Abstract
Background
Pineapple is the most important crop with CAM photosynthesis, but its molecular biology is underexplored. MADS-box genes are crucial transcription factors involving in plant development and several biological processes. However, there is no systematic analysis of MADS-box family genes in pineapple (Ananas comosus).
Results
Forty-eight MADS-box genes were identified in the pineapple genome. Based on the phylogenetic studies, pineapple MADS-box genes can be divided into type I and type II MADS-box genes. Thirty-four pineapple genes were classified as type II MADS-box genes including 32 MIKC-type and 2 Mδ-type, while 14 type I MADS-box genes were further divided into Mα, Mβ and Mγ subgroups. A majority of pineapple MADS-box genes were randomly distributed across 19 chromosomes. RNA-seq expression patterns of MADS-box genes in four different tissues revealed that more genes were highly expressed in flowers, which was confirmed by our quantitative RT-PCR results. There is no FLC and CO orthologs in pineapple. The loss of FLC and CO orthologs in pineapple indicated that modified flowering genes network in this tropical plant compared with Arabidopsis. The expression patterns of MADS-box genes in photosynthetic and non-photosynthetic leaf tissues indicated the potential roles of some MADS-box genes in pineapple CAM photosynthesis. The 23% of pineapple MADS-box genes showed diurnal rhythm, indicating that these MADS-box genes are regulated by circadian clock.
Conclusions
MADS-box genes identified in pineapple are closely related to flowering development. Some MADS-box genes are involved in CAM photosynthesis and regulated by the circadian clock. These findings will facilitate research on the development of unusual spiral inflorescences on pineapple fruit and CAM photosynthesis.
Keywords: CAM photosynthesis, Diurnal clock, MADS-box genes, Pineapple
Background
MADS-box genes play a crucial role in plant development, especially in flower development. The term ‘MADS’ was derived from four members of the MADS family in fungi, plants and animals: MCM1 in yeast, AGAMOUS in Arabidopsis, DEFICIENS in snapdragon, and SERUM RESPONSE FACTOR in human [1–5]. MADS-box genes possess a highly conserved MADS domain that consists of roughly 60 amino acids at the amino-terminal end of the protein, followed by the I domain, the K domain and the C region from N-termini to C-termini [6, 7]. K domain is also highly conserved, while I domain and C region are quite variable. MADS domain encodes a DNA binding and dimerization function, and K domain encodes a coiled-coil motif that could possibly serve the function of mediating protein-protein interaction [1, 8].
Because of the similarities between the DNA-binding domains of MADS-box genes and subunit A of topoisomerase IIA (TOPOIIA-A), it was postulated that one copy of TOPOIIA-A was the progenitor MADS-box transcription factor [9]. In the second duplication, recent common ancestor was divided into two MADS-box types: type I (SRF-like) and type II (MEF2-like) [9, 10]. type I MADS-box genes can be further classified into Mα, Mβ and Mγ, while Type II s can be divided into MIKC-type and Mδ-type [11]. To date, MADS-box genes have been identified and classified in many dicot and monocot plants including Arabidopsis [12], Vitis vinifera [13], cucumber [14], banana [15], Brachypodium [16], wheat [17], soybean [18] and Chinese jujube [19]. The first group of MADS genes to be characterized in plant were floral organ identity genes, or ABC genes [20]. Floral organ identity genes can be summarized in the ABC model and later expanded to the ABCDE models [21]. In Arabidopsis, 107 MADS-box genes have been identified and their functions have also been determined [12, 22].
Pineapple (Ananas comosus (L.) Merr.) is an economically valuable fruit crop cultivated in tropical regions. But the molecular and genetic mechanisms of flower and fruit development have not been explored extensively. MADS-box family genes were reportedly playing an important role in the flower and fruit development process [22]. Analyzing the MADS-box genes in pineapple will be able to facilitate studies of molecular mechanisms in pineapple flower and fruit development and further characterize the function of MADS-box genes in pineapple. Meanwhile, pineapple is a fruit crop utilizing Crassulacean Acid Metabolism (CAM), which is an efficient CO2 fixation pathway [23]. Understanding the circadian rhythm of pineapple MADS-box genes can provide a foundation for elucidating CAM and CAM-related application in crop improvement.
In this study, the MADS-box genes in pineapple were identified and then classified based on their phylogenetic relationships. Gene structures and conserved motifs of pineapple MADS-box genes were analyzed, and the chromosome locations were mapped. The tissue-specific and diurnal expression patterns of MADS-box genes were evaluated. The results can improve our understanding for the evolution and functions of MADS-box genes in pineapple.
Results
Identification and classification of MADS-box genes in pineapple
Initially, 44 pineapple MADS-box genes were identified by Hidden Markov Model (HMM) search. To carry out an exhaustive search for MADS-box genes, BLASTP was conducted to search the pineapple genome database using MADS-box protein sequences in Arabidopsis and rice as queries. Finally, a total of 48 MADS-box genes were identified in the pineapple genome (Table 1) and further confirmed by NCBI Conserved Domain Database. The CDS length of pineapple MADS-box genes ranged from 180 bp (Aco030553.1) to 4569 bp (Aco027629.1). The relative molecular mass varied from 6.68 kDa to 166.54 kDa, and protein IP ranged from 4.80 to 11.23.
Table 1.
MADS-box gene family identified in pineapple
| Gene ID | Gene name | Type | Chr. | Length of CDS (bp) | # of Exons | # of Introns | IP | MW (kDa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AcMADS1 | Aco001069.1 | MIKC | Chr2 | 882 | 9 | 8 | 9.48 | 33.68 |
| AcMADS2 | Aco002729.1 | MIKC | Chr6 | 897 | 9 | 8 | 9.22 | 33.32 |
| AcMADS3 | Aco003018.1 | MIKC | Chr6 | 744 | 8 | 7 | 7.05 | 28.01 |
| AcMADS4 | Aco003667.1 | MIKC | Chr17 | 803 | 11 | 10 | 7.63 | 30.19 |
| AcMADS5 | Aco004028.1 | MIKC | Chr15 | 693 | 8 | 7 | 8.44 | 25.96 |
| AcMADS6 | Aco004785.1 | MIKC | Chr5 | 717 | 7 | 6 | 9.23 | 27.27 |
| AcMADS7 | Aco004839.1 | MIKC | Chr7 | 747 | 8 | 7 | 9.18 | 28.43 |
| AcMADS8 | Aco004987.1 | Mα | Chr7 | 672 | 1 | 0 | 9.26 | 24.16 |
| AcMADS9 | Aco004988.1 | Mα | Chr7 | 1311 | 1 | 0 | 7.66 | 45.32 |
| AcMADS10 | Aco006017.1 | MIKC | Chr16 | 591 | 6 | 5 | 7.78 | 22.88 |
| AcMADS11 | Aco007995.1 | MIKC | Chr21 | 552 | 8 | 7 | 5.80 | 20.77 |
| AcMADS12 | Aco007999.1 | MIKC | Chr21 | 702 | 7 | 6 | 9.49 | 26.89 |
| AcMADS13 | Aco008359.1 | MIKC | Chr19 | 720 | 6 | 5 | 7.16 | 27.54 |
| AcMADS14 | Aco008435.1 | Mα | Chr19 | 996 | 1 | 0 | 6.93 | 35.79 |
| AcMADS15 | Aco008623.1 | Mα | Chr9 | 687 | 1 | 0 | 6.86 | 24.66 |
| AcMADS16 | Aco009993.1 | MIKC | Chr10 | 762 | 7 | 6 | 9.30 | 29.60 |
| AcMADS17 | Aco011341.1 | MIKC | Chr1 | 705 | 7 | 6 | 9.35 | 26.96 |
| AcMADS18 | Aco011374.1 | Mβ | Chr1 | 1263 | 2 | 1 | 9.87 | 49.21 |
| AcMADS19 | Aco011677.1 | Mα | Chr8 | 573 | 1 | 0 | 6.35 | 21.25 |
| AcMADS20 | Aco012428.1 | MIKC | Chr1 | 1074 | 9 | 8 | 8.19 | 39.44 |
| AcMADS21 | Aco013229.1 | MIKC | Chr24 | 639 | 7 | 6 | 9.11 | 24.13 |
| AcMADS22 | Aco013324.1 | Mα | Chr15 | 717 | 1 | 0 | 8.68 | 25.85 |
| AcMADS23 | Aco013644.1 | Mγ | Chr13 | 762 | 1 | 0 | 9.39 | 28.25 |
| AcMADS24 | Aco013736.1 | Mδ | Chr13 | 1053 | 10 | 9 | 5.61 | 39.54 |
| AcMADS25 | Aco014671.1 | MIKC | Chr20 | 711 | 7 | 6 | 8.43 | 26.95 |
| AcMADS26 | Aco015104.1 | MIKC | Chr1 | 759 | 6 | 5 | 9.04 | 27.92 |
| AcMADS27 | Aco015105.1 | MIKC | Chr1 | 741 | 8 | 7 | 8.43 | 28.22 |
| AcMADS28 | Aco015487.1 | MIKC | Chr3 | 726 | 8 | 7 | 9.26 | 27.53 |
| AcMADS29 | Aco015491.1 | MIKC | Chr3 | 762 | 8 | 7 | 9.59 | 28.31 |
| AcMADS30 | Aco015492.1 | MIKC | Chr3 | 492 | 3 | 2 | 11.23 | 18.66 |
| AcMADS31 | Aco016643.1 | MIKC | Chr8 | 627 | 7 | 6 | 9.12 | 24.01 |
| AcMADS32 | Aco017499.1 | MIKC | Chr22 | 605 | 6 | 5 | 8.88 | 23.37 |
| AcMADS33 | Aco017563.1 | MIKC | Chr9 | 744 | 8 | 7 | 8.67 | 28.16 |
| AcMADS34 | Aco017589.1 | MIKC | Chr9 | 768 | 5 | 4 | 9.56 | 18.24 |
| AcMADS35 | Aco018015.1 | MIKC | Chr1 | 645 | 6 | 5 | 6.37 | 24.37 |
| AcMADS36 | Aco019026.1 | Mδ | Chr2 | 288 | 3 | 2 | 8.71 | 10.84 |
| AcMADS37 | Aco019039.1 | Mα | Chr20 | 630 | 5 | 4 | 9.64 | 23.14 |
| AcMADS38 | Aco019365.1 | MIKC | Chr5 | 594 | 7 | 6 | 9.28 | 22.88 |
| AcMADS39 | Aco019839.1 | Mγ | Chr15 | 360 | 5 | 4 | 9.01 | 13.99 |
| AcMADS40 | Aco019842.1 | MIKC | Chr15 | 420 | 5 | 4 | 9.98 | 15.13 |
| AcMADS41 | Aco022101.1 | Mγ | Chr4 | 804 | 1 | 0 | 8.37 | 29.60 |
| AcMADS42 | Aco025594.1 | MIKC | scaffold_679 | 468 | 5 | 4 | 9.56 | 18.24 |
| AcMADS43 | Aco027629.1 | Mγ | scaffold_622 | 4569 | 19 | 18 | 4.80 | 166.54 |
| AcMADS44 | Aco027879.1 | MIKC | scaffold_1163 | 693 | 8 | 7 | 8.77 | 25.90 |
| AcMADS45 | Aco028086.1 | Mβ | scaffold_1517 | 1056 | 3 | 2 | 5.00 | 39.81 |
| AcMADS46 | Aco030142.1 | MIKC | Chr22 | 525 | 5 | 4 | 6.85 | 19.56 |
| AcMADS47 | Aco030553.1 | MIKC | scaffold_1319 | 180 | 1 | 0 | 10.60 | 6.68 |
| AcMADS48 | Aco030656.1 | Mα | scaffold_2479 | 315 | 5 | 4 | 6.11 | 11.94 |
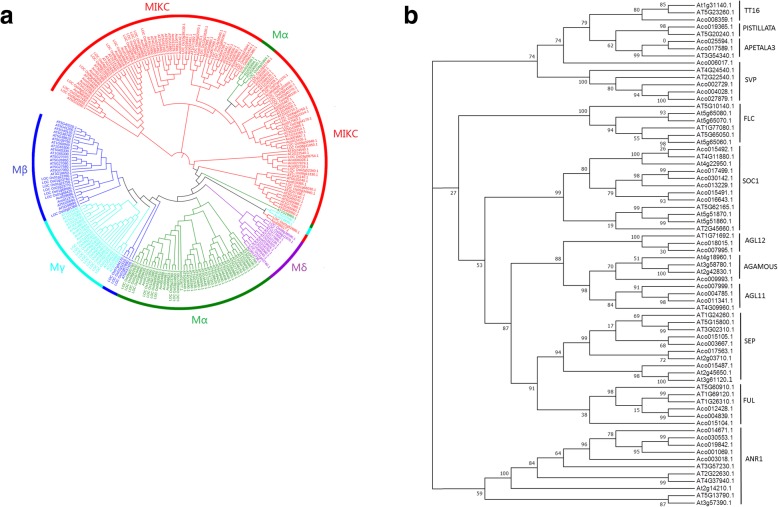
In order to study the evolutionary relationship between pineapple MADS-box genes and the known MADS-box genes from Arabidopsis and rice, multiple sequence alignments were conducted and then a phylogenetic tree was constructed based on amino acids of MADS-box genes in pineapple, Arabidopsis and rice. Thirty-four pineapple genes were classified as type II MADS-box genes including 32 MIKC-type and 2 Mδ-type (Fig. 1a). Fourteen type I MADS-box genes were further divided into Mα, Mβ and Mγ subgroups. Mα was the type I subgroup with the most genes. Eight out of 14 type I genes were classified as Mα subgroup, while 2 and 4 type I genes were classified into Mβ and Mγ subgroup, respectively (Fig. 1a). 32 MIKC-type pineapple genes were further divided into 11 clusters: TT16, APETALA3, PISTILLATA, SVP, ANR1, SEP, FUL, AGL12, AGAMOUS, AGL11 and SOC1 (Fig. 1b).
Fig. 1.
a Phylogenetic analysis of the MADS-box genes from Arabidopsis, rice and pineapple. b Phylogenetic analysis of the type II MADS-box genes from Arabidopsis and pineapple
Gene structure and conserved motif analysis
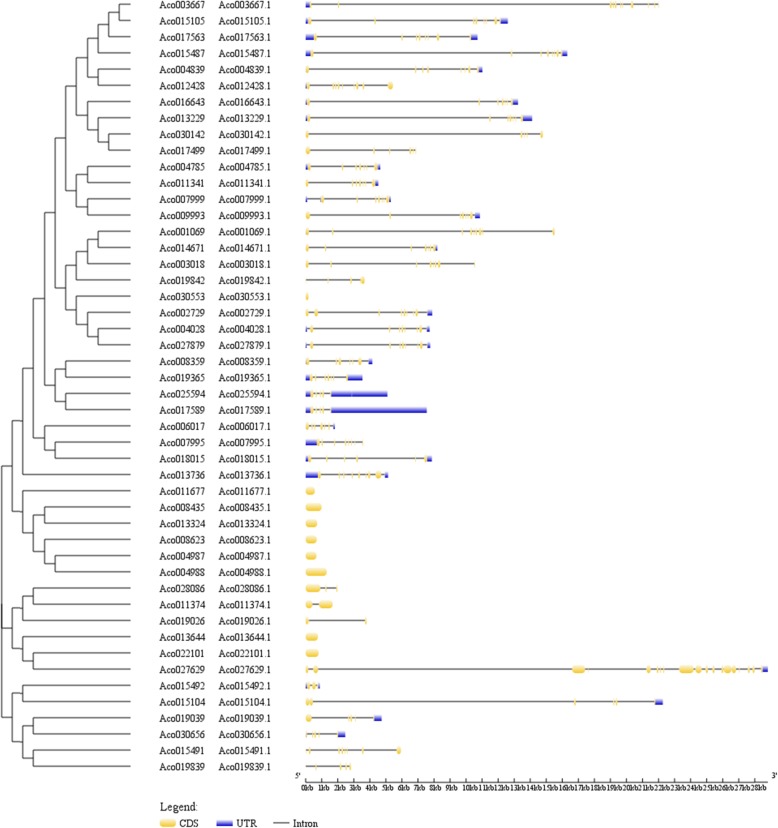
To explore the structural evolution of MADS-box genes in pineapple, structural arrangements of MADS-box genes were examined by Gene Structure Display Server. The result showed that the closely related genes were usually more similar in gene structure, such as genes Aco004785.1, Aco011341.1, Aco007999.1 and Aco009993.1, which all had 7 exons. However, some closely related genes showed significant difference in structural arrangements (Fig. 2). For instance, Aco022101.1 possesses only one exon, while Aco027629.1, its closely related gene, had 19 exons. Furthermore, pineapple MADS-box genes contained exons ranging from 1 to 19. Nine out of 48 MADS-box genes had only one exon, and those genes with one exon except for Aco030553.1 belong to type I. The exon number of most pineapple MADS-box genes was less than 10, only three genes Aco013736.1, Aco003667.1 and Aco027629.1 had 10, 11 and 19 exons, respectively (Fig. 2).
Fig. 2.
Phylogenetic relationship and gene structure analysis of MADS in pineapple
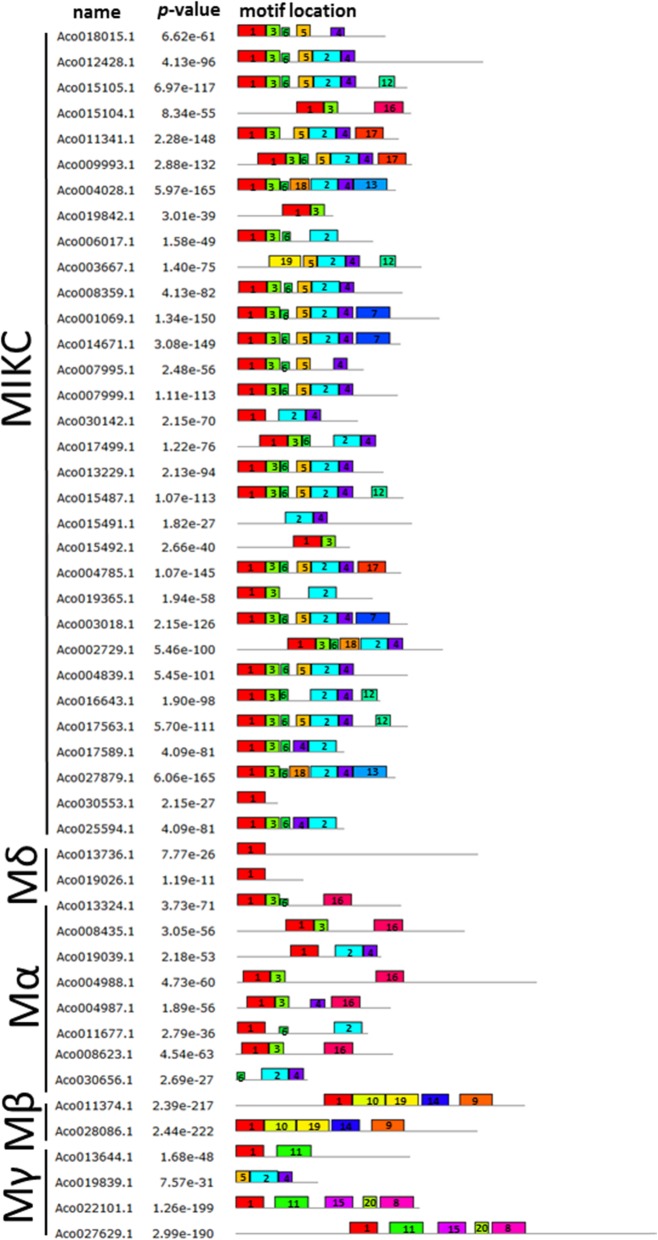
MEME software was used to analyze motifs in the MADS-box proteins. Twenty conserved motifs were identified (Fig. 3) and these conserved motifs were annotated by SMART program. Motif 1, 3, 7 and 11 are MADS domains, motif 2 represents K domain, and motif 6 is C domain. All of MADS-box genes (except for 4 genes: Aco003667.1, Aco015492.1, Aco030656.1 and Aco019839.1) contained motif 1, and the 4 genes without motif 1 all contained motif 2. Meanwhile, motif 2 was identified in the majority of type II MADS-box genes, while it was only discovered in four type I genes (Aco019039.1, Aco011677.1, Aco030656.1 and Aco019839.1). Genes in the same group tend to have commonly shared motifs. For example, Mδ-type group includes Aco013736.1 and Aco019026.1 contained only motif 1. Aco022101.1 and Aco027629.1, in Mγ group, both possessed motifs 1, 8, 11, 15 and 20.
Fig. 3.
Conserved motif analysis of pineapple MADS-box genes
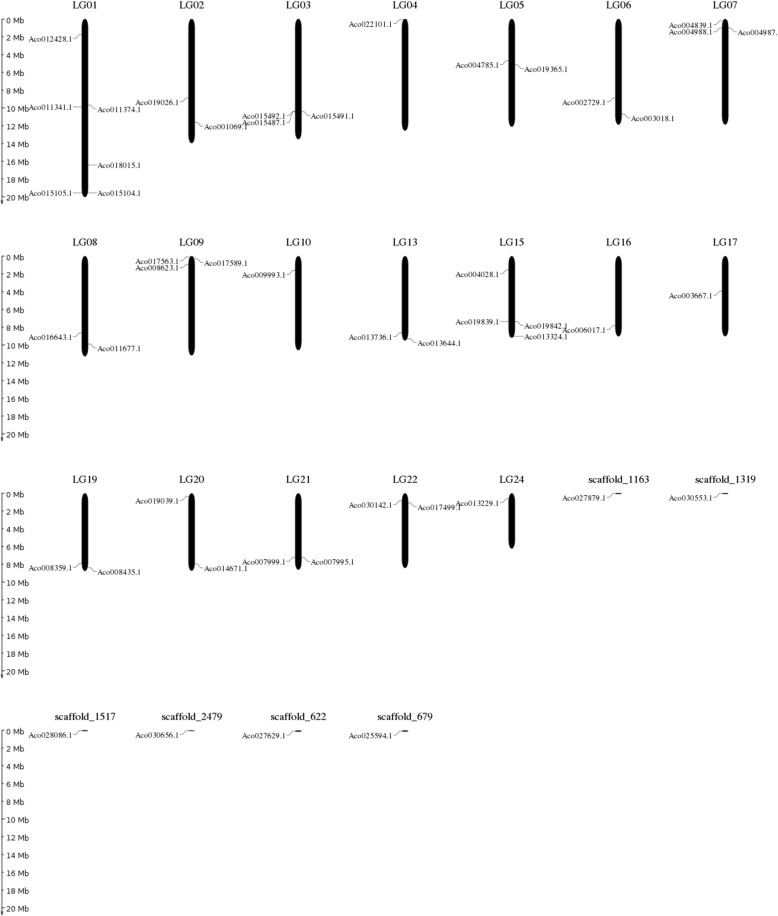
Location on chromosomes of pineapple MADS-box genes
The majority of pineapple MADS-box genes (42 out of 48) were randomly distributed across 19 chromosomes, while only 6 genes were scattered in 6 scaffolds that could not be assigned to chromosomes (Table 1, Fig. 4). Six genes (12.5%) were on chromosome 1, followed by 4 genes (8.3%) on chromosome 15. Type II MADS-box genes were mapped to 18 chromosomes (except from chromosome 4), while type I MADS-box genes were scattered to only 9 chromosomes due to fewer members. Out of type I genes, Mα group genes were distributed on chromosomes 7, 8, 9, 15, 19 and 20, whereas two Mβ group genes were clustered across chromosomes 1 and scafford_1517. Genes in Mγ group were located on chromosomes 4, 13 and 15.
Fig. 4.
Distribution of MADS-box genes in pineapple linkage groups (LGs)
Expression analysis of the pineapple MADS-box genes in different tissues
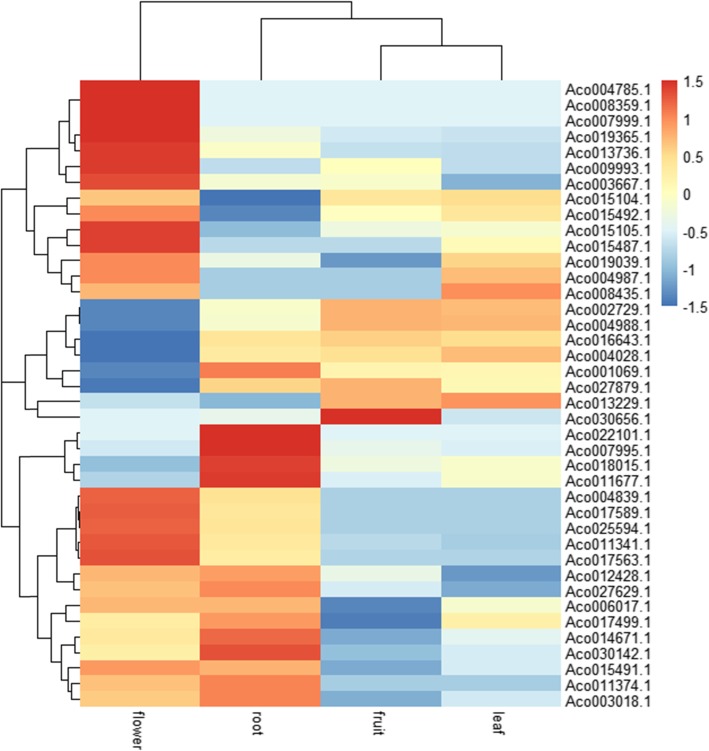
To investigate the expression patterns of pineapple MADS-box genes in different tissues, RNA-seq libraries prepared from four pineapple tissues: leaf, flower, root and fruit were constructed and RNA-seq analysis was further performed to obtain FPKM values of MADS-box genes in pineapple. Forty MADS-box genes were expressed in at least one tissue, while the other 8 genes (Aco019026.1, Aco008623.1, Aco013644.1, Aco019842.1, Aco019839.1, Aco013324.1, Aco030553.1 and Aco028086.1) were not detectable in any of those four tissues. Therefore, 8 genes with no detectable expression (FPKM value equals “0” in all four tissues) were filtered out and the expression level of 40 genes was shown in a heat map (Fig. 5).
Fig. 5.
A heat map of tissue-specific expression data of MADS-box genes in pineapple
RNA-seq expression profile of pineapple MADS-box genes revealed that a majority of genes were highly expressed in flower. Besides, some genes, such as Aco019365.1, Aco017589.1 and Aco025594.1, were expressed much higher in flower than in other tissues. In leaf tissues, many genes had relatively lower expression, but some genes (Aco027629.1 and Aco002729.1) expressed higher in leaves than in flowers. In fruit tissue, a few genes, such as Aco002729.1, Aco016643.1 and Aco013229.1 showed high expression level. Two genes, Aco007995.1 and Aco018015.1, were highly expressed in root, and Aco022101.1 was only expressed in root.
Ten MADS-box genes were randomly selected for quantitative RT-PCR analysis in flower and leaf tissues to verify the RNA-seq data (Fig. 6). The qRT-PCR results confirmed that most of MADS-box genes had high expression in flower and had low expression in leaves. However, a few genes, such as Aco027629.1 and Aco002729.1, expressed higher in leaves, which exhibited the same trend as RNA-seq data. These results showed that our RNA-seq data is suitable for investigating the expression patterns of MADS genes in different tissues of pineapple.
Fig. 6.
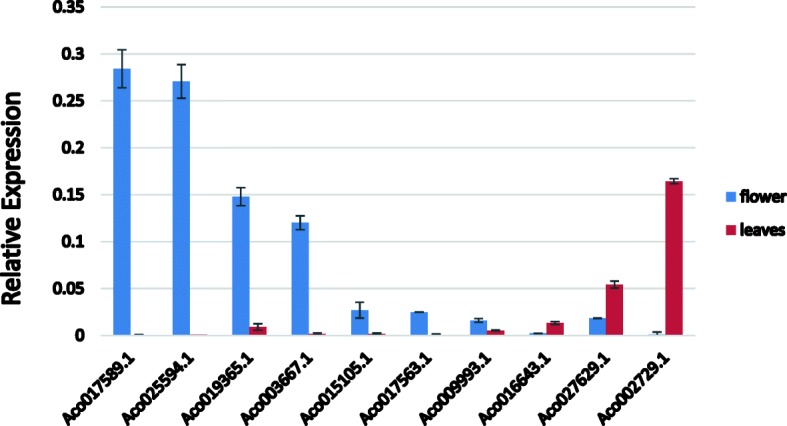
Relative expression of MADS-box genes in pineapple flower and leaves by qRT-PCR
Expression analysis of pineapple MADS-box genes in green tip and white base leaves
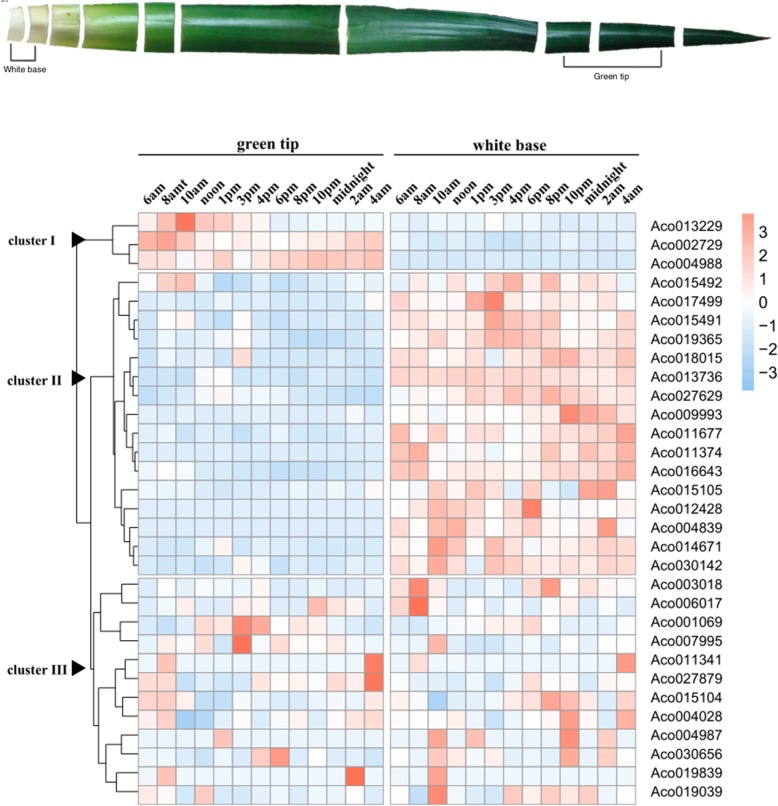
Pineapple is a CAM plant that achieves greater net CO2 uptake than their C3 and C4 counterparts [24]. To investigate the potential roles of MADS-box genes in pineapple CAM photosynthesis, we studied the expression pattern of MADS-box genes in photosynthetic (green tip) and non-photosynthetic (white base) leaf tissues. The green and white leaves are physiologically different, the green tip has very high concentration of chlorophyll, while white base contains extremely low chlorophyll concentration, which shows the difference of green and white leaves in photosynthetic rate [25]. The genes with no detectable expression and low expression (FPKM less than 1 in both tissues) were filtered out. As shown in Fig. 7, MADS-box genes can be classified into three clusters. Over the 24-h period, the expression level of cluster I genes in green tip leaf was higher than that in white base leaf. However, the cluster II genes showed opposite expression: genes in white base expressed higher than in green tip leaf. In cluster III, genes did not exhibit obvious differential expression between green tip and white base tissues. Meanwhile, some MADS-box genes showed peak expression at certain time period in either green tip or white base. For example, Aco012428.1 had highest expression at 6 pm in white base leaf, while Aco027629.1 exhibited highest expression at 12 am in green tip leaf.
Fig. 7.
Expression profiles of pineapple MADS-box genes in both photosynthetic and non-photosynthetic leaf tissues
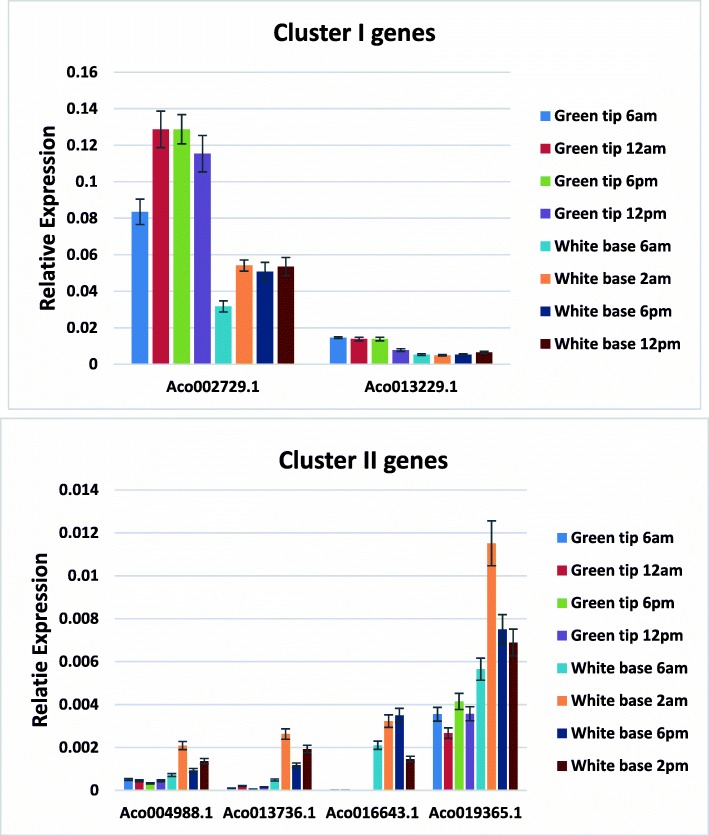
There are 14 genes in cluster I and II, we chose 6 genes for qRT-PCR analysis to verify their expression level in green and white leaves (Fig. 8). According to qRT-PCR results, the genes in cluster I also showed the similar expression pattern: expressed higher in green tip leaves than white base leaves, and cluster II genes had higher expression in white base leaves. Besides, our qRT-PCR results confirmed that Aco027629.1 had highest expression at 12 am in green tip leaves.
Fig. 8.
Relative expression of cluster l and ll MADS-box genes in green and white leaves at different time points by qRT-PCR
Diurnal expression analysis of pineapple MADS-box genes
To identify the circadian expression pattern of MADS-box genes in pineapple, RNA-Seq data of pineapple green tip and white base leaf tissues over 24-h period were used to determine MADS-box genes whose expression patterns fit the model of cycling genes in Haystack [26]. Transcription factors with a strong correlation (r > 0.7) were empirically considered as genes with diurnal rhythm [27], we used the same correlation cutoff as the threshold for analyzing diurnal expression pattern of MADS-box genes. 11 out of 48 (23%) of MADS-box genes were cycling in either green tip or white base leaf tissues. Out of these cycling genes, 4 genes (Aco013229.1, Aco015104.1, Aco004028.1 and Aco019365.1), which all belong to type II group, were cycling in both green tip and white base leaf tissues (Table 2).
Table 2.
Diurnal expression pattern of pineapple MADS-box genes
| pineapple gene | types | gropus | description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aco004988.1 | type I | Mα | Cycling in Green tip leaf tissue |
| Aco015492.1 | type II | MIKC | Cycling in Green tip leaf tissue |
| Aco015492.1 | type II | MIKC | Cycling in Green tip leaf tissue |
| Aco016643.1 | type II | MIKC | Cycling in Green tip leaf tissue |
| Aco011677.1 | type I | Mα | Cycling in White base leaf tissue |
| Aco012428.1 | type II | MIKC | Cycling in White base leaf tissue |
| Aco018015.1 | type II | MIKC | Cycling in White base leaf tissue |
| Aco013229.1 | type II | MIKC | Cycling in both green tip and white base leaf tissue |
| Aco004028.1 | type II | MIKC | Cycling in both green tip and white base leaf tissue |
| Aco015104.1 | type II | MIKC | Cycling in both green tip and white base leaf tissue |
| Aco019365.1 | type II | MIKC | Cycling in both green tip and white base leaf tissue |
Four genes were cycling in green tip leaf only, as shown in Fig. 9. Aco015492.1 exhibited peak expression at 10 am and lowest expression at 1 pm, while Aco004988.1 had lowest expression at 10 am and highest expression at 1 pm. Aco002729.1 and Aco016643.1 showed similar diurnal rhythm: peak expression at 8 am and lowest expression at 6 pm. There were three genes cycling only in white base leaf tissues (Fig. 9). What’s interesting is that Aco012428.1 exhibited two peak expressions at 6 am and 10 am. Four genes were cycling in both green tip and white base leaves (Fig. 10). Aco013229.1 had much higher expression in green tip than in white base during daytime from 6 am to 6 pm and similar expression level in both tissues at night. Aco019365.1 exhibited similar expression pattern in both green tip and white base: highest expression at 3 pm, lowest expression at 10 pm, while Aco004028.1 showed opposite expression profiles: highest expression in white base at 10 pm and in green tip at 8 am.
Fig. 9.
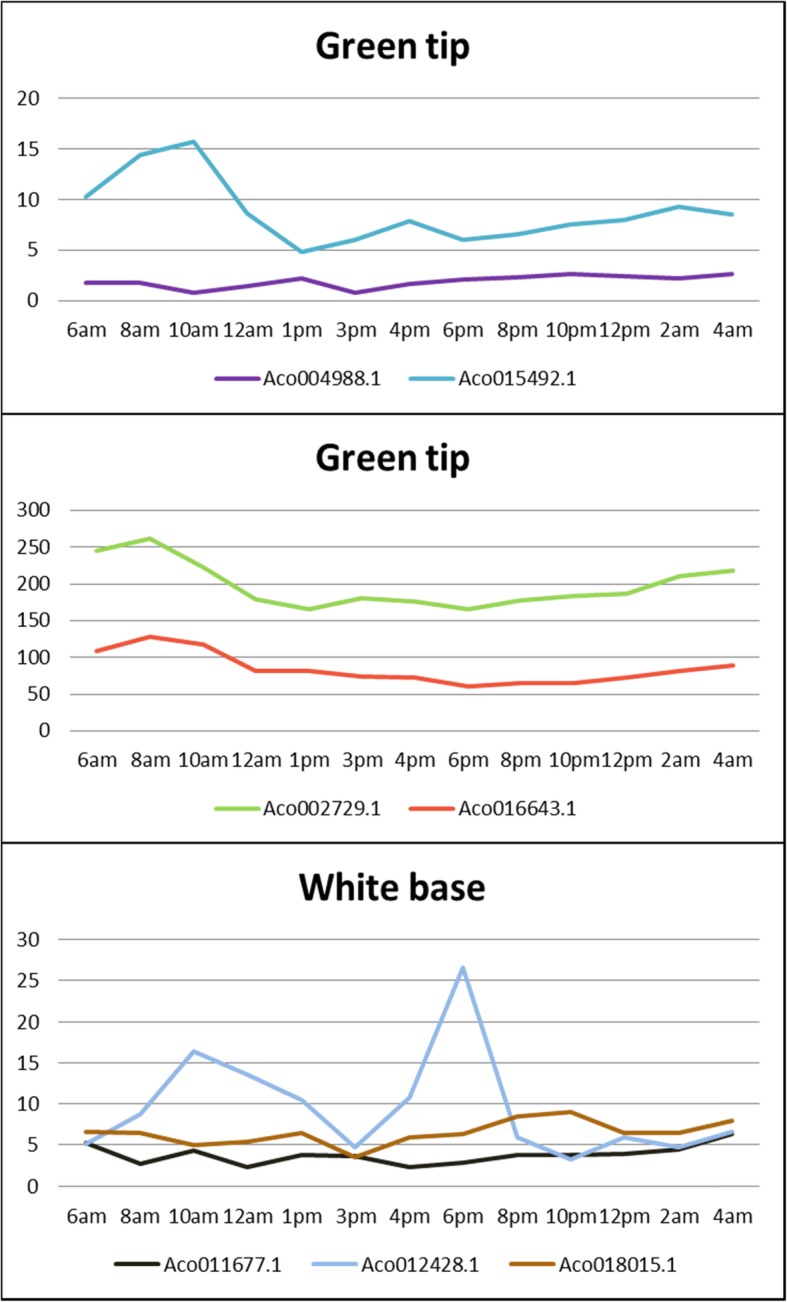
Diurnal expression patterns of MADS-box genes cycling in green tip or white base only
Fig. 10.
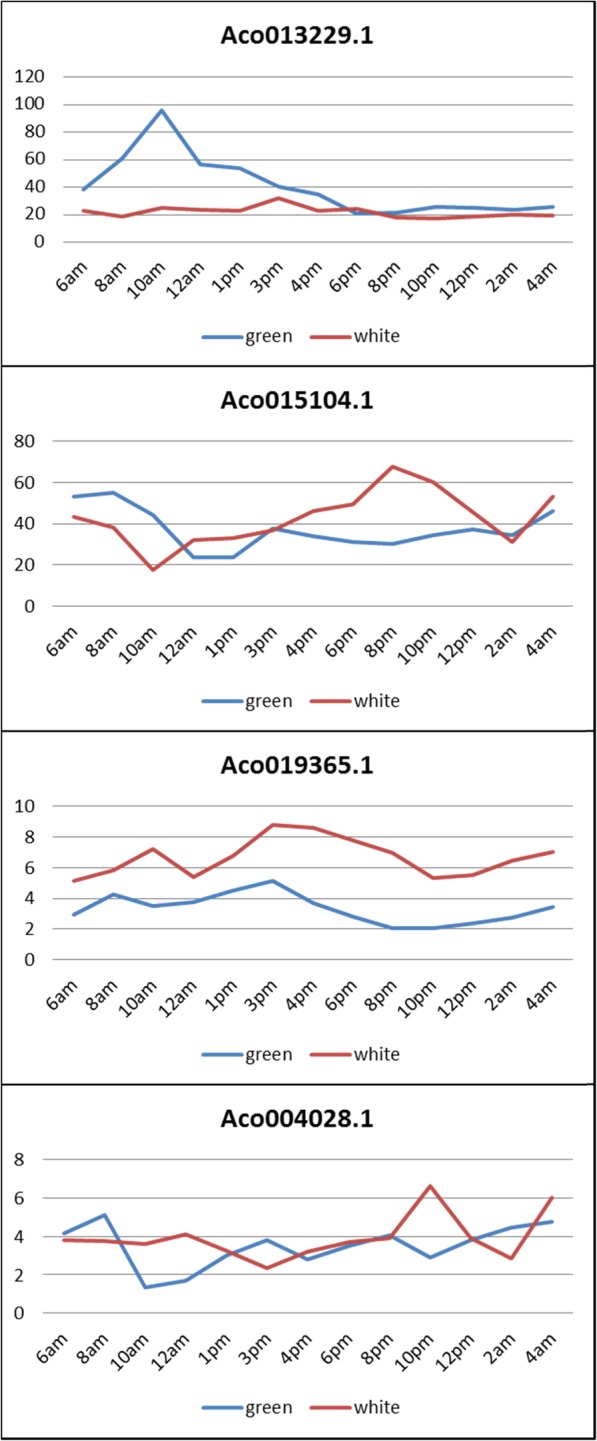
Diurnal expression patterns of MADS-box genes cycling in both green tip and white base leaf
Discussion
Compared with other plant species, pineapple has a relatively lower number of MADS-box genes. A total of 48 MADS-box genes were identified in pineapple, while 106, 75, 105 and 147 genes were discovered in Arabidopsis, rice, poplar and apple, respectively [28–31]. Previous studies showed that MADS-box family genes expand by whole genome duplication and gene duplication events [32, 33]. The difference of MADS-box gene numbers among species might be the result of recent duplications. Pineapple has undergone two ancient whole genome duplications (σ and τ), while rice has undergone a recent whole genome duplication (ρ) after the σ [24, 34]. It explains that the number of the pineapple MADS-box genes are less than that of rice and other species.
MADS-box genes are divided into two classes: type I and type II, and these two types have distinct evolutionary histories [10]. Type II MADS-box genes are mainly the result of whole genome duplications, while type I genes are caused by smaller scale and more recent duplications. It has been relatively easy to identify the orthologs of Arabidopsis type II MADS-box genes in different species, but orthologs of Arabidopsis type I MADS-box genes are difficult to be discovered in other species, mainly because that most duplicated type I genes are caused by genus-specific localized duplications [29]. The chromosomal distribution of MADS-box genes could also explain the idea that type I genes have resulted from smaller scale duplication. In Arabidopsis, type II genes were distributed across all chromosomes, whereas type I genes were clustered into only chromosomes I and V [12]. Type II MADS-box genes in pineapple were located on 18 chromosomes, while type I MADS-box genes were only scattered to 9 chromosomes.
Based on phylogenetic analysis, type II MADS-box genes in pineapple contain 32 MIKC-type and 2 Mδ-type and 32 MIKC-type genes could be divided into 11 subfamilies. There was no pineapple gene identified as FLC (FLOWERING LOCUS C) subfamily. FLC plays the important role in floral transition and serves as a major floral repressor in the autonomous and vernalization pathways [35]. The absence of pineapple FLC members indicated that pineapple could not require vernalization for flowering, a loss will not have any impact on this tropical plant. SOC1 is a MADS-box gene in Arabidopsis regulated by two flowering regulators, CONSTANS (CO) and FLC, serving as floral activator and repressor, respectively [36, 37]. Three SOC1-like pineapple genes were identified, while no CO member was found in pineapple. The regulatory mechanisms of flowering in pineapple might be different from that of Arabidopsis. Type I MADS-box genes could be divided into Mα, Mβ and Mγ. In Arabidopsis, type I genes play important role in plant reproduction as well as the maintenance of species barriers and are required for endosperm development [38–40]. Studies showed that type I MADS-box genes had faster birth and death compared with type II genes, which could further explain the different pattern of type I and type II genes in phylogenetic tree.
Knowing where the genes are expressed is important for understanding the molecular mechanisms of biological development. The expression patterns of MADS-box genes in different organs of pineapple indicated that the pineapple MADS-box genes were expressed differently in the different tissues. The higher expression level of MADS-box genes in the flowers indicated that MADS-box genes play the important roles in the flower development in pineapple. The MADS-box transcription factors were regarded as the genes involved in floral organ identity. For example, AGAMOUS 1 (TAG1) was involved in flower and fruit development of tomato [41]. Although most MADS-box genes were reported to be related to flower development, we want to know whether some MADS-box genes were also involved in the CAM photosynthesis. Thus, the expression patterns of MADS-box genes in both photosynthetic and non-photosynthetic leaf tissues was studied to investigate the potential roles of MADS-box genes in pineapple CAM photosynthesis. The results showed that many MADS-box genes have different expression levels in white base (non-photosynthetic) and green tip (photosynthetic) leaf tissues and more genes expressed higher in white base than in green tip, which indicating that MADS-box genes are not typical genes involved in photosynthesis, but some genes might play certain roles in pineapple CAM photosynthesis.
Circadian clock, as an important regulator, plays a crucial role in the biological mechanisms such as developmental or metabolic process [27]. 23% (11 out of 48) of MADS-box genes displayed diurnal expression, the proportion of pineapple MADS-box genes with circadian rhythm was lower than expected partially because only leaf samples were used for diurnal expression analysis. However, the results still indicated that some MADS-box genes in pineapple could be involved in the circadian clock. In Arabidopsis, circadian clock has been widely studied and mutants with perturbed circadian rhythms were large-scale screened [42].
Conclusions
In this study, we conducted the whole-genome analysis of MADS-box genes and then identify 48 MADS-box genes in the pineapple genome. Forty-eight MADS-box genes can be divided into 14 type I and 34 type II MADS-box genes. a majority of pineapple MADS-box genes are highly expressed in flowers, which indicates that pineapple MADS-box genes are closely related to flowering development. Some MADS-box genes express differently in photosynthetic and non-photosynthetic leaf tissues, suggesting that MADS-box genes could be involved in CAM photosynthesis. 23% of pineapple MADS-box genes are regulated by the circadian clock. These findings will facilitate research on the development of unusual spiral inflorescences on pineapple fruit and CAM photosynthesis.
Methods
Whole-genome identification of MADS-box genes in pineapple
The protein sequences of pineapple, rice and Arabidopsis were obtained from Phytozome (https://phytozome.jgi.doe.gov/pz/portal.html), RGAP (http://rice.plantbiology.msu.edu/) and TAIR (http://www.arabidopsis.org/) databases, respectively. To identify the MADS-box genes in pineapple, the Hidden Markov Model (HMM) profiles of the SFR (type I) domain (PF00319) and the MEF2 (type II) domain (PF09047), downloaded from Pfam database (http://pfam.xfam.org, Pfam 31.0), were used to search the pineapple genome database [43, 44]. All of the proteins with an E-value lower than 0.01 were selected. Secondly, using all Arabidopsis and rice MADS-box genes as queries, the predicted pineapple MADS genes were checked by BLASTP searches (https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi). Finally, the predicted MADS models detected were examined manually. The retrieved pineapple MADS genes were further verified by the NCBI Conserved Domain Database (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/cdd).
Classification of pineapple MADS-box genes
MADS-box genes in Arabidopsis and rice were used for classifying the pineapple MADS-box genes. Multiple sequence alignments were performed based on protein sequences of MADS-box genes in pineapple, Arabidopsis and rice using MAFFT (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/msa/mafft/). A phylogenetic tree was then constructed based on multiple sequence alignments using RAxML with the parameters: pair wise gap deletion and 1000 bootstrap iterations [45]. The phylogenetic tree was further annotated by iTOL program (http://itol.embl.de/).
Gene structure and conserved motif analysis
To identify the gene structure of pineapple MADS-box genes, the full-length coding sequence (CDS) and genomic sequence of MADS-box genes were used to perform gene structure analysis by Gene Structure Display Server program (http://gsds.cbi.pku.edu.cn/) [46]. Online software MEME was used to search motifs in pineapple MADS-box genes (http://meme-suite.org/tools/meme) with the parameters: maximum number of motifs – 20 and optimum motif width set at ≥6 and ≤ 200. The motifs of MADS-box genes were annotated by the SMART program (http://smart.embl-heidelberg.de/).
Location of pineapple MADS-box genes on chromosomes
The pineapple genome has been mapped to 25 chromosomes [24]. To explore the chromosomal location of MADS-box genes, online software MA2C (MapGene2Chromosome v2) (http://mg2c.iask.in/mg2c_v2.0/) was used to map pineapple MADS-box genes onto chromosomes.
Expression analysis of pineapple MADS-box genes in four tissues
Expression patterns of MADS-box genes at different tissues (flower, root, leaf and fruit) were analyzed using RNA-Seq data obtained from Ming et al. [24]. Flower, root and leaf tissues were collected from cultivar F153 and fruit tissue was obtained from cultivar MD-2. The tissues were stored at -80 °C for RNA extraction and transcriptome analysis. The FPKM values were calculated by the Cufflinks/Cuffnorm pipeline (http://cufflinks.cbcb.umd.edu/). Genes with no expression (FPKM values equal “0” in all tissues) were filtered. The expression pattern of pineapple MADS-box genes in different tissues was visualized by a heat map.
Diurnal expression analysis of MADS-box genes
Green tip (photosynthesis) and white base (non- photosynthesis) leaf tissues were collected from field pineapple cultivar MD-2 grown in Hawaii over a 24-h period to examine the diurnal expression patterns of pineapple genes. Five individual plants were collected as one replicate, and three biological replicates were collected. The method of analyzing circadian rhythm was adopted from Sharma et al. [27]. Online software Haystack was used to analyze the time series expression data (http://haystack.mocklerlab.org/), with parameters: correlation cut off 0.7, P value cut off 0.05, fold change cutoff 2 and background cutoff 1.
Plant material, RNA extraction and quantitative RT-PCR analysis
The flower and leaves of pineapple cultivar MD-2 were obtained from the greenhouse of Fujian Agriculture and forestry University (26°4′54″N, 119°13′47″E) on October 25th, 2019. The average temperature of greenhouse is around 28 °C, and the light cycle is from 4:00–20:00. The ways of collecting pineapple samples and designing biological replicates was the same as the protocols in the paper of Ming et al. [24].
Total RNA was extracted using Trizol protocol. Reverse transcription was performed from 2μg of RNA using TransScript One-Step Supermix kit. The cDNA was diluted ten-fold for the following qRT-PCR verification. Primers for pineapple MADS-box genes were designed using online website (https://www.idtdna.com/PrimerQuest/Home/Index). Primers information are listed in the Additional file 1: Table S1. The qRT-PCR reaction was performed in the 20 μL volume containing 1 μL of cDNA, 1 μL of each primezr and 10 μL of SYBR Green mix and was under the following program: 95 °C for 3 min; 32 cycles at 95 °C for 15 s, 60 °C for 15 s, and 72 °C for 30 s; 72 °C for 10 min.
The expression of MADS-box genes in different tissues (flower and leaves), green tip and white base leaves at different time points (6 am, 12 am, 6 pm, 12 pm) were verified by qRT-PCR. All the reactions were performed in three biological replicates.
Supplementary information
Additional file 1: Table S1. The primer sequences for qRT-PCR
Acknowledgments
We thank Lulu Wang and Lihua Zhao for providing pineapple flower samples and primers of reference gene for qRT-PCR experiments, we also thank Ruoyu Li for collecting leaf tissues at different time points.
Abbreviations
- AGL11
Agamous like-11
- AGL12
Agamous like-12
- ANR1
Arabidopsis Nitrate Responsive1
- CAM
Crassulacean Acid Metabolism
- CO
CONSTANS
- FLC
Flowering Locus C
- HMM
Hidden Markov Model
- MEME
Multiple Em for Motif Elicitation
- NCBI
National Center for Biotechnology Information
- SEP
SEPALATA
- SMART
Simple Modular Architecture Research Tool
- SOC1
Suppressor of Overexpression of Co1
- SVP
Short Vegetative Phase
- TT16
Transparent Testa16
Authors’ contributions
R.M. and X.Z. conceived the project and designed experiments. X.Z. and Q.M. carried out the experiment. X.Z., M.F., and P.Z. analyzed the data. X.Z. wrote the manuscript. R.M. revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
The qRT-PCR experiments and publication costs were supported by the grant 2016NZ0001–1 from the Fujian Provincial Department of Science and Technology and startup fund from Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University to RM. The funding bodies had no input on study design, data analysis, data interpretation and manuscript writing.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets analyzed in this study are publicly available in NCBI under BioProject PRJNA305042.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information accompanies this paper at 10.1186/s12864-019-6421-7.
References
- 1.Jack T. Plant development going MADS. Plant Mol Biol. 2001;46(5):515–520. doi: 10.1023/A:1010689126632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Norman C, Runswick M, Pollock R, Treisman R. Isolation and properties of cDNA clones encoding SRF, a transcription factor that binds to the c-fos serum response element. Cell. 1988;55(6):989–1003. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90244-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Passmore S, Maine GT, Elble R, Christ C, Tye BK. Saccharomyces cerevisiae protein involved in plasmid maintenance is necessary for mating of MATα cells ☆. J Mol Biol. 1988;204(3):593–606. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90358-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Sommer H, Beltrán JP, Huijser P, Pape H, Lönnig WE, Saedler H, Schwarzsommer Z. Deficiens, a homeotic gene involved in the control of flower morphogenesis in Antirrhinum majus: the protein shows homology to transcription factors. EMBO J. 1990;9(3):605–613. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08152.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Yanofsky MF, Ma H, Bowman JL, Drews GN, Feldmann KA, Meyerowitz EM. The protein encoded by the Arabidopsis homeotic gene agamous resembles transcription factors. Nature. 1990;346(6279):35–39. doi: 10.1038/346035a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Shore P, Sharrocks AD. The MADS-box family of transcription factors. Eur J Biochem. 1995;229(1):1–13. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1995.tb20430.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Xu Z, Zhang Q, Sun L, Du D, Cheng T, Pan H, Yang W, Wang J. Genome-wide identification, characterisation and expression analysis of the MADS-box gene family in Prunus mume. Mol Gen Genomics. 2014;289(5):903–920. doi: 10.1007/s00438-014-0863-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Riechmann JL, Meyerowitz EM. MADS domain proteins in plant development. Biol Chem. 1997;378(10):1079–1101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Gramzow L, Ritz MS, Theißen G. On the origin of MADS-domain transcription factors. Trends Genet. 2010;26(4):149–153. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2010.01.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Airoldi CA, Davies B. Gene duplication and the evolution of plant MADS-box transcription factors. J Genet Genomics. 2012;39(4):157–165. doi: 10.1016/j.jgg.2012.02.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Ng M, Yanofsky MF. Function and evolution of the plant MADS-box gene family. Nat Rev Genet. 2001;2(3):186–195. doi: 10.1038/35056041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Parenicová L, Folter SD, Kieffer M, Horner DS, Favalli C, Busscher J, Cook HE, Ingram RM, Kater MM, Davies B. Molecular and Phylogenetic Analyses of the Complete MADS-Box Transcription Factor Family in Arabidopsis New Openings to the MADS World. Plant Cell. 2003;15(7):1538–1551. doi: 10.1105/tpc.011544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Grimplet J, Martínez-Zapater JM, Carmona MJ. Structural and functional annotation of the MADS-box transcription factor family in grapevine. BMC Genomics. 2016;17(1):80. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-2398-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Gan DF. Genome-wide sequence characterization analysis of mads-box transcription factor gene family in cucumber (Cucumis sativusL.). J Nucl Agricl Sci. 2012;9(1):85.
- 15.Liu J, Jing Z, Zhang J, Miao H, Wang J, Gao P, Wei H, Jia C, Zhuo W, Xu B. Genome-wide analysis of banana MADS-box family closely related to fruit development and ripening. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):3467. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-03897-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Wei B, Zhang RZ, Guo JJ, Liu DM, Li AL, Fan RC, Mao L, Zhang XQ. Genome-wide analysis of the MADS-box gene family in Brachypodium distachyon. PLoS One. 2014;9(1):e84781. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0084781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Ma J, Yang Y, Luo W, Yang C, Ding P, Liu Y, Qiao L, Chang Z, Geng H, Wang P. Genome-wide identification and analysis of the MADS-box gene family in bread wheat (Triticum aestivumL.) PLoS One. 2017;12(7):e0181443. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0181443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Ghosh A, Islam T. Genome-wide analysis and expression profiling of glyoxalase gene families in soybean (Glycine max) indicate their development and abiotic stress specific response. BMC Plant Biol. 2016;16(1):87. doi: 10.1186/s12870-016-0773-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Zhang L, Zhao J, Feng C, Liu M, Wang J, Hu Y. Genome-wide identification, characterization of the MADS-box gene family in Chinese jujube and their involvement in flower development. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):1025. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-01159-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Coen ES, Meyerowitz EM. The war of the whorls: genetic interactions controlling flower development. Nature. 1991;353(6339):31–37. doi: 10.1038/353031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Causier B, Schwarz-Sommer Z, Davies B. Floral organ identity: 20 years of ABCs. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2010;21(1):73–79. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2009.10.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Smaczniak C, Immink RG, Angenent GC, Kaufmann K. Developmental and evolutionary diversity of plant MADS-domain factors: insights from recent studies. Development. 2012;139(17):3081. doi: 10.1242/dev.074674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Lüttge U. Ecophysiology of Crassulacean acid metabolism (CAM) Ann Bot. 2004;93(6):629–652. doi: 10.1093/aob/mch087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Ming R, Vanburen R, Wai CM, Tang H, Schatz MC, Bowers JE, Lyons E, Wang ML, Chen J, Biggers E. The pineapple genome and the evolution of CAM photosynthesis. Nat Genet. 2015;47(12):1435–1442. doi: 10.1038/ng.3435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Li X, Kanakala S, He Y, Zhong X, Yu S, Li R, Sun L, Ma J. Physiological characterization and comparative transcriptome analysis of white and green leaves of Ananas comosusvar. bracteatus. PLoS One. 2017;12(1):e0169838. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0169838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Mockler TC, Michael TP, Priest HD, Shen R, Sullivan CM, Givan SA, Mcentee C, Kay SA, Chory J. The diurnal project: diurnal and circadian expression profiling, model-based pattern matching, and promoter analysis. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2007;72(8):353. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2007.72.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Sharma A, Wai CM, Ming R, Yu Q. Diurnal cycling transcription factors of pineapple revealed by genome-wide annotation and global Transcriptomic analysis. Genome Biol Evol. 2017;9(9):2170–2190. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evx161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Parenicová L, de Folter S, Kieffer M, Horner DS, Favalli C, Busscher J, Cook HE, Ingram RM, Kater MM, Davies B, Angenent GC, Colombo L. Molecular and phylogenetic analyses of the complete MADS-box transcription factor family in Arabidopsis: new openings to the MADS world. Plant Cell. 2003;15(7):1538–1551. doi: 10.1105/tpc.011544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Tyagi AK, Vijay S, Ashok S, Swatismita R, Pinky A, Rita A, Sanjay K. MADS-box gene family in rice: genome-wide identification, organization and expression profiling during reproductive development and stress. BMC Genomics. 2007;8(1):242. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-8-242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Leseberg CH, Li A, Kang H, Duvall M, Mao L. Genome-wide analysis of the MADS-box gene family in Populus trichocarpa. Gene. 2006;378(1):84–94. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2006.05.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Velasco R, Zharkikh A, Affourtit J, Dhingra A, Cestaro A, Kalyanaraman A, Fontana P, Bhatnagar SK, Troggio M, Pruss D. The genome of the domesticated apple (Malus × domestica Borkh.) Nat Genet. 2010;42(10):833–839. doi: 10.1038/ng.654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Paterson AH, Bowers JE, Chapman BA. Ancient polyploidization predating divergence of the cereals, and its consequences for comparative genomics. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101(26):9903–9908. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0307901101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Yu J, Wang J, Lin W, Li S, Li H, Zhou J, Ni P, Dong W, Hu S, Zeng C, et al. The Genomes of Oryza sativa: a history of duplications. 2005;3(2):266–81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 34.Jiao Y, Li J, Tang H, Paterson AH. Integrated Syntenic and Phylogenomic analyses reveal an ancient genome duplication in monocots. Plant Cell. 2014;26(7):2792. doi: 10.1105/tpc.114.127597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Boss PK, Bastow RM, Mylne JS, Dean C. Multiple pathways in the decision to flower: enabling, promoting, and resetting. Plant Cell. 2004;16(Suppl):S18. doi: 10.1105/tpc.015958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Lee J, Lee I. Regulation and function of SOC1, a flowering pathway integrator. J Exp Bot. 2010;61(9):2247–2254. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erq098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Samach A, Onouchi H, Gold SE, Ditta GS, Schwarz-Sommer Z, Yanofsky MF, Coupland G. Distinct roles of CONSTANS target genes in reproductive development of Arabidopsis. Science. 2000;288(5471):1613–1616. doi: 10.1126/science.288.5471.1613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Köhler C, Hennig L, Spillane C, Pien S, Gruissem W, Grossniklaus U. The Polycomb-group protein MEDEA regulates seed development by controlling expression of the MADS-box gene PHERES1. Genes Dev. 2003;17(12):1540–1553. doi: 10.1101/gad.257403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Bemer M, Woltersarts M, Grossniklaus U, Angenent GC. The MADS domain protein DIANA acts together with AGAMOUS-LIKE80 to specify the central cell in Arabidopsis ovules. Plant Cell. 2008;20(8):2088–2101. doi: 10.1105/tpc.108.058958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Walia H, Josefsson C, Dilkes B, Kirkbride R, Harada J, Comai L. Dosage-dependent deregulation of an AGAMOUS-LIKE gene cluster contributes to interspecific incompatibility. Curr Biol. 2009;19(13):1128–1132. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2009.05.068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Pan IL, McQuinn R, Giovannoni JJ, Irish VF. Functional diversification of AGAMOUS lineage genes in regulating tomato flower and fruit development. J Exp Bot. 2010;61(6):1795–1806. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erq046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Staiger D. Circadian rhythms in Arabidopsis: time for nuclear proteins. Planta. 2002;214(3):334–344. doi: 10.1007/s004250100662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Finn RD, Coggill P, Eberhardt RY, Eddy SR, Mistry J, Mitchell AL, Potter SC, Punta M, Qureshi M, Sangrador-Vegas A. The Pfam protein families database: towards a more sustainable future. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016;44(Database issue):D279–D285. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv1344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Finn RD, Clements J, Arndt W, Miller BL, Wheeler TJ, Schreiber F, Bateman A, Eddy SR. HMMER web server: 2015 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015;43(1):30–38. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Stamatakis A. RAxML version 8: a tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics. 2014;30(9):1312–1313. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Guo AY, Zhu QH, Chen X, Luo JC. GSDS: a gene structure display server. Yi Chuan. 2007;29(8):1023–1026. doi: 10.1360/yc-007-1023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Additional file 1: Table S1. The primer sequences for qRT-PCR
Data Availability Statement
The datasets analyzed in this study are publicly available in NCBI under BioProject PRJNA305042.