Abstract
Seed germination is a developmental process regulated by numerous internal and external cues. Our previous studies have shown that calcium influx mediated by the Arabidopsis glutamate receptor homolog 3.5 (AtGLR3.5) modulates the expression of the ABSCISIC ACID INSENSITIVE 4 (ABI4) transcription factor during germination and that L-methionine (L-Met) activates AtGLR3.1/3.5 Ca2+ channels in guard cells. However, it is not known whether L-Met participates in regulation of germination and what cellular mechanism is responsible for Met production during germination. Here, we describe Arabidopsis methionine synthase 1 (AtMS1), which acts in the final step of Met biosynthesis, synthesizes the Met required for the activation of AtGLR3.5 Ca2+ channels whose expression is up-regulated during germination, leading to the regulation of seed germination. We show that exogenous L-Met promotes germination in an AtGRL3.5-dependent manner. We also demonstrate that L-Met directly regulates the AtGLR3.5-mediated increase in cytosolic Ca2+ level in seedlings. We provide pharmacological and genetic evidence that Met synthesized via AtMS1 acts upstream of the AtGLR3.5-mediated Ca2+ signal and regulates the expression of ABI4, a major regulator in the abscisic acid response in seeds. Overall, our results link AtMS1, L-Met, the AtGLR3.5 Ca2+ channel, Ca2+ signals, and ABI4, and shed light on the physiological role and molecular mechanism of L-Met in germination.
Keywords: Calcium channels, AtGLR3.5, methionine, methionine synthase 1, seed germination
Methionine synthase 1 provides methionine that activates the glutamate receptor homolog 3.5 calcium channel during seed germination in Arabidopsis.
Introduction
Germination is a critical developmental process that transforms non-dormant seeds into a highly active state and plays a major role in the life cycle of the plant (Rajjou et al., 2012). The germination process comprises three phases, namely imbibition by the dry seed, re-initiation of metabolic processes, and the protrusion of the radicle through seed envelopes (Bewley, 1997; Penfield et al., 2006; Holdsworth et al., 2008; Weitbrecht et al., 2011). The progression of germination is largely controlled by internal signaling cascades, such as those related to phytohormones including abscisic acid (ABA) and gibberellins (GAs), as well as by environmental cues (Bewley, 1997; Holdsworth et al., 2008; Weitbrecht et al., 2011; Rajjou et al., 2012; Han and Yang, 2015).
Numerous studies have examined the regulatory mechanisms that underlie seed germination (Gallardo et al., 2001; Rajjou et al., 2004; Nakabayashi et al., 2005; Fait et al., 2006; Catusse et al., 2008; Sreenivasulu et al., 2008; North et al., 2010; Bassel et al., 2011; Dekkers et al., 2013; Bellieny-Rabelo et al., 2016; Feenstra et al., 2017) and have shown that it is collectively coordinated by temporally distinct transcriptomic, proteomic, and metabolic switches. Several studies have highlighted the role of the latter during germination (Fait et al., 2006; Sreenivasulu et al., 2008; Bellieny-Rabelo et al., 2016; Feenstra et al., 2017), with numerous pathways being associated with the turnover of proteins, polysaccharides, and lipids. It has also been reported that the contents of free amino acids are altered during the course of germination (Fait et al., 2006; Dekkers et al., 2013; Galland et al., 2014; Angelovici et al., 2017). The levels of amino acids such as Asp, Thr, and Ser significantly increase during the transition from stratification to germination sensu stricto in Arabidopsis seeds, although the amounts of Gly, Gln, Ile, and the non-proteogenic r-aminobutyrate are reduced (Fait et al., 2006). Genes related to the biosynthesis of several amino acids are up-regulated during imbibition (Fait et al., 2006). In addition to being the building blocks of proteins and the precursors of plant hormones and secondary metabolites (Amir, 2010), amino acids act as signaling molecules in diverse biological processes, including pollen-tube growth, plant–microbe interactions, stomatal movements, and defense responses (Michard et al., 2011; Li et al., 2013; Kong et al., 2016; Toyota et al., 2018). However, the physiological functions of amino acids and the molecular regulatory mechanisms that underlie the dynamic changes in their contents during seed germination remain largely unknown.
Our previous study demonstrated that the Arabidopsis glutamate receptor homolog 3.5 (AtGLR3.5, At2g32390) plays a critical role in seed germination through modulation of the cytosolic free Ca2+ concentration, [Ca2+]cyt, and antagonization of the inhibitory effects of ABA via suppression of the transcription of ABSCISIC ACID INSENSITIVE4 (ABI4), a key ABA-response regulator (Kong et al., 2015). Consistent with the activation mechanism by ligands in animal glutamate receptors, several studies have demonstrated that amino acids such as L-Met, D-Ser, and Glu can activate plant GLR Ca2+ channels (Qi et al., 2006; Michard et al., 2011; Vincill et al., 2012; Tapken et al., 2013; Kong et al., 2016; Toyota et al., 2018). For example, L-methionine (L-Met) activates guard cell heteromeric AtGLR3.1/3.5 Ca2+ channels in the plasma membrane in order to regulate stomatal aperture (Kong et al., 2016). In addition, a proteomic study reported that two housekeeping enzymes involved in methionine (Met) biosynthesis are temporally accumulated during radicle protrusion (Gallardo et al., 2002), suggesting that Met has a role in seed germination. However, it remains unknown whether Met functions in AtGLR3.5-mediated germination control and which cellular mechanism is the source of the amino acid in the process.
In the present study, we demonstrate that L-Met promotes seed germination through up-regulation of the AtGLR3.5-mediated cytosolic Ca2+ signal in Arabidopsis. We provide evidence that L-Met positively regulates germination, and that this requires Arabidopsis methionine synthase 1 (AtMS1), activation of AtGLR3.5 Ca2+ channels by L-Met, and modulation of the expression of ABI4.
Materials and methods
Plant material and growth conditions
The Arabidopsis genetic background Columbia (Col-0) was used as the wild-type. Seeds expressing 35S::Yellow Cameleon3.60 (YC3.60) were kindly provided by Dr Magaly Rincón-Zachary and Dr Elison B. Blancaflor (Samuel Roberts Noble Foundation, Oklahoma). The AtGLR3.5-RNAi lines and their lines expressing YC3.60 have been previously described by Kong et al. (2015). The T-DNA insertion mutants Atms1 (CS480822), Atglr3.5-1 (Salk_035264), and Atglr3.5-2 (CS859735) were obtained from the Arabidopsis Biological Resource Center (ABRC; https://abrc.osu.edu/). Seeds were stratified at 4 °C for 3 d before sowing in soil and the plants were grown in controlled growth chambers at 22 °C under white fluorescent light (110 μmol m−2 s−1) in long-day conditions (16/8 h light/darkness). Seed germination assays were performed as described previously (Kong et al., 2015), with seeds sown on Murashige and Skoog (MS)-based media containing MS major salts with the indicated amounts of CaCl2, MS minor salts, vitamins, 1% (w/v) sucrose, and 0.8% (w/v) agar. Amino acids (L-Met, L-Asp, L-Thr, D-Ser, or L-Glu), LaCl3 (a Ca2+-channel blocker), EGTA (a Ca2+-chelating agent ), or DL-propargylglycine (PAG, a Met synthesis inhibitor; all Sigma Aldrich) were added to the MS media prior to sowing when required. Seeds harvested the same day were used for each germination experiment. For each sample, 80–100 seeds per treatment were carefully examined for germination, and three biological replicates were conducted.
Measurement of Ca2+ levels in the cytosol
YC3.60-based fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET)-sensitized emission imaging analysis was used to measure the level of cytosolic free calcium, [Ca2+]cyt, in the wild-type and AtGLR3.5-RNAi lines before and after L-Met or L-Glu treatment. The experiments were performed using 4-d-old seedlings expressing YC3.60 placed under a TCS SP5 confocal laser-scanning microscope (Leica Microsystems) as described previously (Rincón-Zachary et al., 2010; Kong et al., 2015). Ten seedlings of each genotype were examined for each treatment.
Gene expression analysis
Total RNA extraction, reverse-transcription, and quantitative PCR were carried out as described previously (Kong et al., 2015). The gene-specific primers used for expression were as follows: AtMS1, 5´-CGTCGTGAGTACAAGGCCAAAAAG-3´ and 5´-CAGTGAAGG CAAAACCAGACAACTG-3´; AtMS2, 5´-GCCCAGAAGGTTGTT GAAGTTGACG-3´ and 5´-GCCTTGCGCTAACTTCAGTTGTACG-3´; and AtMS3, 5´-CCAACGTCCTATGAAGGGGATGC-3´, and 5´-GGACGGCCCAGTCAAGGTAAAAC-3´. The primer set used for AtGLR3.5 is described by Kong et al. (2015) and the primers used for ABI4 are as described by Footitt et al. (2011). Relative gene expression values were obtained by normalization to the housekeeping gene ACTIN2. Three biological repeats were used for each analysis.
Generation of Arabidopsis transgenes expressing AtMS1p::GUS
The AtMS1p::GUS construct used for plant transformation was created using the Gateway method (Invitrogen). The 2-kb promoter region of AtMS1 was PCR-amplified using the primers 5´-CACCGCAAAAGAGCTTATAACGTAGTTTATGC-3´ and 5´-TTTGATTTTCTTTTACTGCATTAAAACAC-3´. The fragment was cloned into the pENTR/D-TOPO cloning vector and then fused to the GUS reporter gene in the binary vector pMDC163 (Karimi et al., 2002). The resulting plasmid that harbored the GUS reporter driven by the AtMS1 promoter (AtMS1p::GUS) was introduced into the Agrobacterium strain GV3101, and then Arabidopsis transformation was performed using the floral dip method (Clough and Bent, 1998). Transgenic plants were identified through selection for hygromycin resistance. Homozygous T3 lines carrying a single insertion were used for the analysis.
Histochemical staining with X-Gluc
GUS activity was examined as described by Jefferson et al. (1987). Seeds were incubated at 37 °C overnight in the dark in GUS staining solution containing 5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl-b-D-glucuronic acid (X-Gluc), as used previously by Kong et al. (2015), and were then washed three times in 100% ethanol and once in 70% ethanol (v/v). The seed coats were carefully removed under a SV6 dissection microscope and pictures taken with an Axio Cam ICC digital camera (both Zeiss).
Identification of AtMS1 and AtGLR3.5 T-DNA insertion lines
Three T-DNA insertion lines (SALK_205174, CS828436, and CS480822) of the AtMS1 gene (At5g17920) were obtained from ABRC, and homozygous seedlings were only identified in the CS480822 line. The two sets of primers used for genotyping this line were as follows: Sul2, 5´-GTCGAACCTTCAAAAGCTGAAGT-3´; Sul4, 5´-ATTTCA CACAGGAAACAGCTATGA-3´; 8474, 5´-ATAATAACGCTGCGGA CATCTACATTTT-3´; and TH39, 5´-GAGGCTGCACTTAGAGAA GGACTA-3´. For the primers used for the genotyping of Atglr3.5-1 (Salk_035264), the sequences of the left genomic primer (LP) and right genomic primer (RP) were 5´-TGAAGTTGC TGCAAATGTGAG-3´ and 5´-TGTCGACATGTCCACAGCTAG-3´. The sequences of the LP and RP primers used for the genotyping of Atglr3.5-2 (CS859735) were 5´-TTCAAAAGCCAACCAAATTTG-3´ and 5´-CTGAAGATTGTGGACCAATGG-3´. The primer LBb1.3 used in genotyping of both Atglr3.5-1 and Atglr3.5-2 lines was 5´-ATTTTGCCGATTTCGGAAC-3´.
Measurement of amino acid contents in seeds
Seeds that had been stratified for 3-d were incubated at 22 °C for 0 h or 24 h and collected for analysis. The amino acid contents were measured by OE BioTech (Shanghai, China) according to standard procedures for GC-MS. All chemicals and solvents used were of analytical grade. The analyses were carried out on a GC-MS system (Agilent, model 7890B) coupled with a mass-selective detector (Agilent, model 5977A). A DB-5MS fused-silica capillary column (30 m×0.25 mm×0.25 μm; Agilent J & W Scientific) was used to separate the derivatives. The analysis was performed under the following settings: Helium (>99.999%) was used as the carrier gas at a constant flow rate of 1 ml min–1 through the column; the injector temperature was maintained at 260 °C; the injection volume was 1 μl by splitless mode and the solvent delay time was set to 5 min; the initial oven temperature was 60 °C, ramped to 125 °C at a rate of 15 °C min–1, to 210 °C at a rate of 5 °C min–1, to 270 °C at a rate of 10 °C min–1, to 305 °C at a rate of 20 °C min–1, and finally held at 305 °C for 5 min; the temperatures of the MS quadrupole and electron impact ion source were set to 150 °C and 230 °C, respectively; and the collision energy was 70 eV. Mass spectrometric data were acquired in full-scan mode (m/z 50–500).
Statistical analyses
Student’s t-test (one-tailed distribution) was used to determine the significance of the data.
Results
L-methionine promotes seed germination
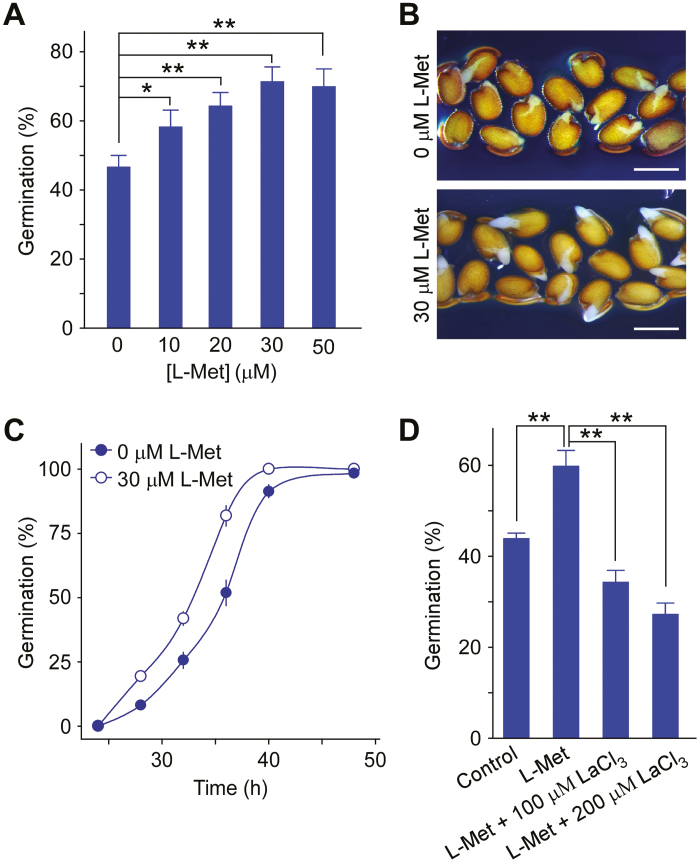
We have previously demonstrated that AtGLR3.5 modulates [Ca2+]cyt and seed germination (Kong et al., 2015). To determine how the ligand regulates AtGLR3.5 activity during germination, we focused on amino acids whose levels are known to increase during germination (Fait et al., 2006) and that have been reported to activate plant GLR Ca2+ channels (Michard et al., 2011; Li et al., 2013; Kong et al., 2016). We tested the effects of L-Met, D-Ser, L-Asp, and L-Thr at physiological concentrations (10 µM and 30 µM) on germination in Arabidopsis wild-type (WT) seeds at 36 h after sowing, at which time germination rates reach approximately half of their maximum value under our experimental conditions (Kong et al., 2015). In addition, the expression of AtGLR3.5 is highly up-regulated between 24–36 h after imbibition, and knock-down of AtGLR3.5 expression results in reduced germination at 36 h after imbibition (Kong et al., 2015). We observed that L-Met enhanced germination in a dose-dependent manner, with an optimal effect at 30 µM (Fig. 1A, B; Supplementary Fig. S1 at JXB online). Time-course analysis further confirmed that there was more rapid seed germination in the presence of L-Met than in its absence (Fig. 1C). Since the positive effect of L-Met on germination was similar to what we had previously observed for Ca2+ treatment (Kong et al., 2015), we next tested whether the effect of L-Met was related to Ca2+ or Ca2+ channel(s). Seed germination rates were therefore examined following treatment with L-Met in combination with a Ca2+-channel blocker, LaCl3. We found that LaCl3 eliminated the promotional effects of L-Met, resulting in a germination rate that was lower than that of the control (Fig. 1D). This suggested that the promotional effects of L-Met on germination were achieved via Ca2+ channel(s), or that L-Met activated Ca2+ channel(s) to promote germination.
Fig. 1.
L-methionine (L-Met) promotes seed germination in Arabidopsis. (A) Seed germination at various concentrations of L-Met in the growth medium. Wild-type seeds were sown on half-strength MS medium supplemented with the indicated amounts of L-Met and incubated in the dark at 4 °C for 3 d before being transferred to a growth chamber at 22 °C for 36 h. (B) Germination phenotypes in the presence or absence of 30 µM L-Met at 36 h in the growth chamber. Representative images from three biological replicates are shown. Scale bars are 0.5 mm. (C) Time-course of seed germination in the presence or absence of L-Met (30 µM). Seeds were sown as described in (A) and incubated at 22 °C. (D) Effect of the Ca2+-channel blocker LaCl3 on Met regulation of seed germination. Seeds were incubated on half-strength MS medium (control) or on medium supplemented with L-Met (10 µM), or L-Met (10 µM) plus LaCl3 (100 µM or 200 µM) for 36 h and scored for germination. Data in (A, C, D) are means (±SE) from three independent replicates. Significant differences were determined using Student’s t-test: *P<0.05, **P<0.01. (This figure is available in colour at JXB online.)
AtGLR3.5 mediates L-Met-dependent seed germination
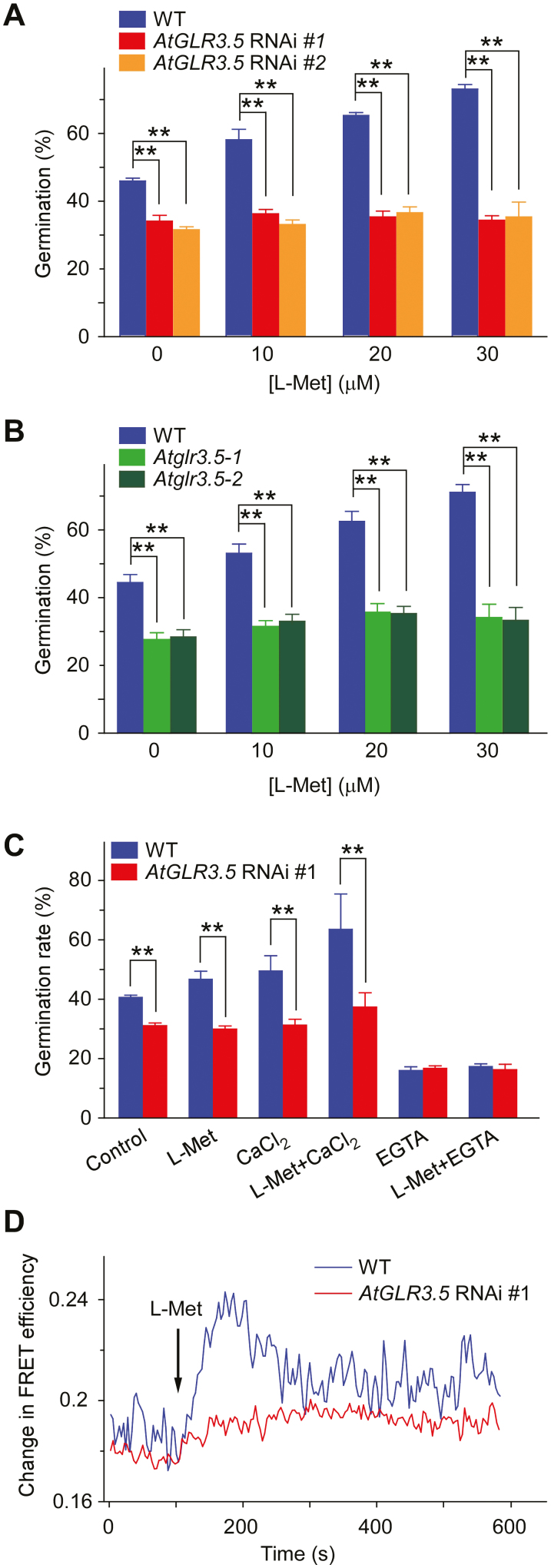
Since AtGLR3.5 is essential for Arabidopsis seed germination (Kong et al., 2015) and functions as a Ca2+ channel (Kong et al., 2015, 2016), we investigated whether it was involved in the L-Met-modulated control of germination. We examined germination rates in the presence of L-Met in AtGLR3.5-RNAi lines and in AtGLR3.5 T-DNA insertion lines (Atglr3.5-1 and Atglr3.5-2), all of which have largely reduced AtGLR3.5 transcript levels (Kong et al., 2015; Supplementary Fig. S2). In contrast to the enhanced germination rates in WT seeds in response to L-Met, the two independent AtGLR3.5-RNAi and the two T-DNA insertion lines showed no apparent changes in germination under the concentrations of L-Met applied (Fig. 2A, B), which suggested a crucial role of AtGLR3.5 in L-Met-mediated germination. The simultaneous application of L-Met and CaCl2 led to greater enhancement of germination in WT seeds than when each was applied separately (Fig. 2C). In contrast, this enhanced germination was largely attenuated in the AtGLR3.5-RNAi lines, which have defects in the [Ca2+]cyt increase in response to CaCl2 (Kong et al., 2015). When the Ca2+ chelating agent EGTA was added to medium containing L-Met, germination was severely inhibited in both the WT and the AtGLR3.5-RNAi lines (Fig. 2C). These results suggested that the regulation of seed germination by L-Met involved AtGLR3.5 and a Ca2+ signal.
Fig. 2.
L-methionine (L-Met) induces AtGLR3.5-dependent increases in [Ca2+]cyt in Arabidopsis. (A) Germination of wild-type (WT) and AtGLR3.5-RNAi seeds at different concentrations of L-Met. Seeds were sown on half-strength MS medium supplemented with L-Met and were scored for germination after incubation at 22 °C for 36 h. (B) Germination of WT and AtGLR3.5 T-DNA insertion lines (Atglr3.5-1 and Atglr3.5-2) at different concentrations of L-Met. Seeds were examined for germination after incubation at 22 °C for 36 h. (C) Germination of WT and AtGLR3.5-RNAi seeds in response to various treatments. Seeds were sown on modified MS media containing 0 mM CaCl2 (control), 0 mM CaCl2 and 10 µM L-Met, 1 mM CaCl2, 1 mM CaCl2 and 10 µM L-Met, 0 mM CaCl2 and 10 mM EGTA, or 0 mM CaCl2 supplemented with 10 µM L-Met and 10 mM EGTA, and were scored for germination after incubation at 22 °C for 36 h. Data in (A–C) are means (±SE) from three independent experiments. Significant differences were determined using Student’s t-test: **P<0.01. (D) [Ca2+]cyt-dependent FRET efficiency changes in WT and AtGLR3.5-RNAi plants in response to 1 mM L-Met. The primary roots of seedlings expressing yellow cameleon 3.60 (YC3.60) were used for the analysis and the time point when plants were treated with L-Met is indicated. Ten seedlings of each genotype were tested, and representative results are shown. (This figure is available in colour at JXB online.)
To obtain direct evidence that L-Met regulates AtGLR3.5-dependent fluctuations in [Ca2+]cyt, we performed FRET-sensitized emission imaging analysis and monitored the dynamics of changes in [Ca2+]cyt using plants harboring the Ca indicator protein YC3.60 (Kong et al., 2015). L-Met triggered a transient increase in [Ca2+]cyt in the root cells of WT seedlings, whilst this response was largely eliminated in the AtGLR3.5-RNAi seedlings (Fig. 2D). In contrast, L-Glu induced a rise in [Ca2+]cyt (Qi et al., 2006; Rincón-Zachary et al., 2010; Toyota et al., 2018) in both the WT and AtGLR3.5-RNAi seedlings (Supplementary Fig. S3), indicating that changes in [Ca2+]cyt triggered by L-Glu did not require AtGLR3.5. Consistent with these results, L-Met stimulated germination in the WT but not in AtGL3.5-RNAi and AtGL3.5 T-DNA insertion lines (Fig. 2A, B), whereas L-Glu had no obvious effects on germination in any of the genotypes (Supplementary Figs S4, S5). Taken together, these data indicated that L-Met activated the AtGLR3.5 Ca2+ channel and caused an increase in [Ca2+]cyt during seed germination.
AtGLR3.5 function is regulated by Met that is biosynthesized via Met synthase 1
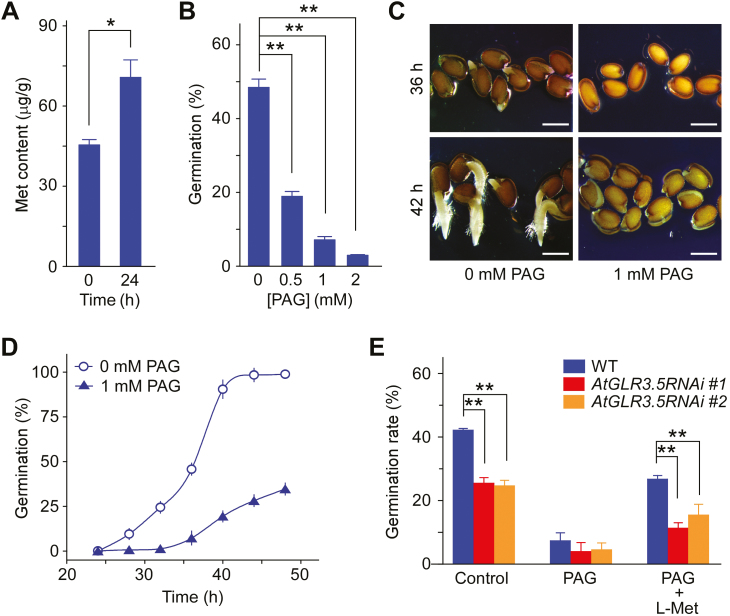
Since it promoted seed germination (Fig. 1A–C), we examined Met contents in germinating seeds at 0 h and 24 h after transfer to germination conditions. The Met content in the WT increased ~1.6-fold during this period (Fig. 3A). We then investigated the source of the Met that induced the AtGLR3.5-mediated increases in [Ca2+]cyt during germination. Met in plants can be produced either via de novo biosynthesis or via recycling (Gallardo et al., 2002; Amir, 2010; Willke, 2014). Given that germination is the earliest physiological step in the life cycle of a plant, we focused on biosynthesis. Pharmacological analyses showed that PAG, a Met-synthesis inhibitor (Thompson et al., 1982; Ravanel et al., 1998), retarded germination in a dose-dependent manner (Fig. 3B). As reported previously (Gallardo et al., 2002), PAG dramatically impeded seed radicle protrusion and germination (Fig. 3C, D), and this impairment could to some extent be lessened by supplementation with L-Met (Fig. 3E); however, this effect was much lower in AtGLR3.5-RNAi seeds. These data indicated that the de novo biosynthesis of Met was critical for AtGLR3.5-mediated germination.
Fig. 3.
The biosynthesis of methionine (Met) plays a role in AtGLR3.5-modualtion of seed germination in Arabidopsis. (A) Met contents in wild-type (WT) seeds at 0 h and 24 h after incubation of the seeds under germination conditions. (B) Germination of WT seeds with different concentrations of the Met-biosynthesis inhibitor DL-propargylglycine (PAG). Seeds were sown on half-strength MS media supplemented with the indicated concentrations of PAG and scored for germination after incubation at 22 °C for 36 h. (C) Germination phenotypes of WT seeds in the presence or absence of PAG. Seeds were sown on half-strength MS media supplemented with 0 mM or 1 mM PAG and were incubated at 22 °C for 36 h (top) or 42 h (bottom). Representative images of three biological replicates are shown. (D) Time-course of seed germination in the presence or absence of PAG. Seeds were sown in the same medium as in (C) and incubated at 22 °C. (E) Germination of AtGLR3.5-RNAi seeds in the presence of PAG (1 mM) or PAG plus Met (30 µM). Seeds were scored for germination after incubation at 22 °C for 36 h. Data in (A, B, D, E) are means (±SE) from three independent experiments. Significant differences were determined using Student’s t-test: *P<0.05, **P<0.01. (This figure is available in colour at JXB online.)
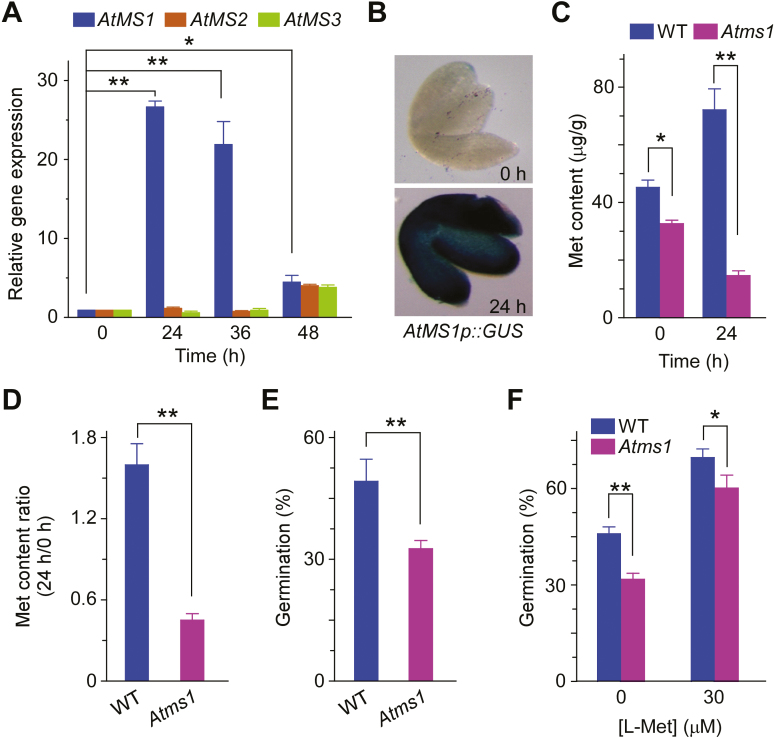
Met is synthesized in plants from O-phosphohomoserine (OPH) via three successive enzyme reactions, with vitamin B12-independent Met synthase being responsible for the final step (Ravanel et al., 1998; Gallardo et al., 2002). The Arabidopsis genome harbors three functional isoforms of Met synthase (AtMS) genes (Ravanel et al., 2004). To identify which of them was responsible for the production of the Met required for seed germination, we performed quantitative reverse-transcription PCR (qRT-PCR) analysis and found large changes in expression of AtMS1 (At5g17920) during germination (Fig. 4A). Transcript levels of AtMS1 peaked 24 h after the onset of germination and then decreased gradually until its completion. In line with the qRT-PCR data, transgenic seeds expressing the GUS reporter gene driven by a 2.0-kb promoter sequence of AtMS1 exhibited a significant increase in GUS activity after 24 h incubation under germination conditions (Fig. 4B). The AtMS1 transcription data are consistent with previous results from a proteomic study that showed that levels of the AtMS1 protein greatly increase 1 d after imbibition (Gallardo et al., 2002). To further assess the role of AtMS1 in germination, we isolated a T-DNA insertion mutant, Atms1, that has a reduced level of AtMS1 transcripts (Supplementary Fig. S6). The Atms1 mutant produced lower amounts of Met than WT seeds at both 0 h and 24 h under germination conditions (Fig. 4C), thus indicating a role of AtMS1 in Met biosynthesis during germination. Interestingly, in contrast to the WT (Fig. 3A), the Met content in the mutant decreased between 0 h and 24 h (Fig. 4C), which may have been attributable to consumption of a significant amount of Met during germination and the low amounts of Met biosynthesized in the mutant. The ratio of Met content at 24 h versus 0 h was much lower in the mutant than that in the WT (Fig. 4D), suggesting that the mutant had lower amounts of Met available for facilitating germination. In line with this result, the germination rate of Atms1 seeds was reduced relative to the WT (Fig. 4E). The germination rate in both the WT and the mutant was increased in the presence of exogenously supplemented L-Met (30 µM), but the effect was proportionally greater in Atms1 seeds (Fig. 4F), which implied that the reduced level of Met was the cause of lower germination in the mutant. The results from these experiments, together with those relating to the reduced sensitivity of AtGLR3.5-RNAi seeds to L-Met (Fig. 2A, B) and the reduced effect of L-Met applied to PAG-treated AtGLR3.5-RNAi seeds (Fig. 3E) compared to the WT, demonstrated that AtMS1-derived Met played an essential role in the regulation of seed germination by AtGLR3.5.
Fig. 4.
Methionine (Met) derived from AtMS1 positively regulates seed germination in Arabidopsis. (A) qRT-PCR analysis of AtMS1, AtMS2, and AtMS3 expression at 0–48 h during seed germination. Wild-type (WT) seeds were incubated in the dark at 4 °C for 3 d and transferred to a growth chamber at 22 °C for 0–48 h prior to the analysis. Expression is relative to that of ACTIN2. (B) Expression patterns of AtMS1 in seed embryos as indicated by AtMS1pro::GUS. The seeds were stratified and incubated in a growth chamber at 22 °C for 0 h or 24 h before GUS staining, and images were taken after the removal of seed coats. Representative images are shown. (C) Met contents in WT and Atms1 seeds. Seeds were incubated at 22 °C for 0 h or 24 h prior to the analysis. (D) The ratio of Met content at 24 h versus at 0 h at 22 °C in WT and Atms1 seeds based on the results in (C). (E) Germination of WT and Atms1 seeds. Germination was scored after incubation at 22 °C for 36 h. (F) Germination of WT and Atms1 seeds with or without treatment with L-Met. Seeds were scored for germination after incubation at 22 °C for 36 h. All data are means (±SE) from three replicates. Significant differences were determined using Student’s t-test: *P<0.05, **P<0.01. (This figure is available in colour at JXB online.)
Met differentially regulates the expression of AtGLR3.5 and ABI4 in germinating seeds
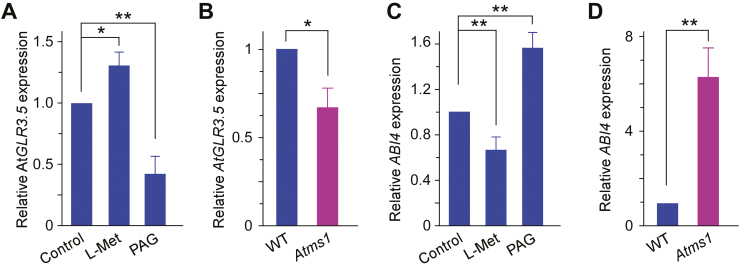
Our results indicated that Met induced AtGLR3.5-mediated increases in [Ca2+]cyt (Fig. 2D) and that it modulated AtGLR3.5-dependent seed germination (Fig. 2A). To further investigate the regulation by Met, we examined its effect on AtGLR3.5 expression. As shown in Fig. 5A, addition of L-Met up-regulated AtGLR3.5 expression, while the Met biosynthesis inhibitor PAG reduced its expression. In the Atms1 mutant with lower Met content, AtGLR3.5 transcript levels were significantly lower than in the WT (Fig. 5B). These data suggested that in addition to activation of the AtGLR3.5 channel, L-Met up-regulated AtGLR3.5 expression in germinating seeds. In our previous study, we observed that an AtGLR3.5-mediated increase in [Ca2+]cyt suppresses ABI4 expression in germinating seeds (Kong et al., 2015). Therefore, we examined the effect of Met on ABI4 expression. L-Met decreased the expression of ABI4, while PAG increased its expression (Fig. 5C). In addition, the transcript levels of ABI4 in the Atms1 mutant were ~6-fold higher than in the WT (Fig. 5D). Overall, these results suggested that L-Met acted upstream of the AtGLR3.5–Ca2+–ABI4 cascade in seed germination and that it antagonistically regulated the functions of AtGLR3.5 and ABI4.
Fig. 5.
Methionine (Met) modulates the expression of AtGLR3.5 and the key seed germination regulator ABI4 in Arabidopsis. (A) qRT-PCR analysis of AtGLR3.5 expression in wild-type (WT) seeds in response to treatment with L-Met (30 µM) or PAG (1 mM). (B) Expression of AtGLR3.5 in WT and Atms1 seeds. (C) Expression of ABI4 in WT seeds in response to L-Met (30 µM) or PAG (1 mM). (D) ABI4 expression in WT and Atms1 seeds. All seeds were incubated in the dark at 4 °C for 3 d and then transferred to 22 °C for 36 h prior to the analysis. Expression is relative to that of ACTIN2. Data are means (±SE) from three replicates. Significant differences were determined using Student’s t-test: *P<0.05, **P<0.01. (This figure is available in colour at JXB online.)
Discussion
Since the discovery of homologs of animal glutamate receptor Ca2+ channels in plant genomes (Lam et al., 1998), plant GLRs have been expected to function similarly to Ca2+ channels (Lacombe et al., 2001; Ward et al., 2009; Hedrich, 2012). Numerous studies have demonstrated the involvement of plant GLRs in Ca2+-associated developmental and physiological processes (Kim et al., 2001; Kang et al., 2004; Meyerhoff et al., 2005; Li et al., 2006, 2013; Cho et al., 2009; Michard et al., 2011; Mousavi et al., 2013; Vincill et al., 2013; Kong et al., 2015, 2016; Toyota et al., 2018). In addition, several reports have demonstrated that plant GLRs can be gated by amino acids such as D-Ser and L-Met, in a manner similar to their counterparts in animals (Qi et al., 2006; Michard et al., 2011; Tapken et al., 2013; Forde and Roberts, 2014; Kong et al., 2016). We have previously observed that AtGLR3.5 modulates [Ca2+]cyt and is essential for Arabidopsis seed germination (Kong et al., 2015), and therefore in the present study we investigated whether it is regulated by some amino acid(s). Using a pharmacological approach, we first demonstrated that regulation of seed germination by L-Met required AtGLR3.5 and Ca2+ signaling (Fig. 2A, B). Furthermore, using plants harboring the calcium marker protein YC3.60, we found that L-Met triggered a transient rise in [Ca2+]cyt in the primary roots of WT seedlings but that this was largely abolished in AtGLR3.5-RNAi seedlings (Fig. 2D). Together with the results from our previous study (Kong et al., 2016), this indicated that L-Met activates the AtGLR3.5-dependent increase in [Ca2+]cyt, thereby regulating germination. The positive effect of L-Met that we observed is consistent with previous studies of other plant GLRs (Tapken et al., 2013; Kong et al., 2016). Using the Xenopus oocyte heterologous expression system, Tapken et al. (2013) investigated the relative efficacy of all 20 common amino acids on AtGLR1.4 channel activity and found that L-Met was the most effective. Our recent in planta study showed that L-Met acts as an agonist on AtGLR3.1/3.5 heteromeric Ca2+ channels in the stomatal movement process (Kong et al., 2016). Our current findings, together with those of previous studies, highlight the regulation of plant GLR channel activity by ligand amino acids.
Our germination data (Fig. 2A, B) suggested that an AtGLR3.5-dependent increase in [Ca2+]cyt triggered by L-Met occurred in germinating seeds, and direct evidence for this could be obtained by monitoring the changes in [Ca2+]cyt in the embryo during seed germination. However, to our knowledge, no suitable technique is available to monitor [Ca2+]cyt in a tissue enveloped in the seed coat. Given that we and others have successfully recorded changes in [Ca2+]cyt in response to CaCl2 in the primary roots of young seedlings containing YC3.60 (Rincón-Zachary et al., 2010; Kong et al., 2015), we examined changes in response to L-Met treatment in seedling roots as a proxy for the germinating seeds. In this way, we demonstrated a role of exogenous L-Met in the AtGLR3.5-mediated increase in [Ca2+]cyt. These results together with the promotion by L-Met of AtGLR3.5-dependent seed germination (Fig. 2A, B) lead to the proposition that L-Met activation of AtGLR3.5 activity occurs in vivo during germination. However, because Met can be converted to other metabolites during germination, we cannot exclude the possibility that they might play a role.
An intriguing finding of our study was that although both L-Met and L-Glu triggered increases in [Ca2+]cyt in WT seedlings (Fig. 2D; Supplementary Fig. S3), only L-Met stimulated germination (Fig. 1; Supplementary Figs S4, S5). According to the eFP Browser (http://bar.utoronto.ca/efp/cgi-bin/efpWeb.cgi;Winter et al., 2007), AtGLR3.5 and AtGLR3.7 are the two AtGLRs that are highly up-regulated during the transition from dry to imbibed seeds. Histochemical analysis of transgenic seeds harboring AtGLR3.5p::GUS has shown that AtGLR3.5 is indeed highly up-regulated in imbibed seeds, suggesting that it plays a crucial role in germination (Kong et al., 2015). In contrast, GLR3.3 and GLR3.6, which are reported to be required for systemic increases in [Ca2+]cyt triggered by Glu (Toyota et al., 2018), show very low expression levels in imbibed seeds according to the eFP Browser. This is probably why the L-Glu treatment did not enhance seed germination despite the increases in Ca in the seedling roots (Supplementary Figs S3–S5). Furthermore, L-Met and L-Glu acted differently in WT and AtGLR3.5-RNAi plants: L-Met failed to trigger an increase in [Ca2+]cyt in AtGLR3.5-RNAi plants, whereas L-Glu triggered increases up to the WT level (Fig. 2D, Supplementary Fig. S3). These results indicate that the increase in [Ca2+]cyt evoked by L-Glu is independent of AtGLR3.5 and thus has no effect on seed germination.
Met is one of the essential amino acids and is of great nutritional significance, so its level determines the quality of crops and cereal-based human diets (Hesse et al., 2004; Galili and Amir, 2013). As a building-block for protein synthesis and a precursor of several key metabolites (Amir, 2010), Met is tightly intertwined with numerous indispensable cellular processes. The amount of synthase protein that catalyses the last step in Met biosynthesis increases greatly in 1-d imbibed seeds but rapidly decreases back to the dry seed level upon drying of the seeds, indicating the importance of Met in seed germination (Gallardo et al., 2002). However, the molecular function of Met in seed germination and the underlying signaling networks have remained largely unclear. Our study shows that L-Met acts as a positive regulator of seed germination: L-Met enhanced AtGLR3.5- and Ca2+-dependent seed germination (Figs 1D; 2A, B), triggered AtGLR3.5-mediated increases in [Ca2+]cyt (Fig. 2D), and repressed the expression of ABI4 (Fig. 5C), a component acting downstream of AtGLR3.5 in seed germination (Kong et al., 2015). Together with our previous work (Kong et al., 2015), this current study links Met to AtGLR3.5-mediated Ca2+ signaling and ABI4 during seed germination. In addition to its nutritional value and its role as a fundamental metabolite, we have shown that Met plays a signal role in modulating cellular events that facilitate plants to achieve the initial step in their life cycle, seed germination.
De novo biosynthesis provides a critical source of the Met required for germination. A previous proteomic study identified two Arabidopsis enzymes that are differentially accumulated during germination, both of which are associated with Met biosynthesis (Gallardo et al., 2002). Our findings further point to the significance of Met biosynthesis during germination. The fact that exogenously supplied Met promoted seed germination in a dose-dependent manner (Fig. 1A–C) suggested that there was an increase in Met content during germination, which was confirmed by GC-MS analysis (Figs 3A; 4C, D). In addition, treatment with the Met synthesis inhibitor PAG resulted in reduced germination (Fig. 3B–D), implying that de novo synthesis of Met is important for germination. We also demonstrated that the mRNA levels of AtMS1 were greatly increased (~25-fold) as seed germination began, reaching a maximum level at 24 h and then decreasing through to 48 h (Fig. 4A, B). Knocking out AtMS1 impaired Met biosynthesis as well as seed germination (Fig. 4C, E). Furthermore, our expression analysis data were consistent with a previous proteomics study that showed that Met synthase is induced during the first day of imbibition, prior to radicle emergence, but decreases on the second day of imbibition when the protrusion of the radicle occurs (Gallardo et al., 2002). Notably, the drastic change in AtMS1 expression levels (Fig. 4A) were very similar to the expression pattern of AtGLR3.5 during germination (Kong et al., 2015), suggesting a functional correlation between the two proteins in the control of seed germination. Our finding that addition of L-Met led to a lower degree of recovery in germination in the presence of PAG in the AtGLR3.5-RNAi plants than in the WT (Fig. 3E) further supports the importance of Met biosynthesis in the AtGLR3.5-dependent regulation of germination. Overall, we have demonstrated that Met biosynthesis by AtMS1 positively regulates the AtGLR3.5 channel during germination.
Met is not the only amino acid that increases during germination in Arabidopsis. Asp and Thr (which belong to the Asp family together with Met) also exhibit significant increases (>40-fold) during the transition from stratification to germination (Fait et al., 2006). Enhancing the metabolism of Lys, another member of the Asp family, alters the levels of other amino acids during early seed germination (Angelovici et al., 2011). It has also been reported that Met content is positively correlated with the levels of Lys or Thr in plants (Amir, 2010). In our present study, knocking-out of AtMS1 not only lowered the amounts of Met, but also reduced the levels of other Asp family amino acids (Supplementary Fig. S7). Since Thr also displayed a certain degree of promotional effects on germination (Supplementary Fig. S1), future examination of its role, as well as those of other amino acids not tested here, would provide more comprehensive insights into their functions during seed germination.
Given the wide range of roles of plant GLR channel-mediated Ca2+ signals in responses to various biotic and abiotic stimuli (Kim et al., 2001; Meyerhoff et al., 2005; Li et al., 2013; Mousavi et al., 2013; Ortiz-Ramírez et al., 2017; Cheng et al., 2018; Toyota et al., 2018) and the potential role of amino acids in stress resistance (Slama et al., 2015), the L-Met–AtGLR3.5–ABI4 cascade may function in response to external signals to control seed germination. Future studies are needed to elucidate the molecular mechanisms of amino acid and Ca2+ signals in the adaptive responses of plants under stress conditions.
Supplementary data
Supplementary data are available at JXB online.
Fig. S1. Effects of different amino acids on seed germination.
Fig. S2. Genotyping of AtGLR3.5 T-DNA insertion mutants and relative expression of AtGLR3.5 in the two independent alleles.
Fig. S3. Changes in [Ca2+]cyt in WT and AtGLR3.5-RNAi plants in response to 1 mM L-Glu as determined by changes in FRET efficiency.
Fig. S4. Germination of seeds of the WT and two independent AtGLR3.5-RNAi lines at different concentrations of L-Glu.
Fig. S5. Germination of WT, Atglr3.5-1, and Atglr3.5-2 seeds at different concentrations of L-Glu.
Fig. S6. Genotyping of the Atms1 mutant and relative AtMS1 transcript levels in the WT and mutant.
Fig. S7. Contents of Asp, Thr, and Lys in WT and Atms1 seeds.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Dr. Florent Villiers for assistance in data analysis and Drs. Magaly Rincón-Zachary and Elison B. Blancaflor for providing the YC3.6 seeds. We also thank Amy Beaven for confocal microscopy and Jin-Young Lee for assistance in the laboratory. This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31770296) and the Beijing Natural Science Foundation (6172002) to CJ, IBS-R013-G2 from the Institute for Basic Science and start-up funds from DGIST to JMK, and in part by Research Resettlement Funds (0409-20180189) from Seoul National University and by the BK21 Research Fellowship from the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology, Republic of Korea to YL.
References
- Amir R. 2010. Current understanding of the factors regulating methionine content in vegetative tissues of higher plants. Amino Acids 39, 917–931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angelovici R, Batushansky A, Deason N, Gonzalez-Jorge S, Gore MA, Fait A, DellaPenna D. 2017. Network-guided GWAS improves identification of genes affecting free amino acids. Plant Physiology 173, 872–886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angelovici R, Fait A, Fernie AR, Galili G. 2011. A seed high-lysine trait is negatively associated with the TCA cycle and slows down Arabidopsis seed germination. New Phytologist 189, 148–159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassel GW, Lan H, Glaab E, Gibbs DJ, Gerjets T, Krasnogor N, Bonner AJ, Holdsworth MJ, Provart NJ. 2011. Genome-wide network model capturing seed germination reveals coordinated regulation of plant cellular phase transitions. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA 108, 9709–9714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellieny-Rabelo D, De Oliveira EA, Ribeiro ES, Costa EP, Oliveira AE, Venancio TM. 2016. Transcriptome analysis uncovers key regulatory and metabolic aspects of soybean embryonic axes during germination. Scientific Reports 6, 36009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bewley JD. 1997. Seed germination and dormancy. The Plant Cell 9, 1055–1066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catusse J, Job C, Job D. 2008. Transcriptome- and proteome-wide analyses of seed germination. Comptes Rendus Biologies 331, 815–822. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y, Zhang X, Sun T, Tian Q, Zhang WH. 2018. Glutamate receptor homolog 3.4 is involved in regulation of seed germination under salt stress in Arabidopsis. Plant & Cell Physiology 59, 978–988. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho D, Kim SA, Murata Y, Lee S, Jae SK, Nam HG, Kwak JM. 2009. De-regulated expression of the plant glutamate receptor homolog AtGLR3.1 impairs long-term Ca2+-programmed stomatal closure. The Plant Journal 58, 437–449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clough SJ, Bent AF. 1998. Floral dip: a simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. The Plant Journal 16, 735–743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dekkers BJ, Pearce S, van Bolderen-Veldkamp RP, et al. 2013. Transcriptional dynamics of two seed compartments with opposing roles in Arabidopsis seed germination. Plant Physiology 163, 205–215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fait A, Angelovici R, Less H, Ohad I, Urbanczyk-Wochniak E, Fernie AR, Galili G. 2006. Arabidopsis seed development and germination is associated with temporally distinct metabolic switches. Plant Physiology 142, 839–854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feenstra AD, Alexander LE, Song Z, Korte AR, Yandeau-Nelson MD, Nikolau BJ, Lee YJ. 2017. Spatial mapping and profiling of metabolite distributions during germination. Plant Physiology 174, 2532–2548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Footitt S, Douterelo-Soler I, Clay H, Finch-Savage WE. 2011. Dormancy cycling in Arabidopsis seeds is controlled by seasonally distinct hormone-signaling pathways. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA 108, 20236–20241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forde BG, Roberts MR. 2014. Glutamate receptor-like channels in plants: a role as amino acid sensors in plant defence? F1000Prime Reports 6, 37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galili G, Amir R. 2013. Fortifying plants with the essential amino acids lysine and methionine to improve nutritional quality. Plant Biotechnology Journal 11, 211–222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galland M, Huguet R, Arc E, Cueff G, Job D, Rajjou L. 2014. Dynamic proteomics emphasizes the importance of selective mRNA translation and protein turnover during Arabidopsis seed germination. Molecular & Cellular Proteomics 13, 252–268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallardo K, Job C, Groot SP, Puype M, Demol H, Vandekerckhove J, Job D. 2001. Proteomic analysis of Arabidopsis seed germination and priming. Plant Physiology 126, 835–848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallardo K, Job C, Groot SP, Puype M, Demol H, Vandekerckhove J, Job D. 2002. Importance of methionine biosynthesis for Arabidopsis seed germination and seedling growth. Physiologia Plantarum 116, 238–247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han C, Yang P. 2015. Studies on the molecular mechanisms of seed germination. Proteomics 15, 1671–1679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedrich R. 2012. Ion channels in plants. Physiological Reviews 92, 1777–1811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesse H, Kreft O, Maimann S, Zeh M, Hoefgen R. 2004. Current understanding of the regulation of methionine biosynthesis in plants. Journal of Experimental Botany 55, 1799–1808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holdsworth MJ, Bentsink L, Soppe WJ. 2008. Molecular networks regulating Arabidopsis seed maturation, after-ripening, dormancy and germination. New Phytologist 179, 33–54. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jefferson RA, Kavanagh TA, Bevan MW. 1987. GUS fusions: beta-glucuronidase as a sensitive and versatile gene fusion marker in higher plants. The EMBO Journal 6, 3901–3907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang J, Mehta S, Turano FJ. 2004. The putative glutamate receptor 1.1 (AtGLR1.1) in Arabidopsis thaliana regulates abscisic acid biosynthesis and signaling to control development and water loss. Plant & Cell Physiology 45, 1380–1389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karimi M, Inzé D, Depicker A. 2002. GATEWAY vectors for Agrobacterium-mediated plant transformation. Trends in Plant Science 7, 193–195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim SA, Kwak JM, Jae SK, Wang MH, Nam HG. 2001. Overexpression of the AtGluR2 gene encoding an Arabidopsis homolog of mammalian glutamate receptors impairs calcium utilization and sensitivity to ionic stress in transgenic plants. Plant & Cell Physiology 42, 74–84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kong D, Hu HC, Okuma E, et al. 2016. L-Met Activates Arabidopsis GLR Ca2+ channels upstream of ROS production and regulates stomatal movement. Cell Reports 17, 2553–2561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kong D, Ju C, Parihar A, Kim S, Cho D, Kwak JM. 2015. Arabidopsis glutamate receptor homolog3.5 modulates cytosolic Ca2+ level to counteract effect of abscisic acid in seed germination. Plant Physiology 167, 1630–1642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacomber B, Becker D, Hedrich R, et al. 2001. The identity of plant glutamate receptors. Science 292, 1486–1487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam HM, Chiu J, Hsieh MH, Meisel L, Oliveira IC, Shin M, Coruzzi G. 1998. Glutamate-receptor genes in plants. Nature 396, 125–126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li F, Wang J, Ma C, Zhao Y, Wang Y, Hasi A, Qi Z. 2013. Glutamate receptor-like channel3.3 is involved in mediating glutathione-triggered cytosolic calcium transients, transcriptional changes, and innate immunity responses in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiology 162, 1497–1509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J, Zhu S, Song X, et al. 2006. A rice glutamate receptor-like gene is critical for the division and survival of individual cells in the root apical meristem. The Plant Cell 18, 340–349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyerhoff O, Müller K, Roelfsema MR, Latz A, Lacombe B, Hedrich R, Dietrich P, Becker D. 2005. AtGLR3.4, a glutamate receptor channel-like gene is sensitive to touch and cold. Planta 222, 418–427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michard E, Lima PT, Borges F, Silva AC, Portes MT, Carvalho JE, Gilliham M, Liu LH, Obermeyer G, Feijó JA. 2011. Glutamate receptor-like genes form Ca2+ channels in pollen tubes and are regulated by pistil D-serine. Science 332, 434–437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mousavi SA, Chauvin A, Pascaud F, Kellenberger S, Farmer EE. 2013. GLUTAMATE RECEPTOR-LIKE genes mediate leaf-to-leaf wound signalling. Nature 500, 422–426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakabayashi K, Okamoto M, Koshiba T, Kamiya Y, Nambara E. 2005. Genome-wide profiling of stored mRNA in Arabidopsis thaliana seed germination: epigenetic and genetic regulation of transcription in seed. The Plant Journal 41, 697–709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North H, Baud S, Debeaujon I, et al. 2010. Arabidopsis seed secrets unravelled after a decade of genetic and omics-driven research. The Plant Journal 61, 971–981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortiz-Ramírez C, Michard E, Simon AA, Damineli DSC, Hernández-Coronado M, Becker JD, Feijó JA. 2017. GLUTAMATE RECEPTOR-LIKE channels are essential for chemotaxis and reproduction in mosses. Nature 549, 91–95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penfield S, Li Y, Gilday AD, Graham S, Graham IA. 2006. Arabidopsis ABA INSENSITIVE4 regulates lipid mobilization in the embryo and reveals repression of seed germination by the endosperm. The Plant Cell 18, 1887–1899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qi Z, Stephens NR, Spalding EP. 2006. Calcium entry mediated by GLR3.3, an Arabidopsis glutamate receptor with a broad agonist profile. Plant Physiology 142, 963–971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajjou L, Duval M, Gallardo K, Catusse J, Bally J, Job C, Job D. 2012. Seed germination and vigor. Annual Review of Plant Biology 63, 507–533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajjou L, Gallardo K, Debeaujon I, Vandekerckhove J, Job C, Job D. 2004. The effect of alpha-amanitin on the Arabidopsis seed proteome highlights the distinct roles of stored and neosynthesized mRNAs during germination. Plant Physiology 134, 1598–1613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravanel S, Block MA, Rippert P, Jabrin S, Curien G, Rébeillé F, Douce R. 2004. Methionine metabolism in plants: chloroplasts are autonomous for de novo methionine synthesis and can import S-adenosylmethionine from the cytosol. The Journal of Biological Chemistry 279, 22548–22557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravanel S, Gakière B, Job D, Douce R. 1998. The specific features of methionine biosynthesis and metabolism in plants. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA 95, 7805–7812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rincón-Zachary M, Teaster ND, Sparks JA, Valster AH, Motes CM, Blancaflor EB. 2010. Fluorescence resonance energy transfer-sensitized emission of yellow cameleon 3.60 reveals root zone-specific calcium signatures in Arabidopsis in response to aluminum and other trivalent cations. Plant Physiology 152, 1442–1458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slama I, Abdelly C, Bouchereau A, Flowers T, Savouré A. 2015. Diversity, distribution and roles of osmoprotective compounds accumulated in halophytes under abiotic stress. Annals of Botany 115, 433–447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sreenivasulu N, Usadel B, Winter A, et al. 2008. Barley grain maturation and germination: metabolic pathway and regulatory network commonalities and differences highlighted by new MapMan/PageMan profiling tools. Plant Physiology 146, 1738–1758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tapken D, Anschütz U, Liu LH, Huelsken T, Seebohm G, Becker D, Hollmann M. 2013. A plant homolog of animal glutamate receptors is an ion channel gated by multiple hydrophobic amino acids. Science Signaling 6, ra47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson GA, Datko AH, Mudd SH. 1982. Methionine synthesis in Lemna. Inhibition of cystathionine gamma-synthase by propargylglycine. Plant Physiology 70, 1347–1352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyota M, Spencer D, Sawai-Toyota S, Jiaqi W, Zhang T, Koo AJ, Howe GA, Gilroy S. 2018. Glutamate triggers long-distance, calcium-based plant defense signaling. Science 361, 1112–1115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincill ED, Bieck AM, Spalding EP. 2012. Ca2+ conduction by an amino acid-gated ion channel related to glutamate receptors. Plant Physiology 159, 40–46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincill ED, Clarin AE, Molenda JN, Spalding EP. 2013. Interacting glutamate receptor-like proteins in phloem regulate lateral root initiation in Arabidopsis. The Plant Cell 25, 1304–1313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward JM, Mäser P, Schroeder JI. 2009. Plant ion channels: gene families, physiology, and functional genomics analyses. Annual Review of Physiology 71, 59–82. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weitbrecht K, Müller K, Leubner-Metzger G. 2011. First off the mark: early seed germination. Journal of Experimental Botany 62, 3289–3309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willke T. 2014. Methionine production—a critical review. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology 98, 9893–9914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winter D, Vinegar B, Nahal H, Ammar R, Wilson GV, Provart NJ. 2007. An “Electronic Fluorescent Pictograph” browser for exploring and analyzing large-scale biological data sets. PLoS ONE 2, e718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.