Abstract
Sanitary sewer overflows (SSOs) are a common problem across the United States. An estimated 23,000–75,000 SSOs occurred annually in 2004 discharging between 11 and 38 billion liters of untreated wastewater to receiving waters. SSOs release many contaminants, including engineered nanomaterials (ENMs), to receiving water bodies. Measuring ENM concentrations in environmental samples remains a key challenge in environmental nanotechnology and requires the distinction between natural and engineered particles. This distinction between natural and engineered particles is often hampered by the similarities in the intrinsic properties of natural and engineered particles such as particle size, composition, density, surface chemistry, and by the limitations of the available nanometrology tools. To overcome these challenges, we applied a multi-method approach to measure the concentrations and properties of TiO2 engineered particles (e.g., ENMs and pigments) including 1) multi-element single particle-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (ME-SP-ICP-MS) to identify elemental associations and to determine elemental ratios in natural particles, 2) total elemental concentrations and ratios calculated from total metal concentrations measured following total sample digestion to estimate engineered particle concentrations, and 3) transmission electron microscopy (TEM) to characterize engineered particle size and morphology. ME-SP-ICP-MS analysis revealed that natural TiO2 particles are often associated with at least one of the following elements Al, Fe, Ce, Si, La, Zr, Nb, Pb, Ba, Th, Ta, W and U, and that elemental ratios of Ti to these elements is typical of riverine particulates and the average crustal ratios, except for Pb likely due to anthropogenic Pb contamination. High TiO2 engineered particle concentrations up to 100 μg L−1 were found in SSOs-impacted surface waters. TEM analysis demonstrated the presence of regular-shape TiO2 particles in SSOs-impacted surface waters. This study provides a comprehensive approach for measuring TiO2 engineered particle concentrations in surface waters. The quantitative data produced in this work can be used as input for modeling studies and pave the road toward routine monitoring of ENMs in environmental systems, validation of ENM fate models, and more accurate ENM exposure and risk assessment.
Graphical Abstract
1. Introduction
Nanotechnology is a rapidly growing industry with global markets worth hundreds of billions of dollars1, high production volumes (thousands of metric tons) of engineered nanomaterials (ENMs, 1–100 nm in size)2, and development of hundreds of novel applications for ENMs3. Release of ENMs from consumer products is inevitable resulting in exposure of environmental systems to ENMs, and this exposure will increase with the rapidly-expanding production of ENMs4. Hence, there is an imminent need for indepth risk assessment of ENMs to ensure environmental and human health safety5. Risk assessment of ENMs requires an understanding of: 1) the inherent hazard (toxicity) of ENMs, and 2) the potential for exposure (i.e. environmental concentrations) to ENMs. So far, the risk-related research on ENMs had a strong focus on ENMs’ toxic effects (thousands of studies on ENM toxicity), whereas exposure assessment research is lagging behind. Data on ENM concentrations in different environmental compartments are currently largely based on model predictions6. So far, the consensus has been that ENMs (including TiO2) are likely to occur in the surface waters at very low concentrations (e.g., ng to low μg L−1 range)7,8. However, these predictions may suffer from significant uncertainties because they are based on modeling approaches that have not been validated against field measurements9. Additionally, modeling approaches provide average concentrations over broad environmental compartments such as soil, air, water, etc10,11. However, releases greater than these predicted averages are likely to occur in localized regions, in particular at the point of discharge8. There are currently few reported experimentally determined concentrations of ENMs in the environment and these values are in line with the modeled exposure concentrations7,8,12. For example, low concentrations of TiO2-containing particles were reported in Clear Creek in Golden, Colorado (0.4–110 ng L−1)8 and in the Old Danube lake water during (e.g., 1.7 to 27.1 μg L−1) due to TiO2 input from sunscreens12.
TiO2 ENMs are the most widely produced and used type of ENMs2, but the production and use of TiO2 ENMs represent a minute fraction of the overall use of TiO2 engineered particles (e.g., ENMs and pigments). The global consumption of TiO2 is estimated at 6.1 million metric tons in 2016 and is projected to reach 8.83 million metric tons by 202513. TiO2 is the most widely used white pigment due to its brightness and capacity to reflect light. The theoretical optimum average particle size for TiO2 pigments for coatings is between 100 and 300 nm in diameter. However, TiO2 pigments cover a range of size distributions extending from the nanorange to several hundreds of nanometers14. Thus, the majority of TiO2 pigments contains a fraction of TiO2 ENMs2. The major applications of TiO2 are architectural and industrial paints and coatings (60%), plastic (28%), paper (5%), and other applications (7%)13. Other uses of TiO2 include catalysts, ceramics, coated fabrics, floor covering, printing ink, and roofing granules15. TiO2 is also commonly used in many foods, cosmetics, toothpaste, and in sun blocks. Current applications for TiO2 ENMs fall into the small category of “others”, which has historically represented a small percentage (e.g., 7% or 0.427 million metric tons) of the global TiO2 use.
TiO2 used in foods (pigment size), cosmetics, toothpaste, and in sun blocks (ENMs) are likely to end up in municipal wastewater. The concentration of TiO2 ENMs in waste water influent and effluent was estimated, based on mass flow models, to be approximately 100–200 and 10–70 μg L−1 16. The measured concentrations of titanium in waste water treatment plants influent vary from 181 to 1233 μg L−1 (median of 26 samples was 321 μg L−1) and those in the effluent were less than 25 μg L-1. Another study reported the concentration of Ti in waste water treatment plant influent and effluent to be 3500 and 710 μg L−1 17. Sanitary Sewer overflows (SSOs) are a common problem across the United States. An estimated 23,000–75,000 SSOs occurred annually in 2004 discharging between 11 and 38 billion liters of untreated wastewater to receiving waters18. SSOs release many contaminants, including ENMs, to receiving water bodies. Thus, SSOs offer a direct route of TiO2 engineered particles to surface waters.
Release and exposure assessment of ENMs in environmental systems remain a key challenge in environmental nanotechnology19 due to the significant unsolved challenges in detection and quantification of ENMs in the natural environment20. Measuring ENMs in environmental samples can be impeded by 1) high background concentration of natural nanomaterials (NNMs, ca. 1 to 1000 mg L−1 in fresh waters) 21, 2) low environmental concentrations of ENMs10,22, 3) similarity ofthe physicochemical properties of ENMs and NNMs, 4) similarity of the elemental composition of ENMs and larger size engineered particles (e.g., TiO2 ENMs and pigments), 5) transformation processes altering the properties of ENMs, and 6) underdeveloped methodologies for accurately characterizing ENMs and NNMs with sufficient specificity and sensitivity. Whereas there are several analytical techniques suitable for analysis of pristine ENMs, only a few analytical approaches are adequate for detection and quantification of ENMs in complex environmental samples23. The basic concept of the applied methodologies is to measure ENMs by tracing their physiochemical properties (e.g. elemental composition24, elemental ratios12,25, size and morphology26, fluorescence27) which are expected to be different compared to their natural homologues. Spectroscopic approaches, such as inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (ICP-MS), and energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS) coupled to transmission electron microscopy (TEM), are the most widely used methods for analysis of metal ENMs in complex samples due to their chemical specificity25. More recently, multi element-single particle inductively coupled plasma-mass spectroscopy (ME-SP-ICP-MS) has been applied to differentiate natural and engineered particles (e.g., CeO228 and TiO27). Although each of these analytical techniques has its own limitations, together they provide complementary data on the occurrence, concentrations, and properties of ENMs in surface waters.
This study aims at quantifying concentrations and characterizing the properties of TiO2 engineered particles in surface waters impacted by SSOs. In this contribution, we describe in detail how we identified TiO2 engineered particle contamination, how we differentiated engineered from naturally occurring TiO2 particles, and how we quantified the concentrations of TiO2 engineered particles in surface waters receiving SSOs.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling sites
Water samples were collected once per month from December 2015 to March 2016, following Hurricane Joaquin. Surface water samples were collected from Crane Creek, Stoop Creek, and Gills Creek, which discharge into rivers that feed the Congaree River in Columbia, South Carolina, United States (Figure 1). These sites were selected because each site had a history of SSOs and/or other sewage-related issues61. Crane Creek discharges into the Lower Broad River, which is the intake for Columbia drinking water supply. Stoop Creek discharges into the Lower Saluda River, which is a popular site for recreational activities (e.g., tubing and kayaking). For Stoop Creek, surface water samples were collected routinely from a wastewater treatment facility effluent outfall (S2), upstream from the outfall (S1, approximately 100 m), directly below the outfall S3 (within two to three meters of the outfall), and one site further downstream from the outfall (S4, approximately 90 m downstream from the outfall). Another sample was collected on Stoop creek on Feb 17th and March 30th after discovering a ruptured sewer force main (S5) (approximately 120 m downstream from the outfall). It has been estimated that the sewage discharged from the ruptured main may have been as high as 19 million liters because the sewage overflow was not reported for over a month. The incident was discovered by our team and reported to the South Carolina Department of Health and Environmental Control; repairs were completed within 48 hours29. At Crane Creek, samples were collected in a ditch (C1), which funneled untreated sewage released from a manhole into crane creek and downstream (C2) (approximately 50 m downstream from the ditch). At Gills Creek, sample were collected from one site (G1), which was ~1.6 km downstream from Lake Katherine, where SSOs occurred routinely. Additionally, eight reference water samples were collected from Lake Katherine and Gills creek in the absence of SSOs in January 2018.
Figure 1.
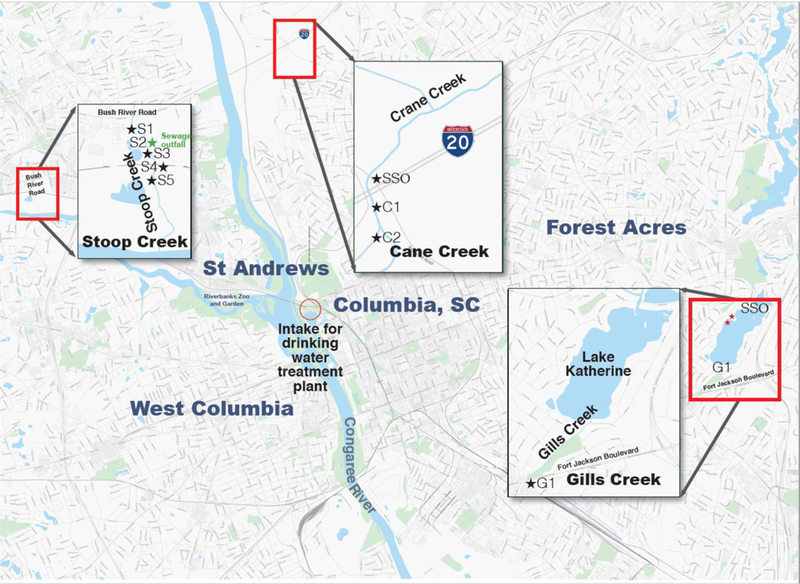
A map of Columbia, South Carolina, illustrating sampling sites. Water samples were collected once per month from December 2015 to March 2016 from Crane Creek, Stoop Creek, and Gills Creek, which discharge into the Congaree River, following Hurricane Joaquin. These sites were selected because each site had a history of sewage spills (SS) and/or other sewage-related issues.
2.2. Sample collection
Surface water samples were collected in 1 L high density polyethylene bottles (Thermo Scientific, USA). Prior to use, bottles were acid-washed in 10% nitric acid (Acros Organics, Czech Republic) for at least 24 hours, and soaked in ultrahigh purity water (PURELAB Option-Q, ELGA, UK) for 24 hours, air dried, and then double-bagged. In the field, the sampling bottles were rinsed three times in the surface water and then filled with the water sample, samples were individually double-bagged, and returned to the lab the same day.
2.3. Sample Digestion and elemental analysis
Trace metal concentrations of the water samples were determined by ICP-MS after complete digestion. The water samples were digested in 15 mL Teflon vessels (Savillex, USA) on custom-made Teflon covered hotplates placed in a box equipped with double-HEPA filtered forced air in a metal-free HEPA filtered air clean lab. A 10 mL water aliquot was placed in the vessel and weighed (Mettler Toledo, Excellence Plus, Switzerland). Samples were dried down at 110°C and treated with 1 mL of 30% H2O2 (Fisher Chemical, USA) for 2 h at 70°C to remove organic matter. H2O2 was then evaporated and the sample was digested with 2 mL of HF: HNO3 (3:1) mixture (ACS grade acids distilled in the laboratory) for 24 h at 110°C. After evaporation of the acid mixture at 110°C, the residue was reacted with 1 mL of distilled HNO3 to break up insoluble fluoride salt that may have formed during the sample digestion and HNO3 was left to evaporate at 110°C. This step was repeated twice before weighing the sample and adding 5 mL of 2% HNO3. The sample was sonicated for 10 min in a sonication bath (Branson, 2800, 40kHz, Mexico) and warmed for 2 h at 50°C for full dissolution. The solution was transferred to 15 mL polypropylene centrifuge tubes (Eppendorf, Mexico) and stored at 4°C. Samples were centrifuged (Eppendorf, 5810 R, Germany) for 5 min at 3,100 g prior ICP-MS analysis to remove any undigested minerals.
Elemental concentrations of the digested water samples were analyzed by high resolution inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometery (ICP-MS) (ThermoFisher Element II)30. Samples were injected to the ICP-MS using a quartz cyclonic spray chamber and a 100 μl min−1 PFA nebulizer (~120–150 μL min−1 actual uptake). The isotopes measured were 107Ag, 27Al, 139Ba, 111Cd, 140Ce, 59Co, 53Cr, 133Cs, 63Cu, 163Dy, 167Er, 151Eu, 57Fe, 69Ga, 157Gd, 178Hf, 165Ho, 115In, 139La, 7Li, 175Lu, 25Mg, 55Mn, 93Nb, 146Nd, 60Ni, 208Pb, 141Pr, 85Rb, 45Sc, 149Sm, 118Sn, 88Sr, 181Ta, 159Tb, 232Th, 47Ti, 169Tm, 238U, 51V, 89Y 173Yb, 66Zn,90Zr. Elements with potential interferences (e.g., Al, Ca, Co, Cr, Cu, Fe, Ga, Mg, Mn, Ni, Ti, V, and Zn) were measured in medium resolution (m/Δm=4000), while the rest in low resolution for maximum sensitivity (m/Δm=300). Concentrations were calculated against a multi-element standard solution composed of a mixture of IV- ICPMS-71A (ICP-MS Complete Standard, Inorganic Ventures) and ICP-MS-68A-B (68 Element Standard, High-Purity Standards) multi-element standards.
Full procedural digestion blanks for titanium and niobium was < 4% of samples’ analyte signal. Therefore, blanks are insignificant to the calculations of Ti concentrations or total Ti/Nb elemental ratios. The elemental concentrations of the USGS reference materials BCR-2 and BIR −1 basalts run as unknowns after digestion following the digestion procedure described above demonstrate high recovery (approximately 100%) for most elements Table S1. This Table further demonstrates the precision (2–3%) and accuracy of our method (e.g., better than 5% for most elements, including Ti, and Nb).
2.4. Calculation of total TiO2 engineered particle concentration
The natural elements present in natural Ti-particles were used to distinguish natural and engineered TiO212. Whereas TiO2 engineered particles are relatively pure, naturally occurring TiO2 particle contain other elements such as Nb, Ta, W, Zr, Fe, U, Pb, and Ba12. Here we used Ti/Nb ratio to differentiate natural TiO2 particles from TiO2 engineered particles released from SSOs to surface waters. The concentration of TiO2 engineered particles was calculated according Eq. 1
| (Eq. 1) |
Where, [TiO2]engineered particles is the concentration of TiO2 engineered particles, TiMM and TiO2 MM are the molar masses of Ti and TiO2, Ti/Nb is the mass ratio of Ti to Nb. Background Ti/Nb ratios were calculated on eight reference samples collected from Lake Katherine and Gills creek in the absence of SSOs.
2.5. Multi-element single particle-ICP-MS
Water samples were treated with tetrasodium pyrophosphate (Alfa Aesar, Analytical grade, Japan) to break engineered-natural particle heteroaggregates (Figure S1) and thus release engineered and natural particles as primary particles and/or as small aggregates31. Briefly, 4 ml of 100 mM sodium pyrophosphate was added to 36 ml water sample in 50 ml centrifuge tubes (Eppendorf, Mexico). The mixture was stirred overnight in a tube rotator at 30 rpm (Fisher Scientific, China) and then sonicated in a batch sonicator for 1 hour. The 450 nm size fraction was then separated by centrifugation (Eppendorf, 5810 R, Germany) at 2,000 × g for 30 min based on a particle density of 2.5 and Stokes’ law calculation32 and top 30 ml of the supernatant was collected for further analysis.
Multi-element single particle ICP-MS (ME-SP-ICP-MS) was conducted on an inductively coupled plasma-time of flight-mass spectrometer (ICP-TOF-MS, TOFWERK, Switzerland). Detailed description of the instrument and its analytical performance for single particle analysis is reported in a previous study33. Samples were diluted in ultrahigh purity water by a factor of 10 prior to the analysis. The ME-SP-ICP-MS measures all isotopes simultaneously at a sampling rate of 33 kHz. The spectral data, however, was pre-averaged before readout, resulting in integration time of 1.8 ms. Elemental mass in single particles was quantified using the method reported by Pace et al. 34 Element specific instrument sensitivities were measured with a multi-element solution mix prepared from a multi-element solution (SPEX CertiPrep, USA) and a Nb single element standard (InorganicVentures, USA). The transport efficiency was calculated using the known size method as described by Pace et al34 using both Au nanoparticles with the certified particle size of 60 nm (NIST, USA) and Au standard solutions prepared in ultrahigh purity water.
Transient particle signal processing was performed using a Python script, to automatically identify particle signals from the entire data set and to obtain quantitative results for particle mass, and particle number concentration from mass-calibrated ICP-TOF-MS spectra. For all time-series, time-resolved particle/baseline signal separation was performed using a running window of 100 data points (each data point represents an average of 60 single complete mass spectra). For each such window, means and standard deviations (σ) of the means were calculated for every single isotope. A threshold for particle detection was calculated for every single isotope according to Eq. 2, where the (3.29σ+2.71) term describes low intensity noise more accurately than 3* σ35. The mean was added to correct for the signal offset arising from dissolved ions, whose concentration was sample specific.
| (Eq. 2) |
The threshold was calculated for an interval of 100 points at a time. All peaks of a particular isotope exceeding the threshold in this interval were selected as particle signals and extracted from the dataset. This process was repeated iteratively for the same interval up to ten times for each isotope, or until no more peaks were detected. The signal fraction arising from dissolved ions, mean counts/1.8 ms integration time, was subtracted from peak signals for each interval of 100 points. Some peaks – corresponding to particle events – were split between two or maximum three integration times (1.8 ms integration time). These split-peak signals were summed up after peak/background subtraction and reported as a single particle.
The number concentration of TiO2 particles was calculated from the total number of Ti signal spikes detected by ME-SP-ICP-MS after split-peak correction, transport efficiency of the sample introduction system, and total sample volume measured. The intensities of the liquid calibration series were fitted using a linear regression, giving sensitivities in counts/g (mass of analyte was determined using transport efficiency and liquid uptake flow rate as described elswhere34). The results of these calibrations were used to convert particle signal intensities into element masses, while propagating the fit error to the quantified values. The data for every isotope were treated separately, but the time stamps were kept throughout data processing for every isotope, allowing for identification of isotope correlations in a single particle. For example, if 48Ti and 93Nb signal spikes have the same time stamps, they are assumed to be generated from the same particle. If no other isotopes are detected together with 48Ti, Ti is considered to be a pure TiO2 particle. For these particles, masses were converted to sizes, assuming spherical particle shape, pure TiO2 composition and density of 4.2 g/cm3.
2.6. Transmission electron microscopy
Extensive TEM analysis was performed to obtain visual evidence of the presence of engineered particles in samples by looking at the distinct morphological properties of engineered compared to natural particles. Overall, samples from 7 sites (Crane C1, C2, Gills G1, Stoop S1, S2, S3, and S4) were observed during two sampling campaigns (December 15th and January 18th). TEM samples were prepared by ultracentrifugation of natural waters (4 mL) at 150,000 g for 60 minutes using a Sorvall TM MTX 150 Micro-Ultracentrifuge (ThermoFisher Scientific, USA) with a S52-ST swinging-Bucker Rotor on a TEM grid36. A Teflon insert was placed at the bottom of the centrifuge tubes to create a flat surface that supports the 300 mesh Cu TEM grid (Ted Pella, Pelco®, USA). Natural waters were diluted 5–25 folds to avoid overloading of the TEM grids with natural particles. The surface of the TEM grids was functionalized with a positively charged poly-L-lysine polymer (Sigma Aldrich, USA) to enhance particle retention on the grids. For TEM grid surface functionalization, the TEM grids were covered with a droplet of 0.1% poly-L- lysine for 15 minutes followed by rinsing three consecutive times in ultrahigh purity water to remove excess poly-L-lysine.
Samples were analyzed on a LaB6 Jeol 2100 Transmission Electron Microscope, operated at 200 keV and equipped with a Jeol EX-230 Silicon Drift Detector (SDD) with a 60 cm2 window of acquisition for Energy Dispersive Spectra (EDS) of elements. Micrographs were acquired at different magnifications, ranging from 500× to 400,000×, to gather information about the average size, morphology and degree of agglomeration of nanomaterials on the grid.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Initial discovery of TiO2 engineered particles
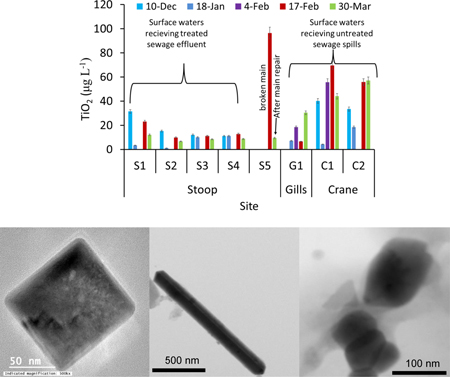
Water total metal concentrations showed temporal and spatial variations for all investigated metals (Figure 2 and S2). In, Sn, Cd, Ni, Cu, Zn, and Ag had relatively small variability among all samples (Figure S2a-f). The concentrations of Ti, Nb, Ta, Zr, Hf, Ce, La, Fe, and Pb were generally higher in waters receiving SSOs (Gills Creek, and Crane Creek, G1, C1 and C2) compared to those receiving waste water treatment effluents (Stoop Creek, S2, S3 and S4, Figure 2 and S2g-l). Titanium concentrations were 6–68 μg L−1 in the samples collected upstream of the sewage treatment outfall (S1), 1–25 μg L−1 in the samples collected from the outfall of the sewage treatment facility effluent (S2) and downstream of the sewage treatment effluent (S3-S4, Figure 1a). Total Ti concentration was 95 μg L−1 further downstream in Stoop Creek (S5) on February 17th, which decreased to 14 μg L−1 on March 30th. Site S5 directly received sewage from a broken force main on February 17th, which was repaired prior to the sampling on March 30th. Ti concentrations were 8–150 μg L−1 in the samples collected from Gills and Crane Creek waters. These two creeks (G1, C1, and C2) often received SSOs following intense rain events in Columbia, South Carolina, USA (Table S2). The high Ti concentration in site S1 could be due to upstream input, potentially SSO upstream of the sampling site, which was not investigated in this study. The high Ti concentrations in surface waters receiving SSOs (S5, G1, C1 and C2) compared to those in surface water receiving waste water treatment effluents (S2-S4) provides initial evidence that SSOs are a source of elevated Ti concentrations in receiving surface waters, likely in particulate form due to the low TiO2 solubility in surface waters37. The number particle concentration of all Ti-containing particles in S5, measurd by ME- SP-ICP-MS, decreased by 82% (Figure 3a) after the repair of the broken main (March 30th) compared to that measured during the sewage spill (February 17th). Additionally, the number concentration of all Ti- containing particles was higher in sites G1, C1 and C2 compared to those measured in S5 March 30th. These findings provide further support that the increase in Ti concentration is due to particle discharge with SSOs. However, total elemental concentration and total number particle concentrations do not allow differentiating natural from engineered TiO2 particles. ME-SP-ICP-MS measures all elements in a single particle and thus can be used to identify elemental associations and ratios within individual particles, and ultimately differentiating natural from engineered particles.
Figure 2.
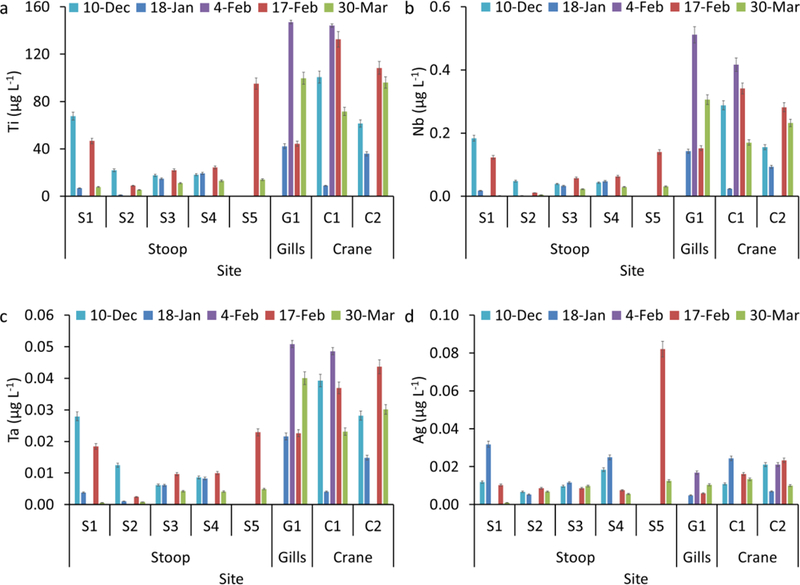
Total concentration of a selected set of elements (a) Ti, (b) Nb, (c) Ta, and (d) Ag in surface waters collected from Stoop, Gills and Crane creeks.
Figure 3.
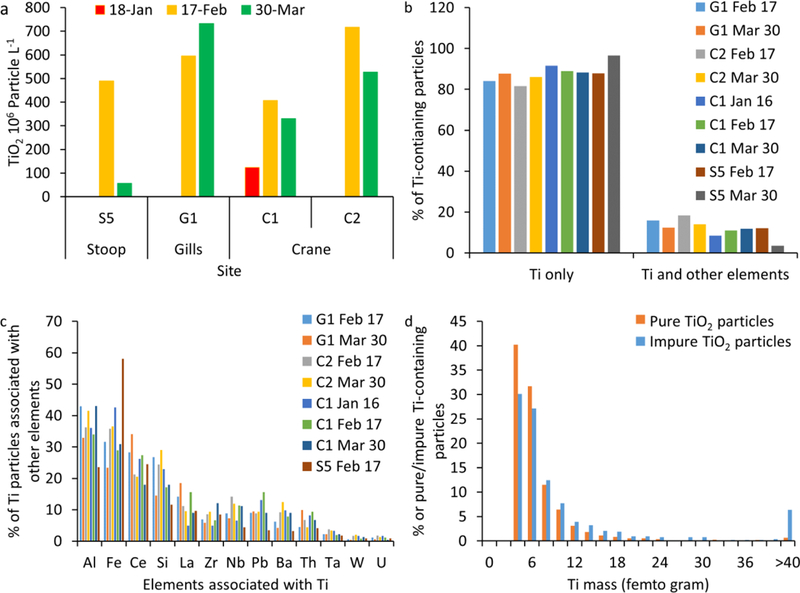
(a) Total number particle concentration of Ti-containing particles measured by multi-element single particle-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectroscopy (ME-SP-ICP-MS), (b) % of particles containing Ti only and particles containing Ti and other elements, (c) % of Ti particles associated with other elements, and (d) mass distribution of pure and impure Ti-containing particles.
3.2. Elemental associations and ratios in natural TiO2 particles
ME-SP-ICP-MS analysis was conducted on individual particles from selected samples, notably those with high Ti concentrations, to identify which elements and at which quantity are associated with Ti on a particle-per-particle basis. The majority of Ti-containing particles (e.g., 82–97%) contained Ti only (Figure 3b). The remaining (e.g., 3–18%) Ti-containing particles contained at least one of the following elements at a level higher than the ME-SP-ICP-MS limit of detection: Al, Fe, Ce, Si, La, Zr, Nb, Pb, Ba, Th, Ta, W and U (Figure 3c). Both pure and impure Ti-containing particles exhibit the same mass distribution (Figure 3d). Natural TiO2 minerals (e.g., rutile and ilmenite) have been shown to be the dominant carrier (>90–95% of the whole rock content) for Ti, Nb, Ta, Sb, and W as well as an important carrier (5–45% of the whole rock content) for V, Cr, Mo, and Sn in TiO2-bearing metamorphic rocks38,39. Additionally, naturally occurring TiO2 minerals could be associated with Zr, Fe, U and Pb40. These elemental impurities are generally removed during the manufacturing of TiO2 engineered particles from natural parent minerals by dissolution and reprecipitation as TiO2 particles, resulting in pure TiO2 particles41. However, all TiO2 engineered particles, except TiO2 used as a food additive, contain 1% to 15% of artificial coatings by weight, most commonly oxyhydrates and oxides of silicon and aluminum42. Therefore, the information on elemental associations alone is not sufficient to differentiate natural from engineered particles as some of these elements such as Al, Si, and Zr are associated with TiO2 natural particles and are used as coatings on the surface of TiO2 engineered particles. Therefore, elemental ratios were quantified on single particles to see whether they can serve as fingerprints for natural and engineered TiO2 particles.
Elemental ratio calculations are illustrated for TiO2 particles measured in Gills creek (G1, 2/17th/2016, Figure 4). A total of 18,333 particles were measured by ME-SP-ICP-MS in G1 (2/17th/2016) sample, among which 3,348 particles contained Ti, among which 2,817 contained Ti only and 531 contained Ti and at least another element (e.g., 295, 112, 75, 31, 8, 6, 2, 1, and 1 particles contained 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, and 11 elements in addition to Ti, respectively). The majority of Al- and Si-containing TiO2 particles (e.g., 66% and 93%, respectively) were also associated with other elements. Elemental ratios of Ti to Al and Si varied between 0.02 to 0.4 (Figure 4a and b). Most of the particles had a Ti/Al <0.2 and Ti/Si < 0.1, which is consistent with natural clays, average riverine particulates, and the average crustal ratios (Table S3). These elemental ratios are lower than those (e.g., Ti/Al = 9,7) measured in a commercial sunscreen products7, and generally lower than the ratios expected from Al- and Si- coated TiO2 particles (e.g., Ti/Al, or Ti/Si = 6.7100 based on a 1–15% coating content)42. Most of Fe-containing TiO2 particles (66%) were also associated with other elements. The elemental ratios of Ti to Fe (Figure 4c) are typical of natural TiO2 particles such as ilmenite (FeTiO2, Ti/Fe = 0.86), pseudobrookite (Fe2TiO5, Ti/Fe = 0.43) and pseudorutile (Fe2Ti3O9, Ti/Fe = 0.29). The elemental ratios of Ti to Ce (Figure 4d), Zr (Figure 4e), Nb (Figure 4f), Ba (Figure 4g) were in agreement with the average riverine particulate and/or crustal material elemental ratios (Table S3). Thus, the elemental ratios on single particles of Ti to Al, Si, Fe, Ce, Zr, Nb, and Ba show a dominant contribution from crustal sources, consistent with material mobilized in riverine systems (as average river particulate), average upper continental crust ratios, and natural minerals, indicating that impure TiO2 particle are natural particles. The elemental ratios of Ti to Pb (Figure 4h) were lower than the average river particulates, which might be attributed to enrichment in Pb from anthropogenic sources. Nonetheless, the majority (85%) of Pb-containing particles were also associated with other elements such as Ce, La, Ba, and Nb which were attributed to natural TiO2 particles, indicating that these Pb-containing Ti particles are natural particles. Only few measured TiO2 particles contained W (3), Sn (4), U (6), Ta (12), and Th (24), and thus, the elemental ratios of Ti to these elements were not investigated. This is the first time, to the best of our knowledge, that these elemental associations and ratios of Ti to natural elemental tracers have been identified and quantified on an individual particle basis. These findings are indicative of the considerable advantages offered by the ME-SP-ICP-MS in identifying natural tracers of natural particles, which will be extended to other types of particles in the future.
Figure 4.
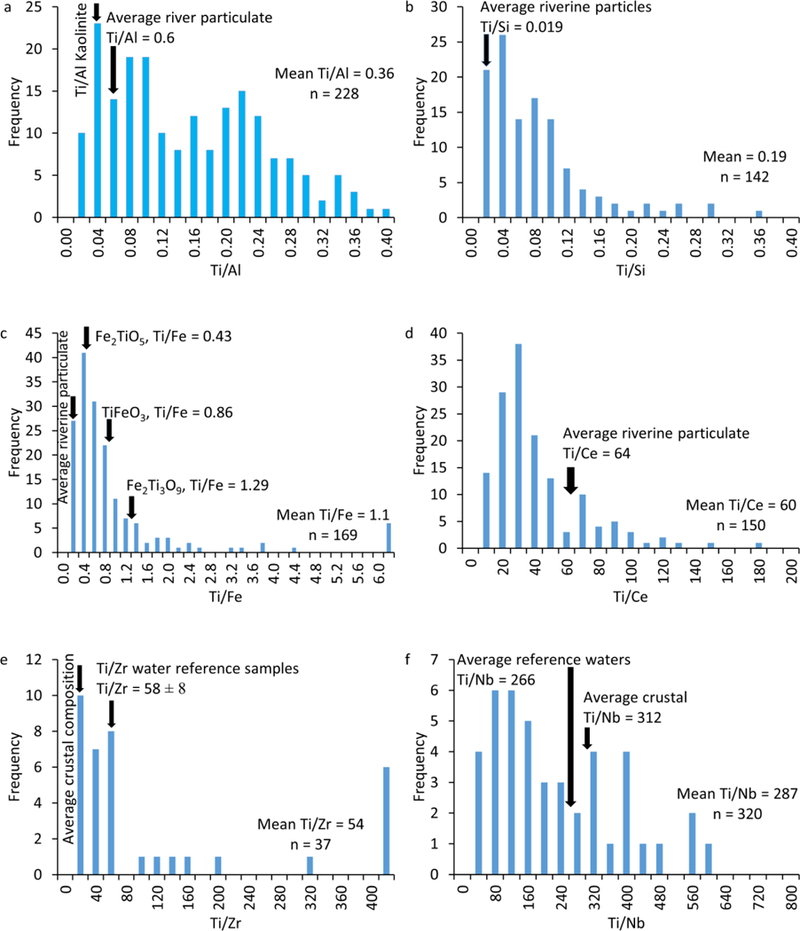
Elemental ratio distribution occurring in individual particles in a representative water sample (G1, 17 February 2016): (a) Ti to Al, (b) Ti to Si, (c) Ti to Fe, (d) Ti to Ce, (e) Ti to Zr, (f) Ti to Nb, (g) Ti to Ba, and (h) Ti to Pb. The average river particulate elemental ratios, average crustal elemental ratios, or elemental ratio in natural minerals are also presented for comparison. The mean elemental ratios and the number of counted particles are presented in the figures.
The elemental ratios on single particle of Ti to Nb and Zr were in good agreement with those measured in water samples from reference background sites. This suggests that these Nb and Zr are most likely exclusively associated with natural Ti-bearing particles. Natural TiO2 minerals (e.g., rutile and ilmenite) have been shown to be the dominant carrier (>90–95% of whole rock content) for Nb, Ta, Sb, and W38,39. The elemental ratios on single particle of Ti to Al, Fe, Ce, Ba, and Pb were higher than those measured in water samples from reference background sites. This suggests that these elements are not exclusively associated with Ti bearing particles. These elements can be associated with other natural and/or engineered particles such as clays, iron oxides, and cerium oxides. Therefore, Nb was selected as a tracer of natural Ti- particles and the Ti to Nb ratio was used to quantify the total concentration of TiO2 engineered particles.
3.3. Quantification of the total concentrations of TiO2 engineered particle
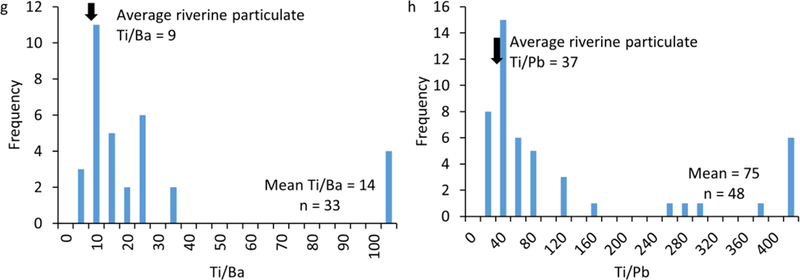
Elemental ratios of Ti to Nb calculated on total metal concentrations in the water samples were used to calculate the total concentrations of TiO2 engineered particles in the water samples, by estimating the Ti attributed to natural and engineered TiO2 particles. The background elemental ratio (Ti/Nb = 266±9) was determined as the average elemental ratio of 8 water samples collected from the different sampling sites in the absence of SSOs (dashed line, Figure 5a). Thus, the limit of detection (mean + 3σ) and the limit of quantification (mean + 10σ) for TiO2 engineered particles based on Ti/Nb ratio is 293 and 356, respectively. All measured Ti/Nb ratios were > the limit of detection indicating the presence of TiO2 engineered particles. The majority of measured Ti/Nb ratios were higher than the limit of quantification (Figure 5a). Ti/Nb are higher in the samples with low total Ti concentrations (S1-S4) compared to those with higher total Ti concentrations (S5, G1, C1 and C2), which we attribute to the higher concentration of natural TiO2 particles in the samples with higher Ti concentrations, thus reducing the impact of TiO2 engineered particles on increasing the overall Ti/Nb ratios.
Figure 5.
(a) Elemental ratios of Ti to Nb in the bulk water samples compared to natural background Ti to Nb ratio (dashed line). (b) Total TiO2 engineered particle concentration in surface waters calculated using Ti to Nb elemental ratios and total Ti concentrations in the bulk water samples. LoD and LoQ indicates the Ti to Nb ratios corresponding to the limit of detection and limit of quantification for TiO2 engineered particles.
The concentration of TiO2 engineered particles in the sewage overflow in site S5 from the ruptured main was approximately 97 μg L−1 (Figure 5b), which is within the range of reported TiO2 concentrations in raw sewage43,44. The ruptured main was reported to the authorities and was repaired. This resulted in the decrease in TiO2 concentration to 10 μg L−1 in site S5 during March sampling campaign, a clear indication of the release of TiO2 engineered particles from SSOs. The concentration of TiO2 engineered particles in Stoop Creek (S2, S3, and S4) ranged from 2–10 μg L−1 except on December 10th where a relatively higher TiO2 concentration was measured. This high concentration on December 10th is likely to originate from other sources of contamination upstream as a high TiO2 concentration was measured in the upstream water (site S1). Thus, treated sewage effluent has very low TiO2 engineered particles concentrations (typically <10 μ L−1), representing approximately 10% of TiO2 concentration in the water sample collected from the ruptured sewer main. This is in good agreement with the high removal efficiency (e.g., 90–95%) of engineered particles in wastewater treatment plants45. The concentration of TiO2 in sites G1, C1, and C2 ranged from 5 to 80 μ L-1. These sites received SSOs regularly.
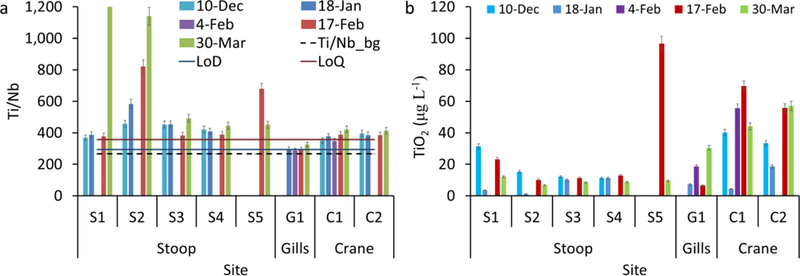
TiO2 particles with regular shapes (n = 29) including cubic, rod shaped, and truncated/near spherical TiO2 particles were identified only in samples collected from Gills Creek and Crane Creek (Figure 6a-c). The elemental analysis (Figure 6d-f) of these particles demonstrates that these particles are composed mainly of Ti and O, with trace amounts of Al, Si, and Fe, which can be attributed to either engineered coating on the surface of TiO2 particles, or to sorption of Al, Si and Fe from surface water. The cube edge was 85 nm, the rod is 100 nm wide x 950 nm long and spherical particles are 70–180 in diameter. These particles are similar in size, shape, and composition with TiO2 engineered particles12,14. TiO2 particles were detected by TEM in Stoop Creek water samples in very low numbers, with only 2 spherical particles (Figure 7a) and 1 irregular particle (Figure 7b).
Figure 6.
Morphological and chemical analysis of TiO2 particles in sewage impacted surface waters. Transmission electron microscopy micrographs and the corresponding chemical analysis using energy dispersive spectroscopy of TiO2 particles in (a, d) Gills Creek G1_March 30, (b, c, e, and f) Crane Creek C2_January 18.
Figure 7.
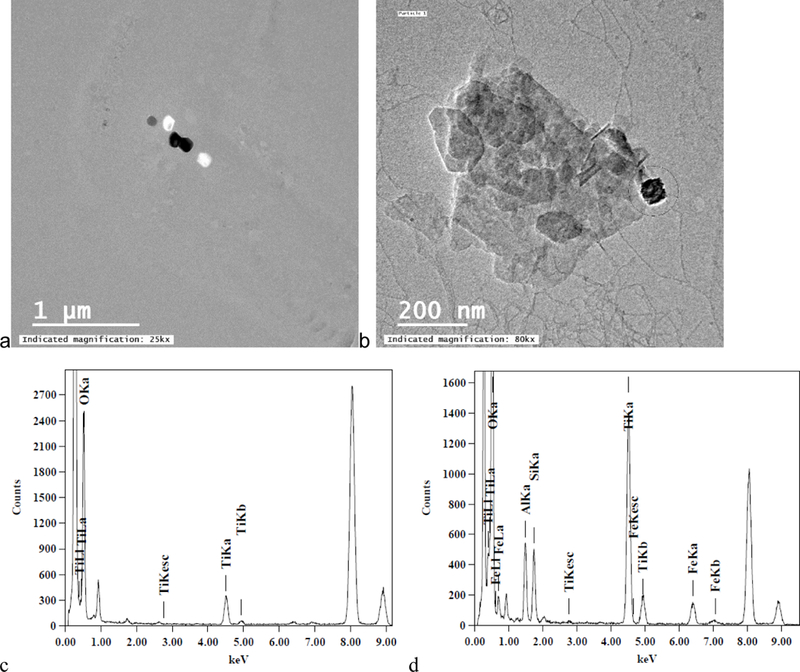
Morphological and chemical analysis of Ti-rich particles observed in Stoop Creek (a, c) sample S2 December 10th, (b, d) sample S3_January 18.
The sizes of TiO2 engineered particles indicate that they represent a mixture of TiO2 ENMs and TiO2 pigments. Titanium dioxide pigment is a common additive in many food, personal care, and other consumer products used by people, which after use can enter the sewage system14. TiO2 pigments cover a range of size distributions extending from the nanorange (<100 nm) to several hundreds of nanometers. Thus, the majority of TiO2 pigments contains a fraction of TiO2 ENMs. For instance, the size distribution of food grade TiO2 additives (e.g., E171) have been shown to contain a significant fraction (up to 36%) of TiO2 ENMs14. Assuming that all the released TiO2 engineered particles are pigments and that 36% of the TiO2 in these pigments is in the nanoscale range as demonstrated by Weir et al (2012) 14, then the highest measured TiO2 ENM concentration can be estimated to be approximately 36 μg L-1. Nonetheless, there could be other inputs of TiO2 ENMs into the sewage systems, and TiO2 ENM concentrations in sewage spills might be significantly higher than those estimated based on the % of TiO2 ENMs in food additives grade TiO2 pigments. Additionally, it is likely that the bulk TiO2 production will transition to TiO2 ENM production in the near future because of the many advantages of the TiO2 ENMs compared to their bulk counterparts46. Thus, the upper bound of TiO2 ENM discharge in sewage spills could in the near future reach the maximum concentrations measured in this study (e.g., 100 μg L−1 TiO2).
3.4. Comparison between analytical techniques: advantages and limitations
Three analytical techniques have been applied pragmatically in this study to gain complementary information on the occurrence, concentration, and properties of TiO2 natural and engineered particles. Total Ti concentration was used as a first proof of the possible release of TiO2 particles with SSOs; reference sites were used to calculate the background elemental ratios in natural particles; ME-SP-ICP-MS was used to further confirm these elemental ratios on single particle basis; and mass-balance calculations were implemented to calculate the total concentrations of the released TiO2 engineered particles.
Total elemental concentration combined with elemental ratios (e.g., Ti/Nb) provides a quantitative measure of the total concentration of TiO2 engineered particles above the natural background concentration of natural Ti-rich particles. However, this method does not provide any information on TiO2 particle size distribution and thus does not differentiate between TiO2 ENMs and pigments based on differences in particle size. Thus, the total TiO2 concentrations calculated here using this approach refers to the sum of all TiO2 particles that do not contain the natural tracers of Nb, including TiO2 ENMs, pigments, and potentially other Ti-rich particles that are not associated with Nb. ME-SP-ICP-MS measures the mass of all detectable elements in Ti-rich particles or aggregates of particles at the single particle level, enabling calculating elemental ratios in individual particles. Thus, ME-SP-ICP-MS allows overcoming the need for reference sites to calculate background elemental ratios. This is supported by the close proximity between Ti/Nb measured by ME-SP-ICP-MS and those measured in the reference sites by total digestion. However, further research is needed to further validate the relationship between elemental ratios calculated based on total metal concentrations and those calculated on a particle-per-particle basis.
In principle, ME-SP-ICP-MS allows differentiating TiO2 engineered particles from Ti-rich natural particles that contain natural elemental tracers. However, the concentration of these tracers in natural particles must be sufficiently high to be detectable by ME-SP-ICP-MS analysis. If the concentration of these natural elements in a natural TiO2 particles is below the lower size detection limit of the ME-SP-ICP- MS, then such a natural particle will be detected as pure TiO2 particle, resulting in misleading identification of such a particle as pure/engineered particle. Therefore, the pure TiO2 particles detected in these samples can be a combination of engineered TiO2 particles and natural TiO2 particles associated with elemental tracers below the size detection limit of ME-SP-ICP-MS. Further analytical/sample preparation (e.g., removal of dissolved ions and natural organic matter, or coupling with size fractionation techniques) can be implemented to lower the size detection limit of ME-SP-ICP-MS analysis, and thus improving the probability of differentiating natural from engineered particles based on elemental associations and ratios47. With the used operating conditions, the best achievable size detection limit of TiO2 in ultrahigh purity water was approximately 40 nm. Furthermore, some TiO2 ENMs might contain the same elements as those present in natural Ti-particles, which may further underestimate the concentration of TiO2 engineered particles when considering only pure TiO2 particles as engineered particles. Such a gap can be filled in future studies by investigating the elemental composition of a wide array of TiO2 ENMs, pigments, and natural particles and by using elemental ratios (if different) as a tracer of the different types and sources of TiO2 engineered particles. This can be achieved through machine learning as proposed elsewhere28.
The measured particle mass can be converted to equivalent particle diameter assuming spherical particles. The calculated size can be that of a primary particle or the equivalent spherical diameter of an aggregate of primary particles. The measured TiO2 particle size in this study using ME-SP-ICP-MS varied in the size range of 100–200 nm. However, smaller particles are present in these samples as evidenced by TEM, but not detected by ME-SP-ICP-MS due to the size detection limit of the ME-SP-ICP-MS method used in this study and the measured samples (e.g., 100 nm for TiO2). Additionally, these measured sizes can be those of primary particles (e.g., pigment sized TiO2), or those of aggregates of smaller primary particles (e.g., TiO2 ENMs). The total mass concentration of the measured TiO2 particles can be calculated as the sum of the mass of the measured particles. However, ME-SP-ICP-MS measures only particles larger than the size detection limit. Thus, ME-SP-ICP-MS underestimates the total concentration of TiO2 engineered particles.
TEM was implemented to provide qualitative visual proof of the presence of TiO2 ENMs based on their size, shape, and elemental composition. Unlike ME-SP-ICP-MS, TEM is capable of detecting ENMs across the entire nanoscale range and of determining particle morphology. However practical limitations including the demanding operator time, the presence of high concentrations of natural particles, the poor statistical power due to limited number of particles that can be imaged and analyzed within a reasonable time and cost frame, hamper the quantification of ENMs in complex matrices7. These limitations can potentially be overcome through better sample preparation e.g., particle disaggregation, followed by density-based separation to concentrate the particle of interest, followed by total particle deposition on the TEM grids36. Therefore, pragmatically, TEM should be used to provide complementary (qualitative data) to support more statistically powerful techniques such as ME-SP-ICP-MS.
Other analytical techniques can be used to fill some of the gaps identified here. For instance, field flow fractionation-coupled with inductively coupled plasma mass-spectroscopy can be implemented to investigate the elemental associations and ratios for particles smaller than the ME-SP-ICP-MS lower size detection limit48,49.
3.5. Environmental implications
Here, we report that SSOs are hot spots of TiO2 engineered particle (e.g., ENM and pigments) release (up to 100 μg L−1 TiO2 concentrations in receiving waters) into the environment. Based on these data, we also hypothesize that there are other hot spots of engineered particle release into the environment that have been overlooked in previous studies and should be investigated in the future. It is worth noting that Ag total concentrations <0.1 μg L−1 were measured in all samples and thus even if all Ag occur as ENMs, the environmental exposure is very low compared to that of TiO2 ENMs. Similarly, no CeO2 ENMs were detected in all investigated samples as Ce/La ratio was not significantly different from the natural background ratio (Figure S3a).
The immediate impact of this work is relevant to aquatic organisms in water bodies receiving sewage overflows. In terms of environmental hazards, the measured TiO2 concentrations (1–100 μg L−1) in creek water samples is in the same order of magnitude as the predicted no effect concentration (PNEC) for TiO2 pigments (e.g., 127–184 μg L−1) and is higher than the PNEC for TiO2 ENMs to freshwater organisms (e.g., 1–18 μg L−1) 11,50. Transport of TiO2 engineered particles with river water to the ocean could also pose a significant risk for coral reefs. TiO2 ENMs has been shown to bioaccumulate in microflora and induce coral bleaching, which could contribute to an overall decrease in coral populations51. This is in line with the coral bleaching observed for other sunscreen products -based on UV filter formulation- such as ethylhexyl salicylate, propylene glycol, and others52. The majority of environmental ecotoxicological studies of TiO2 in the literature focused on photocatalytic TiO2 particles such as P25. However, given the potential significant release of TiO2 pigments with sewage spills, future studies should address the environmental fate and effects of TiO2 pigments.
Although SSOs directly affect aquatic ecosystems, there are also translational implications for human health. Humans are exposed to untreated sewage through drinking contaminated water, water recreational activities, and/or ingesting contaminated fish/shelfish18. For instance, Crane Creek discharges into the Lower Broad River, which is used as part of the intake for the city of Columbia’s drinking water supply. Stoop Creek discharges into the Lower Saluda River, which is a popular site for recreational activities (e.g., tubing and kayaking). Gills Creek sample (G1) was collected ~1.6 km downstream from Lake Katherine, where SSOs routinely occurred. Residents around Lake Katherine use the lake for recreational purposes such as swimming and fishing. Given the high volume of sewage released annually by SSOs (11–38 billion liters) and combined sewer overflows (CSOs; 3200 billion liters) in the U.S. 18, it is possible that other water bodies, and thus populations, in the U.S. are similarly exposed to significantly high TiO2 engineered particle (e.g., ENMs and pigments) concentrations, which should be further investigated. In vitro toxicity assessments show that TiO2 ENMs can induce cytotoxic, genotoxic, inflammatory, and oxidative stress responses in cells53,54. TiO2 ENM exposure induces toxicity in various organs in mice55. In most studies, TiO2 ENMs appeared to have caused oxidative stress, histopathological alterations, carcinogenesis, genotoxicity and immune disruption. Additionally, numerous studies have shown that food additive TiO2 pigments (e.g., E171) can pass and be absorbed by the mammalian gastrointestinal tract, can result in bioconcentration, bioaccumulation, and biomagnification in the tissue of mammals and other vertebrates, have very limited elimination rate, and can cause histopathological and physiological changes in various organs of animals56. Therefore, the human exposure to such materials must be either avoided or strictly managed to minimize risks for human health57.
SSOs are a chronic issue in Columbia, South Carolina, due to aging sanitary sewer system. The total reported sewage overflows volume in SC is on average 115 million liters per year for the past 3 years58. Assuming a 100 μg L−1 TiO2 concentration results in a total of 11.5 kg TiO2 per year, and these amounts are expected to be higher, as the estimated unreported sewage overflows are expected to be higher than the reported overflows. In 2004, the U. S. EPA estimated between 23,000 and 75,000 SSOs occurred annually, releasing between 11 and 38 billion liters of untreated wastewater18. Assuming TiO2 concentration of 100 μg L−1 TiO2, this results in a total discharge of 1,1 to 3,8 tons of TiO2 per year into surface waters in the USA through SSOs. Additionally, combined sewer overflows (CSOs) are common in the northeast of the United States with an estimated discharge of 3,200 billion liters of untreated sewage annually18. This results in a total discharge of 320 tons of TiO2 per year into surface waters in the USA through CSOs. These estimates are in good agreement with the estimated discharge of TiO2 ENMs to surface waters with untreated sewage10. Nonetheless, the actual concentration of TiO2 engineered particles in untreated wastewater is most likely to be higher than the highest concentration measured in the impacted surface waters. Thus, the actual discharge of TiO2 engineered particles into the environment through SSOs and CSOs is likely to be even higher than the estimated values above. Given the widespread use of TiO2 engineered particles in the outdoor urban environment, such as self-cleaning surfaces, road paints and other applications59, the total TiO2 engineered particles discharge to surface waters is expected to be even higher. This situation clearly invites further studies aimed at comprehensive evaluation of TiO2 engineered particles environmental exposure, fate modeling, and toxicity. Furthermore, sewage overflows discharge many other contaminants to surface waters, suggesting the need to study the effect of these mixtures of contaminants on environmental and human health.
This work presents opportunities to advance the field of environmental nanotechnology, ENM exposure assessment, and ENM risk assessment. Visualization and investigation of ENM morphologies helps in determining the type of ENM that should receive more attention in future exposure, hazard and risk assessment studies. The ability to quantitatively measure ENM concentrations in surface waters opens the door to a better understanding of the environmental fate and transport pathways of ENMs in natural systems, and to validate ENM fate models. Numerous ENM fate models have been developed over the past two decades9,60. These models suffer several limitations including 1) they are based on estimates of ENM production volumes and release rates from products under simulated environmental conditions, which will most likely differ from real environmental scenarios, and 2) these models have not been validated against measured ENM concentrations. Measuring ENM concentrations at the point of discharge to the environment and the ability to monitor ENM concentrations downstream from the discharge points will allow better parameterization and validation of ENM fate models. Future studies will be designed to generate ENM concentration data that can be used for this purpose. Given the assessment that high concentrations of TiO2 ENMs are found in sewage overflows, and given the high volume of sewage overflows in the US18 and world-wide, modeling approaches should take into account the potential local “hot spots” of high environmental exposure to ENMs through sewage overflows. Thus, high spatiotemporal resolutions models will be ideal to study these scenarios9.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by US National Science Foundation CAREER (1553909) grant to Dr. Mohammed Baalousha, Swiss National Science Foundation postdoctoral mobility funding (P2GEP2_165046) to Dr. Frederic Loosli, the U.S. National Institutes of Health (R21 ES026412, L30 ES023165) to Dr. Rothenberg, and funding from the University of South Carolina, Office of Research to Drs. Rothenberg, Bizimis, and Baalousha. This work was supported by the Virginia Tech National Center for Earth and Environmental Nanotechnology Infrastructure (NanoEarth), a member of the National Nanotechnology Coordinated Infrastructure (NNCI), supported by NSF (ECCS 1542100).
Reference List
- 1.Harper T Global funding of nanotechnologies and its impact. London: Científica Ltd 2011, 8. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Piccinno F; Gottschalk F; Seeger S; Nowack B Industrial production quantities and uses of ten engineered nanomaterials in Europe and the world. J. Nanopart. Res. 2012, 14 (9), 1–11.22448125 [Google Scholar]
- 3.Woodrow Wilson data base. The project on emerging nanotechnologies (http://www.nanotechproject.org/). 2014.
- 4.Gottschalk F; Nowack B The release of engineered nanomaterials to the environment. J. Environ. Monit. 2011, 13 (5), 1145–1155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Tiede K; Hassellov M; Breitbarth E; Chaudhry Q; Boxall ABA Considerations for environmental fate and ecotoxicity testing to support environmental risk assessments for engineered nanoparticles. J. Chromatogr. A. 2009, 1216 (3), 503–509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Nowack B; Baalousha M; Bornhoft N; Chaudhry Q; Cornelis G; Cotteril J;Gondikas A; Hasselloev M; Lead JR; Mitrano DM; von der Kammer F; Wontner-Smith T Progress towards the validation of modeled environmental concentrations of engineered nanomaterials by analytical measurements. Environ. Sci. Nano. 2015, 2 (5), 421–428. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Gondikas A; von der Kammer F; Kaegi R; Borovinskaya O; Neubauer E; Navratilova J; Praetorius A; Cornelis G; Hofmann T Where is the nano? Analytical approaches for the detection and quantification of TiO2 engineered nanoparticles in surface waters. Environ. Sci. Nano. 2018, 5 (2), 313–326. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Reed RB; Martin DP; Bednar AJ; Montano MD; Westerhoff P; Ranville JF Multi-day diurnal measurements of Ti-containing nanoparticle and organic sunscreen chemical release during recreational use of a natural surface water. Environ. Sci. Nano. 2017, 4 (1), 69–77. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Dale AL; Casman EA; Lowry GV; Lead JR; Viparelli E; Baalousha M Modeling Nanomaterial Environmental Fate in Aquatic Systems. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49 (5), 2587–2593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Gottschalk F; Sonderer T; Scholz RW; Nowack B Modeled Environmental Concentrations of Engineered Nanomaterials (TiO2, ZnO, Ag, CNT, Fullerenes) for Different Regions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43 (24), 9216–9222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Mueller NC; Nowack B Exposure Modeling of Engineered Nanoparticles in the Environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42 (12), 4447–4453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Gondikas AP; von der Kammer F; Reed RB; Wagner S; Ranville JF; Hofmann T Release of TiO2 nanoparticles from sunscreens into surface waters: a one-year survey at the Old Danube recreational lake. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48 (10), 5415–5422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Cision Titanium Dioxide (TiO2) - A Global Market Overview; 16. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Weir A; Westerhoff P; Fabricius L; Hristovski K; Von Goetz N Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles in Food and Personal Care Products. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46 (4), 2242–2250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Swiler DR Pigments, inorganic. Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology; 2005. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Keller AA; Lazareva A Predicted releases of engineered nanomaterials: From global to regional to local. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2013, 1 (1), 65–70. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Bitragunta SP; Palani SG; Gopala A; Sarkar SK; Kandukuri VR Detection of TiO2 Nanoparticles in Municipal Sewage Treatment Plant and Their Characterization Using Single Particle ICP-MS. Bull. Environ. Cont. Toxicol. 2017, 98 (5), 595–600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Environmental Protection Agency US (USEPA) Report to Congress on impacts and control of combined sewer overflows and sanitary sewer overflows;EPA 833-R- 04–001; USEPA: Washington, D.C.: Office of Water., 04. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Alvarez PJJ; Colvin V; Lead J; Stone V Research Priorities to Advance Eco- Responsible Nanotechnology. ACS Nano 2009, 3 (7), 1616–1619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Montano MD; Lowry GV; von der Kammer F; Blue J; Ranville JF Current status and future direction for examining engineered nanoparticles in natural systems. Environ. Chem. 2014, 11 (4), 351–366. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Buffle J; Van Leeuwen H Environmental particles; Lewis: Boca Raton, FL, 1992; Vol. 1. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Gottschalk F; Sun T; Nowack B Environmental concentrations of engineered nanomaterials: Review of modeling and analytical studies. Environmental Pollution 2013, 181 (0), 287–300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Kammer F v. d.; Legros S; Hofmann T; Larsen EH; Loeschner K. Separation and characterization of nanoparticles in complex food and environmental samples by field-flow fractionation. TrAC Trend Anal. Chem. 2011, 30 (3), 425–436. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Tong T; Hill AN; Alsina MA; Wu J; Shang KY; Kelly JJ; Gray KA; Gaillard JF Spectroscopic Characterization of TiO2 Polymorphs in Wastewater Treatment and Sediment Samples. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2015, 2 (1), 12–18. [Google Scholar]
- 25.von der Kammer F; Ferguson PL; Holden PA; Masion A; Rogers KR; Klaine SJ; Koelmans AA; Horne N; Unrine JM Analysis of engineered nanomaterials in complex matrices (environment and biota): General considerations and conceptual case studies. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2012, 31 (1), 32–49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Luo Z; Wang Z; Li Q; Pan Q; Yan C; Liu F Spatial distribution, electron microscopy analysis of titanium and its correlation to heavy metals: occurrence and sources of titanium nanomaterials in surface sediments from Xiamen Bay, China. J. Environ. Monit. 2011, 13 (4), 1046–1052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Part F; Zecha G; Causon T; Sinner EK; Huber-Humer M Current limitations and challenges in nanowaste detection, characterisation and monitoring. Waste Manag. 2015, 43, 407–420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Praetorius A; Gundlach-Graham A; Goldberg E; Fabienke W; Navratilova J; Gondikas A; Kaegi R; Gunther D; Hofmann T; von der Kammer F Single-particle multi-element fingerprinting (spMEF) using inductively-coupled plasma time-of-flight mass spectrometry (ICP-TOFMS) to identify engineered nanoparticles against the elevated natural background in soils. Environ. Sci. Nano.2017, 4 (2), 307–314. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Fretwell S Sewage leaks into Saluda River tributary. http://www.thestate.com/news/local/article61424152.html, (accessed January 11, 2018). 2016.
- 30.Frisby C; Bizimis M; Mallick S Seawater-derived rare earth element addition to abyssal peridotites during serpentinization. Lithos 2016, 248–251, 432–454. [Google Scholar]
- 31.Loosli F; Berti D; Yi Z; Baalousha M Toward a better extraction and stabilization of titanium dioxide engineered nanoparticles in model water. NanoImpact. 2018, 11, 119–127. [Google Scholar]
- 32.Tang Z; Wu L; Luo Y; Christie P Size fractionation and characterization of nanocolloidal particles in soils. Environ. Geochem. Health. 2009, 31 (1), 1–10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Hendriks L; Gundlach-Graham A; Hattendorf B; Günther D Characterization of a new ICP-TOFMS instrument with continuous and discrete introduction of solutions. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2017, 32 (3), 548–561. [Google Scholar]
- 34.Pace HE; Rogers NJ; Jarolimek C; Coleman VA; Higgins CP; Ranville JF Determining Transport Efficiency for the Purpose of Counting and Sizing Nanoparticles via Single Particle Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83 (24), 9361–9369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Tanner M Shorter signals for improved signal to noise ratio, the influence of Poisson distribution. J. Anal. Atom. Spectrom. 2010, 25 (3), 405–407. [Google Scholar]
- 36.Prasad A; Baalousha M; Lead JR An electron microscopy based method for the detection and quantification of nanomaterial number concentration in environmentally relevant media. Sci. Tot. Environ. 2015, 537, 479–486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Schmidt J; Vogelsberger W Aqueous long-term solubility of titania nanoparticles and titanium (IV) hydrolysis in a sodium chloride system studied by adsorptive stripping voltammetry. J. Solution chem. 2009, 38 (10), 1267–1282. [Google Scholar]
- 38.Nakashima K; Imaoka T Niobian and zincian ilmenites in syenites from Cape Ashizuri, Southwest Japan. Mineral. Petrol. 1998, 63 (1), 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- 39.José CG; Wyllie PJ Ilmenite (high Mg, Mn, Nb) in the carbonatites from the Jacupiranga complex, Brazil. Am. Mineral. 1983, 68, 960–971. [Google Scholar]
- 40.Zack T; Kronz A; Foley SF; Rivers T Trace element abundances in rutiles from eclogites and associated garnet mica schists. Chem. Geol. 2002, 184 (1–2), 97–122. [Google Scholar]
- 41.International Agency for Research on Cancer Carbon black, titanium dioxide, and talc; 93 ed; IARC Press, International Agency for Research on Cancer: 2010. [Google Scholar]
- 42.IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans Carbon black, titanium dioxide, and talc. IARC monographs on the evaluation of carcinogenic risks to humans 2010, 93, 1. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Kiser MA; Westerhoff P; Benn T; Wang Y; Perez-Rivera J; Hristovski K Titanium nanomaterial removal and release from wastewater treatment plants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 6757–6763. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Westerhoff P; Song G; Hristovski K; Kiser MA Occurrence and removal of titanium at full scale wastewater treatment plants: implications for TiO2 nanomaterials. J. Environ. Monit. 2011, 13 (5), 1195–1203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Limbach LK; Bereiter R; ller E; Krebs R; lli R; Stark WJ Removal of Oxide Nanoparticles in a Model Wastewater Treatment Plant: Influence of Agglomeration and Surfactants on Clearing Efficiency. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42 (15), 5828–5833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Robichaud CO; Uyar AE; Darby MR; Zucker LG; Wiesner MR Estimates of Upper Bounds and Trends in Nano-TiO2 Production As a Basis for Exposure Assessment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43 (12), 4227–4233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Hadioui M; Peyrot C; Wilkinson KJ Improvements to Single Particle ICPMS by the Online Coupling of Ion Exchange Resins. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86 (10), 4668–4674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Baalousha M; v.d.Kammer F.; Motelica-Heino M.; Coustumer P 3D characterization of natural colloids by FlFFF-MALLS -TEM. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2005, 308, 549–560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Baalousha M; Kammer F; Motelica-Heino M; Baborowski M; Hofmeister C; Lecoustumer P Size-based speciation of natural colloidal particles by flow-field flow fractionation, inductively coupled plasma-mass spectroscopy, and transmission electron microscopy/X-ray energy dispersive spectroscopy: colloids- trace element interaction. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40 (7), 2156–2162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Lützh∅ft HCH; Hartmann NB; Brinch A; Kjolholt J; Baun A Environmental Effects of Engineered Nanomaterials: Estimations of Predicted No-Effect Concentrations (PNECs);978–87-93352–70-4; The Danish Environmental Protection Agency: Copenhagen, Denmark, 15. [Google Scholar]
- 51.Jovanovic B; Guzman HM Effects of titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles on caribbean reef-building coral (Montastraea faveolata). Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2014, 33 (6), 1346–1353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Danovaro R; Bongiorni L; Corinaldesi C; Giovannelli D; Damiani E; Astolfi P; Greci L; Pusceddu A Sunscreens cause coral bleaching by promoting viral infections. Environ. Health Perspec. 2008, 116 (4), 441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Iavicoli I; Leso V; Bergamaschi A Toxicological effects of titanium dioxide nanoparticles: a review of in vivo studies. J. Nanomater. 2012, 2012, 5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Shi H; Magaye R; Castranova V; Zhao J Titanium dioxide nanoparticles: a review of current toxicological data. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2013, 10 (1), 15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Hong F; Yu X; Wu N; Zhang YQ Progress of in vivo studies on the systemic toxicities induced by titanium dioxide nanoparticles. Toxicol. Res. 2017, 6 (2), 115–133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Jovanovic B Critical review of public health regulations of titanium dioxide, a human food additive. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2015, 11 (1), 10–20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Shakeel M; Jabeen F; Shabbir S; Asghar MS; Khan MS; Chaudhry AS Toxicity of nano-titanium dioxide (TiO 2-NP) through various routes of exposure: a review. Biol. Trace. Elem. Res. 2016, 172 (1), 1–36. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.SCdhec. Sewer Sanitary Overflow. http://www.scdhec.gov/apps/environment/SSO/. 2018.
- 59.Baalousha M; Yang Y; Vance ME; Colman BP; McNeal S; Xu J; Blaszczak J; Steele M; Bernhardt E; Hochella MF JR Outdoor urban nanomaterials: The emergence of a new, integrated, and critical field of study. Sci. Tot. Environ. 2016, 557–558, 740–753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Baalousha M; Cornelis G; Kuhlbusch TAJ; Lynch I; Nickel C; Peijnenburg W; van den Brink NW Modeling nanomaterial fate and uptake in the environment: current knowledge and future trends. Environ. Sci. Nano. 2016, 3 (2), 323–345. [Google Scholar]
- 61.Emmons AM, Bizimis M, Lang SQ, Stangler W, Geidel G, Baalousha M, Wanamaker E and Rothenberg SE, Rothenberg, Enrichments of metals, including methylmercury, in sewage spills in South Carolina, USA, J. Environ. Qual., 2018, 47, 1258–1266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.


