Abstract
Phenological differences between host plants can promote temporal isolation among host-associated populations of insects with life cycles tightly coupled to plant phenology. Divergence in the timing of spring budbreak between two sympatric sister oak species has been shown to promote temporal isolation between host plants and their host-associated populations of a cynipid gall wasp. Here, we examined the generality of this mechanism by testing the hypothesis of cascading temporal isolation for five additional gall-formers and three natural enemy species associated with these same oak species. The timing of adult emergence from galls differed significantly between host-associated populations for all nine species and parallels the direction of the phenological differences between host plants. Differences in emergence timing can reduce gene flow between host-associated populations by diminishing mating opportunities and/or reducing the fitness of immigrants due to differences in the availability of ephemeral resources. Our study suggests that cascading temporal isolation could be a powerful ‘biodiversity generator’ across multiple trophic levels in tightly coupled plant–insect systems.
Keywords: allochronic isolation, gall wasp, host-associated differentiation, sequential divergence, phenology
1. Introduction
Understanding the origins of biodiversity presents an enduring challenge for biologists. Sequential speciation posits that speciation events within one lineage can have cascading effects across an entire community, by promoting divergence and speciation across multiple species [1–4]. Emerging from this perspective, cascading reproductive isolation describes the process whereby trait divergence that generates reproductive isolation (RI) between populations in one species transcends trophic levels to generate population divergence within interacting species [5]. The diversity of host-specific insect herbivores with their close ties to host plants offers opportunities to test whether cascading RI is a common mechanism promoting divergence [5–8].
Phenological difference between host plants is a key selective force that promotes phenological differences and initial population divergence of host-specific insects with life histories tied to host plants (e.g. Rhagoletis fruit flies [9]; Eurosta gall flies [10] and Enchenopa treehoppers [11]; reviewed in [12,13]). For example, Hood et al. [5] demonstrated that temporal RI between two sympatric sister species of live oaks, Quercus virginiana (Qv), and Q. geminata (Qg) cascades as a reproductive barrier among populations of the host-specific, gall-former, Belonocnema treatae. Divergence in the timing of budbreak, which is linked to male flower production, generates temporal RI between the two sister plant species [14]. Simultaneous temporal RI between B. treatae populations associated with each oak species is also generated as budbreak leads to the formation of new leaves that the wasps require at an early developmental stage (less than 72 h old) to induce gall formation [5,15]. Temporal isolation reduces gene flow between host-associated gall-former populations by decreasing mating opportunities and lowering immigrant fitness in non-natal host plant environments (i.e. immigrant inviability) due to a mismatch in timing of ephemeral host resources [15]. Thus, budbreak acts as a ‘multitrophic, multi-effect trait,’ whereby differences in budbreak phenology generates RI between both the oak species and their obligately dependent insect herbivores [5].
These sister oak species share a diverse community of gall-formers and their associated insect natural enemies are similarly dependent on plant phenology [16,17]. Thus, the stage is set to test whether differences in host plant phenology drive temporal isolation across multiple species and trophic levels. To accomplish this, we monitor the emergence phenology of five additional gall-former species and three natural enemy species found on the two oaks [18–20].
2. Material and methods
(a). Study system
Gall-formers are specialist insect herbivores that induce three-dimensional outgrowths of nutritive plant tissues (i.e. ‘galls’) within which larvae feed and develop, and from which adults emerge [21]. Many species within the major gall-forming lineage Cynipidae (Hymenoptera) exhibit cyclical parthenogenesis, wherein alternating sexual and asexual generations develop on different plant tissues to complete a bivoltine life cycle [21–23]. Both generations require newly formed plant tissues as oviposition sites to successfully induce galls. Oviposition into these tissues at the wrong time, often by only a week or two, can preclude gall formation [15]. Thus, the timing of tissue availability is critical for gall formation and insect survival [15,22].
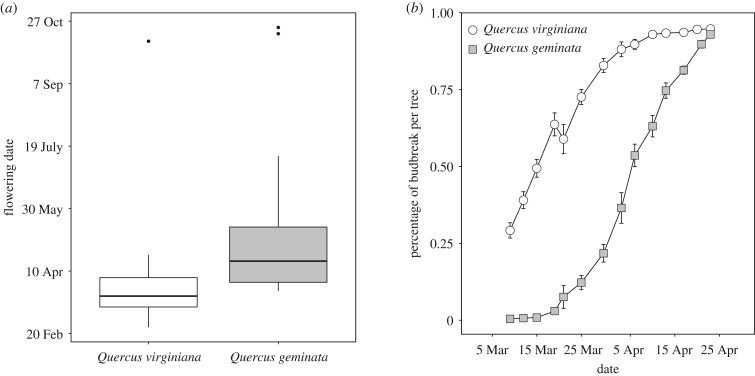
The gall-former community of Qv and Qg includes five common cynipid species: Andricus quercuslanigera, A. quercusfoliatus, B. treatae, Callirhytis quercusbatatoides and Disholcaspis quercusvirens; and the gall-forming midge, Arnoldiola atra (Diptera: Cecidomyiidae) [18]. The geographical ranges of Qv and Qg overlap in the southeastern USA, but the production of new flowers and leaves takes place an average of three weeks earlier in the spring for Qv (figure 1). Cavender-Bares & Pahlich [14] suggested that this phenological difference is a response to selection against hybridization. The development of these six gall-formers depends on the new spring growth of plant tissues [19,20,24]. Sexual generation B. treatae and A. atra emerge and oviposit into the new leaves and shoots, respectively [24,25]. Similarly, asexual generation A. quercuslanigera and D. quercusvirens oviposit into developing buds inducing galls that harbour the sexual generations on catkins and manipulated buds, respectively [19,20]. Lastly, while the sexual generations of A. quercusfoliatus and C. quercusbatatoides are unknown, asexuals emerge from rapidly developing bud and stem galls, respectively. The reproductive life stage of gall-formers is typically brief, with adults surviving 2–7 days in ideal laboratory conditions, and oviposition beginning immediately upon emergence [5,20,22,24]. Therefore, differences in the timing of ephemeral resources between alternative host plant species likely results in divergent selection on the timing of emergence and oviposition [5,15,21,22].
Figure 1.
Phenological differences between host plants Q. virginiana (Qv) and Q. geminata (Qg). (a) Boxplot of the average flowering date by host illustrating the median, 25th and 75th percentiles, and the 95% confidential intervals displayed. The dots outside of the boxes are outliers. (b) Cumulative frequency of budbreak of Qv and Qg (mean % budbreak per tree ± s.e.). Panels modified from Hood et al. [5].
Gall-formers are attacked by a diverse community of natural enemies, including inquilines that compete for plant resources within galls and often negatively impact gall-formers [10,20]. In this study, we focused on gall-formers and their inquilines because both are directly dependent on host plant resources, the timing of which differs between host plants [26]. The dominant inquilines of galls on live oaks are Synergus spp. (Cynipidae: Synerginae) [17,27]. Inspection of the COI and cytb regions in the mtDNA genome (approx. 1000 bp total) showed that Synergus emerging from galls induced by A. quercuslanigera, C. quercusbatatoides and D. quercusvirens on Qv and Qg represent distinct evolutionary lineages based on sequence divergence, which ranged from 11% to 17% between groups (electronic supplementary material, figure S1). Therefore, we also tested whether phenological differences between host plant species cascade to phenological differences in emergence timing within the Synergus natural enemy community.
(b). Sample collection
From November to December 2014–2018, we collected and husbanded galls potentially housing the six gall-formers and the three Synergus species from Qv and Qg from 72 sites in Florida and Alabama where the geographical ranges of the host plants overlap. Galls of each species were placed in separate 1 l glass jars that were covered by filter paper and misted twice weekly. In 2014–2016 and 2018, galls were reared under ambient environmental conditions at ≈23°C in the laboratory. In 2017, galls were maintained outdoors under natural conditions in Houston, TX, USA. Each year, the numbers of emergent individuals were monitored once every 2 days through mid-May. In total, we identified 10 249 gall-formers and 706 Synergus that emerged from galls induced by A. quercuslanigera; C. quercusbatatoides and D. quercusvirens (see electronic supplementary material).
(c). Statistical analysis
To test the hypothesis that gall-formers and their natural enemies emerge earlier on Qv than those on Qg, linear mixed model analysis was conducted in each individual species using the nlme package in R v. 3.5.2, with standardized z-scores of transformed emergence times (Julian dates) in each year as the response variable, host plant and collection year as fixed effects, and collection site as a random effect [28]. We also analysed models with latitude as a fixed effect, but results were similar (electronic supplementary material, table S1). We report least squared means of z-scores, (calculated using emmeans package in R, [29]) to illustrate differences in emergence between Qv- and Qg-associated populations across years for each species. We also report differences in average (±s.e.) emergence time in days to show biologically relevant values by back-transforming the least square mean z-score from the linear mixed model into the average emergence date for each host-associated population each year. Finally, to test the generality of cascading temporal isolation in this system, we compliment individual analyses with a standard sign test to compare the least square means of emergence date from our linear mixed model across all nine species.
(d). Temporal isolation
Temporal isolation between host-associated populations for all nine species was estimated as the percent of individuals for each host-associated population that overlaps temporally based on emergence date and average adult longevity [19,20,30]. Estimated longevity of B. treatae (3 days) and D. quercuesvirens (7 days) were adopted from Hood et al. [5] and Bird et al. [20]. In the remaining seven species, we used the average adult longevity of B. treatae and D. quercusvirens (i.e. 5 days) to calculate temporal overlap (5 days) was used to calculate temporal overlap. We quantified temporal isolation (TI) between Qv- and Qg-associated populations following Feder et al. [30]:
Here, xi and yi are the percentage of wasps from populations x and y alive on day i based on emergence time and probabilities of survival to day i based on average longevity estimates.
Temporal isolation estimates RI and ecological isolation for sexual and asexual generations emerging in the spring, respectively.
3. Results
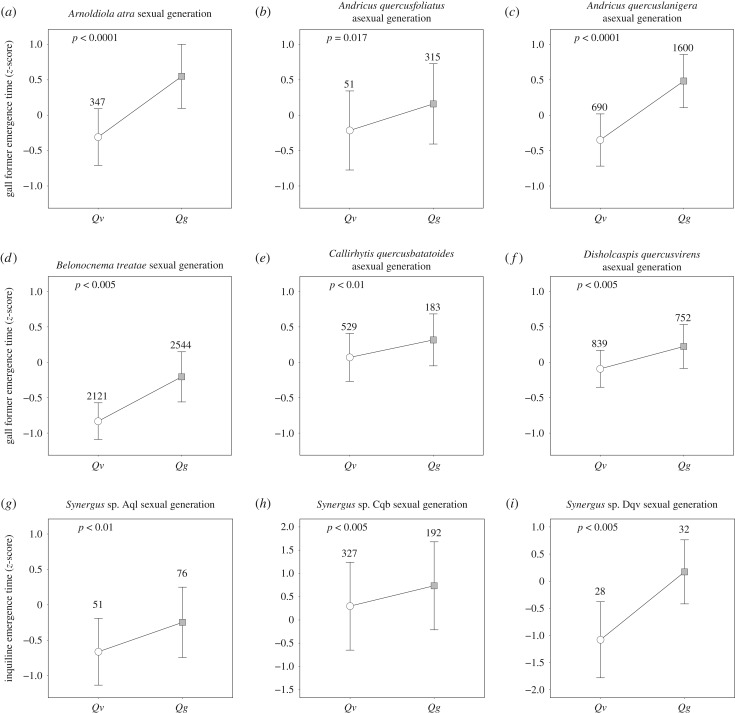
Across all nine species, we observed consistent differences in emergence timing, with Qv-associated populations emerging significantly earlier, on average, than Qg-associated populations (figure 2 and table 1; sign test: z = 3.0, p = 0.0027). This suggests that a community-wide difference of gall-formers and natural enemies is associated with the observed differences in host plant phenology (figure 1). However, there is significant variation in the difference in emergence times between hosts across gall-former species: A. atra = 16.5 ± 5.5 days, A. quercusfoliatus = 7.0 ± 0.8 days, A. quercuslanigera = 18.1 ± 4.9, B. treatae = 9.3 days, C. quercusbatatoides = 4.3 days and D. quercusvirens = 6.9 ± 1.3 days, Synergus from A. quercuslanigera = 10.1 ± 2.3 days, Synergus from C. quercusbatatoides = 5.2 ± 0.6 days and Synergus from D. quercusvirens = 72 ± 27 days.
Figure 2.
(a–i) The timing of adult emergence (standardized as z-scores) for six gall-formers and three Synergus associated with three gall-formers (Aql: A. quercuslanigera; Cqb: C. quercusbatatoides and Dqv: D. quercusvirens). The values above each confidence interval indicate sample sizes per host plant. Least squared means of emergence time were displayed with 95% confidence intervals, calculated from linear mixed models with host plants and sampling years as fixed factors. All p-values from one-tailed hypothesis testing.
Table 1.
Results of linear mixed model analysis with host plant as a fixed effect and temporal isolation between populations of nine species developing on different host plants.
| species | generation | tissue gall forms on | expected longevity (days) | effect of host plant in LMM |
estimate of temporal isolation |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| coefficient | d.f. | t-value | p-value | year 2015 | year 2016 | year 2017 | year 2018 | average across years | ||||
| Arnoldiola atra | sexual | Bud | 5 | 0.61 | 35 | 4.88 | <0.0001 | 0.53 | 1 | 0.25 | 0.69 | 0.62 |
| A. quercusfoliatus | asexual | Bud | 5 | 0.27 | 31 | 2.26 | 0.012 | — | — | 0.39 | 0.9 | 0.65 |
| A. quercuslanigera | asexual | bud | 5 | 0.59 | 42 | 11.59 | <0.0001 | 1 | 0.59 | 0.52 | 0.34 | 0.62 |
| B. treatae | sexual | root | 3 | 0.44 | 1 | 18.1 | 0.018 | — | — | 0.47 | — | 0.47 |
| C. quercusbatatoides | asexual | stem | 5 | 0.18 | 28 | 2.52 | 0.006 | — | — | 0.31 | — | 0.31 |
| D. quercusvirens | asexual | stem | 7 | 0.22 | 46 | 2.36 | 0.009 | 1 | 0.96 | 0.05 | 0.15 | 0.54 |
| Synergus spp. from A. quercuslanigera | sexual | n.a. | 5 | 0.29 | 21 | 2.48 | 0.007 | — | — | 0.62 | 0.58 | 0.6 |
| Synergus spp. from C. quercusbatatoides | sexual | n.a. | 5 | 0.31 | 15 | 2.79 | 0.003 | — | — | 0.36 | 0.47 | 0.42 |
| Synergus spp. from D. quercusvirens | sexual | n.a. | 5 | 0.7 | 13 | 2.51 | 0.008 | — | — | 1 | 0.88 | 0.94 |
Note: italic indicates p-value < 0.05; 0–1 in temporal isolation means the population completely overlapped (0) to not overlapped at all (1).
Estimated temporal isolation between host-associated populations of each of the nine species across years ranges from a low of 0.31 in C. quercusbatatoides, to a high of 0.94 in Synergus attacking D. quercusvirens (table 1).
4. Discussion
Cascading RI could be an important evolutionary mechanism to promote divergence and RI between populations within species across adjacent trophic levels [4]. Our results demonstrate that herbivore and natural enemy populations of each species on Qv emerged earlier than populations on Qg, consistent with the phenological differences in plant tissue growth between the live oak species. Even though the overall pattern is consistent across the community, there is remarkable variation in the phenological differences among species, from just 4 days in C. quercusbatatoides to 72 days for the Synergus sp. attacking D. quercusvirens. This suggests that there are likely many important natural history details underlying the degree to which temporal host plant RI cascades.
Our data suggest that the observed phenological differences among host-associated populations are a result of individuals specializing on each host plant rather than a generalist bet-hedging strategy, as a generalist strategy should require either that individuals emerge over a broad length of time or live long enough to oviposit on either host plants. Both assumptions contradict our observations in this and previous studies [5]. The emergence time differences between populations of sexual generations in the gall-formers A. atra and B. treatae, and the three Synergus species directly translates into temporal RI. Temporal RI across these sexual lineages ranges from 0.42 to 0.94, which represents a significant direct reduction in the opportunity for gene flow. Differences in emergence time between populations in the four asexual lineages may also promote RI indirectly since galling insects require developing plant tissues with a narrow time window to induce and form galls (e.g. [13]). Thus, the time mismatch between the emergent gall-formers and the ephemeral plant tissues from an alternative host plant could translate into reduced immigrant fitness [13]. There are 10–30 different natural enemy species that attack the gall-former in this system, many of which are host-specific [5,9,10]. Future research will explore the extent to which temporal isolation continues to cascade across these natural enemy species and how phenological divergence contributes to the total RI between populations throughout this oak-gall wasp community.
How common is cascading temporal isolation in nature? Our study shows that this phenomenon is common among this guild of host-specific herbivores, where the difference in ephemeral tissue resources presents strong selection on the phenology of herbivores, and eventually cascades to the third trophic level. Cascading temporal isolation occurs in two key steps: (i) temporal isolation evolves in one focal (keystone) species and (ii) temporal isolation extends to other species at different trophic levels that rely on the traits of the focal species. Accumulating case studies suggest that temporal isolation initiates divergence and promotes speciation in a diverse range of taxa including plants, insects and coral reefs, thus building a case that it is a widespread phenomenon [31–33]. The second step of cascading temporal isolation requires temporal isolation in one species to exert strong selection on timing of other interacting species in the community. This situation is likely in systems with highly specialized interactions, such as parasitism or mutualism, when one of the interacting species is closely tied with the focal organism's reproduction, or when the development of the resources the interacting species depends on is strongly linked with the focal organism's reproduction time. Since specialists compose a majority of the biodiversity on Earth [34], this highlights the possible generality of cascading temporal isolation in promoting species diversity.
Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgements
We thank Robert Busbee, Amanda Driscoe, Jiajia Zheng, Aling Li, Jian Zhang, Elaine Hu, Charles Davis and Shih An Shzu for sample collection.
Data accessibility
Data are available from the Dryad Digital Repository: https://dx.doi.org/10.5061/dryad.h44j0zpf9 [35].
Authors' contributions
L.Z., G.R.H., J.R.O. and S.P.E. designed the study and all authors collected data. L.Z. analysed the data and wrote the manuscript. All authors edited and approved the final version. All authors agree to be held accountable for the work performed.
Competing interests
We declare we have no competing interests.
Funding
This work was supported by Rice University (S.P.E. and L.Z.), a Rosemary Grant Award from the Society for the Study of Evolution (L.Z.), a Howard McCarley student research award from the Southwestern Association of Naturalist (L.Z.) and the Diana McSherry and Patrick Poe research award (L.Z.).
References
- 1.Stireman JO III, Nason JD, Heard SB, Seehawer JM. 2006. Cascading host-associated genetic differentiation in parasitoids of phytophagous insects. Proc. R. Soc. B 273, 523 ( 10.1098/RSPB.2005.3363) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Forbes AA, Powell THQ, Stelinski LL, Smith JJ, Feder JL. 2009. Sequential sympatric speciation across trophic levels. Science 323, 776–779. ( 10.1126/science.1166981) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Feder JL, Forbes AA. 2010. Sequential speciation and the diversity of parasitic insects. Ecol. Entomol. 35, 67–76. ( 10.1111/j.1365-2311.2009.01144.x) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Hood GR, Forbes AA, Powell THQ, Egan SP, Hamerlinck G, Smith JJ, Feder JL. 2015. Sequential divergence and the multiplicative origin of community diversity. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 112, E5980–9. ( 10.1073/pnas.1424717112) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Hood GR, Zhang L, Hu EG, Ott JR, Egan SP. 2019. Cascading reproductive isolation: plant phenology drives temporal isolation among populations of a host-specific herbivore. Evolution 73, 554–568. ( 10.1111/evo.13683) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Stireman JO III, Nason JD, Heard SB. 2005. Host-associated genetic differentiation in phytophagous insects: general phenomenon or isolated exceptions? Evidence from a goldenrod-insect community. Evolution 59, 2573–2587. ( 10.1111/j.0014-3820.2005.tb00970.x) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Medina RF, Dickey AM, Harrison K, Miller GL. 2017. Host-associated differentiation in a pecan and water hickory Aphidomorpha community. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 162, 366–378. ( 10.1111/eea.12553) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Forbes AA, Devine SN, Hippee AC, Tvedte ES, Ward AKG, Widmayer HA, Wilson CJ. 2017. Revisiting the particular role of host shifts in initiating insect speciation. Evolution 71, 1126–1137. ( 10.1111/evo.13164) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Smith DC. 1988. Heritable divergence of Rhagoletis pomonella host races by seasonal asynchrony. Nature 336, 66–67. ( 10.1038/336066a0) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Craig TP, Itami JK, Abrahamson WG, Horner JD. 1993. Behavioral evidence for host-race formation in Eurosta solidaginis. Evolution 47, 1696–1710. ( 10.1111/j.1558-5646.1993.tb01262.x) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Wood TK, Olmstead KL, Guttman SI. 1990. Insect phenology mediated by host-plant water relations. Evolution 44, 629–636. ( 10.1111/j.1558-5646.1990.tb05943.x) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Berlocher SH, Feder JL. 2002. Sympatric speciation in phytophagous insects: moving beyond controversy? Annu. Rev. Entomol. 47, 773–815. ( 10.1146/annurev.ento.47.091201.145312) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Taylor RS, Friesen VL. 2017. The role of allochrony in speciation. Mol. Ecol. 26, 3330–3342. ( 10.1111/mec.14126) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Cavender-Bares J, Pahlich A. 2009. Molecular, morphological, and ecological niche differentiation of sympatric sister oak species, Quercus virginiana and Q. geminata (Fagaceae). Am. J. Bot. 96, 1690–1702. ( 10.3732/ajb.0800315) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Zhang L, Driscoe A, Izen R, Toussaint C, Ott JR, Egan SP. 2017. Immigrant inviability promotes reproductive isolation among host-associated populations of the gall wasp Belonocnema treatae. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 162, 379–388. ( 10.1111/eea.12548) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Forbes AA, Hall MC, Lund J, Hood GR, Izen R, Egan SP, Ott JR. 2016. Parasitoids, hyperparasitoids, and inquilines associated with the sexual and asexual generations of the gall former, Belonocnema treatae (Hymenoptera: Cynipidae). Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 109, 49–63. ( 10.1093/aesa/sav112) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Busbee RW. 2018. Host plant and spatial influences on the natural enemy community structure of a host specific insect herbivore. MSc thesis, Texas State University, San Marcos, TX. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Egan SP, Hood GR, DeVela G, Ott JR. 2013. Parallel patterns of morphological and behavioral variation among host-associated populations of two gall wasp species. PLoS ONE 8, e54690 ( 10.1371/journal.pone.0054690) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Hood GR, Zhang L, Topper L, Brandão-Dias PFP, Del Pino GA, Comerford MS, Egan SP. 2018. ‘Closing the Life Cycle’ of Andricus quercuslanigera (Hymenoptera: Cynipidae). Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 111, 103–113. ( 10.1093/aesa/say005) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Bird JP, Melika G, Nicholls JA, Stone GN, Buss EA. 2013. Life history, natural enemies, and management of Disholcaspis quercusvirens (Hymenoptera: Cynipidae) on live oak Trees. J. Econ. Entomol. 106, 1747–1756. ( 10.1603/ec12206) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Ananthakrishnan 1925- TN. (ed.). 1984. Biology of gall insects (ed. TN Ananthakrishnan) New Delhi, India: Oxford & IBH. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Egan SP, Hood GR, Martinson EO, Ott JR. 2018. Cynipid gall wasps. Curr. Biol. 28, R1370–R1374. ( 10.1016/j.cub.2018.10.028) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Stone GN, Schönrogge K, Atkinson RJ, Bellido D, Pujade-Villar J. 2002. The population biology of oak gall wasps (Hymenoptera: Cynipidae). Annu. Rev. Entomol. 47, 633–668. ( 10.1146/annurev.ento.47.091201.145247) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Lund JN, Ott JR, Lyon RJ. 1998. Heterogony in Belonocnema treatae Mayr (Hymenoptera: Cynipidae). Proc. Entomol. Soc. Wash. 100, 755–763. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Gagné RJ, Riley EG. 1999. A new gall midge (Diptera: Cecidomyiidae) pest of live oak in Texas. Southwest. Entomol. 24, 159–165. [Google Scholar]
- 26.LeBlanc DA, Lacroix CR. 2001. Developmental potential of galls induced by Diplolepis rosaefolii (Hymenoptera: Cynipidae) on the leaves of Rosa virginiana and the influence of Periclistus species on the Diplolepis rosaefolii galls. Int. J. Plant Sci. 162, 29–46. ( 10.1086/317900) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Ronquist F. 1994. Evolution of parasitism among closely related species: phylogenetic relationships and the origin of inquilinism in gall wasps (Hymenoptera, Cynipidae). Evolution 48, 241–266. ( 10.1111/j.1558-5646.1994.tb01310.x) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Lenth R, Singmann H, Love J, Buerkner P, Herve M. 2019. emmeans: estimated marginal means, aka least-squares means. R package version 1.4 See https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=emmeans.
- 29.Pinheiro J, Bates D, DebRoy S, Sarkar D, R Core Team. 2019. nlme: Linear and nonlinear mixed effects models. R package version 3.1–141 See https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=nlme.
- 30.Feder JL, Hunt TA, Bush L. 1993. The effects of climate, host plant phenology and host fidelity on the genetics of apple and hawthorn infesting races of Rhagoletis pomonella. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 69, 117–135. ( 10.1111/j.1570-7458.1993.tb01735.x) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Sirkiä PM, McFarlane SE, Jones W, Wheatcroft D, Ålund M, Rybinski J, Qvarnström A. 2018. Climate-driven build-up of temporal isolation within a recently formed avian hybrid zone. Evolution 72, 363–374. ( 10.1111/evo.13404) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Santos H, Rousselet J, Magnoux E, Paiva M-R, Branco M, Kerdelhué C. 2007. Genetic isolation through time: allochronic differentiation of a phenologically atypical population of the pine processionary moth. Proc. R. Soc. B 274, 935–941. ( 10.1098/rspb.2006.3767) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Fukami H, Omori M, Shimoike K, Hayashibara T, Hatta M. 2003. Ecological and genetic aspects of reproductive isolation by different spawning times in Acropora corals. Mar. Biol. 142, 679–684. ( 10.1007/s00227-002-1001-8) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Forister ML, et al. 2015. The global distribution of diet breadth in insect herbivores. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 112, 442–447. ( 10.1073/pnas.1423042112) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Zhang L, Hood GR, Ott JR, Egan SP. . 2019. Temporal isolation between sympatric host plants cascades across multiple trophic levels of host-associated insects Dryad Digital Repository ( 10.5061/dryad.h44j0zpf9) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Citations
- Zhang L, Hood GR, Ott JR, Egan SP. . 2019. Temporal isolation between sympatric host plants cascades across multiple trophic levels of host-associated insects Dryad Digital Repository ( 10.5061/dryad.h44j0zpf9) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
Data are available from the Dryad Digital Repository: https://dx.doi.org/10.5061/dryad.h44j0zpf9 [35].