Abstract
Background
Use of humidifier disinfectants (HD) at home leads to chemical airborne exposure, causing HD associated lung injury (HDLI) with high mortality. However, the lung function in children diagnosed with HDLI is not well studied. We investigated the effect of HD exposure on lung function, prognosis, and exposure characteristics associated with the lung function phenotype in children.
Methods
Eighty-one children diagnosed with HDLI in a nationwide cohort were tested for spirometry and diffusing capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide (DLco) from July 2013 and followed up with at five time points over 2 years. The results were compared with 122 children without HD exposure as controls. Home investigation and questionnaire analysis were conducted to assess HD inhalation exposure.
Results
HDLI survivor’s mean percent of predicted forced expiratory volume in 1 s (FEV1), forced vital capacity (FVC), and corrected DLco were significantly lower compared with the control group. On longitudinal assessment, FVC was within the normal range, but flattened, and spirometry showed a predominantly restrictive pattern. Corrected DLco did not normalize above 80% despite increasing age. The persistently low phenotype of lung function was associated with initial exposure age, especially less than 12 months of age. Higher density HD exposure during sleep and close distance between the bed and the humidifier were significantly associated with persistently low corrected DLco.
Conclusions
HD exposure affects prolonged decrement in lung function, especially DLco, particularly among children who are exposed within the first year of life. These results suggested that early-life HD exposure determines long-term prognosis of lung function in children.
Keywords: Chemical airborne exposure, Humidifier disinfectants, Lung function, Diffusing capacity, Children
Background
Humidifier disinfectants (HD), as household chemicals, have been used to prevent microbial growth in humidifier water tanks since 1994 in South Korea and contain various concentrations of chemicals, including oligoethoxyethyl-guanidinium chloride (PGH), polyhexamethylene-guanidine phosphate (PHMG), and chloromethylisothiazol/methyl-isothiazol (CMIT/MIT). These chemicals have been widely used in either industrial or various consumer products, including cosmetics, as biocides [1, 2]. However, HD inhalation from a humidifier’s aerosolizer was finally identified as a respiratory toxicant [3, 4] after an epidemic outbreak of idiopathic childhood interstitial lung disease (chILD) characterized by spontaneous air leak, rapid progression, and high mortality among immunocompetent children in South Korea in 2006 [5, 6]. Thereby, the novel forms of HD associated lung injury (HDLI) were defined in 2011, and HDLI has been added in the chILD classification of exposure-related ILD, worldwide [7, 8]. HD use in early-life was also recently found to independently increase the risk of childhood asthma [9].
Many chemical airborne exposures are associated with a decrement in lung function in adults, including in cases of large man-made disasters, such as the 1984 Bhopal Union Carbide methyl isocyanate gas release, the 2005 chlorine gas release from the Graniteville train accident, and current 2006 epidemic HD exposure (Additional file 1: Table S1). HD inhalation causing HDLI has been found to be characterized by restrictive lung defect in adults [10, 11]. Despite the associations observed in HDLI adults, the potential effects and the long-term consequences of HDLI children on lung function have not been explored, although children’s lungs are more susceptible to airborne exposures than those of adults [12, 13]. Even in case of the other chemical-related fatalities, no study on lung function in children has been reported. This continues to be a significant public health issue because there is no reference on chemical-related health crises of children, although thousands of toxic chemicals are used worldwide. Therefore, the characteristics of lung function and the presence of associated risk factors after HD inhalation are important in determining whether lung function can improve in the future in HDLI children. Furthermore, most studies in adults about chemical inhalants have been quantified by spirometric indexes, whereas less is known about diffusing capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide (DLco), which is important to evaluate the alteration of small airways after chemical exposure. Study of changes in DLco over time is useful to follow the course of disease [14].
Therefore, we investigated the effect of inhalation exposure to HD on lung function using both spirometry and DLco. In addition, we studied the long-term prognosis during childhood, which suggested the lung function phenotype and exposure characteristics associated with the phenotype.
Methods
Study design and participants
HDLI survivors
The Korean Government completed the third round of investigation from July 2013 to August 2016 in individuals with lung disease presumed to be related to HD exposure. Complete medical records, including demographics, laboratory findings, chest radiographs, and computed tomography scans and/or biopsy were collected. A Lung Injury Investigation Committee was formed by pulmonologists, radiologists, and pathologists to confirm the diagnosis of HDLI on the basis of clinical, radiological, and pathological findings and HD exposure assessment. Pulmonologists, radiologists, and pathologists then independently assessed the records of each case for relevant features based on diagnostic criteria and classified the features in each area into definite, probable, possible, or unlikely groups [15]. Thus, independent assessments of clinical features, radiographic findings, and pathology were combined to obtain an overall assessment for each case. Subsequently, the class of HDLI (definite, probable, possible, or unlikely) was determined. This study analyzed subjects with definite or probable diagnoses of HDLI. The subjects were prospectively followed in a nationwide cohort study and underwent spirometry and DLco. We excluded pulmonary function test (PFT) results that were repeated less than 3 months after the examination.
Control group
To compare the PFT between HDLI survivors and healthy Korean children, children as controls were recruited from the outpatients of Asan Medical Center from June 2016 through March 2018. All subjects were born at full term and had no history of exposure to HD. Subjects had no other diseases known to influence the respiratory system, either directly or indirectly.
Pulmonary function testing
Spirometry and DLco were performed using Vmax229D instrument (SensorMedics, Yorba Linda, CA, USA) according to the American Thoracic Society (ATS)/European Respiratory Society (ERS) recommendations and extrapolated to ages over 7 years [14, 16]. Reference equations from a study by Morris et al. were used for spirometric parameters and from Polgar et al. for DLco [17]. We considered a percent predicted forced vital capacity (FVC) less than 80% to be abnormal [18]. Patterns of spirometry abnormality were defined as follows: normal [FEV1/FVC ≥ lower limit of normal (LLN) and FVC ≥ LLN], restrictive, (FEV1/FVC > LLN and FVC < LLN), obstructive (FEV1/FVC < LLN, FVC > LLN and FEV1 < LLN), and mixed (FEV1/FVC < LLN and FVC < LLN) [19]. Corrected DLco (adjusted for Hb, as recommended by the ATS/ERS [14]) less than 80% was defined as a significant diffusion defect [20–22]. The severity of the corrected DLco of 60 to 80%, 40 to 60%, and less than 40% were classified as mild, moderate, and severe abnormalities, respectively [22].
Exposure assessment to humidifier disinfectant
The methods used for investigating use characteristics of HD based on personal interviews and home investigations have been described in Text S1 (“exposure assessment to HD”). These systematic and transparent exposure assessment approaches used to estimate the probability, frequency, and intensity of exposure to HD have been used in many published epidemiologic analyses to examine the association between HD exposure and clinically diagnosed lung disease [15, 23].
Statistical analysis
Lung function outcomes were expressed as means with standard errors of the estimated mean (SE). The Chi-square or Student t-test was used to determine group differences on variables, as appropriate. Associations between initial exposure age and lung function were analyzed with the Cox proportional hazard regression model adjusting for height and weight at PFT performance, HD strands, and total months of HD use and were reported as hazard ratios (HR) with 95% confidence intervals (CI). Analyses were performed using SPSS, version 24.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). Figures were generated using GraphPad Prism 5.0 (Graphpad, San Diego, CA, USA). P < 0.05 was considered as statistically significant.
Results
Follow-up and demographics of the study subjects
Additional file 2: Figure S1 depicts the progression of participation in the Korean government survey. Final criteria were met by 81 HDLI survivors and 122 controls. Furthermore, 81 HDLI survivors were followed up in five time points with a mean interval of 7.2 months for spirometry and 6.1 months for DLco over approximately 2 years. Table 1 summarizes the study population characteristics, and no discernable demographic differences were observed between HDLI survivors and controls.
Table 1.
Demographics of study population
| HDLI survivors (n = 81) | Control group (n = 122) | P-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| mean or n (SD or %) | mean or n (SD or %) | ||
| Age at spirometry (years) | 8.6 (2.2) | 8.7 (1.8) | 0.744 |
| Age at DLco (years) | 9.3 (2.6) | 8.7 (1.8) | 0.085 |
| Sex | |||
| Boy | 47 (58.0) | 81 (66.4) | 0.226 |
| Girl | 34 (42.0) | 41 (33.6) | |
| Height (cm) at spirometry | 133.5 (15.2) | 133.7 (12.4) | 0.925 |
| Weight (kg) at spirometry | 32.6 (14.0) | 32.7 (11.5) | 0.952 |
| BMI (kg/m2) at spirometry | 17.5 (3.5) | 17.8 (2.9) | 0.542 |
| Height (cm) at DLco | 137.6 (16.1) | 133.7 (12.4) | 0.064 |
| Weight (kg) at DLco | 35.9 (15.9) | 32.7 (11.5) | 0.123 |
| BMI (kg/m2) at DLco | 18.1 (3.8) | 17.8 (2.9) | 0.468 |
Data are presented as mean (standard deviation) or frequency (percentage) of subjects. P values for the comparison between HDLI survivors and controls calculated with the use of the Pearson chi-square test or the Student t test, as appropriate. HDLI, HD associated lung injury; N, number; SD, standard deviation; DLco, diffusing capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide; BMI, body mass index
Comparison of pulmonary function test results: HDLI survivors vs. control subjects
HDLI survivors had a significantly reduced mean percent of predicted FVC, FEV1, DLco, and corrected DLco compared with controls in both sexes of children aged over 7 years (Table 2, total group). To determine the acceptable age to apply the normal criteria for corrected DLco (> 80%) in children, as less than 80% of corrected DLco was observed among girls over 7 years of age used a controls and since we had no reference in Asian children, we further analyzed the findings in children over 8 years and over 9 years of age (Table 2, subgroup). Controls of both sexes over 8 years of age showed a greater than 80% in corrected DLco, and the result was more pronounced in girls over 9 years of age. The age-related difference could be accounted for by the greater somatic size in boys than in girls [24].
Table 2.
Comparison of PFT in HDLI survivors vs. control subjects
| HDLI survivors | Control group | P-value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | mean (SE) | n | mean (SE) | ||
| A. Boy, Over 7 years | |||||
| FVC (% of pred) | 47 | 87.4 (2.2) | 75 | 98.5 (1.2) | < 0.001 |
| FEV1 (% of pred) | 47 | 86.0 (2.0) | 75 | 96.7 (1.3) | < 0.001 |
| FEV1/FVC | 47 | 89.1 (0.7) | 75 | 89.0 (0.5) | 0.907 |
| cor. DLco (% of pred) | 47 | 74.0 (2.4) | 81 | 87.1 (1.3) | < 0.001 |
| Girl, above 7 years | |||||
| FVC (% of pred) | 34 | 84.4 (2.2) | 39 | 94.1 (1.4) | < 0.001 |
| FEV1 (% of pred) | 34 | 82.4 (2.4) | 39 | 93.5 (1.5) | < 0.001 |
| FEV1/FVC | 34 | 90.4 (1.1) | 39 | 91.8 (0.6) | 0.256 |
| cor. DLco (% of pred) | 34 | 68.3 (1.9) | 41 | 78.2 (1.8) | < 0.001 |
| B. Boy, above 8 years | |||||
| FVC (% of pred) | 23 | 83.1 (3.4) | 52 | 98.5 (1.5) | < 0.001 |
| FEV1 (% of pred) | 23 | 81.7 (3.1) | 52 | 95.9 (1.6) | < 0.001 |
| FEV1/FVC | 23 | 89.7 (1.0) | 52 | 88.6 (0.6) | 0.308 |
| cor. DLco (% of pred) | 28 | 74.4 (3.5) | 55 | 89.3 (1.5) | < 0.001 |
| Girl, above 8 years | |||||
| FVC (% of pred) | 15 | 80.9 (2.3) | 27 | 92.1 (1.5) | < 0.001 |
| FEV1 (% of pred) | 15 | 77.3 (2.7) | 27 | 90.4 (1.4) | < 0.001 |
| FEV1/FVC | 15 | 89.8 (2.2) | 27 | 91.5 (0.8) | 0.465 |
| cor. DLco (% of pred) | 19 | 67.9 (2.0) | 29 | 80.8 (2.3) | < 0.001 |
| C. Boy, above 9 years | |||||
| FVC (% of pred) | 18 | 81.0 (3.6) | 31 | 98.1 (1.8) | < 0.001 |
| FEV1 (% of pred) | 18 | 79.3 (3.0) | 31 | 95.1 (1.9) | < 0.001 |
| FEV1/FVC | 18 | 89.7 (1.1) | 31 | 88.5 (0.7) | 0.390 |
| cor. DLco (% of pred) | 25 | 74.1 (3.4) | 32 | 89.6 (2.3) | < 0.001 |
| Girl, above 9 years | |||||
| FVC (% of pred) | 13 | 80.8 (2.6) | 15 | 90.5 (1.7) | 0.004 |
| FEV1 (% of pred) | 13 | 76.6 (3.0) | 15 | 87.7 (1.4) | 0.004 |
| FEV1/FVC | 13 | 89.2 (2.5) | 15 | 91.3 (1.1) | 0.462 |
| cor. DLco (% of pred) | 15 | 68.3 (2.1) | 15 | 83.7 (2.6) | < 0.001 |
P values for the comparison between HDLI survivors and controls calculated with the Student t test. HDLI, HD associated lung injury; N, number; SE, standard errors of the estimated mean; pred, predicted; FVC, forced vital capacity; FEV1, forced expiratory volume in 1 sec; FEV1/FVC, the ratio of forced expiratory volume in 1 sec to forced vital capacity; FEF25–75: forced expiratory flow between 25 and 75% of vital capacity; DLco, diffusing capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide; cor. DLco, corrected DLco
Longitudinal assessment of spirometry and DLco in HDLI survivors
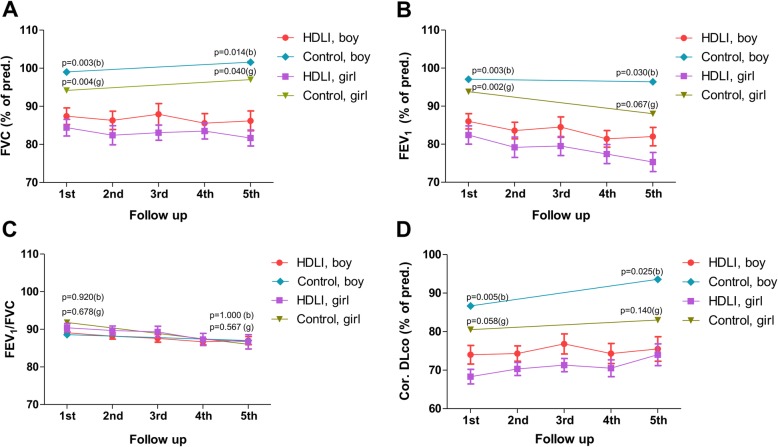
In the long-term growth characteristics of HDLI survivors and control subjects, there was no apparent difference in the final growth in both spirometry and DLco assessment in Additional file 3: Figure S2. The longitudinal assessment of lung function at the five time points in HDLI survivors compared with controls is shown in Fig. 1. The mean percent of predicted FVC in HDLI survivors of both sexes was within the normal range during the follow-up. However, FVC were not more than 90% in both sexes (in detail, mean percent of predicted value of FVC was 87.4% at 1st, 86.3% at 2nd, 87.9% at 3rd, 85.6% at 4th, and 86.2% at the 5th follow-up in boys and 84.4% at 1st, 82.4% at 2nd, 83.1% at 3rd, 83.5% at 4th, and 81.7% at the 5th follow-up in girls) and significantly lower compared with the control group in both sexes. Corrected DLco was persistently reduced to less than 80% in both sexes without recovery in HDLI survivors (boys, 74.0% in 1st, 74.3% in 2nd, 76.8% in 3rd, 74.3% in 4th, and 75.5% in the 5th follow-up; girls, 68.3% in 1st, 70.3% in 2nd, 71.3% in 3rd, 70.5% in 4th, and 74.0% in the 5th follow-up), compared with controls, especially boys. The mean percent of predicted FEV1 was also significantly lower compared with that of the control group. The ratio of FEV1/FVC remained relatively similar between HDLI survivors and controls within the normal range. These results also remained significant in FVC and corrected DLco of the z-scores from Global Lung Function Initiative (GLI) equations in Additional file 4: Figure S3 [25, 26].
Fig. 1.
Longitudinal assessment of spirometry and DLco in HDLI survivors compared with control. Figures show the mean changes in FVC (a), FEV1 (b), FEV1/FVC (c), and corrected DLco (d) in the follow-up period, presented as the percent of the predicted values for HDLI survivors compared to controls. Controls were compared with age- and sex-matched HDLI children both at the 1st and 5th follow-up. P-values were calculated for the comparisons between groups for each sex using the Kruskall-Wallis test. Pred, predicted; FVC, forced vital capacity; FEV1, forced expiratory volume in 1 sec; Cor., corrected; DLco, carbon monoxide diffusion capacity; b, boy; g, girl
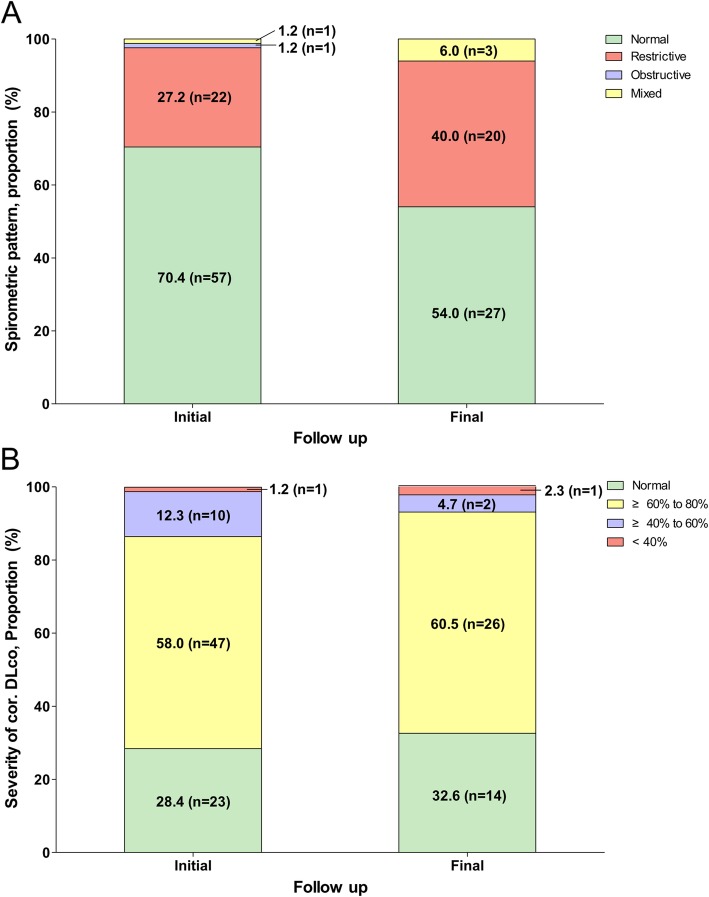
Additional analyses of spirometry abnormalities and severity of corrected DLco were also performed between the initial and final tests (Fig. 2). The prevalence of a restrictive pattern in both the initial and final tests was remarkable (27.2 and 40.0%, restrictively). In addition, the proportion of low corrected DLco for the initial test was 58 (71.5%) survivors, including 47 (58.0%) with mildly reduced DLco, 10 (12.3%) with moderated defect, and 1 (1.2%) with severe defect. At the final follow-up, 29 (67.5%) had abnormal DLco, with 26 (60.5%) mild, 2 (4.7%) moderate, and 1 (2.3%) severely low values.
Fig. 2.
Spirometry pattern and DLco at initial and final follow-up in HDLI survivors. Figures show changes in the proportion of the spirometric pattern (a) and severity of corrected DLco (b) between the initial and final tests in HDLI survivors. In panel A, 81 and 50 children underwent spirometry at the 1st and 5th follow-ups, respectively. Participants showed the tendency to change to a restrictive pattern. In panel B, 81 and 43 children underwent DLco at the 1st and 5th follow-up, respectively. Most participants showed persistent decline in the diffusion defect, although some showed improvement
Lung function phenotype of HDLI survivor associated exposure characteristics
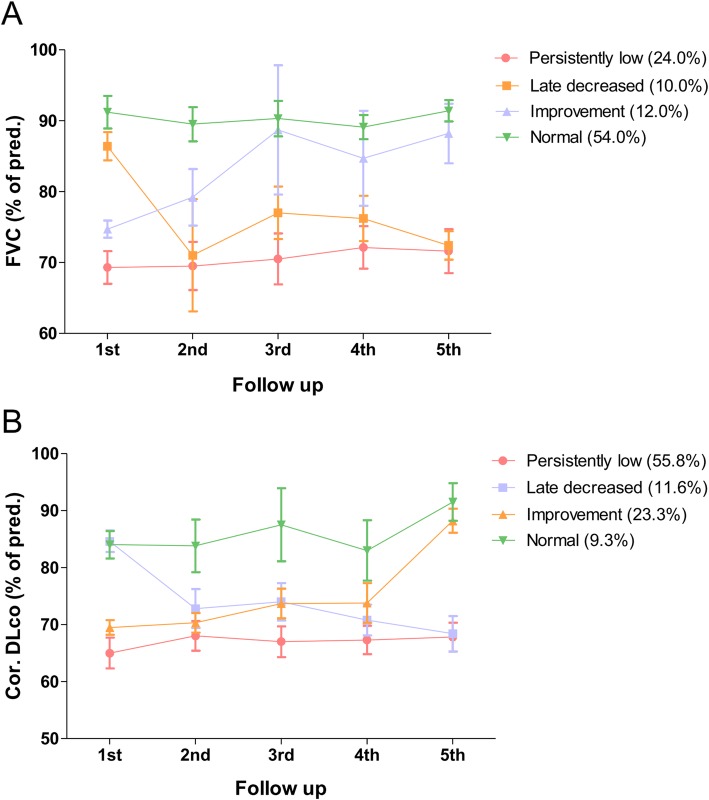
We classified the four prognosis phenotypes in FVC and corrected DLco by comparing the initial and final examination as follows: (1) persistently low, (2) late decreased, (3) improvement, and (4) normal (Fig. 3). As the late decreased and improvement phenotypes are mixed with normal values, we selected the two patterns, which are persistently low and normal, and compared the exposure characteristics between the two phenotypes (Table 3). Interestingly, most proportion of children with persistently low lung function in both FVC and corrected DLco has the initial exposure within the first year of the age with statistically significant difference compared with normal lung function (FVC, 83.3% vs. 37.0%, P = 0.008; corrected DLco, 62.5% vs. 0.0% P = 0.020, respectively). Among the children with exposure to HD during the first year of life, none were in the range of normal corrected DLco. These significances of initial exposure age were also observed in the comparison between the four prognostic phenotypes (persistently low, late decreased, improvement, and normal) in both FVC and corrected DLco (Additional file 1: Table S2). There is a higher proportion of children with a history of fetal exposure to HD who have a persistent decrement in lung function compared with continued normal PFT, although with no statistically significant difference (FVC, 16.7% vs. 3.7%, P = 0.161; corrected DLco, 8.3% vs. 0.0%, P = 0.549, respectively).
Fig. 3.
Prognosis phenotypes in corrected DLco and FVC over time by mean predicted %. Data for the prognosis of phenotypes in the follow-up period in HDLI survivors are shown. Considering the significant diffusion defect to be less than 80% at each follow-up, from the 1st to 5th, the proportion of each type of prognosis of HDLI is evaluated. HDLI children predominantly presented with abnormal lung function phenotypes (persistently low and late decreased) with respect to the corrected DLco (67.4%) and FVC (34.0%). Bars indicate standard errors of the estimated mean (persistently low and late decreased)
Table 3.
Comparison of exposure characteristics based on lung function phenotype in HDLI survivors
| FVC | Corrected DLco | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Persistently low (n = 12) | Normal (n = 27) |
p-value | Persistently low (n = 24) | Normal (n = 4) |
p-value | |
| HD type (%) | ||||||
| PHMG, only use | 50.0 | 51.9 | 0.787 | 50.0 | 25.0 | 0.353 |
| PGH, only use | 0.0 | 3.7 | 0 | 0 | ||
| CMIT/MIT, only use | 0.0 | 3.7 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Mixed | 50.0 | 40.7 | 50.0 | 75.0 | ||
| aHD exposure intensity/weight at exposure (%) | ||||||
| 1st quartile | 16.7 | 33.3 | 0.749 | 29.2 | 25.0 | 0.564 |
| 2nd quartile | 33.3 | 25.9 | 20.8 | 50.0 | ||
| 3rd quartile | 33.3 | 29.6 | 29.2 | 25.0 | ||
| 4th quartile | 16.7 | 11.1 | 20.8 | 0.0 | ||
| aHD exposure intensity during sleep/weight at exposure (%) | ||||||
| 1st quartile | 25.0 | 29.6 | 0.509 | 33.3 | 25.0 | 0.037 |
| 2nd quartile | 25.0 | 33.3 | 12.5 | 75.0 | ||
| 3rd quartile | 25.0 | 29.6 | 33.3 | 0.0 | ||
| 4th quartile | 25.0 | 7.4 | 20.8 | 0.0 | ||
| Age on initial exposure (%) | ||||||
| < 12.0 months | 83.3 | 37.0 | 0.008 | 62.5 | 0.0 | 0.020 |
| ≥ 12.0 months | 16.7 | 63.0 | 37.5 | 100.0 | ||
| Fetal exposure (%) | 16.7 | 3.7 | 0.161 | 8.3 | 0.0 | 0.549 |
| Total duration of use (month) | 13.7 | 15.9 | 0.690 | 15.7 | 22.9 | 0.466 |
| Distance between bed and HD (%) | ||||||
| < 1.0 m | 50.0 | 44.5 | 0.748 | 54.2 | 0.0 | 0.044 |
| ≥ 1.0 m | 50.0 | 55.6 | 45.8 | 100.0 | ||
| Direction dispersed into room (%) | ||||||
| Diagonal | 41.7 | 44.4 | 0.736 | 37.5 | 25.0 | 0.459 |
| Forward | 33.3 | 40.7 | 41.7 | 25.0 | ||
| Unknown | 25.0 | 14.8 | 20.8 | 50.0 | ||
| Use of HD during sleep (%) | 91.7 | 100.0 | 0.129 | 95.8 | 100.0 | 0.678 |
P values for the comparison between persistently low and normal calculated with the Chi-square or Student t-test, as appropriate, in FVC and corrected DLco. aAirborne disinfectant intensity = [bulk level of disinfectant (μg/mL) × disinfectant volume (mL) × disinfectant frequency/day × room ventilation factor]/room volume (m3)/weight at exposure [23, 27]. FVC, forced vital capacity; DLco, diffusing capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide; N, number; HD, humidifier disinfectants; PHMG, polyhexamethyleneguanidine phosphate; PGH, poligoethoxyethyl-guanidinium chloride; CMIT/MIT, chloromethylisothiazol/methylisothiazol
The airborne HD exposure intensity showed no statistical difference between persistently low lung function and normal. However, airborne HD exposure intensity during sleep among the persistently low cases had a high proportion of 3rd and 4th quartile compared with normal cases, showing a statistically significant difference in corrected DLco (FVC, 50.0% vs. 37.0%, P = 0.509; corrected DLco, 54.1% vs. 0.0%, P = 0.037, respectively). Differences in the distance from the humidifier to the sleeping place also showed a statistically significant difference in persistently low corrected DLco. Half of the cases of persistently low corrected DLco were exposure within 1.0 m, whereas all the subjects of the normal corrected DLco were exposed to HD beyond 1.0 m. Neither HD type, total months, nor direction was associated with abnormal lung function during long-term follow-up. The Cox proportional hazards model for examining the association between age on initial exposure and lung function phenotype showed that exposure during the first year of life significantly increased the hazard ratio (HR) for persistently low corrected DLco [HR 1.030 (95% CI 1.001–1.060), P = 0.044] (Additional file 5: Figure S4A), but was not associated with the HR for persistently low FVC (Additional file 5: Figure S4B).
Discussion
Lung function including FVC, FEV1, DLco, and corrected DLco were markedly decreased in HDLI survivors compared with controls in the cross-sectional study. In the longitudinal assessment, FVC was found to be consistently low despite being within the normal range, and the corrected DLco was found to have no normalization over 80% with increasing age, although no apparent difference was seen in final growth between HDLI survivors and controls. Children with exposure within the first year of life have been associated with persistently low lung function, suggesting a critical period related to airborne chemicals. Notably, initial exposure age under 1 year increased the hazard risk of persistent decrement in corrected DLco adjusted for height and weight at DLco performance, HD type, and total months of use. These findings suggest that we may consider prolonged decrement in corrected DLco as a valuable marker of lung involvement in children with a history of HD exposure. Furthermore, persistent abnormalities with corrected DLco are also associated with higher intensity HD exposure during sleep and close distance between the bed and the humidifier. As most subjects were exposed during sleep, the difference in airborne disinfectant exposure intensity during sleep is believed to be significant.
To the best of our knowledge, this analysis is the first to address lung function impairment and the phenotype-associated sensitive window in relation to HD inhalation exposure in children with a combination of case–control and cohort designs. In addition, we confirmed the first longitudinal lung impairment in children by chemical inhalants and may provide guidance on evaluating lung injury caused by chemical inhalation.
Many recent studies have reported that environmental exposure in early-life affects the long-term prognosis of respiratory disease during childhood [28, 29]. Furthermore, identification of the critical exposure window can suggest more effective interventions for lung development during childhood [30–32]. The present study has addressed these concerns using the association between lung function and the use of household chemical disinfectant. This study highlights the need for further evaluation and continued follow-up of pulmonary function in children with chemical inhalation during the critical period, regardless of the duration following the exposure.
The mechanism by which HD exposure affects prolonged decrement in lung function, especially corrected DLco among children who are exposed within the first year of life, remains unknown. Possibilities include that HDs were dissolved in water and then dispersed into the air by the humidifier’s aerosolizer, and the nano-sized particles allowed them to easily reach the distal airways causing lung injury. HDLI with pathologic findings such as bronchiolar destruction and obliteration, centrilobular alveolar damage, and remodeling by inflammatory may support the above-mentioned evidence [10, 11]. Respiratory inhalational toxicants including irritant gases or sensitizers have also been investigated to cause acute inhalation injury by tissue asphyxiation including inhibition of mitochondrial electron transport and oxygen use or direct airway cellular injury [33]. Additionally, in the first 2 years of life, the alveolar volume increases with age and somatic growth [24]. High density and close exposure to HD during sleep within the first year of life causes accelerated lung injury and disruption of alveolar development, resulting in lower corrected DLco. As the bronchioles, alveolar ducts, and alveolus functionally mature at approximately 2 years of age, alterations in these tissues could result in inappropriate distal lung development, resulting in restrictive lung disease. An additional explanation of the association between lung function in children and HD exposure in the first year of life [34] is that infants may spend more time at home and may be at a high risk because they take in more of the contaminant than adults relative to their body size, and have particularly vulnerable physiologies, as the minute ventilation per pound in an infant is significantly greater than that of an adult [35]. Particularly, children breath 50% more air per kg of weight compared to adults, and their habits are conducive to greater exposures [36]. As an infant’s room is in a relatively confined space, and infants cannot change positions by themselves during sleep, this can result in considerable cumulative exposure during sleep and association between corrected DLco and HD exposure intensity during sleep than the usual HD exposure intensity in our study. These results are consistent with those of a previous report on impulse oscillometry abnormality in HD-exposed children [37]. Further investigation is required to identify the pathophysiological mechanisms of this association.
Furthermore, a high proportion of children with a history of fetal exposure to HD showed persistent decrement in lung function, although without statistical significance, due to the small sample size. The placenta plays a role in exchanging foreign molecules between the maternal and fetal circulations, suggesting that HD may cause developmental toxicity in the fetuses [38]. Future studies are required to investigate whether HD chemicals cross the placenta and accumulate in the fetal tissues.
To date, no longitudinal research on DLco in children has investigated the pathophysiology of chemical airborne lung injury. DLco is an outcome of particular interest, as exposure related lung function in asymptomatic children without a chronic respiratory disease because exposure to respiratory irritants is known to cause small airway disease and affect transfer capability [39]. Impairment recovery of corrected DLco in HD-exposed children, and association between exposure characteristics and the corrected DLco outcome in our study may support the above-mentioned evidence. These findings suggest that the corrected DLco seems to be more sensitive for detecting lung damage as one of the alternative biomarkers of children with HDLI and as a long-lasting indicator in lung injury after exposure to HD in children. As approximately 30% of young Korean children were exposed to HD, although without any obvious clinical or radiologic findings, this reflects the importance of corrected DLco in the detection of latent respiratory effects in children [40]. The measurement of DLco in children is under investigation, with no generally available apparatus, and we may be unable to detect potential lung damage in many children. Therefore, in cases of absence of risk factors (including chronic respiratory disease), other than the exposure to HD in early-life, the persistent decrement in corrected DLco in Korean school children may imply an adverse impact of HD exposure on the lung function.
The strengths of the present study are that this is a well-characterized, relatively large HDLI cohort study. The PFT result was also provided by highly skilled leaders using a fixed standard operating procedure in a pediatric pulmonology laboratory. Second, the study participants are purely control subjects, in which there was no exposure to HD compared other studies about exposure to air pollution and other household chemicals. Furthermore, as a lower prevalence of chronic respiratory conditions, including smoking history, was reported in children than in adults, HDLI survivors were considered to be a pure disease group. Therefore, we may suggest adequate data to make conclusions about the HD exposure-lung function relationship.
We are aware that this study has limitations. First, we did not perform spirometry in the event because of too young children and severely affected patients (expired or not performed), and thus we cannot determine whether for some patients there was an even more severe immediate decrease in lung function and subsequent incomplete recovery. This may have resulted in a weaker exposure-response relationship. Second, there could be a risk of recall bias because most characteristics on disinfectant use were obtained from a direct questionnaire given to the study subjects. However, it is fairly reliable, considering that previous studies have already reported HDLI characteristics using this exposure data [15, 23]. Third, we could not explore the effects of exposure from adolescence to young adulthood, and the long-term clinical significance with respect to lung function is still unknown. Considering the lung growth prognosis of children exposed to HD, a longer follow-up is required to investigate whether children with HDLI with an early exposure will catch up in lung growth to peak lung function in adolescence and adulthood or will continue to have a decline in lung function [41].
Conclusions
In conclusion, HD inhalation exposure within the first year of life may constitute a risk to respiratory health not only in terms of HDLI, but also as a long-term impact resulting in decreased lung function in children. Although the disease-specific biomarkers remain unclear, periodic evaluation of the children using PFTs will provide a unique opportunity to follow disease progression and to identify alternative diagnostic markers for children with HDLI.
Supplementary information
Additional file 1: Table S1. Chemical airborne exposure-related lung function. Table S2. Comparison of characteristics and exposure index based on 4 lung function phenotype (FVC (A) and corrected DLco (B)) in HDLI survivors.
Additional file 2: Figure S1. HDLI patients and control enrollment flow diagram.
Additional file 3: Figure S2. Longitudinal assessment of age and height.
Additional file 4: Figure S3. Longitudinal assessment in HDLI vs. control subjects for z-score.
Additional file 5: Figure S4. Cox proportional hazard regression model showing the effect of exposure periods on persistently low corrected DLco.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Financial disclosure
The authors have indicated that they have no financial relationships relevant to this article to disclose.
Abbreviations
- chILD
Childhood interstitial lung disease
- DLco
Diffusing capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide
- FEV1
Forced expiratory volume in 1 s
- FEV1/FVC
The ratio of forced expiratory volume in 1 sec to forced vital capacity
- FVC
Forced vital capacity
- HD
Humidifier disinfectants
- HDLI
Humidifier disinfectant associated lung injury
- PFT
Pulmonary function test
Authors’ contributions
H-JC, SYL, DP, and SJH had full access to all the data in the study and take responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis. H-JC drafted the manuscript. S-HR, JY, and EL provided study materials, laboratory samples, and instrumentation. SJ and S-IY developed and designed the methodology. All authors gave final approval to the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the Korea Ministry of Environment (MOE) as “the Environmental Health Action Program” (2016001360006), and the Environmental Health Center for Hazardous Chemical Exposure funded by Ministry of Environment Republic of Korea (2019). The funding sponsors had no role in the design of the study, in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data, in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of the Asan Medical Center (approval number: 2015–0510).
Written informed consent was obtained from parents or guardians of all participants.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information accompanies this paper at 10.1186/s12890-019-1028-y.
References
- 1.McDonnell G, Russell AD. Antiseptics and disinfectants: activity, action, and resistance. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1999;12(1):147–179. doi: 10.1128/CMR.12.1.147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.de Groot AC, Herxheimer A. Isothiazolinone preservative: cause of a continuing epidemic of cosmetic dermatitis. Lancet. 1989;1(8633):314–316. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(89)91318-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Kim HJ, Lee MS, Hong SB, Huh JW, Do KH, Jang SJ, Lim CM, Chae EJ, Lee H, Jung M, et al. A cluster of lung injury cases associated with home humidifier use: an epidemiological investigation. Thorax. 2014;69(8):703–708. doi: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2013-204132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Yang HJ, Kim HJ, Yu J, Lee E, Jung YH, Kim HY, Seo JH, Kwon GY, Park JH, Gwack J, et al. Inhalation toxicity of humidifier disinfectants as a risk factor of children's interstitial lung disease in Korea: a case-control study. PLoS One. 2013;8(6):e64430. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0064430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Lee E, Seo JH, Kim HY, Yu J, Jhang WK, Park SJ, Kwon JW, Kim BJ, Do KH, Cho YA, et al. Toxic inhalational injury-associated interstitial lung disease in children. J Korean Med Sci. 2013;28(6):915–923. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2013.28.6.915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Kim KW, Ahn K, Yang HJ, Lee S, Park JD, Kim WK, Kim JT, Kim HH, Rha YH, Park YM, et al. Humidifier disinfectant-associated children's interstitial lung disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2014;189(1):48–56. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201306-1088OC. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Spagnolo P., Bush A. Interstitial Lung Disease in Children Younger Than 2 Years. PEDIATRICS. 2016;137(6):e20152725–e20152725. doi: 10.1542/peds.2015-2725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Kitazawa H, Kure S. Interstitial lung disease in childhood: clinical and genetic aspects. Clin Med Insights Circ Respir Pulm Med. 2015;9(Suppl 1):57–68. doi: 10.4137/CCRPM.S23282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Yoon Jisun, Lee So-Yeon, Lee Seung-Hwa, Kim Eun Mi, Jung Sungsu, Cho Hyun-Ju, Lee Eun, Yang Song-I, Hong Soo-Jong. Exposure to Humidifier Disinfectants Increases the Risk for Asthma in Children. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. 2018;198(12):1583–1586. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201805-0840LE. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Hong SB, Kim HJ, Huh JW, Do KH, Jang SJ, Song JS, Choi SJ, Heo Y, Kim YB, Lim CM, et al. A cluster of lung injury associated with home humidifier use: clinical, radiological and pathological description of a new syndrome. Thorax. 2014;69(8):694–702. doi: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2013-204135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Kim WY, Park S, Kim HJ, Chae EJ, Do KH, Huh JW, Lim CM, Koh Y, Hong SB. Lung function in patients with lung injury due to household chemical inhalation: Post hoc analysis of a prospective nationwide cohort. Respirology (Carlton, Vic) 2017;22(2):345–351. doi: 10.1111/resp.12918. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Rovira E, Cuadras A, Aguilar X, Esteban L, Borras-Santos A, Zock JP, Sunyer J. Asthma, respiratory symptoms and lung function in children living near a petrochemical site. Environ Res. 2014;133:156–163. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2014.05.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Zock JP, Plana E, Jarvis D, Anto JM, Kromhout H, Kennedy SM, Kunzli N, Villani S, Olivieri M, Toren K, et al. The use of household cleaning sprays and adult asthma: an international longitudinal study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2007;176(8):735–741. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200612-1793OC. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Macintyre N, Crapo RO, Viegi G, Johnson DC, van der Grinten CP, Brusasco V, Burgos F, Casaburi R, Coates A, Enright P, et al. Standardisation of the single-breath determination of carbon monoxide uptake in the lung. Eur Respir J. 2005;26(4):720–735. doi: 10.1183/09031936.05.00034905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Paek D, Koh Y, Park DU, Cheong HK, Do KH, Lim CM, Hong SJ, Kim YH, Leem JH, Chung KH, et al. Nationwide Study of Humidifier Disinfectant Lung Injury in South Korea, 1994-2011. Incidence and Dose-Response Relationships. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2015;12(12):1813–1821. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.201504-221OC. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Miller MR, Hankinson J, Brusasco V, Burgos F, Casaburi R, Coates A, Crapo R, Enright P, van der Grinten CP, Gustafsson P, et al. Standardisation of spirometry. Eur Respir J. 2005;26(2):319–338. doi: 10.1183/09031936.05.00034805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Polgar G. Pulmonary function testing for pediatric chest diseases. Pediatr Ann. 1977;6(8):526–539. doi: 10.3928/0090-4481-19770801-08. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Gauderman WJ, Urman R, Avol E, Berhane K, McConnell R, Rappaport E, Chang R, Lurmann F, Gilliland F. Association of improved air quality with lung development in children. N Engl J Med. 2015;372(10):905–913. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1414123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Vaz Fragoso CA, McAvay G, Gill TM, Concato J, Quanjer PH, Van Ness PH. Ethnic differences in respiratory impairment. Thorax. 2014;69(1):55–62. doi: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2013-203631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Thomas H, Risma KA, Graham TB, Brody AS, Deutsch GH, Young LR, Joseph PM. A kindred of children with interstitial lung disease. Chest. 2007;132(1):221–230. doi: 10.1378/chest.06-2476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Buchvald F, Petersen BL, Damgaard K, Deterding R, Langston C, Fan LL, Deutsch GH, Dishop MK, Kristensen LA, Nielsen KG. Frequency, treatment, and functional outcome in children with hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2011;46(11):1098–1107. doi: 10.1002/ppul.21479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Zorzi AP, Yang CL, Dell S, Nathan PC. Bleomycin-associated lung toxicity in childhood Cancer survivors. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2015;37(8):e447–e452. doi: 10.1097/MPH.0000000000000424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Park DU, Friesen MC, Roh HS, Choi YY, Ahn JJ, Lim HK, Kim SK, Koh DH, Jung HJ, Lee JH, et al. Estimating retrospective exposure of household humidifier disinfectants. Indoor Air. 2015;25(6):631–640. doi: 10.1111/ina.12180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Balinotti JE, Tiller CJ, Llapur CJ, Jones MH, Kimmel RN, Coates CE, Katz BP, Nguyen JT, Tepper RS. Growth of the lung parenchyma early in life. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2009;179(2):134–137. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200808-1224OC. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Stanojevic Sanja, Graham Brian L., Cooper Brendan G., Thompson Bruce R., Carter Kim W., Francis Richard W., Hall Graham L. Official ERS technical standards: Global Lung Function Initiative reference values for the carbon monoxide transfer factor for Caucasians. European Respiratory Journal. 2017;50(3):1700010. doi: 10.1183/13993003.00010-2017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Quanjer PH, Stanojevic S, Cole TJ, Baur X, Hall GL, Culver BH, Enright PL, Hankinson JL, Ip MS, Zheng J, et al. Multi-ethnic reference values for spirometry for the 3-95-yr age range: the global lung function 2012 equations. Eur Respir J. 2012;40(6):1324–1343. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00080312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Williams PR, Patterson J, Briggs DW. VCCEP pilot: progress on evaluating children's risks and data needs. Risk Anal. 2006;26(3):781–801. doi: 10.1111/j.1539-6924.2006.00766.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Norback D, Lu C, Zhang Y, Li B, Zhao Z, Huang C, Zhang X, Qian H, Sun Y, Sundell J, et al. Onset and remission of childhood wheeze and rhinitis across China - associations with early life indoor and outdoor air pollution. Environ Int. 2019;123:61–69. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2018.11.033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Yang SI, Lee SY, Kim HB, Kim HC, Leem JH, Yang HJ, Kwon H, Seo JH, Cho HJ, Yoon J, et al. Prenatal particulate matter affects new asthma via airway hyperresponsiveness in schoolchildren. Allergy. 2019;74(4):675–684. doi: 10.1111/all.13649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Deng Q, Lu C, Ou C, Chen L, Yuan H. Preconceptional, prenatal and postnatal exposure to outdoor and indoor environmental factors on allergic diseases/symptoms in preschool children. Chemosphere. 2016;152:459–467. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.03.032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Deng Q, Lu C, Li Y, Sundell J, Dan N. Exposure to outdoor air pollution during trimesters of pregnancy and childhood asthma, allergic rhinitis, and eczema. Environ Res. 2016;150:119–127. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2016.05.050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Deng Q, Lu C, Ou C, Liu W. Effects of early life exposure to outdoor air pollution and indoor renovation on childhood asthma in China. Build Environ. 2015;93:84–91. doi: 10.1016/j.buildenv.2015.01.019. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Miller K, Chang A. Acute inhalation injury. Emerg Med Clin North Am. 2003;21(2):533–557. doi: 10.1016/S0733-8627(03)00011-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Litonjua AA, Gold DR. Early-life exposures and later lung function. Add pollutants to the mix. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2016;193(2):110–111. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201510-1963ED. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Landrigan PJ, Goldman LR. Children's vulnerability to toxic chemicals: a challenge and opportunity to strengthen health and environmental policy. Health Aff (Millwood) 2011;30(5):842–850. doi: 10.1377/hlthaff.2011.0151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Fuentes-Leonarte V, Tenias JM, Ballester F. Environmental factors affecting children's respiratory health in the first years of life: a review of the scientific literature. Eur J Pediatr. 2008;167(10):1103–1109. doi: 10.1007/s00431-008-0761-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Cho HJ, Park DU, Yoon J, Lee E, Yang SI, Kim YH, Lee SY, Hong SJ. Effects of a mixture of chloromethylisothiazolinone and methylisothiazolinone on peripheral airway dysfunction in children. PLoS One. 2017;12(4):e0176083. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0176083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Prouillac C, Lecoeur S. The role of the placenta in fetal exposure to xenobiotics: importance of membrane transporters and human models for transfer studies. Drug Metab Dispos. 2010;38(10):1623–1635. doi: 10.1124/dmd.110.033571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Ghanei M, Adibi I, Farhat F, Aslani J. Late respiratory effects of sulfur mustard: how is the early symptoms severity involved? Chron Respir Dis. 2008;5(2):95–100. doi: 10.1177/1479972307087191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Yoon J, Cho HJ, Lee E, Choi YJ, Kim YH, Lee JL, Lee YJ, Hong SJ. Rate of humidifier and humidifier disinfectant usage in Korean children: a nationwide epidemiologic study. Environ Res. 2017;155:60–63. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2017.01.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.McGeachie MJ, Yates KP, Zhou X, Guo F, Sternberg AL, Van Natta ML, Wise RA, Szefler SJ, Sharma S, Kho AT, et al. Patterns of growth and decline in lung function in persistent childhood asthma. N Engl J Med. 2016;374(19):1842–1852. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1513737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Additional file 1: Table S1. Chemical airborne exposure-related lung function. Table S2. Comparison of characteristics and exposure index based on 4 lung function phenotype (FVC (A) and corrected DLco (B)) in HDLI survivors.
Additional file 2: Figure S1. HDLI patients and control enrollment flow diagram.
Additional file 3: Figure S2. Longitudinal assessment of age and height.
Additional file 4: Figure S3. Longitudinal assessment in HDLI vs. control subjects for z-score.
Additional file 5: Figure S4. Cox proportional hazard regression model showing the effect of exposure periods on persistently low corrected DLco.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.