Abstract
The black blow fly, Phormia regina (Meigen) (Diptera: Calliphoridae) is one of the most abundant carrion flies in North America. Calliphorids are important in agriculture and animal production, veterinary sciences, forensics and medical entomology. While the role of flies in the epidemiology of human and animal diseases is an active area of research, little is known about the microorganisms associated with these insects. We examined the diversity of wild-caught black blow fly endogenous (internal body) and exogenous (external body) microbial communities using 16S rRNA gene sequencing. Overall, 27 phyla, 171 families and 533 genera were detected, and diversity was significantly higher (P < 0.05) on external body surfaces. At the genus level, Dysgonomonas, Ignatzschineria, Acinetobacter, Vagococcus, Myroides, and Wohlfahrtiimonas were predominant. Cloning and sequencing of nearly full-length fragments of the 16S rRNA gene showed that some of the species identified are known to be pathogenic to humans, animals, and plants. Myroides odoratimimus and Acinetobacter radioresistens are well-known, multi-drug resistant bacteria. These results provide a snapshot of the microbial communities harbored by adult black blow flies and call for more comprehensive studies to better characterize the role these flies may play in the transmission of pathogenic microorganisms.
Subject terms: Ecology, Microbiology
Introduction
Blow flies (Diptera: Calliphoridae) are a group of medium to large flies with a worldwide distribution, usually harboring bright or metallic colors1. In calyptrate flies, calliphorids represent about 1,500 described species and account for 8% of species diversity2,3. They are saprophagous/necrophagous insects, breeding in decaying organic matter of plant and animal origins and are of medical4–6, veterinary/agricultural7, and forensic importance8,9. For example, adult calliphorids are known to be the first insects to colonize animal and human remains and are frequently used in the estimation of the minimum postmortem interval (minPMI) in medico-legal investigations10. Several species of blow flies, such as the primary screwworm, Cochliomyia hominivorax (Coquerel) and the Australian sheep blow fly, Lucilia cuprina (Wiedmann) (Diptera: Calliphoridae), are notorious myiasis (flystrike) agents in livestock causing hundreds of millions of dollars in economic losses7,11.
The presence of blow flies in microbe-rich substrates, such as manure, carrion and corpses, confer them a high probability of encountering/interacting with a large variety of microorganisms such as bacteria12, while their synanthropic nature (association with human environments) as well as strong flight abilities13, allow them to potentially disseminate those organisms over long distances into human habitat; they have the potential of infecting different substrates through contact by just landing on a surface but also by regurgitation of their gut content and defecation14–16. In addition, it has also been shown that blow flies can carry and mechanically transmit several bacterial pathogens, including Burkholderia pseudomallei17, Providencia rettgeri, Morganella morganii, Klebsiella spp. and Staphylococcus aureus18; Escherichia coli19,20; and Helicobacter pylori21.
The black blow fly, Phormia regina (Meigen) (Diptera: Calliphoridae), the focus of this paper, is a Holarctic fly and is distributed throughout the Northern Hemisphere22. In the USA, P. regina is typically a cold weather fly, as it is more abundant during the “chilled” summer months in the Northern part of the US while being more frequent in the cooler months of spring and fall in the South23,24. However, high population densities of P. regina have previously been recorded during the summer in Kansas25 and California26. Phormia regina has been of interest since it is one of the most abundant carrion flies in North America27 and is one of the primary insects used to estimate the minimum postmortem interval (minPMI) in forensic entomology28. Phormia regina is also listed by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) as one of the 22 pests (the “Dirty 22”) that could potentially spread food-borne pathogens29 and is an important research model for the study of fly physiology30–32. Several studies have been conducted on P. regina morphology33, genomics27, biology and ecology9,34–36, including aspects of the interactions that exist between this species and bacteria37. However, studies that investigated the microbial communities in free-flying, wild-type adult P. regina using 16S rRNA gene sequencing are absent. Weatherbee et al.37 investigated the internal microbiome of P. regina collected from swine carcasses but focused on third-stadium larvae. Russell et al.38 investigated the presence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria in adult Calliphorids collected from piglet cadavers introduced into a forest environment but only identified the flies to the family level. Also, the study was based on culture-dependent techniques.
In the present study, we investigated the endogenous and exogenous bacterial microbiomes of wild-caught adult black blow flies collected in a suburban environment using high-throughput 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing. We hypothesized that (i) the microbial communities from these two regions of the fly body would be different, (ii) bacterial diversity on the outside will be higher compared to the gut and (iii) the flies collected will harbor known pathogenic bacteria.
Material and Methods
Fly collection, identification, and initial sample preparation
Adult blow flies (mixed sexes) were collected at the Lake Wheeler Road experiment station at NC State University (NCSU), Raleigh, North Carolina in November 2017. This field station contains several animal production systems including a feed mill laboratory, equine education center, poultry waste management facility, etc.) and plant-related units (an agroecology farm, soil & water research center, etc.). This experiment station is located close to the main NCSU campus and urban areas in the city. Blow flies are strong fliers and highly adapted to evasion making it difficult to collect them individually in flight or after they have landed, therefore, an effective alternative approach is trapping. Flies were collected at a dump site (35°43′50.54′′N, 78°42′13.52′′W) using a Captivator fly trap jug (Starbar Products, Schaumburg, IL, USA) that contained 900 ml of a Flies-Be-Gone fly attractant solution (Flies-Be-Gone, Toms River, NJ, USA) (Fig. S1). The jug was covered with window screening (Model FCS8678-M, Saint-Gobain ADFORS, Grand Island, NY, USA) to prevent fly access to the attractant solution, and the trap was placed beneath a partially screened pyramid. The 1.2 m × 1.2 m × 1.2 m pyramid was constructed with standard framing lumber, and the screen was attached to the upper half with staples. Attracted flies that entered the pyramid were trapped at the top in an inverted 1.9 L Rubbermaid food storage canister (Model #007420216, Walmart, Raleigh, NC, USA). To prevent contamination of the flies from the trapping container itself, this container was washed with detergent, rinsed with sterile water and then cleaned with 95% ethanol. To reduce possible fly-fly interactions and fly-trap-fly interactions from affecting the fly microbiome, flies were collected only one hour after placement of the fly trap and transferred to the laboratory immediately. Flies were placed individually in 1.5 ml sterile microcentrifuge tubes (USA Scientific, Ocala, FL, USA), and the surface microbiota was collected by rinsing each fly 5 times, each time in 200 µl of sterile phosphate-buffered saline (PBS, Cat #00-3000, Invitrogen, MD, USA). All washes per fly were pooled into a 2 mL sterile microcentrifuge tube. The pooled surface washes (per fly) as well as the adult flies were then stored at −40 °C until further use. The flies were identified based on morphological characteristics39.
DNA extraction and quantification
Prior to endogenous microbial DNA extraction, each adult fly was surface sterilized using 70% ethanol (30 s) followed by 1% bleach in water (30 s) and then washed 5 times with sterile water. The final washes were pooled together for subsequent verification of sterility. DNA extraction from internal (12 endogenous samples) and external body (12 exogenous samples) extracts was modified from Ponnusamy et al.40. Briefly, the pooled exogenous PBS wash (1 mL) was lyophilized and reconstituted with 200 µL of TNE buffer. For endogenous sampling of the microbiome, each fly was transferred to a sterilized screw cap 2 mL microcentrifuge tube (Catalog # 02-681-344, Fisher Scientific, Pittsburgh, PA, USA) containing 10 sterilized 3 mm solid glass beads (Catalog #11-312 A, Fisher Scientific, Pittsburgh, PA, USA) each and was homogenized in 200 µL TNE buffer using the FastPrep FP120 system (Thermo Electron Corporation, Waltham, MA, USA) for 30 s. For lysis, we added 160 µL of lysis buffer 1 (TNE buffer [100 mM Tris, 0.2 M NaCl, 10 mM EDTA, pH 7.4] containing 20 µL of proteinase K and 20 µl lysozyme). The samples were then incubated at 37 °C for 1 h. After which 200 µl of lysis buffer 2 (1% cetyltrimethylammonium bromide [CTAB], 1.5 M NaCl, 0.5 M Tris-HCl [pH 8.0], 0.1 M EDTA [pH 8.0]) was added, and the samples were further incubated at 56 °C for 1 h. The use of the whole body to sample the endogenous microbiome allowed us to account for bacteria present internally but localized to organs other than the gut. DNA was isolated through phenol-chloroform extraction and ethanol precipitation, and the resulting DNA was resuspended in 100 µl of molecular grade water. The DNA samples were further purified using the Wizard DNA cleanup system (Promega, Madison, WI, USA). The DNA quality and quantity were assessed using a NanoDrop 1000 Spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). The total genomic DNA was normalized to 50-100 ng/µl and stored at −40 °C until PCR amplification.
16S rRNA gene amplification and NGS sequencing
To characterize the bacterial communities present in the samples (see S1 File), the hypervariable V4 region of the 16S rRNA gene was targeted using the 515 F (GTGCCAGCMGCCGCGGTAA) and 806 R (GGGACTACHVGGGTWTCTAAT) primers41. The 16S rRNA sequencing libraries were constructed according to the Illumina’s 16S rRNA metagenomics sequencing library preparation protocol (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA). During library preparation, the amplicon products were cleaned following each PCR round using magnetic beads from the AxyPrep Mag PCR Clean-up kit (AXYGEN, Big Flats, NY, USA), and the size of the amplicons was verified each time on a 1.5% agarose gel. One endogenous sample failed to generate PCR amplicons and was excluded. Illumina sequencing libraries were constructed for all 23 remaining samples (11 endogenous and 12 exogenous), and amplicon DNA concentration was measured with Quant-iT PicoGreen (Molecular Probes, Inc. Eugene, OR, USA). Final libraries were pooled in equimolar amounts. Illumina sequencing (250-bp paired-ends) was performed at the Microbiome Core Facility, School of Medicine, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, NC, USA.
Bioinformatics and statistical analyses
The sequencing data were processed using the Quantitative Insights Into Microbial Ecology 2 (QIIME2) program42. Illumina paired-end sequence reads were first demultiplexed to assign the sequences to their sample of origin using the QIIME2 demux emp-paired command and then quality filtered using the DADA243 algorithm as a QIIME2 plugin. Through the DADA2 pipeline, the paired-end reads were joined together, denoised, and chimeras, as well as residual PhiX reads, were removed. This results in the identification of all unique bacterial sequences called amplicon sequence variants (ASVs) which are technically equivalent to 100% OTUs but without errors44,45. Primers sequences were trimmed off the reads, but the sequences were not truncated to increase the chances of joining the paired-end reads efficiently. The 16S rRNA gene sequence variants (representative sequences) were assigned taxonomic classification using a pretrained Naïve Bayes classifier which was trained on the Greengenes database (gg_13_8, 99% OTUs, as recommended in QIIME2)46. Taxonomy was assigned using the Qiime feature-classifier classify-sklearn command. To calculate the statistical difference between the exogenous and endogenous groups, relative abundances of taxa with abundance higher than 1% (across all samples) were arcsine square root transformed, and a Welch two-sample t-test47 was run using abundances from each sample as replicates. Relative abundance data were imported from QIIME2 into the R statistical software48 for running the t-tests.
Prior to computing diversity metrics, the representative sequences obtained after DADA2 were aligned and masked to remove gaps, and a mid-point rooted phylogenetic tree was constructed using the QIIME2 FastTree 2 plugin49. To avoid biases due to sample-based variations in library sizes and to retain all of our samples in the subsequent analyses, each sample was rarefied to a depth of 18,000 sequences per sample. Alpha diversity was estimated by the Shannon index (integrates both richness and evenness)50, the number of observed OTUs (ASVs), and Faith’s phylogenetic index51. The statistical significance of alpha diversity between groups (exogenous and endogenous samples) was inferred using pairwise Kruskal-Wallis H-tests. Beta diversity was calculated using the weighted UniFrac52 metric, and a PERMANOVA test was run to determine if there was any statistical difference between the two treatment groups. The principal coordinate analysis (PCoA) result was visualized using EMPEROR53.
16S rRNA gene cloning and sequencing
The short-read length of sequences produced by the Illumina MiSeq platform limited taxonomic resolution during taxonomy assignment of the 16S rRNA gene sequences. To improve classification, especially for the most abundant taxa (relative abundance ≥10% across all samples), a nearly full-length fragment of the 16S rRNA gene was amplified using the universal bacterial primers, 27 f and 1492r54 following a protocol previously described in Ponnusamy et al.55. DNA from four fly samples that contained the highest abundances of the targeted taxa were used (Table 1). In order to construct the 16S clone libraries, the PCR products were verified for their sizes on a 1.5% agarose gel stained with ethidium bromide and purified using the AxyPrep Mag PCR Clean-up kit. Purified PCR products from each sample were cloned into the pGEM-T Vector (Promega) as per manufacturer’s instructions. Colonies were picked at random, and the presence of the insert was verified by amplifying the clones with the vector primers M13F (CCCAGTCACGACGTTGTAA AACG) and M13R (AGCGATAACAATTTCACACAGG). In total, 30 colonies with inserts were first Sanger sequenced using only the M13F primer, and the sequencing results were blasted against the BLASTn (Basic Local Alignment Search Tool) sequence database to identify homologous sequences and examine phylogenetic relationships. Then, four colonies (one per sample/targeted taxa) were further Sanger sequenced using two additional internal primers (520F, 968F or 518R, 984R) based on the direction in which the insert was cloned into the vector. Sanger sequencing for all samples was done at Eton Bioscience, Inc (Research Triangle Park, NC, USA).
Table 1.
Overall relative abundances (%) across samples at the family level.
| Sample IDs | Porphyromonadaceae | Xanthomonadaceae | Moraxellaceae | Enterococcaceae | Enterobacteriaceae | Pseudomonadaceae | Flavobacteriaceae |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fi2 | 73.56 | 18.04 | 0 | 0.48 | 0.305 | 0.02 | 0 |
| Fi3 | 47.51 | 27.5 | 0 | 1.6 | 0.101 | 0.03 | 0 |
| Fi4 | 51.41 | 26.69 | 0 | 1.62 | 0.038 | 0.04 | 0 |
| Fi5 | 6.18 | 12.19 | 0 | 5.27 | 0.25 | 0.046 | 0.05 |
| Fi6 | 65.01 | 19.89 | 0 | 0.6 | 0.379 | 0.04 | 0 |
| Fi7 | 89.87 | 5.8 | 0 | 1.17 | 0 | 0.02 | 0 |
| Fi10 | 46.34 | 27.9 | 0 | 1.78 | 0.061 | 0.03 | 0 |
| Fi11 | 72.36 | 17.38 | 0 | 0.96 | 0.151 | 0 | 0 |
| Fi12 | 92.26 | 4.87 | 0 | 0.58 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Fi13 | 7.18 | 13.17 | 0 | 5.1 | 0.34 | 0.07 | 0.11 |
| Fi14 | 91.73 | 5.04 | 0 | 0.77 | 0.032 | 0.012 | 0 |
| Fo1 | 34.33 | 23.85 | 21.18 | 3.53 | 2.15 | 1.3 | 2.11 |
| Fo2 | 6.99 | 45.27 | 12.04 | 6.96 | 8.85 | 4.2 | 1.15 |
| Fo3 | 7.69 | 43.36 | 11.86 | 9.44 | 7.6 | 4.2 | 1.12 |
| Fo5 | 32.05 | 24.72 | 20.37 | 3.58 | 2.46 | 1.6 | 2.53 |
| Fo6 | 17.59 | 25.99 | 20.92 | 6.85 | 1.54 | 1.4 | 4.7 |
| Fo7 | 32.68 | 23.65 | 21.44 | 3.19 | 2.26 | 1.4 | 2.51 |
| Fo10 | 7.36 | 43.53 | 11.81 | 8.41 | 8.1 | 4.1 | 1.1 |
| Fo11 | 17.14 | 25.92 | 20.91 | 6.5 | 1.7 | 1.6 | 4.9 |
| Fo12 | 12.8 | 18.47 | 36.04 | 6.55 | 2.86 | 3 | 3.11 |
| Fo13 | 14.46 | 19.7 | 32.72 | 6.26 | 2.86 | 3.65 | 3.05 |
| Fo14 | 12.04 | 17.86 | 34.95 | 7.92 | 2.78 | 4.9 | 2.65 |
| Fo15 | 8.49 | 16.83 | 12.69 | 9.14 | 13.34 | 10.6 | 4.12 |
| Average all | 36.83 | 22.07 | 11.17 | 4.27 | 2.53 | 1.83 | 1.44 |
Sample IDs: Fi2 to Fi14, internal body (endogenous) sample; Fo1 to Fo15 external body (exogenous) sample.
Phylogenetic analyses of 16S rRNA gene clones
For each of the four colonies, each targeting a different taxon, the DNA sequences obtained using the M13F and two internal 16S rRNA gene primers were imported into the Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA version 7.0) software56. The sequences were aligned using the ClustalW program. Due to sequencing errors and low-quality reads towards the ends of the reads when using Sanger sequencing, a less error-bearing 16S rRNA gene DNA sequence was reconstructed by joining three DNA contigs (500-600 bp each) together using a minimum 100 bp overlap between the sequences. First, 16S rRNA gene sequences were screened for vector contamination using the NCBI VecScreen program and sequences that were identified to be of vector origin were removed. The final version of each 16S rRNA gene clone sequence was then blasted against the NCBI GenBank database using BLASTn. The 16S rRNA gene sequences were blasted against the NCBI 16S ribosomal RNA database on February 6, 2019. Clones with DNA sequences sharing 99-100% query coverage and at least 99% identity with GenBank sequences were assigned to that specific phylotype. Multiple alignments were performed using the ClustalW algorithm. The phylogenetic relationship between these clones and a selection of other closely related species was reconstructed using the kimura two-parameter model57 and neighbour-joining algorithms as implemented in the MEGA7 software package.
Results
Data summary
DNA extraction from pooled washes (from surface sterilization) yielded no bands on agarose gel after PCR amplification and thus was not sequenced. A total of 23 16S rRNA gene libraries from exogenous and endogenous P. regina extracts for each fly separately were subjected to Illumina paired-end sequencing. A total of 10,622,697 16S rRNA gene sequences were obtained. After quality filtering using DADA2, 7,684,848 reads remained with an average of 334,124 reads (minimum of 18,504 and maximum of 517,162). The remaining sequences were clustered into 2,452 sequence variants and assigned to 27 phyla, 171 families and 533 genera (with some further classified into species).
Alpha and beta diversity measures
The asymptotic shape of the rarefaction curves of the observed OTUs (ASVs) suggests that our sequencing depth of 18,000 was sufficient to capture the majority of taxa present in the samples (Fig. 1). Comparisons between outside and inside samples of the black blow flies revealed significant differences in alpha diversities. In fact, the number of observed ASVs was significantly higher from the outside samples compared to inside samples (Kruskal-Wallis, P < 0.001) (Fig. 2A). Similarly, Shannon diversity (Kruskal-Wallis, P < 0.001) (Fig. 2B) as well as phylogenetic diversity (Kruskal-Wallis, P < 0.001) (Fig. 2C) were significantly higher outside.
Figure 1.
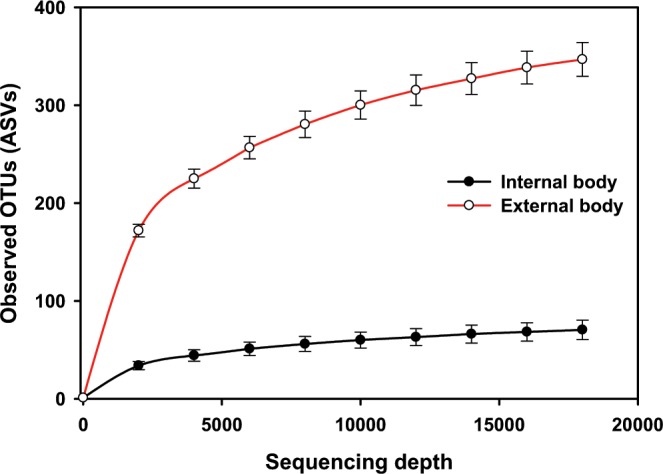
Rarefaction curves of the mean number of observed OTUs (sequence variants) in internal (endogenous) versus external body (exogenous) samples.
Figure 2.
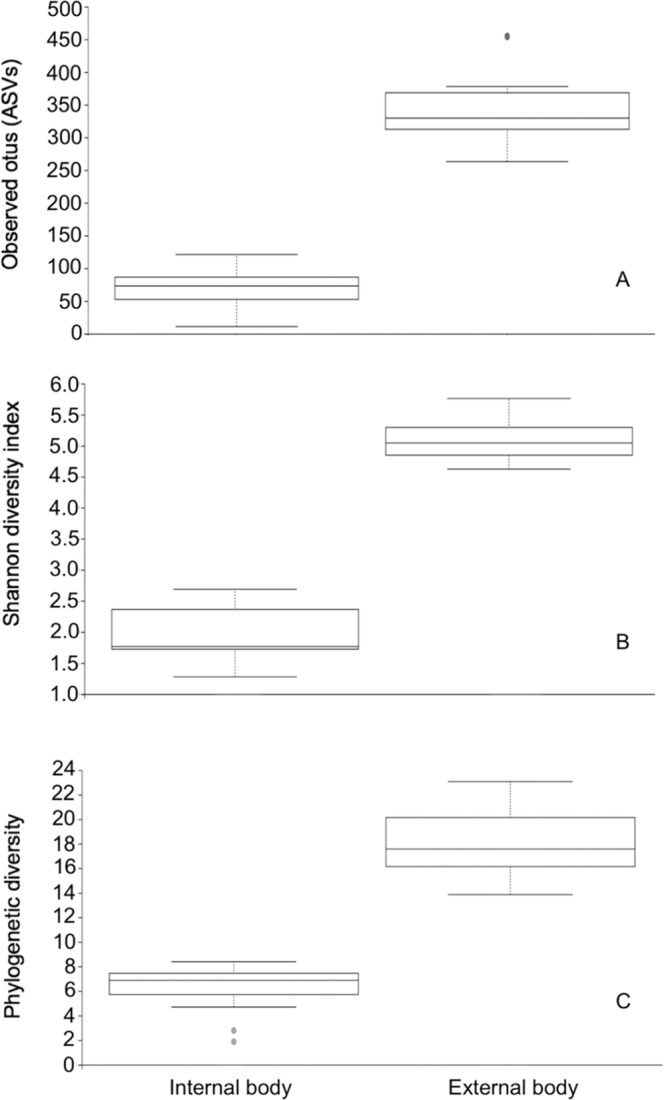
Alpha diversity measures of the internal (endogenous) and external body (exogenous) microbiomes of adult black blow flies. (A) Observed OTUs, (B) Shannon diversity and (C) Faith’s phylogenetic diversity.
Bacterial community difference between the two groups (β-diversity of exogenous vs. endogenous communities) was tested using the weighted Unifrac metric. This analysis revealed that the majority of the variation in bacterial diversity across the samples could be attributed to where the samples originated from (Fig. 3). Principal coordinates analysis showed distinct clustering of exogenous and endogenous samples, suggesting differences in the microbial communities of these groups (Fig. 3). This was further confirmed by a permutation multivariate analysis of variance (PERMANOVA) which found a significant difference between these groups at the β-diversity level (PERMANOVA, P = 0.001).
Figure 3.
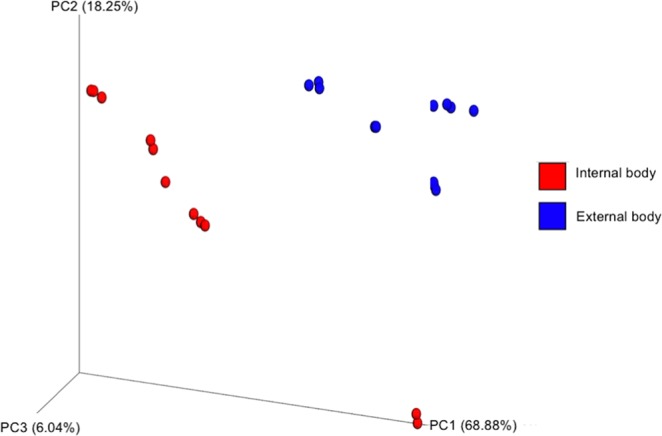
Principal coordinate analysis of bacterial composition between internal (endogenous) and external body (exogenous) samples of adult black blow flies. Analysis was based on the weighted Unifrac metric.
Bacterial community composition
Overall, the most sequence-abundant bacterial taxa at the phylum level were Proteobacteria (50.6%), Bacteroidetes (38.9%), Firmicutes (8.5%) and Actinobacteria (1.1%) (Fig. S2; see S2 File). Seven families were found to be the most sequence-rich and include Porphyromonadaceae (36.8%), Xanthomonadaceae (22.1%), Moraxellaceae (11.2%), Enterococcaceae (4.3%), Enterobacteriaceae (2.5%), Flavobacteriaceae (1.4%) and Pseudomonaceae (1.8%) (Table 1). At the highest taxonomic resolution (level 7, species level), most taxa were classified up to the genus level. In general, and across all samples, 6 genera were identified to be the most abundant: Dysgonomonas (36.8%), Ignatzschineria (20.6%), Acinetobacter (10.0%), Vagococcus (3.8%), Myroides (1.1%, further classified into species see Fig. 4) and Wohlfahrtiimonas (1.1%) (Fig. 4; see S2 File). These taxa were all differentially abundant between the two sites on the fly (Welch’s t-test, P < 0.05). In the exogenous samples, Dysgonomonas (16.9%), Ignatzschineria (24.9%), Acinetobacter (19.2%), Vagococcus (5.6%), Myroides (2.2%) and Wohlfahrtiimonas (1.8%) were the most abundant. The endogenous samples harbored Dysgonomonas (58.5%), Ignatzschineria (15.9%) and Vagococcus (1.8%), as the most abundant genera. Myroides (0.01%) and Acinetobacter (0.01%) were almost absent from the inside samples while Wohlfahrtiimonas had a very marginal relative abundance (0.3%) (Fig. 4). A bacterial taxon with 10% of the reads was classified only to the class level as a Betaproteobacteria (Fig. 4).
Figure 4.
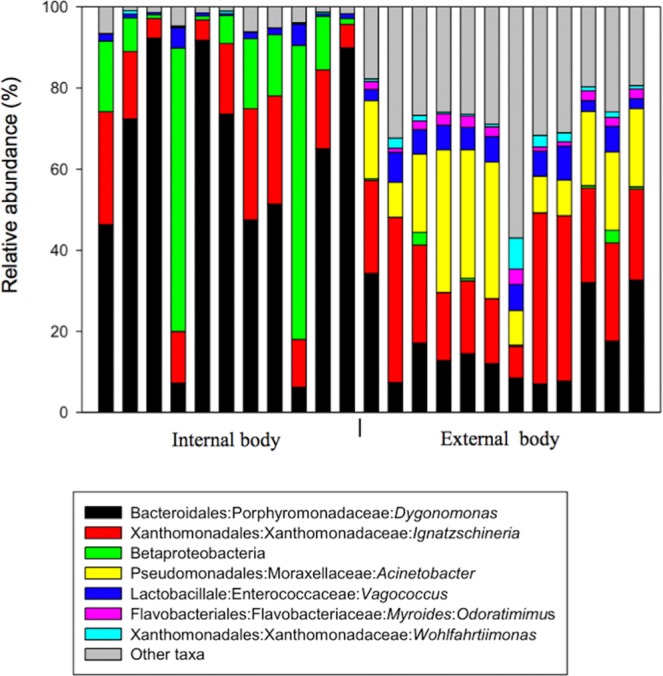
Relative abundance of major bacteria in internal (11 samples) and external body (12 samples) DNA samples from P. regina adults at the highest taxonomic resolution. Bars represent proportions of each taxa. “Other taxa” refers to all the taxa with relative abundance below 1% over the total number of reads. Ten per cent of the reads (10%) of the reads across all samples were classified as Betaproteobacteria. In the legend from left to right: Order:Family:Genus:Species.
We also compared the bacterial diversity between individuals for the 7 predominant taxa found on the outside of the flies, the relative abundance of Dysgonomonas ranged from 7 to 34%; for Ignatzschineria ranged from 8 to 42%; for Betaproteobacteria ranged from 0.02 to 0.3%; for Acinetobacter, from 8 to 35%; for Vagococcus, from 2 to 8%; for Myroides odoratimimus, from 1 to 4%; for Wohlfahrtiimonas, from 0.4 to 8%. Furthermore, we detected several low relative abundance (<1%) bacteria (i.e. Sphingobacterium multivorum, Faecalibacterium prausnitzii, Psychrobacter pulmonis) found on some flies not found on others (see S2 File).
16S rRNA gene cloning and phylogeny results
All 30 16S rRNA cloned colonies that were Sanger sequenced using the M13 primers matched to their respective targeted taxa when the clone sequences were blasted against the NCBI database (http://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/). The nearly full-length reconstructed 16S rRNA gene clones had an average length of 1496 bp. The 16S rRNA gene clone sequence “Clone A1” matched to the species Ignatzschineria ureiclastica strain FFA (NR_116121.1) and Ignatzschineria larvae DSM 13226 (NR_025381.1) with 99% similarity. BLASTn searches with “Clone B9” affiliation to the species Acinetobacter radioresistens with 99% similarity to both the strains NBRC 102413 (NR_114070.1) and FO-1 (NR_026210.1). The first three highest BLAST matches for “Clone C8” were 16S rRNA gene sequences from Dysgonomonas capnocytophagoides strain JCM 16697 (NR_113133.1) (93%), Dysgonomonas capnocytophagoides strain CDC F9047 (NR_044778.1) (93%) and Dysgonomonas alginatilytica strain HUA-2 (NR_137388.1) (92%). The first four top hits after BLAST searches for “Clone D17” were: Paraburkholderia rhizoxinica strain HKI 454 (NR_102769.1) (94%), Paraburkholderia rhizoxinica strain HKI 454 (NR_042393.1) (94%), Burkholderia rinojensis strain A396 (NR_118637.1) (94%) and Paraburkholderia endofungorum strain HKI 454 (NR_042584.1) (94%).
The sequences used for constructing the trees were type species retrieved from the Ribosomal Database Project hierarchy browser (RDP; http://rdp.cme.msu.edu/)58. The 16S “CLONE A1” was placed within the genus Ignatzschineria (bootstrap value = 100) and more similar to Ignatzschineria larvae (Fig. S3). Clone B9 was more closely related to Acinetobacter radioresistens (bootstrap value = 100) within the Acinetobacter genus (Fig. S4). The placement of Clone C8 within the genus Dysgonomonas was well supported (bootstrap value = 100) and was more closely related to both Dysgonomonas capnocytophagoides and Dysgonomonas macrotermitis (Fig. 5). The phylogenetic tree revealed that the cloned sequence “Clone D17” was placed in a completely different clade from the genus Burkholderia sensus lato (Fig. S5).
Figure 5.
Neighbour-joining tree based on 16S rRNA gene sequences showing the relationship between cloned sequences from Phormia regina adults and sequences of other closely related bacterial species. Clone “16S CLONE C8” originated from sample (Fi12) that contained 92% of sequences assigned to the genus Dysgonomonas. Aquifex pyrophilus was used as an outgroup. The sequences were aligned using the ClustalW algorithm. Bootstrap values based on 500 replications, are given at the branching nodes. Bar represents 0.05 substitutions per nucleotide position.
Discussion
In this study, we investigated, for the first time, the bacterial microbiome associated with the internal body (endogenous) and external body surfaces (exogenous) of Phormia regina adults collected from the wild in a suburban area but associated with a multi-use animal and Ag research production system in the NCSU campus. The study revealed the presence of several bacterial taxa that were, most of the time differentially abundant between the two environments. The results also showed that these flies harbored an appreciable number of potentially pathogenic as well as several potentially multi-drug resistant bacteria.
Our findings revealed the number of observed ASVs (OTUs), Shannon diversity, and Faith’s phylogenetic diversity were all significantly higher in the outside samples representing DNA extracted from the surface of each fly. This demonstrates that diversity was higher on the external surface of the fly’s body compared to the gut and therefore the flies harbored more different bacterial species on the outside of their bodies. This result was not unexpected and has been shown previously in flies. For example, using culture-dependent techniques, Adeyemi et al.59 demonstrated that both the number and variety of bacteria isolated from external surfaces of filth flies were significantly higher compared to the gut. One possible reason for higher diversity on the fly surface is the availability of high microbe-laden feeding/breeding sites; black blow flies are known for example to frequently visit human and/or animal dung60. In addition, blow flies, house flies, and flesh flies have adhesive pads between the tarsal claws of their legs called pulvilli which are covered in fine hairs or “tenant setae”. The setae have been shown to secrete an adhesive substance to increase surface area for attachment to smooth surfaces but are also deemed to retain many microorganisms on the legs21,61–63. Microorganisms also attach to other body parts such as the wings, the mouthparts and abdomen21,62.
Although the transfer of bacteria between flies during the trapping period cannot be ruled out, there was no indication that the trapping method was an issue. Alpha diversity and bacterial community composition analyses showed that the exogenous microbiomes were not homogenous between the flies; variability was determined to have resulted from differences in bacterial composition and taxonomic abundances between samples. Additionally, minor taxa (abundances <1%) included several bacterial species that were detected on some flies while absent (relative abundance of 0%) on others, suggesting that the exogenous samples were independent. Further, the timing (November) and the methods by which trapping was conducted permitted the collection of a single species (Phormia regina). Trapping of a single species mitigated potential contamination of our target flies by bacteria associated with other flies.
As shown in the PCoA plot for the abundance-weighted UniFrac distance, the exogenous samples formed a cluster that is separated from the endogenous samples. This could be due to the differential abundance of some important bacterial taxa between the two environments but also to the presence/absence aspects of those taxa from one environment to another (discussed more later).
Overall, Proteobacteria, Bacteroidetes, Firmicutes and Actinobacteria were the predominant phyla in our samples. This result is in agreement with findings in houseflies64, fruit flies65, flesh flies66 and other blow flies21,37,67. It is worth noting that the overall average relative abundances of the last four families were essentially driven by outside samples as members from those families were barely detected in inside samples (abundances ranging between 0 and 0.15%). No Moraxellaceae was detected inside. A similar trend was also observed by Weatherbee et al.37 who investigated the internal microbial communities of third-instar specimens of P. regina as well as the external microbiome of the larval mass (larva aggregate composed of multiple fly species including P. regina) present on swine carcasses at different time points. At 132 and 156 h after carcass placement, where P. regina larvae were the most predominant species (over 85% of the larval mass), several taxa at the family level identified outside were not detected within the larvae. These results suggest that both the immature and adult stages of P. regina may selectively control the gut bacteria either through digestion or other unknown mechanisms. Several families (Bacteroidaceae and Bifidobacteriaceae) identified among the 10 most abundant families in the swine carcass study were marginally present in our samples while Porphyromonadaceae, the most abundant family taxon found internally in this study, was not present and/or abundant within P. regina larvae. These differences may be due to several factors including developmental stage-related differences (adults and larvae may be differentially associated with certain types of bacteria), the geographic locations of the studies (Indiana vs. North Carolina) as well as the feeding sources available to the flies and different bacteria or differences in bacteria abundance in the available feeding sources. All those factors have been shown to significantly impact the microbiomes of several insects68.
At the genus level, Dysgonomonas, Ignatzschineria, Acinetobacter, Vagococcus, Myroides, and Wohlfahrtiimonas were the most predominant taxa in our study. These genera, even though their relative abundance may vary, have been isolated from various insect species before. The majority of them, however, are frequently detected together (in 16S-based NGS studies) and often times in high abundances in insects associated with filth and most particularly in saprophagous and/or necrophagous insects/flies64–67,69,70. This result may be due to similar ecological niches in those insects and their overlapping range of feeding sources, an adaptation of these bacterial taxa to physicochemical conditions of the guts of these insects and to the role that these microorganisms may be playing in host nutrition and/or fitness.
Dysgonomonas, the genus with the highest abundance has been isolated from a burying beetle Nicrophorus vespilloides (Herbst) (Coleoptera: Silphidae)69, a bombardier beetle Brachinus elongatus (Chaudoir) (Coleoptera: Carabidae)45, a wood-feeding termite Reticulitermes speratus (Kolbe) (Isoptera: Rhinotermitidae)71, the common house fly Musca domestica (Diptera: Muscidae)64, the oriental latrine fly Chrysomya megacephala (Diptera: Calliphoridae)67, the Australian sheep blow fly, Lucilia cuprina (Wiedmann) and the common green bottle fly Lucilia sericata (Meigen) (Diptera: Calliphoridae). Similarly, results from analyses of this genus isolated from termites, dung beetles, black soldier flies and mosquitoes suggest that Dysgonomonas is implicated in the breakdown of carbohydrates namely cellulose and hemicellulose as well as the production of vitamin B1272–76. Whether Dysgonomonas plays similar roles in the black blow fly is yet to be confirmed. However, the high abundance of this genus in internal samples in this study points to that direction.
Ignatzschineria77 and Wohlfahrtiimonas78 were both originally described in the larvae of a parasitic fly, the spotted flesh fly Wohlfahrtia maginifica (Schiner) (Diptera: Sarcophagidae) a major myasis agent in animals66. Phylogenetically, they are two related genera but belong to two different lineages. These two genera have been isolated from other flesh flies66,79, house flies64, blow flies67,70 and carrion beetles69. Little is known about the role that members of these genera play in insects. However, they both exhibit strong chitinase activity, and Toth et al.77 have suggested a possible role of Ignatzschineria in metamorphosis. The role that they play in adult insects needs investigation. The genus Vagococcus was previously isolated from fruit flies80, house flies64, blow flies21,70, red imported fire ants, Solenopsis invicta81 and burying beetles69. They are deemed to produce antiviral metabolites in Aedes albopictus82, but nothing is known about their role in Phormia regina.
Acinetobacter was almost exclusively located externally (abundance inside was 0.01%). In fact, Acinetobacter spp. are widespread in natural environments and thus are frequently recovered from soil, polluted water, plants, animals and humans83. However, they have also been isolated from the guts of different insects84,85. For example, Coon et al.86, showed that the inoculation of Acinetobacter spp. restored larval development in axenic mosquito larvae while Minard et al.87 suggested they aided in the digestion of plant nectar consumed by Aedes albopictus mosquitoes. It was also suggested that they may help detoxify defensive plant compounds for tropical herbivorous beetles88. They also secrete antiparasitic compounds in the guts of several insects89. The presence of this genus on the outer body of the flies is probably of environmental origin; they may have been picked up mechanically from a contaminated source and may not have a function role in fly biology. It would be interesting to investigate if the bacteria could sustain the black blow fly gut environment and what possible role those bacteria could play.
Myroides odoratimimus, previously known as Flavobacterium odoratum90, was also exclusively observed in outside samples (abundance inside was 0.01%). Like some of the previous taxa described in this section, M. odoratimimus are ubiquitous in natural environments and are commonly found in soil, fresh and marine water, meat-processing plants and insects21,90,91. Myroides spp. are well known for their ability to secrete antimicrobial substances90, and thus it is possible that they help protect insects that harbor them against other pathogenic bacteria.
Based on our findings in P. regina, the absence of some taxa on the outside of the fly that are found internally and the fact that the most abundant taxa found inside are also present on the fly’s surface suggests that the microbial communities associated with black blow flies are acquired from the environment probably from feeding/breeding sites. Also, based on previous fly research, it is likely that the internal bacteria present may contribute to the host’s development. Most of the bacterial taxa identified in the P. regina microbiome contained known pathogens (discussed in more detail below).
Most reads (89%) obtained from Illumina sequencing were classified down to the genus level even for the most sequence-rich taxa (except for Betaproteobacteria and Myroides odoratimimus) thus limiting the depth of analysis of the results. A literature search revealed that some of those genera are well known to be pathogenic microorganisms. To improve taxonomic resolution and to verify the detection of potential pathogens in our samples, the first four identified taxa in terms of relative abundance (≥10%, Dysgonomonas, Ignatzschineria, Betaproteobacteria and Acinetobacter) were further targeted by developing nearly full length 16S rRNA gene clones and sequencing them using Sanger sequencing. The results showed some of the most abundant taxa in our samples may be new bacterial taxa and also confirmed the existence of potential human, animal and plant pathogens in our fly samples.
Our results suggest that some of our samples contained a new genus in Burkholderiaceae: Ten percent of the reads was classified as Betaproteobacteria, a class in the phylum Proteobacteria. BLASTn searches for “Clone D17” which was targeting that class for better identification revealed that the clone sequence was 94% similar to two strains of Paraburkholderia rhizoxinica, a strain of Burkholderia rinojensis and a strain of Paraburkholderia endofungorum. During phylogenetic analyses, Clone D17 was placed in a completely different clade from the genus Burkholderia sensus lato (s.l.). Therefore, the bacterium corresponding to that sequence constitutes a distinct lineage with no closely related allied 16S rRNA gene sequences and probably represents a novel genus in the family Burkholderiaceae, order Burkholderiales, class Betaproteobacteria in the phylum Proteobacteria. The genus Burkholderia sensus lato (s.l.) is the original genus described by Yabuuchi et al.92. Since then, the taxonomy of this genus has been evaluated several times with the addition of several new taxa, and today it is subdivided into 5 different groups or “sub-genera”93,94. The most interesting issue is that during the phylogenetic tree reconstruction, we made sure to include at least one member from each of the five groups (based on type species present in RDP), but Clone D17 was placed as a sister group to Burkholderia and Pandoraea with strong support (bootstrap value = 93). No assumptions can be made at the current stage about the pathogenicity of this potentially new genus.
Our results indicate that our samples contained a new Dysgonomonas species: The taxa previously classified as Dysgonomonas was targeted with Clone C8. The sequence from this clone had 93% similarity with two strains of Dysgonomonas capnocytophagoides and 92% similarity with a strain of Dysgonomonas alginatilytica based on BLASTn searches. Phylogenetically, it clustered with all the other Dysgonomonas (bootstrap value = 100) but was more closely related to both Dysgonomonas capnocytophagoides and Dysgonomonas macrotermitis with strong statistical support (bootstrap value = 100). These results suggest that this molecular isolate represents a potential new species within the genus Dysgonomonas, family Porphyromonadaceae, order Bacteroidales, class Bacteroidia in the phylum Bacteroidetes. Dysgonomonas capnocytophagoides, formerly known as CDC group DF-3 (Center for Disease Control group dysgonic fermenter-3) is an opportunistic bacterium associated with diarrhea and bacteremia95,96. Dysgonomonas macrotermitis, on the other hand, was only recently isolated from a fungus-growing termite72,97 and has not been associated with any disease so far. More work is needed to better characterize the bacterium represented by Clone C8 (this study).
New Ignatzschineria species: The sequence from “Clone A1” matched to the species Ignatzschineria ureiclastica and Ignatzschineria larvae with 99% similarity based on BLASTn searches conducted in February 2019. Clone A1 clustered together with all the species in the genus Ignatzschineria (bootstrap value = 100) in the phylogenetic analyses but was more closely related to Ignatzschineria larvae (bootstrap value = 75) which can cause bacteremia98. This finding is indicative of a potential new species in the genus Ignatzschineria, family Xanthomonadaceae, order Xanthomonadales, class Gammaproteobacteria within the phylum Proteobacteria.
Acinetobacter radioresistens: Both BLASTn searches and phylogenetic analyses revealed the sequence of Clone B9 belonging to the bacterium, A. radioresistens. It was originally isolated from cotton and soil99. Like several other members of the genus Acinetobacter, this species has emerged as an opportunistic human pathogen. It can cause septicemia100, nosocomial bloodstream infection and community-acquired infections in immune-compromised patients101,102 and has the potential to damage human epithelial kidney cells through the production of outer membrane vesicles (OMVs)103. A. radioresistens have also been shown recently to cause nosocomial bacterial infection outbreaks in research animals104. Another concerning fact about this species is its ability to withstand harsh environmental conditions as well as its strong and well-established resistance to several antimicrobials. In fact, A. radioresistens is highly resistant to desiccation and radiation105 and is known to be resistant to Carbapenem, a class of antibiotic normally highly effective against multidrug-resistant bacteria102,103,106,107.
Myroides odoratimimus: This bacterium is also an opportunistic pathogen causing a variety of diseases/infections of which some are life-threatening. M. odoratimimus can cause bacteremia, endocarditis, pericarditis, pneumonia and septic shock, urinary tract infections, calcaneal ulcer and several other important bacteria-related infections in humans64,66,108–111. This species can also cause lethal infections in fish112.
In addition to the taxa reported here as the most abundant (≥1%), it is important to note the detection in our samples of Pseudomonas viridiflava (relative abundance of 0.7%), a multi host plant pathogen. P. viridiflava causes foliar and stem necrosis as well as stem and root rot in a wide range of plants such as tomato, melon and eggplant113–115. Finally, in insects, Wohlfahrtiimonas chitiniclastica, the most frequently identified species of the genus Wohlfahrtiimonas is known to cause human infections21,66.
In summary, this study provides, for the first time, a snapshot of the bacterial communities harbored both internally and externally by free-flying, black blow flies. The results revealed that the flies harbored a higher diversity of bacterial species on their body surfaces probably owing to their ecology and behavior. Even though the majority of the most abundant bacterial taxa identified in this study have also been reported in other flies/insects, the presence of many potentially new taxa further confirms the necessity to conduct microbiome studies in insects in general but more importantly in synanthropic insects that breed in microbe-rich substrates such human and animal dung. Arguably, the most intriguing fact is the identification of known human, animal and plant pathogens such as Myroides odoratimimus, Acinetobacter radioresistens and Pseudomonas viridiflava on the fly body of which several are also resistant to several antibiotics.
Supplementary information
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by two DWFP (Deployed Warfighter Protection) grants, W911QY10004 with DWW as PI and W911QY1910003 with RMR as PI and Southeast Center for Agricultural Health and Injury Prevention (SCAHIP). JMD was also supported by an NCSU entomology teaching assistantship and a Fulbright scholarship. We are grateful to Dr. Charles S. Apperson for his comments on the manuscript.
Author contributions
J.Z., A.C. and S.D. collected the fly samples, and J.Z. extracted DNA from the samples. J.M.D., J.Z. and N.T. prepared the libraries for next-generation sequencing. J.M.D., N.T. and L.P. analyzed the data. J.M.D. wrote the original draft of the manuscript, and J.M.D., N.T., J.Z., A.C., S.D., M.H.R., D.W.W., R.M.R. and L.P. reviewed and edited the final version of the manuscript.
Data availability
The next-generation sequencing data associated with this study have been deposited in GenBank under SRA accession: PRJNA554278. Cloned sequences have been deposited in GenBank under accession numbers: MN172461-MN172464.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
is available for this paper at 10.1038/s41598-019-56733-z.
References
- 1.Hall, D. G. The Blowflies of North America. (Thomas Say Foundation; London, 1948).
- 2.Kutty SN, Pape T, Wiegmann BM, Meier R. Molecular phylogeny of the Calyptratae (Diptera: Cyclorrhapha) with an emphasis on the superfamily Oestroidea and the position of Mystacinobiidae and McAlpine’s fly. Syst Entomol. 2010;35:614–635. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3113.2010.00536.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Singh B, Wells JD. Molecular systematics of the Calliphoridae (Diptera: Oestroidea): evidence from one mitochondrial and three nuclear genes. J Med Entomol. 2013;50:15–23. doi: 10.1603/me11288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Baumgartner DL, Greenberg B. Distribution and medical ecology of the blow flies (Diptera: Calliphoridae) of Peru. Ann Entomol Soc Am. 1985;78:565–587. doi: 10.1093/aesa/78.5.565. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Erzinclioglu YZ. The larvae of some blowflies of medical and veterinary importance. Med Vet Entomol. 1987;1:121–125. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2915.1987.tb00332.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Setyaningrum H, Al Dhafer HM. The calliphoridae the blow flies (Diptera: Oestroidea) of Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Egypt Acad J Biol Sci. 2014;7:49–139. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Bergamo LW, Fresia P, Lyra ML, Azeredo-Espin AML. High genetic diversity and no population structure of the new world screwworm fly Cochliomyia hominivorax (Diptera: Calliphoridae) on a microgeographic scale: Implications for management units. J Econ Entomol. 2018;111:2476–2482. doi: 10.1093/jee/toy171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Greenberg B. Flies as forensic indicators. J Med Entomol. 1991;28:565–577. doi: 10.1093/jmedent/28.5.565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Weidner LM, Gemmellaro MD, Tomberlin JK, Hamilton GC. Evaluation of bait traps as a means to predict initial blow fly (Diptera: Calliphoridae) communities associated with decomposing swine remains in New Jersey, USA. Forensic Sci Int. 2017;278:95–100. doi: 10.1016/j.forsciint.2017.06.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Cammack JA, Cohen AC, Kreitlow KL, Roe RM, Watson DW. Decomposition of concealed and exposed porcine remains in the North Carolina Piedmont. J Med Entomol. 2016;53:67–75. doi: 10.1093/jme/tjv183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Yan G, et al. Behavior and electrophysiological response of gravid and non-gravid Lucilia cuprina (Diptera: Calliphoridae) to carrion-associated compounds. J Econ Entomol. 2018;111:1958–1965. doi: 10.1093/jee/toy115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Nayduch D. Special collection: filth fly–microbe interactions. Ann Entomol Soc of Am. 2017;110:2–5. doi: 10.1093/aesa/saw084. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Nazni W, et al. Determination of the flight range and dispersal of the house fly, Musca domestica (L.) using mark release recapture technique. Trop Biomed. 2005;22:53–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Sasaki T, Kobayashi M, Agui N. Epidemiological potential of excretion and regurgitation by Musca domestica (Diptera: Muscidae) in the dissemination of Escherichia coli O157: H7 to food. J Med Entomol. 2000;37:945–949. doi: 10.1603/0022-2585-37.6.945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Pava-Ripoll M, Pearson REG, Miller AK, Ziobro GC. Prevalence and relative risk of Cronobacter spp., Salmonella spp., and Listeria monocytogenes associated with the body surfaces and guts of individual filth flies. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2012;78:7891–7902. doi: 10.1128/aem.02195-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.El-Bassiony GM, Stoffolano JG., Jr Comparison of sucrose intake and production of elimination spots among adult Musca domestica, Musca autumnalis, Phormia regina and Protophormia terraenovae. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed. 2016;6:640–645. doi: 10.1016/j.apjtb.2016.06.002. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Sulaiman S, Othman MZ, Aziz AH. Isolations of enteric pathogens from synanthropic flies trapped in downtown Kuala Lumpur. J Vector Ecol. 2000;25:90–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Förster M, et al. Pilot study on synanthropic flies (e.g. Musca, Sarcophaga, Calliphora, Fannia, Lucilia, Stomoxys) as vectors of pathogenic microorganisms. Parasitol Res. 2007;101:243–246. doi: 10.1007/s00436-007-0522-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Szalanski AL, Owens CB, McKay T, Steelman CD. Detection of Campylobacter and Escherichia coli O157:H7 from filth flies by polymerase chain reaction. Med Vet Entomol. 2004;18:241–246. doi: 10.1111/j.0269-283x.2004.00502.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Blaak H, et al. Detection of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL)-producing Escherichia coli on flies at poultry farms. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2014;80:239–246. doi: 10.1128/aem.02616-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Junqueira, A. C. M. et al. The microbiomes of blowflies and houseflies as bacterial transmission reservoirs. Sci Rep7, 10.1038/s41598-017-16353-x (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 22.Abdel-Hafeez EH, et al. Human wound myiasis caused by Phormia regina and Sarcophaga haemorrhoidalis in Minia Governorate, Egypt. Parasitol Res. 2015;114:3703–3709. doi: 10.1007/s00436-015-4599-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Núñez-Vázquez C, Tomberlin JK, Cantú-Sifuentes M, García-Martínez O. Laboratory development and field validation of Phormia regina (Diptera: Calliphoridae) J Med Entomol. 2013;50:252–260. doi: 10.1603/me12114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Wilson JM, Lafon NW, Kreitlow KL, Brewster CC, Fell RD. Comparing growth of pork- and venison-reared Phormia regina (Diptera: Calliphoridae) for the application of forensic entomology to wildlife poaching. J Med Entomol. 2014;51:1067–1072. doi: 10.1603/me14012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Savage EP, Schoof HF. The species composition of fly populations at several types of problem sites in urban areas. Ann Entomol Soc Am. 1955;48:251–257. doi: 10.1093/aesa/48.4.251. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Denno RF, Cothran WR. Competitive interactions and ecological strategies of sarcophagid and calliphorid flies inhabiting rabbit carrion. Ann Entomol Soc Am. 1976;69:109–113. doi: 10.1093/aesa/69.1.109. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Andere AA, Platt RN, Ray DA, Picard CJ. Genome sequence of Phormia regina Meigen (Diptera: Calliphoridae): implications for medical, veterinary and forensic research. BMC Genomics. 2016;17:842. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-3187-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Byrd JH, Allen JC. The development of the black blow fly, Phormia regina (Meigen) Forensic Sci Int. 2001;120:79–88. doi: 10.1016/s0379-0738(01)00431-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Olsen AR, Gecan JS, Ziobro GC, Bryce JR. Regulatory action criteria for filth and other extraneous materials V. strategy for evaluating hazardous and nonhazardous filth. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 2001;33:363–392. doi: 10.1006/rtph.2001.1472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Nascarella MA, Stoffolano JG, Stanek EJ, Kostecki PT, Calabrese EJ. Hormesis and stage specific toxicity induced by cadmium in an insect model, the queen blowfly, Phormia regina Meig. Environ Pollut. 2003;124:257–262. doi: 10.1016/s0269-7491(02)00479-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Stoffolano JG, Lim MA, Downer KE. Clonidine, octopaminergic receptor agonist, reduces protein feeding in the blow fly, Phormia regina (Meigen) J Insect Physiol. 2007;53:1293–1299. doi: 10.1016/j.jinsphys.2007.07.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Jordaens K, et al. DNA barcoding and the differentiation between North American and West European Phormia regina (Diptera, Calliphoridae, Chrysomyinae) ZooKeys. 2013;365:149–174. doi: 10.3897/zookeys.365.6202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Szpila, K. In Current Concepts in Forensic Entomology 43–56 (Springer Netherlands, 2010).
- 34.Stoffolano JG., Jr Influence of diapause and diet on the development of the gonads and accessory reproductive glands of the black blowfly, Phormia regina (Meigen) Can J Zool. 1974;52:981–988. doi: 10.1139/z74-130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Stoffolano JG, Danai L, Chambers J. Effect of channel blockers on the smooth muscle of the adult crop of the queen blowfly, Phormia regina. J Insect Sci. 2013;13:1–10. doi: 10.1673/031.013.9701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Stoffolano JG, Schauber E, Yin C-M, Tillman JA, Blomquist GJ. Cuticular hydrocarbons and their role in copulatory behavior in Phormia regina (Meigen) J Insect Physiol. 1997;43:1065–1076. doi: 10.1016/s0022-1910(97)00050-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Weatherbee CR, Pechal JL, Eric Benbow M. The dynamic maggot mass microbiome. Ann Entomol Soc Am. 2017;110:45–53. doi: 10.1093/aesa/saw088. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Russell SM, Chittick VA, Sangweme DT, Lampert EC. Potential of saprophage Diptera to acquire culturable livestock-associated antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Zoonoses and Public Health. 2018;65:e216–e221. doi: 10.1111/zph.12431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Marshall, S., Whitworth, T. & Roscoe, L. Blow flies (Diptera: Calliphoridae) of eastern Canada with a key to Calliphoridae subfamilies and genera of eastern North America, and a key to the eastern Canadian species of Calliphorinae, Luciliinae and Chrysomyiinae. Can J Arthropod Identification11 (2011).
- 40.Ponnusamy L, et al. Diversity of Rickettsiales in the microbiome of the lone star tick, Amblyomma americanum. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2014;80:354–359. doi: 10.1128/aem.02987-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Caporaso JG, et al. Ultra-high-throughput microbial community analysis on the Illumina HiSeq and MiSeq platforms. ISME J. 2012;6:1621–1624. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2012.8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Caporaso JG, et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat Methods. 2010;7:335–336. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.f.303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Callahan Benjamin J, McMurdie Paul J, Rosen Michael J, Han Andrew W, Johnson Amy Jo A, Holmes Susan P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nature Methods. 2016;13(7):581–583. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.3869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Callahan BJ, McMurdie PJ, Holmes SP. Exact sequence variants should replace operational taxonomic units in marker-gene data analysis. ISME J. 2017;11:2639–2643. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2017.119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.McManus R, Ravenscraft A, Moore W. Bacterial associates of a gregarious riparian beetle with explosive defensive chemistry. Front Microbiol. 2018;9:2361. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.02361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.DeSantis TZ, et al. Greengenes, a chimera-checked 16S rRNA gene database and workbench compatible with ARB. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2006;72:5069–5072. doi: 10.1128/aem.03006-05. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Derrick B, Toher D, White P. How to compare the means of two samples that include paired observations and independent observations: A companion to Derrick, Russ, Toher and White. Quantit Meth Psychol. 2017;13:120–126. doi: 10.20982/tqmp.13.2.p120. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Team, R. D. C. R: a language and environment for statistical computing [online]. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria (2016).
- 49.Price MN, Dehal PS, Arkin AP. FastTree 2 – approximately maximum-likelihood trees for large alignments. Plos One. 2010;5:e9490. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0009490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Shannon CE. A mathematical theory of communication. Bell Sys Tech J. 1948;27:379–423. doi: 10.1002/j.1538-7305.1948.tb01338.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Faith DP. Conservation evaluation and phylogenetic diversity. Biol Conserv. 1992;61:1–10. doi: 10.1016/0006-3207(92)91201-3. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Lozupone C, Knight R. UniFrac: a new phylogenetic method for comparing microbial communities. Appl Env Microb. 2005;71:8228–8235. doi: 10.1128/aem.71.12.8228-8235.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Vázquez-Baeza, Y., Pirrung, M., Gonzalez, A. & Knight, R. EMPeror: a tool for visualizing high-throughput microbial community data. GigaScience2, 10.1186/2047-217x-2-16 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 54.Lane, D. 16S/23S rRNA sequencing. Nucleic Acid Techniques in Bacterial Systematics, 115–175 (1991).
- 55.Ponnusamy L, et al. Identification of bacteria and bacteria-associated chemical cues that mediate oviposition site preferences by Aedes aegypti. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105:9262–9267. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0802505105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K. MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol. 2016;33:1870–1874. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msw054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Kimura M. A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J Mol Evol. 1980;16:111–120. doi: 10.1007/bf01731581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Cole JR, et al. Ribosomal Database Project: data and tools for high throughput rRNA analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013;42:D633–D642. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt1244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Adeyemi O, Dipeolu O. The numbers and varieties of bacteria carried by filth flies in sanitary and unsanitary city area. Int J Zoonoses. 1984;11:195–203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Coffey MD. Studies on the association of flies (Diptera) with dung in southeastern Washington. Ann Entomol Soc Am. 1966;59:207–218. doi: 10.1093/aesa/59.1.207. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Gorb SN. The design of the fly adhesive pad: distal tenent setae are adapted to the delivery of an adhesive secretion. Proc R Soc London. B: Biol Sci. 1998;265:747–752. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1998.0356. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Graczyk TK, Knight R, Gilman RH, Cranfield MR. The role of non-biting flies in the epidemiology of human infectious diseases. Microbes Infect. 2001;3:231–235. doi: 10.1016/s1286-4579(01)01371-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Sukontason KL, et al. Ultrastructure of adhesive device in fly in families calliphoridae, muscidae and sarcophagidae, and their implication as mechanical carriers of pathogens. Parasitol Res. 2006;98:477–481. doi: 10.1007/s00436-005-0100-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Gupta AK, et al. Phylogenetic characterization of bacteria in the gut of house flies (Musca domestica L.) FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 2012;79:581–593. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6941.2011.01248.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Yong H-S, Song S-L, Chua K-O, Lim P-E. Microbiota associated with Bactrocera carambolae and B. dorsalis (Insecta: Tephritidae) revealed by next-generation sequencing of 16S rRNA gene. Meta Gene. 2017;11:189–196. doi: 10.1016/j.mgene.2016.10.009. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Gupta AK, et al. Molecular phylogenetic profiling of gut-associated bacteria in larvae and adults of flesh flies. Med Vet Entomol. 2014;28:345–354. doi: 10.1111/mve.12054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Wang X, et al. The gut bacteria across life stages in the synanthropic fly Chrysomya megacephala. BMC Microbiol. 2018;18:131. doi: 10.1186/s12866-018-1272-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Yun J-H, et al. Insect gut bacterial diversity determined by environmental habitat, diet, developmental stage, and phylogeny of host. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2014;80:5254–5264. doi: 10.1128/aem.01226-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Vogel H, et al. The digestive and defensive basis of carcass utilization by the burying beetle and its microbiota. Nat Commun. 2017;8:15186. doi: 10.1038/ncomms15186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Singh B, et al. A metagenomic assessment of the bacteria associated with Lucilia sericata and Lucilia cuprina (Diptera: Calliphoridae) Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2015;99:869–883. doi: 10.1007/s00253-014-6115-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Pramono AK, Sakamoto M, Iino T, Hongoh Y, Ohkuma M. Dysgonomonas termitidis sp. nov., isolated from the gut of the subterranean termite Reticulitermes speratus. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2015;65:681–685. doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.070391-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Sun, X., Yang, Y., Zhang, N., Shen, Y. & Ni, J. Draft genome sequence of Dysgonomonas macrotermitis strain JCM 19375 T, isolated from the gut of a termite. Genome Announc3, 10.1128/genomea.00963-15 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 73.Minard, G. et al. French invasive Asian tiger mosquito populations harbor reduced bacterial microbiota and genetic diversity compared to Vietnamese autochthonous relatives. Front Microbiol6, 10.3389/fmicb.2015.00970 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 74.Shukla SP, Sanders JG, Byrne MJ, Pierce NE. Gut microbiota of dung beetles correspond to dietary specializations of adults and larvae. Mol Ecol. 2016;25:6092–6106. doi: 10.1111/mec.13901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Lee C-M, et al. Isolation and characterization of a halotolerant and protease-resistant α-galactosidase from the gut metagenome of Hermetia illucens. J Biotechnol. 2018;279:47–54. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2018.05.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Bruno D, et al. The intestinal microbiota of Hermetia illucens larvae is affected by diet and shows a diverse composition in the different midgut regions. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2019;85:01864–01818. doi: 10.1128/aem.01864-18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Tóth E, et al. Schineria larvae gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from the 1st and 2nd larval stages of Wohlfahrtia magnifica (Diptera: Sarcophagidae) Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2001;51:401–407. doi: 10.1099/00207713-51-2-401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Toth EM, et al. Wohlfahrtiimonas chitiniclastica gen. nov., sp. nov., a new gammaproteobacterium isolated from Wohlfahrtia magnifica (Diptera: Sarcophagidae) Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2008;58:976–981. doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.65324-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Gupta AK, et al. Ignatzschineria indica sp. nov. and Ignatzschineria ureiclastica sp. nov., isolated from adult flesh flies (Diptera: Sarcophagidae) Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2011;61:1360–1369. doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.018622-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Chandler JA, Morgan Lang J, Bhatnagar S, Eisen JA, Kopp A. Bacterial communities of diverse Drosophila species: ecological context of a host–microbe model system. PLoS Genet. 2011;7:e1002272. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Li H, Medina F, Vinson SB, Coates CJ. Isolation, characterization, and molecular identification of bacteria from the red imported fire ant (Solenopsis invicta) midgut. J Invertebr Pathol. 2005;89:203–209. doi: 10.1016/j.jip.2005.05.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Dennison NJ, Jupatanakul N, Dimopoulos G. The mosquito microbiota influences vector competence for human pathogens. Curr Opin Insect Sci. 2014;3:6–13. doi: 10.1016/j.cois.2014.07.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Maravić A, et al. Urban riverine environment is a source of multidrug-resistant and ESBL-producing clinically important Acinetobacter spp. Environ Sci and Pollut Res. 2016;23:3525–3535. doi: 10.1007/s11356-015-5586-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Guégan M, et al. The mosquito holobiont: fresh insight into mosquito-microbiota interactions. Microbiome. 2018;6:49. doi: 10.1186/s40168-018-0435-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Pais IS, Valente RS, Sporniak M, Teixeira L. Drosophila melanogaster establishes a species-specific mutualistic interaction with stable gut-colonizing bacteria. PLOS Biol. 2018;16:e2005710. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.2005710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Coon KL, Vogel KJ, Brown MR, Strand MR. Mosquitoes rely on their gut microbiota for development. Mol Ecol. 2014;23:2727–2739. doi: 10.1111/mec.12771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Minard G, et al. Prevalence, genomic and metabolic profiles of Acinetobacter and Asaia associated with field-caught Aedes albopictus from Madagascar. FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 2013;83:63–73. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6941.2012.01455.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Blankenchip CL, Michels DE, Braker HE, Goffredi SK. Diet breadth and exploitation of exotic plants shift the core microbiome of Cephaloleia, a group of tropical herbivorous beetles. PeerJ. 2018;6:e4793. doi: 10.7287/peerj.preprints.26692v1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Maeda H, Morihara K. Serralysin and related bacterial proteinases. Methods Enzymmol. 1995;248:395–413. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(95)48026-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Dharne MS, et al. Antibacterial activities of multi drug resistant Myroides odoratimimus bacteria isolated from adult flesh flies (Diptera: Sarcophagidae) are independent of metallo beta-lactamase gene. Braz J Microbiol. 2008;39:397–404. doi: 10.1590/s1517-83822008000200035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Licker M, et al. Extensively drug-resistant Myroides odoratimimus–a case series of urinary tract infections in immunocompromised patients. Infect Drug Resist. 2018;11:743–749. doi: 10.2147/idr.s161069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Yabuuchi E, et al. Proposal of Burkholderiagen. nov. and transfer of seven species of the genus Pseudomonas homology group II to the new genus, with the type species Burkholderia cepacia (Palleroni and Holmes 1981) comb. nov. Microbiol Immunol. 1992;36:1251–1275. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1992.tb02129.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Dobritsa AP, Samadpour M. Transfer of eleven species of the genus Burkholderia to the genus Paraburkholderia and proposal of Caballeronia gen. nov. to accommodate twelve species of the genera Burkholderia and Paraburkholderia. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2016;66:2836–2846. doi: 10.1099/ijsem.0.001065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Estrada-de los Santos Paulina, Palmer Marike, Chávez-Ramírez Belén, Beukes Chrizelle, Steenkamp Emma, Briscoe Leah, Khan Noor, Maluk Marta, Lafos Marcel, Humm Ethan, Arrabit Monique, Crook Matthew, Gross Eduardo, Simon Marcelo, dos Reis Junior Fábio, Whitman William, Shapiro Nicole, Poole Philip, Hirsch Ann, Venter Stephanus, James Euan. Whole Genome Analyses Suggests that Burkholderia sensu lato Contains Two Additional Novel Genera (Mycetohabitans gen. nov., and Trinickia gen. nov.): Implications for the Evolution of Diazotrophy and Nodulation in the Burkholderiaceae. Genes. 2018;9(8):389. doi: 10.3390/genes9080389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Hofstad T, et al. Dysgonomonas gen. nov. to accommodate Dysgonomonas gadei sp. nov., an organism isolated from a human gall bladder, and Dysgonomonas capnocytophagoides (formerly CDC group DF-3) Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2000;50:2189–2195. doi: 10.1099/00207713-50-6-2189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Hansen PS, Jensen TG, Gahrn-Hansen B. Dysgonomonas capnocytophagoides bacteraemia in a neutropenic patient treated for acute myeloid leukaemia. Case report. APMIS. 2005;113:229–231. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0463.2005.apm1130313.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Yang YJ, et al. Dysgonomonas macrotermitis sp. nov., isolated from the hindgut of a fungus-growing termite. Int J Syst Evol. Microbiol. 2014;64:2956–2961. doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.061739-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Maurin M, et al. Human Infection with Schineria larvae. Emerg Infect Dis. 2007;13:657–659. doi: 10.3201/eid1304.061151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Nishimura Y, Ino T, Iizuka H. Acinetobacter radioresistens sp. nov. isolated from cotton and soil. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1988;38:209–211. doi: 10.1099/00207713-38-2-209. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Verma R, Baroco AL. Acinetobacter radioresistens septicemia associated with pneumonia in a patient with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and hepatitis C. Infect Dis Clin Pract. 2017;25:e12–e13. doi: 10.1097/ipc.0000000000000521. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Visca P. Community-acquired Acinetobacter radioresistens bacteremia in an HIV-positive patient. Emerg Infect Dis. 2001;7:1032–1035. doi: 10.3201/eid0706.010621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Luo, Y., Javed, M. A., Deneer, H. & Chen, X. Nutrient depletion-induced production of tri-acylated glycerophospholipids in Acinetobacter radioresistens. Sci Rep8, 10.1038/s41598-41018-25869-41599, 10.1038/s41598-018-25869-9 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 103.Fulsundar S, et al. Molecular characterization of outer membrane vesicles released from Acinetobacter radioresistens and their potential roles in pathogenesis. Microb Pathog. 2015;83-84:12–22. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2015.04.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Katzir Z, et al. An unusual infection outbreak in rats held in a human hospital research laboratory. Lab Anim. 2015;49:255–257. doi: 10.1177/0023677215575864. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Dias MF, et al. Changes in mouse gut bacterial community in response to different types of drinking water. Water Res. 2018;132:79–89. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2017.12.052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Poirel L, Figueiredo S, Cattoir V, Carattoli A, Nordmann P. Acinetobacter radioresistens as a silent source of carbapenem resistance for Acinetobacter spp. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2008;52:1252–1256. doi: 10.1128/aac.01304-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Crippen, C. S., Huynh, S., Miller, W. G., Parker, C. T. & Szymanski, C. M. Complete genome sequence of Acinetobacter radioresistens Strain LH6, a multidrug-resistant bacteriophage-propagating strain. Microbiol Resour Announc7, 10.1128/mra.00929-18 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 108.Benedetti P, Rassu M, Pavan G, Sefton A, Pellizzer G. Septic shock, pneumonia, and soft tissue infection due to Myroides odoratimimus: report of a case and review of Myroides infections. Infection. 2011;39:161–165. doi: 10.1007/s15010-010-0077-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Beharrysingh R. Myroides bacteremia: A case report and concise review. IDCases. 2017;8:34–36. doi: 10.1016/j.idcr.2017.02.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Lorenzin G, et al. Myroides odoratimimus urinary tract infection in an immunocompromised patient: an emerging multidrug-resistant micro-organism. Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. 2018;7:96. doi: 10.1186/s13756-018-0391-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Pompilio A, et al. Infection of recurrent calcaneal ulcer caused by a biofilm-producer Myroides odoratimimus strain. Folia Microbiol. 2018;63:203–207. doi: 10.1007/s12223-017-0552-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Ravindran C, Vasudevan L, Babu Vinoth Kannan SR. Disease symptoms and growth performance of grey mullet infected with Myroides odoratimimus. Aquac Res. 2017;48:5122–5125. doi: 10.1111/are.13124. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Dowson D. On the systematic position and generic names of the Gram negative bacterial plant pathogens. Zentralblatt fur Bakteriologie, Parasitenkunde und Infektionskrankheiten. 1939;100:177–193. [Google Scholar]
- 114.Sarris PF, Trantas EA, Mpalantinaki E, Ververidis F, Goumas DE. Pseudomonas viridiflava, a multi host plant pathogen with significant genetic variation at the molecular level. PLoS One. 2012;7:e36090. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0036090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Ruinelli M, Blom J, Pothier JF. Complete genome sequence of Pseudomonas viridiflava CFBP 1590, isolated from diseased cherry in France. Genome Announc. 2017;5:e00662–00617. doi: 10.1128/genomea.00662-17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
The next-generation sequencing data associated with this study have been deposited in GenBank under SRA accession: PRJNA554278. Cloned sequences have been deposited in GenBank under accession numbers: MN172461-MN172464.



