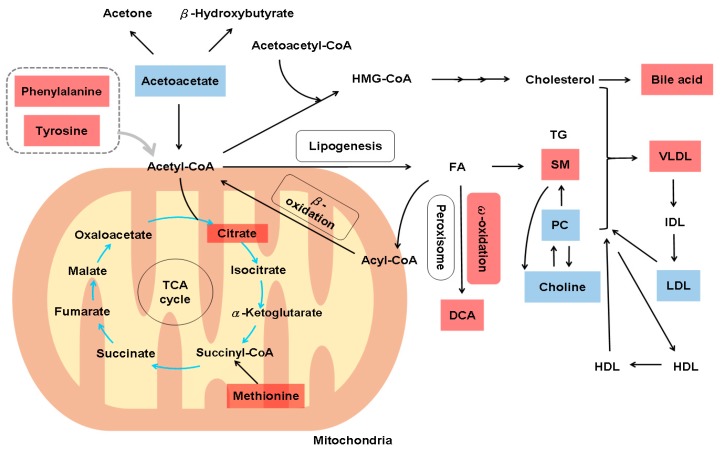
Figure 4.
Metabolic alterations in hepatitis C virus-related hepatic fibrosis. In addition to decreasing Fisher’s ratio, hepatitis C virus-related hepatic fibrosis might lead to the impairment of mitochondrial processes, including impaired fatty acid oxidation, oxidative phosphorylation and responses to oxidative stress and reactive oxygen species. HMG-CoA, 3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl-coenzyme A; FA, fatty acids; TG, triglycerides; SM, sphingomyelin; PC, phosphatidylcholine; DCA, dicarboxylic acids; VLDL, very low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol; IDL, intermediate-density lipoprotein-cholesterol; LDL, low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol; HDL, high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol; TCA, tricarboxylic acid cycle; ROS, reactive oxygen species. Upregulated metabolites are shown in red boxes, and downregulated metabolites are shown in blue boxes.