Abstract
The emergence and spread of carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae infections have worsened the current situation worldwide, in which totally drug-resistant strains (bad bugs) are becoming increasingly prominent. Bacterial biofilms enable bacteria to tolerate higher doses of antibiotics and other stresses, which may lead to the drug resistance. In the present study, we performed proteomics on the carbapenem-resistant NDM-4-producing K. pneumoniae clinical isolate under meropenem stress. Liquid chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry (LC–MS/MS) analysis revealed that 69 proteins were down-regulated (≤0.42-fold change) under meropenem exposure. Within the identified down-regulated proteome (69 proteins), we found a group of 13 proteins involved in flagellar, fimbriae, and pili formation and their related functions. Further, systems biology approaches were employed to reveal their networking pathways. We suggest that these down-regulated proteins and their interactive partners cumulatively contribute to the emergence of a biofilm-like state and the survival of bacteria under drug pressure, which could reveal novel mechanisms or pathways involved in drug resistance. These down-regulated proteins and their pathways might be used as targets for the development of novel therapeutics against antimicrobial-resistant (AMR) infections.
Keywords: Klebsiella pneumoniae (NDM-4), proteomics, bioinformatics, pathway enrichment, biofilm, carbapenem resistance
Introduction
Klebsiella pneumoniae is a gram-negative bacteria of the family Enterobacteriaceae. In clinical settings, the emergence and spread of drug-resistant K. pneumoniae are worsening the medical situation worldwide. Carbapenems have been considered the last line of defense in the treatment of drug-resistant infections (Paterson, 2000; Paterson and Bonomo, 2005). Interrupted use of carbapenem during the course of treatment leads to the emergence of carbapenem-resistant infections. Carbapenemases are produced that cleave or hydrolyze the carbapenem drugs and contribute to carbapenem resistance. Carbapenemase over-production and porin deficiency are the two major causes of carbapenem resistance (Ambler et al., 1991; Martínez-Martínez et al., 1999; Jacoby et al., 2004; Loli et al., 2006). Several explanations have been put forward to explain the mechanisms of carbapenem resistance, but our information is as yet incomplete or fragmentary.
Biofilm formation is among the mechanisms known to be responsible for microbial drug resistance. During biofilm formation, bacteria first become sessile and then colonize and grow up from surfaces. The biofilm protects the bacteria from various stresses like altered pH, osmolarity, and nutrient scarcity (Costerton and Lewandowski, 1995; Fux et al., 2005; McCarty et al., 2012) and blocks the entry of drugs to the bacterial communities (Costerton et al., 1999; Stewart and William Costerton, 2001; Sharma et al., 2019c). In the first step of biofilm formation, bacteria lose their motility and become sessile. We assume that decreased expression of proteins related to motility could lead to biofilm formation and thus might contribute to the development of drug resistance. Comparative proteomics addressing the whole-cell proteins of drug-resistant microbes with or without drug pressures have been reported previously (Lata et al., 2015; Khan et al., 2017; Sharma et al., 2018a; Qayyum et al., 2019; Sharma et al., 2019a). However, little information is available regarding the bacterial proteome related to biofilm, and, to the best of our knowledge, no data has yet been reported related to the proteome of drug-resistant microbes, especially carbapenem-resistant K. pneumonia, in relation to motility-mediated drug resistance.
In this study, we used comparative proteomics and systems biology-based approaches to investigate the correlation of the decreased expression of motility-related proteins (flagellar, fimbriae, and pili) with biofilm formation, which may lead to the development of drug resistance. Proteomics and systems biology approaches are both among the potential strategies for exploring biological problems such as the mechanisms of drug resistance. In the present study, we used liquid chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry (LC–MS/MS) to determine the expression of the motility-related proteome of a carbapenem-resistant K. pneumoniae (NDM-4) clinical isolate under meropenem stress. The results of this study could lead to the exploration of novel therapeutics targets against carbapenem resistance.
Materials and Methods
Strain Selection and Drug Susceptibility Testing
An NDM-4-encoding carbapenem-resistant K. pneumoniae clinical isolate (AK-97) was selected for this study. This was reported in our earlier study, which showed its presence in the NICU of a northern Indian Hospital (Ahmad et al., 2018). Drug susceptibility testing (DST) against the drug meropenem was carried out via the micro-dilution method according to CLSI guidelines (Wayne, 2014).
Culture Scaling, Drug Induction, and Protein Sample Preparation
A single colony of K. pneumoniae was inoculated in LB broth and kept at 37°C at 220 rpm, and a sub-MIC (32 μg/ml) of meropenem was used for induction in a 200 ml culture flask. Bacteria were grown up to the exponential phase (OD600 = 0.8), and cells were harvested by centrifugation at 8000 × g for 8 min at 4°C. The cells were washed with normal saline and re-suspended in a lysis buffer [50 mM Tris–HCl containing 10 mM MgCl2, 0.1% sodium azide, 1 mM phenyl-methyl-sulfonyl-fluoride (PMSF), and 1 mM ethylene glycol tetra-acetic acid (EGTA); pH 7.4] at a concentration of 1 g wet weight per 5 ml. Cell lysis was performed by intermittent sonication with a sonicator with the power at 35% amplitude (Sonics & Materials Inc., Newtown, CT, United States) for 10 min at 4°C. Further, the homogenate was centrifuged at 12,000 × g for 20 min at 4°C, and the supernatant was precipitated overnight at −20°C by adding cold acetone in excess (1:4) (Lata et al., 2015; Sharma and Bisht, 2016; Sharma et al., 2019a). The precipitated protein was collected by centrifugation (12,000 × g, 20 min), allowed to air dry, and then suspended in an appropriate volume of protein-dissolving buffer. The protein concentration was estimated using the Bradford (1976) assay. All of the experiments were replicated biologically and technically.
Separation and Identification of the Proteome by nanoLC-TripleTOF 5600 MS
Equal concentrations of protein samples were trypsinized, and digested proteins were analyzed using a TripleTOF 5600 MS (AB Sciex, Foster City, CA, United States) equipped with an Eksigent MicroLC 200 system (Eksigent, Dublin, CA, United States) with an Eksigent C18 reverse-phase column (150 × 0.3 mm, 3 μm, 120 Å) (Sharma et al., 2019a). For protein identification, spectral libraries were generated using information-dependent acquisition (IDA) mode after injecting 2 gm of tryptic digest on the column using an Eksigent NanoLC-UltraTM 2D Plus system coupled with a SCIEX Triple TOF® 5600 system fitted with a NanoSpray III source. The samples were loaded on the trap (Eksigent Chrom XP 350 μm × 0.5 mm, 3 μm, 120 Å) and washed for 30 min at 3 μl/min. A 120 min gradient in multiple steps (ranging from 5 to 50% acetonitrile in water containing 0.1% formic acid) was set up to elute the peptides from the ChromXP 3-C18 (0.075 × 150 mm, 3 μm, 120 Å) analytical column. Technical replicates of the nanoLC-TripleTOF 5600 MS experiments were performed.
Sequential Window Acquisition of all Theoretical Fragment Ion Spectra (SWATH) Analysis for Label-Free Quantification
For label-free quantification (SWATH analysis), data-dependent analysis (DDA) mode was applied for both samples to generate high-quality spectral ion libraries by operating the mass spectrometer with specific parameters (Sharma and Bisht, 2016). In the SWATH acquisition method, the Q1 transmission window was set to 12 Da from the mass range 350–1250 Da. A total of 75 windows were acquired independently with an accumulation time of 62 ms, along with three technical replicates for each of the sets. The total cycle time was kept constant at <5 s. Protein PilotTM v. 5.0 was used to generate the spectral library. For label-free quantification, peak extraction and spectral alignment were performed using PeakView® 2.2 Software with the parameters set as follows: number of peptides, 2; number of transitions, 5; peptide confidence, 95%; XIC width, 30 ppm; XIC extraction window, 3 min. The data were further processed in MarkerView software v. 1.3 (AB Sciex, Foster City, CA, United States) for statistical data interpretation. In MarkerView, the peak area under the curve (AUC) for the selected peptides was normalized by the internal standard protein (beta-galactosidase) spike during SWATH accumulation. The results were extracted as three output files containing the AUC of the ions, the summed intensity of peptides for protein, and the summed intensity of ions for the peptide. All SWATH acquisition data were processed using SWATH Acquisition MicroApp 2.0 in PeakView® Software.
Data Analysis
Data were processed with Protein Pilot Software v. 5.0 (AB Sciex, Foster City, CA, United States) utilizing the Paragon and Progroup Algorithm. The analysis was done using the tools integrated into Protein Pilot at a 1% false discovery rate (FDR) with statistical significance. In brief, the UniProt database searched for the K. pneumoniae taxonomy, which was download from the database in July 2018. The download included total combined (reviewed and un-reviewed) entries of 409,060 proteins. We used cRAP analysis to identify the proteins commonly found in proteomics experiments (unavoidable contamination) of protein samples. E. coli beta-galactosidase (BGAL_ECOLI-[P00722]) was used as a molecular weight marker to calibrate the system for sample acquisition. The internal standard was used for the normalization of statistical parameters. We exported the label-free quantified data and imported them into MarkerView software V1.3 to obtain statistical data for further interpretation. Triplicate data for each sample were normalized using the internal protein (beta-galactosidase) area, which was initially spiked in the samples. After normalization, principal component analysis (PCA) was performed to check the possible correlated variables within the group. We plotted a volcano curve to determine the statistical significant fold change versus p-value for the control and test. Proteins with a significant fold change < 0.42 were considered down-regulated proteins. Peak extraction and spectral alignment were performed using PeakView software (v. 2.2, AB Sciex, Foster City, CA, United States) with the following parameter settings: number of peptides per protein, 5; number of transitions per peptide, 6; selected peptide confidence, 1% FDR; XIC width, 30 ppm; XIC extraction window, 3 min.
Gene Ontology Term Assignment and Analysis
Klebsiella pneumonia subsp. pneumoniae (strain ATCC 700721/MGH 78578) was used as a reference strain to carry out the functional studies. The proteins obtained from LC–MS/MS were firstly aligned to the reference strain proteome. Reference strain proteins that showed alignment identity of ≥50% over 80% of the sequence length of the reference strain protein were considered as homologs of the LC–MS/MS identified proteins. The Gene Ontology (GO) terms associated with the reference strain protein were used for the functional annotation. We used the slim version of GO terms, which were obtained from the Gene Ontology Consortium1 (Camon et al., 2003).
Protein–Protein Interaction Network Integration
To find the interaction partner(s) of down-regulated proteins, protein–protein interaction (PPI) information were obtained from the STRING database v10.02 and Cytoscape (version 3.6.1) (Shannon et al., 2003; Sharma and Bisht, 2017a,b,c; Sharma et al., 2018b, 2019b; Sharma and Khan, 2018). The PPI information provided by the STRING database has been established by experimental studies or by genomic analyses like domain fusion, phylogenetic profiling high-throughput experiments, co-expression studies, and gene neighborhood analysis. In the present study, only interactions with a score of ≥0.4 were used.
Results
Identification of Proteins by LC–MS/MS
In this study, we grew the carbapenem-resistant isolate at meropenem sub-MIC 32 mg/L. Further, we identified the down-regulated proteome of the same bacteria by LC–MS/MS using a SWATH workflow; 1156 proteins were quantified at 1% FDR with statistical significance as per the log fold change vs. p-value. Among them, 69 proteins were down-regulated (<0.42 log fold change vs. p-value) and are tabulated in the Supplementary Material (Supplementary Table S1).
In the present work, our main focus was on motility-related proteins. After critical analysis of the 69 down-regulated proteins, we found 13 proteins (around 19%) that belonged to the flagella-, fimbriae-, and pili-related protein functional groups (Table 1). These proteins are flagellar motor switch protein FliG, flagellar hook protein FlgE, negative regulator of flagellin synthesis FlgM, putative fimbriae major subunit StbA, flagellar hook-associated protein 2, chaperone FimC protein, flagellar biosynthesis protein FlgN, flagellar basal body protein, conjugal transfer protein TraC, fimbrial subunit type 1, chemotaxis regulator-transmits chemoreceptor signals to flagellar motor components CheY, and flagellin, all of which are involved in motility and its supporting processes.
TABLE 1.
Details of the down-regulated proteome (flagella-, fimbriae-, and pili-related proteins) under meropenem stress in Klebsiella pneumonia clinical isolates (NDM-4).
| S. No. | Protein name | Log fold change vs. p-value | Accession number | Protein symbol | Matched organism strain |
| 1 | Flagellar motor switch protein FliG | 0.42 | W1AYD1 | FliG | K. Pneumoniae IS22 |
| 2 | Flagellar hook protein FlgE | 0.32 | W1AUQ1 | FlgE | K. Pneumoniae IS22 |
| 3 | Negative regulator of flagellin synthesis FlgM | 0.23 | W1AWJ3 | FlgM | K. Pneumoniae IS22 |
| 4 | Putative fimbriae major subunit StbA | 0.23 | A6T548 | StbA | K. pneumoniae subsp. pneumoniae (strain ATCC 700721/MGH 78578) |
| 5 | Flagellar hook-associated protein 2 | 0.22 | W1B018 | ……. | K. Pneumoniae IS22 |
| 6 | FimC protein | 0.17 | W1AP20 | FimC | K. Pneumoniae IS22 |
| 7 | Chaperone FimC | 0.15 | W1BBF2 | FimC | K. Pneumoniae IS22 |
| 8 | Flagellar biosynthesis protein FlgN | 0.09 | W1ATC5 | FlgN | K. Pneumoniae IS22 |
| 9 | Flagellar basal body protein | 0.08 | W1AT19 | ……. | K. Pneumoniae IS22 |
| 10 | Conjugal transfer protein TraC | 0.06 | W1B0W2 | TraC | K. Pneumoniae IS22 |
| 11 | Fimbrial subunit type 1 | 0.05 | W1B9X4 | FimA | K. Pneumoniae IS22 |
| 12 | Chemotaxis regulator-transmits chemoreceptor signals to flagelllar motor components CheY | 0.04 | W1BDF3 | CheY | K. Pneumoniae IS22 |
| 13 | Flagellin | 0.01 | W1AZS9 | ……. | K. Pneumoniae IS22 |
On the basis of the parameters described in the section “Materials and Methods,” we were able to map 67 out of the 69 down-regulated proteins on the proteome of the ATCC 700721/MGH 78578 strain of K. pneumoniae (Supplementary Table S2). Our GO results for down-regulated genes also show that most down-regulated proteins were involved in nitrogen and other small molecule metabolism, ion binding, and oxidoreductase activity (Table 2).
TABLE 2.
Functional analysis of down-regulated genes associated with Klebsiella pneumonia subsp. pneumonia (strain ATCC 700721/MGH 78578).
| GO ID | Function | Gene name | No. of genes in which |
| GO term was found | |||
| (A) Biological functions | |||
| GO:0005975 | Carbohydrate metabolic process | deoC, dhaK, dhaL, glk, gmhB, gnd, lacZ2, malP, talB, treC, uxaC | 11 |
| GO:0006091 | Generation of precursor metabolites and energy | aspA, fdhF, glk, gor | 4 |
| GO:0006259 | DNA metabolic process | ung, uvrD | 2 |
| GO:0006399 | tRNA metabolic process | gltX, pheS, thrS | 3 |
| GO:0006412 | Translation | gltX, pheS, thrS | 3 |
| GO:0006457 | Protein folding | fimC | 1 |
| GO:0006461 | Protein complex assembly | hscB | 1 |
| GO:0006464 | Cellular protein modification process | ppiD, ptsH | 2 |
| GO:0006520 | Cellular amino acid metabolic process | aspA, gcvH, gcvP, gcvT, gltX, hisD, ilvC, pheS, thrS | 9 |
| GO:0006629 | Lipid metabolic process | dxs, glpQ | 2 |
| GO:0006790 | Sulfur compound metabolic process | dxs, gor | 2 |
| GO:0006810 | Transport | artI, copA, pcoC, ptsH | 4 |
| GO:0006950 | Response to stress | sodB, ung | 2 |
| GO:0007155 | Cell adhesion | fimA | 1 |
| GO:0007165 | Signal transduction | artI | 1 |
| GO:0009056 | Catabolic process | deoC, gcvH, gcvP, gcvT, glk, glpA, treC, uxaC | 8 |
| GO:0009058 | Biosynthetic process | dxs, hisD, hns, ilvC, nadE, pdxY, rmlD, rnk, sul, udp, uvrD | 11 |
| GO:0034641 | Cellular nitrogen compound metabolic process | cpdB, dxs, glk, gnd, gor, hisD, hns, nadE, pdxY, rmlB, rmlD, rnk, sul, talB, udp | 15 |
| GO:0034655 | Nucleobase-containing compound catabolic process | cdd, cpdB, deoC, udp | 4 |
| GO:0042592 | Homeostatic process | Gor | 1 |
| GO:0044281 | Small molecule metabolic process | aspA, cdd, cpdB, deoC, dhaK, dhaL, dxs, fdhF, glk, glpA, gnd, nadE, pdxY, sul, talB, udp, uxaC | 17 |
| GO:0051186 | Cofactor metabolic process | glk, gnd, nadE, pdxY, sul, talB | 6 |
| GO:0051276 | Chromosome organization | uvrD | 1 |
| GO:0051604 | Protein maturation | hscB | 1 |
| GO:0055085 | Transmembrane transport | copA | 1 |
| GO:0071554 | Cell wall organization or biogenesis | fimC | 1 |
| (B) Molecular functions | |||
| GO:0003677 | DNA binding | hns, rnk, uvrD | 3 |
| GO:0003723 | RNA binding | gltX, pheS, thrS | 3 |
| GO:0004386 | Helicase activity | uvrD | 1 |
| GO:0004871 | Signal transducer activity | artI | 1 |
| GO:0008168 | Methyltransferase activity | gcvT | 1 |
| GO:0016301 | Kinase activity | dhaK, dhaL, glk, pdxY, ptsH, rnk | 6 |
| GO:0016491 | Oxidoreductase activity | KPN_02441, fdhF, gcvP, glpA, gnd, gor, hisD, ilvC, nfnB, nfsA, rmlD, sodB, ydgJ | 13 |
| GO:0016746 | Transferring acyl groups | Maa | 1 |
| GO:0016757 | Transferring glycosyl groups | malP, udp | 2 |
| GO:0016765 | Transferring alkyl or aryl (other than methyl) groups | Sul | 1 |
| GO:0016791 | Phosphatase activity | aphA, gmhB | 2 |
| GO:0016798 | Acting on glycosyl bonds | lacZ2, rihC, treC, ung | 4 |
| GO:0016810 | Acting on carbon–nitrogen (but not peptide) bonds | Cdd | 1 |
| GO:0016829 | Lyase activity | acnA, aspA, deoC, rmlB, yhbL | 5 |
| GO:0016853 | Isomerase activity | ppiD, uxaC | 2 |
| GO:0016874 | Ligase activity | gltX, nadE, pheS, thrS | 4 |
| GO:0016887 | ATPase activity | copA, uvrD | 2 |
| GO:0019899 | Enzyme binding | Rnk | 1 |
| GO:0022857 | Transmembrane transporter activity | artI, copA | 2 |
| GO:0030234 | Enzyme regulator activity | hscB | 1 |
| (B) Molecular functions | |||
| GO:0043167 | Ion binding | KPN_pKPN3p05899, aphA, cdd, copA, cpdB, dxs, fdhF, glk, glpA, gltX, gmhB, gor, hisD, ilvC, lacZ2, malP, nadE, pcoC, pdxY, pheS, sodB, sul, thrS, uvrD, yiiM | 25 |
| (C) Cellular component | |||
| GO:0005622 | Intracellular | artI, copA, lacZ2, ppiD | 1 |
| GO:0005623 | Cell | Hns | 6 |
| GO:0005737 | Cytoplasm | aphA, artI, fimA, fimC, gor, pcoC | 15 |
| GO:0005886 | Plasma membrane | deoC, gcvH, glk, glpA, gltX, gmhB, maf, pheS, ptsH, talB, thrS, treC, udp, ung, uvrD | 2 |
Protein Network Analysis
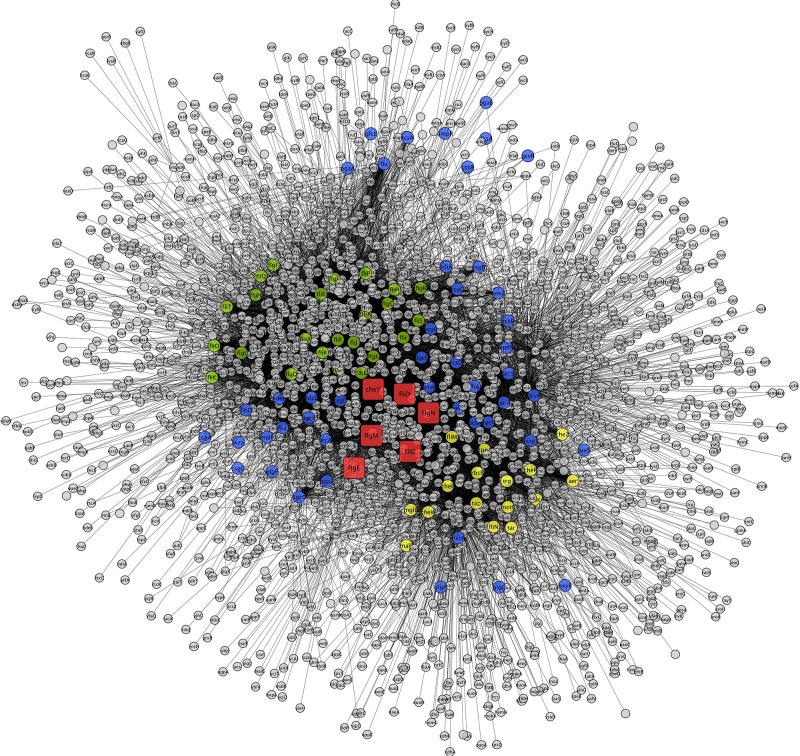
To construct the PPI network, the down-regulated proteins with motility-related functions were annotated using E. coli K12 strain DH10B homologs, as tabulated in Table 3. Among them, few proteins showed no hits in E. coli, and the rest of the proteins interacted with other proteins to make an interactome; this was visualized through Cytoscape (version 3.6.1) (Figure 1). Interacting proteins were color-coded by their functions: biofilm formation, blue; chemotaxis proteins, yellow; flagellar assembly, green. Square red nodes indicate down-regulated proteins.
TABLE 3.
List of Klebsiella pneumonia sp. proteins mapped on E. coli K12 substr.DH10B.
| K. pneumoniae | Sequence | K. pneumoniae | E. coli K12 substr. | Sequence | E. coli K12 substr. | Identity (%) |
| IS22 protein entry | length | protein name | DH10B protein entry | length | DH10B gene name | |
| W1AYD1 | 331 | Flagellar motor switch protein FliG | P0ABZ1 | 331 | fliG | 99.698 |
| W1AUQ1 | 206 | Flagellar hook protein FlgE | P75937 | 402 | flgE | 91.304 |
| W1AWJ3 | 97 | Negative regulator of flagellin synthesis | P0AEM4 | 97 | flgM | 100.000 |
| W1B018 | 468 | Flagellar hook-associated protein 2 | P24216 | 97 | fliD | 99.786 |
| W1AP20 | 224 | Chaperone FimC | No hit | – | – | – |
| W1ATC5 | 138 | Flagellar biosynthesis protein FlgN | P43533 | 468 | flgN | 100.000 |
| W1AT19 | 191 | Flagellar basal body protein | P75937 | 138 | flgE | 95.812 |
| W1BDF3 | 129 | Chemotaxis regulator-transmits chemoreceptor signals to flagelllar motor components CheY | P0AE67 | 129 | cheY | 100.000 |
| W1B0W2 | 533 | Conjugal transfer protein traC | No hit | – | – | – |
| W1AZS9 | 447 | Flagellin | No hit | – | – | – |
| A6T548 | 178 | Putative fimbriae major subunit StbA | No hit |
FIGURE 1.
Interaction networks for down-regulated genes of K. pneumoniae using E. coli K12 substr. DH10B homologs. Interacting proteins were color coded by functions, biofilm formation (blue), chemotaxis proteins (yellow), and flagellar assembly (green). Square nodes in red color indicate down-regulated protein mapped on E. coli.
Discussion
The development of carbapenem-resistant K. pneumoniae has worsened the medical situation around the globe. The emergence of carbapenem resistance is usually due to the over-expression of carbapenemases and loss of porins. Recently, we reported a cluster of over-expressed proteins in carbapenem-resistant K. pneumoniae under meropenem pressure. These could be responsible for the drug resistance and belong to various categories such as the protein translational machinery complex, DNA/RNA modifying enzymes or proteins, proteins involved in carbapenem cleavage, modification, and transport, and energy metabolism- and intermediary metabolism-related proteins (Sharma et al., 2019a). Therefore, we suggested that they could be potential targets for the development of novel therapeutics against this resistance. Biofilm formation is also one of the mechanisms that leads to the development of drug resistance. In the present study, we have found a group flagellar, fimbriae, and pili proteins that are down-regulated under meropenem stress (sub-MIC). We hypothesize that the down-regulation of these proteins under meropenem stress makes the bacteria sessile or non-motile, leading to the emergence of a biofilm-like state that could contribute to carbapenem resistance in K. pneumoniae (NDM-4). Earlier microarray analysis of K. pneumoniae also reported the down-regulation of genes related to nitrogen metabolism, porin genes, and some membrane-associated proteins in association with the antibiotic resistance phenomenon (Doménech-Sánchez et al., 2006). The significance of the aforementioned pathways in antibiotic-evading mechanisms is also highlighted in several other reports (Yeung et al., 2011; Piek et al., 2014).
A Hub of Flagellar, Fimbriae, and Pili Proteins Could Regulate Resistance
A group of flagellar, fimbriae, and pili proteins involved in the formation of the flagellar machinery complex and the regulation of motility processes were found to be down-regulated in meropenem-induced carbapenem-resistant K. pneumoniae clinical strains. These proteins are flagellar motor switch protein FliG, flagellar hook protein FlgE, negative regulator of flagellin synthesis FlgM, putative fimbriae major subunit StbA, flagellar hook-associated protein 2, chaperone FimC protein, flagellar biosynthesis protein FlgN, flagellar basal body protein FlgF, conjugal transfer protein TraC, fimbrial subunit type 1, chemotaxis regulator-transmits chemoreceptor signals to flagellar motor components CheY, and flagellin.
The observed expression down-regulation of flagella-, fimbriae-, and pili-related proteins provides clues to a novel mechanism of drug resistance. Flagellin, flagellar biosynthesis protein FlgN, and FlgM, respectively, cumulatively maintain equilibrium in the biosynthesis of flagella. Flagellin protein is part of the structural component of flagella, and biosynthesis of flagella is favored by flagellar biosynthesis protein FlgN (Bennett et al., 2001). FlgM is a negative regulator that switches off flagellar transport. FlgM can be exported from the cell via a flagellum, and the transport occurs only after the completion of hook formation (Hughes et al., 1993). This unique regulatory mechanism further postpones flagellin synthesis in the cell. Cumulatively, the expression of these proteins is involved in the flagella formation, regulation, and motility of the bacteria. Therefore, we suggest that, under meropenem pressure, down-regulation of these proteins might make the bacteria sessile, which is the first step in biofilm-formation. Therefore, we assume that down-regulation of these proteins could create a biofilm-like state, which ultimately leads to the drug resistance.
Flagella are composed of three different parts: a filament (helical and long), hook (a curved and short structure), and basal body (a complex structure with a central rod and a series of rings). Flagellar motor switch protein (FliG), flagellar hook protein FlgE, flagellar hook-associated protein 2, and flagellar basal body protein FlgF together make up part of the flagellar motor switch complex (FliG, FliN, and FliM), which is involved in bacterial motility, after receipt and transduction of the signal by chemotaxis (Djordjevic and Stock, 1998). This is a complex apparatus that senses the signal from the chemotaxis sensory signaling system and is transduced into motility. Chemotaxis response regulator CheY transmits chemoreceptor signals to flagellar motor components and is believed to be the “on” switch that directly induces tumbles in the swimming pattern (Robinson et al., 2000). Physical interactions of CheY and switch proteins have not been reported. Chemotactic stimuli change the association of the CheY signal protein with the distal FliMNCFliN C ring (Dyer et al., 2009; Sarkar et al., 2010). In the present study, down-regulation of the chemotaxis response regulator (CheY) subsequently down-regulates signal transmission to the flagellar motor components, which may act as an “off” switch and make the bacteria sessile or non-motile. Further, it might lead to a biofilm-like state and could contribute to the drug resistance.
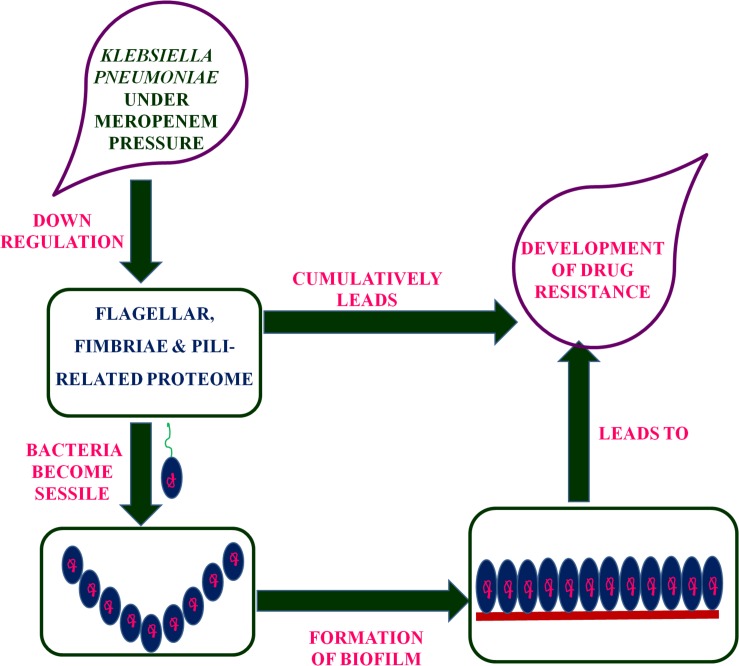
Putative fimbriae major subunit StbA, Fimbrial subunit type 1, conjugal transfer protein TraC, and chaperone FimC protein are involved in pillus organization, fimbriae formation, and their associated assemblies (Johnson and Clegg, 2010). FimC protein acts as a periplasmic pilin chaperone that not only protects the bacteria under stress through chaperone-mediated folding but is also involved in pillus formation (Klemm, 1992). In the periplasm, the FimC chaperone binds to the major and minor structural components and protects them from degradation. Conjugal transfer protein TraC, encoded by a gene, traC, presents on plasmid and is involved in the conjugation process as well as pili formation (Winans and Walker, 1985; Kado, 1994), leading to the transfer of drug-resistant plasmid to bacteria. These down-regulated proteins (flagellar, fimbriae, and pili proteins) form a hub of proteins in the PPI network, which indicates their important role in flagellar, fimbriae, and pili assemblies, signaling through chemotaxis proteins, and biofilm formation (Figure 1). In this study, the down-regulation of fimbriae-, pili-, and conjugative-related proteins leads to the creation of the biofilm-like state, which may contribute to drug resistance. On the basis of the flagella-, fimbriae-, and pili-related proteome, we propose a model (Figure 2) that suggests the potential path or mechanism of carbapenem resistance in K. pneumoniae (NDM-4) clinical isolates. Overall this group of down-regulated proteins and their interactive protein partners cumulatively make a hub that leads to the formation of a biofilm-like scenario and could contribute to meropenem resistance.
FIGURE 2.
Proposed model based on the flagellar-, fimbriae-, and pili-related proteome suggested the mechanism of carbapenem-resistance in K. pneumoniae (NDM-4) clinical isolates.
Conclusion
In brief, the present study focused on the down-regulated proteome of carbapenem-resistant K. pneumoniae clinical isolate (NDM-4) under meropenem pressure through proteomics and systems biology approaches. A group of down-regulated proteins was identified that belongs to the flagellar, fimbriae, and pili proteins. Therefore, we suggest that these proteins and their interactive protein partners cumulatively lead to the bacteria becoming sessile, which further creates a biofilm-like state and could contribute to the survival of bacteria under meropenem pressure, which might reveal a novel mechanism of drug resistance. Further research on these motility-related protein targets and their pathways may lead to the development of novel therapeutics against the worsening situation of drug resistance.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation, to any qualified researcher.
Author Contributions
DS designed the concept, and experimented and wrote the manuscript. AG and MK carried out the systems biology analysis. FR provided support in the LC–MS experiments and analysis. AK designed and guided the study and finalized the manuscript. All authors approved the final manuscript.
Conflict of Interest
FR was employed by SCIEX Pvt. Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
- CLSI
Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute
- ESBLs
extended spectrum beta-lactamases
- LB
Luria–Bertani
- MIC
minimum inhibitory concentration
- STRING
Search Tool for the Retrieval of Interacting Genes/Proteins.
Funding. Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB) is gratefully acknowledged for providing fellowship and funds to DS (SERB-N-PDF/2016/001622) to work at IBU-AMU Aligarh. The authors also acknowledge SCIEX Pvt. Ltd., Gurgaon, India, for data acquisition and proteomics facility support.
Supplementary Material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmicb.2019.02865/full#supplementary-material
References
- Ahmad N., Khalid S., Ali S. M., Khan A. U. (2018). Occurrence of blaNDM variants among Enterobacteriaceae from a neonatal intensive care unit in a northern India hospital. Front Microbiol. 9:407. 10.3389/fmicb.2018.00407 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambler R. P., Coulson A. F., Frère J. M., Ghuysen J. M., Joris B., Forsman M., et al. (1991). A standard numbering scheme for the class A beta-lactamases. Biochem. J. 276(Pt 1), 269–270. 10.1042/bj2760269 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett J. C., Thomas J., Fraser G. M., Hughes C. (2001). Substrate complexes and domain organization of the Salmonella flagellar export chaperones FlgN and FliT. Mol. Microbiol. 39 781–791. 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2001.02268.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. (1976). A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72 248–254. 10.1006/abio.1976.9999 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camon E., Barrell D., Lee V., Dimmer E., Apweiler R. (2003). The Gene Ontology Annotation (GOA) database-an integrated resource of GO annotations to the UniProt Knowledgebase. Silico Biol. 4 5–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costerton J. W., Lewandowski Z. (1995). Microbial biofilms. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 49 711–745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costerton J. W., Stewart P. S., Greenberg E. P. (1999). Bacterial biofilms: a common cause of persistent infections. Science 1999 1318–1322. 10.1126/science.284.5418.1318 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Djordjevic S., Stock A. M. (1998). Structural analysis of bacterial chemotaxis proteins: com-ponents of a dynamic signaling system. J. Struct. Biol. 124 189–200. 10.1006/jsbi.1998.4034 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doménech-Sánchez A., Javier Benedi V., Martínez-Martínez L., Alberti S. (2006). Evaluation of differential gene expression in susceptible and resistant clinical isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae by DNA microarray analysis. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 12 936–940. 10.1111/j.1469-0691..01470.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyer C. M., Vartanian A. S., Zhou H., Dahlquist F. W. (2009). A molecular mechanism of bacterial flagellar motor switching. J. Mol. Biol. 388 71–84. 10.1016/j.jmb.2009.02.004 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fux C. A., Costerton J. W., Stewart P. S., Stoodley P. (2005). Survival strategies of infectious biofilms. Trends Microbiol. 13 34–40. 10.1016/j.tim.2004.11.010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes K. T., Gillen K. L., Semon M. J., Karlinsey J. E. (1993). Sensing structural intermediates in bacterial flagellar assembly by export of a negative regulator. Science 262 1277–1280. 10.1126/science.8235660 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacoby G. A., Mills D. M., Chow N. (2004). Role of beta-lactamases and porins in resistance to Ertapenem and other beta-lactams in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 48 3203–3206. 10.1128/aac.48.8.3203-3206.2004 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. G., Clegg S. (2010). Role of MrkJ, a phosphodiesterase, in type 3 fimbrial expression and biofilm formation in Klebsiella pneumoniae. J. Bacteriol. 192 3944–3950. 10.1128/JB.00304-10 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kado C. I. (1994). Promiscuous DNA transfer system of Agrobacterium tumefaciens: role of the virB operon in sex pilus assembly and synthesis. Mol. Microbiol. 12 17–22. 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1994.tb00990.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan A., Sharma D., Faheem M., Bisht D., Khan A. U. (2017). Proteomic analysis of a carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae strain in response to meropenem stress. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 8 172–178. 10.1016/j.jgar.2016.12.010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemm P. (1992). FimC, a chaperone-like periplasmic protein of Escherichia coli involved in biogenesis of type 1 fimbriae. Res. Microbiol. 143 831–838. 10.1016/0923-2508(92)90070-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lata M., Sharma D., Deo N., Tiwari P. K., Bisht D., Venkatesan K. (2015). Proteomic analysis of ofloxacin-mono resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates. J. Proteomics 127 114–121. 10.1016/j.jprot.2015.07.031 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loli A., Tzouvelekis L. S., Tzelepi E., Carattoli A., Vatopoulos A. C., Tassios P. T., et al. (2006). Sources of diversity of carbapenem resistance levels in Klebsiella pneumoniae carrying blaVIM-1. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 58 669–672. 10.1093/jac/dkl302 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Martínez L., Pascual A., Hernández-Allés S., Alvarez-Díaz D., Suárez A. I., Tran J., et al. (1999). Roles of β-lactamases and porins in activities of carbapenems and cephalosporins against Klebsiella pneumoniae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 43 1669–1673. 10.1128/aac.43.7.1669 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarty S. M., Cochrane C. A., Clegg P. D., Percival S. L. (2012). The role of endogenous and exogenous enzymes in chronic wounds: a focus on the implications of aberrant levels of both host and bacterial proteases in wound healing. Wound Repair Regen. 20 125–136. 10.1111/j.1524-475X.2012.00763.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson D. L. (2000). Recommendation for treatment of severe infections caused by Enterobacteriaceae producing extended-spectrum beta-lactamases(ESBLs). Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 6 460–463. 10.1046/j.1469-0691.2000.00107.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson D. L., Bonomo R. A. (2005). Extended-spectrum beta-lactamases: a clinical update. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 18 657–686. 10.1128/cmr.18.4.657-686.2005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piek S., Wang Z., Ganguly J., Lakey A. M., Bartley S. N., Mowlaboccus S., et al. (2014). The role of oxidoreductases in determining the function of the neisserial lipid A phosphoethanolamine transferase required for resistance to polymyxin. PLoS One 9:e106513. 10.1371/journal.pone.0106513 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qayyum S., Sharma D., Bisht D., Khan A. U. (2019). Identification of factors involved in Enterococcus faecalis biofilm under quercetin stress. Microb. Pathog. 126 205–211. 10.1016/j.micpath.2018.11.013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson V. L., Buckler D. R., Stock A. M. (2000). A tale of two components: a novel kinase and a regulatory switch. Nat. Struct. Biol. 7 626–633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar M. K., Paul K., Blair D. (2010). Chemotaxis signaling protein CheY binds to the rotor protein FliN to control the direction of flagellar rotation in Escherichia coli. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 107 9370–9375. 10.1073/pnas.1000935107 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shannon P., Markiel A., Ozier O., Baliga N. S., Wang J. T., Ramage D., et al. (2003). Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 13 2498–2504. 10.1101/gr.1239303 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma D., Bisht D. (2016). An efficient and rapid method for enrichment of lipophilic proteins from Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv for two dimensional gel electrophoresis. Electrophoresis 37 1187–1190. 10.1002/elps.201600025 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma D., Bisht D. (2017a). M.tuberculosis hypothetical proteins and proteins of unknown function: hope for exploring novel resistance mechanisms as well as future target of drug resistance. Front. Microbiol. 8:465. 10.3389/fmicb.2017.00465 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma D., Bisht D. (2017b). Role of bacterioferritin & ferritin in M.tuberculosis pathogenesis and drug resistance: a future perspective by interactomic approach. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 7:240 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00240 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma D., Bisht D. (2017c). Secretory proteome analysis of streptomycin resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis clinical isolates. SLAS Discov. 22 1229–1238. 10.1177/2472555217698428 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma D., Bisht D., Khan A. U. (2018a). Potential alternative strategy against drug resistant tuberculosis: a proteomics prospect. Proteomes 6:26. 10.3390/proteomes6020026 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma D., Singh R., Deo N., Bisht D. (2018b). Interactome analysis of Rv0148 to predict potential targets and their pathways linked to aminoglycosides drug resistance: an insilico approach. Microb. Pathog. 121 179–183. 10.1016/j.micpath.2018.05.034 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma D., Garg A., Kumar M., Khan A. U. (2019a). Proteome profiling of carbapenem-resistant K. pneumoniae clinical isolate (NDM-4): exploring the mechanism of resistance and potential drug targets. J. Proteomics 200 102–110. 10.1016/j.jprot.2019.04.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma D., Lata M., Faheem M., Khan A. U., Joshi B., Venkatesan K., et al. (2019b). Role of M.tuberculosis protein Rv2005c in the aminoglycosides resistance. Microb. Pathog. 132 150–155. 10.1016/j.micpath.2019.05.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma D., Misba L., Khan A. U. (2019c). Antibiotics versus Biofilm: an emerging battleground in microbial communities. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 8:76. 10.1186/s13756-019-0533-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma D., Khan A. U. (2018). Role of cell division protein divIVA in Enterococcus faecalis pathogenesis, biofilm and drug resistance: a future perspective by in silico approaches. Microb. Pathog. 125 361–365. 10.1016/j.micpath.2018.10.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart P. S., William Costerton J. (2001). Antibiotic resistance of bacteria in biofilms. Lancet 358 135–138. 10.1016/s0140-6736(01)05321-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wayne P. A. (2014). Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing: 24 informational supplement. CLSI 100 S24. [Google Scholar]
- Winans S. C., Walker G. C. (1985). Conjugal transfer system of the IncN plasmid pKM101. J. Bacteriol. 161 402–410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeung A. T., Bains M., Hancock R. E. (2011). The sensor kinase CbrA is a global regulator that modulates metabolism, virulence, and antibiotic resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Bacteriol. 15 918–931. 10.1128/JB.00911-10 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation, to any qualified researcher.