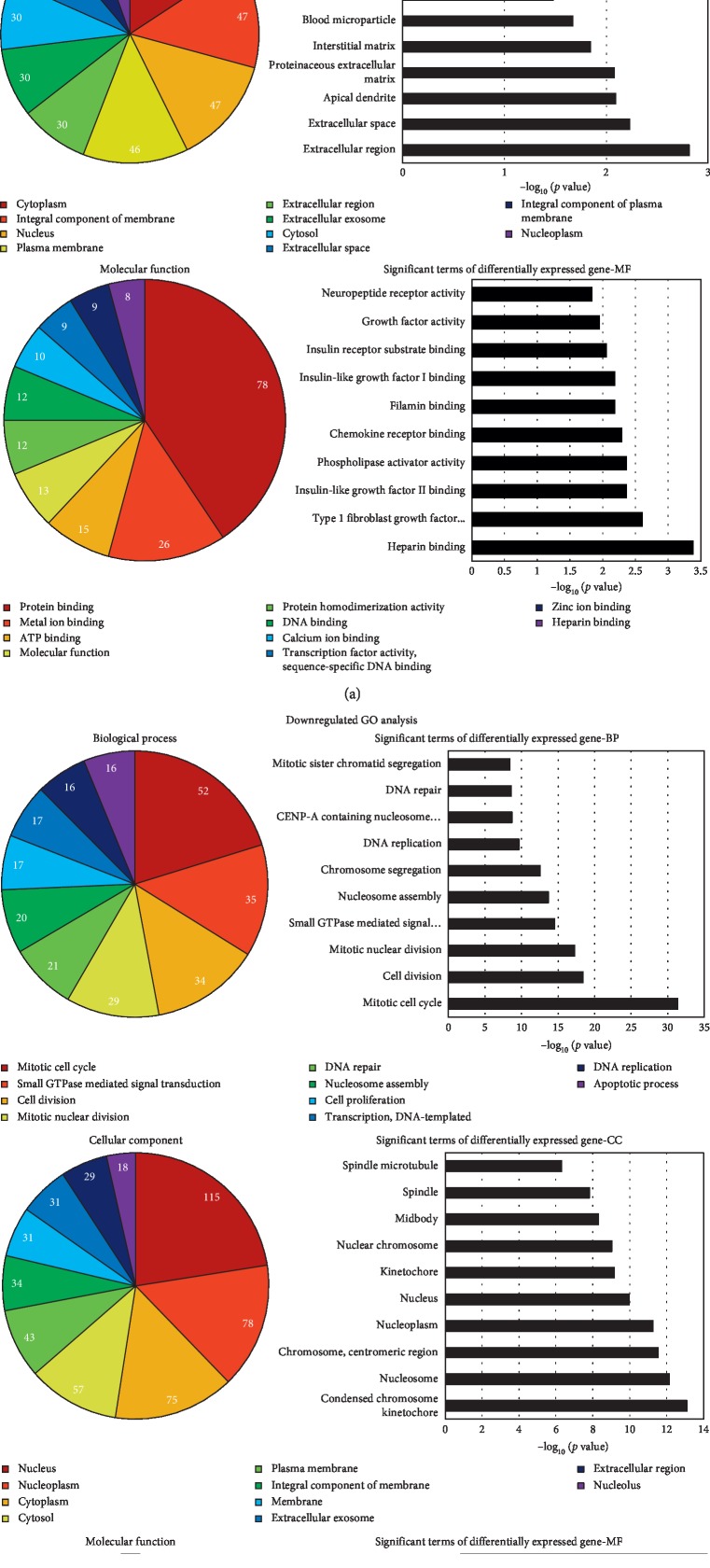
In the article titled “The Effect of Botulinum Toxin Type A on Expression Profiling of Long Noncoding RNAs in Human Dermal Fibroblasts” [1], there was an error in Figure 4, where the second and third graphs of Figure 4(a) were mistakenly duplicated during the production process. The correct figure is shown below.
Figure 4.
Bioinformatic analysis of the differentially expressed genes. The p value denotes the significance of GO terms enrichment in the differentially expressed genes. The lower the p value, the more significant the GO term (p value ≤0.05 is recommended). We can choose the target genes for further study based on the combination of the analysis provided by GO and the biologic significance.
References
- 1.Miao Y.-Y, Liu J., Zhu J., et al. The effect of botulinum toxin type A on expression profiling of long noncoding RNAs in human dermal fibroblasts. BioMed Research International. 2017;2017:13. doi: 10.1155/2017/2957941.2957941 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]