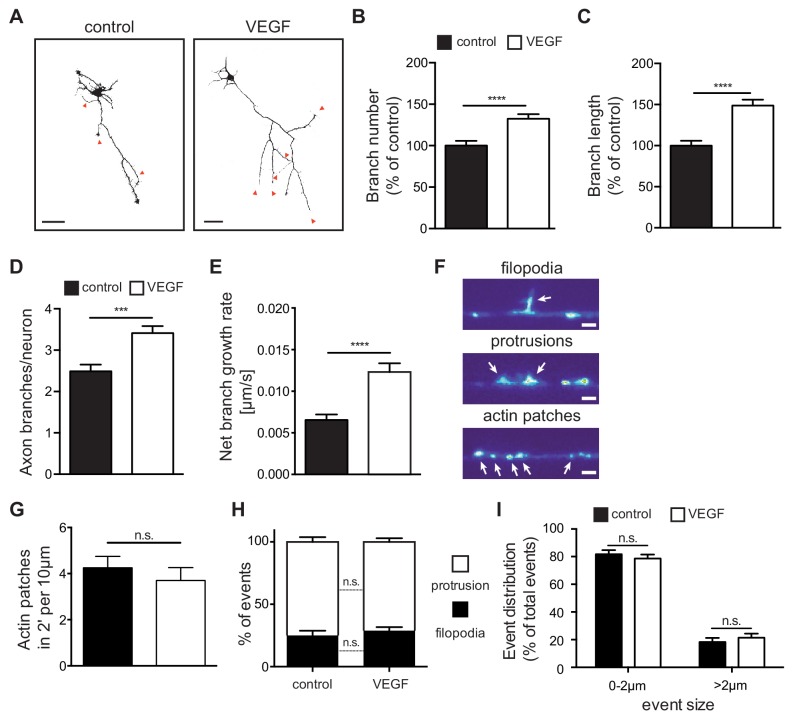
Figure 3. VEGF stimulation promotes the growth of axon branches in hippocampal neurons.
(A) Representative images of 3 DIV hippocampal neurons stimulated with or without 100 ng/ml VEGF for 48 hr and stained with beta-III-tubulin. Scale bars 50 µm. (B,C) Quantification of axonal branch number (B) and branch length (C). Data are represented as % of non-stimulated control. Mean ± SEM,>60 neurons from n = 4. ****p<0.0001; unpaired Student’s ttest. (D,E) 1 DIV hippocampal neurons were stimulated with 50 ng/ml VEGF or vehicle control and time-lapse movies were recorded over the course of 4 hr. The number of extending axon branches (D) was quantified over the course of the movies and the net growth rate of axon branch was calculated (E). Data represents mean ± SEM from 39 neurons, n = 3 independent experiments. ***p<0.001; ****p<0.0001; unpaired Student’s ttest. (F) Hippocampal neurons were transfected with mCherry-UtrCH and imaged in TIRF-mode at 3 DIV. Using this approach, actin patches, membrane bending protrusions and filopodia could be identified and differentiated. Time-lapse movies were recorded over the course of 2 min (actin patches) or 10 min (protrusions and filopodia) to study the dynamic formation of such events. Scale bar 2 µm. (G) The number of newly forming actin patches during 2 min per 10 µm axon segment were counted before and after VEGF stimulation (100 ng/ml). Data represents mean ± SEM from at least 11 neurons of 2 independent experiments. n.s. not significant; paired Student’s ttest. (H,I) The number and the size of newly forming protrusions and filopodia were analyzed during the course of 10 min before and after VEGF stimulation (100 ng/ml). Data represents mean ± SEM from at least 12 neurons of at least three independent experiments. n.s. not significant; paired Student’s ttest.