Highlights
-
•
Concomitant use of ultrasonography and MIBI-SPECT/CT is highly recommended for better depiction of parathyroid adenoma.
-
•
It also helps in accurate localization of parathyroid adenoma especially those of ectopic location.
-
•
It will provide better success for parathyroid exploration and minimally invasive surgery.
Keywords: SPECT/CT, Parathyroid adenoma
Abstract
Purpose
Evaluating the diagnostic performance of combined protocol of ultrasonography and Tc-99 m MIBI SPECT/CT in preoperative depiction and localization of parathyroid adenoma.
Methods and materials
60 patients were enrolled in this retrospective study who had primary hyperparathyroidism and parathyroidectomy for parathyroid adenoma, all of them underwent ultrasonography examination of parathyroid gland and MIBI SPECT/CT for exact pre-operative localization of parathyroid adenoma, surgical and pathological results were used as standard reference then sensitivity, specificity and accuracy for each modalility and for combined protocol of both modalities was calculated.
Results
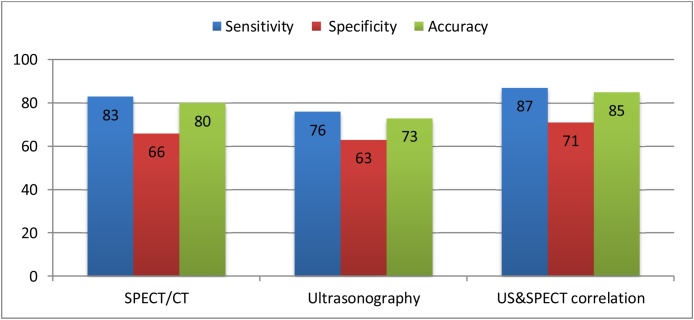
The sensitivity, specificity and accuracy were highest with combined protocol of ultrasonography and MIBI-SPECT/CT (87 %), (71 %) and (85 %) respectively and lowest sensitivity, specificity and accuracy with ultrasonography alone (76 %), (63 %) and (73 %) respectively while (83 %), (66 %) and (80 %) with MIBI-SPECT/CT alone.
Conclusion
Concomitant use of ultrasonography and MIBI SPECT/CT is highly recommended for better preoperative depiction and localization of parathyroid adenoma.
1. Introduction
Primary hyperparathyroidism is a disease mainly affecting female patients as it occurs in 1 per 500 women and 1 per 2000 men; It is characterized by overproduction of parathyroid hormone and by turn hypercalcemia [1]. Hyperparathyroidism can affect any age group, it can affect children and old ages as well but its peak age is in fourth and fifth decades, it has many manifestations which are symptomatic like musculo-skeletal and renal disorders [2], the most common cause of primary hyperparathyroidism is single parathyroid adenoma [3].
Recently, wide neck dissection operations for parathyroidectomy have been replaced by minimally invasive surgery and endoscopic operations owing to rapid progress in imaging techniques used for preoperative parathyroid evaluation [4,5], that also reduces the operative failure rate [6].
Primary imaging modality for diagnosis is Ultrasonography which is noninvasive simple tool with good sensitivity for parathyroid adenoma [7]. Although that it has some pitfalls including misdiagnosis of parathyroid adenoma in cases of multi-nodular goiter and cases of ectopic parathyroid adenoma in addition to being operator dependant tool [8].
Dual-phase parathyroid scintigraphy using Technetium-99 m-MIBI is also important diagnostic tool with good quality and high sensitivity for depiction of parathyroid adenoma especially ectopic one, this sensitivity is improved with addition of single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) [9].
Although SPECT has good performance in depiction of parathyroid adenoma deeply located in neck and in ectopic regions and also that associated with multiple thyroid nodules, it does not provide accurate anatomical details. Accurate anatomical localization is achieved by SPECT/computed tomography (SPECT/CT) that is very important before surgery [10].
2. Aim of work
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the diagnostic performance of combined protocol of ultrasonography and Tc-99 m MIBI SPECT/CT in depiction and anatomical localization of parathyroid adenoma before surgery in comparison to each modality alone.
3. Materials and method
3.1. Patients
This retrospective study was done between January 2017- October 2018 on 60 adult patients (43 women and 17 men, mean age 55 years; range, 16–76 years) who had primary hyperparathyroidism and parathyroidectomy for parathyroid adenoma, their diagnosis confirmed by biochemical evidence like elevated parathyroid hormone (PTH) and serum calcium (Ca) levels than normal range, (10–65 pg/ml) for parathyroid hormone and (8.5–10.5 mg/dl) for calcium, Patients underwent Ultrasonography and MIBI SPECT-CT for exact pre-operative localization of parathyroid adenoma. Patients with secondary hyperparathyroidism due to chronic renal disease were excluded from the study. This study protocol was approved by the institutional Review Board
3.2. Imaging
3.2.1. Parathyroid ultrasonography
High resolution ultrasonography of parathyroid gland and neck was performed was done by radiologists who had experience ranging from 8 to 10 years in thyroid and parathyroid scan and images of abnormal nodules in parathyroid glands were obtained by using (Accuvix A30 Ultrasound System, Medison) and a 12- MHz linear array probe which has good resolution for superficial soft tissue, Detailed ultrasonographic examination of thyroid gland and neck lymph nodes was also obtained.
3.2.2. Interpretation of parathyroid ultrasonography
parathyroid adenomas mostly appears as homogeneously hypoechoic nodule versus the overlying thyroid gland with echogenic thyroid capsule separating it from thyroid tissue, By Doppler study usually there is increased internal vascularity of parathyroid adenoma in a peripheral distribution but sometimes there is hypervascularity of the overlying thyroid gland as in cases of thyroiditis that may help to locate an underlying adenoma.
3.2.3. Tc-99 m MIBI SPECT/CT fusion images
Patients were injected intravenously by 25 mCi of Tc 99 m MIBI, neck and chest images in anterior position were taken in supine position with a high resolution, low energy collimator with 128 × 128 matrix at 10 min (for early phase) and 2 h (delayed phase) after MIBI injection, Any foci of increased or separate tracer uptake relative to the thyroid on either early or delayed images or both was noted for further evaluation by SPECT/CT by (Symbia Intevo, Siemens Healthcare), where SPECT of the neck and upper thorax was done using 32 projection over a 180° anterior arc, images were reconstructed to 3-D planes, After SPECT acquisitions, CT acquisitions of were performed using 1 mm slice thickness, voltage of 130 kV and current of 20 mA without contrast medium injection. Then, by using Siemens syngo™ software SPECT/CT fusion images were obtained and CT images and reconstructed SPECT images were evaluated.
3.2.4. Interpretation Tc-99 m MIBI SPECT/CT fusion images
Systematic interpretations of Tc-99 m MIBI SPECT/CT Fusion images was done by experienced nuclear medicine physician, First he started examination of coronal SPECT/CT images from most anterior slice of thyroid gland and going posteriorly with slow continuous scrolling through the thyroid gland while observing any focal increased tracer uptake inferior to thyroid lobes which is expected site of inferior parathyroid adenomas, also accurate examination of any focal increased uptake in the few slices just posterior to thyroid gland in different cranio-caudal levels which is expected site for superior parathyroid adenoma since most of superior parathyroid glands tend to grow in the tracheoesophageal groove. After that axial SPECT/CT images were examined for more accurate localization of parathyroid adenoma in relation to the surrounding anatomic structures, particularly the thyroid gland and trachea.
The interpreting physician determined the presence or absence of abnormal glands; if present he determined lesions number whether one or more, their location (ie, inferior, superior or ectopic), exact numbers and locations of the parathyroid adenomas were compared with ultrasonographic and surgical results.
3.3. Statistical analysis
Surgical and pathologic results were used as standard reference to determine the accuracy of ultrasonography and Tc 99 m MIBI SPECT/CT.
True-positive findings by either ultrasonography and/or SPECT/CT were considered if abnormal parathyroid nodule was identified and confirmed by surgery and pathology. Conversely, true-negative results were considered when there are no pathological findings in both imaging and surgery. False-positive findings were considered when lesion depicted by imaging thought to be abnormal parathyroid nodule was not confirmed at surgery and finally, False-negative results was considered when abnormal nodule was found in surgery and not depicted on preoperative imaging.
Data analysis was evaluated using the McNemar test (SPSS software, version 14.0, 2006; SPSS. Chicago, IL) and the sensitivity, specificity and accuracy of ultrasonography and Tc 99 m MIBI SPECT were calculated. Then these results were correlated with the surgical findings. P value of less than 0.05 was considered to indicate a statistically significant difference.
4. Result
Laboratory results of 60 patients were available and demonstrated in Table (1), mean PTH level of patients was 95 pg/ml (its range 78–136 pg/ml) and mean Ca level was 11.8 mg/dl (its range 10.2–13.4 mg/dl) (Table 1).
Table 1.
Patient demographics and baseline characteristics.
| Parameter | value |
|---|---|
| Mean age (years)* | 55 (16-76) |
| Gender | |
| Women n, (%) | 43, (71.7%) |
| Men n, (%) | 17, (28.3%) |
| Pathological findings | |
| Parathyroid adenoma n, (%) | 48, (80%) |
| Parathyroid hyperplasia n, (%) | 4, (6.7%) |
| Negative pathological findings n, (%) | 8, (13.3%) |
| Laboratory results | |
| Mean serum parathyroid hormone (pg/mL) | 95 (78-136) |
| Mean serum calcium (mg/dL) | 11.8 (10.2–3.4) |
Normal ranges for parathyroid hormone and serum calcium are 10–65 pg/mL and 8.5–10.5 mg/dL, respectively.
Pathological findings done after surgery in 60 patients revealed the following, pathologically proved para-thyroid adenoma seen in 48 patients (80 %), 4 patients (6.6 %) had parathyroid hyperplasia, 8 patients (13.3.%) with no detected parathyroid pathological findings (Table 1).
In the 48 patients with pathologically proved parathyroid adenomas, 40 adenomas were depicted in MIBI-SPECT/CT, Figs. 2,3,4,5 and 6 and 8 adenomas identified at surgery that had been missed, By Ultrasonography 38 adenomas were detected, Figs. 2,3,4 and 5 and 10 adenomas had been missed and By combined ultrasonography and MIBI-SPECT/CT 42 adenomas were detected, Figs. 2,3,4,5 and 6 and only 6 missed (Table 2).
Fig. 2.
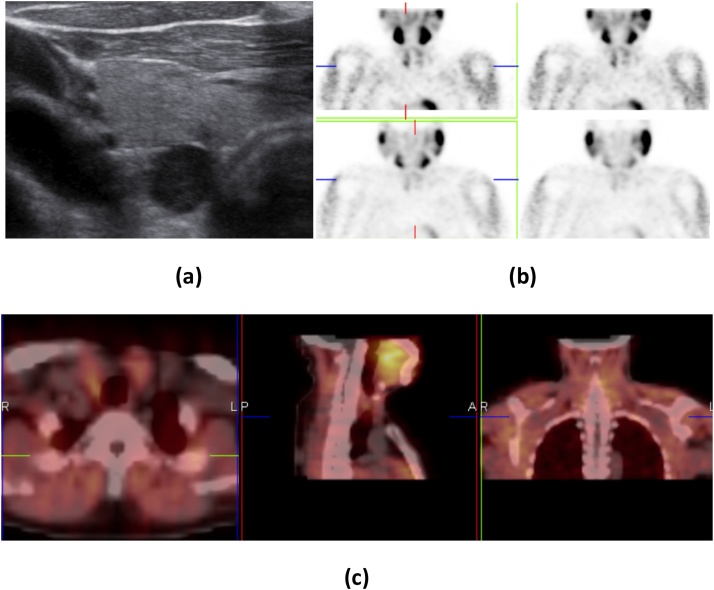
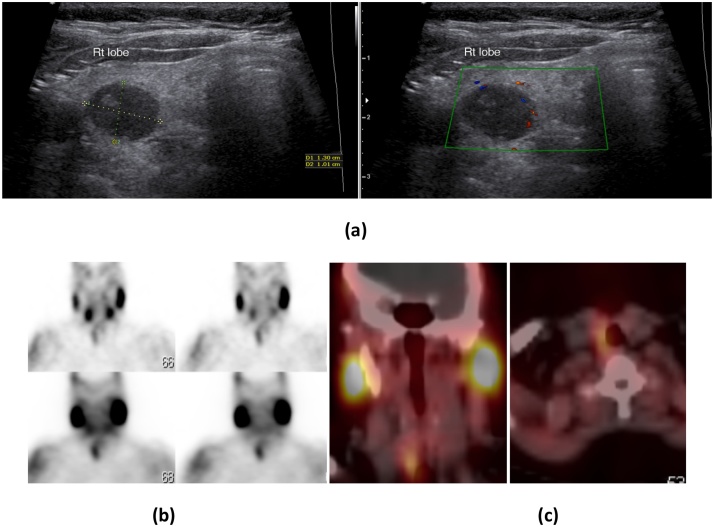
Right parathyroid adenoma in 26-year-old female with high S.calcium and PTH levels: (a) USG neck shows a well defined hypoechoic mass at the postero-inferior aspect of the right thyroid lobe with separable hyperechoic line from thyroid tissue. (b) Early images of Tc99 m sestamibi (upper two images) scan showed intense tracer uptake inferior to right thyroid lobe and along with uptake in both lobes of the thyroid gland and delayed images (lower two images) at 2 h show tracer retention with wash out from thyroid gland. (c) SPECT/CT imaging localizes the tracer uptake inferior to right thyroid lobe.
Table 2.
the imaging findings results in detection of parathyroid adenoma in relation to pathological findings:
| Patients no | % | ||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Positive | 40 | 83.3 |
| Negative | 8 | 16.7 | |
|
Positive | 38 | 79.2 |
| Negative | 10 | 20.8 | |
|
Positive | 42 | 87.5 |
| Negative | 6 | 12.5 | |
Abbreviation: MIBI-SPECT, technetium Tc 99 m sestamethoxyisobutylisonitrile scan (sestamibi) scan combined with single photon emission computed tomography.
The sensitivity, specificity and accuracy were highest with combined protocol of ultrasonography and MIBI-SPECT/CT (87 %), (71 %) and (85 %) respectively and lowest sensitivity, specificity and accuracy with ultrasonography alone (76 %), (63 %) and (73 %) respectively while (83 %), (66 %) and (80 %) with MIBI-SPECT/CT alone (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1.
Sensitivity, Specificity, and Accuracy of Imaging For Parathyroid Adenoma by different imaging modalities.
12 patients with concomitant thyroid disease (7 with thyroiditis and 5 with thyroid nodules), ultrasound showed parathyroid adenoma in 4 patients (33.3.%), 6 patients (50 %) by MIBI-SPECT/CT and 6 patients (50 %) in combined ultrasonography and MIBI-SPECT/CT protocol
From 10 case missed by ultrasound 4 cases were diagnoised by MIBI-SPECT/CT and combined ultrasound and MIBI-SPECT/CT as an ectopic parathyroid nodules, Fig. 6.
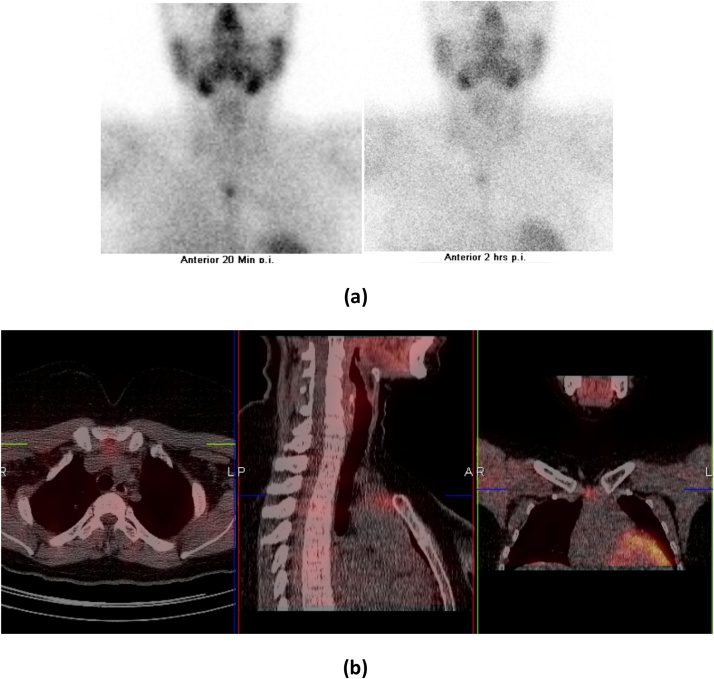
Fig. 6.
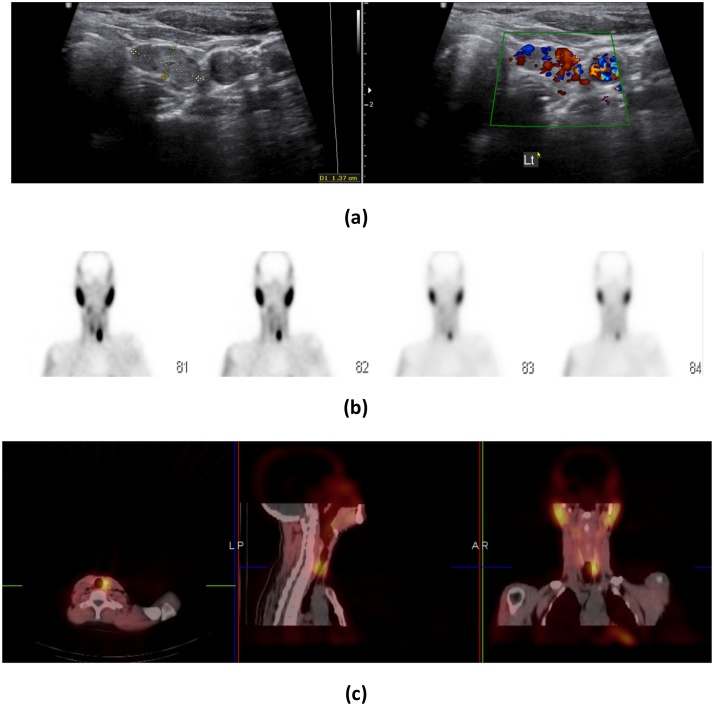
Ectopic midline retrosternal parathyroid adenoma in 35 Y/O female, known case of thyroid ca and thyroidectomy. Presented with hypercalcemia and hyperparathyroidism. (a) Early image (after 20 min of injection) and late image (after 2 h) shows midline focal area of enhanced radiotracer uptake and retention respectively noted at the level of thoracic inlet posterior to the manubrium sterni. (b) SPECT/CT imaging localizes upper retrosternal soft tissue density lesion located anterior to the left innominate vein and superior border of the aortic arch.
2 patients had bilateral adenomas at surgery; there are diagnoised by both ultrasonography and MIBI-SPECT/CT, Fig. 5.
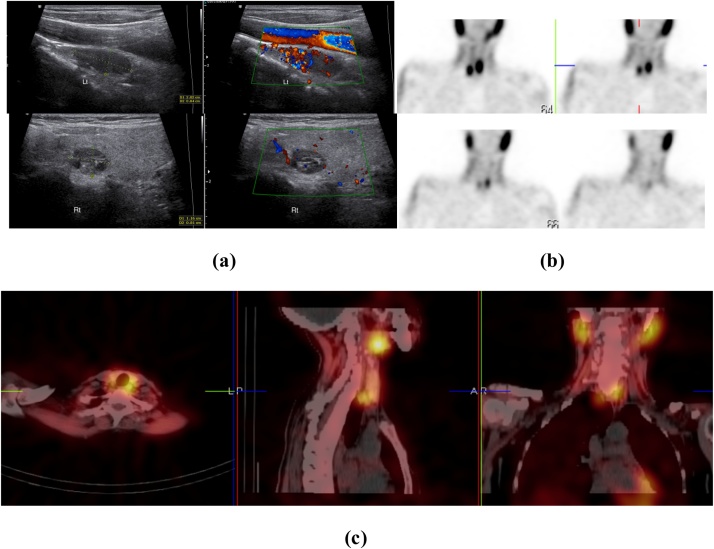
Fig. 5.
Bilateral parathyroid adenoma in 21-year-old female with high serum calcium level. (a) USG neck with two hypoechoic nodules, one on the inferior aspect of left thyroid lobe with seperable hyperechoic line from thyroid tissue and increased vascularity inside on color Doppler (upper two images) and another one on the posterior aspect of middle part of right thyroid lobe with mild vascularity inside (lower two images). (b) Early images of Tc99 m sestamibi (upper two images) scan showed intense tracer uptake on the two nodules more marked on the one inferior to left thyroid lobe and along with uptake in both lobes of the thyroid gland and delayed images (lower two images) at 2 h show tracer retention with wash out from thyroid gland. (c) SPECT/CT imaging localizes the tracer uptake of both nodules more marked on that inferior to left thyroid lobe.
4 patients had parathyroid hyperplasia observed in surgical pathology and 8 patients with no detected parathyroid pathological findings.
Ultrasonography failed to detect 10 adenomas and 7 of these adenomas were detected by MIBI-SPECT/CT. Only one adenomas were detected by ultrasonography and missed by MIBI-SPECT/CT with Statistical analysis of fair agreement between them in localization of parathyroid adenoma in relation to pathological results, Kappa test 0.345 (Table 3)
Table 3.
Agreement between Imaging Tests in the Diagnosis of Parathyroid Adenoma.
| Ultrasonography |
Kappa | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive | Negative | |||
|
Positive | 34 | 7 | 0.345 |
| Negative | 1 | 3 | ||
Abbreviation: MIBI-SPECT, technetium Tc 99 m sestamethoxyisobutylisonitrile scan (sestamibi) scan combined with single photon emission computed tomography.
5. Discussion
Minimally invasive parathyroidectomy has been rapidly replacing bilateral neck dissection operations for parathyroid adenoma with more progress in its advanced techniques, It depends mainly on accurate preoperative localization of parathyroid adenoma by imaging, that markedly decrease operative time, bleeding and post operative morbidity [11].
Ultrasonography has many advantages as initial preoperative imaging modality in diagnosis of parathyroid adenoma as it is easy technique, of low cost, available everywhere and has no radiation hazards [12].
In Ultrasonography parathyroid adenomas appear as a well defined hypoechoic lesion as compared to thyroid gland tissue with hyperechoic line separating it from thyroid representing connective tissue band, it may have cystic changes or calcification inside [13], Fig. 2, Fig. 3, Fig. 4, Fig. 5, By adding color Doppler parathyroid adenomas show increased vascularity inside from an artery surrounding it which is which is a branch from thyroid artery giving branches inside the adenoma that decreased towards the center that helps differentiate adenomas from lymph nodes supplied by central vessels in its hilum [14], Fig. 3, Fig. 4, Fig. 5.
Fig. 3.
Right parathyroid adenoma in 35-year-old male patient with high PTH level: (a) USG neck shows a well defined hypoechoic mass at the posterior aspect of middle part of the right thyroid lobe with mild increased vascularity inside by color Doppler. (b) Early images of Tc99 m sestamibi (upper two images) scan showed intense tracer uptake by the nodule and delayed images (lower two images) at 2 h show tracer retention with wash out from thyroid gland. (c) SPECT/CT imaging localizes the tracer uptake posterior to right thyroid lobe.
Fig. 4.
Left parathyroid adenoma in 43 yrs. old male, with Elevated PTH of 11.5 pmol/L. (a) USG neck shows hypoechoic solid focal lesion seen related to the undersurface of the left thyroid lobe measures about 1.37 × 0.61 cm with separable hyperechoic line from thyroid tissue and increased vascularity inside on color Doppler. (b) Early images: (first two images) Rather homogenous radiotracer uptake is displayed by the thyroid gland with a large ovoid area of focal radiotracer uptake noted abutting the inferior pole of left thyroid lobe, On Late static (second two images) there is partial washout of the tracer from the thyroid gland with tracer retention abutting the inferior pole of left thyroid lobe. (c) SPECT/CT imaging localizes left paratracheal soft tissue density lesion abutting the posterior aspect of the inferior pole of left thyroid lobe.
In our study sensitivity, specificity and accuracy with ultrasonography alone were (76 %), (63 %) and (73 %) respectively which is the lowest as compared to that of MIBI-SPECT/CT alone and combined protocol of ultrasonography and MIBI-SPECT/CT.
In our study 10 cases were missed by ultrasound, false-negative test results occurred in cases with ectopic parathyroid adenoma that have been seen in 4 cases in our study (Fig. 6) and small size adenoma, that occurs in about 6 cases in our study, In study by Reading et al., only 35 % of parathyroid adenoma lesions weighing less than 200 mg were visible on ultrasonography [15].
In our study 4 cases gave false-positive test result occurred in cases with enlarged lymph node adjacent to thyroid gland and cases of multi-nodular goiter.
Scintigraphic imaging like planar images and SPECT plays important role in preoperative depiction of parathyroid adenomas mainly those of ectopic locations like retrotracheal region, retrosternal region, upper mediastinal and intrathymic regions [16].
By adding CT to SPECT study accurate anatomical details could be reached and inconclusive results by planar or SPECT images could be validated by using MIBI-SPECT/CT [17], Figs. 2,3,4,5 and 6.
In our study sensitivity, specificity and accuracy with MIBI-SPECT/CT alone were (83 %), (66 %) and (80 %) respectively which is intermediate between that of ultrasonography when used alone and combined protocol of ultrasonography and MIBI-SPECT/CT.
In our study 3 false positive cases occurred due to uptake and concentration of Tc-99 m MIBI in structures not pathologically proved to be parathyroid adenoma in degree higher than other thyroid tissues, these lesions were pathologically proved to be lymph nodes and thyroid adenoma.
In our study 8 cases were missed by using MIBI-SPECT/CT alone and pathologically proved to have parathyroid adenoma, this false-negative test occurred in cases with small size adenoma. Qiu et al (2014). Stated that 1.03 cm is optimal size for depiction and localization of parathyroid adenoma by MIBI scintigraphy.
Combined use of ultrasonography and MIBI-SPECT/CT increases accuracy of preoperative depiction and localization of parathyroid adenoma in patients with hyperparathyroidism Fig. 2, Fig. 3, Fig. 4, Fig. 5, where MIBI-SPECT/CT is superior to ultrasonography in detection of ectopic adenomas and ultrasonography is useful in cases with low intensity retention of MIBI [18].
According to Assante et al (2019), SPECT/CT had a sensitivity of 97 %, compared with 63 % for planar imaging, SPECT/CT allowed to detect hyperfunctioning parathyroid tissue in 14 (64 %) of the 22 patients with negative planar scintigraphy [19], while in our study we stressed mainly on role of concomitant use of ultrasonography and MIBI-SPECT/CT in comparison to each modality alone.
In 2015 Ozkaya et al. reported that combined use of ultrasonography and MIBI-SPECT/CT is recommended as it achieved accuracy of about more than 90 % [20], and according to Patel et al. (2010) sensitivity and specificity for combined protocol of both modalities were 95 % and 91 % respectively [21].
In our study sensitivity, specificity and accuracy for combined use of MIBI-SPECT/CT and ultrasonography were (87 %), (71 %) and (85 %) respectively which is the highest as compared to that of each of ultrasonography and MIBI-SPECT/CT when used alone.
Limitations of our study includes that it is retrospective study and operator dependant ultrasonography was done by different radiologists having different expertise that could affect statistical results.
6. Conclusion
In conclusion based on our results, concomitant use of ultrasonography and MIBI-SPECT/CT is highly recommended for better depiction and localization of parathyroid adenoma and that will provide better success for parathyroid exploration and minimally invasive surgery
Declaration of Competing Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Contributor Information
Ahmed Ibrahim Tawfik, Email: ahmedtawfik82@yahoo.com.
Wael Hamza Kamr, Email: dr.waelkamr@gmail.com.
Walaa Mahmoud, Email: walaamahmoud@mans.edu.eg.
Islam Ahmed Abo Shady, Email: Islam_abo_shady@yahoo.com.
Mohamed Hosny Mohamed, Email: mkeshk2010@gmail.com.
References
- 1.Clark O.H. Surgical treatment of primary hyperparathyroidism. Adv. Endocrinol. Metab. 1995;6:1–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Bilezikian J.P., Silverberg S.J. Clinical practice. Asymptomatic primary hyperparathyroidism. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004;350:1746–1751. doi: 10.1056/NEJMcp032200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Shaha A.R., Jaffe B.M. Cervical exploration for primary hyperparathyroidism. J. Surg. Oncol. 1993;52:14–17. doi: 10.1002/jso.2930520105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Irvin G.L., Solorzano C.C., Carneiro D.M. Quick intraoperative parathyroid hormone assay: surgical adjunct to allow limited parathyroidectomy, improve success rate, and predict outcome. World J. Surg. 2004;28:1287–1292. doi: 10.1007/s00268-004-7708-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Udelsman R. Six hundred fifty-six consecutive explorations for primary hyperparathyroidism. Ann. Surg. 2002;235:665–670. doi: 10.1097/00000658-200205000-00008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Howe J.R. Minimally invasive parathyroid surgery. Surg. Clin. North Am. 2000;80:1399–1426. doi: 10.1016/s0039-6109(05)70236-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Solorzano C.C., Carneiro-Pla D.M. Irvin GL Surgeon performed ultrasonography as the initial and only localizing study in sporadic primary hyperparathyroidism. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2006;202:18–24. doi: 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2005.08.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Tublin M.E., Pryma D.A., Yim J.H., Ogilvie J.B., Mountz J.M. Localization of parathyroid adenomas by sonography and technetium Tc99m sestamibi single-photon emission computed tomography before minimally invasive parathyroidectomy: are both studies really needed? J. Ultrasound Med. 2009;28:183–190. doi: 10.7863/jum.2009.28.2.183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Billotey C., Sarfati E., Aurengo A., Duet M., Mündler O., Toubert M.E. Advantages of SPECT in technetium-99m-sestamibi parathyroid scintigraphy. J. Nucl. Med. 1996;37:1773–1778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Patel C.N., Salahudeen H.M., Lansdown M., Scarsbrook A.F. Clinical utility of ultrasound and 99mTc sestamibi SPECT/CT for preoperative localization of parathyroid adenoma in patients with primary hyperparathyroidism. Radiology. 2010;65:278–287. doi: 10.1016/j.crad.2009.12.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Grant C.S., Thompson G., Farley D., van Heerden J. Primary hyperparathyroidism surgical management since the introduction of minimally invasive parathyroidectomy: mayo Clinic experience. Arch Surg. 2005;140:472–478. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.140.5.472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.American Institute of Ultrasound in Medicine; American College of Radiology; Society for Pediatric Radiology; Society of Radiologists in Ultrasound: AIUM practice guideline for the performance of a thyroid and parathyroid ultrasound examination. J. Ultrasound Med. 2013;32:1319–1329. doi: 10.7863/ultra.32.7.1319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Acar T., Ozbek S.S., Ertan Y., Kavukcu G., Tuncyurek M., Icoz R.G. Variable sonographic spectrum of parathyroid adenoma with a novel ultrasound fi nding: dual concentric echo sign. Med. Ultrason. 2015;17:139–146. doi: 10.11152/mu.2013.2066.172.tka. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Rumack C.M., Wilson S.R., Charboneau J.W., Levine D. 4th ed. Elsevier Mosby; Philadelphia: 2011. Diagnostic Ultrasound. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Reading C.C., Charboneau J.W., James E.M., Karsell P.R., Purnell D.C., Grant C.S. High-resolution parathyroid sonography. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 1982;139:539–546. doi: 10.2214/ajr.139.3.539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Noda S., Onoda N., Kashiwagi H., Kawajiri H., Takashima T., Ishikawa T. Strategy of operative treatment of hyperparathyroidism using US scan and Tc-99m-MIBI SPECT/CT. Endocr. J. 2014;61:225–230. doi: 10.1507/endocrj.ej13-0292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Mahajan A., Starker L., Ghita M., Udelsman R., Brink J.A., Carling T. Parathyroid four-dimensional computed tomography: evaluation of radiation dose exposure during preoperative localisation of parathyroid tumors in primary hyperparathyroidism. World J. Surg. 2012;36:1335–1339. doi: 10.1007/s00268-011-1365-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Gedik G.K., Bozkurt F.M., Ugur O., Grassetto G. Rubello D The additional diagnostic value of a single-session combined scintigraphic and ultrasonographic examination in patients with thyroid and parathyroid diseases. Panminerva Med. 2008;50:199–205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Assante R., Zampella E., Nicolai E., Acampa W. Incremental value of sestamibi SPECT/CT over dual-phase planar scintigraphy in patients with primary hyperparathyroidism and inconclusive ultrasound. Front. Med. (Lausanne) 2019;16(July 6):164. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2019.00164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Ozkaya M., Elboga U., Sahin E., Kalender E., Korkmaz H., Demir H.D. Evaluation of conventional imaging techniques on preoperative localization in primary hyperparathyroidism. Bosn. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2015;15:61–66. doi: 10.17305/bjbms.2015.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Patel C.N., Salahudeen H.M., Lansdown M., AF Scarsbrook. Clinical utility of ultrasound and 99mTc sestamibi SPECT/CT for preoperative localization of parathyroid adenoma in patients with primary hyperparathyroidism. Clin. Radiol. 2010;65:278–287. doi: 10.1016/j.crad.2009.12.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]