Abstract
Background
Beta-carotene (BC) is a carotenoid which exerts anti-cancer effects in several types of cancer, including colorectal cancer. Epigenetic modifications of genes, such as histone deacetylation and DNA hypermethylation, have also been detected in various types of cancer. To understand the molecular mechanism underlying cancer preventive and therapeutic effects of BC, microRNAs (miRNAs), histone acetylation, and global DNA methylation in colon cancer stem cells (CSCs) were investigated.
Methods
HCT116 colon cancer cells positive for expression of CD44 and CD133 were sorted by flow cytometry and used in subsequent experiments. Cell proliferation was examined by the MTT assay and self-renewal capacity was analyzed by the sphere formation assay. The miRNA sequencing array was used to detect miRNAs regulated by BC. Histone acetylation levels were measured by the Western blot analysis. mRNA expression of DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs) was examined by qPCR and global DNA methylation levels were determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
Results
Treatment of CD44+CD133+ colon CSCs with BC caused a reduction in both cell proliferation and sphere formation. Analysis of the miRNA sequencing array showed that BC regulated expression of miRNAs associated with histone acetylation. Histone H3 and H4 acetylation levels were elevated by BC treatment. In addition, BC treatment down-regulated DNMT3A mRNA expression and global DNA methylation in colon CSCs.
Conclusions
These results suggest that BC regulates epigenetic modifications for its anti-cancer effects in colon CSCs.
Keywords: Beta carotene, microRNAs, DNA methylation, Epigenomics, Colorectal neoplasms
INTRODUCTION
Beta-carotene (BC) is a carotenoid which has been known to exhibit anti-cancer effects in various cancers [1–3]. Its anti-cancer effects are mediated by induction of apoptosis, regulation of cell growth, inhibition of cell proliferation, delay in cell cycle progression, antioxidant activity, and modulation of the immune system [1,3–5]. In particular, BC has been shown to inhibit the cancer cell stemness in neuroblastoma [6].
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the third most commonly diagnosed cancer in the United States and the second highest cause of mortality among men and women [7]. Prevalence of CRC risk is closely related to various lifestyle factors, including alcohol consumption [8], obesity [9], physical inactivity [10], and smoking [11]. Numerous reports have additionally suggested that dietary factors related to the CRC risk include a low consumption of fruits and vegetables, a low fiber diet, a low residual diet [12], and high consumption of red/processed meats [13]. CRC patients often experience tumor recurrence after cancer treatment, and this can be explained by the existence of cancer stem cells (CSCs). CSCs are a small population of cancer cells which possess a self-renewal capacity and an ability to initiate clonal tumors [14]. CSCs resist treatments such as radiation therapy and chemotherapy. Therefore, targeting of CSCs has been identified as a fundamental strategy to effectively eliminate tumor cells and prevent the tumor relapse.
Epigenetic alterations can involve modifications of specific amino acid present in histone tails, particularly changes in the methylation status of cytosine residues in DNA and regulation of small non-coding RNAs. Promoter hypermethylation and histone hypomethylation have been associated with poor prognosis in various cancers, including colon, lung, prostate, and breast cancers [15–18]. Previous studies also have shown that microRNAs (miRNAs) modulate histone modifications and gene promoter DNA methylation [19,20]. MiRNAs target the 3′ noncoding region of mRNA to induce gene silencing, thereby regulate gene expression. In addition, miRNAs are associated with the development and progression of cancer, including regulation of cell proliferation, cell cycle progression, and apoptosis [21,22]. Thus, it is important to elucidate miRNAs, as well as interactions between miRNAs and their target genes, which play a role in the development and progression of cancer.
Many cancers are characterized by a loss of global histone acetylation. Correspondingly, mutation of histone deacetylase (HDAC) encoding genes and deregulation of HDAC proteins have been linked to tumor development since they regulate cell cycle progression, proliferation, and apoptosis [23,24]. However, HDAC inhibitors (HDACi) can help compensate for global histone loss in cancer and re-activate silenced genes. For example, HDACi can block utilization of HDAC substrates, induce apoptosis, and enhance sensitivity to cancer therapies [25,26]. Dietary factors can also regulate histone modification. For example, sulforaphane from broccoli, cauliflower, and cabbage have been reported to exert anti-cancer effects on pancreatic, prostate, and CRCs by targeting HDAC [27,28].
Many cancers exhibit global hypomethylation and promoter hypermethylation in the distinct set of tumor suppressor genes. Correspondingly, DNA hypermethylation has been associated with poor cancer prognosis and therapy resistance [29]. In a clinical trial, azacytidine (AZA), a representative demethylating agent, improves bioavailability and survival for myelodysplastic syndromes in clinical trial [30]. Thus, regulation of DNA represents an attractive strategy for cancer treatment.
In the present study, we demonstrate that BC is able to suppress the proliferation of colon cancer cells by regulating miRNAs, H3 and H4 acetylation, and global DNA methylation.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
1. Cell culture and treatment
The human colon cancer cell line, HCT116 was purchased from American Type Culture Collection (ATCC, Manassas, VA, USA). HCT116 cells were double-stained with CD133 and CD44 monoclonal antibodies (Miltenyi Biotec, Bergisch Gladbach, Germany) and sorted with a FACSAria flow cytometer (BD, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA). CD133+CD44+ HCT116 CSCs were maintained in McCoy’s 5A Medium (Welgene, Daegu, Korea) supplemented with 10% FBS (Gibco, Gaithersburg, MD, USA) and 1% penicillin streptomycin (100 U/mL and 100 μg/mL, respectively; Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA). BC (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) was dissolved in tetrahydrofuran (Sigma-Aldrich) under dim light. Concentration of 20 μM BC (BC 20) and 40 μM BC (BC 40) were applied to HCT116 cells for 6 days. Following the dissolution of 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine (AZA; Sigma-Aldrich) in dimethylsulphoxide (DMSO; Sigma Aldrich), this solution was incubated with cells for 3 days. Cultured medium was replaced every 48 hours with fresh media and BC.
2. Cell proliferation and viability evaluations
To analyze cell proliferation and viability, the MTT assays and the trypan blue exclusion tests were performed, respectively. Briefly, CD133+CD44+ HCT116 cells were seeded and treated with various concentrations of BC. After treatment, media was removed from each well and was replaced with 200 μL MTT solution (Sigma-Aldrich). After 3 hours at 37°C, the supernatants were removed and 100 μL DMSO solution (Sigma-Aldrich) was added to each well. After any remaining formazan crystals were fully dissolved in DMSO, absorbance values at 570 nm were recorded by a microplate reader (Molecular Devices, Sunnyvale, CA, USA). For the trypan blue assay, the cells were harvested and stained with 0.4% trypan blue solution (Sigma-Aldrich). Both viable and non-viable cells were counted under a phase contrast microscope (Nikon Instruments Co. Ltd., Tokyo, Japan).
3. Sphere formation assay
CD133+CD44+ HCT116 cells were seeded (1 × 104 cells/well) and cultured in 6-well plate coated with a 1.2% poly-2-hydroxymethyl methacrylate (Sigma-Aldrich) solutions. The seeded cells were maintained in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium/Ham’s F-12 Medium (1:1, Welgene) medium supplemented with 2% B27 (Invitrogen), 20 ng/mL recombinant human epidermal growth factor (Pepro Tech, Rocky Hill, NJ, USA), and 40 ng/mL recombinant human fibroblast growth factor (Pepro Tech). After incubation for 10–14 days, the spheres were photographed and counted under a phase contrast microscope (Nikon Instruments Co. Ltd.).
4. High-throughput RNA sequencing of small non-coding RNAs
Total RNA was isolated from cells treated with 40 μM BC. Both quality and quantity of the RNA samples collected were checked by using a Nanodrop One instrument (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). A library was prepared from the total RNA samples by using a NEXTflex Small RNA-Seq Kit v3 (Illumina Inc., San Diego, CA, USA). A raw data quality check was conducted and low-quality bases were trimmed from the 3′ end of the adapter sequences by Cutadapt (v 1.13) [31]. After an initial quality check, the miRNAs were filtered. Small non-coding RNA data were then generated with a HiSeq2500 high-throughput sequencing system (Illumina) at Theragen Etex Bio Institute (Suwon, Korea).
5. Analysis of expressed microRNAs and target gene predictions
Annotation of non-coding RNAs was conducted according to instructions provided by Theragen Etex Bio Institute. Differentially expressed mRNAs in the BC treated group were selected based on cutoff criteria of > 1.5 fold change and P < 0.05. Target genes of candidate miRNAs significantly regulated by BC treatment were predicted by miRDB (http://www.mirdb.org/). Target genes were further analyzed with use of DAVID (https://david.ncifcrf.gov/), Gene Ontology (GO) term enrichment and the KEGG pathway of target genes (scoring > 85) analyzed.
6. Western blot analysis
Cells were lysed with 200 μL ice-cold lysis buffer containing 10 μM Tris-Cl (pH 8.0), 1 mM KCl, 1.5 mM MgCl2, 10 mM sodium butyrate, 1 mM dithothreitol, 100 μM phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride, and 10 × protease inhibitor cocktail. Histone proteins were extracted with 0.4 M sulfuric acid solution overnight at 4°C. Extracted proteins were subsequently precipitated with 25% trichloroacetic acid (Daejung, Siheung, Korea) and washed with acetone-HCl and cold acetone. Total protein concentrations were determined with a Bio-Rad Protein Assay Kit (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA). Total protein concentrations were loaded into 18% SDS PAGE gels and transferred to polyvinylidene difluoride membranes (Millipore, Billerica, MA, USA). The membranes were subsequently blocked and then incubate with primary antibodies recognizing H3ac (Active Motif, Carlsbad, CA, USA), H4ac (Active Motif), H3 (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Dallas, TX, USA), and H4 (Cell Signaling Technology, Boston, MA, USA). Bound antibodies were visualized with chemiluminescence reagents (Animal Genetics Inc., Suwon, Korea) and quantified with Image J software (US National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, USA).
7. Quantitative real-time PCR
Total RNA was isolated from cells by using TRIzol Reagent (Invitrogen). RNA concentrations and purities were determined with a Nanodrop One (Thermo Fisher Scientific). Complementary DNA (cDNA) was synthesized with a RevertAid First Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific). Quantitative real-time PCR was conducted by using SYBR Green mater mix and a Rotor-gene Q (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany). Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) was used as an internal control to normalize gene expression. Sequences of primers used in this study are followed: DNMT1 forward, 5′-CCGAGTTGGTGATGGTGTGTAC-3′, DNMT1 reverse, 5′-AGGTTGATGTCTGCGTGGTAGC-3′; DNMT3A forward, 5′-TATTGATGAGCGCACAAGAGAGC-3′, DNMT3A reverse, 5′-GGGTGTTCCAGGGTAACATTGAG3′; GAPDH forward, 5′-AGAAG GCTGGGGCTCATTTG-3′, GAPDH reverse, 5′-AGGGGCC ATCCACAGTCTTC-3′.
8. DNA 5-mC determination
Genomic DNA (gDNA) was extracted from cells and purified by using an AccuPrep® Genomic DNA Extraction Kit (Bioneer, Daejeon, Korea). Methylation levels of the gDNA samples were examined by the MethylFlash Global DNA Methylation (5-mC) ELISA Easy Kit (EpiGentek Group Inc., Farmingdale, NY, USA). Colorimetric absorbance values were recorded at 450 nm by a microplate reader (Molecular Devices). Levels of DNA methylation (5-mC) were calculated based on a standard curve (R2 = 0.9927).
9. Statistical analysis
All experimental results are expressed as means ± SEM derived from at least three separate experiments. Statistical analyses were performed by using GraphPad PRISM Software (GraphPad Software, SanDiego, CA, USA). Analysis of variance was followed by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Newman–Keuls multiple comparison (post hoc) test. P < 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
1. Effects of beta-carotene on cell proliferation and sphere formation of colon cancer stem cells
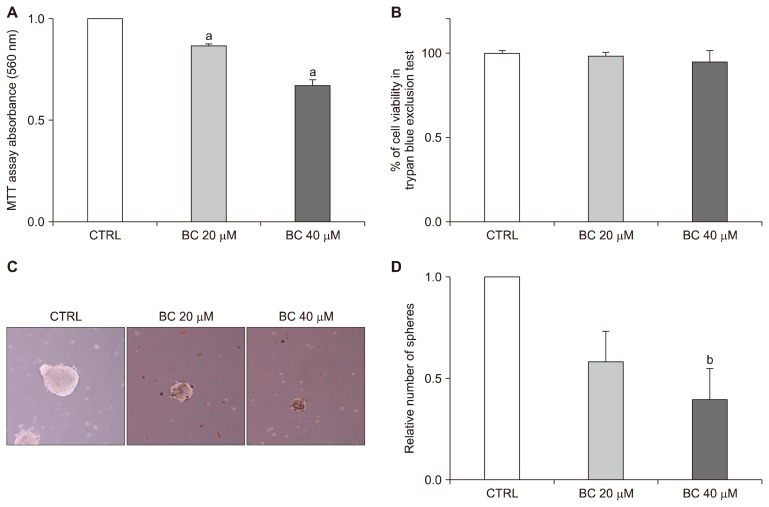
To evaluate the effect of BC on cell proliferation, the MTT assay was performed. CD133+CD44+ HCT116 cells treated with 20 μM and 40 μM BC exhibited significant decreases in the proliferation of 13.29% and 32.85%, respectively (both P < 0.01) (Fig. 1A). Additionally, the trypan blue exclusion test indicated that BC treatment did not induce toxicity (Fig. 1B). To analyze the effect of BC on self-renewal capacity, the sphere formation assay was conducted. This characteristic of CSC was decreased at both BC treatment for CD133+CD44+ HCT116 cells (Fig. 1C). The relative number of spheres was also significantly decreased in the BC 40 group compared to the control group (P < 0.05) (Fig. 1D).
Figure 1.
Effects of BC on the proliferation and sphere formation capacity of CD133+CD44+ HCT116 cells. CD133+CD44+ double-stained HCT116 cells were treated with 20 μM and 40 μM BC for 6 days. (A) Cell proliferation was examined by the MTT assays as described in Materials and Methods. (B) The trypan blue exclusion assay determined the percentage of live cells after BC treatment. (C) Spheres formation was photographed under a phase contrast microscopy (× 100 magnification). (D) The relative numbers of spheres formed were counted. All data are presented as the means ± SEM. Subscripts on top of each bar indicate significant differences of group means (P < 0.05). CTRL, control; BC, beta-carotene. aP < 0.001 compared to the control group; bP < 0.05 compared to the control group.
2. Effect of beta-carotene on the expression profiles of various microRNAs
To determine whether BC could alter the expression profiles of various miRNAs, high-throughput small non-coding RNA sequencing was performed. Trimmed small RNAs, ranging in length from 17–25 nts, were selected by size fractionation. A total of 1,477 reliable miRNAs were identified. Among these 10 miRNAs exhibited significantly different expression profiles between the BC group and the control group (i.e., |fold changes| >1.5 with P < 0.05). Unexpectedly, all 10 miRNAs were down-regulated in response to 40 μM BC compared to the control group (Table 1). When target genes of the top 9 significant miRNAs were analyzed, 741 genes were identified.
Table 1.
Differentially expressed miRNAs between the control group and the β-carotene treatment group
| Down-regulated miRNA | Log2fold change | P-valuea |
|---|---|---|
| hsa-miR-7974 | 1.266014 | 3.93E-09 |
| hsa-miR-92a-1-5p | 1.350586 | 5.06E-08 |
| hsa-miR-33b-3p | 0.953524 | 3.89E-07 |
| hsa-miR-1260b | 0.611769 | 7.92E-07 |
| hsa-miR-5100 | 1.971224 | 1.38E-06 |
| hsa-miR-1260a | 0.593539 | 1.04E-05 |
| hsa-miR-4521 | 1.113696 | 0.000153 |
| hsa-miR-581 | 4.868677 | 0.000510 |
| hsa-miR-296-3p | 1.808432 | 0.001185 |
| hsa-miR-4461 | 1.181834 | 0.001300 |
miRNA, microRNA.
Ten miRNAs were shown to be significantly different by 1.5-fold changes with P < 0.05 (n = 3).
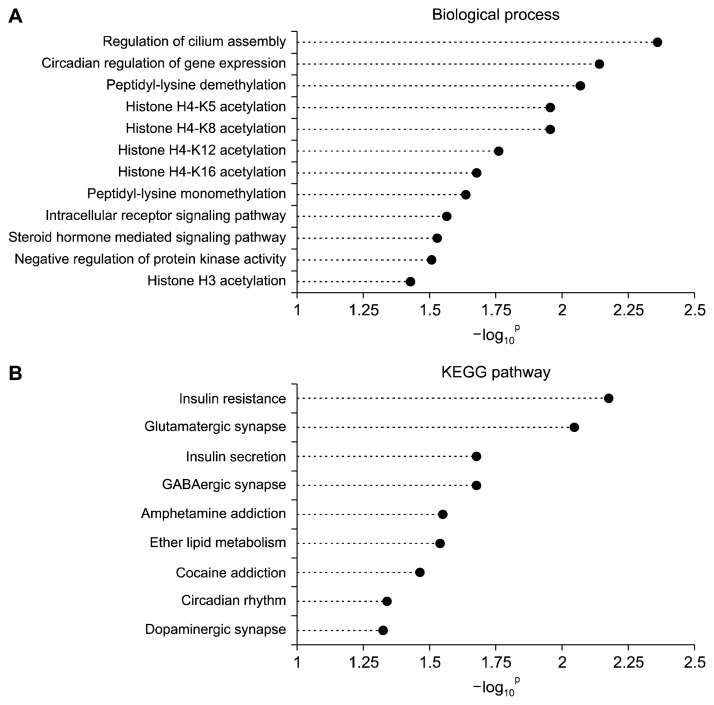
Next, the selected target genes were analyzed and clustered by GO enrichment and the KEGG pathways (Fig. 2). Twelve GO biological processes were identified as significantly enriched (P < 0.05). These processes include cilium assembly, circadian regulation of gene expression, peptidyl-lysine dimethylation, histone H4-K5 acetylation, histone H4-K8 acetylation, histone H4-K12 acetylation, histone H4-K16 acetylation, peptidyl-lysine monomethylation, intracellular receptor signaling pathway, steroid hormone mediated signaling pathway, negative regulation of protein kinase activity, and histone H3 acetylation. In addition, nine KEGG pathways were identified as significantly enriched (P < 0.05): Insulin resistance, Glutamatergic synapse, Insulin secretion, GABAergic synapse, Amphetamine addiction, Ether lipid metabolism, Cocaine addiction, Circadian rhythm, and Dopaminergi synapse.
Figure 2.
Categories of GO biological processes and the KEGG pathways identified as enriched. (A) GO biological processes and (B) the KEGG pathways associated with the top 9 down-regulated miRNAs in the BC treatment group. GO, Gene Ontology; BC, beta-carotene.
3. Effect of beta-carotene on acetylation of histones H3 and H4 in colon cancer stem cells
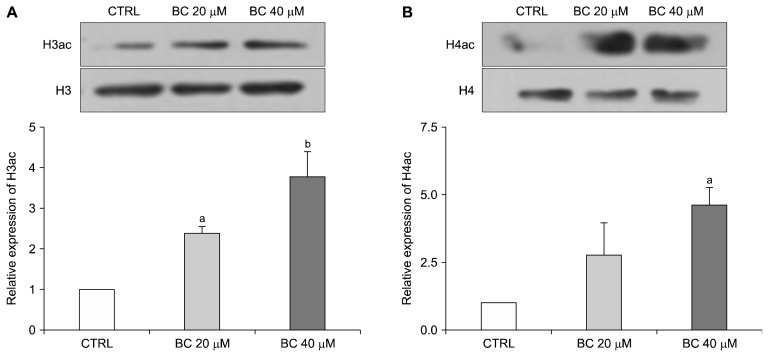
Since miRNAs regulated by BC correlate with multiple target genes which affect histone acetylation, we assayed the effect of BC on acetylation of histones H3 and H4. Compared to the control group, protein levels of H3ac increased by about 1.5-fold (P < 0.05) and 3-fold (P < 0.01) in the BC 20 and BC 40 groups, respectively (Fig. 3A). Meanwhile, expression of H4ac was significantly up-regulated by about 3.5-fold (P < 0.05) in the BC 40 group compared with the control group (Fig. 3B). Taken together, these results indicate that BC affects histone modifications by increasing acetylation of histones H3 and H4.
Figure 3.
Effect of BC on expression of H3ac and H4ac. CD133+CD44+ HCT116 cells were treated with 20 μM and 40 μM BC for 6 days. Histone protein lysates from treated cells were subjected to Western blot analysis for the measurement of H3ac (A) and H4ac (B) expression levels. Representative blots are shown in the upper panel, and quantification of these blots is presented in the lower panel. Histone H3 and H4 are included as internal controls. All data are presented as means ± SEM. One-way ANOVA and the Newman–Keuls multiple comparison test were performed. Subscripts on top of each bar indicate significant differences of group means (P < 0.05). CTRL, control; BC, beta-carotene. aP < 0.05 compared to the control group; bP < 0.01 compared to the control group.
4. Effect of beta-carotene on expression of DNMT3A and global DNA methylation in colon cancer stem cells
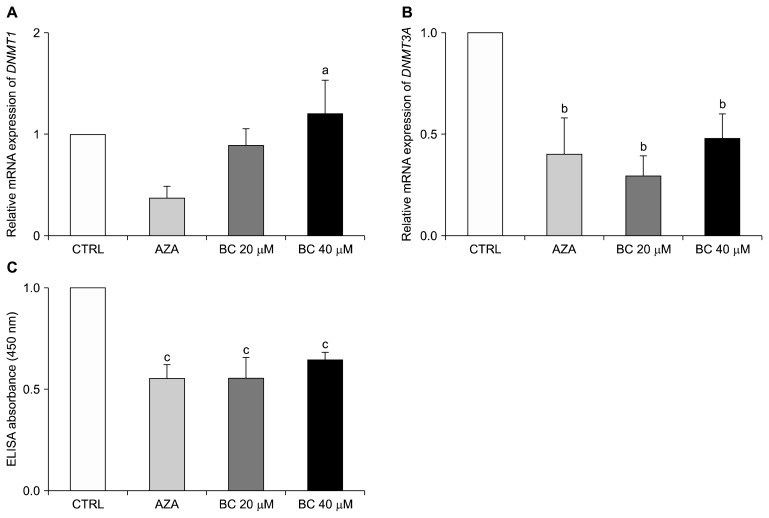
To examine the effect of BC on DNA methylation, expression of DNMT and levels of global DNA methylation were analyzed. Treatment with AZA was included as a positive control. Neither Aza, nor BC, treatment affected expression of DNMT1 compared to the control group (Fig. 4A). However, the mRNA level of DNMT3A was down-regulated in both the AZA and BC groups compared to the control group. Specifically, the levels of DNMT3A were decreased by 70 % and 52% in the BC 20 and BC 40 groups, respectively (both P < 0.05) (Fig. 4B).
Figure 4.
Effect of BC on DNA methylation in CD133+CD44+ HCT116 cells. Relative mRNA levels of DNMT1 (A) and DNMT3A (B) were analyzed by qPCR as described in Materials and Methods. GAPDH was detected as a loading control. (C) Global DNA methylation levels were determined in ELISAs. The AZA treatment group was used as a positive control. All analyses were conducted at least three independent experiments. One-way ANOVA and the Newman–Keuls multiple comparison test were performed. CTRL, control; AZA, 1 μM 5-aza-dC; BC, beta-carotene; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase. aP < 0.05 compared to 5-aza-dC group; bP < 0.05 compared to the control group; cP < 0.01 compared to the control group.
Global DNA methylation levels were also found to be decreased by 44% and 36% in the BC 20 and BC 40 groups, respectively compared to the control group (both P < 0.01; Fig. 4C). In comparison, a significant reduction in both DNMT3A expression and global DNA methylation levels was observed in the AZA group (P < 0.01). Taken together, these results indicate that BC down-regulates DNA methylation in colon CSCs.
DISCUSSION
In the present study, BC exerted an anti-cancer effect on colon CSCs through epigenetic regulation mechanisms involving expression of miRNAs, histone acetylation, and global DNA methylation. For example, BC treatment induced an increase in histone acetylation and down-regulation of both DNMT3A mRNA expression and global DNA methylation levels. In addition, BC suppressed proliferation and the self-renewal potential of CD133+CD44+ HCT116 cells.
In cancer, promoter-specific hypermethylation, global hypomethylation and loss of global histone acetylation are events which mediate epigenetic regulation [32]. In particular, inhibition and interference of DNA methylation events can lead to reactivation of silenced genes. In clinical trials, two novel demethylating agents, AZA and decitabine, have exhibited the therapeutic effects [33]. Clinical trials involving patients with colon cancer have also demonstrated that HDACi can be used as an anti-cancer drug [34]. In the present study, BC exhibited an anti-cancer potential by regulating DNA demethylation and histone acetylation in colon CSCs.
It has been demonstrated that some miRNAs are associated with various stages of cancer [35,36]. In the present study, BC down-regulated miRNA-1260b and miRNA-296-3p, both of which are known to have an oncogenic function in several types of cancer. For example, miRNA-1260b targets Wnt antagonist genes and inhibits tumor suppressor genes in renal cancer [37]. In addition, overexpression of miRNA-1260b has been reported to be involved in the metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer [38]. For miR-296-3p, it has exhibited resistance to natural killer cells to increase metastatic potential of prostate cancer cells [39]. Higher levels of miR-296-3p have also been detected in non-small cell lung cancer [40].
It has previously been shown that miRNAs can regulate enzymes involved in histone acetylation and DNA methylation [41,42]. Thus, a noteworthy result of the present study is that BC down-regulates the expression of miRNAs associated with histone acetylation. Furthermore, in the GO term analysis we conducted, acetylation of histone H4 lysine, including lysines H4-K5, H4-K8, H4-K12, and H4-K16, were identified as significant biological process categories. Loss of histone H4-K16 monoacetylation has been shown as a signature of human cancer [43]. In addition, histone H3 acetylation is associated with significant enrichment in biological processes. Based on these findings, we speculate that BC up-regulates histone acetylation through down-regulation of oncogenic miRNAs in colon CSCs. It remains for further studies to confirm this hypothesis.
Consistent with our miRNA sequencing data, protein expression of histones H3 and H4 acetylation was significantly increased following BC treatment. Previously, a decrease in histone modifications was associated with an increase in cancer recurrence risk and poor cancer prognosis [44,45]. Moreover, overexprssion of HDAC has been in cancer progression [24]. Therefore, HDAC can be a promising target for chemoprevention as well as therapy. For example, when the epigenetic drug, sulforaphane is used as a cancer treatment, significant HDAC inhibition and increased global acetylation at histones H3 and H4 have been observed [46].
The overexpression of DNMT has been detected in various types of cancers [47]. In the present study, BC treatment of CD133+CD44+ HCT116 cells did not affect DNMT1 expression, and it down-regulated expression of DNMT3A. In line with this observation, the expression of DNMT1 and DNMT3B was decreased in colon cancer cells after anthocyanin treatment [48]. In HCT116 cells treated with epigallocatechin gallate, present in green tea, DNMT3A expression was also decreased [49]. In the present study, we found that BC treatment significantly decreased global DNA methylation levels in the colon CSCs examined. Consistent with our findings, a previous study has demonstrated that BC suppresses the global DNA methylation in human umbilical vein endothelial cells [50].
In conclusion, the present study demonstrates that BC suppresses the proliferation and self-renewal capacity of colon CSCs by regulating epigenetic modifications. Specifically, BC regulates miRNAs and increases the expression of miRNA-mediated histone acetylation. Concomitantly, BC decreases mRNA expression of DNMT3A and global DNA methylation levels. Taken together, this study suggests anti-cancer effects of BC in CRC and its potential for use in the management of cancer treatment.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by Ministry of Education (NRF-2016R1D1A1B03932018).
Footnotes
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
REFERENCES
- 1.Gloria NF, Soares N, Brand C, Oliveira FL, Borojevic R, Teodoro AJ. Lycopene and beta-carotene induce cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis in human breast cancer cell lines. Anticancer Res 2014;34:1377–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Park Y, Choi J, Lim JW, Kim H. β-Carotene-induced apoptosis is mediated with loss of Ku proteins in gastric cancer AGS cells. Genes Nutr 2015;10:467. 10.1007/s12263-015-0467-1 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Palozza P, Serini S, Maggiano N, Angelini M, Boninsegna A, Di Nicuolo F, et al. Induction of cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human colon adenocarcinoma cell lines by beta-carotene through down-regulation of cyclin A and Bcl-2 family proteins. Carcinogenesis 2002;23:11–8. 10.1093/carcin/23.1.11 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Burton GW, Ingold KU. beta-Carotene: an unusual type of lipid antioxidant. Science 1984;224:569–73. 10.1126/science.6710156 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Santos MS, Meydani SN, Leka L, Wu D, Fotouhi N, Meydani M, et al. Natural killer cell activity in elderly men is enhanced by beta-carotene supplementation. Am J Clin Nutr 1996;64:772–7. 10.1093/ajcn/64.5.772 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Kim YS, Gong X, Rubin LP, Choi SW, Kim Y. β-Carotene 15,15′-oxygenase inhibits cancer cell stemness and metastasis by regulating differentiation-related miRNAs in human neuroblastoma. J Nutr Biochem 2019;69:31–43. 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2019.03.010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 2018;68:394–424. 10.3322/caac.21492 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Fedirko V, Tramacere I, Bagnardi V, Rota M, Scotti L, Islami F, et al. Alcohol drinking and colorectal cancer risk: an overall and dose-response meta-analysis of published studies. Ann Oncol 2011;22:1958–72. 10.1093/annonc/mdq653 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Renehan AG, Tyson M, Egger M, Heller RF, Zwahlen M. Body-mass index and incidence of cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective observational studies. Lancet 2008;371:569–78. 10.1016/S0140-6736(08)60269-X [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Samad AK, Taylor RS, Marshall T, Chapman MA. A meta-analysis of the association of physical activity with reduced risk of colorectal cancer. Colorectal Dis 2005;7:204–13. 10.1111/j.1463-1318.2005.00747.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Liang PS, Chen TY, Giovannucci E. Cigarette smoking and colorectal cancer incidence and mortality: systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Cancer 2009;124:2406–15. 10.1002/ijc.24191 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Modan B, Barell V, Lubin F, Modan M, Greenberg RA, Graham S. Low-fiber intake as an etiologic factor in cancer of the colon. J Natl Cancer Inst 1975;55:15–8. 10.1093/jnci/55.1.15 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Chan DS, Lau R, Aune D, Vieira R, Greenwood DC, Kampman E, et al. Red and processed meat and colorectal cancer incidence: meta-analysis of prospective studies. PLoS One 2011;6:e20456. 10.1371/journal.pone.0020456 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Clevers H. The cancer stem cell: premises, promises and challenges. Nat Med 2011;17:313–9. 10.1038/nm.2304 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Lee M, Han WS, Kim OK, Sung SH, Cho MS, Lee SN, et al. Prognostic value of p16INK4a and p14ARF gene hypermethylation in human colon cancer. Pathol Res Pract 2006;202:415–24. 10.1016/j.prp.2005.11.011 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Hsu HS, Wen CK, Tang YA, Lin RK, Li WY, Hsu WH, et al. Promoter hypermethylation is the predominant mechanism in hMLH1 and hMSH2 deregulation and is a poor prognostic factor in nonsmoking lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2005;11:5410–6. 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-0601 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Rosenbaum E, Hoque MO, Cohen Y, Zahurak M, Eisenberger MA, Epstein JI, et al. Promoter hypermethylation as an independent prognostic factor for relapse in patients with prostate cancer following radical prostatectomy. Clin Cancer Res 2005;11:8321–5. 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-1183 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Arai T, Miyoshi Y, Kim SJ, Taguchi T, Tamaki Y, Noguchi S. Association of GSTP1 CpG islands hypermethylation with poor prognosis in human breast cancers. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2006;100: 169–76. 10.1007/s10549-006-9241-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Wang S, Wu W, Claret FX. Mutual regulation of microRNAs and DNA methylation in human cancers. Epigenetics 2017;12:187–97. 10.1080/15592294.2016.1273308 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Varambally S, Cao Q, Mani RS, Shankar S, Wang X, Ateeq B, et al. Genomic loss of microRNA-101 leads to overexpression of histone methyltransferase EZH2 in cancer. Science 2008;322:1695–9. 10.1126/science.1165395 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.O’Donnell KA, Wentzel EA, Zeller KI, Dang CV, Mendell JT. c-Myc-regulated microRNAs modulate E2F1 expression. Nature 2005;435:839–43. 10.1038/nature03677 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Chang TC, Wentzel EA, Kent OA, Ramachandran K, Mullendore M, Lee KH, et al. Transactivation of miR-34a by p53 broadly influences gene expression and promotes apoptosis. Mol Cell 2007;26:745–52. 10.1016/j.molcel.2007.05.010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Siddiqui H, Solomon DA, Gunawardena RW, Wang Y, Knudsen ES. Histone deacetylation of RB-responsive promoters: requisite for specific gene repression but dispensable for cell cycle inhibition. Mol Cell Biol 2003;23:7719–31. 10.1128/MCB.23.21.7719-7731.2003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Kawai H, Li H, Avraham S, Jiang S, Avraham HK. Overexpression of histone deacetylase HDAC1 modulates breast cancer progression by negative regulation of estrogen receptor alpha. Int J Cancer 2003;107:353–8. 10.1002/ijc.11403 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Fandy TE, Shankar S, Ross DD, Sausville E, Srivastava RK. Interactive effects of HDAC inhibitors and TRAIL on apoptosis are associated with changes in mitochondrial functions and expressions of cell cycle regulatory genes in multiple myeloma. Neoplasia 2005;7:646–57. 10.1593/neo.04655 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Catalano MG, Fortunati N, Pugliese M, Poli R, Bosco O, Mastrocola R, et al. Valproic acid, a histone deacetylase inhibitor, enhances sensitivity to doxorubicin in anaplastic thyroid cancer cells. J Endocrinol 2006;191:465–72. 10.1677/joe.1.06970 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Kallifatidis G, Labsch S, Rausch V, Mattern J, Gladkich J, Moldenhauer G, et al. Sulforaphane increases drug-mediated cytotoxicity toward cancer stem-like cells of pancreas and prostate. Mol Ther 2011;19:188–95. 10.1038/mt.2010.216 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kaminski BM, Weigert A, Brüne B, Schumacher M, Wenzel U, Steinhilber D, et al. Sulforaphane potentiates oxaliplatin-induced cell growth inhibition in colorectal cancer cells via induction of different modes of cell death. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 2011;67:1167–78. 10.1007/s00280-010-1413-y [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Roman-Gomez J, Castillejo JA, Jimenez A, Barrios M, Heiniger A, Torres A. The role of DNA hypermethylation in the pathogenesis and prognosis of acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma 2003;44:1855–64. 10.1080/1042819031000116689 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Marcucci G, Silverman L, Eller M, Lintz L, Beach CL. Bioavailability of azacitidine subcutaneous versus intravenous in patients with the myelodysplastic syndromes. J Clin Pharmacol 2005;45:597–602. 10.1177/0091270004271947 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Martin M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet J 2011;17:10–2. 10.14806/ej.17.1.200 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Ropero S, Esteller M. The role of histone deacetylases (HDACs) in human cancer. Mol Oncol 2007;1:19–25. 10.1016/j.molonc.2007.01.001 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Howell PM, Liu Z, Khong HT. Demethylating agents in the treatment of cancer. Pharmaceuticals (Basel) 2010;3:2022–44. 10.3390/ph3072022 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Minucci S, Pelicci PG. Histone deacetylase inhibitors and the promise of epigenetic (and more) treatments for cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2006;6:38–51. 10.1038/nrc1779 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Du B, Wu D, Yang X, Wang T, Shi X, Lv Y, et al. The expression and significance of microRNA in different stages of colorectal cancer. Medicine (Baltimore) 2018;97:e9635. 10.1097/MD.0000000000009635 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Yerukala Sathipati S, Ho SY. Identifying a miRNA signature for predicting the stage of breast cancer. Sci Rep 2018;8:16138. 10.1038/s41598-018-34604-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Hirata H, Ueno K, Nakajima K, Tabatabai ZL, Hinoda Y, Ishii N, et al. Genistein downregulates onco-miR-1260b and inhibits Wnt-signalling in renal cancer cells. Br J Cancer 2013;108:2070–8. 10.1038/bjc.2013.173 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Xu L, Li L, Li J, Li H, Shen Q, Ping J, et al. Overexpression of miR-1260b in non-small cell lung cancer is associated with lymph node metastasis. Aging Dis 2015;6:478–85. 10.14336/AD.2015.0620 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Liu X, Chen Q, Yan J, Wang Y, Zhu C, Chen C, et al. MiRNA-296-3p-ICAM-1 axis promotes metastasis of prostate cancer by possible enhancing survival of natural killer cell-resistant circulating tumour cells. Cell Death Dis 2013;4:e928. 10.1038/cddis.2013.458 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Hu L, Ai J, Long H, Liu W, Wang X, Zuo Y, et al. Integrative microRNA and gene profiling data analysis reveals novel biomarkers and mechanisms for lung cancer. Oncotarget 2016;7: 8441–54. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Lujambio A, Esteller M. CpG island hypermethylation of tumor suppressor microRNAs in human cancer. Cell Cycle 2007;6:1455–9. 10.4161/cc.6.12.4408 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Iorio MV, Visone R, Di Leva G, Donati V, Petrocca F, Casalini P, et al. MicroRNA signatures in human ovarian cancer. Cancer Res 2007;67:8699–707. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-1936 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Fraga MF, Ballestar E, Villar-Garea A, Boix-Chornet M, Espada J, Schotta G, et al. Loss of acetylation at Lys16 and trimethylation at Lys20 of histone H4 is a common hallmark of human cancer. Nat Genet 2005;37:391–400. 10.1038/ng1531 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Kurdistani SK. Histone modifications in cancer biology and prognosis. Prog Drug Res 2011;67:91–106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Seligson DB, Horvath S, Shi T, Yu H, Tze S, Grunstein M, et al. Global histone modification patterns predict risk of prostate cancer recurrence. Nature 2005;435:1262–6. 10.1038/nature03672 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Myzak MC, Karplus PA, Chung FL, Dashwood RH. A novel mechanism of chemoprotection by sulforaphane: inhibition of histone deacetylase. Cancer Res 2004;64:5767–74. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-1326 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Robertson KD, Uzvolgyi E, Liang G, Talmadge C, Sumegi J, Gonzales FA, et al. The human DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs) 1, 3a and 3b: coordinate mRNA expression in normal tissues and overexpression in tumors. Nucleic Acids Res 1999;27:2291–8. 10.1093/nar/27.11.2291 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Wang LS, Kuo CT, Cho SJ, Seguin C, Siddiqui J, Stoner K, et al. Black raspberry-derived anthocyanins demethylate tumor suppressor genes through the inhibition of DNMT1 and DNMT3B in colon cancer cells. Nutr Cancer 2013;65:118–25. 10.1080/01635581.2013.741759 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Moseley VR, Morris J, Knackstedt RW, Wargovich MJ. Green tea polyphenol epigallocatechin 3-gallate, contributes to the degradation of DNMT3A and HDAC3 in HCT 116 human colon cancer cells. Anticancer Res 2013;33:5325–33. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Kiec-Wilk B, Polus A, Mikolajczyk M, Mathers JC. Beta-carotene and arachidonic acid induced DNA methylation and the regulation of pro-chemotactic activity of endothelial cells and its progenitors. J Physiol Pharmacol 2007;58:757–66. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]