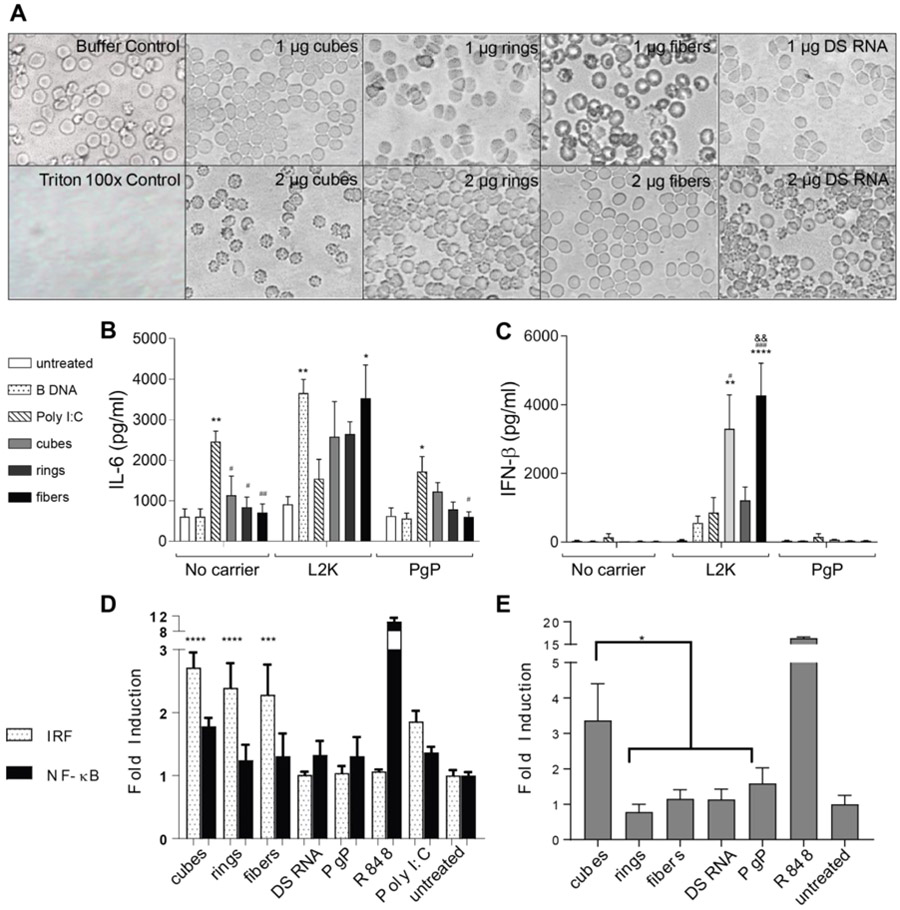
Figure 6.
Blood compatibility and immunostimulation with PgP/NANP(GFP) polyplexes. In all experiments, cubes (PgP/cubes(GFP)), rings (PgP/rings(GFP)), fibers (PgP/fibers(GFP)), and individual DS RNAs(GFP) are compared. (A) Hemolysis assay was conducted using primary rat erythrocytes and demonstrated no lysis. (B-C) Immunostimulation of PgP/NANP(GFP) polyplexes measured via ELISA of inflammatory cytokines and type I interferons in hμglia cells. (D) IRF and NF-κB stimulation as measured by luciferase production and SEAP production, respectively, in THP1-Dual™ cells, and (E) TLR stimulation from polyplexes as measured by SEAP secretion from HEK-Blue™ hTLR7 cells. In B and C, statistical significance relevant to cells, poly I:C, and ring is denoted by *, #, and & respectively (*/# p<0.05, **/##/&& p<0.005, ### p<0.001, **** p<0.0001). (D) The role of IRF and NF-κB stimulation were measured using THP1-Dual™ cells. Statistical significance compared to cells denoted by *** with p<0.0005 and **** with p< 0.0001). (E) HEK-Blue™ hTLR7 cells were transfected with the various PgP/NANP complexes and the TLR stimulation was measured using QUANTI-Blue™ detection media (* denotes p<0.005).