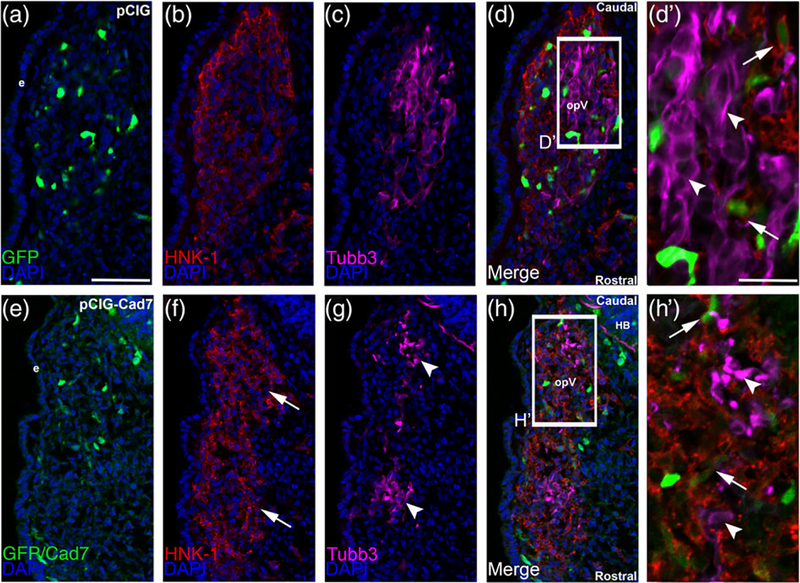
FIGURE 8.
Overexpression of Cadherin-7 in migratory cranial neural crest cells alters the distribution of neural crest cells and placodal neurons within the forming trigeminal ganglion. Representative transverse sections taken at the axial level of the forming ophthalmic lobe of the trigeminal ganglion after electroporation of the pCIG control vector (pCIG, a–d′) or the pCIG-Cadherin-7 vector (pCIG-Cad7, e–h′) into premigratory neural crest cells at the 3ss followed by immunohistochemistry for HNK-1 (red) and Tubb3 (purple) at HH15. The pCIG vector contains an IRES-GFP cassette to label electroporated cells. (d′, h′) Higher magnification images of the boxed regions in (d, h). (a–d′) pCIG control vector (a)-containing neural crest cells (b) coalesce with placodal neurons (c, d). At higher magnification (d′), HNK-1-positive neural crest cells (arrows) form corridors around Tubb3-positive placodal neurons (arrowheads), many of which are elaborating neurites indicative of neuronal maturation. On the other hand, neural crest cells with elevated levels of Cadherin-7 protein (e) migrate to the ganglionic anlage (f, arrows) but likely localize there incorrectly given the inappropriate positioning of placodal neurons (g, arrowheads). At higher magnification (h′), neural crest cells are noted around the placodal neurons (arrows), but placodal neuron morphology is abnormal, with neurons appearing round and/or misshapen (arrowheads). Rostral and caudal orientation, the hindbrain (HB), and the ophthalmic lobe of the trigeminal (opV) are indicated in (d) and (h). DAPI (blue) labels cell nuclei. e = ectoderm. Scale bar in (a) is 50 μm and applicable to (b–h), while scale bar in (d′) is 20 μm and applicable to (h′)