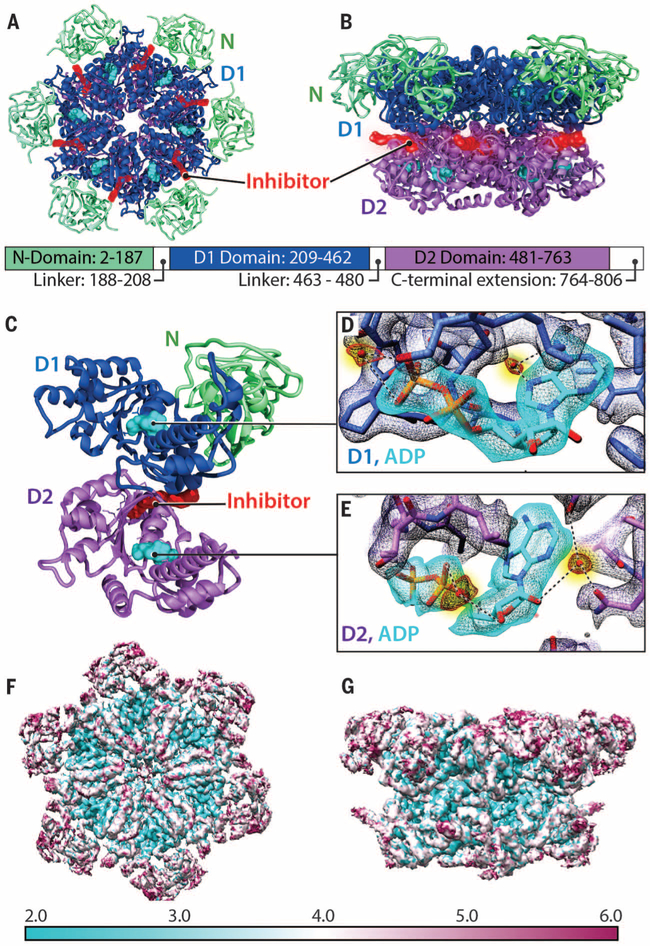
Fig. 1. Atomic-resolution model derived from cryo-EM structure of p97 in the presence of bound inhibitor.
(A and B) Top and side views, respectively, of the cryo-EM structure of the p97 hexamer presented as a ribbon diagram, showing the N (green), D1 (blue), and D2 (purple) domains. The ADP molecule is colored cyan. The inhibitor (red) is bound at the junction between the D1 and D2 domains. The relative position of each domain in the primary sequence is indicated. (C) Ribbon diagram of a p97 protomer highlighting the location of the bound inhibitor (red) relative to the two bound nucleotides (cyan) in D1 and D2 domains. (D and E) Density maps for bound nucleotides, establishing that ADP is bound to both D1 and D2 domains, and visualization of densities for tightly bound water molecules (colored red, highlighted in yellow) at the nucleotide-binding sites. (F and G) Top and side views, respectively, of the structure (uncorrected density map), color-coded to represent variation in resolution across the protein as determined using ResMap (28).