Abstract
Tuberculous osteomyelitis is an uncommon form of tuberculosis (TB); the isolated involvement of the wrist joint is particularly rare. The symptoms and clinical manifestation mimic other conditions; hence, careful diagnosis is required. The authors present two cases of patients presenting with soft tissue mass and a lytic bone lesion. The biopsy revealed granulomatous osteomyelitis. Lesion culture identified Mycobacterium tuberculosis . The authors urge clinicians to include TB as a differential diagnosis when investigating the primary cause of lytic bone lesions, even in the absence of pulmonary symptoms or risk factors of TB infection. The inclusion of mycobacterial cultures when analyzing biopsies of lytic bone lesions is also advised.
Keywords: bone neoplasms/diagnosis, biopsy, fine-needle/methods, tuberculosis, osteoarticular/diagnosis, anti-bacterial agents/therapeutic use
Introduction
The causes of lytic bone lesions include benign, malignant, or infectious processes. It is a mandatory to have broad differential diagnosis and astute observation to accurately diagnose and manage it. Many of the assays distinguishing these conditions require fresh and/or sterile material, so an awareness of the potential etiologies for such lesions and prospective ordering of the correct diagnostic tests is essential for avoiding additional diagnostic procedures or treatments.
Tuberculosis (TB) has the ability to mimic the symptoms of many other diseases, including other infections and various cancers. Tuberculosis of the bone is an infrequent form, which accounts for 1 to 2% of all TB cases in the western world. 1 The involvement of the wrist joint is rare, and the isolated involvement of the wrist accounts for only 1% of all peripheral osteoarticular TB cases. 2 Although it is rare, TB of the bone is an important cause of lytic bone lesions. The diagnosis may be easily missed, leading to inadequate and disadvantageous treatments. Here, we present two cases of patients presenting with soft tissue mass and a lytic bone lesion. The biopsy revealed granulomatous osteomyelitis. Lesion culture eventually identified Mycobacterium tuberculosis .
Case Report
Case 1
The patient was female, 27 years old, referred from an internist with suspect giant cell tumor (GCT) of the right wrist. The patient complained of pain on her right wrist for 3 months. The patient also complained that, after 2 months, a lump on her right wrist was getting bigger ( Fig. 1 ). She had no history of trauma, fever, weight loss or other systemic symptoms. No history of tumor or chronic disease in her family.
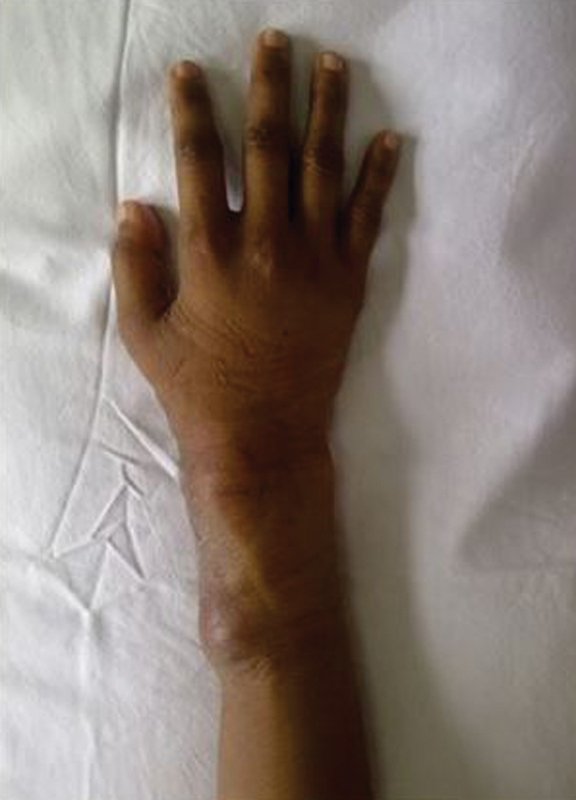
Fig. 1.
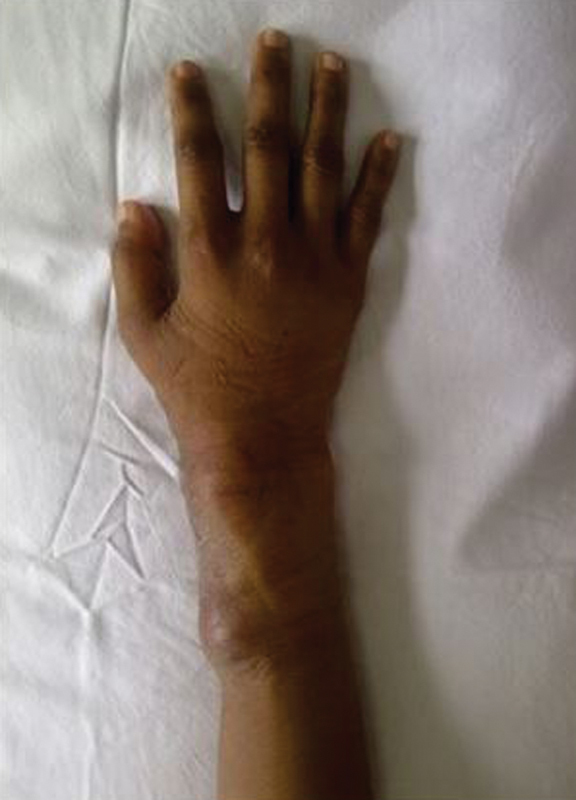
A 27-year-old female with tuberculous osteomyelitis on her right wrist. Clinical photograph of the right wrist revealed a mass on the dorsomedial side measuring approximately 3 × 3 cm, supple, well bordered, and tender.
On physical examination, the patient showed good general condition and vital sign within the normal limit. On the right wrist, we found a mass on the dorsomedial side, measuring about 3 × 3 cm. The mass was supple, well bordered, the same color of the patient's skin, and tender. The range of motion of the right wrist was limited. The remaining findings of the examination were normal.
The laboratory test revealed increase of erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and C-reactive protein (CRP) (ESR I 25 nm; ESR II 100 nm; CRP 45 mg/L). Plain radiograph of the right wrist revealed a lytic lesion with soft tissue swelling, interpreted as suspect GCT by the radiologist ( Fig. 2 ). But in the open biopsy, the sample was interpreted as granulomatous osteomyelitis. No malignant cells could be observed ( Fig. 3 ). Lesion culture eventually identified M. tuberculosis .
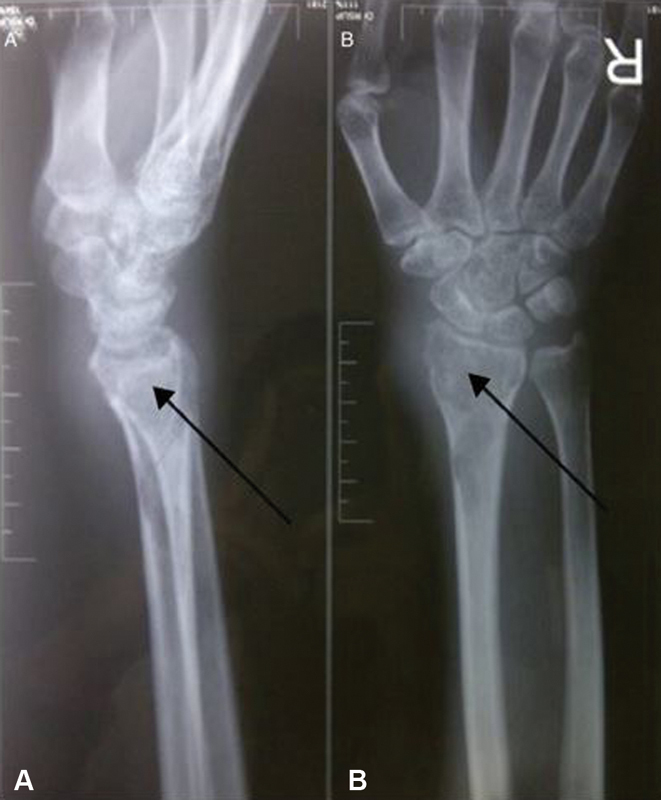
Fig. 2.
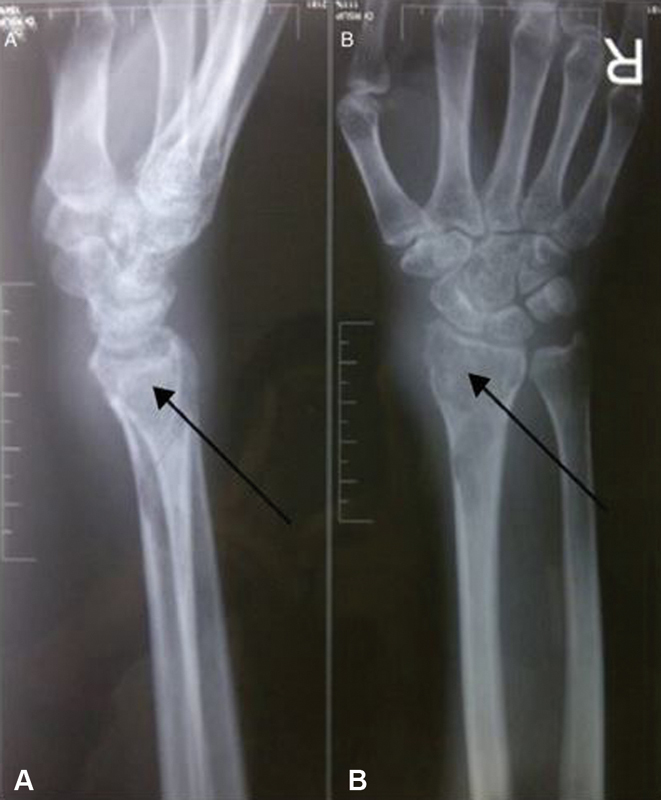
A 27-year-old female with tuberculous osteomyelitis on her right wrist. Lateral ( A ) and anteroposterior ( B ) views of plain radiograph of the right wrist revealed a lytic lesion with soft tissue swelling, suspected diagnosis of giant cell tumor (GCT).
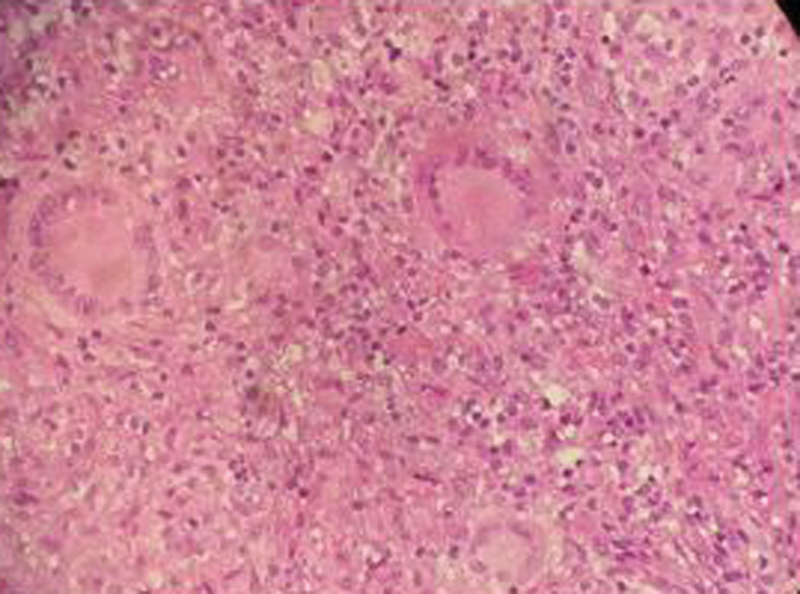
Fig. 3.
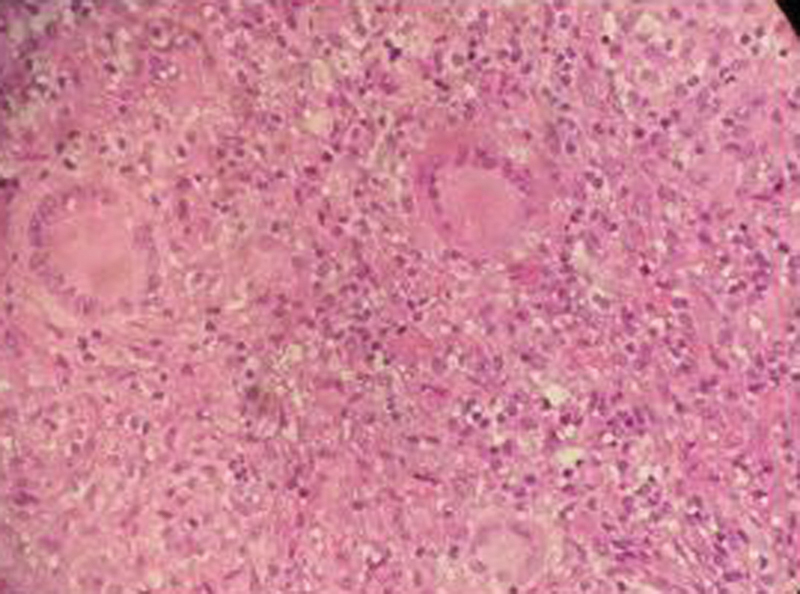
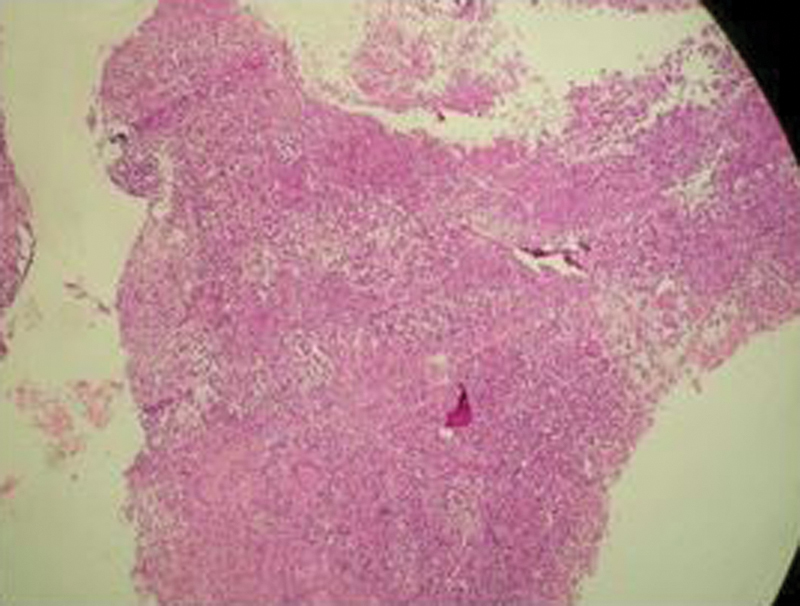
Histopathologic examination of 27-year-old female with tuberculous osteomyelitis on her right wrist. Central caseation area surrounded by macrophages and lymphocytes but without malignant cells.
On the basis of this pathology and microbiology, we diagnosed the patient with tuberculous osteomyelitis of the right wrist. Therapy was initiated with isoniazid (10 mg/kg/d), rifampin (10 mg/kg/d), pyrazinamide (15 mg/kg/d), and ethambutol (15 mg/kg/d), using directly observed therapy. We also per- formed debridement, curettage, and bone graft. Presently, the patient shows clinical improvement.
Case 2
The patient was male, 44 years old, referred from a general surgeon with suspect malignant tumor of the right wrist. The patient complained about a lump on his right wrist for 1 year ( Fig. 4 ). The lump was initially small but was getting bigger. The patient also complained of pain on the right wrist for 6 months. He had no history of trauma, fever, weight loss or other systemic symptoms. No history of tumor or chronic disease in his family.
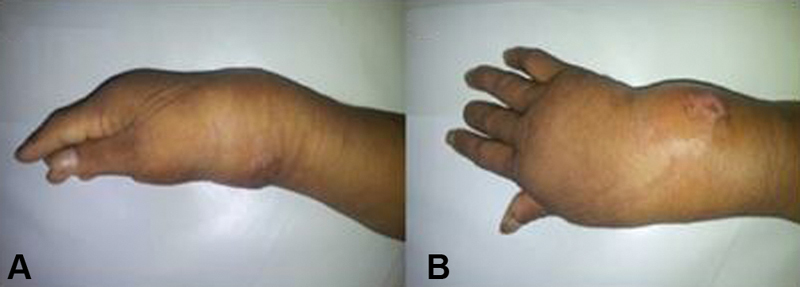
Fig. 4.
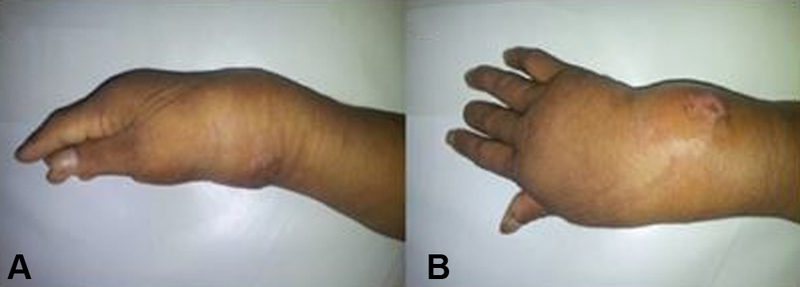
A 44-years-old male with tuberculous osteomyelitis on his right wrist. Lateral ( A ) and anteroposterior ( B ) views of the right wrist revealed a lump with the approximate size of 10 × 10 cm, supple, with ill-defined borders, and tender.
On physical examination, the patient showed good general condition and vital sign within the normal limit. On the right wrist, we found a mass measuring about 10 × 10 cm. The mass was supple, with ill-defined border, same color as the patient's skin, and tender. The range of motion of the right wrist was limited. The remaining findings of the examination were normal
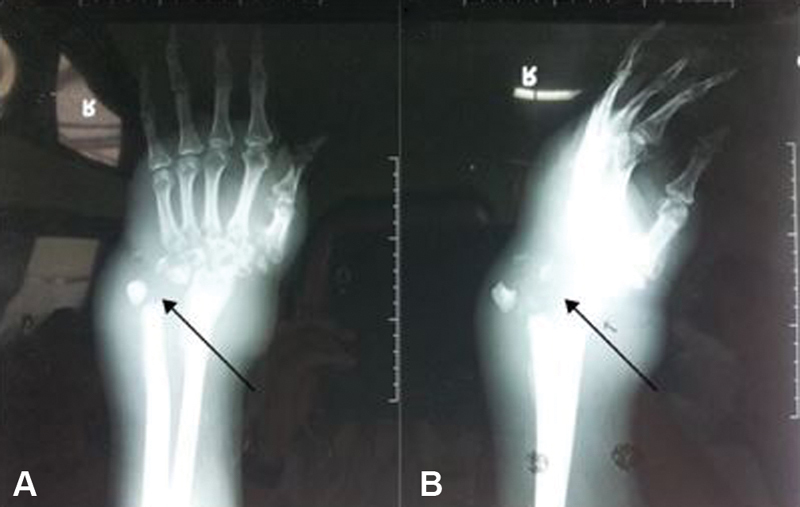
The laboratory test revealed increase of ESR and CRP (ESR I 19 nm; ESR II 90 nm; CRP 40 mg/L). Plain radiograph of the right wrist revealed a lytic lesion on distal radius, ulna, and carpal bone with soft tissue swelling ( Fig. 5 ). But in the open biopsy, the sample was interpreted as granulomatous osteomyelitis. No malignant cells could be observed ( Fig. 6 ). Lesion culture eventually identified M. tuberculosis .
Fig. 5.
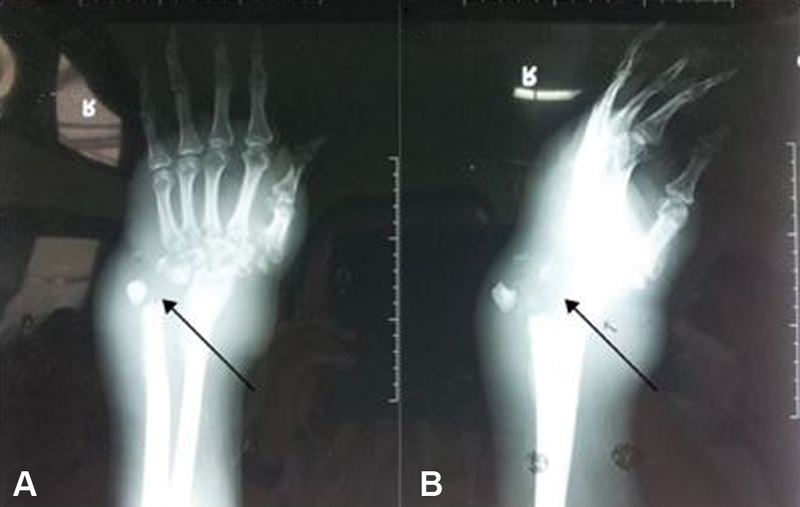
A 44-year-old male with tuberculous osteomyelitis on his right wrist. Anteroposterior ( A ) and lateral ( B ) views of plain radiograph of the right wrist revealed a lytic lesion on the distal radius, ulna, and carpal bone, with soft tissue swelling.
Fig. 6.
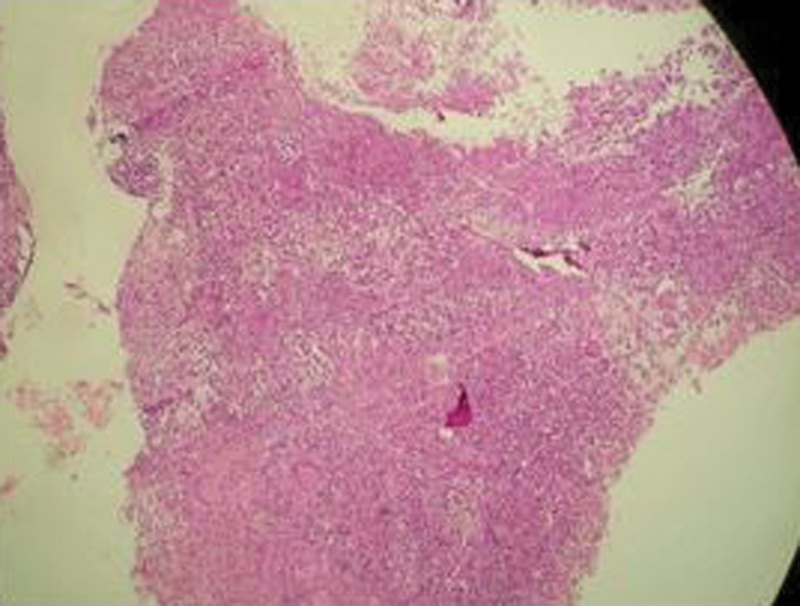
Histopathologic examination of 44 years old male with tuberculous osteomyelitis on his right wrist. Central caseation area surrounded by macrophages and lymphocytes but without malignant cells.
On the basis of this pathology and microbiology, we diagnosed the patient with tuberculous osteomyelitis of the right wrist. Therapy was initiated with isoniazid (10 mg/kg/d), rifampin (10 mg/kg/d), pyrazinamide (15 mg/kg/d), and ethambutol (15 mg/kg/d), using directly observed therapy. We also performed debridement and wrist arthrodesis
Discussion
Tuberculosis remains a major global health issue. The most common manifestation of this infection is pulmonary TB; however, extrapulmonary tuberculosis (EPTB) is found in 20% of all TB cases. Spinal TB is the most frequent pathology among the cases with skeletal TB, while extraspinal tuberculous osteomyelitis is rare. 3 It consists of only 2 to 3% of all cases of osteoarticular TB. Furthermore, it is uncommon to see cases of isolated involvement of bones with tubercular infection. The most frequent bones involved are the hip and knee joints, while the isolated involvement of the wrist is rare. It only accounts for 1% of all cases of peripheral osteoarticular TB. 2 4
Tuberculosis of the bone comes from hematogenous infection; therefore, it is theoretically able to infect all parts of the bone. During mycobateremia of primary infection, the bacteria becomes lodged in the bone. The immune response may restrain the infection in these sites; however, it does not eradicate it. In this case, the patient had a lytic lesion on the distal radius and ulna. The enormous vascular supply of the long bones' growth plate may predispose it to infection, 5 but the presence of infection in the distal metaphysis and epiphysis is an uncommon presentation, so this report presents unique cases. 6 The alternative pathway for isolated involvement of TB infection of the bone may come from trauma. Soman et al 7 reported a 50- year-old patient with osteoarticular TB of the wrist with the involvement of the carpal and metacarpal bones, the ulna, and the radius. The patient had history of trauma on the affected site and managed it by percutaneous pinning. However, in these cases, all of the patients had no history of trauma.
All of the patients in the present study complained of pain and progressive swelling in the right wrist, with no symptoms of fever or other systemic symptoms. According to the literature, the symptoms are not specific, at first, and commonly present as joint pain, swelling, effusion, stiffness, and limitation of movement. 8 In a study by Ali et al 9 involving 66 patients with extraspinal osteoarticular TB, the most frequent presenting symptoms were swelling and pain (45.45%). In this occasion, the constitutional symptoms, such as low-grade fever, night sweats, weight loss, and anorexia, did not appear. The signs of inflammation are mild. 10 Soman et al 7 also reported one patient with osteoarticular TB on the left wrist without the constitutional symptoms. The symptoms that occur may not be considerable, but the chronic infection may become progressive and result in radiographically evident destruction of the bone. 11 As for the laboratory diagnosis, blood tests may reveal normal or mildly raised inflammatory markers. 8 The peripheral leucocytes count is commonly normal, and the ESR could also be normal or elevated. 9 Tuberculin test may performed, and a positive result can help in the suspicion of TB, but the negative result cannot rule out the possibility of TB infection. 7 In this case report, all patients showed increase of ESR and CRP, which marked the existence of inflammation.
The main radiographic features of TB of the bone include sclerosis and osteolytic lesions. However, these features are not specific. Those also exist in other conditions, such as malignancies, inflammatory arthritis, or pyogenic osteomyelitis. 12 It is also known that osteopenia, narrowing of the joint space, soft tissue swelling, bone cysts, and periosteal reaction are other features of TB of the bone. 12 13 14 Computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are other modalities to obtain imaging of the bone; however, these two modalities are not specific; they may be advantageous for the differential diagnosis and for evaluating the extent of the lesion. Magnetic resonance imaging defines soft tissue better, and CT is good for bone lesions. The patients in this case report exhibit lytic lesions either at the distal radius, the ulna, or the carpal bones with soft tissue swelling on plain radiographs, in line with the literature.
Histologic examination is important for the diagnosis. 15
Biopsy from the bone lesion, synovium, or soft tissue mass are needed to remove the confusion in the diagnosis. 16 In a study by Enache et al 17 involving 18 cases of osteoarticular TB lesions, biopsy was diagnostic in 18 cases exhibiting epithelioid granulomas and caseous necrosis. In the study by Muangchan et al, 19 the diagnosis by biopsy was achieved in 46.5% of cases. The gold standard is culture of M. tuberculosis from the bone tissue. On open biopsy, the patients in the present case presented with granulomatous osteomyelitis without the presence of malignant cells, and the lesion culture identified M. tuberculosis . With basis on these findings, the patients were diagnosed with tuberculous osteomyelitis.
The mainstay treatment for tuberculous osteomyelitis is anti-TB drug therapy, and, in the advanced-staged lesions with permanent restriction of joint movements, surgical joint fusion or replacement may be indicated. 9 The patients in the present case report were prescribed the 4 following drugs: isoniazid (10 mg/kg/d), rifampin (10 mg/kg/d), pyrazinamide (15 mg/kg/d), and ethambutol (15 mg/kg/d), and they were also subjected to wrist arthrodesis or curettage and bone graft. The early treatment with anti-TB may achieve near-complete resolution and preservation of function. 18 In most cases, good healing with return of function may be obtained with therapy alone. As for the duration of the treatment, there still is controversy regarding the accurate duration of treatment. At least 12 months of therapy is recommended for bone and joint tuberculosis. 20 21 But, still, the optimal duration for the treatment remains a subject of considerable debate.
The current cases emphasize the importance of broad differential diagnosis of lytic bone lesion. Tuberculosis of the bone should become one of the differential diagnoses, especially in countries where TB is endemic, even without the involvement of pulmonary system and the presence of constitutional symptoms of TB.
Conflitos de Interesse Os autores declaram não haver conflitos de interesse.
Estudo conduzido no Departamento de Cirurgia Ortopédica e Traumatológica, Sanglah General Hospital-Medical Faculty of Udayana University, Denpasar, Indonésia. Originalmente Publicado por Elsevier Editora Ltda.
Study conducted at the Department of Orthopaedic and Traumatology Surgery, Sanglah General Hospital-Medical Faculty of Udayana University, Denpasar, Indonesia. Originally Published by Elsevier Editora Ltda.
Referências
- 1.Shah B A, Splain S. Multifocal osteoarticular tuberculosis. Orthopedics. 2005;28(03):329–332. doi: 10.3928/0147-7447-20050301-22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Turgut M. Spinal tuberculosis (Pott's disease): its clinical presentation, surgical management, and outcome. A survey study on 694 patients. Neurosurg Rev. 2001;24(01):8–13. doi: 10.1007/pl00011973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Wares F, Balasubramanian R, Mohan A, Sharma S K. New Delhi: Directorate General of Health Services, Ministry of Health & Family Welfare; 2005. Extrapulmonary tuberculosis: management and control; pp. 95–114. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Monir Madkour M. Berlin: Springer; 2004. Tuberculosis. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Gardam M, Lim S. Mycobacterial osteomyelitis and arthritis. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2005;19(04):819–830. doi: 10.1016/j.idc.2005.07.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Burnwal R, Neogi D S. Tubercular osteomyelitis of distal ulna presenting as epiphyseal injury. Maedica (Buchar) 2012;7(03):247–250. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Soman S M, Patel B N, Shah P D. Persistent posttraumatic wrist pain – tuberculosis infection should be in the differential diagnosis. A rare case report. J Orthop Case Rep. 2015;5(04):17–20. doi: 10.13107/jocr.2250-0685.335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Mussa M A, O'Connor E F, Waterston S, Taylor M, Iwuagwu F. Isolated tuberculosis of the wrist: a rare case of extrapulmonary tuberculosis. IJCRI. 2013;4(10):541–545. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Ali R, Jalil A, Qureshi A. Extra spinal osteoarticular tuberculosis: a case series of 66 patients from a tertiary care hospital in Karachi. J Pak Med Assoc. 2012;62(12):1344–1348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Watts H G, Lifeso R M. Tuberculosis of bones and joints. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1996;78(02):288–298. doi: 10.2106/00004623-199602000-00019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Garrido G, Gomez-Reino J J, Fernández-Dapica P, Palenque E, Prieto S. A review of peripheral tuberculous arthritis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1988;18(02):142–149. doi: 10.1016/0049-0172(88)90007-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Agarwal S, Caplivski D, Bottone E J. Disseminated tuberculosis presenting with finger swelling in a patient with tuberculous osteomyelitis: a case report. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 2005;4:18. doi: 10.1186/1476-0711-4-18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Berney S, Goldstein M, Bishko F. Clinical and diagnostic features of tuberculous arthritis. Am J Med. 1972;53(01):36–42. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(72)90113-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Wallace R, Cohen A S. Tuberculous arthritis: A report of two cases with review of biopsy and synovial fluid findings. Am J Med. 1976;61(02):277–282. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(76)90177-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Titov A G, Vyshnevskaya E B, Mazurenko S I, Santavirta S, Konttinen Y T. Use of polymerase chain reaction to diagnose tuberculous arthritis from joint tissues and synovial fluid. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2004;128(02):205–209. doi: 10.5858/2004-128-205-UOPCRT. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Haider A LM. Bones and joints tuberculosis. Bahrain Med Bull. 2007;29:1–9. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Enache S D, Pleşea I E, Anuşca D, Zaharia B, Pop O T. Osteoarticular tuberculosis--a ten years case review. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2005;46(01):67–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Chen S C, Chen K T. Updated diagnosis and management of osteoarticular tuberculosis. J Emerg Med Trauma Surg Care. 2014;1(01):1–7. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Muangchan C, Nilganuwong S. The study of clinical manifestation of osteoarticular tuberculosis in Siriraj Hospital, Thailand. J Med Assoc Thai. 2009;92 02:S101–S109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Chandir S, Hussain H, Salahuddin N et al. Extrapulmonary tuberculosis: a retrospective review of 194 cases at a tertiary care hospital in Karachi, Pakistan. J Pak Med Assoc. 2010;60(02):105–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Agarwal A, Qureshi N A, Khan S A, Kumar P, Samaiya S. Tuberculosis of the foot and ankle in children. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong) 2011;19(02):213–217. doi: 10.1177/230949901101900217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]