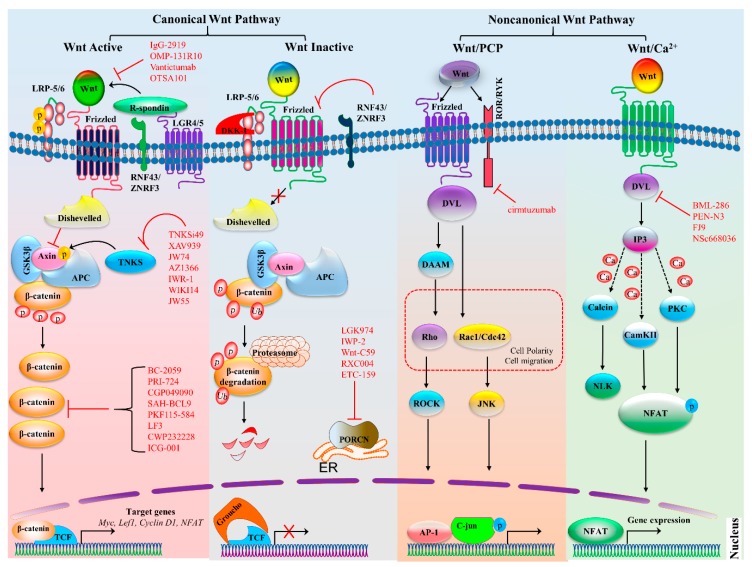
Figure 1.
Canonical and noncanonical Wnt signaling pathways. The canonical Wnt pathway is activated by the binding of a Wnt ligands to a frizzled (FZD) family receptor and co-receptor LRP5 or LRP6, which recruits disheveled (Dvl), consequently inactivating the destruction complex composed of APC, GSK3β, and axin. This inactivation prevents β-catenin from proteasomal degradation and allows for the accumulation of β-catenin, which then enters the nucleus. There, it binds to transcription factor TCF or LEF and initiates the transcription of target genes. Tankyrases (TNKSs) also promote signaling by targeting axin for degradation. Moreover, when R-spondin binds to LGR4 or LGR5, RNF43, and ZNRF3, it is not capable of targeting FZD family receptors for degradation and enhances Wnt signaling. There are various inhibitors of the Wnt signaling pathway, particularly those targeting Wnt ligands, Dvl, TNKS, β-catenin, and PORCN, which are highlighted in red; bars indicate the inhibitory effect. In the absence of Wnt ligands, the destruction complex becomes active and starts the proteasomal degradation of β-catenin. Proteins RNF43 and ZNRF3 also inhibit the binding of FZD and target it for degradation. The noncanonical Wnt–PCP pathway is triggered by Wnt ligands that increase the heterodimerization of a receptor-like tyrosine kinase (RYK) and tyrosine kinase–like orphan receptor (ROR). The binding to the receptor activates the Dvl protein and downstream signaling, for instance, DAAM activates GTPases Rho and ROCK, whereas the activation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) by Rac is independent of DAAM. They collectively regulate cell polarity and migration and have also been implicated in cancer. The Wnt–Ca2+ pathway is activated by ligand Wnt, which raises the intracellular Ca2+ levels and generates inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate-3 (IP3). The Ca2+ levels increase and switch on downstream Ca2+-dependent enzymes such as calmodulin-dependent protein kinase (CaMKII), calcineurin, and protein kinase C (PKC). As a consequence, CaMKII and PKC phosphorylate nuclear factor of activated T cells (NFAT) and activate the expression of target genes. Protein symbols and abbreviations: APC, adenomatous polyposis coli protein; AP-1, activator protein 1; DKK1, dickkopf related protein 1; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; GSK3β, glycogen synthase kinase 3β; LEF1, lymphoid enhancer-binding factor 1; LRP, lipoprotein receptor-related protein; LGR4/5, Leucine-rich-repeat–containing G protein–coupled receptor 4 or 5; NLK, Nemo like kinase; RNF43, Ring finger protein 43; and ZNRF3, zinc ring finger 3.