Significance
Phthiocerol dimycocerosates (DIMs) are characteristic lipids present in the envelope of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb), the causative agent of tuberculosis, and other pathogenic mycobacteria. Due to the very hydrophobic nature of DIM and the difficulty of working with such pathogenic bacteria, these lipids are especially difficult to study. Based on a multidisciplinary research strategy involving mass spectrometry, solid-state NMR, multiscale modeling, and cell biology, we discovered how the conical shape of DIM lipids modulates macrophage phagocytosis of Mtb. These results provide insights into the biophysical action of Mtb lipid virulence factors on macrophage membranes and how this mechanism can modulate the regulation of macrophage phagocytosis.
Keywords: mycobacterial lipids shape, nonbilayer membrane structure, multiscale molecular dynamics, solid-state NMR, macrophage infection
Abstract
Phthiocerol dimycocerosate (DIM) is a major virulence factor of the pathogen Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb). While this lipid promotes the entry of Mtb into macrophages, which occurs via phagocytosis, its molecular mechanism of action is unknown. Here, we combined biophysical, cell biology, and modeling approaches to reveal the molecular mechanism of DIM action on macrophage membranes leading to the first step of Mtb infection. Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight (MALDI-TOF) mass spectrometry showed that DIM molecules are transferred from the Mtb envelope to macrophage membranes during infection. Multiscale molecular modeling and 31P-NMR experiments revealed that DIM adopts a conical shape in membranes and aggregates in the stalks formed between 2 opposing lipid bilayers. Infection of macrophages pretreated with lipids of various shapes uncovered a general role for conical lipids in promoting phagocytosis. Taken together, these results reveal how the molecular shape of a mycobacterial lipid can modulate the biological response of macrophages.
Phthiocerol dimycocerosates (DIMs/PDIMs) are highly hydrophobic lipids containing 2 multiple methyl-branched fatty acid chains (Fig. 1A). These lipids are mostly found in the cell wall of pathogenic mycobacteria and are particularly abundant in Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) (1), the causative agent of tuberculosis. They constitute one of the main Mtb virulence factors (2). Indeed, Mtb strains lacking DIM are drastically attenuated (3) and are more likely to be killed by the early pulmonary innate immune response (4) when the bacteria encounter macrophages. Recent work has revealed that DIMs modulate macrophage metabolism (5) and immune functions (6, 7). In particular, DIMs increase the ability of Mtb to infect macrophages by modulating phagocytosis (8), a fundamental immune process involving membrane remodeling. However, how DIMs intervene in these cellular processes remains poorly understood.
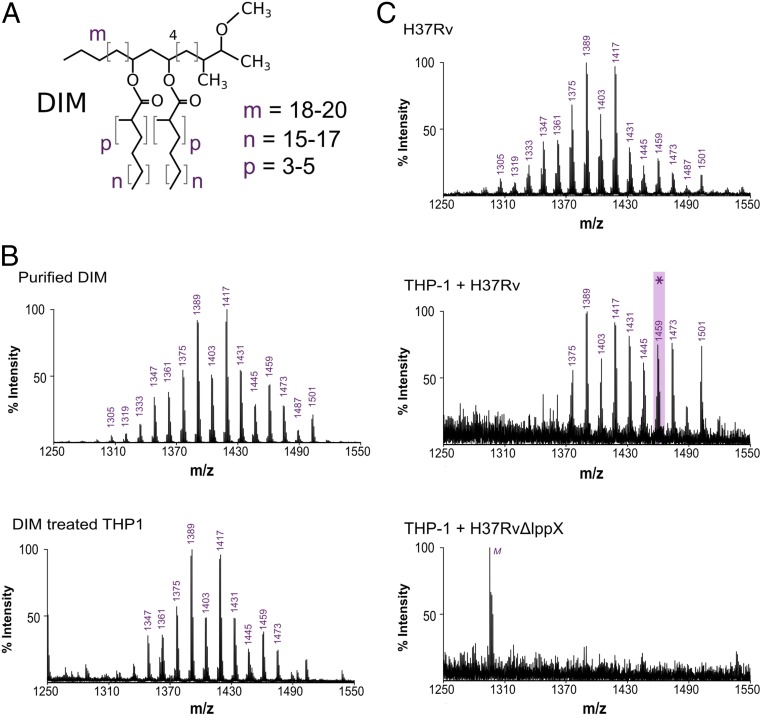
Fig. 1.
DIMs are transferred from the bacterial envelope to macrophage membranes. (A) Structure of the DIM family of lipids, where m denotes the range of carbon atoms on the phthiocerol moiety, and n and p on the mycocerosate moieties. (B) MALDI-TOF mass spectra of purified DIM and of the membrane fraction of macrophages treated with DIM. (C) MALDI-TOF mass spectra of WT Mtb (HR37v) and of the membrane fraction of macrophages infected by H37Rv or by the H37RvΔlppX mutant. M, low intensity peak corresponding to the detection of the matrix molecule in the DIM region of interest. The asterisk highlights the mass of the DIM molecule chosen for the modeling, with m = 18, n = 17, and p = 4.
Mtb synthesizes a large variety of lipid virulence factors, most of which are amphipathic glycolipids. These glycolipids act through their saccharide domains as potential ligands for membrane receptors on macrophages to induce Mtb phagocytosis (9). Lacking a saccharide moiety, DIM cannot engage in such interactions. In contrast, the molecular mechanism involving DIM may be related to a global effect on the physical properties of the host cell membrane, such as its fluidity and organization (8). Modifying such properties can be a successful strategy for bacteria to modulate eukaryotic cell functions. Several types of pathogenic mycobacteria apply this strategy to influence the fate of their host cells. For example, Mycobacterium ulcerans produces the lipid-like endotoxin mycolactone, which interacts with host membranes and disturbs their lipid organization (10). In addition, pathogenic mycobacteria use lipoarabinomannan to enter neutrophils and prevent phagolysosome formation (11).
The biophysical properties of DIM in biological membranes have not yet been characterized at the molecular level. In particular, it is unclear if such a complex and large lipid can be incorporated in a simple phospholipid bilayer and what shape DIM must adopt in such a membrane. The shape of lipid molecules, determined by structural properties (12) like their head group size, acyl chain lengths, and degrees of acyl chain unsaturation, can drastically affect the structure and organization of biological membranes (13, 14). Studying how the molecular shape of lipids may disorganize lipid bilayers and how this can be related to biological function is still a challenge (15). It requires linking the structure of molecules and their biophysical actions at the nanoscale to macroscopic consequences on the cell functions. To achieve this for DIM, we developed a multidisciplinary approach combining multiscale molecular dynamics (MD) simulations, solid-state NMR, and cell biology experiments. This revealed how the molecular shape of DIM can affect macrophage membranes to promote phagocytosis.
Results
DIMs Are Transferred to Host Cell Membranes during Macrophage Infection.
First, we used matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight (MALDI-TOF) mass spectrometry to assess whether DIM added to host cells is incorporated into their membranes. Human macrophage (THP-1) cells were treated with purified DIM, and the mass spectrum of the extracted lipids was compared with the spectrum of purified DIM. The structure of DIM consists of a long chain of phthiocerol (3-methoxy, 4-methyl, 9,11-dihydroxy glycol) esterified with 2 mycocerosic acids (long-chain multiple methyl-branched fatty acids) (Fig. 1A). In agreement with the MycoMass database (16), the purified DIM mass spectrum is characterized by a cluster of pseudomolecular ions [M + Na]+ between m/z = 1,305 and m/z = 1,501 in increments of m/z = 14 (Fig. 1B), reflecting the variability of chain lengths and methylations of the molecule. We observed that the spectrum of the extracted lipids from DIM-treated THP-1 cells showed a very similar series of peaks to that of purified DIM (Fig. 1B). These peaks were absent in the spectrum of lipid extracts from untreated cells (SI Appendix, Fig. S1A). Hence, exogenously delivered DIM can be inserted into macrophage membranes and were detectable by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry.
We next investigated if DIM could be transferred from the Mtb envelope to macrophage membranes during infection. To test this, we infected THP-1 macrophages with the wild-type (WT) Mtb strain H37Rv for 2 h at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 15:1. At 40 h postinfection, the membrane fraction of the infected macrophages showed a mass spectrum similar to the lipid signature of DIM isolated from the H37Rv inoculum (Fig. 1C). We noticed a distinct shift toward longer DIM chain lengths, consistent with the reported increase in molecular mass of DIM during Mtb infection (17). The residual bacterial contamination of the macrophage membrane fractions was less than 1,500 colony-forming units (cfu), well below the threshold for detection of DIM extracted directly from bacteria (between 105 and 107 cfu) (SI Appendix, Fig. S1B). Our data therefore strongly support the model that DIM is transferred from Mtb to the membranes of infected macrophages.
To verify whether DIM exposure at the surface of Mtb is required for their transfer to macrophage membranes, we infected macrophages with a mutant strain (H37RvΔlppX) lacking LppX, a lipoprotein required for the translocation of DIM to the outer membrane of Mtb (18). After infection, we did not observe the typical mass spectrum of DIM in the membrane fraction of H37RvΔlppX-infected cells (Fig. 1C). We verified that the WT and mutant strains produced similar amounts of DIM (SI Appendix, Fig. S1C).
Taken together, these results demonstrate that DIM molecules are indeed transferred to the membranes of macrophages during infection, provided they are exposed at the surface of M. tuberculosis.
DIMs Accommodate into a Bilayer Membrane by Adopting a Conical Shape.
Given their long aliphatic chains and their overall hydrophobic properties, we sought to understand how DIM might physically be accommodated in a bilayer membrane. We used a multiscale modeling approach to gain insight into the conformation of such a complex lipid embedded in a simple phospholipid bilayer.
During macrophage infection, Mtb produces DIM of higher molecular weight than under noninfectious conditions (17) (Fig. 1C). We therefore modeled the structure of a DIM molecule with a molecular mass of 1,436 Da (corresponding to a peak of m/z = 1,459, see asterisk in Fig. 1C): i.e., having chain lengths and number of methylations corresponding to m = 18, n = 17, and p = 4 (Fig. 1A). Then, 800 ns of atomistic molecular dynamics (MD) simulations of a single DIM molecule in a 1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (POPC) lipid bilayer revealed that DIM is deeply embedded in the membrane and may transit between the 2 opposing leaflets (Fig. 2A). DIM oxygen atoms preferentially remained in the proximity of the POPC ester bonds while the acyl chains stretched into the membrane hydrophobic core. The very long acyl chains (containing up to 27 carbon atoms) prevented confinement of the DIM molecule to 1 single leaflet. Instead, DIM seemed to be accommodated within the phospholipid bilayer by extending these chains in the interleaflets space (see density profile in Fig. 2A).
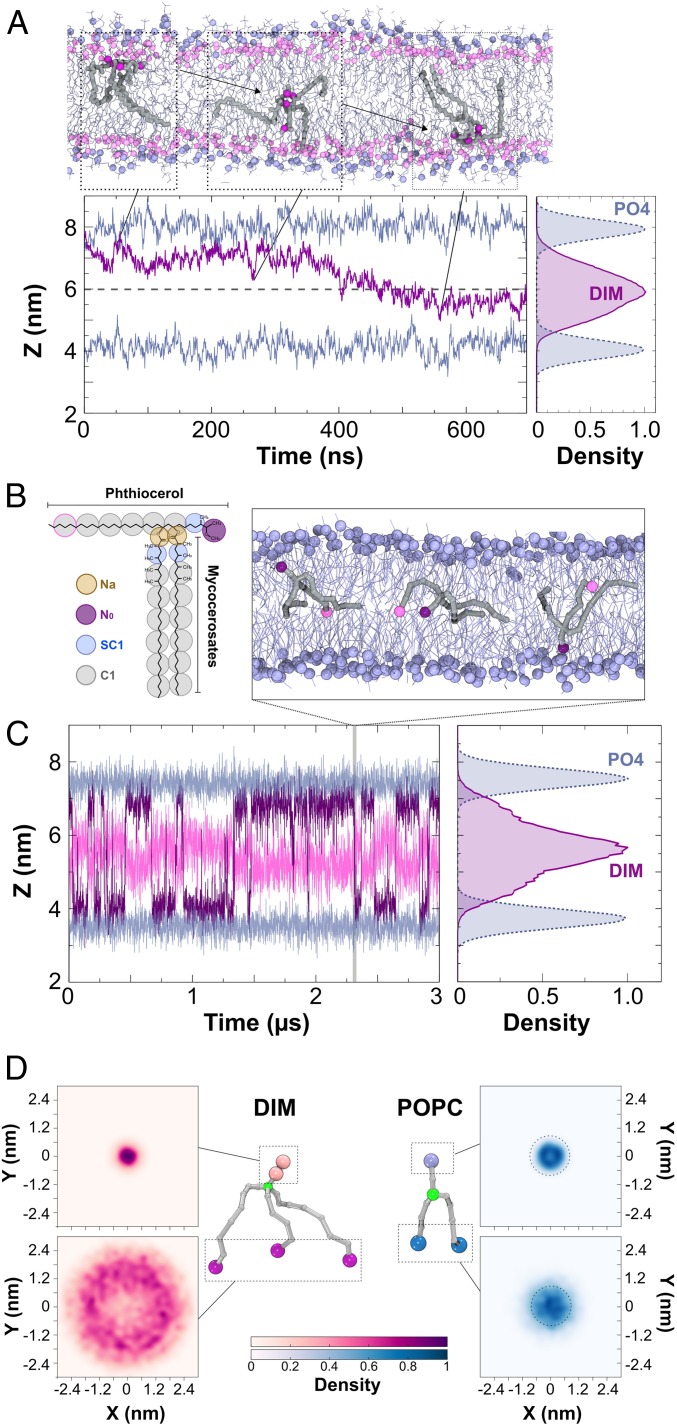
Fig. 2.
Position and shape of a single DIM molecule in a POPC bilayer. (A, Top Inset) Atomistic simulation of a DIM molecule (in gray licorice) showing its passage from one leaflet of the POPC bilayer to the opposite one. DIM oxygen atoms are represented in purple, POPC phosphorous atoms are displayed in light blue, and POPC oxygen atoms in pink. (A, Bottom Left) In purple, evolution of the z-position for the center of mass of DIM’s oxygen atoms during the course of the atomistic simulation. In light blue, averaged z-position of the phosphorous atoms of the POPC molecules. (A, Bottom Right) Densities of the positions of the DIM lipid and POPC phosphate groups revealing the embedded DIM position in the bilayer. (B) Coarse-grained model of the DIM molecule (see Materials and Methods and SI Appendix, Fig. S3 for details). (C) Evolution of N0 and the last C1 particles on the phthiocerol moieties (in purple and pink, respectively) during the course of the CG simulation. This plot shows a C1 particle confined around the interleaflet space while the N0 particle stayed in the proximity of the POPC oxygen atoms. (Top Inset) DIM (in gray) transit from one leaflet to the other during CG simulation. (Right Inset) Densities of the DIM lipid and POPC phosphate groups. (D) The 2D density projections of each extremity for DIM and POPC molecules in the x–y membrane plane (CG simulation) (see also SI Appendix, Fig. S5 displaying densities for atomistic simulations), highlighting the conical shape of DIM and the cylindrical shape of POPC, respectively. Particles depicted in green were used for molecule centering.
To further explore the dynamics of the DIM molecule within the membrane, we designed a coarse-grained (CG) model (Fig. 2B) based on the MARTINI force field (Materials and Methods and SI Appendix, Fig. S3). This force field is well adapted to model a large variety of lipids and their actions on membranes and proteins (19, 20). CG modeling of a single DIM molecule in a POPC bilayer confirmed that DIM extended its long acyl chains in between the 2 leaflets as seen in the atomistic simulation (Fig. 2 B and C). Using CG modeling, we were able to extend the simulation to longer time scales to see multiple DIM translocations from one leaflet to the other (Fig. 2C). We then increased the number of DIM molecules up to a molar DIM-to-POPC ratio of about 7% (SI Appendix, Fig. S4). At low concentrations (1%, 2%, and ∼4%), DIM molecules diffused freely inside the bilayer while, at 7%, they started to strongly interact with each other and form aggregates in between the 2 leaflets. This behavior is also observed, both experimentally and computationally, for molecules with similar structural features, like triglycerides (21, 22).
We next sought to understand how the position of the DIM acyl chains in the interleaflet space affected its overall shape. To do so, we projected the positions of the lipid extremities onto the two-dimensional (2D) membrane plane (Fig. 2D). When centering the molecule on the junction of the chains, this revealed very large movements of the 3 acyl chain extremities while the most polar end of the phthiocerol chain remained largely static. For POPC, a similar projection displayed a completely different behavior, with comparable densities for both the headgroup and the hydrophobic acyl chain extremities (Fig. 2D). Comparable results were obtained from atomistic simulations (SI Appendix, Fig. S5). These results can be related to the effective shape of each molecule: while it is known that POPC has a cylindrical shape, consistent with our simulations, which is suitable to form planar lipid membranes, our results indicated that DIM molecules adopt a strongly conical shape in a lipid bilayer.
DIMs Drive the Formation of Nonbilayer Membrane Structures in a DOPE/SOPC Lipid Mixture.
This conical molecular shape of DIM may have important consequences for the organization of DIM-containing membranes. Indeed, conical lipids are known to destabilize the lamellar membrane phase (Lα) and favor the appearance of a nonbilayer inverted-hexagonal phase (HII) (23). The transition from an Lα phase to an HII phase can be studied using 31P-NMR spectroscopy by monitoring the NMR spectra at increasing temperature (Materials and Methods). We have employed magic angle spinning (MAS) NMR spectroscopy for enhanced sensitivity. A mixture of the phospholipids 1,2-dioleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine (DOPE) and 1-stearoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (SOPC) (24) has been used for a range of lipids to study their propensity to induce nonbilayer phases (25, 26). To study the influence of DIM, we used lipid membranes made of a 3:1 (mol/mol) mixture of DOPE and SOPC (Materials and Methods). With this lipid composition, the membranes remained in the Lα phase for temperatures up to 322 K (Fig. 3 A and C). However, incorporating 5% of DIM into the lipid mixture destabilized the Lα phase and induced a transition from an Lα phase at low temperature (284 K) (Fig. 3A) to an HII phase configuration at high temperature (310 K and 322 K) (Fig. 3A), as evidenced by the 31P-NMR spectra. Thus, DIMs destabilize the Lα phase in our model membranes and promote the transition to the HII phase.
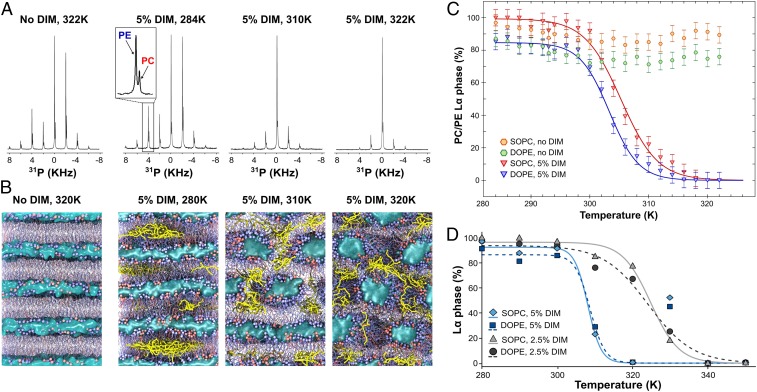
Fig. 3.
DIMs induce HII phases for a DOPE/SOPC (3:1, mol/mol) lipid mixture. (A) 31P-NMR spectra at different temperatures for DOPE/SOPC (3:1, mol/mol) without DIM or containing 5% of DIM. In the MAS 31P-NMR spectra, each spinning sideband consists of a DOPE and an SOPC peak. (B) Coarse-grained models of the phase transition in DOPE/SOPC (3:1, mol/mol) without DIM or containing 5% of DIM. Increasing the temperature leads to the formation of tubular structures for the DIM-containing systems while the systems without DIM stay fully lamellar. Snapshots shown are taken at the end of the 3-µs simulations. SOPC molecules are colored in red. DOPE molecules are colored in blue. DIM molecules are colored in yellow. Water molecules are represented as a blue surface. (C) Spectral deconvolution of the 31P-NMR spectra giving the percentage of the Lα phase as a function of the temperature for DOPE/SOPC (3:1) without DIM (orange and green hexagons) and with addition of 5% DIM (red and blue triangles). In the case of 5% DIM, the phase transition can be approximated by a sigmoid (red and blue lines). (D) SOPC and DOPE phase transitions calculated from CG-MD simulations for 2.5% and 5% of DIM. For the DOPE/SOPC mixture with 5% of DIM, we removed the outlier values at 330 K from the curve fitting based on statistical tests (SI Appendix, Supplementary Text).
As a complementary approach to monitor the ability of DIM to induce nonbilayer phases, we performed CG-MD simulations. This method is especially well suited to study lipid phase transitions in lipids (27, 28) and polymers (29, 30). We modeled a stack of 4 lipid bilayers of identical composition (3:1 DOPE/SOPC) as in the 31P-NMR experiments, for temperatures ranging from 280 K to 350 K (see Materials and Methods for details). Similar to the 31P-NMR experiments, the membranes remained in the lamellar phase in the absence of DIM (SI Appendix, Fig. S6), but a temperature-driven transition occurred when 5% of DIMs were added (Fig. 3B). These simulations allow a deeper understanding of the molecular process of the HII phase transition in the presence of DIM. At low temperatures, molecules of DIM formed aggregates in the interleaflet space (Figs. 3B, 280 K), as also seen in the POPC bilayer (SI Appendix, Fig. S4). Increasing the temperature led to the formation of fusion stalks, hourglass-shaped lipid structures formed between neighboring bilayers. DIM aggregated in these stalks to extend their large hydrophobic tails (Movie S1). This aggregation stabilized and helped to increase the width of the stalks, eventually leading to the formation of tubular water-filled membrane structures (Fig. 3B, 310 K). At still higher temperatures (320 K and higher), DIM molecules diffused freely in the hydrophobic membrane core, thus stabilizing the HII configuration (Fig. 3B, 320 K and Movie S1).
We deconvoluted the 31P-NMR spectra recorded between 282 K and 322 K in 2 K steps for DOPE/SOPC (3:1) with 5% of DIM, using a set of parameters obtained from reference datasets (Materials and Methods and SI Appendix, Table S2). The 31P chemical shifts of DOPE and SOPC are different. Therefore, each spinning sideband in our spectra consisted of 2 resolved peaks (Fig. 3A), enabling us, in a single spectrum, to independently analyze the percentages of the Lα and HII phases for DOPE and for SOPC. For both lipids, we observed a continuous transition from the Lα to the HII phase described by a sigmoid (Fig. 3C and SI Appendix, Table S3 and Supplementary Text). The phase transition midpoint temperatures (T50) were 303.5 K (± 0.4) for DOPE and 305.3 K (± 0.5) for SOPC. It should be noted that the phase transitions of SOPC and DOPE molecules are not independent from each other. The small difference of 2 °C which is observed reflects the tendency of DOPE molecules to accumulate in nonlamellar domains more than SOPC molecules, a tendency observed in most of the tested conditions (SI Appendix, Table S3). This result is in agreement with previous studies showing that conical DOPE prefers the HII phase, in contrast to cylindrical POPC lipids (31), and may also be related to the sorting of lipids as a function of the curvature (32, 33). In the CG-MD simulations, we evaluated the percentage of Lα phase as a function of temperature from the distribution of lipid tilt angles (SI Appendix, Supplementary Material), for SOPC and DOPE (Fig. 3D). Here, too, we observed continuous phase transitions that were fitted by a sigmoid, with a midpoint transition temperature of ∼308 K (SI Appendix, Table S3), which is in broad agreement with the 31P-NMR experiments.
CG-MD simulations revealed that the first stage of the mechanism through which DIMs drive the Lα-to-HII phase transition involves their aggregation in membrane stalks. Hence, blocking the formation of stalks would be expected to reduce the effect of DIM. To test this, and validate our hypothesis, we replaced a fraction of SOPC with lysophosphatidylcholine (lysoPC), a lipid known to hinder the formation of fusion stalks (34, 35). 31P-NMR experiments on liposomes of DOPE/SOPC/lysoPC (75:25:0), (75:20:5), and (75:15:10), each containing 2.5% of DIM, revealed an increase of the transition midpoint temperature T50 (SI Appendix, Fig. S8) with increasing percentage of lysoPC, highlighting a diminished effect of DIM when fusion stalk formation is inhibited. We next performed CG-MD simulations to understand the molecular process involved. Consistent with the NMR experiment, including lysoPC in the simulation increased the value of T50 (SI Appendix, Fig. S8A). From these simulations, we observed that the effect of lysoPC did not involve a direct interaction with DIM as lysoPC was spread throughout the membranes (SI Appendix, Fig. S8B). Indeed, 31P-NMR experiments on DOPE/SOPC (5:1, mol/mol), which displays an Lα-to-HII transition without DIM, also showed an increase in T50 upon replacing a fraction of SOPC by lysoPC (SI Appendix, Fig. S7). Thus, limiting the formation of stalks decreased the ability of DIM to effectively drive the formation of nonbilayer membrane structures.
Effects of DIM on More Complex Lipid Mixtures.
The DOPE/SOPC (3:1, mol/mol) mixture can easily be driven toward the inverted hexagonal phase by the inclusion of extraneous conical lipids. To study the action of DIM lipids in more natural, curvature-neutral systems, we also examined 2 different lipid mixtures. First, we performed 31P-NMR experiments on liposomes of 1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-glycero-3-phosphocoline (POPC)/palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine (POPE)/cholesterol/sphingomyelin (molar ratio 4:3:2:1), a composition chosen to approach the macrophage membrane (36). In the range of temperatures tested (284 K to 324 K), we did not observe a transition to the HII phase for this mixture, neither without DIM nor with the incorporation of 2.5% of DIM lipids (SI Appendix, Fig. S9A). Interestingly, CG-MD simulations predicted that, even with 5% of DIM lipids, a full HII transition would only be reached at very high temperatures (370 K and above) (SI Appendix, Fig. S9B). We then examined a mixture of POPE/cholesterol/sphingomyelin (molar ratio 7:2:1). This system was expected to remain lamellar over the range of temperatures studied (284 K to 324 K) as the full HII transition of POPE, the major constituent of this mixture, is only reached at ∼350 K (37). Indeed, 31P-NMR spectra revealed only a lamellar phase configuration without DIM (SI Appendix, Fig. S10A). However, the inclusion of 5% of DIM in this system drove an Lα-to-HII transition in between 310 K and 324 K (SI Appendix, Fig. S10B), with a midpoint temperature at 318 K (± 0.16). CG-MD simulations also showed a transition between 310 K and 320 K with the addition of 5% of DIM lipids while the lipid mixture without DIM lipids remained in a fully lamellar state for this range of temperatures (SI Appendix, Fig. S10C).
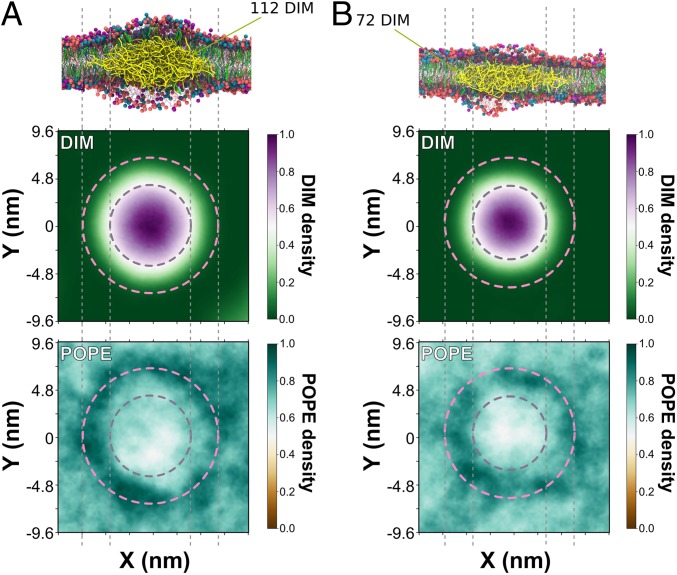
By analyzing CG-MD simulations, we examined how the addition of DIM lipids may change the biophysical properties of lamellar systems. To this end, we first calculated the membrane lateral pressure of the POPC bilayer with different concentrations of DIM (SI Appendix, Fig. S4B). Increasing the concentration of DIM lipids changed the pressure profile of the system. The change in pressure in the center of the bilayer highlights the positioning of DIM lipids in between the 2 leaflets. This may help lower packing stress for other conical lipids, such as phosphoethanolamine (PE) lipids, which may in turn decrease the energy barriers for hexagonal phase formation. Thus, DIM lipids may create a spatially inhomogeneous distribution of the different lipids. To test this hypothesis, we performed CG-MD simulations of a 28 × 28-nm2 membrane patch composed of a mixture of POPC/POPE/cholesterol/sphingomyelin (molar ratio 4:3:2:1) with the addition of 2.5% or 5% of DIM lipids. For both concentrations, we observed an enrichment of POPE around the DIM aggregates (Fig. 4).
Fig. 4.
DIM aggregate in a POPC-POPE-cholesterol-sphingomyelin lipid mixture. Simulations of a 28 × 28-nm2 patch of a macrophage-like membrane constituted of POPC/POPE/cholesterol/sphingomyelin (ratio 4:3:2:1) at 310 K with 5% of DIM (A) or 2.5% of DIM (B). For each system, at the end of 10 µs of simulations, 1 or several aggregates were formed in the center of the bilayer. Here, we focus on the largest aggregate. (Top illustration) DIM aggregates after 10 µs of simulation. POPC molecules are colored in red. POPE molecules are colored in blue. Cholesterol molecules are colored in green. Sphingomyelin molecules are colored in purple. DIM molecules are colored in yellow. (Second and Third row) The density profile for both leaflets (top view of the membrane) of DIM and POPE lipids obtained by centering the DIM aggregates for the last 2.5 µs. Dashed lines broadly define the periphery of DIM aggregates where POPE lipids tend to be enriched while they seem to be depleted in the center of the aggregate.
Altogether, the combination of 31P-NMR and CG-MD simulations revealed the ability of DIM lipids to perturb membrane organization and promote a phase transition from the lamellar to the inverted hexagonal phase. The molecular mechanism involves an initial aggregation of DIM lipids which then can drive the formation and the stabilization of fusion stalks, leading, in some cases, to a complete destabilization of the lamellar phase in favor of the inverted hexagonal phase.
High Potency of DIM to Induce Nonbilayer Phase in Comparison to Other Lipids.
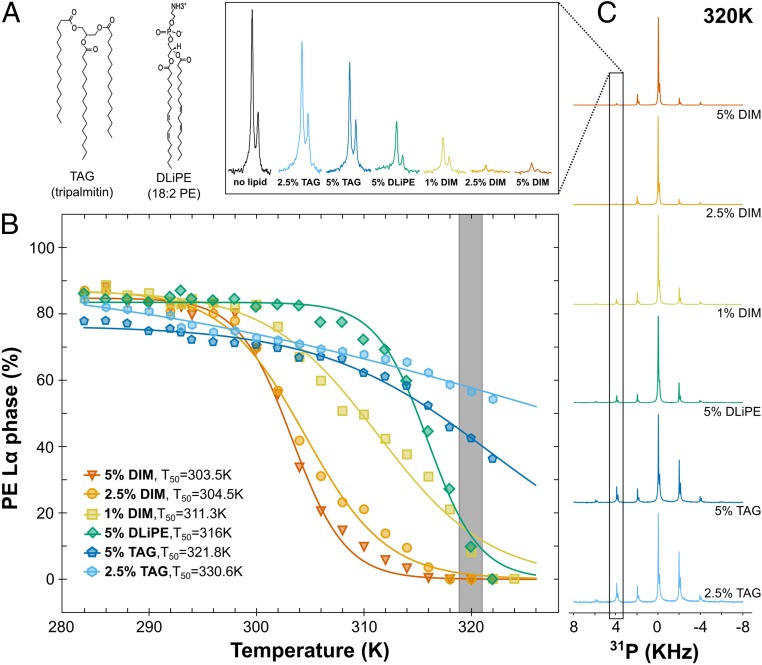
We compared the ability (potency) of DIM to induce the HII phase for a DOPE/SOPC (3:1, mol/mol) mixture to that of lipids with different structural features using 31P-NMR. We first tested the effect of the concentration of DIM on the formation of the HII phase. Fig. 5B shows that decreasing the DIM concentration to 2.5% and 1% still led to the formation of the full HII phase, albeit at a higher temperature. The increased transition midpoint temperature (Fig. 5B) reveals a dose–response relationship, which is also observed in CG-MD simulations Fig. 3D). We then tested the effect of the triglyceride tripalmitin (Fig. 5A), which, like DIM, has 3 acyl chains. However, incorporation of either 2.5% or 5% of tripalmitin did not induce a full HII phase transition (Fig. 5B). Thus, the effect of DIM on nonbilayer structure formation did not seem to be uniquely related to its 3-legged structure.
Fig. 5.
Comparison of DIM potency to induce nonbilayer phase with lipids of different shapes. (A) Molecular structures of the triacylglycerol (TAG) tripalmitin and of 1,2-dilinoleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine (DLiPE). (B) Evolution of the Lα-to-HII phase transition for the DOPE molecules as a function of temperature for DOPE/SOPC (3:1) containing different concentrations of DIM, DLiPE, and TAG (see also SI Appendix, Fig. S11 for the respective curves for SOPC molecules). For clarity, error bars are omitted. As seen in Fig. 3, the error was evaluated to ±5%. The gray bar represents the points obtained from the spectra highlighted in C. (C) 31P-NMR spectra for the lipid mixtures containing TAG, DLiPE, or DIM at 320 K. The second rotation band (4 kHz), which is strongly related to the evolution of the Lα phase, is magnified in the Top. For comparison, the black peak depicts the second rotation band of DOPE/SOPC (3:1) at 320 K.
We finally analyzed the ability of 1,2-dilinoleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine (DLiPE) to induce the Lα-to-HII phase transition and compared it with DIM. With 2 double bonds in each acyl chain (Fig. 5A), DLiPE is expected to be a strong enhancer of hexagonal phase formation (38). With 5% of DLiPE, we observed a full HII phase transition already at 322 K (Fig. 5 B and C) and a transition midpoint temperature for DOPE of 316 K (± 0.4). However, this value is higher than for 5% DIM (303.5K ± 0.4), 2.5% DIM (304.5K ± 0.5), and even 1% DIM (311.3K ± 1.0) (SI Appendix, Table S3). Thus, DIM molecules are strong inducers of nonbilayer phases, even at low concentrations.
Lipid shape can be assessed by studying inverted hexagonal phase in different lipid mixtures (38). Here, using the Lα-to-HII phase transition temperature as a measure to assess lipid conical shape, we ranked the shape of the different molecules: DIMs were strongly conical and DLiPEs were less conical, while the tripalmitins were the least conical.
Lipid Shape Modulates the Entry of Mtb and Zymosan Particles into Macrophages.
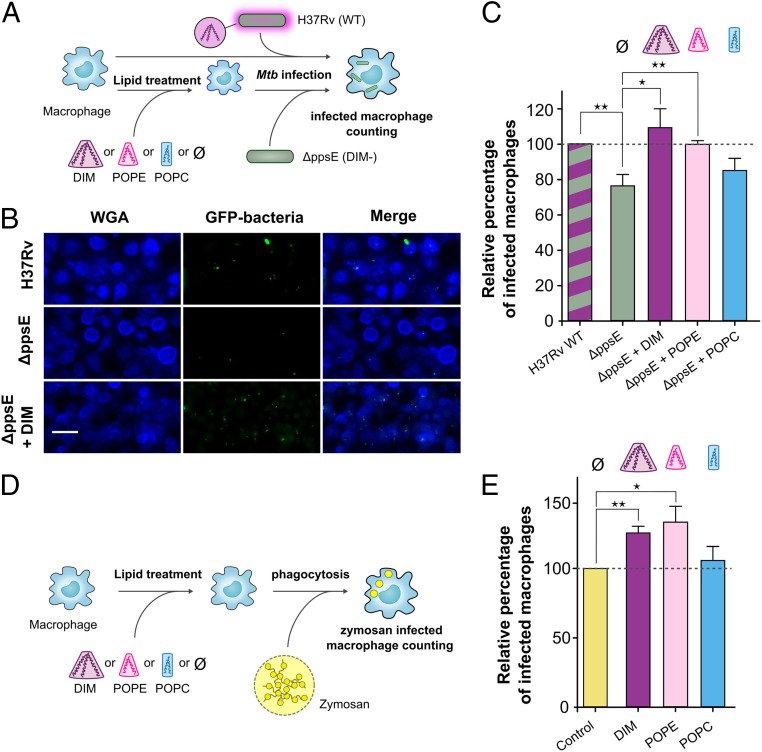
In our previous experiments, the DIM-deficient mutant H37RvΔppsE appeared to infect macrophages with a lower efficiency than the WT strain. Coating these DIM-deficient mutant bacteria with DIM restored the WT phenotype while coating mutants with tripalmitin did not have an effect (8). These results may now be related to their respective conical shapes: strongly conical for DIM and less conical for tripalmitin. To test whether it is specifically the conical shape of DIM that helps Mtb to invade macrophages, we evaluated the impact of exogenously added DIM and various other lipids on the capacity of this mutant to invade human monocyte-derived macrophages (hMDM) in comparison to the WT H37Rv strain (Fig. 6A). We confirmed that the DIM-deficient mutant infected a lower percentage of macrophages than the WT strain (Fig. 6 B and C). Pretreatment of macrophages with DIM restored the percentage of infected cells to a level comparable to that observed with the WT H37Rv strain in untreated macrophages (Fig. 6 B and C). Notably, treating macrophages with the conical phospholipid POPE also enhanced the percentage of macrophages infected with the H37RvΔppsE mutant whereas treatment with the cylindrical lipid POPC had no significant effect (Fig. 6C). These data support the hypothesis that the conical shape of DIM, which induces nonbilayer membrane structures, increases the efficiency of Mtb to infect macrophages.
Fig. 6.
Lipid shapes modulate the entry of the MtbΔppsE mutant and zymosan into macrophages. (A) Macrophages were incubated at 37 °C for 1 h with lipid solvent (Ø) or 70 µM lipids (DIM, POPC, and POPE) and subsequently exposed to GFP-expressing H37Rv WT or ΔppsE (MOI 10:1) for 1 h. Cells were then fixed and processed for the quantification of infected macrophages by fluorescence microscopy. (B) Representative fluorescence microscopy images of untreated or DIM-treated macrophages stained with WGA (membrane marker, blue) and infected with GFP-expressing H37Rv WT or ΔppsE (green). (Scale bar: 30 µm.) (C) The histogram represents the percentage of macrophages infected with ΔppsE in lipid-treated and untreated macrophages, expressed with respect to H37Rv WT (100%). (D) Macrophages were incubated with solvent (Ø) or lipids and then put in contact for 1 h with zymosan particles (MOI 30:1). (E) Percentages of macrophages infected with zymosan in untreated cells or cells treated with lipids. Values are expressed with respect to the uptake of zymosan in untreated cells (100%). The values are means ± SEM of 8 to 10 separate experiments. The significance of difference in the percentage of macrophage infection between H37Rv WT and ΔppsE or between untreated and lipid-treated cells was evaluated: *P < 0.05; **P < 0.015.
To determine whether this effect of DIM on macrophages is restricted to infection by Mtb, we examined the effect of DIM and other lipids on the uptake of zymosan (Fig. 6D) a fungal polysaccharide frequently used to study nonopsonic phagocytosis (39). We found that macrophage preincubation with DIM also increased zymosan uptake by macrophages in comparison to untreated conditions, as did preincubation with POPE but not with POPC (Fig. 6E). These data indicate that DIM and other conical lipids generally promote phagocytosis by macrophages.
Discussion
While lipid transfer from Mtb to the macrophage membranes during infection had been demonstrated for glycolipids (40), this was never shown for DIM. By using MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry, we established that DIM molecules exposed at the envelope of Mtb are indeed transferred to the macrophage membranes during infection (Fig. 1). We envision 2 mechanisms that could account for this process. DIM may be exchanged by direct contact between the surface of the bacteria and the macrophage membrane at contact sites. Such direct exchange of cholesterol and cholesterol-glycolipids has been observed between Borrelia burgdorferi and HeLa cells (41). Alternatively, DIM could be transported in the membranes of extracellular vesicles, which are known to be excreted by Mtb and other mycobacteria (42), followed by fusion of these vesicles with the plasma membrane of the macrophages. Lipid exchange mediated by vesicle fusion was shown for B. burgdorferi (41) and for Pseudomonas aeruginosa (43). For the latter process, lipid transfer could be favored by the conical shape, which promotes the fusion of vesicles with the host cell membrane (44). Here, by combining 31P-NMR with MD simulations, we demonstrated that DIM can adopt such a conical shape and promote the formation of nonbilayer (inverted hexagonal) membrane phases (Fig. 3), structures important for efficient membrane fusion (45). Membrane fusion may also be important for sealing of the phagosomal membrane during the ultimate stage of phagocytosis. Notably, our results showed that even DLiPE, a strong enhancer of nonbilayer phases, did not match the strength of DIM in promoting nonbilayer structures (Fig. 5). This may be explained by the fact that DIM lipids preferentially aggregate in transient stalks (Fig. 3B and Movie S1) to stabilize them, thereby enhancing nonbilayer phase formation. This shape may also be adopted by other long acyl chain lipids that are important for Mtb infection (2) and are transferred to the host cell membrane (40), such as trehalose mono- and di-mycolate and the phenolic glycolipids, molecules structurally related to DIM. While the conical shape is common to PE and DIM lipids, we highlight an additional distinctive property of DIM lipids. The highly hydrophobic nature of DIM may constrain these lipids to aggregate in between the 2 leaflets (as seen in Figs. 3B and 4 and SI Appendix, Fig. S4A). This localization may destabilize the lamellar phase (SI Appendix, Fig. S4B) as was seen recently for other apolar lipids (46, 47), while favoring the partition of other lipids, such as PEs, (as seen in Fig. 4) that can lower activation energy barriers: e.g., for cell fusion.
There is now ample evidence that lipids can modulate membrane protein structure (48) and functions (49, 50). As seen for lipids such as diacylglycerol (51), the conical shape of DIM may modulate membrane protein activity. Accordingly, we find that DIMs increase the nonopsonic phagocytosis of zymosan, a process well known to be mediated by a repertoire of membrane receptors, including complement receptor 3 (CR3) (39) and the mannose receptor (52). DIM may act on membrane proteins via different biophysical mechanisms. First, DIM may impose curvature on the host membrane (12), which in turn may modulate integral membrane protein sorting (53, 54) and function (55). DIM could also trigger reorganization of lipid nano-domains to modulate signaling platforms (14, 56). Thus, our findings should open avenues for understanding how Mtb subverts other receptors involved in its recognition by the immune system (57), including Toll-like receptors, NOD-like receptors, and C-type lectin receptors.
Modulating the activity of membrane proteins will ultimately modulate cellular functions. Indeed, we showed that DIMs promote Mtb infection (Fig. 6). To confirm the relevance of the conical shape, we showed that conical POPE lipids, but not cylindrical POPC lipids, added to macrophages also restored the infection capacity of a DIM-deficient Mtb mutant and improved phagocytosis (Fig. 6). Our results also shed light on previous observations showing that a DIM-deficient Mtb mutant coated with tripalmitin lipid was less effective in infecting macrophages than DIM-coated mutants (8). This can now be understood by the fact that tripalmitin did not promote formation of a nonbilayer phase transition in our model membranes (Fig. 5) and hence did not display a strong conical shape. Our results demonstrate that the conical shape of a lipid promotes phagocytosis. The effect of the conical shape of DIM on disorganizing the membrane may also play a role in the induction of phagosomal membrane rupture and cell death (58, 59). Altogether, understanding how the molecular shape of DIM lipids and their biophysical properties affect biological membranes may help to design host-directed therapeutic strategies to fight tuberculosis (60), by preventing the infection of macrophages by Mtb.
Materials and Methods
Antibodies, Lipids, and Reagents.
The rabbit polyclonal antibody against mycobacteria was produced as previously described (8). The Rhodamine Red-conjugated goat anti-rabbit secondary antibody and wheat germ agglutinin (WGA), Alexa Fluor 350 conjugate were purchased from Invitrogen. DIMs were extracted from Mycobacterium canetti (SI Appendix, Supplementary Materials and Methods). 1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (16:0-18:1 PC, POPC), 1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine (16:0-18:1 PE, POPE), 1-stearoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (18:0-18:1 PC, SOPC), 1,2-dioleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine (18:1-18:1 PE, DOPE), 1-palmitoyl-2-hydroxy-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (16:0 lysoPC), 1,2-dilinoleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine (18:2 PE, DLiPE), cholesterol, and egg sphingomyelin were purchased from Avanti Polar Lipids (Alabaster, AL). Tripalmitin was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. The other reagents were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich, except when specifically mentioned.
NMR Data Acquisition.
Phosphorus NMR spectra were acquired on a 500-MHz Bruker Avance spectrometer, in an HRMAS probe, with deuterium lock. The lipid samples [typically 6 mg of total lipids in 50 µL of Tris buffer (10 mM Tris, 1 mM EDTA, pH 7.4)] were inserted into 4-mm rotors with spherical inserts. The temperature of the sample could be varied between 278 K and 324 K and was controlled to ± 0.1 K with a Bruker variable temperature unit. The temperature was calibrated using the known temperature dependence of methanol chemical shifts. 31P chemical shift anisotropies (CSAs) were determined from the spinning sideband manifolds at a spinning frequency of 2,000 ± 1 Hz. MAS spectra were obtained with a spin-echo sequence (π/2-τ-π) where the π/2 pulse had a length of 5.3 µs (at a power of 107 W), applied at the lipids’ isotropic resonance frequency, and the interpulse delay, τ, was 20 µs. The dwell time was 1 µs, the acquisition time 65 ms, the relaxation delay 1 s, and the number of scans 4,096. No proton decoupling was applied during acquisition since it was shown to have no effect on the linewidth at a 2-kHz spinning frequency (i.e., well above the 1H-31P dipolar coupling of ∼500 Hz in fluid lipid bilayers). For every sample, a 1H NMR spectrum at a spinning frequency of 10 kHz was acquired in order to calibrate the 1H (using the methylene peak at 1.25 parts per million [ppm] with respect to TMS) and 31P chemical shifts (with respect to phosphoric acid at 0 ppm, using γP/γH = 0.40480742). The observed 31P isotropic chemicals shifts were −1.00 ± 0.02 ppm for the phosphatidylcholine head group (in SOPC) and −0.27 ± 0.02 ppm for the phosphatidylethanolamine head group (in DOPE) and varied only slightly with the lipid compositions explored. Typical linewidths were 40 to 60 Hz (i.e., ∼0.25 ppm) so that the PC and PE sideband patterns were well resolved and could be fitted independently.
Every liposome sample was equilibrated overnight at 277 K before NMR measurements. We then measured its 31P MAS spectrum at temperatures from 284 K to 324 K, in 2 K increments every 100 min (25-min equilibration plus 75-min acquisition time for each temperature). For lipid mixtures which did not undergo a lamellar to inverse-hexagonal phase transition (i.e., with a small proportion of DOPE), the spectra were shown to be fully reversible when going down from 324 K to 284 K. However, once the HII phase had formed, it did not revert to the lamellar phase, at least after 1 day of equilibration at 284 K. Hence, all measurements were done for increasing temperatures, starting from the lowest temperature, taking care of maintaining the liposomes at low temperature during their preparation and before NMR measurements. The actual insertion yield of DIM in the lipid bilayers was determined by 1H-NMR (SI Appendix, Supplementary Text).
Spectral Deconvolution.
We analyzed each 31P spinning sideband manifold using the solid line shape analysis tool (SOLA) available in Topspin 3.5. CSA parameters were calculated using the Haeberlin convention for the anisotropy values Δδ = δ// − δ⊥ as commonly done in the membrane literature and as explained before (61). We estimated the uncertainty of Δδ values to be ± 0.2 ppm, based on several measurements and fitting performed on independent samples. We first determined the CSA parameters of lipids organized in a single phase (e.g., SOPC for the lamellar Lα phase and DOPE for the HII phase), at several temperatures between 284 K and 324 K. The CSA parameters for each lipid and each phase varied slightly and linearly with temperature, due to increased motion at higher temperatures: from 49.6 ± 0.2 ppm (293 K) to 45.0 ± 0.2 ppm (333 K) for SOPC in the Lα phase; and from −22.2 ± 0.2 ppm (278 K) to −20.1 ± 0.2 ppm (333 K) for DOPE in the HII phase. The following linear regressions were obtained: Δδ = −0.0944 T + 76.599 for SOPC in the Lα phase and Δδ = −0.0409 T −33.627 for DOPE in the HII phase, where T is the temperature in Kelvin; these regressions were used to calculate CSA values at intermediate temperatures. Since the lipids in the HII phase experience additional motional averaging due to lateral diffusion around the aqueous channels, their CSA is obtained by averaging 2 components, δ// and δ⊥, divided by 2, for reasons discussed by Cullis and De Kruijff (62). The CSA values in the Lα and HII phases have opposite signs. Hence, the CSA value of SOPC in the HII phase was taken to be −0.5 times its value in the Lα phase while the CSA value of DOPE in the Lα phase was 2 times its value in the HII phase. Knowing the temperature-dependent CSA parameters for both lipids in both phases allowed a drastic reduction of the number of parameters to be fitted when analyzing lipid mixtures in which the 2 phases coexist. After optimizing the peak positions and linewidths, the SOLA fitting algorithm only has to search for the Lα-HII proportions that best reproduce the experimental spectra. The intensity of the spinning sideband at +4 kHz is a good reporter of the proportion of Lα phase since this peak is almost absent from the typical HII phase spinning sideband manifold (63) (Fig. 5C). This fitting protocol was very robust and prevented the artifacts and instabilities arising from fitting too many parameters. We should stress that our procedure is based on the assumption that the spectra consist of a linear combination of the spectra of the 2 lipids in the Lα and HII phases, possessing CSA parameters identical to their values in the pure phases at the same temperature. This simplifying assumption was sufficient to characterize the lipid phase transitions although we cannot exclude that the actual lipid behavior is more complex.
MD Simulations.
The atomistic MD simulations were performed with the Amber16 software (64) (http://ambermd.org) in combination with Lipid14 (65) and general AMBER force field (Gaff) (66). The system contained a membrane of 300 POPC molecules and was solvated with a TIP3P water model using the CHARMM-GUI server (67, 68). The DIM molecule was positioned in the POPC bilayer with the polar core in the proximity of the POPC oxygen atoms (Fig. 2A). In order to avoid steric clashes of the DIM molecule with POPC, the system was initially minimized by executing 1,500 iterations of the steepest descent (SD) algorithm, followed by 1,500 iterations of the conjugate gradient (CG) algorithm, with weakly restrained solute (k = 10 kcal/mol/Å2). Next, a short 100-ps MD run was performed on weakly restrained solute with temperature varying linearly from 0 to 303 K. The temperature control was achieved using the Langevin dynamics with the collision frequency parameter γ equal to 1.0 ps−1. The integration step used in this run was 1 fs. Throughout the calculations, a cutoff of 10 Å was used for electrostatic interactions. The MD simulation continued with the equilibration of the system, consisting of 10 consecutive MD steps of 500 ps each, at constant temperature of 303 K with no restraints, with the integration step of 2 fs. The production run was then launched for 800 ns with constant pressure of 1 bar. The Langevin dynamics was used to control the temperature, with γ = 1.0 ps−1, while the pressure was controlled by the anisotropic Berendsen barostat with the pressure relaxation time τp = 1 ps. Bonds involving hydrogen were constrained with the SHAKE algorithm.
Coarse-grain simulations were performed using GROMACS 2016 (69) with the MARTINI force field 2.2 (70, 71). We have designed the CG model of DIM by following the original MARTINI parametrization strategy (72). We approximated 3 to 4 heavy atoms constituting the long hydrophobic acyl chains by 1 C1 particle. Small methyl branched parts were approximated by a small particle SC1. The slightly polar extremity of the phthiocerol chain was approximated by an N0 particle while the glycerol ester moieties were represented by an intermediate hydrophobicity particle Na as usually done for other phospholipids (Fig. 2B). Force constants and equilibrium values for bonds and angles were extracted from the atomistic simulation (SI Appendix, Fig. S3). All of the systems were first gradually equilibrated as proposed in the CHARMM-GUI MARTINI Maker protocol (73). Coulomb interactions were treated using the reaction-field potential, and Lennard–Jones interactions were treated using shifted potentials with a cutoff radius of 1.1 nm. For planar systems of pure SOPC, DIM/DLiPE molecules embedded in a POPC bilayer, or composed of a mixture of POPC/POPE/cholesterol/sphingomyelin (with and without DIM molecules), pressure was maintained at 1 bar using the Parrinello–Rahman algorithm (74) with a semiisotropic pressure control. The temperature was kept at 310 K using the v-rescale algorithm (75). For pure DOPE, SOPC/DOPE, POPC/POPE/cholesterol/sphingomyelin, and POPE/cholesterol/sphingomyelin systems undergoing lamellar-to-hexagonal transitions, we used the protocol described by Marrink and Mark (27). We stacked 4 membranes with a hydration level of ∼2 to 3 water CG-particles per lipid (equivalent to approximately 9 to 10 atomistic water molecules) in order to see the phase transition in a reasonable amount of time, as detailed by Marrink and Mark (27). A Berendsen thermostat in combination with a Berendsen barostat (76) was used. A fully anisotropic coupling pressure was applied with a reference pressure of 1 bar. Systems were equilibrated at 280 K, and then 8 to 11 different simulations were launched, with temperatures ranging from 280 K to 380 K (depending on the system studied) with an increment of 10 K. In all CG systems, a time step of 20 fs was used. See SI Appendix, Table S1 for a summary of the simulations. Parameters for CG and atomistic representations of DIM lipids will be available on the MARTINI website cgmartini.nl and at the address https://github.com/MChavent. Density profiles were performed using the Gromacs tool density (http://manual.gromacs.org/documentation/2016/onlinehelp/gmx-density.html). The lateral pressure profile was calculated using the modified version of Gromacs: Gromacs-LS (http://www.mdstress.org). MD simulation figures were performed using VMD (77). Scripts used to analyze MD simulations are available at https://github.com/MChavent.
Data Availability.
MD simulation material and scripts, as well as tables for NMR phase transitions, are available at https://github.com/MChavent/DIM_data.
A detailed description of materials and methods is provided in SI Appendix, Supplementary Materials and Methods.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by CNRS-Mission pour les Initiatives Transverses et Interdisciplinaires Grants PEPS MPI 2018 and “Modélisation du vivant” 2019, Agence Nationale de la Recherche Grant ANR-16-CE15-0003, the Fondation pour la Recherche Médicale (FRM) (“Equipe FRM” Grant DEQ20160334879), and the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique (CNRS). J.A. was the recipient of a PhD scholarship from the French government. This work was granted access to the high performance computing resources of the Calcul en Midi Pyrénées supercomputing center under allocation 2019-17036. C.A.-D. thanks the Toulouse Réseau Imagerie‐Genotoul Imaging facility (Toulouse, France). M.C. thanks S. J. Marrink for providing setup details for modeling hexagonal phases. We acknowledge Life Science Editors for proofreading the manuscript. We thank Olivier Neyrolles, Jérôme Nigou, Laurence Salomé, and Justin Teissié for fruitful discussions and support.
Footnotes
The authors declare no competing interest.
This article is a PNAS Direct Submission.
Data deposition: MD simulation material and scripts, as well as tables for NMR phase transitions, are available at https://github.com/MChavent/DIM_data.
See Commentary on page 25372.
This article contains supporting information online at https://www.pnas.org/lookup/suppl/doi:10.1073/pnas.1910368116/-/DCSupplemental.
References
- 1.Jackson M., The mycobacterial cell envelope-lipids. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 4, a021105 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Forrellad M. A., et al. , Virulence factors of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex. Virulence 4, 3–66 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Cox J. S., Chen B., McNeil M., Jacobs W. R. Jr, Complex lipid determines tissue-specific replication of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in mice. Nature 402, 79–83 (1999). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Day T. A., et al. , Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains lacking surface lipid phthiocerol dimycocerosate are susceptible to killing by an early innate host response. Infect. Immun. 82, 5214–5222 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Howard N. C., et al. , Mycobacterium tuberculosis carrying a rifampicin drug resistance mutation reprograms macrophage metabolism through cell wall lipid changes. Nat. Microbiol. 3, 1099–1108 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Arbués A., Lugo-Villarino G. C., Neyrolles O., Guilhot C., Astarie-Dequeker C., Playing hide-and-seek with host macrophages through the use of mycobacterial cell envelope phthiocerol dimycocerosates and phenolic glycolipids. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 4, 173 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Cambier C. J., et al. , Mycobacteria manipulate macrophage recruitment through coordinated use of membrane lipids. Nature 505, 218–222 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Astarie-Dequeker C., et al. , Phthiocerol dimycocerosates of M. tuberculosis participate in macrophage invasion by inducing changes in the organization of plasma membrane lipids. PLoS Pathog. 5, e1000289 (2009). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Astarie-Dequeker C., Nigou J., Passemar C., Guilhot C., The role of mycobacterial lipids in host pathogenesis. Drug Discov. Today Dis. Mech. 7, e33–e41 (2010). [Google Scholar]
- 10.Nitenberg M., et al. , The potent effect of mycolactone on lipid membranes. PLoS Pathog. 14, e1006814 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Nakayama H., et al. , Lipoarabinomannan binding to lactosylceramide in lipid rafts is essential for the phagocytosis of mycobacteria by human neutrophils. Sci. Signal. 9, ra101 (2016). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Harayama T., Riezman H., Understanding the diversity of membrane lipid composition. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 19, 281–296 (2018). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Frolov V. A., Shnyrova A. V., Zimmerberg J., Lipid polymorphisms and membrane shape. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 3, a004747 (2011). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Vanni S., Hirose H., Barelli H., Antonny B., Gautier R., A sub-nanometre view of how membrane curvature and composition modulate lipid packing and protein recruitment. Nat. Commun. 5, 4916 (2014). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Bassereau P., et al. , The 2018 biomembrane curvature and remodeling roadmap. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 51, 343001 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Layre E., et al. , A comparative lipidomics platform for chemotaxonomic analysis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Chem. Biol. 18, 1537–1549 (2011). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Jain M., et al. , Lipidomics reveals control of Mycobacterium tuberculosis virulence lipids via metabolic coupling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 104, 5133–5138 (2007). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Sulzenbacher G., et al. , LppX is a lipoprotein required for the translocation of phthiocerol dimycocerosates to the surface of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. EMBO J. 25, 1436–1444 (2006). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Marrink S. J., Tieleman D. P., Perspective on the Martini model. Chem. Soc. Rev. 42, 6801–6822 (2013). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Ingólfsson H. I., Arnarez C., Periole X., Marrink S. J.. Computational “microscopy” of cellular membranes. J. Cell Sci. 129, 257–268 (2016). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Khandelia H., Duelund L., Pakkanen K. I., Ipsen J. H., Triglyceride blisters in lipid bilayers: Implications for lipid droplet biogenesis and the mobile lipid signal in cancer cell membranes. PLoS One 5, e12811 (2010). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Ben M’barek K., et al. , ER membrane phospholipids and surface tension control cellular lipid droplet formation. Dev. Cell 41, 591–604.e7 (2017). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Seddon J. M., Structure of the inverted hexagonal (HII) phase, and non-lamellar phase transitions of lipids. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1031, 1–69 (1990). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Separovic F., Gawrisch K., Effect of unsaturation on the chain order of phosphatidylcholines in a dioleoylphosphatidylethanolamine matrix. Biophys. J. 71, 274–282 (1996). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Fuller N., Rand R. P., The influence of lysolipids on the spontaneous curvature and bending elasticity of phospholipid membranes. Biophys. J. 81, 243–254 (2001). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Kooijman E. E., et al. , Spontaneous curvature of phosphatidic acid and lysophosphatidic acid. Biochemistry 44, 2097–2102 (2005). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Marrink S.-J., Mark A. E., Molecular view of hexagonal phase formation in phospholipid membranes. Biophys. J. 87, 3894–3900 (2004). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Shelley J. C., et al. , Simulations of phospholipids using a coarse grain model. J. Phys. Chem. B 105, 9785–9792 (2001). [Google Scholar]
- 29.Shinoda W., DeVane R., Klein M. L., Coarse-grained molecular modeling of non-ionic surfactant self-assembly. Soft Matter 4, 2454–2462 (2008). [Google Scholar]
- 30.Klein M. L., Shinoda W., Large-scale molecular dynamics simulations of self-assembling systems. Science 321, 798–800 (2008). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Cullis P. R., de Kruijff B., Lipid polymorphism and the functional roles of lipids in biological membranes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 559, 399–420 (1979). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Roux A., et al. , Role of curvature and phase transition in lipid sorting and fission of membrane tubules. EMBO J. 24, 1537–1545 (2005). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Sorre B., et al. , Curvature-driven lipid sorting needs proximity to a demixing point and is aided by proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 106, 5622–5626 (2009). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Yeagle P. L., Smith F. T., Young J. E., Flanagan T. D., Inhibition of membrane fusion by lysophosphatidylcholine. Biochemistry 33, 1820–1827 (1994). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Marrink S. J., Mark A. E., The mechanism of vesicle fusion as revealed by molecular dynamics simulations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 125, 11144–11145 (2003). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Sahu S., Lynn W. S., Lipid composition of human alveolar macrophages. Inflammation 2, 83–91 (1977). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Rappolt M., Hickel A., Bringezu F., Lohner K., Mechanism of the lamellar/inverse hexagonal phase transition examined by high resolution x-ray diffraction. Biophys. J. 84, 3111–3122 (2003). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Tilcock C., Cullis P. R., The polymorphic phase-behavior and miscibility properties of synthetic phosphatidylethanolamines. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 684, 212–218 (1982). [Google Scholar]
- 39.Le Cabec V., Cols C., Maridonneau-Parini I., Nonopsonic phagocytosis of zymosan and Mycobacterium kansasii by CR3 (CD11b/CD18) involves distinct molecular determinants and is or is not coupled with NADPH oxidase activation. Infect. Immun. 68, 4736–4745 (2000). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Rhoades E., et al. , Identification and macrophage-activating activity of glycolipids released from intracellular Mycobacterium bovis BCG. Mol. Microbiol. 48, 875–888 (2003). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Crowley J. T., et al. , Lipid exchange between Borrelia burgdorferi and host cells. PLoS Pathog. 9, e1003109 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Brown L., Wolf J. M., Prados-Rosales R., Casadevall A., Through the wall: Extracellular vesicles in Gram-positive bacteria, mycobacteria and fungi. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 13, 620–630 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Bomberger J. M., et al. , Long-distance delivery of bacterial virulence factors by Pseudomonas aeruginosa outer membrane vesicles. PLoS Pathog. 5, e1000382 (2009). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Chernomordik L. V., Kozlov M. M., Mechanics of membrane fusion. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 15, 675–683 (2008). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Zick M., Stroupe C., Orr A., Douville D., Wickner W. T., Membranes linked by trans-SNARE complexes require lipids prone to non-bilayer structure for progression to fusion. eLife 3, e01879 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Campomanes P., Zoni V., Vanni S., Local accumulation of diacylglycerol alters membrane properties nonlinearly due to its transbilayer activity. Commun. Chem. 2, 1–8 (2019). [Google Scholar]
- 47.Bacle A., Gautier R., Jackson C. L., Fuchs P. F. J., Vanni S., Interdigitation between triglycerides and lipids modulates surface properties of lipid droplets. Biophys. J. 112, 1417–1430 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Barrera F. N., Fendos J., Engelman D. M., Membrane physical properties influence transmembrane helix formation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 109, 14422–14427 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.daCosta C. J. B., Dey L., Therien J. P. D., Baenziger J. E., A distinct mechanism for activating uncoupled nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Nat. Chem. Biol. 9, 701–707 (2013). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Pliotas C., et al. , The role of lipids in mechanosensation. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 22, 991–998 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Hresko R. C., Kraft T. E., Quigley A., Carpenter E. P., Hruz P. W., Mammalian glucose transporter activity is dependent upon anionic and conical phospholipids. J. Biol. Chem. 291, 17271–17282 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Speert D. P., Silverstein S. C., Phagocytosis of unopsonized zymosan by human monocyte-derived macrophages: Maturation and inhibition by mannan. J. Leukoc. Biol. 38, 655–658 (1985). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Rosholm K. R., et al. , Membrane curvature regulates ligand-specific membrane sorting of GPCRs in living cells. Nat. Chem. Biol. 13, 724–729 (2017). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Aimon S., et al. , Membrane shape modulates transmembrane protein distribution. Dev. Cell 28, 212–218 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Hamilton P. J., et al. , PIP2 regulates psychostimulant behaviors through its interaction with a membrane protein. Nat. Chem. Biol. 10, 582–589 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Hirama T., et al. , Membrane curvature induced by proximity of anionic phospholipids can initiate endocytosis. Nat. Commun. 8, 1393 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Liu C. H., Liu H., Ge B., Innate immunity in tuberculosis: host defense vs pathogen evasion. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 14, 963–975 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Augenstreich J., et al. , ESX-1 and phthiocerol dimycocerosates of Mycobacterium tuberculosis act in concert to cause phagosomal rupture and host cell apoptosis. Cell. Microbiol. 19, e12726 (2017). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Quigley J., et al. , The cell wall lipid PDIM contributes to phagosomal escape and host cell exit of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. MBio 8, e00148-17 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Guler R., Brombacher F., Host-directed drug therapy for tuberculosis. Nat. Chem. Biol. 11, 748–751 (2015). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Holland G. P., McIntyre S. K., Alam T. M., Distinguishing individual lipid headgroup mobility and phase transitions in raft-forming lipid mixtures with 31P MAS NMR. Biophys. J. 90, 4248–4260 (2006). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Cullis P. R., De Kruijff B., Polymorphic phase behaviour of lipid mixtures as detected by 31P NMR. Evidence that cholesterol may destabilize bilayer structure in membrane systems containing phosphatidylethanolamine. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 507, 207–218 (1978). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Moran L., Janes N., Tracking phospholipid populations in polymorphism by sideband analyses of 31P magic angle spinning NMR. Biophys. J. 75, 867–879 (1998). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Salomon Ferrer R., Case D. A., Walker R. C., An overview of the Amber biomolecular simulation package. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Comput. Mol. Sci. 3, 198–210 (2012). [Google Scholar]
- 65.Dickson C. J., et al. , Lipid14: The amber lipid force field. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 10, 865–879 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Wang J., Wolf R. M., Caldwell J. W., Kollman P. A., Case D. A., Development and testing of a general amber force field. J. Comput. Chem. 25, 1157–1174 (2004). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Wu E. L., et al. , CHARMM-GUI Membrane Builder toward realistic biological membrane simulations. J. Comput. Chem. 35, 1997–2004 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Jo S., Kim T., Iyer V. G., Im W., CHARMM-GUI: A web-based graphical user interface for CHARMM. J. Comput. Chem. 29, 1859–1865 (2008). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Abraham M. J., et al. , GROMACS: High performance molecular simulations through multi-level parallelism from laptops to supercomputers. SoftwareX 1-2, 19–25 (2015). [Google Scholar]
- 70.de Jong D. H., et al. , Improved parameters for the Martini coarse-grained protein force field. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 9, 687–697 (2013). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Marrink S. J., de Vries A. H., Mark A. E., Coarse grained model for semiquantitative lipid simulations. J. Phys. Chem. B 108, 750–760 (2004). [Google Scholar]
- 72.Marrink S. J., Risselada H. J., Yefimov S., Tieleman D. P., de Vries A. H., The MARTINI force field: Coarse grained model for biomolecular simulations. J. Phys. Chem. B 111, 7812–7824 (2007). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Qi Y., et al. , CHARMM-GUI Martini maker for coarse-grained simulations with the Martini force field. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 11, 4486–4494 (2015). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Parrinello M., Rahman A., Polymorphic transitions in single crystals: A new molecular dynamics method. J. Appl. Phys. 52, 7182 (1981). [Google Scholar]
- 75.Bussi G., Donadio D., Parrinello M., Canonical sampling through velocity rescaling. J. Chem. Phys. 126, 014101 (2007). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Berendsen H., Postma J., Vangunsteren W. F., DiNola A., Haak J. R., Molecular-dynamics with coupling to an external bath. J. Chem. Phys. 81, 3684–3690 (1984). [Google Scholar]
- 77.Humphrey W., Dalke A., Schulten K., VMD: Visual molecular dynamics. J. Mol. Graph. 14, 33–38 (1996). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
MD simulation material and scripts, as well as tables for NMR phase transitions, are available at https://github.com/MChavent/DIM_data.
A detailed description of materials and methods is provided in SI Appendix, Supplementary Materials and Methods.