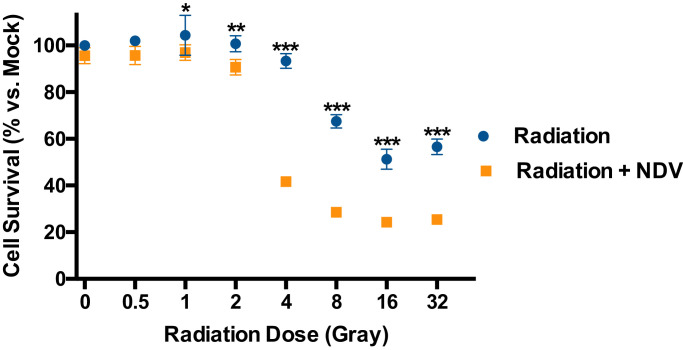
Fig. 1.
Newcastle disease virusradioenhancesmelanoma cellsin vitro. B16-F10 cells in culture were infected with Newcastle disease virus (NDV) at a multiplicity of infection of 3, or mock infected. Twenty-four hours later, cells were irradiated at doses of 0, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, or 32 Gray (Gy). Cell viability was measured by lactate dehydrogenase assay 5 days after radiation and compared to mock treated cells. Mean values from 3 replicates are plotted and error bars depict standard deviations. Multiple t-tests were performed to show significant differences in cell survival between NDV-infected and mock-infected cells at a given radiation dose. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001(multiple t-tests).