Abstract
BACKGROUND
Proteinuria is considered an unfavorable clinical condition that accelerates renal and cardiovascular disease. However, it is not clear whether all forms of proteinuria are damaging. Mutations in CUBN cause Imerslund-Gräsbeck syndrome (IGS), which is characterized by intestinal malabsorption of vitamin B12 and in some cases proteinuria. CUBN encodes for cubilin, an intestinal and proximal tubular uptake receptor containing 27 CUB domains for ligand binding.
METHODS
We used next-generation sequencing for renal disease genes to genotype cohorts of patients with suspected hereditary renal disease and chronic proteinuria. CUBN variants were analyzed using bioinformatics, structural modeling, and epidemiological methods.
RESULTS
We identified 39 patients, in whom biallelic pathogenic variants in the CUBN gene were associated with chronic isolated proteinuria and early childhood onset. Since the proteinuria in these patients had a high proportion of albuminuria, glomerular diseases such as steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome or Alport syndrome were often the primary clinical diagnosis, motivating renal biopsies and the use of proteinuria-lowering treatments. However, renal function was normal in all cases. By contrast, we did not found any biallelic CUBN variants in proteinuric patients with reduced renal function or focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Unlike the more N-terminal IGS mutations, 37 of the 41 proteinuria-associated CUBN variants led to modifications or truncations after the vitamin B12–binding domain. Finally, we show that 4 C-terminal CUBN variants are associated with albuminuria and slightly increased GFR in meta-analyses of large population-based cohorts.
CONCLUSION
Collectively, our data suggest an important role for the C-terminal half of cubilin in renal albumin reabsorption. Albuminuria due to reduced cubilin function could be an unexpectedly common benign condition in humans that may not require any proteinuria-lowering treatment or renal biopsy.
FUNDING
ATIP-Avenir program, Fondation Bettencourt-Schueller (Liliane Bettencourt Chair of Developmental Biology), Agence Nationale de la Recherche (ANR) Investissements d’avenir program (ANR-10-IAHU-01) and NEPHROFLY (ANR-14-ACHN-0013, to MS), Steno Collaborative Grant 2018 (NNF18OC0052457, to TSA and MS), Heisenberg Professorship of the German Research Foundation (KO 3598/5-1, to AK), Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) Collaborative Research Centre (SFB) KIDGEM 1140 (project 246781735, to CB), and Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMB) (01GM1515C, to CB).
Keywords: Genetics, Nephrology
Keywords: Chronic kidney disease, Genetic diseases
Introduction
The loss of proteins into the urine (or proteinuria) is an important risk factor for renal and cardiovascular disease. In particular, albuminuria is associated with an increased risk for chronic kidney disease (CKD) and diabetic kidney disease (DKD), end-stage renal disease (ESRD), and mortality (1–3). Although the reasons are not entirely clear, an overload of the renal tubules with proteins and albumin-bound lipids has been proposed to be damaging for tubular epithelial cells (4, 5). Antiproteinuric therapy, for example through angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) or angiotensin II receptor (AT1) inhibition, is therefore an important renoprotective therapy (6).
The main cause of proteinuria is the dysfunction of the glomerular filtration barrier, which leads to symptoms like edema related to the massive albumin loss into the urine. Genetic forms of glomerular proteinuria are steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome (SRNS) or Alport syndrome (AS). Another form of proteinuria is caused by defects in proximal tubular protein reabsorption. Tubular proteinuria has a smaller range than glomerular proteinuria, because the former only affects proteins that are filtered by the glomerulus. Typically, these are proteins such as β2-microglobulin, which is smaller in size than albumin (7). Albumin itself is filtered to a limited extent and usually accounts for less than half of the urinary protein in tubular proteinuria (8). One example is Dent’s disease, in which mutations in CLCN5 and OCRL1 lead to defective trafficking of the uptake receptor complex (9), consisting of megalin (LRP2), cubilin (CUBN), and amnionless (AMN) (10, 11). Whereas mutations in LRP2 cause Donnai-Barrow syndrome, a multisystem developmental disorder (12), CUBN and AMN mutations lead to Imerslund-Gräsbeck syndrome (IGS), which is characterized by intestinal vitamin B12 malabsorption and, in about half the cases, proteinuria (13). The phenotypes reflect the expression patterns of all 3 proteins: megalin is expressed more broadly, whereas the expression of cubilin and amnionless is mostly limited to the small intestines and kidneys. Within the kidney, recent single RNA-Seq studies of mouse and human kidney have indicated exclusive expression in the proximal tubular compartment for all 3 proteins (14–16).
With regard to the protein structures, megalin and amnionless are type I transmembrane proteins, whereas cubilin is a peripheral protein that requires amnionless for anchoring to the membrane. Anchoring occurs via β-helix–β-helix association between amnionless and the N-terminal hydrophobic stretches of 3 cubilin subunits (17). Each cubilin protomer has 8 EGF domains and 27 CUB (complement C1r/C1s, UEGF [EGF-related sea urchin protein] and bone morphogenic protein 1) domains, some of which are involved in Ca2+-dependent ligand binding (17, 18). Most IGS mutations of CUBN are in the N-terminal half of cubilin, either affecting the interactions with amnionless or the vitamin B12/intrinsic factor–binding (IF-binding) CUB domains 5–8 (CUB5–8) (17). Interestingly, 1 individual with a homozygous deletion of exon 53 harboring CUB20 was shown to have proteinuria without vitamin B12 malabsorption (19). Several CUBN variants have also shown strong associations with albuminuria in recent GWAS (20–22), which is in agreement with the albuminuria observed in cubilin-KO mice (10). Altogether, these findings suggest that cubilin could be necessary for preventing urinary albumin loss in humans. However, it is unclear whether the albuminuria due to cubilin dysfunction impairs renal function.
Here, we identified a large number of patients with isolated proteinuria associated with biallelic variants in the CUBN gene in 3 different cohorts of individuals with suspected genetic renal disease. Almost all variants were located after the vitamin B12/IF–binding domain, suggesting that more C-terminal CUB domains are crucial for renal protein reabsorption. Importantly, we show that cubilin deficiency led to proteinuria with a high proportion of urinary albumin, without impairing renal filtration function. In addition, we found that 4 C-terminal missense variants with strong albuminuria associations in GWAS were related to slightly higher estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) levels in a large meta-analysis of individuals from the general population.
Results
Biallelic CUBN variants cause isolated proteinuria with normal renal function.
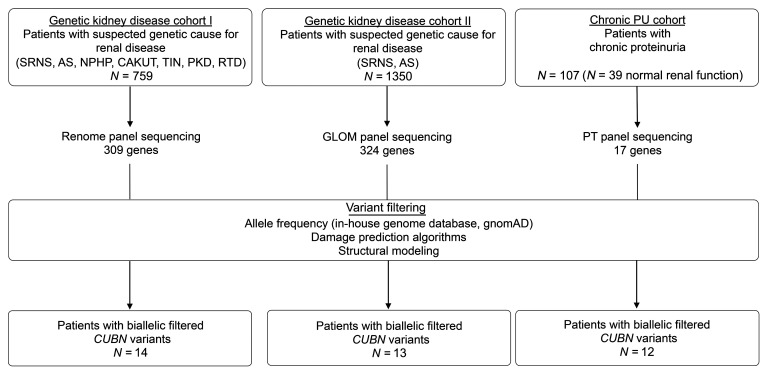
We performed a retrospective analysis of next-generation sequencing (NGS) data obtained using a panel containing 309 renal disease genes (Renome panel) in a French cohort of 759 patients. All patients had been referred to our reference center for genetic testing because of suspected genetic kidney disease (genetic kidney disease cohort I; Figure 1 and Supplemental materials; supplemental material available online with this article; https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI129937DS1).
Figure 1. Flow chart for cohort genotyping.
The 3 different cohorts consisted of individuals with suspected genetic diseases (see Methods for more details). Altogether, 39 individuals with biallelic filtered CUBN variants were identified. In the chronic PU cohort, 11 individuals with biallelic filtered CUBN variants were identified, plus 1 additional individual carrying 1 biallelic filtered CUBN variant and the GWAS variant p.N2157D (see Supplemental Table 7). HGMD, Human Gene Mutation Database; PT, proximal tubule.
We grouped the patients into nonproteinuric and proteinuric groups, with the latter consisting of suspected SRNS or AS (Supplemental Figure 1). Although synonymous and nonsynonymous missense variants were equally distributed between the 2 groups, all protein-truncating variants (PTVs), including splicing, frameshift, and stop-gain variants, were strongly enriched in the proteinuric group (Supplemental Figure 1, A and B), confirming the association of CUBN variants with proteinuria.
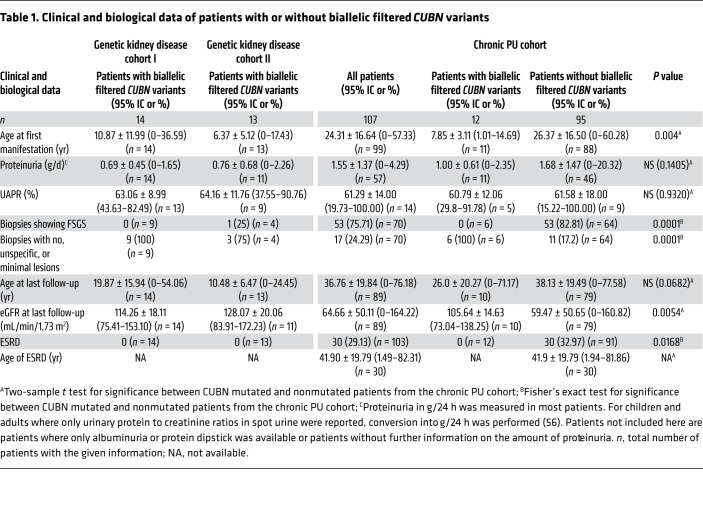
Given the recessive nature of IGS, we asked whether there were any patients with biallelic CUBN variants who passed established filtering criteria for Mendelian disease in the proteinuric group (see Methods for the filtering criteria). We identified 14 patients from 11 families of European or African descent who had biallelic likely pathogenic variants in the CUBN gene (Table 1 and Supplemental Tables 1 and 2). By contrast, the nonproteinuric group had only 2 individuals with biallelic CUBN variants, and a control group matched for ethnicity did not include any such cases (Supplemental Figure 1C). Interestingly, all 14 patients with biallelic CUBN variants showed a very similar phenotype. Although no signs of vitamin B12 deficiency such as megaloblastic anemia could be detected, the patients shared the characteristic of chronic proteinuria ranging from 0.5 to 3 g/24 h. The average age of onset of discovery of the proteinuria was 10.9 years (Table 1 and Supplemental Table 1). Although not measured in all patients, the proportion of albumin in the urinary protein was higher than 50%, and urinary α1- or β2-microglobulin was mostly low or absent (Table 1, Supplemental Table 1, and refs. 7, 8), which is in contrast to other forms of tubular proteinuria, including megalin deficiency (12).
Table 1. Clinical and biological data of patients with or without biallelic filtered CUBN variants.
In all cases, renal function was normal at an average age of 17 years as measured by serum creatinine levels and eGFR (Table 1 and Supplemental Table 1). For this reason, obtaining follow-up clinical information for these patients was sometimes difficult. Renal biopsies had been performed in 9 patients, and for all of them, the lesions were minimal, unspecific, or not present (Table 1 and Supplemental Tables 1 and 2). For 7 patients, treatment with ACE inhibitors had already been started but without any proteinuria-lowering effects. These findings were confirmed in an independent German and Austrian cohort of 1350 individuals with suspected SRNS or AS (Genetic kidney disease cohort II), in which we identified 13 additional individuals from 12 families with biallelic CUBN variants (Table 1 and Supplemental Tables 1, 2, and 3). Also, the chronic subnephrotic proteinuria, featuring a high proportion of urinary albumin, was combined with normal renal function in all patients (Table 1 and Supplemental Table 1).
Proteinuria-associated CUBN variants localize to C-terminal CUB domains.
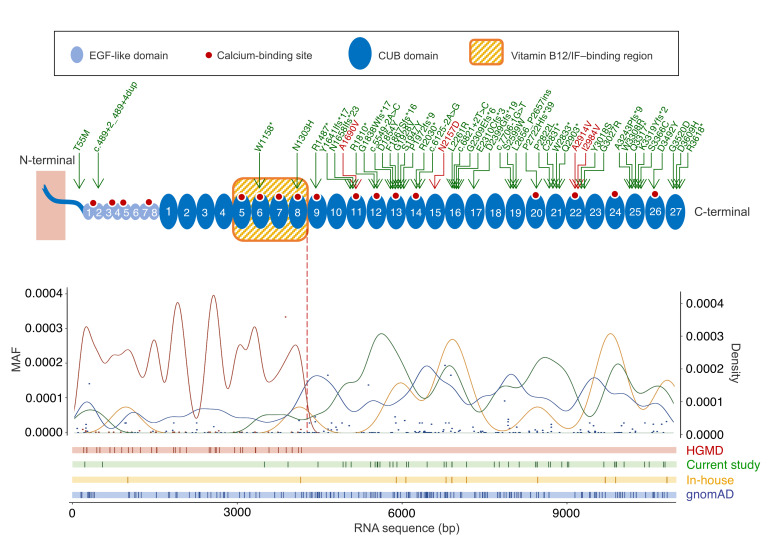
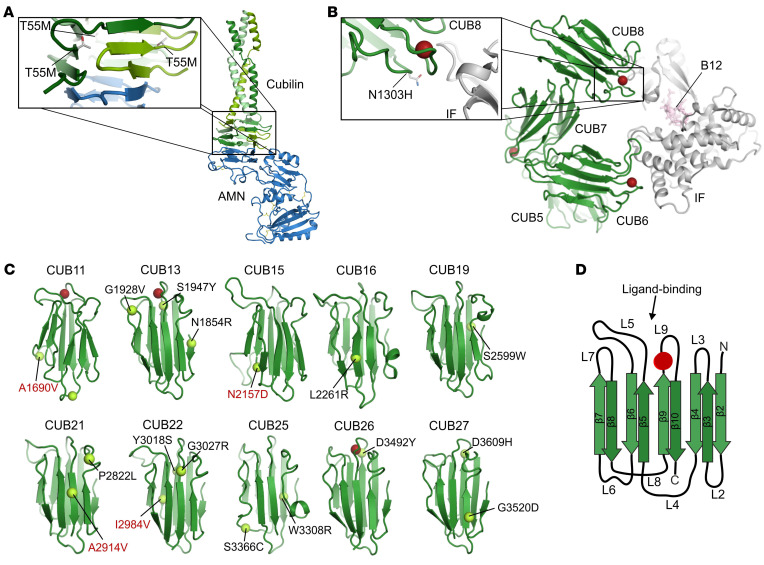
Altogether, we found 30 novel variants in these 2 studies (Figure 2 and Supplemental Figure 2) that were not only associated with proteinuria as an established cubilin phenotype but also passed rather stringent filtering criteria (see Methods). Although 3 variants (c.6125-2A>G, p.R2030*, and p.Y3018S) were found in both cohorts, all variants were found with frequencies below 0.1% in our in-house genome database (mostly enriched for European or African ancestries) or in public reference genome databases (e.g., Genome Aggregation Database [gnomAD]; ref. 23) (Supplemental Table 4). In the crystal structure of cubilin (18) or in silico models of individual CUB domains, all missense variants were predicted to have different detrimental effects on cubilin function, ranging from effects on amnionless binding (p.T55M) to stability and ligand binding of CUB domains (all other variants) (Figure 3, A–D, and Supplemental Table 5). Most variants affected residues or led to truncations after CUB8 (aa 1487–3618), which is in contrast to the previously described IGS mutations that are all before CUB8 (aa 66–1390) (ref. 24, Figure 2, and Supplemental Figure 2). The only 2 variants before CUB8, p.T55M and p.W1158*, were found to be in trans with variants after CUB8, consistent with the association of C-terminal CUBN variants with isolated proteinuria. As most PTVs present in the general population, such as those identified in our in-house genome database and gnomAD, lead to truncations after CUB8 (Figure 2), it may even be concluded that the loss of C-terminal CUB domains is more tolerated than the loss of those related to vitamin B12 absorption.
Figure 2. Frequency, density, and position of CUBN variants along the cubilin protein.
Cubilin protein structure summarized with the 8 EGF-like (light blue) and 27 CUB domains (darker blue). The red dots correspond to the theoretical Ca2+-binding sites, and the arrows on top indicate the variants found in the 3 cohorts of this study (the green arrows represent the filtered CUBN variants, and the red arrows indicate the 4 GWAS missense variants A1690V, N2157D, A2914V, and I2984V). Gaussian kernel density curves (with a 0.2 width parameter) as well as the position of HGMD variants (red), the variants from this study (green), and PTVs from the in-house (yellow) and gnomAD (blue) databases are shown as curves and vertical lines, respectively. The minor allele frequencies (MAFs) of the HGMD and gnomAD variants are shown as red and blue dots, respectively.
Figure 3. Structural modeling of CUBN missense variants.
(A) Location of the cubilin T55M missense variant in RCSB entry 6GJE. The variant is located in the hydrophobic core of the cubilin β-helix that interacts with amnionless. (B) Location of the cubilin N1303H missense variant in RCSB entry 3KQ4. The variant is located in CUB domain 8, close to the interface with IF/B12. Red spheres represent Ca2+ ions binding to the CUB domains. (C) Location of the cubilin missense plus the 4 GWAS variants (in red) in in silico structural models of CUB domains 11–27. Red spheres represent Ca2+ ions predicted to bind CUB domains 11, 13, and 26. The variants S1947Y and D3492Y are notably close to these Ca2+-binding motifs. (D) Example of 1 CUB domain with β-sheets (β2–10) and loops (L2–9).
Biallelic CUBN variants are enriched in patients with normal renal function in a chronic proteinuria replication cohort.
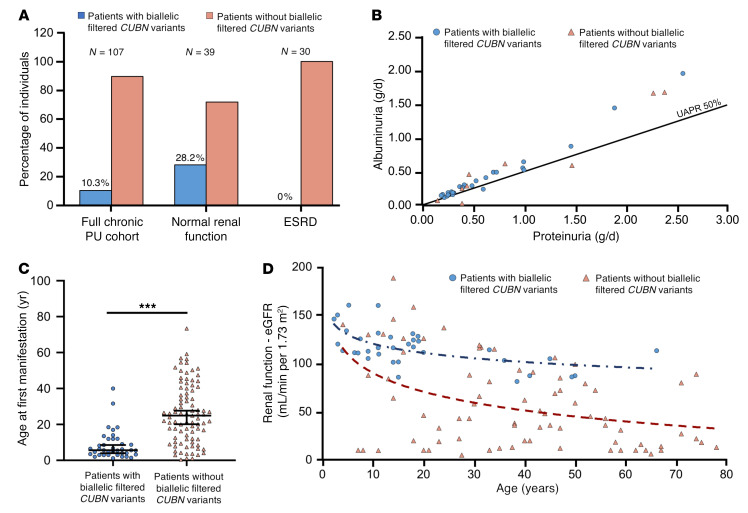
To investigate whether CUBN variants that lead to proteinuria are always associated with normal renal function, we next assembled an additional cohort of 107 patients with chronic subnephrotic proteinuria (chronic PU cohort; see the Supplemental material for details). Similar to the above-described patients, all patients had been referred to our reference center because of a suspected diagnosis SRNS or AS. However, prior efforts using Sanger sequencing or smaller NGS panels than the Renome panel had failed to identify the molecular cause. In this study population, 39 individuals had normal renal function (serum creatinine <110 μmol/L in men and 90 μmol/L in women or an eGFR > 60 ml/min with a minimum of 85 ml/min at the last follow-up in this series), whereas 30 patients had ESRD (<10 mL/min GFR, after renal transplantation or on hemodialysis) (Table 1, Supplemental Table 1, and Figure 4A). We performed sequencing with a smaller custom-made NGS panel enriched for genes important for proximal tubule function that included for the first time in these patients the gene CUBN. The sequencing revealed that 10.3% of the patients in this cohort had homozygous or 2 heterozygous filtered variants in CUBN, which translates into a mutation rate of 28.2% in individuals with chronic proteinuria and normal renal function and 0% in patients with chronic proteinuria and reduced renal function (Table 1, Supplemental Table 1, and Figure 4A).
Figure 4. Clinical and biological profiles of patients carrying biallelic filtered CUBN variants.
(A) Proportions of carriers of biallelic filtered CUBN variants in the chronic PU cohort (n = 107), when considering only patients with normal renal function (eGFR >60 mL/min per 1.73 m2, n = 39) or only patients with ESRD (eGFR <15 mL/min per 1.73 m2, n = 30). (B–D) Patients with biallelic filtered CUBN variants from the 3 cohorts (genetic kidney disease cohorts I and II, chronic PU cohort) were merged into the group of patients with biallelic filtered CUBN variants. (B) The UAPR is plotted for patients with (n = 27) and without (n = 9) biallelic filtered CUBN variants. As a general rule, glomerular proteinuria is characterized by a UAPR above 50%, whereas tubular proteinuria was below 50% (7, 43). (C) Age of first manifestation of proteinuria for patients with (n = 38) and without (n = 88) biallelic filtered CUBN variants. Data represent mean values ± 95% CIs. ***P < 0.0001, by t test. (D) Renal function of patients with biallelic filtered CUBN variants (n = 35) was found to be declining according to normal aging, whereas in patients without biallelic filtered CUBN variants (n = 79), the decline was more rapid. Renal function (eGFR) was calculated using the Schwartz formula for children and the CKD-EPI formula for adults. The blue and red dashed lines represent the logarithmic trend curves for both groups.
The 12 patients from this cohort had a phenotype very similar to that of the above-described patients, including the age of onset, the type and range of proteinuria, the lack of severe lesions in renal biopsies, and the lack of proteinuria-lowering effects with ACE inhibitors (Table 1, Supplemental Table 1, and Figure 4, B and C). Most important, renal function was also normal, even for the oldest patient, aged 66 years (Table 1 and Supplemental Table 1). Figure 4D shows a normal age-dependent eGFR decline for the CUBN+ patients, whereas the CUBN– patients all showed a more rapid decline. Of note, we also identified 2 patients with hemizygous CLCN5 and OCRL1 variants, respectively, which are responsible for Dent’s disease types 1 and 2 (Supplemental Table 6). However, in these patients, serum creatinine levels were elevated, suggesting a fundamental difference between Dent’s disease and cubilin deficiency. Except for 1 single heterozygous variant localized close to the vitamin B12/IF–binding region (p.N1303H; Figure 3B), all 14 likely functional CUBN variants from this cohort were in the C-terminal CUB11–27 (aa 1928–3618; Figure 2). Also, structural models showed that all the variants could have effects on the folding and function of the CUB domains (Figure 3C and Supplemental Table 5). Altogether, these data confirm that biallelic C-terminal CUBN variants are associated with chronic proteinuria and normal renal function.
Four C-terminal missense variants are associated with albuminuria and an increased GFR in population-based studies.
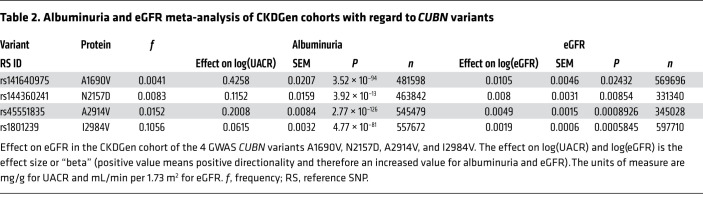
For a more general evaluation of the importance of CUBN variants in kidney function, we turned to large population studies. We focused on 4 C-terminal variants (p.A1690V, p.N2157D, p.A2914V, and p.I2984V) that previously had shown strong associations with albuminuria in GWAS (20–22, 25, 26). The frequencies of these GWAS variants were higher than the 0.1% threshold, which is why they were not included in the initial analysis [in-house genome database: f(A1690V) = 0.00109, f(N2157D) = 0.00667, f(A2914V) = 0.00945, f(I2984V) = 0.0932; gnomAD: f(A1690V) = 0.00173, f(N2157D) = 0.00565, f(A2914V) = 0.0122, f(I2984V) = 0.0875; Supplemental Table 3]. However, one of them (p.N2157D) was identified in the chronic PU cohort in trans, with a low-frequency variant passing our filtering criteria (p.S1947Y) in a child with chronic proteinuria and normal renal function (Supplemental Table 7). As homozygous p.S1947Y has previously been shown to cause proteinuria in a child of similar age (27), p.N2157D seems to be a variant affecting cubilin function. Furthermore, according to the structural modeling, all 4 GWAS variants have the potential to disturb CUB domain stability or ligand binding (Figure 3C and Supplemental Table 5).
To test whether the 4 GWAS variants affect eGFR, we performed a large meta-analysis of the CKDGen Consortium’s population-based cohorts consisting of 331,340 to 597,710 individuals (28). In all 4 cases, we found, in addition to the association with albuminuria, a modest but significant association with a higher eGFR for the minor versus the major allele [P (A1690V) = 0.02432; P (N2157D) = 0.00854; P (A2914V) = 0.0008926; P (I2984V) = 0.0005845; Table 2]. This was also confirmed in a smaller, independent cohort consisting of 13,550 individuals with and without type 2 diabetes (Supplemental Tables 8 and 9). Although p.N2157D was only rarely found in this cohort, both eGFR and albuminuria were significantly increased for the other 3 variants (Supplemental Table 9). Although we tested all associations under an additive model, for the most common variant, p.I2984V, the recessive model could also be performed, confirming that homozygotes indeed had the strongest association with albuminuria (Supplemental Tables 10–12). When stratified for diabetes status, we found that eGFR was significantly associated with A2914V only in persons with diabetes (effect 0.045, P = 0.04) but not in those without diabetes (effect 0.009, P = 0.34), whereas A1690V was significantly associated with eGFR only among those without diabetes (effect 0.037, P = 0.01) but not among those with diabetes [(effect 0.017, P = 0.46); Supplemental Table 9]. Together, these data strongly indicate the benign nature of the albuminuria associated with C-terminal CUBN variants.
Table 2. Albuminuria and eGFR meta-analysis of CKDGen cohorts with regard to CUBN variants.
Discussion
Altogether, the combined analysis of the 3 different cohorts with suspected glomerular disease identified 39 patients with isolated proteinuria and normal renal function due to biallelic filtered CUBN variants. However, despite the early onset, the proteinuria did not seem to be associated with an unfavorable prognosis for kidney disease in our patients. We further show that the high percentage of urinary albumin in these patients was often misinterpreted as glomerular injury in the clinical setting, justifying renal biopsy and ACE or AT1 inhibition as a proteinuria-lowering treatment. Apart from establishing a diagnosis in individuals with isolated subnephrotic proteinuria, the detection of CUBN variants may therefore avoid the use of inefficient therapies aimed at reducing glomerular proteinuria.
Assuming that cubilin mostly functions in the proximal tubules (14–16), the proteinuria is explained by the reduced protein reabsorption on the luminal surface of proximal tubule cells. The reabsorption of albumin was particularly affected, supporting the findings from mouse studies showing that cubilin could be the main albumin receptor in the proximal tubules (10). By contrast, megalin deficiency as seen in Donnai-Barrow syndrome typically leads to lower urinary albumin–to–protein ratios (UAPRs) (7, 8, 12, 29). Moreover, renal function has been reported to be reduced in several families (29–31), which is typically also the case in Dent’s disease, in which both megalin and cubilin are reduced (32). Accordingly, LRP2 variants have been found to be associated with a reduced GFR but not albuminuria (33). Altogether, these findings indicate fundamental differences in the contribution of megalin and cubilin to renal health.
Another unexpected finding is the clear genotype-phenotype correlation associated with CUBN variants (11, 34). Whereas all the IGS mutations can exclusively be found before or within the vitamin B12/IF–binding region (CUB5-8), proteinuria without vitamin B12 absorption was caused by variants located after this region. In contrast to previous in vitro studies (35), this means that the renal ligands, most notably albumin, should bind to more C-terminal CUB domains. In particular, CUB13 and CUB26, which possess proteinuria-causing variants in or close to Ca2+-binding motifs (p.S1947Y and p.D3492Y, respectively), are strong candidate domains for albumin binding. Although this has not yet been studied systematically, it seems that missense variants that only affect vitamin B12/IF binding, such as the Finnish variant p.P1297L, are not associated with proteinuria (36). The reverse conclusion is therefore that patients with IGS who have proteinuria should have mutations that either affect general expression or the interaction with amnionless or lead to cubilin truncation. According to the literature, such patients do not seem to present with renal insufficiency (13, 37–39), which is in agreement with the isolated proteinuria cases described here. Functional studies have also shown that vitamin B12 uptake is maintained when the receptor is truncated after CUB8 (40), consistent with the presence of a putative intestinal transcript truncated directly after CUB8 in the Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx) database (41). Combined with our finding that premature truncation of cubilin is more likely to happen after CUB8 in the normal population, it can thus be concluded that in humans, vitamin B12 malabsorption is less tolerated than albuminuria.
We confirmed our findings and extended them to the general population by performing a meta-analysis of over half a million participants. By evaluating 4 CUBN variants, previously identified due to their strong association with albuminuria (20–22, 25, 26), we found a moderate but significant association with higher eGFR. Although potential correlations of nearby SNPs cannot be excluded for variants identified in GWAS, support for the functional effects of these variants comes from our structural modeling and from the observation that compound heterozygosity with a filtered CUBN variant can also lead to the combination of chronic proteinuria and normal renal function. As evidence for positive selection of a European haplotype containing one of the GWAS variants (p.I2984V) has already been reported (42), it can be speculated that there is some sort of evolutionary advantage in reducing proximal tubule uptake (43), for example in conditions in which the tubules are overloaded with proteins and lipids. Support for this view comes from the clinical observation that tubular damage is key for the progression of DKD and primary focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS) (44, 45), from mouse models of proteinuria and hyperlipidemia (46, 47), in which the reduction of tubular uptake was shown to prevent early injury, and from mice lacking albumin, which become protected against AS (48). However, as our population-based studies were cross-sectional and also included a substantial amount of healthy individuals, it would be interesting to study any protective effects of cubilin deficiency on the progression of specific glomerular diseases in a longitudinal manner. Moreover, given that the observed effects on eGFR were mild and that eGFR itself reflected creatinine clearance with a margin of error, future studies could benefit from more specific tubular damage markers, such as urinary EGF (49).
In summary, our study proposes a new paradigm for the nondetrimental effects of tubular proteinuria, which contrasts with the general dogma that proteinuria is always damaging. Although adverse long-term effects associated with CUBN deficiency cannot be fully excluded, we recommend genetic testing for CUBN variants in individuals with chronic subnephrotic proteinuria to avoid unnecessary further medical treatments. Analogous to the familial renal glucosuria caused by SGLT2 mutations (50), benign Mendelian traits such as the one presented here may have the potential to define safe drug targets, especially if protective effects for a specific disease can be demonstrated for the genetic variants (51).
Methods
DNA extraction and preparation for NGS.
Genomic DNA was extracted from blood samples and washed in Amicon columns (Merck Millipore). DNA quality was evaluated by agarose gel electrophoresis. The concentration of DNA and presence of impurities were calculated using the Xpose scanner (Luescher). For genetic kidney disease cohort I, a total of 759 patients with suspected genetic renal disease were sequenced by the “Renome panel” containing 309 known renal disease genes. The proteinuric group consisted of patients with AS or SRNS. Patients in the nonproteinuric group had renal tubular dysgenesis (RTD), renal hypodysplasia (CAKUT), tubulointerstitial nephritis (TIN), nephronophthisis (NPHP), or polycystic kidney disease (PKD). The control group consisted of 694 individuals with matched ethnic backgrounds (527 whites and 157 Maghrebians). All identified CUBN variants were verified by Sanger sequencing. Whenever DNA of the parents was available, segregation was confirmed in the individuals with compound heterozygosity (Supplemental Table 2). For the chronic PU cohort, 107 selected individuals exhibiting isolated chronic proteinuria (between 0.5 and 3 g/d) but no genetic diagnosis despite the previous testing for several SRNS and/or AS genes were sequenced using a custom-made, NGS panel targeting 17 genes known to have functions in the proximal tubule (SureSelectXT, Agilent Technologies). High-throughput sequencing was carried out using the MiSeq/HiSeq platform (Illumina). The selected patients were heterogeneous in terms of age and were recruited through adult and pediatric nephrology departments throughout France. All the clinical information, including familial information and pedigree, was collected and provided by clinicians who prescribed the genetic testing.
For genetic kidney disease cohort II, DNA was extracted from blood samples from a total of 1350 patients with suspected SRNS or AS. All exons and adjacent intronic boundaries of up to 324 glomerular genes (depending on the version of the customized multigene panel) known or hypothesized to cause SRNS, FSGS, or AS and differential diagnoses were targeted by a custom SeqCap EZ Choice Sequence Capture Library (GLOM panel, Roche NimbleGen) and subsequently sequenced on an Illumina MiSeq or HiSeq platform (2 × 150 paired-end reads [PE]) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. DNA samples were analyzed with an average coverage of 120-fold (MiSeq) or more than 200-fold (HiSeq), respectively. Bioinformatic analysis was performed using the SeqPilot SeqNext Module, version 3.5.2 (JSI Medical Systems) as well as an in-house bioinformatic pipeline. For all approaches, potential pathogenic variants were confirmed by Sanger sequencing. For compound heterozygous individuals, segregation was confirmed by sequencing the parents. All the clinical information was collected and provided by the clinicians prescribing the genetic testing.
Variant filtering.
In order to evaluate the likelihood of pathogenicity for the identified variants, we used the guidelines of the American College of Medical Genetics (52). As a general approach, we combined a defined frequency cutoff, bioinformatic damage prediction, and structural modeling for the filtering of variants. For the filtering of splicing variants, only variants in coding regions or essential splice sites were considered in our study. All missense variants were predicted to be damaging with at least 2 of 3 damage prediction algorithms: MutationTaster (http://www.mutationtaster.org/), PolyPhen-2 (http://genetics.bwh.harvard.edu/php2/), and Sorting Intolerant from Tolerant (SIFT) (http://sift.bii.a-star.edu.sg). Only 1 variant, p.N1303H, was predicted to be damaging only by 1 algorithm. However, structural modeling showed that this variant is located directly in the CUB8–vitamin B12/IF interface (Supplemental Table 5). All variants were either absent from reference populations (e.g., gnomAD) (23) or rare, with global allele frequencies below 0.001. Only p.S1947Y has previously been reported in the Human Gene Mutation Database (24). In CUBN-positive cases, no additional gene variant with pathogenic relevance for the disease phenotype was present among the patients described in this manuscript.
Structural analysis of variants.
Structural models of individual cubilin CUB domains were generated from previously determined structures using the Phyre2 server (53). Figures were prepared using PyMOL software (Schrödinger).
Calculation of the eGFR and proteinuria range.
The eGFR was calculated with the Schwartz formula for pediatric patients (<18 years of age) and the CKD Epidemiology Collaboration (CKD-EPI) formula for adults (54–56). Proteinuria was measured as the total amount of protein in 24-hour urine collections. If only spot urine was available, the urinary protein–to–creatinine ratio (mostly in mg/mmol) was used as an estimate for the 24-hour urine measurement (57).
Statistics.
Continuous values are reported as the mean ± SD. For these values, 95% CIs were calculated using the appropriate Student’s t probabilities. Dichotomous data are shown as percentages. We applied χ2 or Fisher’s exact tests to dichotomous data in order to compare differences between 2 groups. For continuous data comparisons, we used an unpaired t test for the Gaussian sampled data. Two-tailed P values of less than 0.05 were considered statistically significant. Statistical analyses were performed using Rstudio and GraphPad Prism 4 (GraphPad Software).
CUBN variant lookup in the CKDGen Consortium.
Four low-frequency or common missense variants known to be associated with albuminuria from GWAS of population-based cohorts (rs141640975, rs144360241, rs45551835, and rs1801239) (20–22, 25, 26) were evaluated for association with albuminuria and eGFR using summary statistics from a large-scale meta-analysis of mostly population-based studies within the CKDGen Consortium (28, 58). The summary statistics from the CKDGen Consortium are available at http://ckdgen.imbi.uni-freiburg.de Alleles, effect direction, SEM, P values, as well as sample size were extracted from genome-wide results using an additive model. Sample size varied between 331,340 and 597,710 across variants. We used fixed effects in the meta-analysis as previously described (28).
Study of individuals with or without diabetes.
GWAS variants were evaluated for association with albuminuria and eGFR using summary statistics (alleles, effect, SEM, P value, and sample size) from a European exome-wide association study (ExWAS) discovery meta-analysis comprising 5 studies (3 population-based and 2 type 2 diabetes studies) from Denmark (20) under an additive model and for I2984V (rs1801239) also with the recessive model. Similarly, an association summary for the 3 variants for eGFR and albuminuria was also reported and based on stratification for diabetes status. Total sample size varied between 13,124 to 13,550 (3837–3990 individuals with diabetes and 9251– 9449 individuals without diabetes) across variants. We used inverse variance fixed effects in the meta-analysis as previously described (20).
Author contributions
M. Bedin analyzed and compiled patient data with help from OB, AS, MJT, CA, and MS. MB, LVG, MS, OG, CBF, VM, CT, CA, M. Grohmann, EK, TW, and CB performed genotyping and analyzed the sequencing results. M. Bedin, FJH, and PN performed statistical analysis. YL, TSA, and AK performed population-based studies. AC, JH, VB, SK, AB, F. Lammens, F. Louillet, BR, CV, IB, CIB, CJM, TS, LP, M. Gödel, TBH, M. Benz, GK, MH, KL, OB, and AS recruited patients and gathered the clinical data for the study. CBFA performed the structural modeling. MS conceived and supervised the project. MS wrote the manuscript with help from MB and CA. All authors critically reviewed the manuscript.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the ATIP-Avenir program, the Fondation Bettencourt-Schueller (Liliane Bettencourt Chair of Developmental Biology), and state funding by the Agence Nationale de la Recherche (ANR) under the Investissements d’avenir program (ANR-10-IAHU-01) and NEPHROFLY (ANR-14-ACHN-0013, to MS). TSA and MS also received funding from the Novo Nordisk Foundation and a Steno Collaborative Grant 2018 (NNF18OC0052457). TSA thanks all the study participants and acknowledges collaborations with the Novo Nordisk Foundation Center for Basic Metabolic Research, Section of Metabolic Genetics at the University of Copenhagen (Copenhagen, Denmark) and the Center for Clinical Research and Prevention, Bispebjerg and Frederiksberg Hospital (Capital Region, Copenhagen, Denmark), where the genotyping and phenotyping for the Danish studies were performed. We thank the CKDGen Consortium for their collaboration in providing early access to data. The work of AK was supported by a Heisenberg Professorship of the German Research Foundation (KO 3598/5-1). CB received support from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) Collaborative Research Centre (SFB) KIDGEM 1140 (project 246781735) and the Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMB) (01GM1515C).
Version 1. 10/15/2019
In-Press Preview
Version 2. 12/03/2019
Electronic publication
Version 3. 01/02/2020
Print issue publication
Version 4. 06/01/2022
Updated Supplemental Table 9 and corresponding text in Results (last paragraph).
Footnotes
Conflict of interest: The authors have declared that no conflict of interest exists.
Copyright: © 2020, American Society for Clinical Investigation.
Reference information: J Clin Invest. 2020;130(1):335–344.https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI129937.
See the related Commentary at Not all proteinuria is created equal.
Contributor Information
Mathilda Bedin, Email: mathilda.bedin@institutimagine.org.
Olivia Boyer, Email: olivia.boyer@aphp.fr.
Aude Servais, Email: aude.servais@aphp.fr.
Yong Li, Email: yong.li@uniklinik-freiburg.de.
Laure Villoing-Gaudé, Email: laure.villoing@gmail.com.
Marie-Josephe Tête, Email: mjtete-thaunat@orange.fr.
Alexandra Cambier, Email: alexandra.cambier@aphp.fr.
Julien Hogan, Email: julien.hogan@aphp.fr.
Veronique Baudouin, Email: veronique.baudouin@aphp.fr.
Saoussen Krid, Email: saoussen.krid@aphp.fr.
Albert Bensman, Email: albert.bensman@orange.fr.
Florie Lammens, Email: florie.lammens@chru-lille.fr.
Ferielle Louillet, Email: ferielle.louillet@chu-rouen.fr.
Bruno Ranchin, Email: bruno.ranchin@chu-lyon.fr.
Cecile Vigneau, Email: cecile.vigneau@chu-rennes.fr.
Iseline Bouteau, Email: Iseline.BOUTEAU@chu-poitiers.fr.
Corinne Isnard-Bagnis, Email: corinne.bagnis@psl.aphp.fr.
Christoph J. Mache, Email: christoph.mache@medunigraz.at.
Tobias Schäfer, Email: tobias.schaefer@uniklinik-freiburg.de.
Lars Pape, Email: Pape.Lars@mh-hannover.de.
Markus Gödel, Email: m.goedel@uke.de.
Tobias B. Huber, Email: t.huber@uke.de.
Marcus Benz, Email: m.benz@kid-benz.de.
Günter Klaus, Email: guenter.klaus@kfh-dialyse.de.
Matthias Hansen, Email: Matthias.Hansen@kfh-dialyse.de.
Kay Latta, Email: k.latta@ckhf.de.
Olivier Gribouval, Email: olivier.gribouval@inserm.fr.
Vincent Morinière, Email: vincent.moriniere@inserm.fr.
Carole Tournant, Email: carole.tournant@aphp.fr.
Maik Grohmann, Email: maik.grohmann@bioscientia.de.
Elisa Kuhn, Email: timo.wagner@bioscientia.de.
Timo Wagner, Email: elisa.kuhn@bioscientia.de.
Christine Bole-Feysot, Email: christine.bole@inserm.fr.
Fabienne Jabot-Hanin, Email: fabienne.hanin@inserm.fr.
Patrick Nitschké, Email: patrick.nitschke@parisdescartes.fr.
Tarunveer S. Ahluwalia, Email: tarun.veer.singh.ahluwalia@regionh.dk.
Anna Köttgen, Email: anna.koettgen@uniklinik-freiburg.de.
Christian Brix Folsted Andersen, Email: cbfa@biomed.au.dk.
Carsten Bergmann, Email: Carsten.Bergmann@bioscientia.de.
Corinne Antignac, Email: corinne.antignac@inserm.fr.
Matias Simons, Email: matias.simons@institutimagine.org.
References
- 1.Astor BC, et al. Lower estimated glomerular filtration rate and higher albuminuria are associated with mortality and end-stage renal disease. A collaborative meta-analysis of kidney disease population cohorts. Kidney Int. 2011;79(12):1331–1340. doi: 10.1038/ki.2010.550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Gansevoort RT, et al. Lower estimated GFR and higher albuminuria are associated with adverse kidney outcomes. A collaborative meta-analysis of general and high-risk population cohorts. Kidney Int. 2011;80(1):93–104. doi: 10.1038/ki.2010.531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Ninomiya T, et al. Albuminuria and kidney function independently predict cardiovascular and renal outcomes in diabetes. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009;20(8):1813–1821. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2008121270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Abbate M, Zoja C, Remuzzi G. How does proteinuria cause progressive renal damage? J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006;17(11):2974–2984. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2006040377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Moorhead JF, Chan MK, El-Nahas M, Varghese Z. Lipid nephrotoxicity in chronic progressive glomerular and tubulo-interstitial disease. Lancet. 1982;2(8311):1309–1311. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)91513-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Brenner BM, et al. Effects of losartan on renal and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 2001;345(12):861–869. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa011161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Norden AG, et al. Tubular proteinuria defined by a study of Dent’s (CLCN5 mutation) and other tubular diseases. Kidney Int. 2000;57(1):240–249. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1755.2000.00847.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Smith ER, Cai MM, McMahon LP, Wright DA, Holt SG. The value of simultaneous measurements of urinary albumin and total protein in proteinuric patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2012;27(4):1534–1541. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfr708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Christensen EI, et al. Loss of chloride channel ClC-5 impairs endocytosis by defective trafficking of megalin and cubilin in kidney proximal tubules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100(14):8472–8477. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1432873100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Amsellem S, et al. Cubilin is essential for albumin reabsorption in the renal proximal tubule. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2010;21(11):1859–1867. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2010050492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Christensen EI, Nielsen R, Birn H. From bowel to kidneys: the role of cubilin in physiology and disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2013;28(2):274–281. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfs565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Dachy A, et al. In-depth phenotyping of a Donnai-Barrow patient helps clarify proximal tubule dysfunction. Pediatr Nephrol. 2015;30(6):1027–1031. doi: 10.1007/s00467-014-3037-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Wahlstedt-Fröberg V, Pettersson T, Aminoff M, Dugué B, Gräsbeck R. Proteinuria in cubilin-deficient patients with selective vitamin B12 malabsorption. Pediatr Nephrol. 2003;18(5):417–421. doi: 10.1007/s00467-003-1128-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Qiu C, et al. Renal compartment-specific genetic variation analyses identify new pathways in chronic kidney disease. Nat Med. 2018;24(11):1721–1731. doi: 10.1038/s41591-018-0194-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Menon R, et al. Single-cell analysis of progenitor cell dynamics and lineage specification in the human fetal kidney. Development. 2018;145(16):dev164038. doi: 10.1242/dev.164038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Park J, et al. Single-cell transcriptomics of the mouse kidney reveals potential cellular targets of kidney disease. Science. 2018;360(6390):758–763. doi: 10.1126/science.aar2131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Larsen C, Etzerodt A, Madsen M, Skjødt K, Moestrup SK, Andersen CBF. Structural assembly of the megadalton-sized receptor for intestinal vitamin B12 uptake and kidney protein reabsorption. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):5204. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-07468-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Andersen CB, Madsen M, Storm T, Moestrup SK, Andersen GR. Structural basis for receptor recognition of vitamin-B(12)-intrinsic factor complexes. Nature. 2010;464(7287):445–448. doi: 10.1038/nature08874. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Ovunc B, et al. Exome sequencing reveals cubilin mutation as a single-gene cause of proteinuria. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2011;22(10):1815–1820. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2011040337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Ahluwalia TS, et al. A novel rare CUBN variant and three additional genes identified in Europeans with and without diabetes: results from an exome-wide association study of albuminuria. Diabetologia. 2019;62(2):292–305. doi: 10.1007/s00125-018-4783-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Böger CA, et al. CUBN is a gene locus for albuminuria. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2011;22(3):555–570. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2010060598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Haas ME, et al. Genetic association of albuminuria with cardiometabolic disease and blood pressure. Am J Hum Genet. 2018;103(4):461–473. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2018.08.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Lek M, et al. Analysis of protein-coding genetic variation in 60,706 humans. Nature. 2016;536(7616):285–291. doi: 10.1038/nature19057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Stenson PD, et al. The Human Gene Mutation Database: towards a comprehensive repository of inherited mutation data for medical research, genetic diagnosis and next-generation sequencing studies. Hum Genet. 2017;136(6):665–677. doi: 10.1007/s00439-017-1779-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Zanetti D, Rao A, Gustafsson S, Assimes TL, Montgomery SB, Ingelsson E. Identification of 22 novel loci associated with urinary biomarkers of albumin, sodium, and potassium excretion. Kidney Int. 2019;95(5):1197–1208. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2018.12.017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Teumer A, et al. Genome-wide association studies identify genetic loci associated with albuminuria in diabetes. Diabetes. 2016;65(3):803–817. doi: 10.2337/db15-1313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Bullich G, et al. A kidney-disease gene panel allows a comprehensive genetic diagnosis of cystic and glomerular inherited kidney diseases. Kidney Int. 2018;94(2):363–371. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2018.02.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Wuttke M, et al. A catalog of genetic loci associated with kidney function from analyses of a million individuals. Nat Genet. 2019;51(6):957–972. doi: 10.1038/s41588-019-0407-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Storm T, et al. Renal phenotypic investigations of megalin-deficient patients: novel insights into tubular proteinuria and albumin filtration. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2013;28(3):585–591. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfs462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Kumar G, Chaudhry M, Faris K, Al Masri O. Renal involvement in a child with Donnai-Barrow syndrome. Asian J Pediatr Nephrol. 2018;1(2):93–95. doi: 10.4103/AJPN.AJPN_22_18. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Pober BR, Longoni M, Noonan KM. A review of Donnai-Barrow and facio-oculo-acoustico-renal (DB/FOAR) syndrome: clinical features and differential diagnosis. Birth Defects Res Part A Clin Mol Teratol. 2009;85(1):76–81. doi: 10.1002/bdra.20534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Blanchard A, et al. Observations of a large Dent disease cohort. Kidney Int. 2016;90(2):430–439. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2016.04.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Chasman DI, et al. Integration of genome-wide association studies with biological knowledge identifies six novel genes related to kidney function. Hum Mol Genet. 2012;21(24):5329–5343. doi: 10.1093/hmg/dds369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Kozyraki R, Cases O. Vitamin B12 absorption: mammalian physiology and acquired and inherited disorders. Biochimie. 2013;95(5):1002–1007. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2012.11.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Yammani RR, Seetharam S, Seetharam B. Identification and characterization of two distinct ligand binding regions of cubilin. J Biol Chem. 2001;276(48):44777–44784. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M106419200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Kristiansen M, et al. Cubilin P1297L mutation associated with hereditary megaloblastic anemia 1 causes impaired recognition of intrinsic factor-vitamin B(12) by cubilin. Blood. 2000;96(2):405–409. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Broch H, Imerslund O, Monn E, Hovig T, Seip M. Imerslund-Gräsbeck anemia. A long-term follow-up study. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1984;73(2):248–253. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1984.tb09937.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Ercan Z, Demir ME, Ulas T, Ingec M, Horoz M. A long-term follow-up of an Imerslund-Grasbeck syndrome patient with proteinuria. Nefrologia. 2013;33(1):147–148. doi: 10.3265/Nefrologia.pre2012.Aug.11661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Gräsbeck R. Imerslund-Gräsbeck syndrome (selective vitamin B(12) malabsorption with proteinuria) Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2006;1:17. doi: 10.1186/1750-1172-1-17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Pedersen GA, Chakraborty S, Steinhauser AL, Traub LM, Madsen M. AMN directs endocytosis of the intrinsic factor-vitamin B(12) receptor cubam by engaging ARH or Dab2. Traffic. 2010;11(5):706–720. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2010.01042.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.GTEx Consortium. Human genomics. The Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx) pilot analysis: multitissue gene regulation in humans. Science. 2015;348(6235):648–660. doi: 10.1126/science.1262110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Tzur S, Wasser WG, Rosset S, Skorecki K. Linkage disequilibrium analysis reveals an albuminuria risk haplotype containing three missense mutations in the cubilin gene with striking differences among European and African ancestry populations. BMC Nephrol. 2012;13:142. doi: 10.1186/1471-2369-13-142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Simons M. The benefits of tubular proteinuria: an evolutionary perspective. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2018;29(3):710–712. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2017111197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Bonventre JV. Can we target tubular damage to prevent renal function decline in diabetes? Semin Nephrol. 2012;32(5):452–462. doi: 10.1016/j.semnephrol.2012.07.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Alexopoulos E, Stangou M, Papagianni A, Pantzaki A, Papadimitriou M. Factors influencing the course and the response to treatment in primary focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2000;15(9):1348–1356. doi: 10.1093/ndt/15.9.1348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Motoyoshi Y, et al. Megalin contributes to the early injury of proximal tubule cells during nonselective proteinuria. Kidney Int. 2008;74(10):1262–1269. doi: 10.1038/ki.2008.405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Kuwahara S, et al. Megalin-mediated tubuloglomerular alterations in high-fat diet-induced kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016;27(7):1996–2008. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2015020190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Jarad G, Knutsen RH, Mecham RP, Miner JH. Albumin contributes to kidney disease progression in Alport syndrome. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2016;311(1):F120–F130. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00456.2015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Azukaitis K, et al. Low levels of urinary epidermal growth factor predict chronic kidney disease progression in children. Kidney Int. 2019;96(1):214–221. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2019.01.035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Santer R, Calado J. Familial renal glucosuria and SGLT2: from a mendelian trait to a therapeutic target. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2010;5(1):133–141. doi: 10.2215/CJN.04010609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Dewey FE, et al. Genetic and pharmacologic inactivation of ANGPTL3 and cardiovascular disease. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(3):211–221. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1612790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Richards S, et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: a joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet Med. 2015;17(5):405–424. doi: 10.1038/gim.2015.30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Kelley LA, Mezulis S, Yates CM, Wass MN, Sternberg MJ. The Phyre2 web portal for protein modeling, prediction and analysis. Nat Protoc. 2015;10(6):845–858. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2015.053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Selistre L, et al. Comparison of the Schwartz and CKD-EPI equations for estimating glomerular filtration rate in children, adolescents, and adults: a retrospective cross-sectional study. PLoS Med. 2016;13(3):e1001979. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1001979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Schwartz GJ, Work DF. Measurement and estimation of GFR in children and adolescents. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009;4(11):1832–1843. doi: 10.2215/CJN.01640309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Levey AS, et al. A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate. Ann Intern Med. 2009;150(9):604–612. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-150-9-200905050-00006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.National Kidney Foundation K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for chronic kidney disease: evaluation, classification, and stratification. Am J Kidney Dis. 2002;39(2 Suppl 1):S1–S266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Teumer A, et al. Genome-wide association meta-analyses and fine-mapping elucidate pathways influencing albuminuria. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):4130. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-11576-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.