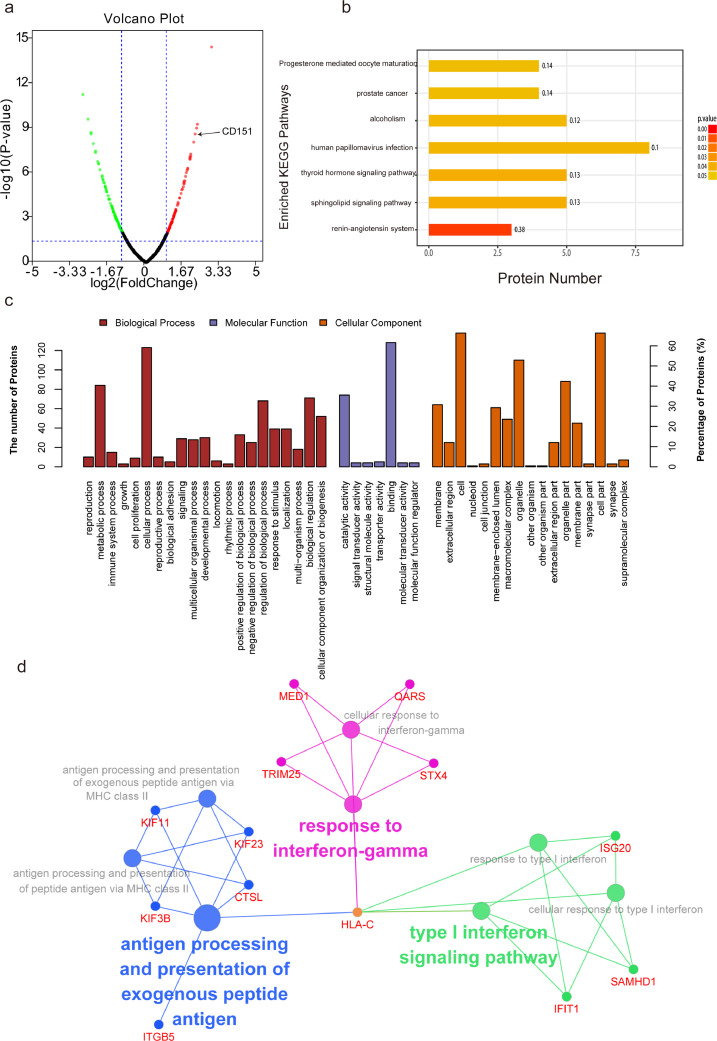
Fig. 1.
Defining potential oncoproteins/TAAs induced by radiation via proteomic analysis. Label-free relative quantitative proteomic analysis was performed to identify potential TAAs induced by radiation. (a) Volcano plot showing the distribution of 209 differentially expressed proteins quantified among non-IR and IR cells with the threshold of |log2 Fold change|>1 and P<0.05. Red dots indicate up-regulated proteins and green dots indicate down-regulated proteins. The expression of CD151 is indicated by the arrow. (b) The Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway analysis of differentially expressed proteins. Y-axis shows KEGG pathway entry, and X-axis shows the number of proteins annotated in the pathway. The intensity of the colour represents P-value. (c) Gene Ontology (GO) function analysis. Y-axis shows the number of proteins annotated in the GO term. X-axis shows the GO pathway, which was mainly categorized as biological process (red), cellular component (orange) and molecular function (purple). (d) The role of differentially expressed proteins induced by IR in immune system process were visualized in ClueGO (ver. 2.5.3) plugin of Cytoscape (ver. 3.5.1).(For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)