Abstract
Objective
It remains unclear what roles placenta-originated angiogenic factors play in the pathogenesis of preeclampsia among hypertensive women. We compared maternal soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase 1 (sFlt-1) and placental growth factor (PlGF) levels throughout pregnancy in women with normal blood pressure (BP), elevated BP and hypertension in early pregnancy and their risks of developing preeclampsia.
Design
A prospective cohort study.
Setting
KK Women’s and Children’s Hospital, Singapore.
Participants
923 women with singleton pregnancy <14 weeks of gestation were included in the prospective Neonatal and Obstetrics Risks Assessment cohort between September 2010 and October 2014. Systolic, diastolic, mean arterial blood pressure (MAP) were measured at 11–14 weeks.
Primary and secondary outcomes
Maternal serum sFlt-1, PlGF and sFlt-1/PlGF ratio were tested at 11–14, 18–22, 28–32 and 34 weeks onwards of gestation. Preeclampsia was main pregnancy outcome.
Results
Women were divided based on their BP in early pregnancy: normal (n=750), elevated BP (n=98) and hypertension (n=75). Maternal sFlt-1 levels and sFlt-1/PlGF ratios were higher in hypertensive women throughout pregnancy, but maternal PlGF levels were not significantly lower. Rise in maternal systolic, diastolic BP and MAP at 11–14 weeks were significantly associated with higher sFlt-1/PlGF ratios during pregnancy. A 10 mm Hg increase in MAP was associated with a 5.6-fold increase in risk of preterm preeclampsia and a 3.3-fold increase in risk of term preeclampsia, respectively.
Conclusion
Women with elevated BP in early pregnancy already had a higher sFlt-1/PlGF ratio in early gestation and throughout pregnancy, and an increased risk of preeclampsia. In contrast, PlGF levels in these women remained normal.
Keywords: blood pressure, soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase 1, placental growth factor, preeclampsia
Strengths and limitations of this study.
This study was based on a well-performed prospective cohort with comprehensive information on clinical, biophysical and biochemical markers.
Covariance analysis was performed to compare differences of angiogenic factors values among groups; multivariable logistic regression analysis was performed to evaluate the association between early pregnancy blood pressure and pregnancy outcomes.
Given that most of our participants were low-risk pregnant women, our results may not be applicable to high-risk women.
Introduction
The imbalance in placenta-originated angiogenic factors has been found to play an important role in the pathogenesis of preeclampsia in recent years. Soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase 1 (sFlt-1) and placental growth factor (PlGF) are the most studied proteins. sFlt-1, a splice variant of the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptor Flt-1, is a circulating antiangiogenic protein that inhibits proangiogenic factors—VEGF and PlGF signalling in the vasculature.1 High levels of circulating sFlt-1 and low levels of PlGF were observed in women with established preeclampsia and even before the onset of clinical symptoms.2 3 These promising findings have been adopted and recommended by the National Institute for Clinical Excellence to rule out preeclampsia in women presenting with clinical suspicion.4
Numerous studies focused on the pathological effects of excess sFlt-1 on endothelial function. It was observed that overexpression of sFlt-1 produced a preeclampsia-like syndrome of hypertension, proteinuria and glomerular endotheliosis in experimental animals.5 sFlt-1 is largely produced by syncytiotrophoblast and secreted into maternal circulation.6 Placental hypoxia may be one of the main triggers of inducing abundant sFlt-1 expression and leading to hypertensive complications.7 8 However, this hypothesis may not totally explain why women with elevated blood pressure (BP) before pregnancy have a substantially higher risk of preeclampsia. Besides, evidence suggests that there might be some racial differences in maternal angiogenic and antiangiogenic factors.9 Thus, the objective of this study was to examine the dynamic changes of angiogenic and antiangiogenic factors throughout pregnancy in Asian women with elevated BP in early gestation and their risks of developing preeclampsia later in pregnancy.
Methods
Study design
The Neonatal and Obstetrics Risks Assessment (NORA) study was a prospective cohort conducted at the KK Women’s and Children’s Hospital in Singapore.10 The cohort was set up to screen factors associated with adverse perinatal outcomes, with a focus on using clinical, biochemical and biophysical markers to predict the risks of pregnancy complications in early pregnancy. In brief, detailed interviews, ultrasound scans and blood sample collections were performed at recruitment (11–14 weeks), 18–22 weeks, 28–32 weeks and 34 weeks onwards, respectively. All four antenatal visits also included measurement of maternal height and weight; recording of BP by validated automated devices according to the recommendations of the American Heart Association.11 Participants were closely followed up till their postnatal discharge from the hospital. Information on pregnancy complications, labour and delivery and neonatal outcomes was collected through medical chart review. A written informed consent was obtained from all participating women.
Study population
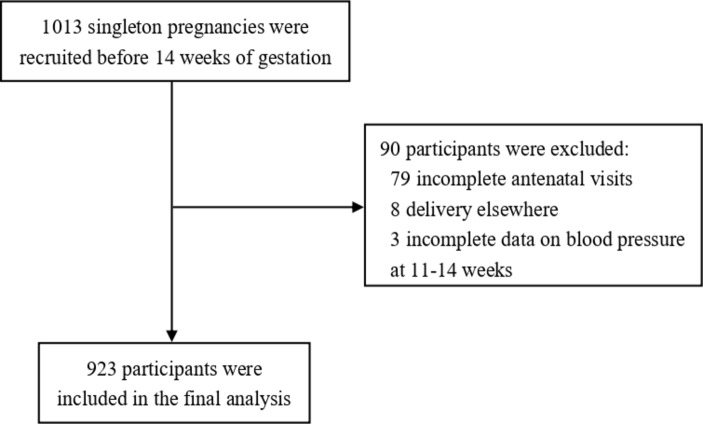
The NORA cohort recruited women with confirmed singleton pregnancies <14 weeks of gestation between September 2010 and October 2014. The exclusion criteria were multiple gestation, severe medical conditions such as chronic renal disease or systemic lupus erythematosus and pregnancies complicated by aneuploidy or fetal anomaly. Gestational age was confirmed by ultrasound at recruitment. A total of 1013 women were enrolled and 934 of them completed all four antenatal visits. Eight participants were delivered elsewhere, leaving 926 eligible women in the cohort. To evaluate the impacts of maternal BP in early pregnancy on angiogenic factors levels and pregnancy outcomes, we used BP at recruitment (11–14 weeks) to classify women into normal, elevated and hypertension groups. As three women did not have BP records at recruitment (11–14 weeks), we included 923 participants for the final analysis (figure 1).
Figure 1.
Flowchart of participants.
Diagnosis
Preeclampsia was defined according to the guidelines of International Society for the Study of Hypertension in Pregnancy12: systolic blood pressure (SBP) ≥140 mm Hg and/or diastolic blood pressure (DBP) ≥90 mm Hg on at least two occasions 4 hours apart after 20 weeks of gestation in a previously normotensive women, and proteinuria: urinary albumin ≥300 mg/24 hours urine collection or ≥1+ dipstick. We used the gestational age at delivery to divide cases of preeclampsia into term (≥37 weeks) and preterm term (<37 weeks). Gestational hypertension was defined as newly onset hypertension after 20 weeks of gestation without proteinuria. Chronic hypertension was defined as women with history of hypertension before conception or the presence of hypertension before 20 weeks of gestation.
To explore the relationship between maternal BP levels in the first trimester and pregnancy outcome, we followed the 2017 guideline from the American College of Cardiology and the American Heart Association (ACC/AHA).13 Normal BP was defined as SBP <120 mm Hg and DBP <80 mm Hg; elevated BP was defined as SBP 120–129 mm Hg and DBP <80 mm Hg; hypertension stage 1 as SBP 130–139 mm Hg or DBP 80–89 mm Hg and hypertension stage 2 as SBP ≥140 mm Hg or DBP ≥90 mm Hg.
Measurement of BP
BP was taken by validated automated devices which were calibrated periodically. The women were in the seated position and their arms were supported. A correct cuff size was used and the middle of cuff was positioned on woman’s upper arm at the level of the right atrium. After a 5 min rest, BP was measured by trained nurses and three recordings were made at 1 min intervals. We calculated SBP and DBP as the average of the three measurements. Mean arterial pressure (MAP) was calculated from SBP and DBP measures using the following formula: MAP=DBP+1/3×(SBP-DBP). BP was modelled continuously in units of 10 mm Hg.
Measurements of angiogenic factors
About 8 mL of maternal venous blood was collected in non-heparinised tubes at each antenatal visit. It was then centrifuged at 2000 rpm for 15 min before separating and storing serum samples at −80℃ for subsequent analysis. Serum levels of sFlt-1 and PlGF were determined by means of the fully automated Elecsys assays on an electrochemiluminescence immunoassay platform (cobas e411 analyzers, Roche Diagnostics). The detection limit was ~6 pg/mL for sFlt-1 and <2 pg/mL for PlGF.
Statistical analysis
Normality of continuous variables was assessed by the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test. Numeric data were expressed as mean (SD) or as median (IQR) for normally and non-normally distributed data, respectively. Maternal characteristics, pregnancy outcomes and maternal BP levels were compared among normal, elevated BP and hypertension (stage 1 and stage 2) groups using one-way ANOVA (Analysis of variance) or Kruskal-Wallis tests for continuous variables and χ2 analysis for categorical variables. Covariance analysis and Dunnett test was used to compare differences of logarithm-transformed angiogenic factors values among groups adjusted for covariants. Geometric means and 95% CIs were calculated by taking the exponent of the logarithm transformed mean. Linear regression analysis was performed to assess the association of BP (10 mm Hg) at recruitment with logarithm-transformed angiogenic factors values during pregnancy. Covariance analysis and linear regression models were adjusted for maternal race, smoking during pregnancy, body mass index (BMI) and gestational age at blood collection as covariant. Logistic regression analysis was performed to evaluate the association between early pregnancy BP (10 mm Hg) and pregnancy outcomes with adjustment of potential confounders, including maternal age, race, education, maternal BMI at recruitment, chronic hypertension and pre-existing diabetes mellitus. We used SAS V.9.4 for all statistical analyses.
Patient and public involvement
Patients and the public were not directly involved in the design, conduct or reporting in our study.
Results
A total of 923 participants in the NORA cohort were included in this analysis. Based on maternal BP at recruitment at 11–14 weeks of gestation, 750 women were classified as normal BP; 98 women as elevated BP, and 75 women as hypertension (stage 1 and stage 2). A comparison of maternal characteristics and pregnancy outcomes are given in table 1. Women with hypertension (stage 1 and stage 2) in the first trimester were slightly older than the other two groups. Chinese women contributed a greater proportion of hypertension (49.3%) than Indian (8.0%) and Malay (30.7%). A higher incidence of maternal overweight (BMI ≥25 kg/m2) and obesity (BMI ≥30 kg/m2) was observed in the elevated BP group and hypertension group than in the normal BP group.
Table 1.
Characteristics and pregnancy outcomes by maternal blood pressure at 11–14 weeks in the NORA cohort
| Variables | Normal BP (n=750) | Elevated BP (n=98) | Hypertension (stage 1 and stage 2) (n=75) | P value |
| Maternal age (year), median (IQR) | 30.0 (26.0–34.0) | 30.0 (26.0–35.0) | 32.0 (29.0–35.0) | <0.001 |
| Race, n (%) | 0.012 | |||
| Chinese | 393 (52.3) | 38 (38.8) | 37 (49.3) | |
| Indian | 88 (11.7) | 6 (6.1) | 6 (8.0) | |
| Malay | 186 (24.8) | 41 (41.8) | 23 (30.7) | |
| Others | 84 (11.2) | 13 (13.3) | 9 (12.0) | |
| Parity, n (%) | 0.091 | |||
| 0 | 419 (55.9) | 49 (50.0) | 33 (44.0) | |
| 1 | 236 (31.5) | 32 (32.7) | 25 (33.3) | |
| ≥2 | 95 (12.7) | 17 (17.3) | 17 (22.7) | |
| Maternal education levels, n (%) | 0.044 | |||
| Less than high school | 166 (22.2) | 28 (28.6) | 25 (33.3) | |
| High school | 299 (40.0) | 44 (44.9) | 23 (30.7) | |
| College and above | 282 (37.8) | 26 (26.5) | 27 (36.0) | |
| Married, n (%) | 699 (93.2) | 90 (91.8) | 72 (96.0) | 0.544 |
| Smoking during pregnancy, n (%) | 19 (2.5) | 4 (4.1) | 0 (0) | 0.230 |
| Maternal BMI at 11–14 weeks of gestation (kg/m2), n (%) | <0.001 | |||
| <18.5 | 62 (8.3) | 2 (2.0) | 0 (0) | |
| 18.5–24.9 | 475 (63.5) | 32 (32.7) | 16 (21.3) | |
| 25.0–29.9 | 162 (21.7) | 35 (35.7) | 32 (42.7) | |
| ≥30.0 | 49 (6.6) | 29 (29.6) | 27 (36.0) | |
| Diabetes mellitus, n (%) | 7 (0.9) | 2 (2.0) | 5 (6.7) | <0.001 |
| ART conception, n (%) | 31 (4.1) | 4 (4.1) | 2 (2.7) | 0.826 |
| Antihypertensive medication, n (%) |
0 (0) | 0 (0) | 3 (4.0) | <0.001 |
| Pregnancy outcomes | ||||
| Delivery age (weeks), median (IQR) | 39.0 (38.1–39.7) | 38.7 (38.0–39.6) | 38.3 (37.6–39.1) | 0.001 |
| Birth weight (kg), median (IQR) | 3.1 (2.9–3.4) | 3.1 (2.9–3.5) | 3.1 (2.8–3.4) | 0.324 |
| Gestational hypertension, n (%) | 10 (1.3) | 3 (3.1) | 5 (6.7) | 0.004 |
| Preeclampsia, n (%) | 6 (0.8) | 3 (3.1) | 12 (16.0) | <0.001 |
| Preterm preeclampsia, n (%) | 4 (0.5) | 0 (0) | 5 (6.7) | <0.001 |
| Term preeclampsia, n (%) | 2 (0.3) | 3 (3.1) | 7 (9.3) | <0.001 |
ART, assisted reproductive technology; BMI, body mass index; BP, blood pressure.
The prevalence of maternal preconception diabetes was 6.7% in hypertension groups which was significantly higher than that of the other two groups. However, the prevalence of conception with assisted reproductive technology were not significantly different among the three groups. As expected, the incidence of gestational hypertension (6.7%), preeclampsia (16.0%), preterm preeclampsia (6.7%) and term preeclampsia (9.3%) were the highest in the hypertension group. Women with hypertension had sustainable higher BP levels during pregnancy (table 2).
Table 2.
Maternal blood pressure levels at four time points during pregnancy by maternal blood pressure at 11–14 weeks in the NORA cohort
| Variables | Normal BP (n=750) | Elevated BP (n=98) | Hypertension (stage 1 and stage 2) (n=75) | P value |
| SBP (mm Hg), mean±SD | ||||
| 11–14 weeks | 104.9±8.3 | 123.2±2.6 | 126.8±11.1 | <0.001 |
| 18–22 weeks | 105.9±10.1 | 118.6±9.9 | 124.0±10.5 | <0.001 |
| 28–32 weeks | 108.2±10.0 | 118.1±9.7 | 123.8±11.4 | <0.001 |
| ≥34 weeks | 110.5±10.7 | 119.5±10.6 | 126.1±15.5 | <0.001 |
| DBP (mm Hg), mean±SD | ||||
| 11–14 weeks | 63.6±6.8 | 71.4±4.4 | 80.8±7.0 | <0.001 |
| 18–22 weeks | 62.9±7.0 | 69.0±7.2 | 76.3±8.1 | <0.001 |
| 28–32 weeks | 64.0±6.9 | 69.8±6.6 | 76.6±9.0 | <0.001 |
| ≥34 weeks | 67.4±7.8 | 73.3±7.3 | 80.0±11.4 | <0.001 |
| MAP (mm Hg), mean±SD | ||||
| 11–14 weeks | 77.3±6.5 | 88.7±3.2 | 96.1±6.5 | <0.001 |
| 18–22 weeks | 77.2±7.2 | 85.5±7.3 | 92.2±8.2 | <0.001 |
| 28–32 weeks | 78.8±7.1 | 85.9±6.3 | 92.4±9.1 | <0.001 |
| ≥34 weeks | 81.8±8.1 | 88.7±7.6 | 95.4±11.9 | <0.001 |
BP, blood pressure; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; MAP, mean arterial pressure; SBP, systolic blood pressure.
Table 3 shows the values of angiogenic factors at four time points in the NORA participants. Logarithm-transformed serum angiogenic factors levels at four time points are presented as well (online supplementary table 1). We used covariance analysis to control for potential confounders that were reported to have impact on serum angiogenic proteins levels, including maternal race, smoking, maternal BMI and gestational age at blood collection. Overall, serum sFlt-1 concentrations continued rising throughout pregnancy. PlGF levels increased from the first trimester, peaked at 28–32 weeks and declined afterwards. Consequently, high levels of sFlt-1/PlGF ratio were observed both at 11–14 and 34 weeks onwards. The dynamic change of serum angiogenic factors during pregnancy was observed in all three groups. Maternal serum sFlt-1 and PlGF levels were not significantly different between elevated BP group and normal BP group at four time points during pregnancy. In hypertension group, a trend of higher maternal sFlt-1 concentrations was observed from early pregnancy and it was dramatically increased during the third trimester compared with sFlt-1 levels in normotensive women. In contrast, PlGF concentrations were not significantly different between hypertension group and normal BP group. Thus, sFlt-1/PlGF ratio in hypertensive women was significantly higher throughout pregnancy than that in normotensive women. Comparisons of angiogenic factors levels throughout gestation in women with or without preeclampsia in each group are presented in supplementary table 2.
Table 3.
Maternal serum angiogenic factors levels at four time points during pregnancy by maternal blood pressure at 11–14 weeks in the NORA cohort
| Angiogenic factors | Time points | Normal BP | Elevated BP | Hypertension (stage 1 and stage 2) | |||||
| N | Mean (95% CI)* | N | Mean (95% CI) * | P value† | N | Mean (95% CI)* | P value‡ | ||
| sFlt-1 (pg/mL) | 11–14 weeks | 746 | 1585 (1549 to 1622) | 98 | 1722 (1585 to 1862) | 0.096 | 75 | 1758 (1585 to 1950) | 0.079 |
| 18–22 weeks | 745 | 1698 (1660 to 1778) | 98 | 1738 (1585 to 1950) | 0.824 | 75 | 1905 (1698 to 2138) | 0.139 | |
| 28–32 weeks | 730 | 1660 (1585 to 1698) | 92 | 1698 (1549 to 1862) | 0.868 | 70 | 2042 (1820 to 2291) | 0.001 | |
| ≥34 weeks | 659 | 2570 (2512 to 2692) | 82 | 2818 (2570 to 3162) | 0.201 | 57 | 3311 (2951 to 3802) | 0.000 | |
| PlGF (pg/mL) | 11–14 weeks | 746 | 37 (36 to 38) | 98 | 35 (32 to 38) | 0.243 | 75 | 35 (32 to 39) | 0.593 |
| 18–22 weeks | 745 | 269 (257 to 275) | 98 | 245 (224 to 269) | 0.261 | 75 | 245 (219 to 275) | 0.364 | |
| 28–32 weeks | 730 | 617 (589 to 646) | 92 | 575 (501 to 676) | 0.718 | 70 | 537 (457 to 631) | 0.270 | |
| ≥34 weeks | 659 | 380 (355 to 398) | 82 | 324 (269 to 380) | 0.178 | 57 | 339 (275 to 427) | 0.585 | |
| sFlt-1/PlGF ratio | 11–14 weeks | 746 | 42.7 (40.7 to 44.7) | 98 | 50.1 (44.7 to 55.0) | 0.013 | 75 | 50.1 (43.7 to 56.2) | 0.042 |
| 18–22 weeks | 745 | 6.5 (6.2 to 6.8) | 98 | 7.1 (6.3 to 7.9) | 0.201 | 75 | 7.8 (6.8 to 8.9) | 0.027 | |
| 28–32 weeks | 730 | 2.7 (2.5 to 2.9) | 92 | 2.9 (2.5 to 3.5) | 0.643 | 70 | 3.8 (3.1 to 4.6) | 0.005 | |
| ≥34 weeks | 659 | 6.9 (6.3 to 7.4) | 82 | 8.9 (6.9 to 11.2) | 0.100 | 57 | 9.8 (7.4 to 13.2) | 0.044 | |
*Means (95% CI) were adjusted for maternal race, smoking during pregnancy, maternal body mass index at blood test and gestational weeks at blood test from models with logarithm-transformed serum angiogenic factors levels as outcomes; presented as geometric means.
†Statistically significant difference between normal BP and elevated BP groups.
‡Statistically significant difference between normal BP and hypertension group.
BP, blood pressure; PlGF, placental growth factor; sFlt-1, soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase 1.
bmjopen-2019-032237supp001.pdf (87.1KB, pdf)
Higher levels of DBP and MAP in early pregnancy were significantly associated with higher log-transformed sFlt-1 values throughout pregnancy. Meanwhile, higher SBP levels were significantly associated with lower log-transformed PlGF levels both at 18–22 weeks (β=−0.02 per 10 mm Hg SBP, p=0.011) and at 28–32 weeks (β=−0.02 per 10 mm Hg SBP, p=0.031). Thus, rises in maternal SBP, DBP and MAP in the first trimester were significantly associated with higher sFlt-1/PlGF ratios during pregnancy (online supplementary table 3).
Table 4 presents the significant association between BP in early pregnancy and risks of preeclampsia (OR 2.5, 95% CI 1.5 to 4.0 per 10 mm Hg SBP; OR 4.3, 95% CI 2.3 to 7.9 per 10 mm Hg DBP; OR 4.1, 95% CI 2.2 to 7.7 per 10 mm Hg MAP, respectively) after adjustment of potential confounders. Preterm preeclampsia was more closely associated with higher DBP than SBP (OR 6.0, 95% CI 2.3 to 7.9 per 10 mm Hg DBP vs OR 1.9, 95% CI 0.9 to 3.8 per 10 mm Hg SBP).
Table 4.
Logistic regression analysis for maternal blood pressure at 11–14 weeks and adverse pregnancy outcomes.
| Variable | Preeclampsia | Preterm preeclampsia | Term preeclampsia | |||
| Crude OR (95% CI) |
Adjusted OR* (95% CI) |
Crude OR (95% CI) |
Adjusted OR* (95% CI) |
Crude OR (95% CI) |
Adjusted OR* (95% CI) | |
| SBP (10 mm Hg) | 3.0 (1.9 to 4.6)† | 2.5 (1.5 to 4.0)† | 1.9 (1.1 to 3.5) | 1.9 (0.9 to 3.8) | 4.1 (2.2 to 7.8)† | 3.2 (1.6 to 6.4)† |
| DBP (10 mm Hg) | 5.2 (2.9 to 9.3)† | 4.3 (2.3 to 7.9)† | 5.8 (2.4 to 14.4)† | 6.0 (2.3 to 16.2)† | 4.4 (2.1 to 9.1)† | 3.1 (1.4 to 6.8)† |
| MAP (10 mm Hg) | 5.1 (2.8 to 9.0)† | 4.1 (2.2 to 7.7)† | 5.1 (2.1 to 11.9)† | 5.6 (2.0 to 15.5)† | 4.7 (2.2 to 9.7)† | 3.3 (1.5 to 7.4) |
*Adjusted for maternal age, race, education, maternal body mass index at 11–14 weeks’ gestation and diabetes mellitus.
†P<0.01.
DBP, diastolic blood pressure; MAP, mean arterial pressure; SBP, systolic blood pressure.
Discussion
Our study confirmed that higher early pregnancy BP levels were prospectively associated with increased risks of preeclampsia, including preterm and term preeclampsia. Furthermore, women with elevated BP in early pregnancy already had a higher sFlt-1 level and sFlt-1/PlGF ratio in early gestation and throughout pregnancy. In contrast, PlGF levels in these women remained normal throughout gestation.
It is well established that women with chronic hypertension have several times the risk of preeclampsia than normotensive women.14 However, the pathogensis is poorly understood and what role these angiogenic and antiangiogenic factors play remains unclear. Although syncytiotrophoblast is a major source of sFlt-1 production, peripheral blood monocytes produce a small amount of sFlt-1 further stimulated by inflammation.15 16 As chronic hypertension is often related to a chronic inflammatory status,17 the slightly increased sFlt-1 level in hypertensive women in early pregnancy, as observed in our study, may reflect the chronic inflammatory status in early pregnancy. Our results showed that hypertensive women in early pregnancy might have an imbalanced angiogenic factors levels and such imbalanced angiogenic environment tended to continue during pregnancy, which might be associated with the increased risks of preeclampsia.
On the other hand, maternal circulating PlGF is highly expressed by the placenta during pregnancy. It has both vasculogenic and angiogenic functions18 and its level is likely to reflect the placental health conditions. For example, low PlGF concentrations preceding clinical onset of preeclampsia often occur in early onset rather than late-onset preeclampsia.19 Women who develop preeclampsia with fetal growth restriction (FGR) have further decreased PlGF levels compared with women who develop preeclampsia without FGR.20–22 Early onset preeclampsia and placenta-derived FGR are associated with placenta pathology such as incomplete remodelling of spiral arteries, acute atherosis and thrombosis in spiral arteries and syncytiotrophoblast necrosis.23 24 In our study, women with elevated BP in early pregnancy, the PlGF level remained by and large normal throughout pregnancy and newborn’s birth weight was not significantly different among the three groups. Thus, our findings seem to suggest that the placental implantation and development might not be impaired in these women.
As poor placentation is not a unique cause of developing preeclampsia, enhanced placental oxidative and endoplasmic reticulum stress and increased maternal systemic inflammatory responses are thought to play crucial roles in preeclampsia as well.25 26 Thus, pre-existing endothelial dysfunction in hypertensive women could be exacerbated as a result of physiological burden of pregnancy even without an abnormal placentation.27 Taking all things considered, we propose that the imbalanced angiogenic factors environment and, perhaps more importantly, pre-existing endothelial susceptibility and dysfunction, may play a critical role in the development of preeclampsia in women with elevated BP in early pregnancy.
To our best knowledge, this was the first prospective cohort study that illustrated the dynamic changes of angiogenic and antiangiogenic factors throughout pregnancy in women with different BP status in early pregnancy. The NORA cohort was a well-performed prospective study with comprehensive information including clinical, biophysical and biochemical markers. The follow-up rate was 99.1% (926/934) at the end of pregnancy. Measurements of BP and serum angiogenic factors were performed according to standardised protocols. In our study, three women reported using antihypertensive medications during pregnancy; thus, the results should not be affected by the medication issue. On the other hand, as most of our participants were low-risk pregnant women, our results may not be applicable to high-risk women. As it was an observational study, the potential residual confounding and selection bias might have some impacts on our results.
Conclusion
Women with elevated BP in early pregnancy already had a higher sFlt-1/PlGF ratio in early gestation and throughout pregnancy, and an increased risk of preeclampsia. In contrast, PlGF levels in these women remained normal throughout gestation. Our findings suggest that the imbalanced angiogenic factors levels throughout gestation might play a crucial role in developing preeclampsia in women with pre-existing elevated BP. Our study also supports that preconception or early pregnancy high BP, defined as SBP ≥130 mm Hg or DBP ≥80 mm Hg according to 2017 ACC/AHA guideline, should cause clinical awareness both during pregnancy and in their later life.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We thank all the NORA cohort (Neonatal and Obstetrics Risks Assessment) participants for their commitment to the study, the NORA cohort investigators and staff.
Footnotes
Contributors: JZ: performed the statistical analysis, searched literature and drafted the manuscript. JZ (corresponding author): had the original idea, provided guidance for the statistical analysis and revised the manuscript. MJN, BC, GSHY and KHT: participated in the data collection, reviewed and revised the manuscript.
Funding: The authors have not declared a specific grant for this research from any funding agency in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sectors.
Competing interests: None declared.
Patient consent for publication: Not required.
Ethics approval: This study was approved by the SingHealth Centralised Institutional Review Board Ethics Committee, Singapore (CIRB Ref No. 2010/214/D).
Provenance and peer review: Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
Data availability statement: All data relevant to the study are included in the article or uploaded as supplementary information.
References
- 1. Kendall RL, Thomas KA. Inhibition of vascular endothelial cell growth factor activity by an endogenously encoded soluble receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1993;90:10705–9. 10.1073/pnas.90.22.10705 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Levine RJ, Maynard SE, Qian C, et al. . Circulating angiogenic factors and the risk of preeclampsia. N Engl J Med 2004;350:672–83. 10.1056/NEJMoa031884 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Zeisler H, Llurba E, Chantraine F, et al. . Predictive Value of the sFlt-1:PlGF Ratio in Women with Suspected Preeclampsia. N Engl J Med 2016;374:13–22. 10.1056/NEJMoa1414838 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. NICE PlGF-based testing to help diagnose suspected pre-eclampsia (triage PlGF test, Elecsys immunoassay sFlt-1/PlGF ratio, DELFIA Xpress PlGF 1-2-3 test, and BRAHMS sFlt-1 Kryptor/BRAHMS PlGF plus Kryptor PE ratio). diagnostics guidance 23. London: NICE, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- 5. Maynard SE, Min J-Y, Merchan J, et al. . Excess placental soluble FMS-like tyrosine kinase 1 (sFlt1) may contribute to endothelial dysfunction, hypertension, and proteinuria in preeclampsia. J Clin Invest 2003;111:649–58. 10.1172/JCI17189 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Sela S, Itin A, Natanson-Yaron S, et al. . A novel human-specific soluble vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1: cell-type-specific splicing and implications to vascular endothelial growth factor homeostasis and preeclampsia. Circ Res 2008;102:1566–74. 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.108.171504 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Gerber HP, Condorelli F, Park J, et al. . Differential transcriptional regulation of the two vascular endothelial growth factor receptor genes. Flt-1, but not Flk-1/KDR, is up-regulated by hypoxia. J Biol Chem 1997;272:23659–67. 10.1074/jbc.272.38.23659 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Warrington JP, George EM, Palei AC, et al. . Recent advances in the understanding of the pathophysiology of preeclampsia. Hypertension 2013;62:666–73. 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.113.00588 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Yang J, Pearl M, DeLorenze GN, et al. . Racial-ethnic differences in midtrimester maternal serum levels of angiogenic and antiangiogenic factors. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2016;215:e1-9:359–359.e9. 10.1016/j.ajog.2016.04.002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Ng QJ, Zhang J, Dai F, et al. . Neonatal and obstetric risk assessment (NorA) pregnancy cohort study in Singapore. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2018;4:31–7. [Google Scholar]
- 11. Pickering TG, Hall JE, Appel LJ, et al. . Recommendations for blood pressure measurement in humans and experimental animals. Circulation 2005;111:697–716. 10.1161/01.CIR.0000154900.76284.F6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Brown MA, Lindheimer MD, de Swiet M, et al. . The classification and diagnosis of the hypertensive disorders of pregnancy: statement from the International Society for the study of hypertension in pregnancy (ISSHP). Hypertens Pregnancy 2001;20:ix–xiv. 10.3109/10641950109152635 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Whelton PK, Carey RM, Aronow WS, et al. . 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA guideline for the prevention, detection, evaluation, and management of high blood pressure in adults: executive summary: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American heart association Task force on clinical practice guidelines. Hypertension 2018;71:1269–324. 10.1161/HYP.0000000000000066 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Bartsch E, Medcalf KE, Park AL, et al. . High risk of pre-eclampsia identification group. clinical risk factors for pre-eclampsia determined in early pregnancy: systematic review and meta-analysis of large cohort studies. BMJ 2016;353:i1753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Rajakumar A, Michael H, Rajakumar P, et al. . Extra-placental expression of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1, (flt-1) and soluble Flt-1 (sFlt-1), by peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) in normotensive and preeclamptic pregnant women. Placenta 2005;26:563–73. 10.1016/j.placenta.2004.09.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Freeman DJ, McManus F, Brown EA, et al. . Short- and long-term changes in plasma inflammatory markers associated with preeclampsia. Hypertension 2004;44:708–14. 10.1161/01.HYP.0000143849.67254.ca [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Dinh QN, Drummond GR, Sobey CG, et al. . Roles of inflammation, oxidative stress, and vascular dysfunction in hypertension. Biomed Res Int 2014;2014:1–11. 10.1155/2014/406960 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. De Falco S. The discovery of placenta growth factor and its biological activity. Exp Mol Med 2012;44:1–9. 10.3858/emm.2012.44.1.025 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. McElrath TF, Lim K-H, Pare E, et al. . Longitudinal evaluation of predictive value for preeclampsia of circulating angiogenic factors through pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2012;207:e1-7:407–407.e7. 10.1016/j.ajog.2012.08.010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Powers RW, Roberts JM, Plymire DA, et al. . Low placental growth factor across pregnancy identifies a subset of women with preterm preeclampsia: type 1 versus type 2 preeclampsia? Hypertension 2012;60:239–46. 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.112.191213 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Romero R, Nien JK, Espinoza J, et al. . A longitudinal study of angiogenic (placental growth factor) and anti-angiogenic (soluble endoglin and soluble vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1) factors in normal pregnancy and patients destined to develop preeclampsia and deliver a small for gestational age neonate. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 2008;21:9–23. 10.1080/14767050701830480 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Chaiworapongsa T, Romero R, Whitten AE, et al. . The use of angiogenic biomarkers in maternal blood to identify which SGA fetuses will require a preterm delivery and mothers who will develop pre-eclampsia. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 2016;29:1214–28. 10.3109/14767058.2015.1048431 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Nelson DB, Ziadie MS, McIntire DD, et al. . Placental pathology suggesting that preeclampsia is more than one disease. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2014;210:e1-7:66–66.e7. 10.1016/j.ajog.2013.09.010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Burton GJ, Jauniaux E. Pathophysiology of placental-derived fetal growth restriction. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2018;218:S745–61. 10.1016/j.ajog.2017.11.577 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Steegers EAP, von Dadelszen P, Duvekot JJ, et al. . Pre-Eclampsia. The Lancet 2010;376:631–44. 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60279-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Redman CW, Sargent IL, Staff AC. IFPA senior Award Lecture: making sense of pre-eclampsia – two placental causes of preeclampsia? Placenta 2014;35:S20–5. 10.1016/j.placenta.2013.12.008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Ness RB, Roberts JM. Heterogeneous causes constituting the single syndrome of preeclampsia: a hypothesis and its implications. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1996;175:1365–70. 10.1016/S0002-9378(96)70056-X [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
bmjopen-2019-032237supp001.pdf (87.1KB, pdf)