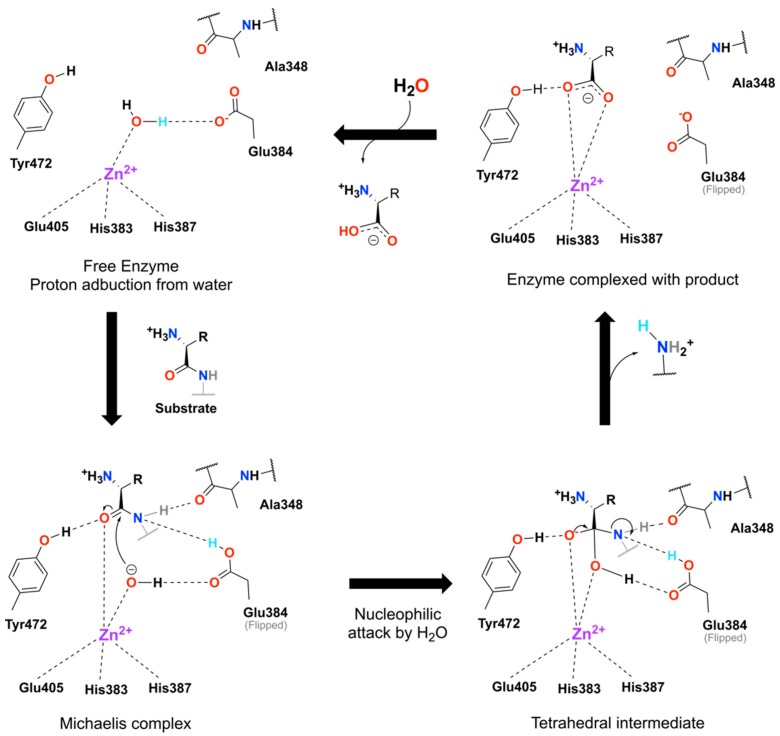
Figure 1.
Aminopeptidase M (AMP) proposed catalytic mechanism. Starting from the free enzyme complexed with the structural water towards the activated state by a proton abduction from the water by the Glu384. Upon substrate binding the hydroxyl group nucleophilic attacks the carbonyl’s carbon in the Michaelis complex leading to the formation of the tetrahedral intermediate, which then reassembles itself expelling one aminated product. The cycle closes with the expulsion of the second product from the active site allowing the entry of a new water molecule. The ionized proton from the water is highlighted in cyan along the cycle. Mechanism was initially proposed by [6,7]. Dashed lines represent interactions and are for illustration purposes only, in the sense that angles and distances are not proportionally realists.