Abstract
BACKGROUND
Although skin avulsions to male external genitalia are rare, they can be both physically and psychologically traumatic. Thus, the necessity for judicious management poses significant challenges to surgeons in order to avoid potential permanent disabilities. We report a case of massive penoscrotal skin avulsion and a composite graft was creatively applied to cover the defect which achieved good results. We believe that this case is of great reference value for fellow surgeons.
CASE SUMMARY
A 52-year-old male presented with massive traumatic avulsion of the penile and scrotal skin following mishandling of an electric drill. The avulsed skin was missing. The patient was diagnosed with massive skin avulsion of external genitalia. Following initial complete debridement of devitalized or infected tissues, Pelnac dermal substitute was secured to the defect with the assistance of negative-pressure wound closure. In the final step, the silicone layer of Pelnac was removed and a split-thickness skin graft was applied. The defect had healed at the two-month follow-up. The patient now has normal erections and satisfactory sexual function.
CONCLUSION
Our experience with this wound repair demonstrated that the combination of a dermal regeneration template and a split-thickness skin graft with vacuum-assisted closure is a safe, well-tolerated and efficient solution for the reconstruction of massive penoscrotal skin defects.
Keywords: Artificial dermis, Dermal regeneration template, Massive skin defect, Penoscrotal defect, Split-thickness skin graft, Case report
Core tip: Skin avulsions of the scrotum and penis are rarely seen, especially massive avulsions. However, when they do occur, it is vital for surgeons to take prompt and judicious measures to repair the defects to avoid possible disabilities which could be both physically and psychologically traumatic. We report a case with massive skin avulsion of the scrota and penis, where we customized treatment by combining a dermal regeneration template (Pelnac) and a split-thickness skin graft to cover the defect with vacuum-assisted closure using three steps. Our experience with this wound repair proved that this combination is a safe, well-tolerated and efficient solution for the reconstruction of massive penoscrotal skin defects.
INTRODUCTION
Due to their intrinsic characteristics[1], skin avulsions in the genital area are rare and poorly reported[2]. However, lifelong sequelae which are both physically and psychologically traumatic are possible if the defects are not immediately and appropriately treated. Therefore, the necessity for judicious management poses significant challenges for surgeons in order to avoid potential permanent disabilities, such as retraction of grafted skin, erectile dysfunction, etc[3,4].
We report a case with massive penoscrotal skin avulsion. The patient was successfully treated with the combination of a dermal regeneration template (Pelnac) and a split-thickness skin graft with vacuum-assisted closure. This treatment technique is analyzed and discussed for further promotion.
CASE PRESENTATION
Chief complaints
A 52-year-old male patient presented in our emergency room with massive traumatic avulsion of the penile and scrotal skin following mishandling of an electric drill during work 9 h earlier. The missing skin was not retrievable.
History of present illness
The patient was taken to the local hospital immediately after the accident. The wound was quickly dressed and the patient was referred to the Emergency Department of our hospital.
History of past illness
The patient was healthy prior to the accident with no history of chronic disease.
Physical examination
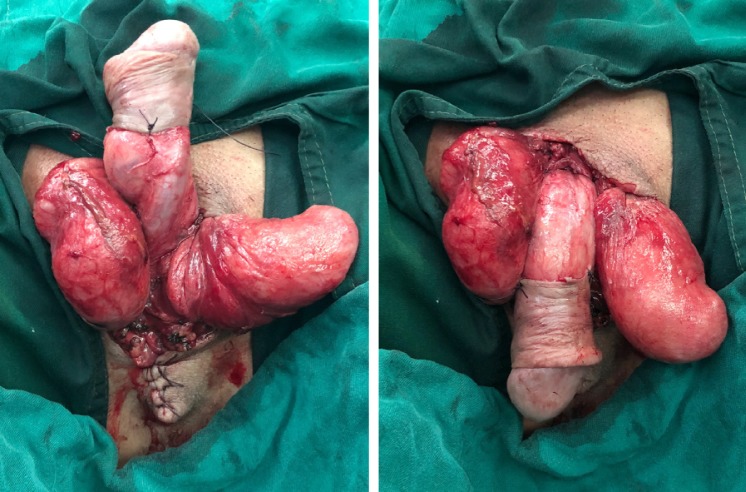
Physical examination showed full-thickness skin of both scrota and the proximal part of the penis was denuded with active bleeding (Figure 1). Urinary catheterization was successfully performed which indicated that there was no damage to the urethra.
Figure 1.
Massive skin defect of both scrota and the proximal part of the penis before surgery.
Laboratory examinations
Laboratory studies revealed a white blood cell count of 12.3 × 109/L (neutrophil percentage, 74.5%) which was higher than the normal level and was believed to be caused by the open trauma. Other results were normal.
Imaging examinations
A pelvic computed tomography scan revealed that the perineum skin had multiple spots of dense shadows, and the subcutaneous fat gap was slightly blurred.
FINAL DIAGNOSIS
The final diagnosis was massive penoscrotal skin avulsion.
TREATMENT
Following discussion, we repaired the skin defect using three steps. First, excision of the necrotic and inflammatory tissues was carefully performed and hemostasis was meticulously achieved to prevent infection, seroma and hematoma. Polyurethane foam was then applied to the wound and sealed with a transparent dressing to avoid air leak. The tube which was previously attached to the dressing was connected to a vacuum setting which was set at a constant negative pressure (125 mmHg) and supplied to the region.
One week later when the graft bed had been appropriately prepared, the Pelnac dermal regeneration template was grafted onto the defect region according to the wound size (Figure 2), and with the assistance of negative pressure therapy described above, the artificial dermis was firmly secured and incorporated into the wound.
Figure 2.
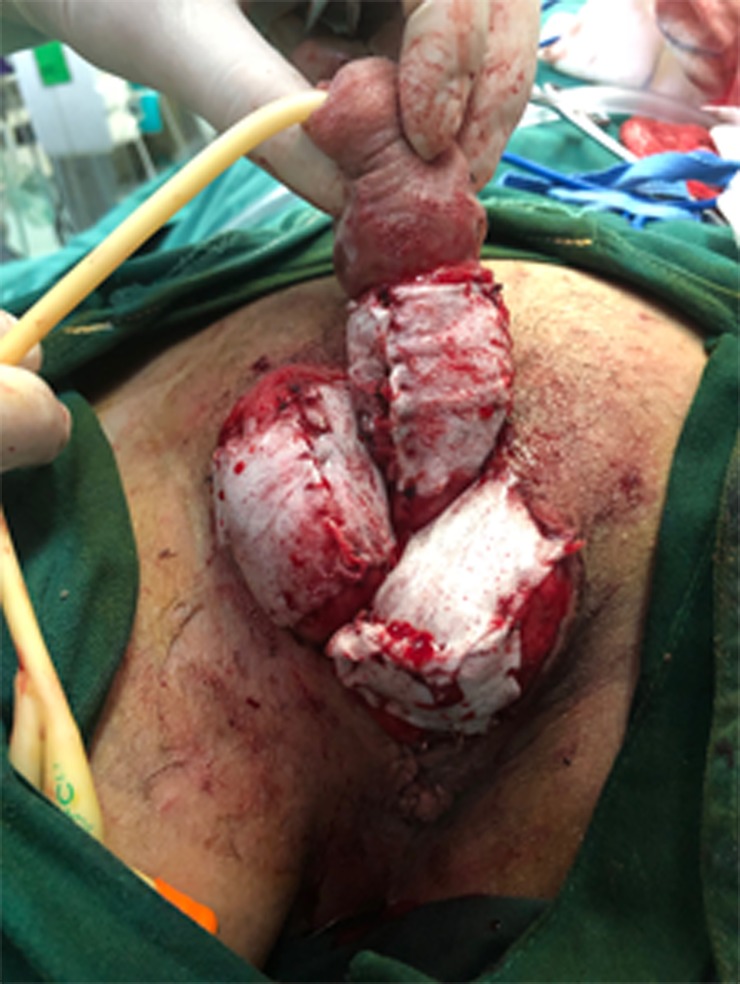
Dermal regeneration template (Pelnac) was grafted onto the defect region.
Finally, after confirmation that Pelnac was clinically incorporated into the defect, the silicone layer was removed and a split-thickness skin graft, which was harvested from the left inner thigh, was applied over the artificial dermis one week later (Figure 3). The vacuum setting was again utilized and maintained at a continuous negative pressure to assist grafting. The device was dismantled seven days later and the skin graft was found to have completely survived.
Figure 3.
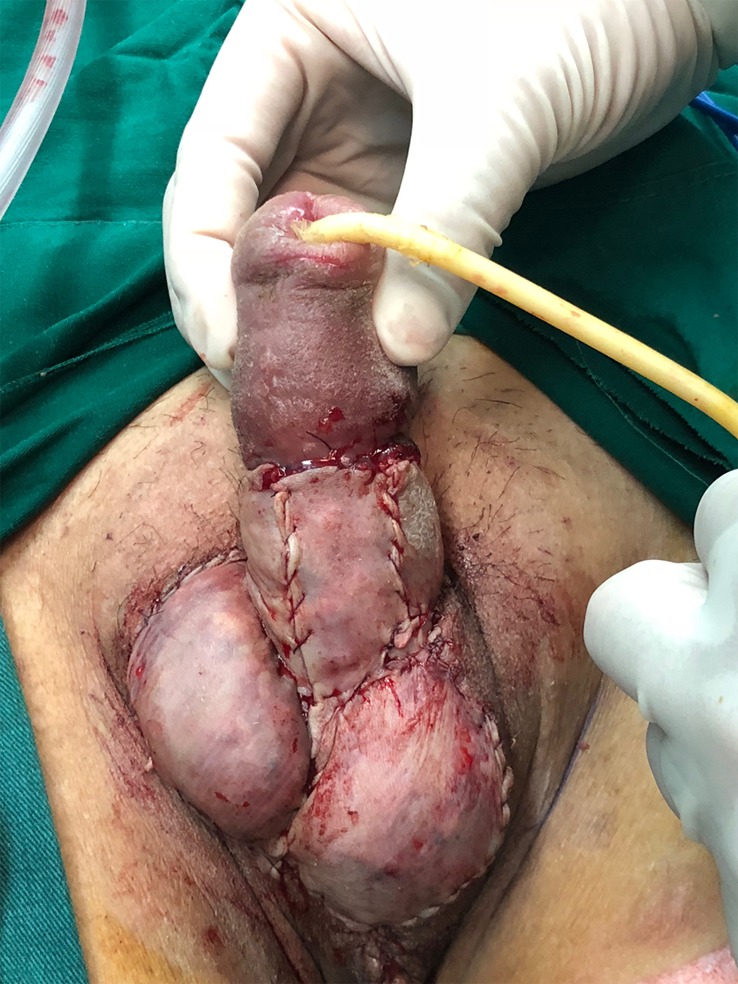
Split-thickness skin grafts were applied over the artificial dermis.
OUTCOME AND FOLLOW-UP
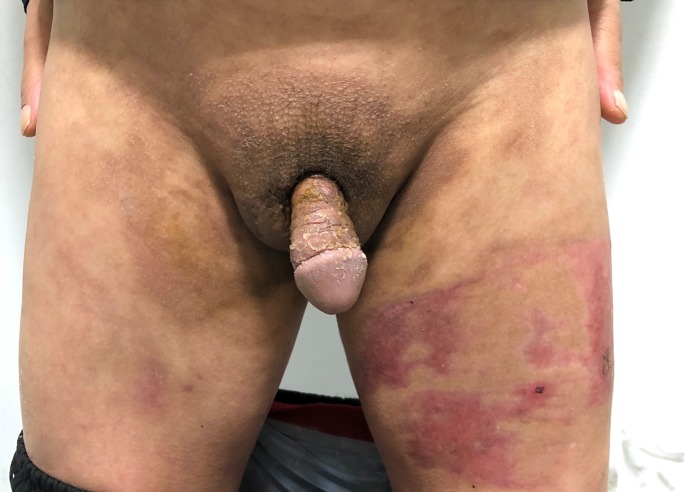
The combined grafting achieved a good cosmetic appearance and stable coverage of the defect which was elastic and of good quality and texture at the three-month follow-up. Furthermore, urination and sexual function in this patient were not greatly affected by his injuries or treatment. He is satisfied with his erectile length and sexual function (Figure 4).
Figure 4.
Follow-up after removal of stitches.
DISCUSSION
Skin avulsions of the scrotum and penis have been poorly reported[2], especially massive avulsions, due to intrinsic factors such as unique location and anatomy[1]. They are generally seen in industrial or agricultural accidents when unprotected rotary gears catch the pants of the workers and draw the scrotum and penis into the machinery[5], which is exactly what our patient experienced. Prompt and judicious treatment should be undertaken to prevent possible disabilities which could be both physically and psychologically traumatic following delayed or inappropriate management[3,4]. Therefore, it is vital for surgeons to make suitable and customized decisions regarding certain defects.
We performed a literature search of skin avulsions of the scrotum and penis, and the results are shown in Table 1[6-16]. In our case, the patient suffered massive skin avulsion of both scrota and the proximal part of the penis. Furthermore, the torn skin was lost during the accident. In addition, according to the experience of Sheridan et al[17], the penoscrotal region is among the poorest areas for graft survival. Therefore, the characteristics of the graft needed for the defect were as follows: easy to survive, abundant quantity and good quality and texture after transplantation for sexual function. The most appropriate option was a split-thickness or full-thickness skin graft. It is known that split-thickness skin graft survive easily and can be obtained easily, but can later retract and be of poor quality and texture[18]. In contrast, the survival of a full-thickness skin graft is relatively difficult and not easily obtained, but would not retract and would be of good quality and texture[19]. In order to adopt the advantages of a split-thickness skin graft in terms of survival and quantity, we decided to introduce artificial dermis[20,21] to prevent retraction and improve the quality and texture after transplantation.
Table 1.
The characteristics of patients with skin avulsions of the scrotum and penis
| Date of publication | Ref. | Age | Cause of defect | Size | Infection | Treatment |
| 1948 | Davis et al[5] | 60 | Trauma | Scrota, penis, spermatic cords, tunica vaginalis and cremaster muscles | No | Thick split-thickness skin graft |
| 1948 | Davis et al[5] | 51 | Trauma | Left testicle, spermatic cord, penile shaft and scrotum | No | Thick split-thickness skin graft |
| 1966 | Cullen TH et al[6] | 16 | Trauma | Left scrotum, penis shaft | No | Subcutaneous tunnel and split-skin graft |
| 2001 | Liu et al[7] | 37 | Trauma | Scrota, penis shaft | No | Replantation of avulsed skin |
| 2002 | Ribuffo et al[8] | 75 | Basal cell carcinoma | Scrota, penis, pubic and inguinal area | No | Split-thickness skin graft |
| 2007 | Jena et al[9] | 28 | Trauma | Scrota, penis | No | Scrotal skin flap |
| 2010 | Selvan et al[10] | 27 | Trauma | Scrota, penis | No | Hypogastric flap and split |
| 2012 | Asimakopoulos et al[11] | - | Radical circumcision | Penis | No | Split-thickness skin graft |
| 2013 | Zhao et al[12] | 39 | Trauma | Scrota, penis | Necrosis | Split-thickness skin graft |
| 2014 | Pieptu et al[13] | 31 | Trauma | Anterior perineal skin, penis and both testicles | No | Split-thickness skin graft for testicles; Integra and ultra-thin split-thickness skin graft for penis |
| 2014 | Wong et al[14] | - | Paraffinoma, burn, circumcision, trauma | Penis | No | Bipedicled scrotal flap |
| 2015 | Djedovic et al[15] | - | - | Penis | No | Acellular dermal template and split-thickness skin graft |
| 2016 | Judge et al[16] | 32 | Elephantiasis | Scrota, penis, perineal area | No | Full-thickness skin graft |
However, the disadvantage of this treatment is a second-stage operation and a potentially higher rate of complications. The main complications include infection, hematoma, seroma and improper mobilization. In the hope of reducing these unfavorable factors, we adopted vacuum-assisted closure which has been confirmed to be effective[12,21] throughout the whole repair procedure. Considering the dirty environment in which the accident occurred, we decided to reconstruct the defect in three steps which proved to be a practical and successful strategy.
This treatment of combining artificial dermis and a split-thickness skin graft allowed successful reconstruction and shows promising clinical application. These types of injuries, which once could only be treated with flaps, for example, exposed bone, tendons and other vital yet poorly vascularized structures[21], can now be successfully covered by this composite graft which is not limited to specific locations. Commonly encountered complications such as infection, hematoma or improper mobilization, can now be reduced due to the introduction of vacuum-assisted closure. This technique is not only reliable in terms of coverage of the defect, but can also reduce complications. Our patient was thankful and satisfied with his care during hospitalization. We highly recommend this method for the repair of various massive and troublesome defects.
CONCLUSION
The combination of a dermal regeneration template and split-thickness skin graft with vacuum-assisted closure is a safe, well-tolerated and efficient solution for the reconstruction of massive penoscrotal skin defects.
Footnotes
Informed consent statement: Informed written consent was obtained from the patient for publication of this report and any accompanying images.
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
CARE Checklist (2016) statement: The authors have read the CARE Checklist (2016), and the manuscript was prepared and revised according to the CARE Checklist (2016).
Manuscript source: Unsolicited manuscript
Peer-review started: June 10, 2019
First decision: October 24, 2019
Article in press: November 14, 2019
Specialty type: Medicine, Research and Experimental
Country of origin: China
Peer-review report classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): B
Grade C (Good): 0
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Papadakis M S-Editor: Zhang L L-Editor: Webster JR E-Editor: Xing YX
Contributor Information
Jia-Jie Fang, Department of Urology, The First Affiliated Hospital, School of Medicine, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310003, Zhejiang Province, China.
Peng-Fei Li, Department of Plastic and Aesthetic Center, The First Affiliated Hospital, School of Medicine, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310003, Zhejiang Province, China.
Jia-Jun Wu, Xingyan Aesthetic Clinic, Hangzhou 310003, Zhejiang Province, China.
Hai-Ying Zhou, Department of Orthopedics, The First Affiliated Hospital, School of Medicine, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310003, Zhejiang Province, China.
Li-Ping Xie, Department of Urology, The First Affiliated Hospital, School of Medicine, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310003, Zhejiang Province, China. xielp@zju.edu.cn.
Hui Lu, Department of Orthopedics, The First Affiliated Hospital, School of Medicine, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310003, Zhejiang Province, China.
References
- 1.Nicola R, Carson N, Dogra VS. Imaging of traumatic injuries to the scrotum and penis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2014;202:W512–W520. doi: 10.2214/AJR.13.11676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Oseni OG, Olaitan PB, Badmus TO, Olajide AO. Accidental Peno-Scrotal Degloving Injuries in a Child. A Case Report and Literature Review. Nig Q J Hosp Med. 2013;23:248–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Lee SH, Bak CW, Choi MH, Lee HS, Lee MS, Yoon SJ. Trauma to male genital organs: a 10-year review of 156 patients, including 118 treated by surgery. BJU Int. 2008;101:211–215. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2007.07265.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Norredam M, Crosby S, Munarriz R, Piwowarczyk L, Grodin M. Urologic complications of sexual trauma among male survivors of torture. Urology. 2005;65:28–32. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2004.08.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Davis AD, Berner RE. Primary repair of total avulsion of skin from penis and scrotum. Plast Reconstr Surg (1946) 1948;3:417–423. doi: 10.1097/00006534-194807000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Cullen TH. Avulsion of the skin of the penis and scrotum. Br J Urol. 1966;38:99–101. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410x.1966.tb09685.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Liu YP, Tang HP, Yang ZX, Pan DD. Replantation of avulsed penoscrotal skin. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2001;107:1800–1802. doi: 10.1097/00006534-200106000-00026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Ribuffo D, Alfano C, Ferrazzoli PS, Scuderi N. Basal cell carcinoma of the penis and scrotum with cutaneous metastases. Scand J Plast Reconstr Surg Hand Surg. 2002;36:180–182. doi: 10.1080/028443102753718087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Jena A, Reddy V, Yootla M, Sarma MS, Gupta V. Repair of an extensive traumatic degloving injury of the penis and scrotum using scrotal skin flap. ANZ J Surg. 2008;77:1131. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-2197.2007.04338.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Selvan SS, Alagu GS, Gunasekaran R. Use of a hypogastric flap and split-thickness skin grafting for a degloving injury of the penis and scrotum: A different approach. Indian J Plast Surg. 2010;42:258–260. doi: 10.4103/0970-0358.59296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Asimakopoulos AD, Iorio B, Vespasiani G, Cervelli V, Spera E. Autologous split‐thickness skin graft for penile coverage in the treatment of buried (trapped) penis after radical circumcision. BJU Int. 2012;110:602–606. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2012.10832.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Zhao JC, Xian CJ, Yu JA, Shi K. Reconstruction of infected and denuded scrotum and penis by combined application of negative pressure wound therapy and split‐thickness skin grafting. Int Wound J. 2013;10:407–410. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-481X.2012.00997.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Pieptu V, Mihai A, Ghetu N. Integra for penile coverage after traumatic degloving–Case report. Arch Clin Cases. 2014 [Google Scholar]
- 14.Wong M, Ong YS, Tan BK. Coverage of circumferential penile shaft defects with the bipedicled scrotal flap: a case series. Eur J Plast Surg. 2014;37:33–36. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Djedovic G, Matiasek J, Morandi E, Pierer G, Rieger UM. Use of an acellular dermal template for defect coverage on the penile shaft. Eur J Plast Surg. 2015;38:421–424. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Judge N, Kilic A. Elephantiasis Nostras Verrucosa. Excision with full-thickness skin grafting of the penis, scrotum, and perineal area. J Dermatol Case Rep. 2016;10:32. doi: 10.3315/jdcr.2016.1229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Sheridan RL, Hegarty M, Tompkins RG, Burke JF. Artificial skin in massive burns- results to ten years. Eur J Plast Surg. 1994;17:91–93. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Hoballah JJ. Split-Thickness Skin Graft. Operative Dictations in General and Vascular Surgery. 2011:1025–1026. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Tran TA, Panthaki ZJ, Hoballah JJ, Thaller SR. 2017. Operative Dictations in Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. Springer International Publishing Switzerland; pp. 199–201. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Widjaja W, Maitz P. The use of dermal regeneration template (Pelnac®) in acute full-thickness wound closure: A case series. Eur J Plast Surg. 2016;39:125–132. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Eo S, Kim Y, Cho S. Vacuum-assisted closure improves the incorporation of artificial dermis in soft tissue defects: Terudermis(®) and Pelnac(®) Int Wound J. 2011;8:261–267. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-481X.2011.00780.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]