participants who could independently complete instrumental or basic activities of daily living (IADL or ADL) at baseline and who had complete follow-up data on IADL and ADL. During the next follow-up (2005–2007), 859 participants dropped out or had missing data for IADL or ADL. Another 354 participants were excluded as they required assistance in one or more IADL or ADL at baseline. Longitudinal analyses for mortality and nursing home referral were conducted for all 2387 participants.
Baseline frailty measures
Mental frailty (MF) consisted of three components:
Cognitive impairment as determined using the validated Chinese version of the Mini-Mental State Examination (CMMSE), with scores ranging from 0 to 30 [17]. Higher scores reflect better cognitive functioning. Cognitive impairment was defined as having a CMMSE score equivalent to or lower than 23.
- Low mood was indicated by the presence of any of the following:
- A score of five or above on the Geriatric Depression Scale, which has been validated for use among Singaporean older adults [18].
- Answering “None of the time” for the SF-12 question: “Have you felt calm and peaceful for the past four weeks?”
- Answering “All of the time” for the SF-12 question: “Have you felt downhearted and low for the past four weeks?”
Poor self-rated health as assessed via the question, “In general, would you say your health is excellent, very good, good, fair, or poor?” Self-rated health was included as a component of MF as it is a rating of one’s overall health status that is driven by cognitive and psychological processes [19].
Scores were assigned to each MF component (1 = present, 0 = absent). Participants with summed scores of one or more were deemed to have MF.
Social frailty (SF) was assessed via socio-demographic variables and self-reported survey questionnaires related to living arrangements, educational attainment, socio-economic status and social network and support. Briefly, the criteria are listed below:
Living alone: Yes = 1, No = 0
No education: Yes = 1, No = 0
Absence of a confidant: Yes = 1, No = 0
Infrequent visits or calls with family, friends or loved ones (assessed via two different questions) (none or no more than once a year), or receives little help when required (none to a very little): Having any of the three criterion = 1, else = 0.
Infrequent social activities across 6 activity categories: rarely or not at all participate in all categories of social activities = 1, else = 0.
Financial difficulty: Limited to a great extent in ability to pay for necessary medical expenses = 1, else = 0.
Socio-economic deprivation as indexed by housing type, which has been found to predict readmission risk and increased utilization of hospital services in Singapore [20]: Living in 1–2 room public housing = 1, else = 0
Additional details regarding this operationalization are available in a previous publication [15]. Scores were assigned to each SF indicator (1 = present, 0 = absent). Participants with summed scores of two or more were categorized as having SF. The SF operationalization was shown to predict prevalent IADL and severe disability [15].
Physical frailty (PF) was based on the Fried’s criteria used in the Cardiovascular Health Study, with operational modifications detailed in previous publications and shown to predict IADL-ADL disability, depression, hospitalization and poor quality of life [21, 22]. Scores were assigned to each of the five components (1 = present, 0 = absent). Participants were categorized as frail (score = 3–5), pre-frail (score = 1–2) or robust (score = 0) using the summed score.
Adverse health outcomes
Ability to perform IADL or ADL was assessed via self-reports [23, 24]. Functional disability was defined as requiring assistance on one or more IADL or ADL item(s). Severe disability was denoted by dependency on three or more ADL items, which in Singapore often necessitates formal help in nursing home care placement and qualifies for disability insurance payouts.
Nursing home referral data between 30th August 2010 and 24th February 2018 was obtained via computerized record linkage with the Ministry of Health (MOH)‘s national database. Referral coordinators assessed the older adult’s care needs before making a referral for nursing home placement. Social factors, such as the availability of a caregiver, play a substantial role in prioritizing nursing home referral and placement. Individuals who receive nursing home services via such referrals are assessed for eligibility for government subvention via means testing.
Mortality data (date and cause of mortality) up to the end of November 2016 was obtained via computerized record linkage with the National Death Registry of Singapore through MOH’s National Disease Registry Office.
Other variables
Socio-demographic data included age and gender. Medical morbidity was determined through self-reported doctor’s diagnosis and treatment for 16 specified or other medical condition(s) in the past year, medications used, body mass index, blood pressure, spirometry measurements, blood tests for fasting glucose, lipid panels and creatinine for estimated glomerular filtration rate. Participants with three or more medical conditions were deemed to have medical comorbidity. Lifestyle variables included self-reported current and past history of smoking and daily alcohol drinking. Hospitalization and physician visits were assessed via self-reported hospitalizations and physician visits for the above medical conditions over the previous year. Polypharmacy was defined as taking six or more medications and was determined through self-reported medication intake. Nutritional risk was defined as scoring three or more on the 10-item Nutrition Screening Initiative [25]. Hearing impairment was assessed via self-reports and the standard whisper test while visual impairment was defined as having corrected binocular vision worse than 20/40 [26].
Statistical analyses
Pearson χ2 and one-way ANOVAs were used to examine differences in baseline characteristics across the three different frailty dimensions. For each adverse health outcome, odds ratios (ORs) or hazard ratios (HRs) and their 95% confidence intervals were estimated for each frailty dimension and for six different categories of PF (Robust, Pre-frail, Frail) in combination with MF and/or SF: (1) Robust without SF or MF, (2) Robust with MF and/or SF, (3) Pre-frail without MF or SF, (4) Pre-frail with MF and/or SF, (5) Frail without MF or SF, (6) Frail with MF and/or SF. Estimated ORs and HRs were adjusted for age, gender, medical comorbidity and other frailty dimensions, where relevant. Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) analyses were used to compare the predictive abilities of PF, MF, SF and combined PF-SF(PSF), PF-MF(PMF) and PF-MF-SF(PMSF) dimensions for the aforementioned adverse health outcomes. A two-sided p-value of .05 was considered statistically significant. Analyses were performed using STATA version 14 [27].
Results
The mean age of the study sample was 66.1 years (±7.61), 63.3% were female and 25.2% were single, divorced or widowed at baseline. The prevalence of each frailty dimension and overlaps across dimensions is shown in Fig. 1. Overall, 37.0% did not have any of the three frailty dimensions while the prevalence of any frailty dimension was 63.0%. PF (i.e., physical pre-frailty and frailty) was present in 48.3% (26.2% were PF alone, 10.6% with MF and 4.5% with SF). The prevalence of MF was 27.5% (7.8% were MF alone, 10.6% with PF and 2.1% with SF). SF was present in 18.3% (4.7% were SF alone. 4.5% with PF, 2.1% with MF). A total of 7.0% had all three frailty dimensions.
Fig. 1.
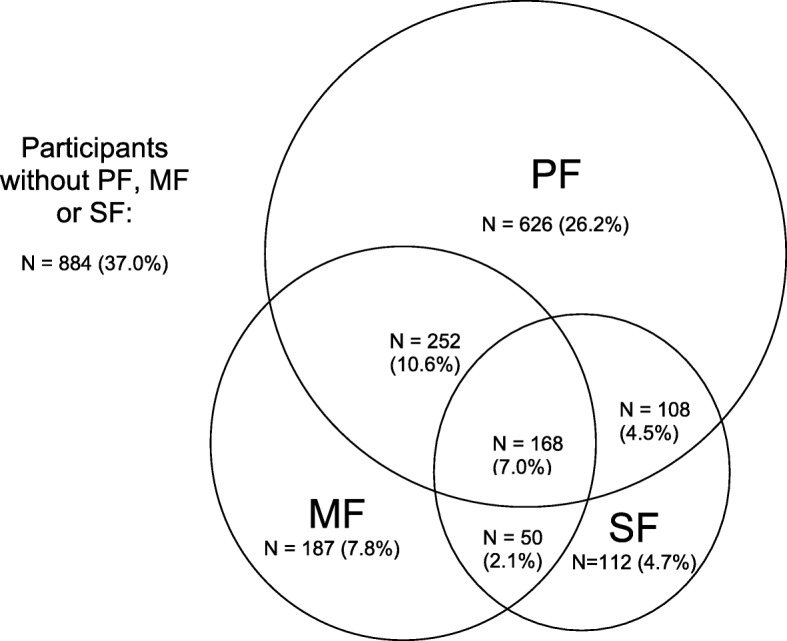
Prevalence and Co-occurrence of Frailty Dimensions in the SLAS-1 Cohort (N = 2387). Physical Frailty (PF) is defined as one or more of Fried’s criteria; Mental Frailty (MF) is defined as having one or more MF Criteria; Social Frailty (SF) is defined as having two of more of the SF Criteria
Inter-relationships between frailty dimensions
There were clear associations among the three frailty dimensions (Table 1). PF was strongly associated with psychological and social functioning components of MF and SF while MF was strongly associated with physical and social functioning components of PF and SF. SF was strongly associated with physical and mental functioning components in PF and MF.
Table 1.
Prevalence of components for social, mental and physical frailty in SLAS-1 Chinese older adults
| Variables | Total | Physical Frailty (PF) | Mental Frailty (MF) | Social Frailty (SF) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N = 2387 (%) | No PF (N = 1233) | PF (N = 1154) | p | No MF (N = 1730) | MF (N = 657) | p | No SF (N = 1949) | SF (N = 438) | p | |
| Fried Shrinking | 209 (8.8) | 0 (0.0) | 209 (18.1) | < 0.001 | 127 (7.3) | 82 (12.5) | < 0.001 | 146 (7.5) | 63 (14.4) | < 0.001 |
| Fried Low Physical Activity | 635 (26.6) | 0 (0.0) | 635 (55.0) | < 0.001 | 439 (25.4) | 196 (29.8) | 0.028 | 495 (25.4) | 140 (32.0) | 0.005 |
| Fried Weak | 471 (19.7) | 0 (0.0) | 471 (40.8) | < 0.001 | 256 (14.8) | 215 (32.7) | < 0.001 | 316 (16.2) | 155 (35.4) | < 0.001 |
| Fried Slow | 77 (3.2) | 0 (0.0) | 77 (6.7) | < 0.001 | 29 (1.7) | 48 (7.3) | < 0.001 | 42 (2.2) | 35 (8.0) | < 0.001 |
| Fried Exhaust | 206 (8.6) | 0 (0.0) | 206 (17.9) | < 0.001 | 73 (4.2) | 133 (20.2) | < 0.001 | 147 (7.5) | 59 (13.5) | < 0.001 |
| Cognitive Impairment | 282 (11.8) | 77 (6.2) | 205 (17.8) | < 0.001 | 0 (0.0) | 282 (42.9) | < 0.001 | 141 (7.2) | 141 (32.2) | < 0.001 |
| Low Mood | 430 (18.0) | 164 (13.3) | 266 (23.1) | < 0.001 | 0 (0.0) | 430 (65.5) | < 0.001 | 314 (16.1) | 116 (26.5) | < 0.001 |
| Poor Health Status | 59 (2.5) | 15 (1.2) | 44 (3.8) | < 0.001 | 0 (0.0) | 59 (9.0) | < 0.001 | 38 (2.0) | 21 (4.8) | 0.001 |
| Live Alone | 174 (7.3) | 79 (6.4) | 95 (8.2) | 0.087 | 114 (6.6) | 60 (9.1) | 0.033 | 61 (3.1) | 113 (25.8) | < 0.001 |
| No Education | 453 (19.0) | 169 (13.7) | 284 (24.6) | < 0.001 | 211 (12.2) | 242 (36.8) | < 0.001 | 215 (11.0) | 238 (54.3) | < 0.001 |
| Infrequent Contact | 487 (20.4) | 215 (17.4) | 272 (23.6) | < 0.001 | 296 (17.1) | 191 (29.1) | < 0.001 | 246 (12.6) | 241 (55.0) | < 0.001 |
| Infrequent Social Activities | 326 (13.7) | 158 (12.8) | 168 (14.6) | 0.215 | 226 (13.1) | 100 (15.2) | 0.170 | 174 (8.9) | 152 (34.7) | < 0.001 |
| Financial Difficulty | 234 (9.8) | 110 (8.9) | 124 (10.8) | 0.134 | 127 (7.3) | 107 (16.3) | < 0.001 | 98 (5.0) | 136 (31.1) | < 0.001 |
| Absence of Confidant | 117 (4.9) | 34 (2.8) | 83 (7.2) | < 0.001 | 58 (3.4) | 59 (9.0) | < 0.001 | 27 (1.4) | 90 (20.6) | < 0.001 |
| Socio-economic Deprivation | 150 (6.3) | 35 (2.8) | 115 (10.0) | < 0.001 | 62 (3.6) | 88 (13.4) | < 0.001 | 31 (1.6) | 119 (27.2) | < 0.001 |
Footnotes: Independent sample t-tests were conducted for continuous variables, chi-square for categorical variables
Socio-demographic, lifestyle, and health and behavioral profiles
Participants with PF, MF and/or SF were more likely to be older, female, single, divorced or widowed, more likely to be smokers, but less likely to be drinkers, more likely to be at risk of malnutrition, to be underweight and to have low cholesterol; to have stroke, asthma/COPD, chronic kidney disease, neurological and psychiatric disorders and visual impairment (Table 2). Prevalence of obesity, high blood pressure, coronary heart disease, cardiac disease and metabolic syndrome was significantly higher in participants with PF as compared to those without PF. The prevalence of these variables, however, were similar regardless of one’s MF or SF status. Having MF was uniquely associated with significantly higher prevalence of arthritis and hospitalizations in the past year. As compared to those without PF or MF, participants with PF or MF reported significantly higher prevalence of diabetes, medical comorbidity, polypharmacy and physician visits. Of note, these variables did not differ by SF status.
Table 2.
Baseline characteristics of SLAS-1 Chinese older adults by physical, mental and social frailty status
| Variables | Total | Physical Frailty (PF) | Mental Frailty (MF) | Social Frailty (SF) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N = 2387 (%) | No PF (N = 1233) | PF (N = 1154) | p | No MF (N = 1730) | MF (N = 657) | p | No SF (N = 1949) | SF (N = 438) | p | |
| Age, mean (SD) years | 66.1 (7.61) | 64.2 (6.36) | 68.0 (8.34) | < 0.001 | 65.1 (6.99) | 68.5 (8.61) | < 0.001 | 65.0 (7.31) | 69.3 (8.12) | < 0.001 |
| Male | 876 (36.7) | 493 (40.0) | 383 (33.2) | 0.001 | 668 (38.6) | 208 (31.7) | 0.002 | 748 (38.12) | 133 (30.4) | 0.002 |
| Single, Divorced Or Widowed | 603 (25.2) | 237 (19.2) | 365 (31.6) | < 0.001 | 378 (21.9) | 224 (34.1) | < 0.001 | 385 (19.8) | 217 (49.5) | < 0.001 |
| Current smoking (versus others) | 154 (6.5) | 61 (5.0) | 93 (8.1) | 0.002 | 101 (5.8) | 53 (8.1) | 0.047 | 113 (5.8) | 41 (9.4) | 0.006 |
| Current and past smoking | 401 (16.8) | 191 (15.5) | 210 (18.2) | 0.080 | 267 (15.4) | 134 (20.4) | 0.004 | 296 (15.2) | 105 (24.0) | < 0.001 |
| Alcohol drinking | 258 (10.8) | 168 (13.6) | 90 (7.8) | < 0.001 | 210 (12.1) | 48 (7.3) | 0.001 | 223 (11.4) | 25 (8.0) | 0.036 |
| NSI Risk (3 and above) | 1185 (49.6) | 527 (42.7) | 658 (57.0) | < 0.001 | 729 (42.1) | 456 (69.4) | < 0.001 | 911 (46.7) | 274 (62.6) | < 0.001 |
| Obese (BMI ≥ 27.5) | 310 (13.0) | 134 (10.9) | 176 (15.3) | 0.001 | 222 (12.8) | 88 (13.4) | 0.696 | 252 (12.9) | 58 (13.3) | 0.834 |
| Underweight (BMI ≤ 18.5) | 133 (5.6) | 0 (0.0) | 133 (11.5) | < 0.001 | 81 (4.7) | 52 (7.9) | 0.002 | 99 (4.8) | 40 (9.1) | < 0.001 |
| Hypertension | 1340 (56.1) | 656 (53.2) | 684 (59.3) | 0.003 | 953 (55.1) | 387 (58.9) | 0.093 | 1073 (55.1) | 267 (61.0) | 0.024 |
| High Blood Pressure | 1087 (45.5) | 532 (43.2) | 555 (48.1) | 0.015 | 770 (44.5) | 317 (48.3) | 0.101 | 886 (45.5) | 201 (45.9) | 0.87 |
| High Cholesterol | 1017 (42.9) | 512 (42.0) | 505 (43.9) | 0.339 | 733 (42.7) | 284 (43.5) | 0.725 | 852 (44.1) | 165 (37.7) | 0.014 |
| Low cholesterol | 179 (7.5) | 78 (6.3) | 101 (8.8) | 0.025 | 118 (6.8) | 61 (9.3) | 0.041 | 135 (6.93) | 44 (10.1) | 0.025 |
| Diabetes | 411 (17.2) | 180 (14.6) | 231 (20.0) | < 0.001 | 276 (16.0) | 135 (20.6) | 0.008 | 329 (16.9) | 82 (18.7) | 0.356 |
| Coronary heart disease | 123 (5.2) | 48 (3.9) | 75 (6.5) | 0.004 | 86 (5.0) | 37 (5.6) | 0.514 | 94 (4.8) | 29 (6.6) | 0.124 |
| Cardiac Disease | 194 (8.1) | 81 (6.6) | 113 (9.8) | 0.004 | 130 (7.5) | 64 (9.7) | 0.075 | 151 (7.8) | 43 (9.8) | 0.152 |
| Stroke | 87 (3.6) | 23 (1.9) | 64 (5.6) | < 0.001 | 45 (2.6) | 42 (6.4) | < 0.001 | 62 (3.2) | 25 (5.7) | 0.011 |
| Cancer | 43 (1.8) | 23 (1.9) | 20 (1.7) | 0.808 | 31 (1.8) | 12 (1.8) | 0.955 | 35 (1.8) | 8 (1.8) | 0.965 |
| Arthritis | 325 (13.6) | 151 (12.3) | 173 (15.0) | 0.052 | 217 (12.6) | 107 (16.3) | 0.016 | 263 (13.5) | 61 (13.9) | 0.823 |
| Asthma/COPD | 596 (25.0) | 270 (21.9) | 326 (28.3) | < 0.001 | 381 (22.0) | 215 (32.7) | < 0.001 | 460 (23.6) | 136 (31.1) | 0.001 |
| Hip Fracture | 20 (0.8) | 5 (0.4) | 15 (1.3) | 0.017 | 8 (0.5) | 12 (1.8) | 0.001 | 13 (0.7) | 7 (1.6) | 0.053 |
| Chronic kidney disease | 993 (42.0) | 428 (34.9) | 565 (49.7) | < 0.001 | 661 (38.5) | 332 (51.5) | < 0.001 | 777 (40.2) | 216 (50.1) | < 0.001 |
| Metabolic Syndrome | 656 (27.7) | 316 (25.8) | 340 (29.8) | 0.032 | 464 (27.1) | 192 (29.5) | 0.220 | 526 (27.2) | 130 (30.0) | 0.246 |
| Neuropsychiatric illness (N = 2384) | 87 (3.7) | 33 (2.7) | 54 (4.7) | 0.009 | 39 (2.3) | 48 (7.3) | < 0.001 | 60 (3.1) | 27 (6.2) | 0.002 |
| Hearing Impairment | 64 (2.7) | 27 (2.2) | 37 (3.2) | 0.124 | 32 (1.9) | 32 (4.9) | < 0.001 | 40 (2.1) | 24 (5.5) | < 0.001 |
| Visual Impairment | 809 (33.9) | 332 (26.9) | 477 (41.3) | < 0.001 | 548 (31.7) | 261 (39.7) | < 0.001 | 642 (32.9) | 167 (38.1) | 0.038 |
| Comorbidity | 1018 (42.65) | 451 (36.58) | 567 (49.13) | < 0.001 | 702 (40.58) | 316 (48.10) | 0.001 | 820 (42.07) | 198 (45.21) | 0.231 |
| Hospitalization for any condition in the past year | 95 (4.0) | 40 (3.2) | 55 (4.8) | 0.057 | 57 (3.3) | 38 (5.8) | 0.005 | 81 (4.2) | 14 (3.2) | 0.353 |
| Polypharmacy (taking 6 or more drugs) | 254 (10.6) | 99 (8.0) | 153 (13.3) | < 0.001 | 155 (9.0) | 97 (14.8) | < 0.001 | 207 (10.6) | 45 (10.3) | 0.831 |
| Physician Visit in the past year (SD) | 4.07 (5.40) | 3.66 (4.51) | 4.50 (6.18) | < 0.001 | 3.83 (4.56) | 4.71 (7.12) | < 0.001 | 4.04 (4.75) | 4.21 (7.65) | 0.28 |
Footnotes: Metabolic syndrome was defined using the International Diabetes Federation (IDF) criteria25: central obesity (waist circumference ≥ 90 for male and ≥ 80 for female) plus at least 2 CVRF: raised triglyceride level (≥150 mg/dL (1.7 mmol/L) or specific treatment for this lipid abnormality); reduced high density lipoprotein cholesterol (< 40 mg/dL (1.03 mmol/L) in males and < 50 mg/dL (1.29 mmol/L) in females or specific treatment for this lipid abnormality); raised blood pressure (BP) (systolic BP ≥ 130 or diastolic BP ≥ 85 mmHg, or treatment of previously diagnosed hypertension), and raised fasting plasma glucose (≥ 100 mg/dL or 5.6 mmol/L), or previously diagnosed type 2 diabetes)
Chronic kidney disease: eGFR (< 60 mL/min/1.73 m2; COPD: FEV1/FVC < 0.70
Neuropsychiatric illnesses: depression, psychosis, anxiety, dementia, Parkinson’s disease
Significance Tests: independent sample t-tests were conducted for continuous variables, chi-square for categorical variables
Frailty dimensions and disability, nursing home referral and mortality
In cross-sectional analyses (Table 3), adjusted for age, gender, medical comorbidity and other frailty dimensions, prevalent functional disability was significantly predicted by MF (OR = 1.78, p < .001) and PF (OR = 1.73, p < .001), but not SF. Prevalent severe disability was predicted by all three frailty dimensions after controlling for age, gender, comorbidity and other frailty dimensions (ORs = 2.19–7.34, ps = < .001–.048). In longitudinal analyses (Table 4), incident functional disability was significantly higher for PF (OR = 1.49, p = .044), but not SF and MF. Only SF significantly predicted nursing home referral after adjusting for age, gender, comorbidity and the two other frailty dimensions (OR = 3.43, p < .001). All frailty dimensions significantly predicted mortality after adjustment, with the highest and lowest HRs found for PF (HR = 1.51, p < .001) and SF respectively (HR = 1.32, p = .018).
Table 3.
Cross-sectional analyses of baseline MF, SF and PF with prevalent functional and severe disability
| Functional Disability | Severe Disability | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | % | OR (95% CI) Un-adjusted | P | OR (95% CI) Adjusted1 | P | N | % | OR (95% CI) Un-adjusted | P | OR (95% CI) Adjusted1 | P | |
| Total | 2387 | 2387 | ||||||||||
| Physical frailty | 382/1154 | 33.1 | 2.45 (2.02–2.98) | < 0.001 | 1.73 (1.40–2.25) | < 0.001 | 28/1154 | 2.4 | 15.31 (3.64–64.39) | < 0.001 | 7.34 (1.68–32.04) | 0.008 |
| Mental frailty | 244/657 | 37.1 | 2.37 (1.95–2.89) | < 0.001 | 1.78 (1.43–2.23) | < 0.001 | 24/657 | 3.7 | 10.89 (4.43–26.77) | < 0.001 | 5.52 (2.15–14.22) | < 0.001 |
| Social frailty | 155/438 | 35.4 | 1.91 (1.53–2.39) | < 0.001 | 1.26 (0.97–1.63) | 0.078 | 16/438 | 3.7 | 5.24 (2.54–10.82) | < 0.001 | 2.19 (1.00–4.76) | 0.048 |
| 2387 | 2387 | |||||||||||
| Robust without MF or SF | 144/884 | 16.3 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 2/884 | 0.2 | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| Robust with MF and/or SF | 63/349 | 18.1 | 1.13 (0.82–1.57) | 0.456 | 1.16 (0.82–1.63) | 0.404 | 0/349 | 0.0 | NE | – | NE | – |
| Pre-frail without MF or SF | 136/611 | 22.3 | 1.47 (1.13–1.91) | 0.004 | 1.31 (1.00–1.74) | 0.053 | 2/611 | 0.3 | 1.45 (0.20–10.31) | 0.711 | 1.39 (0.19–9.98) | 0.741 |
| Pre-frail with MF and/or SF | 183/462 | 39.6 | 3.37 (2.60–4.36) | < 0.001 | 2.58 (1.94–3.43) | < 0.001 | 8/462 | 1.7 | 7.77 (1.64–36.75) | 0.010 | 6.99 (1.43–34.01) | 0.016 |
| Frail without SF or MF | 8/15 | 53.3 | 5.87 (2.10–16.45) | 0.001 | 2.88 (0.99–8.40) | 0.052 | 1/15 | 6.7 | 31.50 (2.70–367.90) | 0.006 | 25.72 (2.10–314.94) | 0.011 |
| Frail with MF and/or SF | 55/66 | 83.3 | 25.69 (13.13–50.29) | < 0.001 | 15.78 (7.76–32.09) | < 0.001 | 17/66 | 25.8 | 153 (34.37–681.01) | < 0.001 | 125.17 (25.97–603.17) | < 0.001 |
| Robust without MF or SF | 144/884 | 16.3 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 2/884 | 0.2 | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| Robust with MF and/or SF | 63/349 | 18.1 | 1.13 (0.82–1.57) | 0.456 | 1.15 (0.82–1.62) | 0.412 | 0/349 | 0.0 | NE | – | NE | – |
| Pre-frail or Frail without SF or MF | 144/626 | 23.0 | 1.54 (1.19–1.99) | 0.001 | 1.34 (1.02–1.77) | 0.036 | 3/626 | 0.5 | 2.12 (0.35–12.75) | 0.410 | 1.82 (0.30–11.06) | 0.514 |
| Pre-frail or Frail with MF and/or SF | 238/528 | 45.1 | 4.22 (3.29–5.40) | < 0.001 | 3.10 (2.36–4.08) | < 0.001 | 25/528 | 4.7 | 21.92 (5.17–92.92) | < 0.001 | 15.37 (3.47–67.98) | < 0.001 |
1Models for Physical frailty, mental frailty and social frailty include: gender, age, comorbidity, physical frailty, mental frailty and social frailty. Models for all other predictors include: gender, age and comorbidity
Table 4.
Longitudinal analyses of MF, SF and PF with functional disability, nursing home referral and mortality
| Functional Disability | Nursing Home Referral | Mortality | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | % | OR (95% CI) | P | N | % | OR (95% CI) | P | N | /1000 py (95% CI) | HR (95% CI) | P | |
| Total | 1174 | 2387 | 2387 | |||||||||
| Unadjusted | ||||||||||||
| Physical frailty | 72/496 | 14.5 | 1.89 (1.30–2.73) | 0.001 | 31/1154 | 2.7 | 2.59 (1.35–4.98) | 0.004 | 268/1154 | 21.47 (19.05–24.20) | 2.29 (1.86–2.81) | < 0.001 |
| Mental frailty | 36/256 | 14.1 | 1.47 (0.97–2.22) | 0.068 | 23/657 | 3.5 | 2.95 (1.62–5.37) | < 0.001 | 174/657 | 24.60 (21.21–28.55) | 2.09 (1.72–2.55) | < 0.001 |
| Social frailty | 28/172 | 16.3 | 1.75 (1.11–2.76) | 0.015 | 23/438 | 5.3 | 5.09 (2.79–9.28) | < 0.001 | 117/438 | 24.76 (20.66–29.68) | 1.89 (1.53–2.35) | < 0.001 |
| Adjusted1 | ||||||||||||
| Physical frailty | 1.49 (1.01–2.20) | 0.044 | 1.54 (0.75–3.17) | 0.238 | 1.51 (1.21–1.89) | < 0.001 | ||||||
| Mental frailty | 1.12 (0.71–1.74) | 0.629 | 1.68 (0.86–3.26) | 0.129 | 1.46 (1.18–1.81) | < 0.001 | ||||||
| Social frailty | 1.27 (0.83–2.08) | 0.331 | 3.43 (1.77–6.65) | < 0.001 | 1.32 (1.05–1.65) | 0.018 | ||||||
| Unadjusted | ||||||||||||
| Robust without MF or SF | 37/499 | 7.4 | 1.00 | 6/884 | 0.7 | 1.00 | 88/884 | 8.64 (7.01–10.65) | 1.00 | |||
| Robust with MF and/or SF | 19/179 | 10.6 | 1.48 (0.83–2.65) | 0.184 | 7/349 | 2.0 | 3.00 (1.00–8.98) | 0.050 | 48/349 | 11.82 (8.91–15.68) | 1.35 (0.95–1.91) | 0.099 |
| Pre-frail or Frail without SF or MF | 43/318 | 13.5 | 1.95 (1.23–3.11) | 0.005 | 4/626 | 0.6 | 0.94 (0.26–3.35) | 0.925 | 103/626 | 14.82 (12.21–17.97) | 1.74 (1.31–2.31) | < 0.001 |
| Pre-frail or Frail with MF and/or SF | 29/178 | 16.3 | 2.43 (1.44–4.09) | 0.001 | 27/528 | 5.1 | 7.89 (3.23–19.23) | < 0.001 | 165/528 | 29.84 (25.62–34.76) | 3.48 (2.69–4.51) | < 0.001 |
| Adjusted2 | ||||||||||||
| Robust without MF or SF | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | |||||||||
| Robust with MF and/or SF | 1.20 (0.66–2.19) | 0.555 | 3.91 (1.08–14.10) | 0.037 | 1.40 (0.99–2.00) | 0.061 | ||||||
| Pre-frail or Frail without SF or MF | 1.59 (0.98–2.58) | 0.059 | 1.33 (0.33–5.41) | 0.689 | 1.52 (1.14–2.03) | 0.005 | ||||||
| Pre-frail or Frail with MF and/or SF | 1.65 (0.95–2.87) | 0.078 | 7.17 (2.32–22.2) | 0.001 | 2.25 (1.70–2.97) | < 0.001 | ||||||
1Model includes: gender, age, comorbidity, physical frailty, mental frailty and social frailty
2Model includes: gender, age and comorbidity
Combined PF, MF, SF dimensions and disability, nursing home referral and mortality
Using physically robust participants without SF or MF as the reference group (Tables 3 and 4), the associations of physically pre-frail and frail in combination with SF and/or MF with functional disability, severe disability, nursing home referral and mortality were examined in cross-sectional and longitudinal analyses.
Functional and severe disability
In cross-sectional analyses (Table 3), the prevalence of functional disability was lowest among the Robust without MF or SF (16.3%) and increased progressively among the PF, MF and SF combination groups to the highest prevalence (83.3%, 55/66) among those who were Frail with MF and/or SF (OR = 15.78, p < .001). ORs increased among the Pre-frail or Frail without MF or SF (OR = 1.34, p = .036), but were greater in the Pre-frail or Frail with MF and/or SF (OR = 3.10, p < .001). Similar trends were found for severe disability, with the Pre-frail or Frail with MF and/or SF recording the highest OR estimate (OR = 15.37, p < .001). In longitudinal analyses (Table 4), the incidence of functional disability increased from 7.4% among the Robust without MF or SF to 16.3% in the Pre-frail or Frail with MF and/or SF (OR = 1.65, p = .078).
Nursing home referral
Nursing home referral increased progressively from the Robust without MF or SF group (0.7%) to the highest level (5.1%) in the Pre-frail or Frail with MF and/or SF group (OR = 7.17, p = .001), after adjusting for age, gender and medical comorbidity (Table 4).
Mortality
Mortality rates increased progressively from 8.6 per 1000 person-years in the Robust without MF or SF group to the highest level (29.8 per 1000 person-years) in the Pre-frail or Frail with MF and/or SF group (HR = 2.25, p < .001), after adjusting for age, gender and comorbidity. The addition of MF, SF or both to PF increases the mortality rate.
Receiver operating characteristic analyses
Areas under ROC (AUCs) for PSF, PMF and PMSF were satisfactory and close in magnitude for all outcome variables (Table 5). Nevertheless, the highest AUC for each outcome variable was obtained only when all three frailty dimensions were included in analyses.
Table 5.
Receiver Operator Characteristics of PF, SF, MF and their various combinations
| Areas Under ROC | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cross-Sectional Analysis | Longitudinal Analysis | ||||
| Functional Disability | Severe Disability | Functional Disability | Mortality | Nursing Home Referral | |
| Social Frailty (SF) | 0.553 (0.533–0.573) | 0.677 (0.586–0.768) | 0.541 (0.503–0.578) | 0.564 (0.540–0.587) | 0.673 (0.598–0.748) |
| Mental Frailty (MF) | 0.592 (0.570–0.614) | 0.766 (0.692–0.839) | 0.536 (0.494–0.576) | 0.594 (0.568–0.620) | 0.621 (0.551–0.701) |
| Physical Frailty (PF) | 0.610 (0.587–0.632) | 0.728 (0.681–0.774) | 0.579 (0.533–0.624) | 0.608 (0.583–0.634) | 0.613 (0.544–0.682) |
| Physical and Social Frailty (PSF) | 0.641 (0.616–0.666) | 0.900 (0.829–0.971) | 0.600 (0.550–0.650) | 0.648 (0.618–0.677) | 0.685 (0.607–0.763) |
| Physical and Mental Frailty (PMF) | 0.654 (0.628–0.679) | 0.892 (0.819–0.965) | 0.597 (0.547–0.647) | 0.654 (0.625–0.683) | 0.656 (0.577–0.735) |
| Physical, Mental and Social Frailty (PMSF) | 0.656 (0.630–0.682) | 0.901 (0.825–0.976) | 0.603 (0.552–0.654) | 0.661 (0.631–0.691) | 0.707 (0.628–0.786) |
Footnotes: 95% confidence intervals are enclosed within brackets
Discussion
This study of the physical, mental and social dimensions of frailty within a multidimensional framework provides empirical evidence for the clinical relevance and utility for each frailty dimension individually and when used in combination as multidimensional frailty. PF, MF and SF were operationalized using existing theoretical models [10] and independently predicted various adverse health outcomes such as functional and severe disability, nursing home referral and mortality. When compared to MF and SF, PF appears to be a stronger predictor of adverse health outcomes, concurring with findings obtained using the TFI [4]. The addition of MF and SF to PF incrementally increased risk estimates of various adverse health outcomes. This is consonant with the findings in the Girona or Spain study [28], which showed that combining various frailty dimensions increases mortality HRs; HRs associated with one frailty dimension = 1.9, with two frailty dimensions = 3.9 and with three frailty dimensions = 10.4.
The three frailty dimensions are related but distinct constructs. There were considerable overlaps of the physical, mental and social functioning components belonging to each of the three frailty dimensions. The co-occurrence of MF and PF is consistent with the known association of impaired cognitive functioning and physical decline in late life [29]. While significant overlaps were present between the three frailty dimensions, it was also interesting to note that a sizable proportion of the population exhibited PF, MF or SF in isolation. The three frailty dimensions also shared many similar associations with socio-demographic, lifestyle, and health and behavioral profiles. These commonalities were unsurprising when viewed holistically within the bio-psycho-social model of common personal, social and environmental factors influencing health, disease and functioning. However, there remain associations unique to each frailty dimension. For instance, strong associations between PF and obesity, high blood pressure, metabolic syndrome, coronary heart disease and cardiac disease may be explained by shared biological factors including neuro-endocrine, hormonal and metabolic imbalances and chronic inflammation. The strong association between MF and arthritis was also unsurprising given the characteristic immune and inflammatory pathophysiology of the chronic disease and co-morbid depression. As expected, both PF and MF were strongly associated with increased physician visits and polypharmacy, while SF was not associated with health service utilization. This may reflect the unique situation of unmet needs and low demands of an under-reached group in this study population and healthcare setting.
Frailty dimensions might change over time. For example, PF transitions have been documented [30–33]. Frailty dimensions might also influence and interact with each other. For instance, SF predicted physical and cognitive decline in Japanese community-dwelling older adults [34]. Similarly, MF might hasten the progression of PF or SF as depression, poor cognitive functioning and poor self-rated health could limit one’s physical and social activities. The above should be further investigated in future studies.
PF has been very intensively studied. Its biological underpinnings with sarcopenia provide a strong basis for developing and validating screening and assessment tools. In contrast, the social and mental dimensions of frailty are rarely investigated. A preponderance of current multidimensional measurement tools are designed as global assessment tools with a total score which is predictive of health and functional outcomes. However, with the exception of the TFI, these multidimensional scales do not provide users with domain scores. There is much value in having individual frailty scores alongside a global multidimensional frailty score. As shown in the current study, PF, MF and SF individually and in combination predicted functional disability, severe disability, nursing home referral and mortality. These findings provide empirical support for the clinical relevance and use of a holistic approach towards frailty conceptualization [10]. In addition, the availability of individual domain scores allows for tailored policies and multi-domain interventions to address frailty in aging populations. Indeed, our multidimensional frailty construct was designed to match frail elderly to targeted community interventions that might be multidimensional in nature, depending on the needs of each older adult. For instance, those with PF and MF would be encouraged to attend interventions that contain exercise and cognitive stimulation while those with MF and SF would attend interventions with cognitive and social components. As the current assessments used may still be lengthy, future work should develop briefer multidimensional frailty screening and assessment tools that are equally predictive of adverse health outcomes. Such tools can be used in community-based assessments where older adults are segmented and directed to multi-domain frailty interventions tailored to their PF, MF and SF statuses.
The observed prevalence of individual and combined frailty dimensions is notable in this Asian population study. With all but 37.0% who were robust, the prevalence of any frailty dimension was 63.0%. PF was the most common frailty dimension observed (48.3%), followed by MF (27.5%) and SF (18.3%). With the exception of PF, single domain frailty was generally less prevalent as compared to multidimensional frailty with two or more frailty domains: PF alone = 26.2%; MF alone = 7.8%, SF alone = 4.7%, multidimensional frailty = 24.2%. Multidimensional frailty with all three PF, MF and SF together was present in 7.0%. Published data on the prevalence of multidimensional frailty in various populations are scarce and are based on differing operational definitions of PF, MF and SF, rendering comparison across studies difficult [4, 28]. For instance, in Girona, Spain, the prevalence of any frailty dimension was 38.8% in a study of rural community-dwelling older residents who were aged 75 and over [28]. Interestingly, MF was more prevalent than PF while SF was the least common. In another study of community-dwelling adults aged 40 to 81 in Netherlands, the prevalence of any frailty dimension was 17.1% [35]. In their study, MF and SF were more prevalent than PF, which was the least common. More studies should be conducted using standardized operational definitions of PF, MF and SF to examine possible variations in the prevalence of each frailty dimensions across different populations and their differing impacts on health, functioning and care outcomes.
Results should be interpreted with reference to the strengths and limitations of this study. The multidimensional frailty construct was derived based on strong theoretical formulations and has been empirically shown to possess face and construct validity [4, 7]. Nevertheless, its construct validity, particularly its convergent and discriminant validity, can be further assessed in future studies. While the multidimensional frailty construct shares the same domains as the TFI, the variables used to index each domain differ across the two scales. In addition, the operationalization of multidimensional frailty could have been limited by the availability of measures. PF is widely assessed using the standard criteria proposed by Fried et al., but may use various operational measures [12]. To assess weakness and slowness, we used proxy measures derived from the Performance Oriented Mobility Assessment of gait balance and control that was available in SLAS-1. We have shown in an independent study using knee extension strength and gait speed from six-meter walk in the second wave SLAS cohort (SLAS-2) that the two different operationalization of PF have good agreement (weighted kappa = 0.63) and were equally and strongly predictive of adverse health outcomes. The operationalization of SF was in line with a recent scoping review, which defined SF as a continuum of being at risk of losing, or having lost general or social resources, social behaviors and activities and self-management abilities that are important for fulfilling one’s basic social needs [14]. This moves beyond narrowly defining SF as the lack of social participation and perceived lack of social contacts and support. For MF, there is general consensus that this term may be applied to the declining mental abilities of older adults, involving cognition, mood and motivation as a consequence of loss of brain functional reserve under stress [13, 36]. PF, MF and SF measures could be standardized along these criteria in future studies to allow for comparison across different populations worldwide.
Some measurement artifacts may exaggerate observed overlaps across frailty dimensions, such as that between PF (due to exhaustion) and MF (due to depression). However, they did not appear to lessen the distinctions among the three frailty dimensions. It should be pointed out that frailty dimension measures in this study were elaborate and not designed to be brief screening tools, such as the TFI or EFS. There is thus room to develop brief screening and assessment tools for multidimensional frailty. Future studies should also investigate transition of MF and SF statuses, as has been shown for PF [30–33].
Singapore’s nursing home context and the nature of collected data should be considered when interpreting results for nursing home referral. Family and social service factors (limited access to affordable nursing home services despite lack of family caregiver) play a substantial role in prioritizing nursing home referral and placement in Singapore. PF and MF were not significant predictors of nursing home referral. This was partly explained by low statistical power from the unsurprisingly low incidence of nursing home referral in the study sample. There was also the possible effect of the time lag between baseline frailty measurements (2003–2005) and nursing home referral data (2010–2018). PF could have changed during this time lag, given its dynamic nature [30–33]. Likewise for MF, due to transitions in participants’ cognitive function, mood and self-rated health. Changes in SF could be less as it is partially made up of stable social resource factors. The low incidence of nursing home referral, low statistical power and time lag effect might thus account for the lack of significant associations between PF and MF and nursing home referral. Nevertheless, SF significantly predicted increased nursing home referral, strongly attesting to its powerful prediction of long-term institutional care.
AUCs obtained in ROC analyses were satisfactory but not large. Figures obtained were within the expected range given that the predicted outcome variables (e.g., mortality, disability) are influenced by a number of factors other than frailty. This is not unique to the current study. For reference, similar AUCs were obtained when the Framingham risk score, designed to predict development of cardiovascular disease, was used to predict the risk of chronic kidney disease in the absence of renal parameters [37].
Conclusion
Compared to PF alone, a multidimensional bio-psycho-social approach to frailty increases its ability to predict adverse health outcomes, such as disability, nursing home referral and morality, amongst Chinese Singaporean community-dwelling older adults. This study highlights the clinical relevance and utility of multidimensional frailty screening tools in the design of targeted multi-domain community-based health and social interventions to reduce frailty in community-dwelling older adults. These results also emphasize the need for upstream preventive health and social services to contain disability burden.
Acknowledgments
We thank the following voluntary welfare organizations for their support: Geylang East Home for the Aged, Presbyterian Community Services, St Luke’s Eldercare Services, Thye Hua Kwan Moral Society (Moral Neighbourhood Links), Yuhua Neighbourhood Link, Henderson Senior Citizens’ Home, NTUC Eldercare Co-op Ltd., Thong Kheng Seniors Activity Centre (Queenstown Centre) and Redhill Moral Seniors Activity Centre. We would also like to thank the Ministry of Health for the opportunity to obtain data for nursing home referrals for participants this study.
Abbreviations
- ADL
Activities of Daily Living
- AUC
Area under ROC
- CMMSE
Chinese version of the Mini-Mental State Examination
- EFS
Edmonton Frail Scale
- HR
Hazard Ratio
- IADL
Instrumental Activities of Daily Living
- MF
Mental Frailty
- MOH
Ministry of Health
- OR
Odds Ratio
- PF
Physical Frailty
- PMF
Combined PF-MF Dimensions
- PMSF
Combined PF-MF-SF Dimensions
- PSF
Combined PF-SF Dimensions
- ROC
Receiver Operating Characteristic
- SF
Social Frailty
- SLAS-1
First cohort of the Singapore Longitudinal Aging Studies
- SLAS-2
Second cohort of the Singapore Longitudinal Aging Studies
- TFI
Tilburg Frailty Indicator
Authors’ contributions
TPN has full access to all study data and primary responsibility for the final content of this manuscript. TPN formulated the hypothesis and research design, supervised and reviewed the data analysis, and reviewed and revised the manuscript. NT formulated the hypothesis, performed the literature review, analyzed the data and drafted and revised the manuscript. PSY analyzed the data and drafted and revised the manuscript. SLW contributed to the conceptualization of the study, interpreted the results, and reviewed and revised the manuscript. MSZN and QG contributed to the study design and data collection, reviewed the results and manuscript drafts. JJF reviewed the results and drafts of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
The study was supported by research grants from the Agency for Science Technology and Research (A*STAR) Biomedical Research Council (BMRC) [Grant: 08/1/21/19/567] and from the National Medical Research Council [Grant: NMRC/1108/2007]. The sponsors had no role in the conduct of the study or preparation of this manuscript.
Availability of data and materials
Data is not available for online access, however readers who wish to gain access to the data can write to the senior author Prof Ng TP at: “pcmngtp@nus.edu.sg”. Access can be granted on reasonable request and subject to the Institutional Review Board and the research collaborative agreement guidelines for the study. This is a requirement mandated for this research study by our IRB and funders.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study procedures were in line with the Declaration of Helsinki and were approved by the National University of Singapore Institutional Review Board. Written informed consent was obtained from all participants.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Nigel Teo, Email: teoqunxuannigel@gmail.com.
Pei Shi Yeo, Email: yeo.pei.shi@geri.com.sg.
Qi Gao, Email: pcmgqi@nus.edu.sg.
Ma Shwe Zin Nyunt, Email: pcmmszn@nus.edu.sg.
Jie Jing Foo, Email: FOO_Jie_Jing@moh.gov.sg.
Shiou Liang Wee, Email: weeshiouliang@gmail.com.
Tze Pin Ng, Email: pcmngtp@nus.edu.sg.
References
- 1.Rockwood K. Frailty and its definition: a worthy vhallenge. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2005;53(6):1069–1070. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.2005.53312.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Rockwood K, Song X, MacKnight C, Bergman H, Hogan DB, McDowell I, et al. A global clinical measure of fitness and frailty in elderly people. CMAJ. 2005;173(5):489–495. doi: 10.1503/cmaj.050051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Gobbens RJJ, van Assen MALM, Luijkx KG, Wijnen-Sponselee MT, Schols JMGA. The Tilburg frailty indicator: psychometric properties. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2010;11(5):344–355. doi: 10.1016/j.jamda.2009.11.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Gobbens RJJ, Van Assen MALM, Luijkx KG, Schols JMGA. The predictive validity of the Tilburg frailty indicator: disability, health care utilization, and quality of life in a population at risk. Gerontologist. 2012;52(5):619–631. doi: 10.1093/geront/gnr135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Rolfson DB, Majumdar SR, Tsuyuki RT, Tahir A, Rockwood K. Validity and reliability of the Edmonton frail scale. Age Ageing. 2006;35(5):526–529. doi: 10.1093/ageing/afl041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Tan LF, Lim ZY, Choe R, Seetharaman S, Merchant R. Screening for frailty and sarcopenia among older persons in medical outpatient clinics and its associations with healthcare burden. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2017;18(7):583–587. doi: 10.1016/j.jamda.2017.01.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Sutton JL, Gould RL, Daley S, Coulson MC, Ward EV, Butler AM, et al. Psychometric properties of multicomponent tools designed to assess frailty in older adults: a systematic review. BMC Geriatr. 2016;16:55. doi: 10.1186/s12877-016-0225-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Coelho T, Paúl C, Gobbens RJJ, Fernandes L. Frailty as a predictor of short-term adverse outcomes. PeerJ. 2015;3:e1121. doi: 10.7717/peerj.1121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Garre-Olmo J, Calvó-Perxas L, López-Pousa S, De Gracia BM, Vilalta-Franch J. Prevalence of frailty phenotypes and risk of mortality in a community-dwelling elderly cohort. Age Ageing. 2013;42(1):46–51. doi: 10.1093/ageing/afs047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Junius-Walker U, Onder G, Soleymani D, Wiese B, Albaina O, Bernabei R, et al. The essence of frailty: a systematic review and qualitative synthesis on frailty concepts and definitions. Eur J Intern Med. 2018;56:3–10. doi: 10.1016/j.ejim.2018.04.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.World Health Organization. Global strategy and action plan on ageing and health. WHO; 2017. 1–56 p. Available from: https://www.who.int/ageing/WHO-GSAP-2017.pdf?ua=1
- 12.Fried LP, Tangen CM, Walston J, Newman AB, Hirsch C, Gottdiener J, et al. Frailty in older adults: evidence for a phenotype. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2001;56(3):146–157. doi: 10.1093/gerona/56.3.M146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Fitten LJ. Psychological frailty in the aging patient. Nestle Nutr Inst Workshop Ser. 2015;83:45–53. doi: 10.1159/000382060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Bunt S, Steverink N, Olthof J, van der Schans CP, Hobbelen JSM. Social frailty in older adults: a scoping review. Eur J Ageing. 2017;14(3):323–334. doi: 10.1007/s10433-017-0414-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Teo N, Gao Q, Nyunt MSZ, Wee SL, Ng T-P. Social frailty and functional disability: findings from the Singapore Longitudinal Ageing Studies. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2017;18(7):637.e13–637.e19. doi: 10.1016/j.jamda.2017.04.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Niti M, Yap K-B, Kua E-H, Tan C-H, Ng T-P. Physical, social and productive leisure activities, cognitive decline and interaction with APOE-epsilon 4 genotype in Chinese older adults. Int Psychogeriatr. 2008;20(2):237–251. doi: 10.1017/S1041610207006655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Feng L, Chong MS, Lim WS, Ng TP. The modified mini-mental state examination test: normative data for Singapore Chinese older adults and its performance in detecting early cognitive impairment. Singap Med J. 2012;53(7):458–462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Nyunt MSZ, Fones C, Niti M, Ng T-P. Criterion-based validity and reliability of the Geriatric Depression Screening Scale (GDS-15) in a large validation sample of community-living Asian older adults. Aging Ment Health. 2009;13(3):376–382. doi: 10.1080/13607860902861027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Jylhä M. What is self-rated health and why does it predict mortality? Towards a unified conceptual model. Soc Sci Med. 2009;69(3):307–316. doi: 10.1016/j.socscimed.2009.05.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Low LL, Wah W, Ng MJ, Tan SY, Liu N, Lee KH. Housing as a social determinant of health in Singapore and its association with readmission risk and increased utilization of hospital services. Front Public Health. 2016;4:109. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2016.00109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Ng TP, Feng L, Nyunt MSZ, Larbi A, Yap KB. Frailty in older persons: multisystem risk factors and the Frailty Risk Index (FRI) J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2014;15(9):635–642. doi: 10.1016/j.jamda.2014.03.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Feng L, Zin Nyunt MS, Gao Q, Feng L, Yap KB, Ng T-P. Cognitive frailty and adverse health outcomes: findings from the Singapore Longitudinal Ageing Studies (SLAS) J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2016;18(3):252–258. doi: 10.1016/j.jamda.2016.09.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Mahoney FI, Barthel DW. Functional evaluation: the barthel index. Md State Med J. 1965;14:61–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Lawton MP, Brody EM. Assessment of older people: self-maintaining and instrumental activities of daily living. Gerontologist. 1969;9(3):179–186. doi: 10.1093/geront/9.3_Part_1.179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Posner BM, Jette AM, Smith KW, Miller DR. Nutrition and health risks in the elderly: the nutrition screening initiative. Am J Public Health. 1993;83(7):972–978. doi: 10.2105/AJPH.83.7.972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Tielsch JM, Sommer A, Witt K, Katz J, Royall RM. Blindness and visual impairment in an American urban population: the Baltimore eye survery. Arch Ophthalmol. 1990;108(2):286–290. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1990.01070040138048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.StataCorp. Stata Statistical Software: Release 14. 2015. College Station, TX: StataCorp LP.
- 28.Vermeiren S, Vella-Azzopardi R, Beckwee D, Habbig AK, Scafoglieri A, Jansen B, et al. Frailty and the prediction of negative health outcomes: a meta-analysis. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2016;17(12):1163.e1–1163.e17. doi: 10.1016/j.jamda.2016.09.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Atkinson HH, Rapp SR, Williamson JD, Lovato J, Absher JR, Gass M, et al. The relationship between cognitive function and physical performance in older women: results from the women’s health initiative memory study. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2010;65(3):300–306. doi: 10.1093/gerona/glp149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Gill TM, Gahbauer EA, Allore HG, Han L. Transitions between frailty states among community-living older persons. Arch Intern Med. 2006;166(4):418–423. doi: 10.1001/archinte.166.4.418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Gill TM, Gahbauer EA, Han L, Allore HG. The relationship between intervening hospitalizations and transitions between frailty states. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2011;66(11):1238–1243. doi: 10.1093/gerona/glr142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Fallah N, Mitnitski A, Searle SD, Gahbauer EA, Thomas MG, Rockwood K. Transitions in frailty status in older adults in relation to mobility: a multi-state modeling approach employing a deficit count. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2011;59(3):524–529. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.2011.03300.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Lee JSW, Auyeung TW, Leung J, Kwok T, Woo J. Transitions in frailty states among community-living older adults and their associated factors. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2014;15(4):281–286. doi: 10.1016/j.jamda.2013.12.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Tsutsumimoto K, Doi T, Makizako H, Hotta R, Nakakubo S, Makino K, et al. Association of social frailty with both cognitive and physical deficits among older people. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2017;18(7):603–607. doi: 10.1016/j.jamda.2017.02.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Van Oostrom SH, Van Der ADL, Rietman ML, Picavet HSJ, Lette M, Verschuren WMM, et al. A four-domain approach of frailty explored in the Doetinchem cohort study. BMC Geriatr. 2017;17:196. doi: 10.1186/s12877-017-0595-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.McDougall GJ, Balyer J. Decreasing mental frailty in at-risk elders. Geriatr Nurs. 1998;19(4):220–224. doi: 10.1016/S0197-4572(98)90156-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Lee C, Yun H-R, Joo YS, Lee S, Kim J, Nam KH, et al. Framingham risk score and risk of chronic kidney disease: a community-based propspective cohort study. Kidney Res Clin Prac. 2019;38(1):49–59. doi: 10.23876/j.krcp.18.0118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
Data is not available for online access, however readers who wish to gain access to the data can write to the senior author Prof Ng TP at: “pcmngtp@nus.edu.sg”. Access can be granted on reasonable request and subject to the Institutional Review Board and the research collaborative agreement guidelines for the study. This is a requirement mandated for this research study by our IRB and funders.


