Abstract
Background
Conventionally used soybean oil‐based lipid emulsion (S‐LE) have high polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) content and phytosterols that may contribute to adverse effects in preterm infants. The newer lipid emulsions (LE) from different lipid sources are currently available for use in preterm infants.
Objectives
To compare the safety and efficacy of all LE for parenteral nutrition (PN) in preterm infants (less than 37 weeks' gestation) including preterm infants with surgical conditions or parenteral nutrition‐associated liver disease (PNALD)/cholestasis using direct comparisons and pair‐wise meta‐analyses.
Search methods
We used the standard search strategy of Cochrane Neonatal to search the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL 2018, Issue 5), MEDLINE (1946 to 18 June 2018), Embase (1974 to 18 July 2018), CINAHL (1982 to 18 June 2018), MIDRIS (1971 to 31 May 2018), conference proceedings, trial registries (ClinicalTrials.gov and WHO's Trials Registry and Platform), and reference lists of retrieved articles.
Selection criteria
Randomised or quasi‐randomised controlled studies in preterm infants with or without surgical conditions or PNALD within the first six months of life.
Data collection and analysis
Data collection and analysis conformed to the methods of Cochrane Neonatal. We used the GRADE approach to assess the quality of evidence for important outcomes in addition to reporting statistical significance of results.
Main results
We included 29 studies (n = 2037) in this review. LE were classified in three broad groups: 1. all fish oil‐containing LE including pure fish oil‐LE (F‐LE) and multisource LE (e.g. medium‐chain triglycerides (MCT)‐olive‐fish‐soybean oil‐LE (MOFS‐LE), MCT‐fish‐soybean oil‐LE (MFS‐LE) and olive‐fish‐soybean oil‐LE (OFS‐LE); 2. conventional S‐LE; 3. alternative‐LE (e.g. MCT‐soybean oil‐LE (MS‐LE), olive‐soybean oil‐LE and borage oil‐based LE).
We considered the following broad comparisons: fish oil LE versus non‐fish oil LE; fish oil LE versus another fish oil LE; alternative‐LE versus S‐LE; alternative‐LE versus another alternative‐LE in preterm infants less than 37 weeks' gestation, preterm infants with surgical conditions and preterm infants with PNALD/cholestasis. Separate subgroup comparisons of each LE preparation were included within these broader groups.
Most studies in preterm infants used PN for mean duration of four weeks or less and for longer duration in infants with cholestasis or surgical conditions.
We defined the primary outcome of PNALD/cholestasis as conjugated bilirubin (Cbil) 2 mg/dL or greater and resolution of PNALD/cholestasis as Cbil less than 2 mg/dL. There was heterogeneity in definitions used by the included studies with Cbil cut‐offs ranging from 17.1 μmol/L (1 mg/dL) up to 50 μmol/L (about 3 mg/dL).
In preterm infants, meta‐analysis found no evidence of a difference in the incidence of PNALD/cholestasis (Cbil cut‐off: 2 mg/dl) between fish oil‐LEs and all non‐fish oil LEs (typical risk ratio (RR) 0.61, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.24 to 1.56; typical risk difference (RD) –0.03, 95% CI –0.08 to 0.02; 4 studies; n = 328; low‐quality evidence).
We also considered an outcome allowing for any definition of PNALD (different Cbil cutoffs). In the meta‐analysis for PNALD/cholestasis, using any definition and restricted to low or unclear risk of bias studies, there was no evidence of a difference between fish oil LE and all non‐fish oil LE for incidence of cholestasis (typical RR 0.80, 95% CI 0.53 to 1.21; typical RD –0.02, 95% CI –0.05 to 0.02; 10 studies; n = 1024; low‐quality evidence). There was no evidence of difference in subgroup meta‐analyses of individual LE types in any comparison.
In preterm infants with surgical conditions or cholestasis, there was only one small study each reporting no evidence of a difference in incidence or resolution of cholestasis respectively with use of a pure F‐LE versus S‐LE (using a Cbil cut‐off of 2 mg/dL).
In preterm infants with PNALD/cholestasis (using any definition), the meta‐analysis showed significantly less cholestasis with the use of fish oil‐LE compared to S‐LE (typical RR 0.54, 95% CI 0.32 to 0.91; typical RD –0.39, 95% CI –0.65 to –0.12; number needed to treat for an additional beneficial outcome (NNTB) 3, 95% CI 2 to 9; 2 studies; n = 40; very low‐quality evidence). However, this outcome had a very low number of participants from two small studies with methodological differences, one of which was terminated early, increasing the uncertainty about effect estimates.
There were no differences between LE types in pair‐wise meta‐analyses for growth in preterm infants. There was paucity of studies in preterm infants with surgical conditions or cholestasis to perform meta‐analyses for growth and most other outcomes.
In the secondary outcomes for preterm infants, there was no difference between fish‐oil LE and non‐fish oil LE in meta‐analysis for severe retinopathy of prematurity (ROP) (stage 3 or greater, or requiring surgery: typical RR 0.80, 95% CI 0.55 to 1.16; typical RD –0.03, 95% CI –0.07 to 0.02; 7 studies; n = 731; very low‐quality evidence). There were no differences in the LE types in pair‐wise meta‐analyses for death, bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD), ventilation duration, patent ductus arteriosus, sepsis, necrotising enterocolitis, intraventricular haemorrhage, periventricular leukomalacia, jaundice, hyperglycaemia, hypertriglyceridaemia, intrahepatocellular lipid content and conjugated bilirubin levels in any comparison.
In surgical infants, one study (n = 19) reported no differences in death, sepsis rates, Cbil and neurodevelopmental outcomes with pure F‐LE versus S‐LE.
In infants with cholestasis, there were no evidence of differences in death or sepsis in meta‐analyses between fish oil‐LE and S‐LE; (2 studies; n = 40; very low‐quality evidence).
Authors' conclusions
In the current review, we did not find any particular LE with or without fish oil to be better than another LE in preterm infants for prevention of PNALD/cholestasis, growth, mortality, ROP, BPD and other neonatal outcomes.
In preterm infants with surgical conditions or cholestasis, there is currently insufficient evidence from randomised studies to determine with any certainty if fish oil LEs offer advantage in prevention or resolution of cholestasis or in any other clinical outcome.
Further research, with larger well‐designed trials, is warranted to evaluate the ideal composition of LE in preterm infants and the role of fish oil‐containing and other LEs in the prevention and resolution of PNALD, ROP and other clinical outcomes.
Plain language summary
Systematic review of lipid emulsions for intravenous nutrition in preterm infants.
Review question: which lipid (fat) emulsions (LE) have the best outcomes in preterm infants with and without liver disease and surgical conditions?
Background: preterm infants who need nutrition (feeding) through intravenous (into a vein; called parenteral nutrition) lines have been conventionally given pure soybean oil‐based fat emulsions. However, high polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) content and phytosterols in pure soybean oil‐based emulsions may be harmful and contribute to parenteral nutrition‐associated liver disease (PNALD). The newer lipid emulsions (LE) from alternative lipid sources, including fish oil, may potentially improve clinical outcomes in preterm infants by decreasing PUFA content and providing lipid source‐specific benefits.
Study characteristics: we searched the medical literature and identified 29 studies (including 2037 preterm infants). The evidence is up to date as of 18 June 2018.
Key findings: in the population of preterm infants, without liver disease or surgical conditions, no particular LE was better than another for growth, liver disease, death, retinopathy (eye disease), infection and chronic lung disease.
While there was very low quality and limited evidence to suggest that fish oil‐based LE may improve liver disease‐related outcomes in infants with pre‐existing liver disease, this evidence was based on a limited number of infants from two small studies, one of which was terminated early, and no certain conclusions can be drawn.
Conclusions: based on this review, no particular LE is better than another for intravenous nutrition in preterm infants. There currently exists insufficient evidence from well‐designed studies about the benefit of fish oil‐LE for improving liver disease‐related outcomes in infants with pre‐existing liver disease or surgical conditions. Further research is required to establish the role of fish oil‐LE for liver disease outcomes in preterm infants and the ideal composition of LE for preterm infants.
Summary of findings
Summary of findings for the main comparison. Fish oil lipid emulsion (LE) compared to non‐fish oil LE for parenterally fed preterm infants.
| Fish oil LE compared to non‐fish oil LE for parenterally fed preterm infants | ||||||
| Patient or population: parenterally fed preterm infants Setting: neonatal intensive care unit Intervention: fish oil LE Comparison: non‐fish oil LE | ||||||
| Outcomes | Anticipated absolute effects* (95% CI) | Relative effect (95% CI) | No of participants (studies) | Quality of the evidence (GRADE) | Comments | |
| Risk with non‐fish oil LE | Risk with fish oil LE | |||||
|
Growth rate – MOFS‐LE vs S‐LE |
The mean rate of weight gain was 0 g/kg/day | MD 0.71 g/kg/day higher (0.17 lower to 1.6 higher) | — | 347 (5 studies) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ Lowa,b,c | Data from studies could not be included, e.g. data as z scores. |
|
PNALD/cholestasis (conjugated bilirubin ≥ 2 mg/dL) – all fish oil LE vs non‐fish oil LE (combined subgroups) |
Study population (conjugated bilirubin ≥ 2 mg/dL) |
RR 0.61 (0.24 to 1.56) |
328 (4 studies) |
⊕⊕⊝⊝ Lowb,c | Unit of analysis error was avoided by combining all arms of multiarm study. | |
| 44 per 1000 |
27 per 1000 (11 to 69) |
|||||
|
PNALD/cholestasis (any definition: low and unclear risk of bias studies) – all fish oil LE vs non‐fish oil LE |
Study population (assumed baseline risk of 10%) |
RR 0.80 (0.53 to 1.21) |
1024 (10 studies) |
⊕⊕⊝⊝ Lowb,c | Primary analysis restricted to studies at low or unclear risk of bias. Unit of analysis error was avoided by combining all arms of multiarm study. | |
| 100 per 1000 | 80 per 1000 (53 to 121) | |||||
|
PNALD/cholestasis (any definition): combined subgroups (all studies) – all fish oil LE vs non‐fish oil LE |
Study population (assumed baseline risk of 10%) | RR 0.63 (0.43 to 0.91) | 1154 (11 studies) |
⊕⊝⊝⊝ Very lowb,d,e | Unit of analysis error was avoided by combining all arms of the multiarm study. | |
| 100 per 1000 | 63 per 1000 (43 to 91) | |||||
|
Death before discharge – MOFS‐LE vs S‐LE |
Study population | RR 1.24 (0.81 to 1.90) | 855 (9 studies) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ Lowb,c | The result is presented for only MOFS‐LE vs S‐LE which was the subgroup with maximum studies in this outcome. | |
| 79 per 1000 | 98 per 1000 (64 to 150) | |||||
|
ROP ≥ stage 3 or requiring surgery – all fish oil LE vs non‐fish oil LE |
Study population | RR 0.80 (0.55 to 1.16) | 731 (7 studies) | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ Very lowb,c,d | — | |
| 108 per 1000 | 86 per 1000 (59 to 125) | |||||
|
CLD (oxygen requirement at 36 weeks' postmenstrual age) – MOFS‐LE vs S‐LE |
Study population | RR 1 (0.75 to 1.34) | 581 (6 studies) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ Lowb,c | The result is presented for only MOFS‐LE vs S‐LE which was the subgroup with maximum studies in this outcome. | |
| 235 per 1000 | 235 per 1000 (176 to 314) | |||||
|
Culture‐positive sepsis – fish oil LE vs non‐fish oil LE |
Study population | RR 1.16 (0.91 to 1.48) | 774 (7 studies) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ Lowb,c | Some studies reported combined culture positive and clinical sepsis. Others provided data on any sepsis. | |
| 223 per 1000 | 258 per 1000 (202 to 329) | |||||
|
Conjugated bilirubin levels – MOFS‐LE vs S‐LE |
The mean conjugated bilirubin levels was 0 µmol/L | MD 0.48 µmol/L lower (1.16 lower to 0.19 higher) | — | 673 (8 studies) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ Lowc,f | The measurement and reporting of conjugated bilirubin varied from 7 days to 6 weeks between studies. |
| *The risk in the intervention group (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). CI: confidence interval; CLD: chronic lung disease; LE: lipid emulsion; MD: mean difference; MOFS‐LE: medium‐chain triglycerides (MCT)‐olive‐fish‐soybean oil‐lipid emulsion; PNALD: parenteral nutrition‐associated liver disease; ROP: retinopathy of prematurity; RR: risk ratio; S‐LE: soybean oil‐based lipid emulsion. | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group Grades of Evidence High quality: we are very confident that the true effect lies close to that of the estimate of the effect Moderate quality: we are moderately confident in the effect estimate: the true effect is likely to be close to the estimate of the effect, but there is a possibility that it is substantially different Low quality: our confidence in the effect estimate is limited: the true effect may be substantially different from the estimate of the effect Very low quality: we have very little confidence in the effect estimate: the true effect is likely to be substantially different from the estimate of effect | ||||||
aStudy reporting bias: some studies that did not find a difference between the groups did not provide data. We were unable to include data from some studies due to the format in which data were presented. bDowngraded by one level as optimal information size not reached. cDowngraded by one level as the CI crossed the null effect and the limit of appreciable harm or benefit (0.75 or 1.25); or crossed limit of clinically appreciable harm or benefit in a continuous outcome (author consensus). dDowngraded by one level as one study that contributed significant weight in the outcome was assigned high risk of bias for incomplete reporting. eDowngraded by one level for moderate heterogeneity and different direction of the effect estimates. fNumber of studies had provided data in median and ranges or interquartile ranges. Therefore, imputation was used in a significant number of studies. In addition, difference in time of measurement may cause variation in the true effect size for conjugated bilirubin in two arms. The evidence was downgraded by one level for these two reasons.
Summary of findings 2. Fish oil lipid emulsion (LE) compared to another fish oil LE for parenterally fed preterm infants.
| Fish oil LE compared to another fish oil LE for parenterally fed preterm infants | ||||||
| Patient or population: parenterally fed preterm infants Settings: neonatal intensive care unit Intervention: fish oil LE (MOFS‐LE) Comparison: another fish oil LE (MFS‐LE) | ||||||
| Outcomes | Illustrative comparative risks* (95% CI) | Relative effect (95% CI) | No of participants (studies) | Quality of the evidence (GRADE) | Comments | |
| Assumed risk | Corresponding risk | |||||
| Other fish oil LE | Fish oil LE | |||||
|
Growth rate – MOFS‐LE vs MFS‐LE |
— | The mean rate of weight gain in the intervention groups was 4 g/kg/day higher (2.03 lower to 10.03 higher) | — | 55 (1 study) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ Lowa,b | — |
|
PNALD/cholestasis (conjugated bilirubin ≥ 2 mg/dL) – MOFS‐LE vs MFS‐LE |
Study population | RR 0.96 (0.06 to 14.65) | 55 (1 study) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ Lowa,b | — | |
| 37 per 1000 | 36 per 1000 (2 to 543) | |||||
|
Death before discharge – MOFS‐LE vs MFS‐LE |
Study population | RR 1 (0.15 to 6.64) | 60 (1 study) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ Lowa,b | — | |
| 67 per 1000 | 67 per 1000 (10 to 443) | |||||
|
CLD (oxygen requirement at 36 weeks' postmenstrual age) – MOFS‐LE vs MFS‐LE |
Study population | RR 1.16 (0.4 to 3.35) | 55 (1 study) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ Lowa,b | — | |
| 185 per 1000 | 215 per 1000 (74 to 620) | |||||
|
Any sepsis (clinical or culture positive (or both)) – MOFS‐LE vs MFS‐LE |
Study population | RR 1.69 (0.56 to 5.11) | 55 (1 study) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ Lowa,b | — | |
| 148 per 1000 | 250 per 1000 (83 to 757) | |||||
|
Conjugated bilirubin levels – MOFS‐LE vs MFS‐LE |
— | The mean conjugated bilirubin levels in the intervention group was 1.4 µmol/L lower (6.4 lower to 3.6 higher) | — | 55 (1 study) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ Lowa,b | — |
| *The basis for the assumed risk (e.g. the median control group risk across studies) is provided in footnotes. The corresponding risk (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). CI: confidence interval; CLD: chronic lung disease; LE: lipid emulsion; MFS‐LE: medium‐chain triglyceride‐fish‐soybean lipid emulsion; MOFS‐LE: medium‐chain triglycerides (MCT)‐olive‐fish‐soybean oil‐lipid emulsion; PNALD: parenteral nutrition‐associated liver disease; RR: risk ratio. | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group Grades of Evidence High quality: further research is very unlikely to change our confidence in the estimate of effect. Moderate quality: further research is likely to have an important impact on our confidence in the estimate of effect and may change the estimate. Low quality: further research is very likely to have an important impact on our confidence in the estimate of effect and is likely to change the estimate. Very low quality: we are very uncertain about the estimate. | ||||||
aDowngraded by one level as optimal information size not reached. bDowngraded by one level as the CI crossed the null effect and the limit of appreciable harm or benefit (0.75 or 1.25); or crossed limit of clinically appreciable harm or benefit in a continuous outcome (author consensus).
Summary of findings 3. Alternative lipid emulsion (LE) versus soybean oil‐based LE (S‐LE) for parenterally fed preterm infants.
| Alternative‐LE vsS‐LE for parenterally fed preterm infants | |||||
| Patient or population: parenterally fed preterm infants Settings: neonatal intensive care unit Intervention: alternative‐LE Comparison: S‐LE | |||||
| Outcomes | Illustrative comparative risks* (95% CI) | Relative effect (95% CI) | No of participants (studies) | Quality of the evidence (GRADE) | |
| Assumed risk | Corresponding risk | ||||
| Control | Alternative‐LE vsS‐LE | ||||
|
Growth rate – MS‐LE vs S‐LE |
— | The mean rate of weight gain in the intervention group was 2.67 g/kg/day lower (8.2 lower to 2.86 higher) | — | 60 (1 study) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ Lowa,b |
|
Growth rate – OS‐LE vs S‐LE |
— | The mean rate of weight gain in the intervention group was 0.42 g/kg/day lower (5.15 lower to 4.3 higher) | — | 123 (2 studies) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ Lowa,b |
|
PNALD/cholestasis (any definition) – OS‐LE vs S‐LE |
Study population (assumed risk 10%) | RR 1.0 (0.26 to 3.86) | 261 (4 studies) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ Lowa,b | |
| 100 per 1000 | 100 per 1000 (26 to 386) | ||||
|
PNALD/cholestasis (conjugated bilirubin ≥ 2 mg/dL) – OS‐LE vs S‐LE |
Study population (assumed risk 10%) | RR 1.0 (0.15 to 6.82) | 159 (2 studies) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ Lowa,b | |
| 100 per 1000 | 100 per 1000 (15 to 68) | ||||
|
Death before discharge – OS‐LE vs S‐LE |
Study population | RR 1.0 (0.21 to 4.82) | 224 (3 studies) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ Lowa,b | |
| 27 per 1000 | 27 per 1000 (6 to 129) | ||||
|
Death before discharge – MS‐LE vs S‐LE |
See comment | See comment | Not estimable | 60 (1 study) | No events in either group |
|
Any ROP – OS‐LE vs S‐LE |
Study population | RR 0.98 (0.67 to 1.43) | 142 (3 studies) | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ Very lowa,b,c | |
| 292 per 1000 | 286 per 1000 (195 to 417) | ||||
|
Any BPD – OS‐LE vs S‐LE (sensitivity analysis) |
Study population | RR 1.01 (0.57 to 1.79) | 197 (3 studies) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ Lowa,b | |
| 150 per 1000 | 151 per 1000 (85 to 268) | ||||
|
Culture‐positive sepsis – OS‐LE vs S‐LE |
Study population | RR 1.22 (0.54 to 2.78) | 164 (2 studies) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ Lowa,b | |
| 110 per 1000 | 134 per 1000 (59 to 305) | ||||
|
Conjugated bilirubin levels – OS‐LE vs S‐LE |
— | The mean conjugated bilirubin levels in the intervention groups was 0.24 µmol/L lower (1.03 lower to 0.55 higher) | — | 310 (5 studies) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ Lowa,b |
| *The basis for the assumed risk (e.g. the median control group risk across studies) is provided in footnotes. The corresponding risk (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). BPD: bronchopulmonary dysplasia; CI: confidence interval; LE: lipid emulsion; MS‐LE: medium‐chain triglyceride‐soybean oil‐based lipid emulsion; OS‐LE: olive oil‐soybean oil‐based lipid emulsion; PNALD: parenteral nutrition‐associated liver disease; ROP: retinopathy of prematurity; RR: risk ratio; S‐LE: soybean oil‐based lipid emulsion. | |||||
| GRADE Working Group Grades of Evidence High quality: further research is very unlikely to change our confidence in the estimate of effect. Moderate quality: further research is likely to have an important impact on our confidence in the estimate of effect and may change the estimate. Low quality: further research is very likely to have an important impact on our confidence in the estimate of effect and is likely to change the estimate. Very low quality: we are very uncertain about the estimate. | |||||
aDowngraded by one level as optimal information size not reached. bDowngraded by one level as the CI crossed the null effect and the limit of appreciable harm or benefit (0.75 or 1.25); or crossed limit of clinically appreciable harm or benefit in a continuous outcome (author consensus). cDowngraded by one level as one study was at high risk of material bias.
Summary of findings 4. Alternative lipid emulsion (LE) compared to another alternative‐LE for parenterally fed preterm infants.
| Alternative‐LE compared to another alternative‐LE for parenterally fed preterm infants | |||||
| Patient or population: parenterally fed preterm infants Settings: neonatal intensive care unit Intervention: alternative‐LE Comparison: another alternative‐LE | |||||
| Outcomes | Illustrative comparative risks* (95% CI) | Relative effect (95% CI) | No of participants (studies) | Quality of the evidence (GRADE) | |
| Assumed risk | Corresponding risk | ||||
| Other alternative‐LE | Alternative‐LE | ||||
|
Growth rate – MS‐LE vs OS‐LE |
— | The mean rate of weight gain in the intervention groups was 1.33 g/kg/day lower (7.36 lower to 4.7 higher) | — | 59 (1 study) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ Lowa,b |
|
PNALD/cholestasis (conjugated bilirubin ≥ 2 mg/dL) – MS‐LE vs OS‐LE |
Study population | RR 2.9 (0.12 to 68.5) | 59 (1 study) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ Lowa,b | |
| 0 per 1000 | 0 per 1000 (0 to 0) | ||||
|
Death before discharge – MS‐LE vs OS‐LE |
See comment | See comment | Not estimable | 60 (1 study) | No events in either group |
|
CLD (oxygen requirement at 36 weeks' postmenstrual age) – MS‐LE vs OS‐LE |
Study population | RR 0.77 (0.23 to 2.6) | 59 (1 study) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ Lowa,b | |
| 172 per 1000 | 133 per 1000 (40 to 448) | ||||
|
Any sepsis (clinical or culture positive (or both)) – MS‐LE vs OS‐LE |
Study population | RR 1.93 (0.65 to 5.73) | 59 (1 study) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ Lowa,b | |
| 138 per 1000 | 266 per 1000 (90 to 790) | ||||
|
Conjugated bilirubin levels – MS‐LE vs OS‐LE |
— | The mean conjugated bilirubin levels in the intervention groups was 2.91 µmol/L lower (6.87 lower to 1.05 higher) | — | 59 (1 study) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ Lowa,b |
| *The basis for the assumed risk (e.g. the median control group risk across studies) is provided in footnotes. The corresponding risk (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). CI: confidence interval; CLD: chronic lung disease; LE: lipid emulsion; MS‐LE: medium‐chain triglyceride‐soybean oil‐lipid‐based emulsion; OS‐LE: olive oil‐soybean oil‐based lipid emulsion; PNALD: parenteral nutrition‐associated liver disease; RR: risk ratio. | |||||
| GRADE Working Group Grades of Evidence High quality: further research is very unlikely to change our confidence in the estimate of effect. Moderate quality: further research is likely to have an important impact on our confidence in the estimate of effect and may change the estimate. Low quality: further research is very likely to have an important impact on our confidence in the estimate of effect and is likely to change the estimate. Very low quality: we are very uncertain about the estimate. | |||||
aDowngraded by one level as optimal information size not reached. bDowngraded by one level as the CI crossed the null effect and the limit of appreciable harm or benefit (0.75 or 1.25); or crossed limit of clinically appreciable harm or benefit in a continuous outcome (author consensus).
Summary of findings 5. Fish oil lipid emulsion (LE) compared to non‐fish oil LE in parenterally fed preterm infants with surgical conditions.
| Fish oil LE compared to non‐fish oil LE in preterm infants with surgical conditions for parenterally fed preterm infants | ||||||
| Patient or population: parenterally fed preterm infants with surgical conditions Settings: NICU Intervention: fish oil LE (pure F‐LE) Comparison: non‐fish oil LE (S‐LE) | ||||||
| Outcomes | Illustrative comparative risks* (95% CI) | Relative effect (95% CI) | No of participants (studies) | Quality of the evidence (GRADE) | Comments | |
| Assumed risk | Corresponding risk | |||||
| Non‐fish oil LE in preterm infants with surgical conditions | Fish oil LE | |||||
|
PNALD/cholestasis (conjugated bilirubin ≥ 2 mg/dL) – pure F‐LE vs S‐LE |
Study population | RR 1.11 (0.08 to 15.28) | 19 (1 study) | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ Very lowa,b,c,d | — | |
| 100 per 1000 | 111 per 1000 (8 to 1000) | |||||
|
Death before discharge – pure F‐LE vs S‐LE |
See comment | See comment | Not estimable | 19 (1 study) | — | No events in either group |
|
Culture‐positive sepsis – pure F‐LE vs S‐LE |
Study population | RR 1.11 (0.39 to 3.19) | 19 (1 study) | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ Very lowa,b,c,d | — | |
| About 400 per 1000 | 444 per 1000 (156 to 1000) | |||||
|
Conjugated bilirubin levels – pure F‐LE vs S‐LE |
— | The mean conjugated bilirubin levels in the intervention group was 0 µmol/L higher (11.3 lower to 11.3 higher) | — | 19 (1 study) | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ Very lowa,b,c,d | — |
|
Neurodevelopmental outcomes (6 months) – pure F‐LE vs S‐LE |
— | Study reported no significant difference in non‐parametric statistics | — | 11 (1 study) |
— | Grade of evidence was likely to be very low. Parametric statistics not available. |
|
Neurodevelopmental outcomes (24 months) – pure F‐LE vs S‐LE |
— | Study reported no significant difference in non‐parametric statistics | — | 10 (1 study) | — | Grade of evidence was likely to be very low. Parametric statistics not available |
| *The basis for the assumed risk (e.g. the median control group risk across studies) is provided in footnotes. The corresponding risk (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). CI: confidence interval; F‐LE: fish oil lipid emulsion; LE: lipid emulsion; PNALD: parenteral nutrition‐associated liver disease; RR: risk ratio; S‐LE: soybean oil‐based lipid emulsion. | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group Grades of Evidence High quality: further research is very unlikely to change our confidence in the estimate of effect. Moderate quality: further research is likely to have an important impact on our confidence in the estimate of effect and may change the estimate. Low quality: further research is very likely to have an important impact on our confidence in the estimate of effect and is likely to change the estimate. Very low quality: we are very uncertain about the estimate. | ||||||
aDowngraded by one level as optimal information size not reached. bDowngraded by one level as the CI crossed the null effect and the limit of appreciable harm or benefit (0.75 or 1.25); or crossed limit of clinically appreciable harm or benefit in a continuous outcome (author consensus). cThe evidence could be potentially further downgraded by one level for this outcome as it was a single small study. This downgrading would not apply if this was a large randomised study. dDowngraded by one level due to potential risk of bias due to early termination of study and due to use of 10% Intralipid.
Summary of findings 6. Fish oil lipid emulsion (LE) compared to non‐fish oil LE for parenterally fed preterm infants with cholestasis.
| Fish oil LE compared to non‐fish oil LE for parenterally fed preterm infants with cholestasis | ||||||
| Patient or population: parenterally fed preterm infants with cholestasis Setting: NICU Intervention: fish oil LE Comparison: non‐fish oil LE | ||||||
| Outcomes | Anticipated absolute effects* (95% CI) | Relative effect (95% CI) | No of participants (studies) | Quality of the evidence (GRADE) | Comments | |
| Risk with non‐fish oil LE | Risk with fish oil LE | |||||
|
Resolution of PNALD/ cholestasis (conjugated bilirubin < 2 mg/dL) Pure F‐LE vs Intralipid Follow‐up: mean 2–4 months |
Study population | RR 5.6 (0.34 to 93.35) | 16 (1 study) | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ Very lowa,b,c,e | Fish oil LE likely reduced resolution of PNALD/ cholestasis. This used 10% Intralipid. | |
| 0 per 1000 (baseline rate) | 0 per 1000 | |||||
| 50 per 1000 (if 5% of infants with cholestasis improve with non‐fish LE) | 280 per 1000 improved with fish oil emulsion (17 to 1000) | |||||
|
PNALD/ cholestasis (any definition) MOFS‐LE vs S‐LE Pure F‐LE vs S‐LE Follow‐up: mean 2–4 months |
Study population | RR 0.54 (0.32 to 0.91) | 40 (2 studies) | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ Very lowb,c,d | Fish oil LE may have reduced PNALD/ cholestasis – MOFS‐LE vs S‐LE. 1 trial was stopped after interim analysis. 1 trial used 10% Intralipid. |
|
|
800 per 1000 continued to have cholestasis (80% rate in non‐fish oil LE) |
432 per 1000 had cholestasis (256 to 728) |
|||||
|
Growth rate Pure F‐LE vs S‐LE |
The mean weight gain 0 g/week |
MD 45 g/week higher (15.00 higher to 75.00 higher) | — | 16 (1 study) | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ Very lowb,c,e | — |
|
Head growth velocity Pure F‐LE vs S‐LE |
The mean head growth velocity was 0 cm/week |
MD 0.16 cm/week higher (0.01 lower to 0.33 higher) | — | 16 (1 study) | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ Very low,a,b,c,e | — |
|
Death before discharge – MOFS‐LE vs S‐LE – Pure F‐LE vs IL |
Study population | RR 0.24 (0.03 to 1.87) | 40 (2 studies) | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ Very lowa,b,c | — | |
| 150 per 1000 | 36 per 1000 (4 to 280) | |||||
|
Any sepsis – MOFS‐LE vs S‐LE – Pure F‐LE vs IL |
Study population | RR 1.21 (0.5 to 2.92) | 40 (2 studies) | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ Very lowa,b,c | — | |
| 300 per 1000 | 363 per 1000 (150 to 876) | |||||
|
Conjugated bilirubin levels – MOFS‐LE vs S‐LE |
The mean conjugated bilirubin levels was 0 μmol/L | MD 47 µmol/L lower (71.65 lower to 22.35 lower) | — | 24 (1 study) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ Lowb,e | Authors excluded 1 infant with sepsis‐related increase in conjugated bilirubin in their analysis. |
| *The risk in the intervention group (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). CI: confidence interval; F‐LE: fish oil lipid emulsion; LE: lipid emulsion; MOFS‐LE: medium‐chain triglycerides (MCT)‐olive‐fish‐soybean oil‐lipid emulsion; PNALD: parenteral nutrition‐associated liver disease; RR: risk ratio; S‐LE: soybean oil‐based lipid emulsion. | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group Grades of Evidence High quality: we are very confident that the true effect lies close to that of the estimate of the effect. Moderate quality: we are moderately confident in the effect estimate: the true effect is likely to be close to the estimate of the effect, but there is a possibility that it is substantially different. Low quality: our confidence in the effect estimate is limited: the true effect may be substantially different from the estimate of the effect. Very low quality: we have very little confidence in the effect estimate: the true effect is likely to be substantially different from the estimate of effect. | ||||||
aDowngraded by one level as the effect size confidence intervals include null effect and RR of 0.75 or 1.25 (or limit of appreciable benefit or harm for continuous outcomes). bDowngraded by one level as the optimal information size is not reached. cTrial stopped prior to full completion. Evidence was downgraded by one level where this trial contributed > 20% or was the only contributor to evidence.
dDowngraded by one level as the two studies in this outcome used different cut‐offs for conjugated bilirubin. eThe evidence would be further downgraded by one level for this outcome as it was a single small study. This downgrading would not apply if this was a large randomised study.
Background
Description of the condition
Preterm infants frequently require total or partial parenteral nutrition (PN) to provide all or part of their caloric requirements to ensure adequate growth. In theory, preterm infants would follow the same growth curves postnatally as those for a normal foetus of the same gestational age (AAP 1985). In reality, this proves challenging, as preterm infants are compromised by their critical illness and immaturity of many of their organs. The growth of nearly all preterm infants in neonatal intensive care lags far behind foetal growth curves in the third trimester (Ehrenkranz 2000). Critically ill preterm infants do not receive sufficient protein and energy to achieve adequate growth (Hay 2008). Lipid emulsions (LEs) have been a vital component of PN in preterm infants since their introduction in the 1960s. Lipids are an attractive energy source because of their high‐density energy and their supply of essential fatty acids necessary for central nervous system development (Vlaardingerbroek 2012). In addition, lipids are needed to prevent essential fatty acid (EFA) deficiency in preterm infants (Lee 1993).
Description of the intervention
LEs serve as a source of high‐density energy and EFAs (i.e. linoleic acid (ω‐6 fatty acid) and alpha‐linolenic acid (ω‐3 fatty acid)). These are precursors for eicosanoids, active in numerous physiological mechanisms such as platelet function, immune response, inflammation, and early visual and neural development (Driscoll 2008; Koletzko 2001; Lapillonne 2013; SanGiovanni 2000).
Pure soybean oil‐based lipid emulsions (S‐LEs; e.g. Intralipid, Ivelip, Liposyn III) have been the standard LEs used in neonatal intensive care units (NICUs) worldwide for the last few decades (de Meijer 2009). However, there is evidence to suggest that S‐LEs may have harmful effects due to excessive polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) and linoleic acid content (Sala‐Vila 2007). Newer LEs aim to decrease the excessive ω‐6 fatty acid content by using lipids from sources other than soybean oil.
Medium‐chain triglyceride (MCT)‐based lipid emulsions (coconut oil‐derived) decrease the ω‐6 content by adding MCT to LEs; for example, Lipovenoes MCT and 20% Lipofundin MCT/long‐chain triglyceride (LCT) are a 1:1 mix of MCT and LCT (Vanek 2012). Structured LEs (e.g. Structolipid) are a modification of MCT‐LCT‐based lipid emulsions and are formed by re‐esterification of medium‐ and long‐chain fatty acids (Waitzberg 2006). Olive oil‐based lipid emulsions which are rich in the monounsaturated fatty acid, oleic acid (18:1; ω‐9), have been available since the 1990s. For example, ClinOleic is an olive oil‐based lipid emulsion with a 4:1 ratio of olive oil to soybean oil, and one‐third of the PUFA content compared with S‐LE (e.g. 20% Intralipid). Fish oil‐containing lipid emulsions (e.g. Omegaven), which are rich in ω‐3 fatty acids and have a low ratio of ω‐6 to ω‐3, have also been developed (Wanten 2007).
More recently, LEs derived from multiple sources have become available for clinical use. SMOFlipid is one such LE; it is a 30:30:25:15 mix of MCT, soybean oil, olive oil and fish oil (Sala‐Vila 2007). Lipidem, also known as Lipiplus in some countries, is a 5:4:1 mix of MCT, soybean oil and fish oil.
However, there is a concern that the lipid profile of the breast milk is significantly different compared to lipid constituents (including arachidonic acid, docosahexaenoic acid and eicosapentanoic acid) in the available LEs for preterm infants including SMOFlipid (Scholtens 2009; Appendix 1).
How the intervention might work
Currently available LE formulations differ in the source of lipid, fatty acid profile, antioxidant levels and presence of additional components (Wanten 2007).
S‐LEs have excessive amounts of PUFA (up to 60%) and linoleic acid (50%) (Sala‐Vila 2007), which exceeds the daily preterm linoleic acid requirement of 0.25 g/kg/day and adds to oxidative stress (Koletzko 2005; Pitkanen 1991). This may aggravate adverse outcomes, including chronic lung disease (Schock 2001), and retinopathy of prematurity (ROP; Mylonas 1999).
Conventional S‐LEs contribute to parenteral nutrition‐associated liver disease (PNALD) in preterm infants (de Meijer 2009); phytosterols, present in soybean oil, may have harmful effects on liver function (de Meijer 2009). However, one randomised study found no association of phytosterols with liver dysfunction (Savini 2013). High amounts of linoleic acid and alpha‐linolenic acid in S‐LEs may lead to substrate inhibition of Δ6desaturase (Göbel 2003), resulting in decreased formation of arachidonic acid and docosahexaenoic acid, which are crucial for visual and cognitive development in preterm infants (Heird 2005; Lehner 2006). S‐LEs also lead to an increase in proinflammatory prostaglandins and leukotrienes (Wanten 2007), which may increase the risk of sepsis (Palmblad 1991), and may adversely affect phagocytic and lymphocytic functions (Gogos 1995).
MCT (coconut oil‐derived) and LCT (soybean oil‐derived)‐based lipid emulsions (MS‐LEs) may have advantages due to reduced ω‐6 content and the rapid metabolism of MCTs. Early data suggested good tolerance in preterm infants with increased eicosapentaenoic acid levels and an equivalent EFA profile compared with S‐LEs (Lehner 2006). However, in vitro studies have raised concerns that MCTs may cause leukocyte activation, impair immune function and decrease killing of Candida albicans (Waitzberg 2006; Wanten 2007). MCT oil LEs have also been associated with impaired lung function and aggravation of tissue inflammation in adults with acute respiratory distress syndrome (Lekka 2004); they may also be ketogenic, which limits their utility in people with acidosis (Waitzberg 2006).
Structured LEs have an even distribution of medium‐chain fatty acids in the lipid droplets, aimed at reducing the immunological adverse effects of MS‐LEs. There is limited evidence to suggest that structured emulsions are well tolerated in people who are critically ill; however, unlike MS‐LEs, they may not affect phagocyte function (Wanten 2007).
Borage oil‐soybean oil‐based lipid emulsions (BS‐LEs) substitute the soybean content partially with borage oil, which is the highest source of gamma‐linolenic acid (18:3; ω‐6). The enzyme Δ6‐desaturase is essential in the conversion from linoleic acid to gamma‐linolenic acid and is considered the rate‐limiting step in the metabolism from linoleic acid to arachidonic acid. Borage oil‐based lipid emulsions were developed to potentially circumvent this enzymatic step. PFE 4501 (Pharmacia, Sweden) is a combination of borage oil (15%) and soybean oil (85%) with increased amounts of carnitine to prevent carnitine deficiency in preterm infants (Magnusson 1997).
Olive oil‐soybean oil‐based lipid emulsions (OS‐LEs) have generated interest due to the immune‐neutral nature of oleic acid (Reimund 2004), decreased PUFA content, higher alpha‐tocopherol content (Sala‐Vila 2007), and reduced peroxidability of low‐density lipoproteins, with an overall reduction in oxidative stress (Goulet 1999; Krohn 2006). OS‐LE (ClinOleic) has a fatty acid composition similar to that of breast milk, and results in higher alpha‐tocopherol levels in preterm infants when compared with S‐LE (Intralipid; Göbel 2003). Studies have reported decreased immunological disturbance, with less inhibition of T‐cell activation, less effect on interleukin‐2 production and decreased alteration in neutrophil responses with OS‐LE compared with S‐LE (Buenestado 2006; Gawecka 2008a; Granato 2000). Olecanthol, a minor component in olive oil, inhibits the cyclo‐oxygenase pathway but not the 5‐lipoxygenase pathway, displaying "ibuprofen‐like" anti‐inflammatory activity (Beauchamp 2005). OS‐LE may decrease the incidence of hyperglycaemia when compared with S‐LE (Intralipid) (Van Kempen 2006). Randomised controlled trials (RCT) of critically ill neonates and preterm infants less than 32 weeks' gestation have shown OS‐LE to be as equally well‐tolerated as conventional S‐LE (Gawecka 2008a).
Fish oil‐containing lipid emulsions (F‐LEs) have increased ω‐3 PUFAs, resulting in inhibition of the cyclo‐oxygenase pathway and preferential use of the lipoxygenase pathway, which in turn decreases proinflammatory prostaglandins (Fürst 2000). Eicosapentaenoic acid (C20:5; ω‐3), present in fish oil, activates the peroxisome proliferator‐activated receptors, alpha and gamma, which in turn antagonise the nuclear factor‐κB signalling pathway, leading to reduced production of inflammatory mediators (Fürst 2000). Studies in adults have indicated that in sepsis, F‐LE decreases the length of hospital stay, readmission rate, rate of mechanical ventilation, and improves survival (Wanten 2007). In observational studies, a pure F‐LE (Omegaven) decreased and reversed PNALD in infants, resulting in decreased mortality and lower levels of triglycerides (TG), conjugated bilirubin and liver enzymes compared with S‐LE (20% Intralipid) (de Meijer 2009; Puder 2009). However, in one randomised study, there was no difference between the SMOFlipid and MS‐LE between the incidence of cholestasis in infants of 34 weeks' gestation and above, who underwent surgery for major gastrointestinal (GI) abnormalities (Pereira‐da‐Silva 2017).
Evidence from one systematic review of preterm infants given F‐LEs suggested that docosahexaenoic acid and eicosapentaenoic acid decreased significantly in red blood cell membranes, and arachidonic acid significantly increased (Zhao 2015).
Multisource lipid emulsions (MCT‐fish‐soybean oil‐based lipid emulsions (MFS‐LEs) and MCT‐olive‐fish‐soybean oil‐based lipid emulsions (MOFS‐LEs) derive the advantages of lipids from multiple sources, including MCTs (rapidly metabolised lipids), soybean oil (essential fatty acid source), olive oil (fewer immune effects) and fish oil (anti‐inflammatory effects). There is evidence of reduced hospital stay, better plasma elimination of TGs, better alpha‐tocopherol levels, and good tolerance profile with a MOFS‐LE (SMOFlipid) in adults (Grimm 2005; Wanten 2007). F‐LE (ClinOleic and Omegaven in a 1:1 combination) decreased cholestasis and the incidence of ROP requiring laser therapy in preterm infants (Pawlik 2011; Pawlik 2014). One prospective observational cohort study in preterm infants reported decreased incidence of bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) with SMOFlipid (Skouroliakou 2012). Meta‐analyses have shown decreases in the incidence of cholestasis and severe ROP with F‐LEs in preterm infants (Kotiya 2016; Vayalthrikkovil 2017).
The abbreviation scheme used for alternative‐LEs is described in Appendix 2.
Why it is important to do this review
The introduction of life‐saving PN was a landmark in neonatal care, but it appears that the conventionally used S‐LEs are far from ideal. Conventional S‐LEs, despite their widespread use, may have harmful effects in infants due to their high PUFA content which may contribute to adverse outcomes including mortality, PNALD, ROP, BPD and sepsis.
We aimed to synthesise evidence from randomised studies comparing different LE regarding various clinical outcomes in preterm infants with or without liver disease or surgical conditions.
Other systematic reviews about LEs for preterm infants include Vlaardingerbroek 2012, Park 2015, and Vayalthrikkovil 2017.
A previous version of this review, comparing newer LE to conventional S‐LE, was published in 2015 (Kapoor 2015). This review will replace the 2015 review and extend the scope to evaluate all available comparisons against each other in a pair‐wise manner.
Objectives
To compare the safety and efficacy of all LE for parenteral nutrition (PN) in preterm infants using direct comparisons and pair‐wise meta‐analyses.
To determine the effectiveness and safety of different LEs in relation to gestational age (less than 30 weeks' gestation; 30 weeks' gestation or more), birth weight (1000 g or less; more than 1000 g)
To determine safety and efficacy of different LEs in preterm infants with clinical condition (infants undergoing surgery, infants with established cholestasis).
Methods
Criteria for considering studies for this review
Types of studies
We included RCTs. Quasi‐randomised trials and cluster‐randomised trials were also eligible for inclusion. We excluded cross‐over RCTs.
Types of participants
We considered three populations in the current review including:
Preterm infants (less than 37 weeks' gestation) who received intravenous LE as part of total parenteral nutrition (TPN) or partial parenteral nutrition (PPN) within the first week of life and for a minimum of five days;
Preterm infants (less than 37 weeks' gestation) with surgical conditions who received intravenous LE as part of TPN or PPN within the first six months of life;
Preterm infants (less than 37 weeks' gestation) with PNALD/cholestasis who received intravenous LE as part of TPN or PPN within the first six months of life.
There was no restriction on comorbidities including surgery in preterm infants with PNALD.
Types of interventions
We included studies comparing various LEs, including newer LEs (lipids derived from olive oil, fish oil and MCT; structured lipids and multisource LEs) and conventional pure S‐LE in preterm infants.
Eligible lipid emulsions
S‐LEs: LEs with 100% lipids derived solely from soybean oil.
Intralipid.
Ivelip.
Liposyn III.
F‐LEs: all fish oil‐containing LEs.
MOFS‐LEs (e.g. SMOFlipid).
MFS‐LEs (e.g. Lipidem).
Pure fish oil (pure F‐LE; e.g. Omegaven).
Alternative‐LEs: all alternative‐LEs with partial or complete substitution of soybean oil from other sources, but not containing fish oil (decreased linoleic acid content).
OS‐LEs (e.g. ClinOleic).
MS‐LEs (e.g. Lipovenoes MCT).
BS‐LEs (e.g. PFE 4501).
Structured lipids (structured MCT‐soybean oil; e.g. Structolipid).
See Appendix 2 for a list of abbreviations for eligible LEs. Constituents of the LEs have been outlined in Appendix 1.
We considered the following comparisons in each of the three predefined populations (i.e. preterm infants, preterm infants with surgical conditions and preterm infants with PNALD/cholestasis.
F‐LE versus non‐fish oil LE.
F‐LE versus another F‐LE.
Alternative LE versus S‐LE.
Alternative LE versus another alternative LE.
Details of all possible comparisons are noted in Appendix 3.
Types of outcome measures
Primary outcomes
-
Physical growth:
days to regain birth weight;
growth rate (g/kg/day) during study period and hospital stay (Fenton 2017).
Parenteral nutrition‐associated liver disease (PNALD), defined as conjugated bilirubin 2 mg/dL or greater (or 34.2 µmol/L or greater) with or without raised liver enzymes (alanine aminotransferase (ALT) greater than 45 IU/L, alkaline phosphatase greater than 420 IU/L) in the absence of other causes (Christensen 2007; Hojsak 2016; Robinson 2008), in preterm infants without PNALD at study entry.
PNALD/cholestasis (any definition)*
Resolution of PNALD, defined as conjugated bilirubin less than 2 mg/dL (34.2 µmol/L), in preterm infants with established PNALD (Lam 2014).
Secondary outcomes
Death before discharge or neonatal death (within the first 28 days of life).
-
Retinopathy of prematurity (ROP):
any ROP reported by study authors;
ROP stage 3 or greater, or observed by direct or indirect ophthalmoscope, as defined by the International Classification of ROP (ICROP) (ICROP 2005) or ROP requiring surgery.*
-
Bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) or chronic lung disease (CLD):
any BPD reported with or without definition by the study authors;*
oxygen therapy or any form of respiratory support at 36 weeks' postmenstrual age.
Duration of ventilation (total days).
Duration of supplemental oxygen (total days).
Duration of hospital stay (days).
Need for home oxygen therapy.
-
Sepsis:
proven sepsis (blood culture positive);
any sepsis (reported with or without definition).*
Necrotising enterocolitis (NEC) stage 2 or greater on Bell's staging system (Bell 1978).
Intraventricular haemorrhage (IVH; grade III to IV) on cranial ultrasound, according to the Papile classification (Papile 1978).
Periventricular leukomalacia (PVL); based on ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) (de Vries 1992).
-
Patent ductus arteriosus (PDA):
any PDA reported by study authors.
significant PDA diagnosed clinically or by echocardiography, requiring treatment either conservatively by fluid restriction, diuretics, indomethacin or ibuprofen, or surgery.
Air leaks (pneumothorax, pneumomediastinum, pulmonary interstitial emphysema), reported individually or as a composite outcome.
Pulmonary haemorrhage needing alterations in respiratory care or causing haemodynamic instability.
Significant jaundice: requiring treatment with phototherapy or exchange transfusion, or both.
Duration of phototherapy (days).
Thrombocytopenia (platelet count less than 50,000/μL).
Hypertriglyceridaemia defined by serum TGs levels greater than 200 mg/dL (2.25 mmol/L; Putet 2000).
Hyperglycaemia (blood sugar level greater than 8.3 mmol/L (150 mg/dL); Sinclair 2011) or hypoglycaemia (blood sugar level less than 2.6 mmol/L (46 mg/dL)).
Essential fatty acid (EFA) deficiency defined by triene/tetraene ratio greater than 0.05 (Cober 2010; Gura 2005).
-
Head growth:
head circumference below third percentile at discharge;
head growth velocity (cm/week).
Length (cm/week).
-
Body composition: measured at corrected term gestation by magnetic resonance spectroscopy and MRI (Ahmad 2010; Roggero 2007; Uthaya 2016):
intrahepatocellular lipid content (IHCL) (intrahepatic lipid:water ratio) values;
non‐adipose tissue mass.
Neurodevelopmental outcome (assessed by a standardised and validated assessment tool or a child developmental specialist) at any age reported (outcome data grouped at 12, 18 and 24 months if available).
Conjugated bilirubin levels*
Outcomes marked with asterisk (*) were added after the protocol stage.
Search methods for identification of studies
We used the criteria and standard searching methods of Cochrane and Cochrane Neonatal (Higgins 2017). We searched for errata or retractions from included studies published in full‐text on PubMed (www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed).
Electronic searches
We conducted a comprehensive search including: Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL 2018, Issue 5); MEDLINE via Ovid (1946 to 18 June 2018); Embase via Ovid (1974 to 18 June 2018); CINAHL (1982 to 18 June 2018) and MIDIRS (1971 to May 31 2018) (see Appendix 4 for the full search strategies for each database). We applied no language restrictions. We searched clinical trials registries for ongoing or recently completed trials on 19 June 2018 (ClinicalTrials.gov, and the World Health Organization's International Trials Registry and Platform).
Searching other resources
We reviewed the reference lists of all identified studies for relevant articles not identified in the primary search.
Data collection and analysis
We used the standard methods of Cochrane Neonatal for data collection and analysis. We specifically designed data extraction forms for this review, tested the forms on two studies, further refined them and then used the forms to collect and collate data. For each included study, we recorded details regarding the method of randomisation, allocation concealment, blinding, intervention, stratification and whether the study was single‐centre or multicentre. We extracted data regarding participants, PN and reported outcomes.
We recorded the selection process in sufficient detail to complete a PRISMA flow diagram (Moher 2009), and Characteristics of included studies; Characteristics of excluded studies; and Characteristics of studies awaiting classification tables.
Selection of studies
Dr William McGuire, Cochrane Neonatal Nutrition Editor, prescreened the deduplicated search at the title and abstract stage. Two review authors (VK, MM) independently reviewed these decisions and the full‐text articles to identify studies eligible for inclusion in the review. We assessed the methodology of the studies with regard to blinding of randomisation, allocation concealment, intervention and outcome measurements, and completeness of follow‐up.
Data extraction and management
Two review authors (VK, MM) independently extracted data for each study on data extraction forms. One review author (VK) entered data into Review Manager 5 (Review Manager 2014) and the other review author (MM) cross‐checked the printout against his own data extraction forms. At each stage, we resolved any differences in opinion by discussion or by consulting a third assessor (RS).
Assessment of risk of bias in included studies
Two review authors (VK, MM) independently assessed the risk of bias (low, high or unclear) of all included trials using the Cochrane 'Risk of bias' tool for the following domains (Higgins 2017).
Sequence generation (selection bias).
Allocation concealment (selection bias).
Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias).
Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias).
Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias).
Selective reporting (reporting bias).
Any other bias.
We resolved any disagreements by discussion or by consulting a third assessor (RS). We performed sensitivity analyses exploring the impact of the level of bias through undertaking sensitivity analyses as predefined in the review protocol (Kapoor 2018). We presented the results from low and unclear risk of bias studies as the primary result as per Cochrane recommendations if significantly different from results including studies with any level of bias.
See Appendix 5 for a more detailed description of risk of bias for each domain.
Measures of treatment effect
We followed the recommendations of Cochrane Neonatal, and used a fixed‐effect model for meta‐analysis. We estimated the treatment effects for categorical outcomes using the typical risk ratio (RR) and typical risk difference (RD) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs). We estimated the number needed to treat for an additional beneficial outcome (NNTB) and number needed to treat for an additional harmful outcome (NNTH) if the RD was statistically significant. For continuous outcomes, we used the mean difference (MD) with 95% CIs to describe the data.
Unit of analysis issues
The unit of analysis was the participating infant in individually randomised trials and neonatal unit for cluster randomised trials. We ensured that there were no unit of analysis issues with double counting of treatment arms when studies with multiple intervention arms were used in the meta‐analyses. To avoid a unit of analysis error, we combined all arms of multiarm studies to create a single pair‐wise comparison for the outcome of PNALD and its subgroup analyses as suggested in the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions (Higgins 2017). We had planned to adjust the sample size of the cluster randomised trials using the methods described in the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions (Higgins 2017); however, found no eligible cluster randomised trials.
Dealing with missing data
We contacted the authors of the included studies or the journal editors if we required clarifications or additional information. The publication authors were sent open‐ended requests as well as a partially completed data extraction forms (with data extracted from their study) if required. In the case of missing data, we described the number of participants with missing data in the Results section and in the Characteristics of included studies table.
Assessment of heterogeneity
We estimated treatment effects in individual trials and examined heterogeneity between trials by inspecting forest plots and quantifying the impact of heterogeneity by using the I² statistic, a measure that describes the proportion of variation in point estimates that is due to variability across studies rather than sampling error (Higgins 2017). We interpreted the I² value as follows.
Less than 25%: no heterogeneity.
25% to 49%: low heterogeneity.
50% to 74%: moderate heterogeneity.
75% to 100%: high heterogeneity.
In outcomes with statistical heterogeneity, we explored possible causes (e.g. differences in study quality, participants, intervention regimens or outcome assessments) by performing post hoc subgroup analyses.
Assessment of reporting biases
We used funnel plots to detect reporting bias for studies comparing F‐LE versus non‐fish oil LE (outcomes 1.5 and 1.6) and for the subgroup comparison of MOFS‐LE versus S‐LE for the outcome of PNALD/cholestasis using any definition. We could not use funnel plots to assess publication bias for most subgroup comparisons (Sterne 2017), as none of the subgroup comparisons between specific LEs had more than 10 studies. We identified and evaluated multiple reports of three studies (multiple publication bias) by comparing the reported baseline characteristics (Table 7), and the author details. We contacted the respective journals and the corresponding author of one study for further clarifications about the duplicate data (Wang 2016).
1. Baseline characteristics of included studies.
| Study | Intervention: alternative lipid emulsion | Control: conventional pure soybean oil‐based lipid emulsion | ||||||||
| Lipid emulsiona | n | Boys | Gestation (weeks)b | Birth weight (g)b | Lipid emulsion | n | Boys | Gestation (weeks)b | Birth weight (g)b | |
| Beken 2014 | SMOFlipid | 40 | 24 | 30 (28–31)c | 1092 (224) | 20% Intralipid | 40 | 22 | 30 (27–31)c | 1160 (251) |
| Biagetti 2016 | MFS‐LE | 26 | NA | 28.7 (2) | 1010 (127) | MS‐LE | 26 | NA | 28.8 (2.28) | 1020 (179) |
| D'Ascenzo 2011 | MFS‐LE | 24 | NA | 28.8 (2.28) | 1017 (203) | MS‐LE | 24 | NA | 27.8 (1.42) | 1009 (211) |
| D'Ascenzo 2014 | SMOFlipid | 39 | 24 | 27.5 (3.4) | 898.5 (309.4) | 20% Intralipid | 41 | 23 | 28.1 (3.1) | 941 (299) |
| Demirel 2011 | ClinOleic | 20 | 9 | 30.3 (2.5) | 1300.2 (480) | 20% Intralipid | 20 | 12 | 29.2 (3.5) | 1252.5 (458) |
| Deshpande 2009 | ClinOleic | 24 | 14 | 26.1 (1.3) | 848.2 (184.2) | 20% Intralipid | 21 | 10 | 25.9 (1.2) | 801.2 (210.9) |
| Deshpande 2014 | SMOFlipid | 17 | 7 | 26.73 (1.62) | 935.58 (163.34) | ClinOleic | 17 | 7 | 26.45 (1.92) | 906.76 (313.42) |
| Diamond 2017 | SMOFlipid | 11 | 6 | 34.5 (3.18) | 2390 (666.7) | 20% Intralipid | 13 | 7 | 35.2 (2.88) | 2550 (629.6) |
| Gawecka 2008b | ClinOleic | 18 | 9 | 27 (1) | 936 (218) | 20% Intralipid | 20 | 9 | 27 (2) | 924 (221) |
| Göbel 2003 | ClinOleic | 24 | 18 | 31.4 (2.4) | 1577 (378) | 20% Intralipid | 21 | 11 | 32 (1.8) | 1694 (475) |
| Hsiao 2018 | SMOFlipid | 30 | 14 | 28.5 (2.9) | 1004 (265) | Lipovenoes | 30 | 15 | 28.3 (2.9) | 962 (194) |
| Köksal 2011 | ClinOleic | 32 | 14 | 30.2 (1.3) | 1520 (420) | 20% Intralipid | 32 | 16 | 30.4 (1.6) | 1460 (280) |
| Lam 2014 | 10% Omegaven | 9 | 6 | 29 (4.44) | 1410 (1403.7) | 10% Intralipid | 7 | 4 | 29 (8.14) | 1240 (970.37) |
| Lehner 2006 | 20% Lipofundin (MCT) | 6 | 6 | 31.4 (1.6) | 1573.3(169.8) | 20% Lipofundin N | 6 | 3 | 33.2 (1.0) | 1781.7 (290.3) |
| Najm 2017 | SMOFlipid | 41 | 24 | 25.5 (1.3) | 799 (225) | ClinOleic | 37 | 19 | 25.6 (1.6) | 799 (225) |
| Nehra 2014 | 10% Omegaven | 9 | 6 | 36 (0.74) | 2450 (129.62) | 20% Intralipid | 10 | 4 | 34.5 (1.48) | 2250 (444.4) |
| Pawlik 2014 | OFS‐LE | 60 | 27 | 28 (25‐31)c | 930 (580‐1250)c | ClinOleic | 70 | 28 | 28 (24‐31)c | 940 (650‐1250)c |
| Rayyan 2012 | SMOFlipid | 26 | 8 | 29.9 (1.9) | 1335.6 (408.8) | 20% Intralipid | 27 | 16 | 30.4 (1.8) | 1364.1 (339.7) |
| Repa 2018 | SMOFlipid | 110 | 64 | 25.87 (1.88) | 788 (180) | 20% Intralipid | 113 | 73 | 26.285 (2.22) | 760 (202.96) |
| Rubin 1994 | 20% Lipofundin (MCT) | 15 | 11 | 31.6 (2.3) | 1570 (400) | 20% Intralipid | 18 | 11 | 31.4 (2.1) | 1420 (400) |
| Rubin 1994 | PFE 4501 | 16 | 9 | 30.5 (2.7) | 1390 (500) | |||||
| Roggero 2010 | ClinOleic | 12 | 5 | 30.6 (1.7) | 1338 (209) | 20% Intralipid | 12 | 7 | 30.8 (2.3) | 1247 (239) |
| Roggero 2010 | 20% Lipofundin (MCT) | 12 | 6 | 30.7 (1.9) | 1305 (332) | |||||
| Savini 2013 | Lipofundin (MCT) | 30 | 14 | 27.7 (1.8) | 937 (222) | 20% Intralipid | 30 | 13 | 28.3 (2.1) | 955 (202) |
| Savini 2013 | Lipidem (MFS) | 27 | 14 | 28.3 (2.3) | 935 (202) | |||||
| Savini 2013 | ClinOleic | 29 | 13 | 27.7 (2.4) | 905 (160) | |||||
| Savini 2013 | SMOFlipid | 28 | 12 | 27.6 (2) | 898 (199) | |||||
| Skouroliakou 2010 | SMOFlipid | 14 | NA | 28.21 (2.9) | 1140 (260) | 20% Intralipid | 18 | NA | 30.3 (1.5) | 1210 (170) |
| Skouroliakou 2016 | SMOFlipid | 25 | 15 | 29.2 (1.6) | 1331 (290) | 20% Intralipid | 26 | 14 | 29.1 (1.3) | 1271 (199) |
| Techasatid 2017 | SMOFlipid | 22 | 8 | 27.6 (2.2) | 947 (208) | 20% Intralipid | 22 | 8 | 28.4 (1.2) | 1,060 (119) |
| Tomsits 2010 | SMOFlipid | 30 | NA | 31.7 (1.90) | 1661.7 (418) | 20% Intralipid | 30 | NA | 31.9 (1.8) | 1676.7 (411.5) |
| Uthaya 2016 | SMOFlipid | 85 | 48 | 27.6 (2.24) | 1055.1 (313.8) | 20% Intralipid | 83 | 49 | 27.9 (1.99) | 1034.9 (283.9) |
| Vlaardingerbroek 2014 | SMOFlipid | 48 | 23 | 27.1 (2.3) | 855 (226) | 20% Intralipid | 48 | 18 | 27.2 (1.9) | 888 (204) |
| Wang 2016 | ClinOleic | 50 | 26 | 32.20 (1.7) | 1486.6 (253.8) | 20% Intralipid | 50 | 31 | 30.8 (4.9) | 1469.8 (250.5) |
aSee Appendix 1 for details of the constituents of lipid emulsions. bGestation and birth weight are presented as mean (standard deviation). cMedian (range). MCT: medium‐chain triglyceride; MFS‐LE: medium‐chain triglyceride‐fish‐soybean lipid emulsion; MS‐LE: medium‐chain triglyceride‐soybean oil‐based lipid emulsion; OFS‐LE: olive‐fish‐soybean oil‐lipid emulsion; n: number of participants; NA: not available. Rubin 1994 and Roggero 2010 had three intervention arms each and Savini 2013 had five intervention arms; total enrolled infants were more than the total number of infants for which the baseline characteristics and results were available due to withdrawals).
Data synthesis
We performed meta‐analyses using Review Manager 5 (Review Manager 2014), Cochrane's software for preparing and maintaining systematic reviews. For estimates of typical RR and typical RD, we used the Mantel‐Haenszel method. We carried out and reported all primary meta‐analyses using the fixed‐effect model, according to the recommendations of Cochrane Neonatal.
Details of calculations and imputations
We replaced any standard error of the mean by the corresponding standard deviation (SD). If the data were described in medians and interquartile ranges, we substituted medians for means and imputed the corresponding SDs by dividing interquartile ranges by 1.35 for a studies in the meta‐analysis where feasible. We did not impute the mean and SD if there was only one study in that outcome and meta‐analysis was not feasible. If the data were described in medians and ranges, we used the formulae proposed by Hozo and colleagues to impute the SD (Hozo 2005). We pooled the means and SDs of weekly observations in a group of study participants using the formulae for pooling means and variances (McNaught 1997). For combining means and SDs of multiple groups, we used the formulae described for pooling means and SDs in the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions (Deeks 2017; Furukawa 2006). If the values were only depicted in graphs, we used software‐assisted extraction of the data values from the graph (using GetData Graph Digitizer Version 2.26).
Where we could not perform meta‐analyses, we presented qualitative inferences as systematically as possible and explained why we could not perform meta‐analyses. We presented the results for important outcomes in the 'Summary of findings' tables.
Quality of evidence
We used the GRADE approach, as outlined in the GRADE Handbook to assess the quality of evidence for the following (clinically relevant) outcomes if reported in a comparison (Schünemann 2013).
Physical growth rate (g/kg/day) during study period and hospital stay.
PNALD (conjugated bilirubin 2 mg/dL or greater (34.2 µmol/L or greater)) with or without raised liver enzymes in the absence of other causes.
Death before discharge.
ROP (stage 3 or greater, or requiring surgery).
Chronic lung disease (oxygen requirement at 36 weeks' postmenstrual age).
Culture‐positive sepsis.
Conjugated bilirubin levels (µmol/L) (Added post hoc)
Head growth velocity (cm/week).
Neurodevelopmental outcome (neurodevelopmental outcome assessed by a standardised and validated assessment tool or a child developmental specialist) at any age reported (outcome data grouped at 12, 18 and 24 months if available).
Two review authors (VK, MM) independently assessed the quality of the evidence for each of the outcomes above. We considered evidence from RCTs as high quality, but downgraded our assessments of the evidence by one level for serious (or two levels for very serious) limitations based upon the following: design (risk of bias), consistency across studies, directness of the evidence, precision of estimates and presence of publication bias. We used the GRADEpro Guideline Development Tool to create a 'Summary of findings' table to report the quality of the evidence (GRADEpro GDT).
We used the following grades of evidence to qualify the effect estimates in the 'Summary of findings' tables.
High quality: we are very confident that the true effect lies close to that of the estimate of the effect.
Moderate quality: we are moderately confident in the effect estimate; the true effect is likely to be close to the estimate of the effect, but there is a possibility that it is substantially different.
Low quality: our confidence in the effect estimate is limited; the true effect may be substantially different from the estimate of the effect.
Very low quality: we have very little confidence in the effect estimate; the true effect is likely to be substantially different from the estimate of effect.
For the 'summary of findings' tables, we focused on results from the major subgroup comparisons (e.g. MOFS‐LE versus S‐LE, OS‐LE versus S‐LE). For the primary outcome of PNALD/cholestasis in comparison we have provided the comparison between all F‐LE and non‐F‐LE (by combining all the subgroups) to explore the effect of all F‐LE compared to all non‐F‐LE.
Subgroup analysis and investigation of heterogeneity
We explored high statistical heterogeneity in the outcomes by visually inspecting the forest plots and by removing the outlying studies in the sensitivity analysis (Deeks 2017). Where statistical heterogeneity was significant, we interpreted the results of the meta‐analyses accordingly; and we downgraded the quality of evidence in the 'Summary of findings' tables, according to the GRADE recommendations.
We planned to perform the following subgroup analyses; they were not feasible because stratified/subgroup data were unavailable.
Gestational age (less than 28 weeks, 28 to 32 weeks, greater than 32 weeks).
Sex.
Birth weight (less than 2500 g, less than 1500 g, 1000 g)
Severity of illness.
Lipid dosing.
Continuous versus intermittent LE infusion.
Sensitivity analysis
We performed sensitivity analyses if there was unexplained moderate to high heterogeneity or a study with high risk of bias was included in the meta‐analysis of an outcome where the other studies had low or unclear risk of bias.
We presented results of the sensitivity analyses only if these were significantly different from the primary results.
Results
Description of studies
We included 29 studies (n = 2037) in the review with 26 studies (n = 1890) contributing data to the meta‐analyses (Characteristics of included studies table).
Results of the search
The search yielded 1673 articles from medical literature databases and 88 clinical trial registry reports. There remained 1164 records after removal of duplicates. We reported the study selection process in the PRISMA flow diagram (Figure 1).
1.
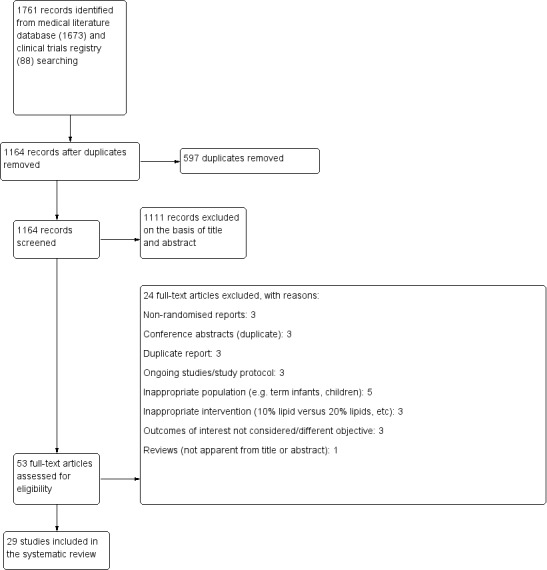
PRISMA flow diagram.
Included studies
The search identified 29 studies (n = 2037). The studies are described in specific subgroups based on the LE being compared under the six broad comparisons that we were able to perform in the review. The first four comparisons were in the population of preterm infants. Comparisons five and six were in preterm infants with surgical conditions and preterm infants with cholestasis respectively.
Fish oil LE versus non‐fish oil LE in preterm infants (Comparison 1)
MOFS‐LE versus S‐LE
Eleven studies compared MOFS‐LE versus S‐LE (Beken 2014; D'Ascenzo 2014; Rayyan 2012; Repa 2018; Savini 2013; Skouroliakou 2010; Skouroliakou 2016; Techasatid 2017; Tomsits 2010; Uthaya 2016; Vlaardingerbroek 2014).
Beken 2014 was a single‐centre RCT at the NICU at Dr Sami Ulus Maternity and Children Research Centre in Ankara, Turkey.
Population: preterm infants less than 1500 g and less than 32 weeks' gestation were eligible. Exclusion criteria were major congenital abnormalities, congenital infections and inborn errors of metabolism.
Objective: to compare the effect of 20% SMOFlipid (MOFS‐LE; 30% MCT, 25% olive oil, 15% fish oil, 30% soybean oil) versus 20% Intralipid (S‐LE) on the development of ROP in very low birth weight infants.
Interventions: infants were randomised to receive either MOFS‐LE (n = 40) or S‐LE (n = 40) starting at 0.5 g/kg/day in infants weighing less than 1000 g and 1 g/kg/day for infants weighing more than 1000 g, infused over 24 hours. Lipids were increased by 0.5 g/kg/day to 1 g/kg/day, to a maximum of 3 g/kg/day. Infants received dextrose and amino acids 1 g/kg/day starting on day one of life. Both groups received enteral feeds of breast milk or docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) enriched formula (Prematil‐LCP, Milupa, GmbH, Friedrichsdorf, Germany). Thirty‐two infants in the MOFS‐LE group and 30 infants in the S‐LE group received their own mothers' breast milk. The intravenous lipid infusion as a component of TPN was progressively replaced with enteral intake so as to maintain 3 g/kg/day of lipid intake. Oxygen saturation was targeted at 90% to 95%.
Outcomes: primary outcomes were the development of ROP and the need for laser photocoagulation. Secondary outcomes included cholestasis, nosocomial infections, NEC, IVH and CLD. The initial ROP examinations were performed at corrected age of 31 weeks in infants born at 27 weeks' gestation or less and fourth to fifth week in infants born at 28 weeks' gestation or greater. The authors reported that "all fundus examinations were performed by the same paediatric ophthalmologist who was blinded to the group assignment." The follow‐up examinations were performed once every two weeks in infants with low‐risk prethreshold disease and at least once a week for infants with high‐risk prethreshold disease.
D'Ascenzo 2014 was a single‐centre, four‐arm RCT on preterm newborn infants in the NICU at the Salesi Children's Hospital, Italy between January 2008 and December 2012.
Population: preterm infants (birth weight 500 g to 1249 g) were randomised in 1:1:1:1 ratio to receive either SMOFlipid or Intralipid at rate of either 3.5 g/kg/day or 2.5 g/kg/day in four groups. Exclusion criteria were severe malformations, inborn errors of metabolism and severe congenital sepsis.
Objective: to compare the plasma fatty acids and lipid tolerance in preterm infants receiving different doses of MOFS‐LE versus pure S‐LE.
Interventions: infants (n = 80) were randomised to receive PN with SMOFlipid (30% MCT, 30% soybean oil, 25% olive oil, 15% fish oil) or Intralipid (100% soybean oil) at two levels of fat intake: 2.5 g/kg/day or 3.5 g/kg/day in 1:1:1:1 ratio. All infants were started on PN within the first hour of life. Lipids were infused at 1.0 g/kg/day, 1.5 g/kg/day, 2.0 g/kg/day and 2.5 g/kg/day from birth to postnatal day four and then kept at 2.5 g/kg/day until day seven in the 2.5 g/kg fat groups. The lipids were increased to a maximum of 3.5 g/kg/day in the 3.5 g/kg fat groups. The enteral feeds were allowed at a rate of 8 mL/kg/day from day one to day four, and 16 mL/kg/day from day five to day eight. The lipids were decreased by 1 g/kg/day if the TG were between 250 mg/dL and 350 mg/dL (2.82 mmol/L and 3.38 mmol/L) and decreased by 2 g/kg/day if the TG were between 350 mg/dL and 450 mg/dL (3.95 mmol/L and 4.5 mmol/L). If TG levels were greater than 450 mg/dL (4.5 mmol/L) then the lipids were stopped for 24 hours and restarted at half dose. All infants had routine biochemistry, TG levels, blood urea and creatinine on days three, five and seven, or more frequently as necessary.
Outcomes: the primary outcomes were plasma phospholipid and DHA measured on postnatal day seven, and other plasma lipid components measured at day seven and day 14. Clinical outcomes including death, growth, BPD, ROP (stage 3 and 4), IVH, sepsis, NEC and cholestasis were also reported.
Rayyan 2012 was a single‐centre RCT at the Department of Neonatology, University Hospitals, Leuven, Belgium between November 2004 and February 2006.
Population: preterm infants less than 34 weeks' gestation with weight between 500 g and 2000 g and expected to receive PN for seven or more days. Exclusion criteria were severe congenital malformations, congenital heart failure, organ damage including anuria, liver disease, haemolytic disease, thrombocytopenia, oxygen saturation (SaO2) less than 80% for over two hours, severe acidosis, use of catecholamines, hypoxic‐ischaemic encephalopathy and multiorgan failure.
Objective: to compare the safety and tolerability of 20% SMOFlipid (MOFS‐LE; 30% MCT, 30% soybean oil, 25% olive oil, 15% fish oil) versus 20% Intralipid (S‐LE) with regard to TG levels, haematological and clinical parameters, adverse events, growth and fatty acid profile.
Interventions: 20% SMOFlipid (n = 26) versus 20% Intralipid (n = 27). LEs were given for at least seven days either peripherally or centrally. Enteral intake was allowed at less than 30% of the total lipid intake on days one to three, less than 50% on days four to seven and less than 70% on days eight to 14. The daily target dosage of fat started at 1.0 g/kg/day on days one to three and was increased to 2 g/kg/day on day four, 3 g/kg/day on day five and 3.5 g/kg/day from day six onwards. Other components of PN were given as standardised solutions at the discretion of the clinician.
Outcomes: the primary safety parameter was change in TG levels from baseline by day eight. The primary efficacy outcome was change in weight at day eight from baseline and change in body length from birth to the last observation. Secondary outcomes were blood counts and biochemical parameters. Clinical assessments (heart rate, temperature, blood pressure, weight, oxygen therapy) were performed daily from the prestudy visit until study termination, either on day 15 or following the last infusion of study treatment (post‐treatment). The authors reported on death, growth rate, duration of ventilation, hypertriglyceridaemia, composite outcomes of infections and infestations (including conjunctivitis, chorioamnionitis, sepsis), hepatobiliary adverse effects (including conjugated and unconjugated bilirubinaemia), and metabolic and nutrition disorders (including acid–base abnormalities and hyperglycaemia).
Repa 2018 was single‐centre, double‐blind RCT in extremely low birth weight (ELBW) infants performed in level four NICU of the University Children's Hospital Vienna (Medical University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria).
Population: inclusion criteria were ELBW infants less than 1000 g admitted before 24 hours. Exclusion criteria were infants with cholestasis (conjugated bilirubin greater than 1.5 mg/dL (25 mol/L)) before intervention, and higher‐order multiple infants with conditions associated with cholestasis independent of PN (i.e. infection with cytomegalovirus, HIV, hepatitis B or C, rhesus‐mediated haemolysis, cystic fibrosis, inborn errors of metabolism or primary liver diseases) were not eligible or excluded post‐randomisation.
Objective: to examine whether a mixed LE reduces the incidence of parenteral nutrition‐associated cholestasis (PNAC) in ELBW (less than 1000 g) infants.
Intervention: ELBW infants less than 1000 g were randomised to receive either 20% SMOFlipid (n = 110) or 20% Intralipid (n = 113). Participants who received full PN from birth using S‐LE (1 g/kg/day) were switched to study lipids after enrolment. Lipids were dosed up to 3 g/kg/day at the discretion of the attending physicians and reduced in relation to enteral nutrition (increased up to 20 mL/kg/day). Serum TGs were measured at least weekly. Lipids were halted for 24 hours if TG levels were more than 400 mg/dL (4.5 mmol/L) or downtitrated if TG were more than 250 mg/dL (2.8 mmol/L). PN was stopped at 140 mL/kg/day to 160 mL/kg/day of enteral feeds. Data on study lipids, nutrition and growth were recorded. Therapy adherence was calculated as the percentage study lipids that were correctly provided (i.e. greater than 80% was considered highly adherent). Ursodeoxycholic acid was administered to infants who developed cholestasis. Parenteral fish oil (Omegaven; Fresenius Kabi, Bad Homburg vor der Höhe, Germany) was permitted as rescue therapy (1 g/kg/day) if conjugated bilirubin was greater than 6 mg/dL (100 mol/L). Infants were followed until their 44th week of postmenstrual age (PMA), discharge or transfer to another hospital. All infants received probiotics and lactoferrin. Enteral feeds were provided every three hours. For growth analysis (anthropometry with z‐score difference from birth to discharge), only survivors were analysed to avoid distortion of measurements by perimortal oedema.
Outcomes: primary outcome: PNAC (conjugated bilirubin greater than 1.5 mg/dL (25 mol/L) at two consecutive measurements). Peak levels of liver enzymes during hospitalisation were recorded. Blood sampling was performed weekly as long as PN was required and then every seven to 14 days. Secondary outcomes: neonatal morbidities (death, duration of hospitalisation, ROP (any, and highest stage requiring treatment (severe ROP)), culture‐confirmed sepsis, IVH III/IV, cystic periventricular leukomalacia, NEC IIa or greater, focal intestinal perforation, abdominal surgery, days on mechanical ventilation, CLD, PDA requiring treatment, number of ibuprofen cycles or requiring surgical ligation, pulmonary hypertension, inhaled nitric oxide/sildenafil treatment.
Savini 2013 was a single‐centre, five‐arm RCT conducted at the NICU of "G. Salesi" Children's Hospital, Ancona, Italy, with 20% SMOFlipid and 20% Intralipid in two out of five intervention arms.
Population: preterm infants weighing 500 g to 1249 g, who received PN from the first hour of life were included. Infants with severe malformations, metabolic disease and severe congenital sepsis were excluded.
Objective: to compare the effect of different LEs on plasma phytosterol concentrations (and the possible association with PNALD).
Interventions: there were five intervention arms; 150 preterm infants were randomly assigned to receive one of the following five lipid formulations: Intralipid (S‐LE; n = 30), Lipofundin (50% MCT, 50% soybean oil; n = 30), Lipidem (50% MCT, 40% soybean oil, 10% fish oil; n = 30), ClinOleic (80% olive oil, 20% soybean oil; n = 30) or SMOFlipid (30% MCT, 30% soybean oil, 25% olive oil, 15% fish oil; n = 30).
Outcomes: primary outcomes were plasma phytosterol concentrations at birth (cord), on day seven (on full TPN) and on day 14 (on 50% enteral calories). Secondary outcomes included clinical data such as death, growth rate, time to regain birth weight, BPD, sepsis, NEC, PNALD and PDA.
Skouroliakou 2010 was a single‐centre RCT at the NICU of 'IASO' Maternity Hospital in Athens, Greece.
Population: preterm infants less than 32 weeks' gestation and birth weight less than 1500 g requiring admission to NICU within 12 hours of birth with estimated greater than 80% energy intake from PN in the first eight days of life and requiring PN for at least seven days were included. Exclusion criteria were inherited metabolic disorders, congenital malformations, transfusion of blood/fresh frozen plasma greater than 15 mL/kg and participation in another study.
Objective: to compare the effect of a parenteral fat emulsion rich in ω‐3 fatty acids on the antioxidant markers of preterm infants, when compared with a standard fat emulsion.
Interventions: 20% SMOFlipid (MOFS‐LE; 30% MCT, 30% soybean oil, 25% olive oil, 15% fish oil; n = 14) versus 20% Intralipid (n = 18). Four different TPN protocols were created based on gestational age, weight and clinical condition. Lipids were started on day one or two of life (based on gestational age) with a maximum of 3 g/kg/day in both groups. Enteral feeds were allowed at 20% or less of total energy intake and started as soon as feasible.
Outcomes: primary outcomes were oxidation potential (vitamin A, vitamin E and total antioxidant potential). Secondary outcomes were growth parameters, blood count, clinical condition, duration of ventilation, duration of phototherapy, hyperglycaemia, sepsis and length of stay (parameters were recorded on day zero, day 14 and at discharge).
Skouroliakou 2016 was a single‐centre RCT in preterm neonates admitted to the NICU of "IASO" Maternity Hospital Thessaloniki, Greece, during the period of September 2012 to September 2013.
Population: inclusion criteria: infant with gestational age 26 to 32 weeks, anticipated need for PN of greater than 60% of total energy requirements for at least 15 days and parental consent for participation to the study.
Objective: to test the hypothesis that administration of MCT/ω‐3 PUFA‐enriched IVFE in preterm neonates is associated with a cytokine and fatty acid (FA) profile consistent with attenuated inflammatory response.
Intervention: the preterm neonates were randomly assigned into the intervention group that received SMOFlipid (Fresenius Kabi HELLAS; MCTs 30%, lipids from soybean oil 30%, olive oil 25%, fish oil 15%), and α‐tocopherol (200 mg/L), whereas the control group received a conventional soybean oil‐based 20% Intralipid (Fresenius Kabi HELLAS), which contained α‐tocopherol 38 mg/L IVFE.
Outcomes: the primary outcome was the profile of proinflammatory cytokines tumour necrosis factor (TNF)‐α, interleukin (IL)‐6 and IL‐8, and the secondary outcomes were plasma α‐tocopherol and FA profiles. Clinical outcomes reported were death, RDS requiring treatment, BPD, clinical and culture‐confirmed sepsis, liver enzymes and cholestasis.
Techasatid 2017 was a double‐blind RCT performed between December 2013 and December 2015 at the NICU of Thammasat Hospital and Nopparat Rajathanee Hospital, both in Bangkok.
Population: the infants with gestational age less than 30 weeks and birth weight less than 1250 g who required PN for at least seven days were eligible for the study. Exclusion criteria were evidence of congenital infection, perinatal asphyxia, congenital anomalies, IVH grade greater than 2, thrombocytopenia, shock or circulation failure, and renal or hepatic disorder.
Objective: to compare the effects of a multicomponent lipid emulsion composed of 30% soybean oil, 30% MCTs, 25% olive oil and 15% fish oil (study group) or to a pure soybean oil (control group) on the incidence of neonatal cholestasis, neonatal growth, neonatal morbidity and the biochemical assessment of liver enzymes.
Interventions: the study group (n = 22) received MOFS‐LE (SMOFlipid 20%) and the control group (n = 22) received S‐LE (Intralipid 20%). Lipids were first administered at 1 g/kg/day within 24 hours after birth for both groups; lipid dosage was increased by an increment of 0.5 g/kg/day until the maximal dose of 3.5 g/kg/day was reached. The other macronutrients and micronutrients were provided using the same products and protocol in both groups. Parenteral lipid and amino acid administration were temporarily stopped when either plasma TG concentrations exceeded 250 mg/dL or when urea concentrations exceeded 35 mg/dL. Minimal enteral feeding was initiated on the day of birth, and intake was advanced with 20 mL/kg/day of breast milk or preterm formula. PN was stopped when the oral feeding reached 120 mL/kg/day.
Primary outcome: incidence of cholestasis, defined as a conjugated bilirubin level of greater than 2 mg/dL on two consecutive measurements and the assessment of biochemical signs of hepatic dysfunction. Secondary outcomes: clinical outcomes included death, duration of hospital stay, respiratory distress syndrome (RDS), duration of respiratory support, BPD, NEC, late‐onset sepsis, haemodynamically significant PDA diagnosed by echocardiography as needing treatment by medication or surgery, IVH and ROP; growth parameters assessed using in hospital growth rates, the gain in head circumference and height from birth until discharge.
Tomsits 2010 was a single‐centre RCT at the Department of Pediatrics, Semmelweis University, Budapest, Hungary.
Population: 60 preterm infants less than 34 weeks' gestation, aged three to seven days, who were expected to receive TPN for at least seven days were randomised in this study. Exclusion criteria were not mentioned.
Objective: to evaluate the safety, tolerability, and efficacy of a MOFS‐LE (20% SMOFlipid) compared with S‐LE (20% Intralipid).
Interventions: 20% MOFS‐LE (n = 30) versus 20% S‐LE (n = 30). The LE was started at 0.5 g/kg/day on day one and was increased by increments of 0.5 g/kg/day daily up to a maximum of 2 g/kg/day on days four to 14. Additional oral/enteral intake comprising less than 20% at baseline, less than 30% on days one to three, and less than 50% on days four to 14 of the total energy intake was permitted if appropriate. Other components of PN were given at the discretion of the investigator.
Outcomes: were evaluated on days zero, eight and 15. The primary efficacy outcome was change in weight from days one to eight. Secondary efficacy variables included red blood cell fatty acid profile, duration of mechanical ventilation and oxygen therapy. Serum TG levels were used as a primary safety outcome. Secondary safety variables were vital signs, haematological variables, coagulation profile and liver enzymes. The authors also reported on sepsis in two groups.
Uthaya 2016 NEON (Nutritional Evaluation and Optimisation in Neonates) was a 2 × 2 factorial, double‐blind, multicentre RCT in four National Health Service neonatal units in London and southeast England.
Population: preterm infants born at less than 31 weeks' gestation were eligible for inclusion. Exclusion: infants with life‐threatening abnormalities and those who could not be administered trial PN within 24 hours of birth were ineligible.
Objective: to compare the effects of high (immediate recommended daily intake (Imm‐RDI)) and low (incremental introduction of amino acids (Inc‐AAs)) parenteral amino acid delivery within 24 hours of birth on body composition and the effect of a multicomponent lipid emulsion containing 30% soybean oil, 30% MCTs, 25% olive oil, and 15% fish oil (SMOF) with that of S‐LE on intrahepatocellular lipid (IHCL) content.
Interventions: 20% SMOFlipid (Fresenius Kabi) and Imm‐RDI of amino acids. The comparators were 20% Intralipid (Fresenius Kabi) and Inc‐AA. The eligible infants were randomly assigned to one of four groups (Inc‐AA/S‐LE; n = 42, Inc‐AA/SMOF; n = 42, Imm‐RDI/S‐LE; n = 41, and Imm‐RDI/SMOF; n = 43). The study incorporated minimisation with a random element and stratification by gestational age (23 to 26 completed weeks or 27 to 31 completed weeks), birth weight (less than 500 g, 500 g to 1000 g or greater than 1000 g), and centre.
Outcomes: primary outcomes were non‐adipose mass for the amino acid intervention and IHCL for the lipid intervention using whole body MRI and hepatic magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Secondary outcomes were total adiposity, adipose tissue depots, insulin sensitivity (quantitative insulin sensitivity check index), total and regional brain volumes, weight, head circumference and length. The study also reported liver function tests, conjugated hyperbilirubinaemia, hypoglycaemia, hyperglycaemia, hypertriglyceridaemia, sepsis, NEC and mortality.
Vlaardingerbroek 2014 was a single‐centre RCT at the NICU of the Division of Neonatology, Sophia Children's Hospital, Rotterdam, the Netherlands. Study enrolment occurred between December 2008 and January 2012. This study looked at the effect of different LE and included data from a larger trial which was reported as a three‐arm study (see Vlaardingerbroek 2014 for reference details of Vlaardingerbroek 2013). In the previous study report, the infants were randomised into three intervention arms (i.e. standard amino acids, early lipids plus standard amino acids or early lipids plus high‐dose amino acids). Within the two early lipid intervention arms of the 2013 study, the infants were randomly assigned to receive two different lipid types. The effect of receiving two different lipid types is reported in Vlaardingerbroek 2014.
Population: inborn VLBW infants (birth weight less than 1500 g) with a central venous catheter for clinical purposes were eligible for the study. Exclusion criteria were congenital anomalies; chromosome defects; metabolic diseases; and endocrine, renal or hepatic disorders.
Objective: to evaluate the safety and efficacy of a multicomponent LE containing 30% soybean oil, 30% MCT, 25% olive oil and 15% fish oil compared with a conventional pure S‐LE in VLBW infants.
Interventions: the study group (n = 49) received MOFS‐LE (20% SMOFlipid) and the control group (n = 49) received S‐LE (20% Intralipid). Minimal enteral feeding was initiated on day one and local feeding protocols were followed. The parenteral lipid intake was decreased by 25% to 50% if TG concentrations were between 265 mg/dL and 442 mg/dL (3 mmol/L and 5 mmol/L) and temporarily stopped if plasma TGs were more than 442 mg/dL (5 mmol/L). Parenteral amino acids were decreased by 25% to 50% if the plasma urea was more than 10 mmol/L (28 mg/dL) and stopped temporarily if the urea was more than 14 mmol/L (39 mg/dL). According to the local protocol, repeated blood glucose concentrations greater than 10 mmol/L (180 mg/dL) were treated with continuous intravenous insulin (starting dose 0.1 U/kg/hour) if reducing the glucose infusion rate to a minimal intake of 4 mg/kg/minute was not effective in lowering the blood sugar. Minimal enteral feeding was initiated on the day of birth and after day three of life the nutritional regimen was left to the discretion of the attending physician.
Outcomes: primary outcomes included fatty acid concentration in plasma TGs and phospholipids. Safety was evaluated by measuring haematological and biochemical parameters, phytosterol concentrations and clinical outcomes. Clinical outcomes included survival, duration of hospital stay, symptomatic PDA, RDS, BPD, NEC, late‐onset sepsis, IVH, PVL and ROP. Cholestasis was defined as conjugated bilirubin concentration greater than 20% of the total bilirubin concentration.
MOFS‐LE versus MS‐LE
Two studies compared MOFS‐LE versus MS‐LE (Hsiao 2018; Savini 2013).
Hsiao 2018 was a single‐centre RCT at Changhua Christian Children's Hospital Neonatal intensive care unit, Changhua, Taiwan.
Population: preterm infants with very low birth weight requiring ventilator support within 24 hours after birth were randomised to the intervention group receiving MOFS‐LE or control group receiving MS‐LE (Lipovenoes). Both emulsions were manufactured by Fresenius Kabi, Bad Homburg vor der Höhe, Germany. The exclusion criteria were lethal congenital abnormalities or chromosomal disorders; congenital cyanotic heart disease; gastrointestinal surgery, such as intestinal perforation, malrotation, volvulus and atresia; confirmed or family history of hereditary metabolic disorder and clinical sepsis at admission.
Objective: the primary outcome was comparing the immune effects of two different LEs, assessed during the first 24 hours and day eight, including IL‐1b and IL‐6 in serum and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF).
Interventions: the intervention group received SMOF lipid and the control group received MS‐LE (Lipovenoes MCT 20% containing 50% soybean oil and 50% MCT).
Outcomes: the primary outcome was the levels of IL‐1b and IL‐6 in the serum and BALF at 24 hours and day eight. The study also reported mortality, length of hospital stay, ventilator‐use days, oxygen‐dependent days, weight gain rate, liver function, PNAC, BPD and ROP, NEC, IVH and late sepsis.
Savini 2013 was a single‐centre, five‐arm RCT at the NICU, "G. Salesi" Children's Hospital, Ancona, Italy. This study contributed to multiple comparisons and was described above.
MOFS‐LE versus OS‐LE
Three studies compared MOFS‐LE versus OS‐LE (Deshpande 2014; Najm 2017; Savini 2013).
Deshpande 2014: a single‐centre double‐blind RCT in a regional tertiary NICU of King Edward Memorial Hospital for Women, Perth, Australia.
Population: preterm neonates aged less than seven days old (less than 30 weeks' gestation) who were admitted to the NICU and required greater than 75% of energy requirements from PN. Exclusion criteria were blood culture‐confirmed sepsis, thrombocytopenia (platelet count less than 150 cells/μL), unconjugated hyperbilirubinaemia (requiring exchange transfusion), metabolic disorders including lactic or uncompensated acidosis (or both), lack of parenteral consent, administration of intravenous lipid infusion before the study, postnatal age more than seven days and bleeding disorder.
Objective: to compare the efficacy (increased omega‐3 long‐chain polyunsaturated fatty acid (LC‐PUFA)) and safety of the fish‐oil containing LE (SMOFlipid, Fresenius Kabi) with olive oil‐based lipid solution (ClinOleic, Baxter) in preterm neonates with gestation less than 30 weeks.
Intervention: 20% ClinOleic (n = 17) versus 20% SMOFlipid (n = 17) were given in a dosing schedule of: day one at 1 g/kg/day; day two at 2 g/kg/day; day three at 3 g/kg/day; and days four to seven at 3/g/kg/day. The duration of study was seven days, after which all of the participants received ClinOleic lipid emulsion, which was the standard of practice in the nursery. Intravenous lipids were continued as long as PN support was determined necessary by the attending neonatologist. The emulsions were dispensed in coded and amber‐coloured syringes and infusion lines suitable for infusion pumps and infused intravenously through a central or peripheral line.
Outcomes: primary outcomes were levels of PUFA in red cell membrane and lipid peroxidation status measured by plasma F2‐isoprostane levels. Secondary outcomes were weight, head circumference, and length at birth at study entry, exit, and at discharge; enteral versus PN proportion; number of episodes of blood culture‐conformed sepsis; IVH; duration of hospital stay; mechanical ventilation; PN support; mortality and vitamin E levels.
Najm 2017: was a single‐centre blinded RCT in infants with gestational age less than 28 weeks admitted to the NICU at Sahlgrenska University Hospital in Gothenburg, Sweden.
Population: 90 infants born at gestational age less than 28 weeks were included. Exclusion criteria were major congenital malformations.
Objective: to determine and compare serum PUFA (DHA, eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and arachidonic acid) profiles, ROP, BPD, NEC, PDA, sepsis and growth in extremely preterm infants receiving PN with an olive oil‐based lipid solution (ClinOleic, Baxter) or a solution containing 15% fish oil with ω‐3 PUFAs (SMOFlipid, Fresenius Kabi).
Interventions: PN was initiated as soon as possible after birth with a standard solution containing Vaminolac and 10% glucose (total protein content 2 g/100 mL) aiming at 80 mL/kg/day to 90 mL/kg/day of the resulting solution during the first 24 hours. Lipid solution (ClinOleic or SMOFLipid) was normally started at six to 12 hours after birth at a rate of 1 g/kg/day with daily increases up to 2 g/kg/day. Enteral nutrition used either maternal or donor breast milk with individualised fortification based on results from breast milk analysis using a commercial bovine milk fortifier. Daily intakes of fatty acids including arachidonic acid, EPA and DHA were prospectively recorded from birth during the first two weeks of life. The parenteral lipids were administered at a rate of 2 g/kg/day to 3 g/kg/day.
Outcomes: primary outcome was ROP. ROP was classified as no ROP or ROP stage 1, 2, 3 or 3+. Other outcomes included: serum LCPUFA (DHA, EPA and arachidonic acid profiles), BPD, NEC, PDA, sepsis and growth between birth and 36 weeks. Conjugated bilirubin blood level of greater than 50 μmol/L for at least two weeks at any time during the follow‐up, unrelated to sepsis was considered significant.
Savini 2013 was a single‐centre, five‐arm RCT at the NICU, "G. Salesi" Children's Hospital, Ancona, Italy. This study contributed to multiple comparisons and was described under the 'MOFS‐LE versus S‐LE' comparison.
MFS‐LE versus S‐LE
Only one eligible study compared MFS‐LE versus S‐LE. Savini 2013 was a single‐centre, five‐arm RCT at the NICU, "G. Salesi" Children's Hospital, Ancona, Italy, with MFS‐LE (Lipidem) and S‐LE (20% Intralipid) in two out of the five intervention arms. Meta‐analysis could not be performed for this comparison as no other eligible studies were identified. Details of this study are described under the 'MOFS‐LE versus S‐LE' comparison.
MFS‐LE versus MS‐LE
Three studies compared MFS‐LE versus MS‐LE (Biagetti 2016; D'Ascenzo 2011; Savini 2013).
Biagetti 2016 was a single‐centre pilot study at the NICU of "G. Salesi" Children's Hospital, Ancona, Italy, between January 2007 and June 2012.
Population: neonates with a birth weight of 500 g to 1249 g, who routinely received PN from the first hour of life and were not participating in other trials were enrolled. Exclusion criteria were severe malformations, inborn errors of metabolism and severe sepsis and infants without an intravenous access suitable for blood sampling on day seven.
Objective: to ascertain if the use of intravenous F‐LE has an effect on lipogenesis in preterm infants.
Interventions: newborn infants were randomly assigned in a 1:1 ratio to receive an LE consisting of a physical mixture of 50% MCT, 40% soybean oil and 10% fish oil, MSF (Lipidem; B Braun, Milan, Italy) or a standard product containing 50:50 MCT:SO, MS (Lipofundin MCT; B Braun).
Outcomes: included plasma phospholipid palmitate biosynthesis (for de novo lipogenesis), lipids and free cholesterol on day seven.
D'Ascenzo 2011 was a single‐centre pilot study at the NICU of "G. Salesi" Children's Hospital, Ancona, Italy, between September 2007 and May 2008.
Population: 500 g to 1249 g infants, who routinely received PN from the first hour of life were consecutively enrolled. Exclusion criteria were severe malformations, inborn errors of metabolism and severe sepsis.
Objective: to compare plasma lipids in preterm infants given an MFS‐LE containing 10% fish oil, 50% MCTs and 40% soybean oil compared with MS‐LE containing MCT and soybean oil in a ratio of 1:1.
Interventions: 48 infants less than 1250 g were randomly assigned to MFS‐LE (10:50:40) (n = 24) or MS‐LE (50:50) (n = 24). The LE was started at 0.5 g/kg/day, increased by increments of 0.5 g/kg/day to reach 2.5 g/kg/day with 8 mL/kg/day EBM or formula from days one to four, and then 16 mL/kg/day from days five to eight. Oral feeding was gradually increased from day nine to reach full oral feeds by day 18, when the TPN was completely tapered.
Outcomes: plasma and RBC FA composition was evaluated on days seven and 14. Daily weight, weekly head circumference and length were measured with z scores calculated using the Italian reference data.
Savini 2013 was a single‐centre, five‐arm RCT at the NICU, "G. Salesi" Children's Hospital, Ancona, Italy, with MFS‐LE (Lipidem) and MS‐LE in two out of the five intervention arms and was described under the 'MOFS‐LE versus S‐LE' comparison.
OFS‐LE versus OS‐LE
Only one study compared OFS‐LE versus OS‐LE (Pawlik 2014).
Pawlik 2014 was a single‐centre RCT in Krakow, Poland from 1 August 2010 to 31 May 2012.
Population: preterm neonates less than 32 weeks' gestation and less than 1250 g. Exclusion criteria were major congenital malformations, inborn errors of metabolism and congenital infection.
Objective: to compare the efficacy of a F‐LE with olive oil‐based lipid solution (ClinOleic, Baxter) in preterm infants less than 32 weeks' gestation for the outcomes of ROP and cholestasis.
Intervention: the infants were randomly assigned to an experimental group that received an intravenous emulsion proportioned to contain a 50% soybean and olive oil (20% ClinOleic, Baxter SA, Norfolk, UK) (n = 60) and 50% fish oil (10% Omegaven, Fresenius Kabi, Bad Homburg vor der Höhe, Germany) and a control group (n = 70) that was given a 20% soybean and olive oil emulsion (20% ClinOleic, Baxter SA). Lipids were increased at a rate of 0.5 g/kg/day for less than 1000 g and 1 g of lipids/kg/day for greater than 1000 g birth weight. The maximal daily dose of lipids was 3.5 g/kg/day. Infants in both groups increased enteral feeds at a rate of 20 mL/kg/day of breast milk or formula.
Outcomes: the primary outcome was an assessment of ROP severity and whether laser photocoagulation was required to save vision. A secondary outcome was cholestasis.
Pure F‐LE versus S‐LE
No studies compared pure F‐LE versus S‐LE in the population of preterm infants.
Fish oil LE versus another fish oil LE in preterm infants (Comparison 2)
MOFS‐LE versus MFS‐LE
Only one study in preterm infants was eligible for this subgroup (Savini 2013). The two out of five arms of this study compared MOFS‐LE versus MFS‐LE. Details of the study are described under the MOFS‐LE versus S‐LE comparison.
Alternative‐LE versus S‐LE in preterm infants (Comparison 3)
OS‐LE versus S‐LE
Eight studies compared OS‐LE versus S‐LE (Demirel 2011; Deshpande 2009; Gawecka 2008b; Göbel 2003; Köksal 2011; Roggero 2010; Savini 2013; Wang 2016).
Demirel 2011 was a single‐centre study at the NICU, Zekai Tahir Burak Maternity Teaching Hospital, Turkey.
Population: preterm infants 32 weeks' gestation or less and receiving 40% or greater parenteral calories at 14th day of life were included in the study.
Objective: to compare S‐LE (Intralipid) and OS‐LE (ClinOleic) in terms of plasma lipids and acyl carnitine profile.
Interventions: OS‐LE (ClinOleic, n = 20) versus S‐LE (Intralipid, n = 20). TPN protocol: LEs were started on the second day of life at a rate of 1 g/kg/day and increased by 1 g/kg/day up to 3 g/kg/day and given over 24 hours. Enteral feeding was started on the second day.
Outcomes: plasma lipid concentrations and acyl carnitine profile were compared between groups. Other outcomes were weight on day 14, RDS, ROP and sepsis. Data values were not provided for NEC and BPD. Liver function tests (alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, gamma‐glutamyl transferase) were reported.
Deshpande 2009 was a single‐centre study at the Department of Neonatal Paediatrics at KEM Hospital in Perth, Western Australia.
Population: preterm infants less than 28 weeks' gestation who were less than seven days old at recruitment, with PN accounting for greater than 75% of energy intake. Exclusion criteria were major congenital malformations, inborn errors of metabolism, transfusion before baseline bloods could be taken and exchange transfusion for hyperbilirubinaemia and LE given before enrolment. Withdrawal criteria were enteral nutrition exceeding 25% at any time.
Objective: to compare the antioxidant status and LC‐PUFA status of infants receiving OS‐LE versus S‐LE and to evaluate the effect of the two different LEs on clinical outcomes.
Interventions: OS‐LE (ClinOleic, n = 24) versus S‐LE (20% Intralipid, n = 21). The amino acids were added on day one and lipids were added on day two with increments of 0.5 g/kg/day, 1 g/kg/day, 2 g/kg/day and 3 g/kg/day every day for the first four consecutive days.
Outcomes: the primary outcomes of the study were plasma F2‐isoprostane levels as indicators of lipid peroxidation, levels of LC‐PUFA in plasma and in RBC membrane. The secondary outcomes were liver and renal function tests, blood culture‐confirmed sepsis, blood cell counts and anthropometry at the study entry and exit.
Gawecka 2008b was a single‐centre RCT at the NICU, Medical Academy Neonatology Department, Warsaw, Poland. The data from this study appeared to be reported in two different publications – data on immunological properties and clinical outcomes were published in the Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition (Gawecka 2008a), while data on TG, cholesterol, bilirubin and cholestasis appear in the polish journal Medycyna Wieku Rozwojowego (Gawecka 2008c). The baseline characteristics were identical for the participants in both published reports; we extracted data from both sources (Table 7).
Population: preterm infants less than 32 weeks' gestation with a birth weight less than 1500 g, admitted to the NICU on day one and requiring PN were eligible for inclusion. Exclusion criteria were severe malformations, metabolic disease, congenital culture‐confirmed sepsis and enteral calories less than 25% of total calories.
Objective: to compare immune effects and clinical outcomes of OS‐LE versus S‐LE.
Interventions: OS‐LE (20% ClinOleic; n = 18) versus S‐LE (20% Ivelip; n = 20). PN was started on day one with amino acids. The LE were started within 72 hours of life at 1 g/kg/day and increased to a maximum dose of 3 g/kg/day to 3.5 g/kg/day. Lipids were infused continuously over 24 hours.
Outcomes: primary outcomes were TNF‐α, IL‐6 and IL‐10 synthesis in unstimulated and anti‐CD3‐induced peripheral blood mononuclear cells of parenterally fed preterm infants. Secondary outcomes were incidence of BPD, ROP, NEC, IVH and nosocomial infections.
Göbel 2003 was a multicentre RCT at two NICUs in Klinikum Rechts der Isar, Klinikum Schwabing, Munich, Germany.
Population: inclusion criteria were 28 weeks to under 37 weeks' gestation preterm infants, admitted to the NICU within 24 hours after birth with TPN requirement expected to be 80% or greater of total energy intake. Exclusion criteria were severe malformations, hyperlipidaemia, metabolic disease, bacterial infection before study inclusion, enteral nutrition greater than 20 mL/kg/day and blood transfusion more than 15 mL/kg before baseline blood sampling.
Objective: to evaluate a new parenteral OS‐LE (ratio 4:1), with less PUFA and more α‐tocopherol than the standard S‐LE in preterm infants.
Interventions: OS‐LE (ClinOleic, n = 24) versus S‐LE (20% Intralipid, n = 21). LE was started within 72 hours of birth as a 24‐hour infusion at 0.5 g/kg/day, 1.0 g/kg/day and 2.0 g/kg/day on the first three consecutive study days and 2 g/kg/day for next four days. Other cointerventions were the same in the two groups. No vitamin E was given and minimal enteral nutrition was allowed. The infants were excluded if the enteral calories increased to more than 20% at any time.
Outcomes: primary efficacy outcome variables were plasma fatty acids, α‐tocopherol and urinary malondialdehyde. Safety outcomes included TG, cholesterol, phospholipids, hyperbilirubinaemia and apnoea. The study reported no serious adverse events in either group. Efficacy outcomes were evaluated (per protocol) in infants on day of birth and day eight.
Köksal 2011 was a single‐centre study at the NICU, Division of Neonatology, Görükle, Bursa, Turkey.
Population: preterm infants 34 weeks' gestation or less, admitted to the NICU within 24 hours after birth with TPN requirement expected to be 80% or greater of the total energy intake were eligible for study inclusion. Exclusion criteria were severe malformations, hyperlipidaemia, metabolic disease, enteral nutrition greater than 20 mL/kg/day and blood transfusion greater than 15 mL/kg/day.
Objective: to compare OS‐LE versus S‐LE in terms of the effects on oxidative stress and safety of use in terms of biochemical indices.
Intervention: OS‐LE (ClinOleic, n = 32) versus S‐LE (20% Intralipid, n = 32). LE was started within 72 hours after the baseline blood samples were obtained. LE was infused at 1 g/kg/day, 2 g/kg/day and 3 g/kg/day on the first three days and 3 g/kg/day over the next four days in both groups. After seven days of LE, infusion was stopped and blood samples were taken six hours later. Cointerventions related to PN were the same in both groups. Glucose, 6% amino acid solution, trace elements and water‐soluble vitamins except vitamin E were given to both groups.
Outcomes: the primary outcome was total antioxidant capacity at day seven. Secondary outcomes were neonatal morbidity and biochemical indices after LE administration. Biochemical indices were compared at day seven; however, neonatal morbidities were reported until discharge (including ROP, BPD, etc.). The study reported results for continuous variables as mean ± data values. We contacted the study authors who confirmed that the values presented in the study report were mean ± standard error. The authors also provided unpublished data on other clinical outcomes including growth rate, days to regain birth weight, IVH and PVL.
Roggero 2010 was a three‐arm single‐centre study at the Università degli Studi di Milano. This study did not contribute to any outcome in the current review.
Population: 36 consecutive preterm infants (gestational age 28 to 33 weeks) were enrolled in the study.
Objective: to study the effects of three different LEs: S‐LE, OS‐LE and MS‐LE on plasma F2‐isoprostanes (F2‐Ip) and total radical‐trapping antioxidant potential (TRAP).
Interventions: infants were randomised to receive one of: Intralipid (LCT 20%; n = 12); or ClinOleic OS‐LE ( n =12) or Lipofundin (MCT‐LCT mix; n = 12).
Outcomes: F2‐Ip and TRAP at baseline, on day seven of PN, and on day seven after stopping PN.
Savini 2013 was a single‐centre, five‐arm RCT done at the NICU of "G. Salesi" Children's Hospital, Ancona, Italy, with OS‐LE (ClinOleic) and S‐LE (Intralipid) in two out of the five intervention arms. Details of the study are described under the 'MOFS‐LE versus S‐LE' comparison.
Wang 2016 was a double‐blind RCT at the NICU of Xin Hua Hospital and Shanghai Children's Medical Center in Shanghai, China. This study was published in Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition (JPEN). We also identified another report by Wang and colleagues published in Clinical Nutrition in 2016 with some duplication of data in the two reports. At the time of submission of this review we were awaiting clarification from the editorial teams of respective journals.
Population: preterm infants with birth weight less than 2000 g, admission within 72 hours after birth and administration of PN for 14 days or more. Two infants from the OS‐LE arm and one infant from the S‐LE arm were excluded from analysis as they did not complete 14 days of PN. The exclusion criteria were administration of PN before screening, calorie intake from enteral nutrition greater than 10%, obstructive jaundice, suspected biliary atresia, neonatal hepatitis, liver or kidney markers increased to twice normal values, congenital abnormalities, major chromosomal diseases, cytomegalovirus infection, viral hepatitis and suspected immunodeficiency.
Objective: to compare the effect of parenteral OS‐LE on liver chemistry and bile acid composition in preterm infants.
Interventions: infants were randomised to receive either S‐LE (Intralipid; n = 51) or OS‐LE (ClinOleic; n = 52) for 14 days. The two LE looked identical and were started at 1 g/kg/day and increased by 0.5 g/kg/day to 1 g/kg/day up to 3 g/kg/day. Amino acids were started at 1.5 g/kg/day to 2.0 g/kg/day and increased up to 3.5 g/kg/day to 4.0 g/kg/day. PN was decreased as enteral intake increased and withheld if enteral calorie intake was greater than 80% of total intake. 'All‐in‐one' solutions were infused continuously over 24 hours with all other cointerventions being identical. Preterm formula was used for enteral nutrition for all infants as feasible.
Outcomes: the primary end point was liver chemistry. The secondary end point was plasma bile acid composition. Serum conjugated bilirubin was reported to be higher after seven days in the S‐LE group. The study reported on mortality, weight gain, days to regain birth weight, duration of ventilation, BPD, NEC and culture‐positive sepsis. Clinical outcomes including ROP, IVH and PVL were not reported in this trial.
MS‐LE versus S‐LE
Three studies compared MS‐LE versus S‐LE (Lehner 2006; Rubin 1994; Savini 2013).
Lehner 2006 was a single‐centre RCT at the Division of Neonatology, University of Pécs, Hungary.
Population: 25 to 37 weeks' gestation preterm infants with birth weight less than 3000 g were eligible for inclusion.
Objective: to compare the effects of a MCT‐LCT emulsion (MS‐LE) and LCT emulsion (S‐LE) on the fatty acid composition of plasma phospholipids and TG.
Interventions: MS‐LE (20% Lipofundin, n = 6) compared with S‐LE (20% Lipofundin N, n = 6). Details of the TPN protocol were not available. Cointerventions with 10% glucose, amino acids, electrolytes (sodium chloride, potassium chloride, calcium gluconate), trace elements (Pedel, Pharmacia, Budapest, Hungary) and water‐soluble vitamins (Soluvit, Baxter, Deerfield, IL) were identical in both groups.
Outcomes: intended outcomes were plasma fatty acid profile, plasma cholesterol level, hypertriglyceridaemia and weight on day eight. Some other clinical and biochemical parameters were recorded but not reported.
Rubin 1994 was a single‐centre RCT at the Beilinson Medical Center, Petach‐Tiqva, Israel and the results from the study were published in the Journal of Pediatrics. Results from this study regarding the fatty acid profiles appeared to have been published in the Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition the following year (Rubin 1995). The baseline characteristics were identical for the participants in both the published reports (Table 7).
Population: 59 preterm infants under 35 weeks' gestation who received TPN for at least six days were included.
Objective: to study the effects of three different LEs, BS‐LE, S‐LE or MS‐LE, on the lipid status and bilirubin levels in preterm infants.
Interventions: infants were randomised to receive one of: PFE 4501 (20% LCT, 15% borage oil, L‐carnitine; n = 16); Intralipid (LCT 20%; n = 18); or Lipofundin (MCT‐LCT mix; n = 15). LE was started on day one at 0.5 g/kg/day, increased to 1.5 g/kg/day on day two to a maximum of 2.5 g/kg/day on day three, and continued to the end of the study period. Cointerventions with amino acid solution (Vamin) and electrolytes were identical in both groups.
Outcomes considered included weight gain, clinical variables, acid–base balance, blood counts, glucose levels and TG.
Savini 2013 was a single‐centre, five‐arm RCT which was described under the 'MOFS‐LE versus S‐LE' comparison.
Roggero 2010 was a single‐centre study at Università degli Studi di Milano, Italy with two out of three arms receiving MS‐LE and S‐LE. This study did not contribute to any outcome and was described under the 'OS‐LE versus S‐LE' comparison.
BS‐LE versus S‐LE
One study compared BS‐LE versus S‐LE (Rubin 1994).
Rubin 1994 was a single‐centre study at Beilinson Medical Center, Petach‐Tiqva, Israel. BS‐LE was one of the three intervention arms in this study. Details of this study have been described under the comparison of 'MS‐LE versus S‐LE'.
Structured LE versus S‐LE
We found no studies comparing structured LE versus S‐LE.
Alternative‐LE versus other alternative‐LE in preterm infants (Comparison 4)
BS‐LE versus MS‐LE
One study compared BS‐LE versus MS‐LE which was described in the MS‐LE versus S‐LE subgroup (Rubin 1994).
OS‐LE versus MS‐LE
Two studies compared OS‐LE versus MS‐LE (Savini 2013; Roggero 2010).
Two of the five arms of the study by Savini 2013 compared OS‐LE versus MS‐LE. This five‐arm RCT was described under the 'MOFS‐LE versus S‐LE' comparison.
Roggero 2010 was a single‐centre study at the Università degli Studi di Milano, Italy with three arms including two arms comparing OS‐LE versus MS‐LE. This study did not contribute data to any outcome and was described under the OS‐LE versus S‐LE comparison.
Fish oil LE versus non‐fish oil LE in preterm infants with surgical conditions (Comparison 5)
In the population of preterm infants with the surgical conditions we found only one eligible study (Nehra 2014) (n=19) which compared a pure fish oil LE (Omegaven) to S‐LE (Intralipid).
We found no studies comparing a fish oil LE versus another fish oil LE, alternative LE versus S‐LE or alternative LE versus another alternative LE in infants with surgical conditions.
Pure F‐LE versus S‐LE
One study compared pure F‐LE versus S‐LE (Nehra 2014).
Nehra 2014 was a single‐centre double‐blind RCT. Authors reported that the study was terminated early due to low incidence of cholestasis among enrolled patients.
Population: neonates and infants (less than three months' age) with baseline conjugated bilirubin less than 1.0 mg/dL and a gastrointestinal disease requiring surgical intervention who were expected to be PN dependent for 21 days or greater were eligible.
Objective: to assess the safety and efficacy of a pureF‐LE in reducing the incidence of cholestasis in neonates compared with the traditional S‐LE.
Interventions: infants with persistently elevated conjugated bilirubin (greater than 2 mg/dL for two or more continuous weeks) were considered treatment failures and were crossed over to the other study arm.
Outcomes: primary outcome was to determine whether the incidence of cholestasis, defined as a serum conjugated bilirubin greater than 2 mg/dL for two or more consecutive weeks differed between the S‐LE and pure F‐LE groups. Secondary outcomes included safety and tolerability of the two LEs, Bayley Scales of Infant Development (BSID‐III) scores at six and 24 months' corrected age.
Fish oil LE versus non‐fish oil LE in preterm infants with PNALD/cholestasis (Comparison 6)
This comparison included those studies which compared the fish oil‐containing LE with non‐fish oil LEs in preterm infants who had developed cholestasis within the first six months of life. The studies in this comparison also included infants who had developed cholestasis or PNALD due to surgical conditions. There were two studies that compared a fish oil‐LE versus a non‐fish oil LE in infants with cholestasis. The two studies were in the following subgroups:
MOFS‐LE versus S‐LE: one study (n = 24) compared MOFS‐LE (SMOFlipid) to S‐LE (10% Intralipid) (Diamond 2017).
Pure F‐LE versus S‐LE: one study (n = 16) compared Omegaven (a pure fish oil‐LE) to S‐LE (10% Intralipid) (Lam 2014).
We found no studies in infants with PNALD/cholestasis that compared a fish oil‐LE versus another fish oil‐LE, alternative‐LE versus S‐LE or alternative‐LE versus another alternative‐LE.
MOFS‐LE versus S‐LE
Diamond 2017 was a multicentre parallel‐group blinded randomised study conducted at multiple sites including the Hospital for Sick Children, Toronto, ON, Canada; McMaster Children's Hospital, Hamilton, ON, Canada; Alberta Children's Hospital, Calgary, AB, Canada; Stollery Children's Hospital, Edmonton, AB, Canada; and CHU Sainte‐Justine, Montreal, QC, Canada. Of the 26 infants randomised, 17 were from the Hospital for Sick Children, five from the Calgary subsite, three from the Hamilton subsite and one from the Edmonton subsite.
Population: primary inclusion criteria were an infant (aged less than 24 months) with short bowel syndrome or intestinal failure who received substantial PN support (greater than 40% total calories) and was demonstrating early hepatic dysfunction (Cbil: 17 µmol/L to 50 µmol/L (1 mg/dL to 3 mg/dL)) in the absence of sepsis. Though the age of inclusion was less than 24 months, all the included infants were in preterm or borderline preterm range with the outer range of the ages being less than six months and, therefore, this study satisfied the population criteria for the review.
Objective: to explore whether SMOFlipid, a composite LE, would reduce the risk of PNALD progression in children receiving PN who were exhibiting early hepatic dysfunction.
Interventions: 26 infants were randomised to MOFS‐LE (30% MCT, 25% olive oil, 15% fish oil, 30% soybean oil; n = 13) or 20% Intralipid (S‐LE; n = 13). Participants received trial lipid for up to 12 weeks. Infants also ended the trial if they achieved full enteral tolerance (autonomy from PN) prior to this time point or if they developed progressive liver disease defined by a serum conjugated bilirubin (Cbil) exceeding 100 µmol/L for more than 14 days. The investigators also had a provision of replacement of the study participants who discontinued the PN prior to second week of the study due to achievement of full enteral tolerance. Lipid dosing was according to a nomogram which adjusted the amount of the lipids proportional to the enteral intake. All types of enteral formulas were allowed except the enteral fish oil solution.
Outcomes: the primary outcome was the last value of the Cbil the week the child received the last dose of the trial lipid (i.e. at 12 weeks, at full enteral tolerance or on the development of the progressive liver disease). Other liver markers in the blood were also measured. Weight, length and head circumference were assessed at baseline, week 6 and post‐trial. A complete blood count was done at weeks 0, 4 and 8, and post‐trial. International normalised ratio, C‐reactive protein, immunological markers (interleukins 1, 6, 8, 10 and 12; tumour necrosis factor‐α), nephelometry, serum cholesterol and serum TGs were assessed at baseline, week 6 and post‐trial. Red blood cell phospholipid composition was assessed at baseline, week 6 and post‐trial.
Pure F‐LE versus S‐LE
Lam 2014 was a single‐centre study conducted at the Departments of Paediatrics, Paediatric Surgery and Pharmacy at the Prince of Wales Hospital, Sha Tin, Hong Kong. The authors reported that the parents were becoming unwilling to consent for the study and the study was terminated prematurely in view of the interim results.
Population: infants who developed PNAC and fulfilled the inclusion criteria: Cbil 34 μmol/L (2 mg/dL) or greater, expected to continue requiring PN for more than two weeks and had informed parental consent. Exclusions included major congenital malformations, multiorgan failure, and a known secondary cause of cholestatic jaundice. This study fulfilled the review inclusion criteria as the upper range of the age of the infants in both groups was 37 weeks or less.
Objective: to evaluate whether pure F‐LE could halt or reverse the progression of PNALD compared with soybean oil‐based parenteral lipid preparation (S‐LP) and to assess the effects of pure F‐LE on liver function and physical growth.
Interventions: eligible infants were randomly assigned to receive either pure F‐LE (10% Omegaven; Fresenius Kabi AG, Bad Homburg vor der Höhe, Germany; n = 9) or S‐LE (10% Intralipid; Fresenius Kabi AG, Uppsala, Sweden; n = 7). Infants randomised to the pure F‐LE arm received F‐LE starting at 0.5 g/kg/day and gradually advanced to the maximum of 1.5 g/kg/day at 0.5 g/kg/day increments every two days. Infants receiving S‐LE had the quantity of parenteral lipid decreased to 1.5 g/kg/day as a reduction has been shown to be beneficial to infants with PNALD.
Outcomes: primary outcome was reversal of PNALD, defined as Cbil level less than 34 μmol/L within four months after commencement of lipid treatment. The secondary outcomes were rate of change of weekly liver function tests, infant growth parameters (head circumference and bodyweight), blood lipid profile and number of episodes of late‐onset infection
Excluded studies
Four randomised studies were excluded as the participants included term infants (Angsten 2002; Ariyawangso 2014; Lima 1988; Webb 2008). One study compared aggressive PN with conventional nutrition (as per the TPN protocols in the 1990s), which was the main objective of the study, besides comparing the LE in the two groups (Wilson 1997). See the Characteristics of excluded studies table for details.
Risk of bias in included studies
The review authors (VK, MM) assessed the quality of included studies using the criteria of Cochrane Neonatal. Assessment of bias was predominantly based on allocation concealment, blinding of intervention, blinding of outcome assessment and completeness of follow‐up. Details of assessment are provided in 'Risk of bias' tables (see Characteristics of included studies table).
Allocation
All included studies were described as randomised. However, 14 studies adequately described the method of the random sequence generation (Demirel 2011; Deshpande 2009; Deshpande 2014; Diamond 2017; Köksal 2011; Lam 2014; Nehra 2014; Pawlik 2014; Rayyan 2012; Repa 2018; Skouroliakou 2010; Skouroliakou 2016; Uthaya 2016; Vlaardingerbroek 2014). Two studies were at a low risk for selection bias based on the description of random sequence generation in previous study reports by the same authors (D'Ascenzo 2014; Savini 2013). By consensus between review authors (VK, MM), three studies were assigned low risk of bias (Najm 2017; Techasatid 2017; Wang 2016). Ten studies were at unclear risk of bias (Beken 2014; Biagetti 2016; D'Ascenzo 2011; Gawecka 2008b; Göbel 2003; Hsiao 2018; Roggero 2010; Rubin 1994; Lehner 2006; Tomsits 2010).
Twenty‐two studies were assigned low risk of bias for allocation concealment including eleven studies that described allocation concealment with the involvement of pharmacy or a member of TPN team (Deshpande 2009; Deshpande 2014; Diamond 2017; Gawecka 2008b; Hsiao 2018; Köksal 2011; Lam 2014; Nehra 2014; Rayyan 2012; Skouroliakou 2010; Skouroliakou 2016), six studies that described use of sealed envelopes (Biagetti 2016; D'Ascenzo 2011; D'Ascenzo 2014; Techasatid 2017; Vlaardingerbroek 2014; Wang 2016) and two studies that described use of sealed envelopes with the involvement of pharmacy (Beken 2014; Savini 2013). Two studies that were assigned low risk of bias reported use of online allocation (Najm 2017) or central voice recognition system (Uthaya 2016). One study (Repa 2018) was assigned low risk of bias for allocation concealment based on the available information from study report by consensus between authors (VK,MM). Seven studies provided insufficient information regarding allocation concealment and were assigned unclear risk of bias (Demirel 2011; Göbel 2003; Lehner 2006; Pawlik 2014; Roggero 2010; Rubin 1994; Tomsits 2010).
Blinding
Eighteen studies were assigned low risk of bias for performance and detection bias including twelve studies that described the intervention and control LE being identical (D'Ascenzo 2014; Deshpande 2009; Deshpande 2014; Hsiao 2018; Lam 2014; Nehra 2014; Rayyan 2012; Repa 2018Savini 2013; Skouroliakou 2010; Skouroliakou 2016; Wang 2016), one that reported preparation of trial formulations by a licensed facility and dispensed by pharmacy staff (Uthaya 2016) and five by author consensus based on the study details (Biagetti 2016; Diamond 2017; Gawecka 2008b; Köksal 2011; Techasatid 2017). Seven studies were described as blinded but were assigned unclear risk of bias for performance and detection bias as no judgement was possible in absence of details on blinding in the study reports (D'Ascenzo 2011; Göbel 2003; Lehner 2006; Roggero 2010; Rubin 1994; Tomsits 2010; Vlaardingerbroek 2014). Three studies were assigned unclear risk of performance bias but low risk for detection bias by author consensus, including two (Beken 2014; Pawlik 2014) that were described to be blinded for the ophthalmologist and one study (Najm 2017) that was described to be blinded only for the ophthalmologist and data analyst. One study was assigned high risk of bias as it was not described as a blinded study (Demirel 2011).
Incomplete outcome data
Five studies were assigned high risk of bias for significant incomplete outcome data or unbalanced exclusions (Biagetti 2016; Lehner 2006; Pawlik 2014; Rubin 1994; Skouroliakou 2010). Rubin 1994 excluded infants who later developed sepsis, hyperbilirubinaemia or thrombocytopenia and performed per protocol analysis (10 infants, amounting to 16% of the study sample). One study reported high mortality rate in both intervention (fish oil‐LE; 20/87 (22.9%)) and control groups (OS‐LE; 18/88 (20.4%) (Pawlik 2014). There were seven participant withdrawals, all in the fish oil‐LE arm. Data were not reported for deaths or withdrawals. This study was considered at high risk of bias for cholestasis and other outcomes.
The other studies reported outcomes for most infants with smaller numbers of withdrawals, for which the reasons were provided, proportions were not very high or intention‐to‐treat analysis was performed, and were, therefore, assessed to be at low risk or unclear risk of attrition bias. We contacted corresponding authors of eight studies by email for further information/clarification; four authors provided further information and one author provided further information including unpublished data which were included in the meta‐analyses (Köksal 2011). We contacted the authors of some published abstracts for clarification regarding publication resulting from their studies and to procure unpublished data. We also contacted some authors for clarification regarding the data in published study reports (Diamond 2017; Köksal 2011).
Selective reporting
In the absence of pre‐specified study protocols the risk of bias was unclear for most studies (Biagetti 2016; D'Ascenzo 2011; D'Ascenzo 2014; Demirel 2011; Deshpande 2009; Gawecka 2008b; Göbel 2003; Hsiao 2018; Köksal 2011; Lehner 2006; Pawlik 2014; Rayyan 2012; Roggero 2010; Rubin 1994; Savini 2013; Skouroliakou 2010; Skouroliakou 2016; Techasatid 2017; Tomsits 2010). The data values for some outcomes in the studies were not available (mentioned as "not significantly different") or presented as composite outcomes and, therefore, could not be included in the meta‐analyses. Data values were not available for NEC and BPD/CLD in one study (Demirel 2011), sepsis in one study (Deshpande 2009), IVH in one study (Gawecka 2008b), and hyperglycaemia in one study (Rubin 1994). Two studies reported sepsis as a composite outcome ("infections and infestations") (Rayyan 2012; Tomsits 2010). One study reported composite outcomes of "hepatobiliary disorder" (included jaundice and cholestasis) and "metabolic and nutrition disorders" (including hyperglycaemia) (Rayyan 2012). Some short duration studies focusing on biochemical aspects did not provide data values on growth rate. All reported outcomes are listed in Table 8.
2. Outcome measures reported in studies comparing alternative‐LE versus pure soybean oil‐based LE.
| Study | n |
Death before D/C |
Growth rate (g/kg/day) |
IHCL |
Days to regain bw |
BPD |
Vent dur (days) |
O2 (days) |
Sepsis | NEC |
IVH 3–4 |
HB |
PTx (d) |
HG | HTG |
PNALD or resol. |
PDA | ROP | Cbil |
Neuro‐ dev |
| Beken 2014 | 80 | Y | — | — | — | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | — | — | Y | — | Y | — | Y | Y | — |
| Biagetti 2016 | 52 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| D'Ascenzo 2011 | 47 | — | NU | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | Y | — |
| D'Ascenzo 2014 | 80 | Y | Y | — | Y | Y | — | — | Y | Y | Y | — | — | — | NU | Y | Y | Y | Y | — |
| Demirel 2011 | 40 | — | NU | — | — | NU | — | — | Y | NU | Y | — | — | — | Y | — | — | NU | — | — |
| Deshpande 2009 | 45 | — | NU | — | — | — | — | — | NU | — | NU | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | Y | — |
| Deshpande 2014 | 34 | Y | NU | — | — | Y | — | — | NU | — | Y | — | — | — | — | NU | Y | — | Y | — |
| Diamond 2017 | 24 | NU | — | — | — | — | — | Y | Y | — | — | — | Y | Y | Y | — | — | Y | — | |
| Gawecka 2008b | 38 | — | — | — | — | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y* | NU | — | Y | — | — | Y | — | NU | Y | — |
| Göbel 2003 | 45 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | Y | — | — | — | — | — | — | Y | — |
| Hsiao 2018 | 60 | Y | Y | — | — | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | — | — | — | — | Y | Y | NU | — | |
| Köksal 2011 | 64 | Y | Y | — | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y* | Y | Y | — | Y | Y | Y | — | NU | Y | — |
| Lam 2014 | 16 | Y | Y | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | Y | — | — | Y | — |
| Lehner 2006 | 12 | — | NU | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | Y | — | — | — | — | — |
| Najm 2017 | 78 | Y | NU | — | — | Y | — | — | Y | Y | — | — | — | — | — | Y | Y | Y | — | — |
| Nehra 2014 | 19 | Y | NU | — | — | — | — | — | Y | — | — | — | — | — | — | Y | — | — | Y | Y |
| Pawlik 2014 | 130 | Y | NU | — | — | Y | — | — | Y | Y | Y* | — | — | — | — | Y | Y | Y | — | — |
| Rayyan 2012 | 53 | Y | Y | — | — | — | NU | — | NU* | — | — | NU | — | NU | NU | NU | — | — | Y | — |
| Repa 2018 | 223 | Y | Y | — | — | Y | Y | — | Y | Y | Y | — | — | — | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | — |
| Roggero 2010 | 36 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| Rubin 1994 | 59 | — | NU | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | NU | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| Savini 2013 | 150 | Y | Y | — | Y | Y | — | — | Y | Y | — | — | — | — | — | Y | Y | Y | Y | — |
| Skouroliakou 2010 | 32 | — | NU | — | — | — | Y | — | Y | — | — | — | Y | Y | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| Skouroliakou 2016 | 51 | Y | — | — | — | Y | — | — | Y | — | — | — | — | — | — | Y | — | — | Y | — |
| Techasatid 2017 | 44 | Y | NU | — | — | Y | Y | — | Y | Y | Y | — | — | — | — | Y | Y | Y | Y | — |
| Tomsits 2010 | 60 | — | Y | — | — | — | Y* | Y* | NU* | — | — | — | — | NU | NU | — | — | — | — | — |
| Uthaya 2016 | 168 | Y | NU | Y | — | — | — | — | Y | Y | — | — | — | — | — | Y | — | — | — | — |
| Vlaardingerbroek 2014 | 96 | Y | Y | — | Y | Y | Y | — | Y | Y | Y | — | — | — | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | — |
| Wang 2016 | 100 | Y | NU | — | Y | Y | Y | — | Y | NU | — | — | — | — | — | Y | — | — | Y | — |
—: outcome not reported; BPD: bronchopulmonary dysplasia; bw: birth weight; Cbil: conjugated bilirubin; d: days; D/C: discharge; HB: hyperbilirubinaemia; HG: hyperglycaemia; HTG: hypertriglyceridaemia; IHCL: intrahepatocellular lipid content; IVH: intraventricular haemorrhage stage III/IV; LE: lipid emulsion; n: total enrolled infants in the study; NEC: necrotising enterocolitis > stage 2; Neurodev: neurodevelopmental outcome; NU: data provided in a format not usable in meta‐analysis or reported as "no difference between groups"; O2: duration of supplemental oxygen; PNALD: parenteral nutrition‐associated liver disease; PTx: phototherapy; ROP: retinopathy of prematurity; Vent dur: ventilation duration; Y: data reported and used in the meta‐analysis.
* Indicates composite outcome or combined stages reported.
Not all outcomes could be presented due to space constraints.
Other potential sources of bias
Köksal 2011 reported high rates of ventilation duration and BPD in the S‐LE intervention arm which was a cause of unexplained heterogeneity in these outcomes (unclear risk of bias). The study did not provide data on the level of sickness of the infants in the two groups (e.g. Köksal 2011), which may be a source of prognostic imbalance. We identified a duplicate report of study by Wang and colleagues (Wang 2016b) with some data irregularities and at the time of submission of this review we were awaiting advice from the editorial teams of the respective journals (unclear risk of bias). Two studies were terminated prematurely and were assigned unclear risk of bias as the reasons for termination included limitations due to the study setting (Lam 2014; Nehra 2014).
Demirel 2011 was at high risk of bias as only the infants who were receiving 40% calories by parenteral route by the 14th day of life were included in the study; this was likely to have introduced bias and issues with randomisation.
The risk of bias in included studies is summarised in Figure 2.
2.
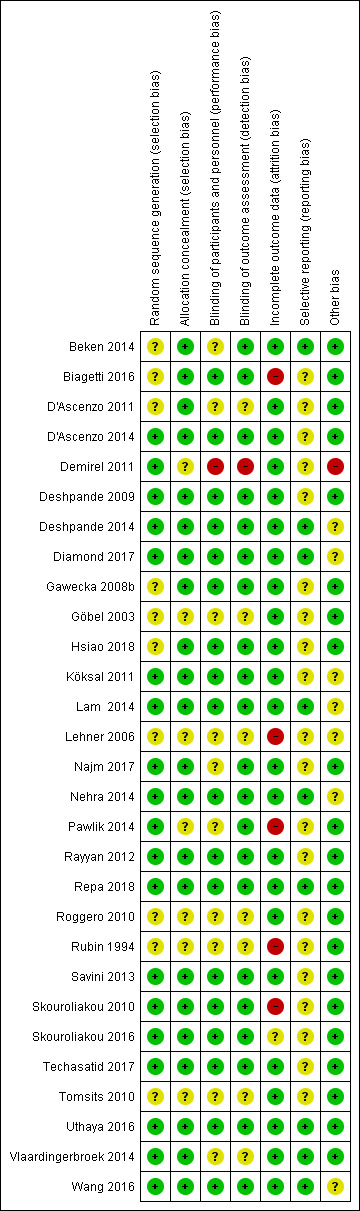
Risk of bias summary: review authors' judgements about each risk of bias item for each included study.
Effects of interventions
See: Table 1; Table 2; Table 3; Table 4; Table 5; Table 6
We included 29 eligible RCTs (n = 2037) with 26 studies (n = 1890) contributing data to the meta‐analyses for the outcomes of interest in this review (Characteristics of included studies table). The authors agreed regarding inclusion and exclusion of the studies, quality assessment and data extraction. We could not perform the planned subgroup analyses based on birth weight and sex due to lack of stratified data.
Fish oil LE versus non‐fish oil LE in preterm infants (Comparison 1)
All studies comparing F‐LE versus non‐fish oil LE in preterm infants without underlying surgical conditions or PNALD were considered in this comparison. Studies in preterm infants with surgical conditions were considered in Comparison 5. Studies in preterm infants with pre‐existing PNALD/cholestasis were considered in Comparison 6.
Seventeen studies compared F‐LE versus non‐fish oil LE (n = 1522) (Beken 2014; Biagetti 2016; D'Ascenzo 2011; D'Ascenzo 2014; Deshpande 2014; Hsiao 2018; Najm 2017; Pawlik 2014; Rayyan 2012; Repa 2018; Savini 2013; Skouroliakou 2010; Skouroliakou 2016; Techasatid 2017; Tomsits 2010; Uthaya 2016; Vlaardingerbroek 2014). One study had five intervention arms and contributed to multiple subgroup comparisons (Savini 2013). The following subgroup comparisons were included:
MOFS‐LE versus S‐LE: 11 studies (n = 973) (Beken 2014; D'Ascenzo 2014; Rayyan 2012; Repa 2018; Savini 2013; Skouroliakou 2010; Skouroliakou 2016; Techasatid 2017; Tomsits 2010; Uthaya 2016; Vlaardingerbroek 2014).
MOFS‐LE versus MS‐LE: two studies (n = 120) (Hsiao 2018; Savini 2013).
MOFS‐LE versus OS‐LE: three studies (n = 184) (Deshpande 2014; Najm 2017; Savini 2013).
MFS‐LE versus S‐LE: one study (n = 60) (Savini 2013).
MFS‐LE versus MS‐LE: three studies (n = 160) (Biagetti 2016; D'Ascenzo 2011; Savini 2013).
MFS‐LE versus OS‐LE: one study (n = 60) (Savini 2013).
OFS‐LE versus OS‐LE: one study (n = 175) (Pawlik 2014).
A summary of the risk estimates and the grading of the evidence are provided in Table 1.
Primary outcomes
Days to regain birth weight (outcome 1.1)
Three studies (n = 326) reported data in a format that could be used for the meta‐analysis (D'Ascenzo 2011; Savini 2013; Vlaardingerbroek 2014) (outcome 1.1; Analysis 1.1). One was a five‐arm study contributing to multiple comparisons (Savini 2013).
1.1. Analysis.
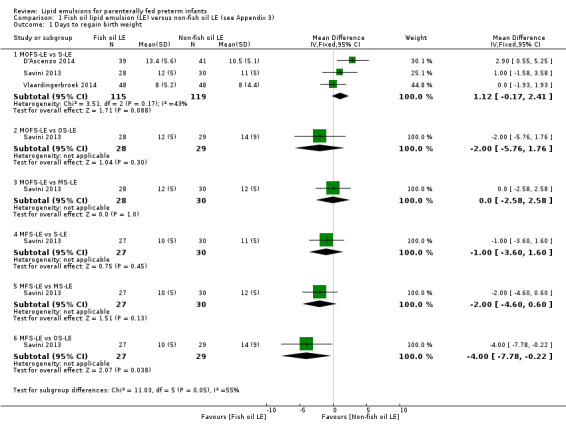
Comparison 1 Fish oil lipid emulsion (LE) versus non‐fish oil LE (see Appendix 3), Outcome 1 Days to regain birth weight.
Three studies compared MOFS‐LE versus S‐LE, with D'Ascenzo 2014 showing statistically significant effect in favour of non‐fish oil LE (MD 2.9 days, 95% CI 0.55 to 5.25). There was no statistically significant difference between groups in the meta‐analysis (MD 1.12 days, 95% CI –0.17 to 2.41; n = 234). There was low heterogeneity (I² = 43%).
One study compared MOFS‐LE versus MS‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (MD 0.00 days, 95% CI –2.58 to 2.58; n = 58; Savini 2013).
One study compared MOFS‐LE versus OS‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (MD –2.00 days, 95% CI –5.76 to 1.76; n = 57; Savini 2013).
One study compared MFS‐LE versus S‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (MD –1.00 days, 95% CI –3.60 to 1.60; n = 57; Savini 2013).
One study compared MFS‐LE versus MS‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (MD –2.00 days, 95% CI –4.60 to 0.60; n = 57; Savini 2013).
One study compared MFS‐LE versus OS‐LE, with statistically significant effect in favour of fish oil LE (MD –4.00 days, 95% CI –7.78 to –0.22; n = 56; Savini 2013).
Growth rate (outcome 1.2)
Five studies (n = 347) provided data in a format that could be used for the meta‐analysis of rate of weight gain (g/kg/day) (Analysis 1.2). One was a five‐arm study contributing to multiple comparisons (Savini 2013). There was significant variation in the presentation of growth data and the duration for which the data were presented, making this a clinically heterogeneous outcome.
1.2. Analysis.
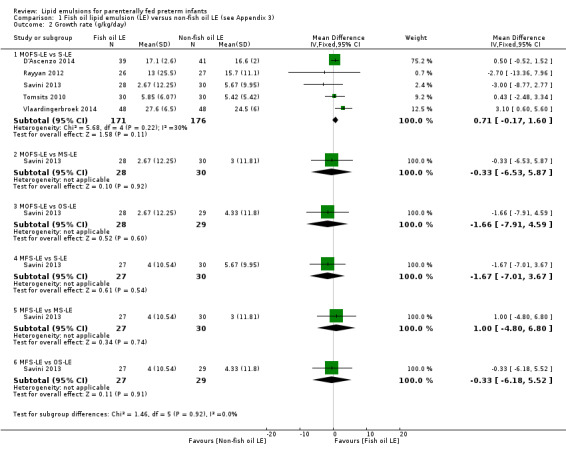
Comparison 1 Fish oil lipid emulsion (LE) versus non‐fish oil LE (see Appendix 3), Outcome 2 Growth rate (g/kg/day).
Vlaardingerbroek 2014 reported weight gain (g/kg/day) as mean with SDs. Rayyan 2012 reported weight gain as mean with SDs until day eight. D'Ascenzo 2014 provided growth rates only after the birth weight had been regained. Savini 2013 provided weekly mean growth rates with SDs for the first three weeks which were pooled by 'lipid type' to give the mean growth rate and SD over three weeks. Tomsits 2010 presented the percentage change in mean with SDs of weight at day eight and at the end of the study (14 days). Skouroliakou 2010 only reported mean with SDs of initial weight and weight on day 14. Other studies reported z scores at baseline and at the study end from different normative data, which, combined with the fact that we did not have correlation coefficients for the participants, and unclear specific information regarding the denominators, meant that we were unable to reliably impute the growth rates (D'Ascenzo 2011; Najm 2017; Repa 2018).
Five studies compared MOFS‐LE versus S‐LE with Vlaardingerbroek 2014 showing statistically significant effect in favour of non‐fish oil LE (MD 3.10 g/kg/day, 95% CI 0.6 to 5.60). There was no statistically significant difference between groups in the meta‐analysis (MD 0.71 g/kg/day, 95% CI –0.17 to 1.60; n = 347; low‐quality evidence). There was low heterogeneity (I² = 30%).
One study compared MOFS‐LE versus MS‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (MD –0.33 g/kg/day, 95% CI –6.53 to 5.87; n = 58; Savini 2013).
One study compared MOFS‐LE versus OS‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (MD –1.66 g/kg/day, 95% CI –7.91 to 4.59; n = 57; Savini 2013).
One study compared MFS‐LE versus S‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (MD –1.67 g/kg/day, 95% CI –7.01 to 3.67; n = 57; Savini 2013).
One study compared MFS‐LE versus MS‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (MD 1.00 g/kg/day, 95% CI –4.80 to 6.80; n = 57; Savini 2013).
One study compared MFS‐LE versus OS‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (MD –0.33 g/kg/day, 95% CI –6.18 to 5.52; n = 56; Savini 2013).
PNALD/cholestasis (conjugated bilirubin 2 mg/dL or greater) (outcome 1.3)
Three studies defined cholestasis as conjugated bilirubin greater than 2 mg/dL on two consecutive occasions (D'Ascenzo 2014; Hsiao 2018; Techasatid 2017) (Analysis 1.3). Savini 2013 defined cholestasis as conjugated bilirubin greater than 2 mg/dL (34.2 μmol/L) at the age of six weeks. Other studies used different definitions for cholestasis.
1.3. Analysis.
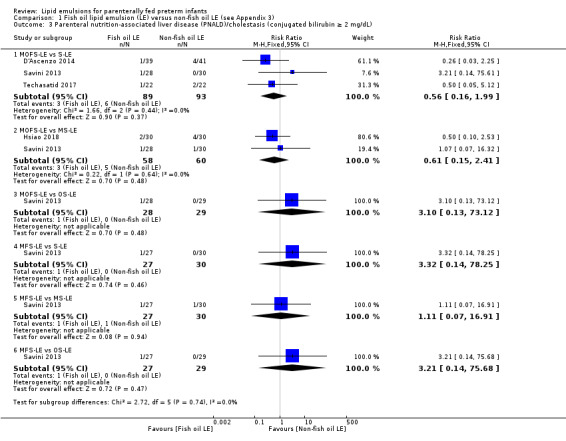
Comparison 1 Fish oil lipid emulsion (LE) versus non‐fish oil LE (see Appendix 3), Outcome 3 Parenteral nutrition‐associated liver disease (PNALD)/cholestasis (conjugated bilirubin ≥ 2 mg/dL).
Three studies compared MOFS‐LE versus S‐LE, with no statistically significant difference in any individual study (D'Ascenzo 2014; Savini 2013; Techasatid 2017). There was no statistically significant difference between groups in the meta‐analysis (typical RR 0.56, 95% CI 0.16 to 1.99; typical RD –0.03, 95% CI –0.10 to 0.03; n = 182). There was no heterogeneity for RR (I² = 0%) and low heterogeneity for RD (I² = 25%).
Two studies compared MOFS‐LE versus MS‐LE (Hsiao 2018; Savini 2013). There were no statistically significant differences reported by any individual study. There was no statistically significant difference between groups in the meta‐analysis (typical RR 0.61, 95% CI 0.15 to 2.41; typical RD –0.03, 95% CI –0.12 to 0.06; n = 118). There was no heterogeneity for RR or RD (I² = 0%).
One study compared MOFS‐LE versus OS‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (RR 3.10, 95% CI 0.13 to 73.12; RD 0.04, 95% CI –0.06 to 0.13).
One study compared MFS‐LE versus S‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (RR 3.32, 95% CI 0.14 to 78.25; RD 0.04, 95% CI –0.06 to 0.13; n = 57; Savini 2013).
One study compared MFS‐LE versus MS‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (RR 1.11, 95% CI 0.07 to 16.91; RD 0.00, 95% CI –0.09 to 0.10; n = 57; Savini 2013).
One study compared MFS‐LE versus OS‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (RR 3.21, 95% CI 0.14 to 75.68; RD 0.04, 95% CI –0.06 to 0.13; n = 56; Savini 2013).
PNALD/cholestasis (conjugated bilirubin 2 mg/dL or greater): combined subgroups (outcome 1.4)
In the combined meta‐analysis for all the subgroups together and adjusting for the unit of analysis error for multiarm study there was no difference between the F‐LE and non‐fish oil LE (typical RR 0.61, 95% CI 0.24 to 1.56; typical RD –0.03, 95% CI –0.08 to 0.02; 4 studies; n = 328; low‐quality evidence; Figure 3; Analysis 1.4). There was no heterogeneity for RR or RD (I² = 0%).
3.
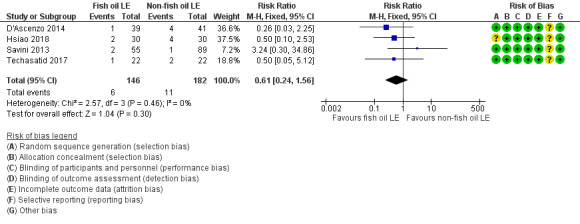
Forest plot of comparison: 1 Fish oil lipid emulsion (LE) versus non‐fish oil LE, outcome: 1.4 Parenteral nutrition‐associated liver disease (PNALD)/cholestasis (conjugated bilirubin ≥ 2 mg/dL): combined subgroups.
1.4. Analysis.
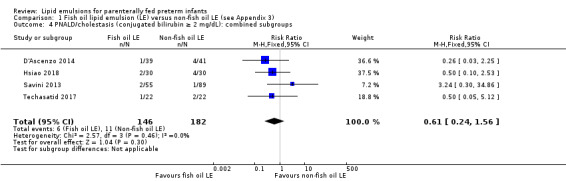
Comparison 1 Fish oil lipid emulsion (LE) versus non‐fish oil LE (see Appendix 3), Outcome 4 PNALD/cholestasis (conjugated bilirubin ≥ 2 mg/dL): combined subgroups.
PNALD/cholestasis (any definition) (outcome 1.5)
Eleven studies reported data in a format that could be used for the meta‐analysis (Beken 2014; D'Ascenzo 2011; Hsiao 2018; Najm 2017; Pawlik 2014; Repa 2018; Savini 2013; Skouroliakou 2016; Techasatid 2017; Uthaya 2016; Vlaardingerbroek 2014) (Analysis 1.5). One was a five‐arm study contributing to multiple comparisons (Savini 2013).
1.5. Analysis.
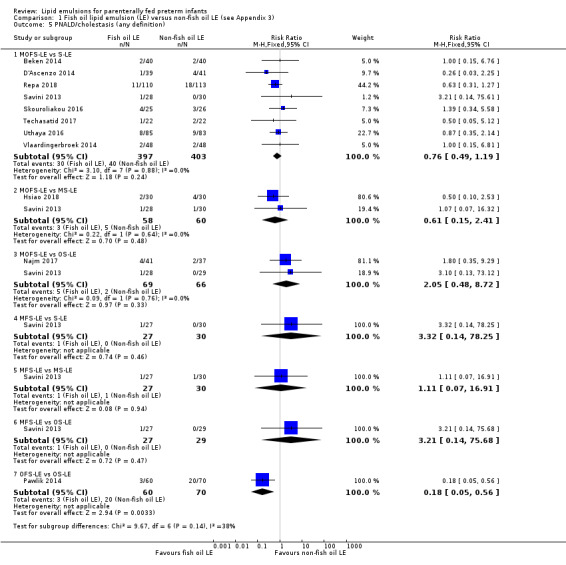
Comparison 1 Fish oil lipid emulsion (LE) versus non‐fish oil LE (see Appendix 3), Outcome 5 PNALD/cholestasis (any definition).
Three studies defined cholestasis as conjugated bilirubin greater than 2 mg/dL on two consecutive occasions (D'Ascenzo 2014; Hsiao 2018; Techasatid 2017). Savini 2013 defined cholestasis as conjugated bilirubin greater than 2 mg/dL (34.2 μmol/L) at the age of six weeks which was similar in cut‐off to many other included studies but was heterogeneous in timing of the outcome evaluation. One study defined cholestasis as conjugated bilirubin greater than 50 μmol/L for at least two weeks any time during follow‐up and not related to sepsis (Najm 2017). One study defined cholestasis as two readings of conjugated bilirubin greater than 1.5 mg/dL (Repa 2018). Two studies defined cholestasis as conjugated bilirubin greater than 1 mg/dL if total bilirubin was less than 5 mg/dL and greater than 20% conjugated fraction if total bilirubin was greater than 5 mg/dL (Beken 2014; Pawlik 2014). One study provided data about study participants with conjugated bilirubin greater than 40 μmol/L (Uthaya 2016). One study provided definition of bilirubin as greater than 20% of total bilirubin (Vlaardingerbroek 2014). Another study did not provide the definition used (Skouroliakou 2016).
Eight studies compared MOFS‐LE versus S‐LE, with no statistically significant difference in any individual study. There was no statistically significant difference between groups in the meta‐analysis (typical RR 0.76, 95% CI 0.49 to 1.19; typical RD –0.02, 95% CI –0.06 to 0.02; n = 800). There was no heterogeneity for RR or RD (I² = 0%).
Two studies compared MOFS‐LE versus MS‐LE, with neither of the studies individually reporting statistically significant difference in PNALD (Hsiao 2018; Savini 2013). One of these studies included a population of preterm infants who required ventilation after birth (Hsiao 2018). However, as this study did not cause any heterogeneity and the results were not an outlier visually, we used the study results in the meta‐analysis. There was no statistically significant difference between groups in the meta‐analysis (typical RR 0.61, 95% CI 0.15 to 2.41; typical RD –0.03, 95% CI –0.12 to 0.06; 2 studies; n = 118). There was no heterogeneity for RR or RD (I² = 0%).
Among the studies comparing MOFS‐LE versus OS‐LE, Deshpande 2009 did not report data and mentioned no difference between groups. Neither of the other two studies that provided data for this outcome reported any statistically significant differences (Najm 2017; Savini 2013). There was no statistically significant difference between groups in the meta‐analysis (typical RR 2.05, 95% CI 0.48 to 8.72; typical RD 0.04, 95% CI –0.04 to 0.12; 2 studies; n = 135). There was no heterogeneity for RR or RD (I² = 0%).
One study compared MFS‐LE versus S‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (typical RR 3.32, 95% CI 0.14 to 78.25; typical RD 0.04, 95% CI –0.06 to 0.13; n = 57; Savini 2013).
One study compared MFS‐LE versus MS‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (typical RR 1.11, 95% CI 0.07 to 16.91; typical RD 0.00, 95% CI –0.09 to 0.10; n = 57; Savini 2013).
One study compared MFS‐LE versus OS‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (typical RR 3.21, 95% CI 0.14 to 75.68; typical RD 0.04, 95% CI –0.06 to 0.13; n = 56; Savini 2013).
One study compared OFS‐LE versus OS‐LE, with a statistically significant effect in favour of F‐LE (typical RR 0.17, 95% CI 0.05 to 0.56; typical RD –0.24, 95% CI –0.36 to –0.12; n = 130; Pawlik 2014).
Further analysis was done for the outcome of PNALD/cholestasis by combining all the subgroups together (see outcome 1.6 below).
PNALD/cholestasis (any definition): combined subgroups (all studies) and sensitivity analysis (outcome 1.6)
In the combined meta‐analysis for all the subgroups together and adjusting for the unit of analysis error (by combining arms of multiarm trial) there was statistically significant effect in favour of F‐LE compared to the non‐fish oil LE (typical RR 0.63, 95% CI 0.43 to 0.91; typical RD –0.04, 95% CI –0.08 to –0.01; 11 studies; n = 1154; Analysis 1.6; very low‐quality evidence). There was no heterogeneity for RR (I² = 9%) and moderate heterogeneity for RD (54%).
1.6. Analysis.
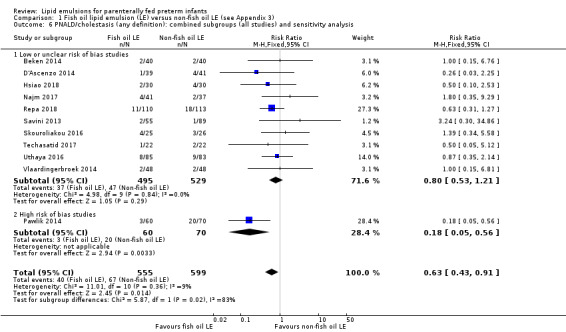
Comparison 1 Fish oil lipid emulsion (LE) versus non‐fish oil LE (see Appendix 3), Outcome 6 PNALD/cholestasis (any definition): combined subgroups (all studies) and sensitivity analysis.
We performed a sensitivity analysis in the outcome of PNALD by separately analysing the studies with low and unclear risk of bias and the study with high risk of bias (Pawlik 2014). The study's result from the high risk of bias study was visually an outlier on the forest plot. There was heterogeneity between the effect estimate from low and unclear risk of bias studies compared to the high risk of bias study, with high heterogeneity of 83% for RR and 91.6% for RD.
Study level differences including the variation in definitions of cholestasis, specific methodological aspects including timing of PNALD detection and differences in intervention (percentage of each lipid type) may also have contributed to high heterogeneity. Another important reason to conduct sensitivity analysis was moderate to high heterogeneity in this outcome.
The pooled estimate from the meta‐analysis of studies with low and unclear risk of bias showed no statistically significant difference between the F‐LE and non‐fish oil LE for PNALD/cholestasis (using any definition) (typical RR 0.80, 95% CI 0.53 to 1.21; typical RD –0.02, 95% CI –0.05 to 0.02; 10 studies; n = 1024; low‐quality evidence; analysis done with adjustment for unit of analysis). There was no heterogeneity for RR or RD among the studies with low and unclear risk of bias (I² = 0%). We presented the pooled effect estimates from the low and unclear risk of bias studies as the primary analysis because it is likely to be a less biased estimate of effect, with higher grade of evidence (Figure 4).
4.
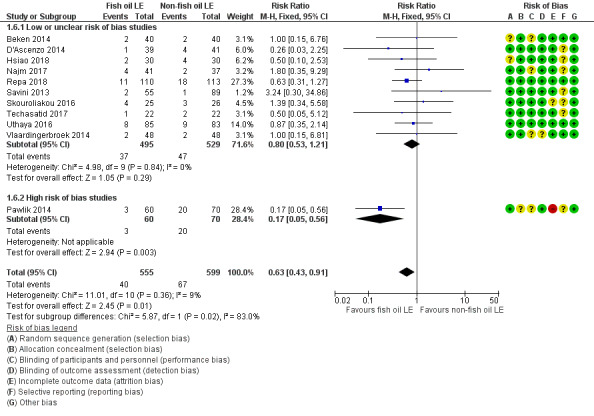
Forest plot of comparison: 1 Fish oil lipid emulsion (LE) versus non‐fish oil LE, outcome: 1.6 Parenteral nutrition‐associated liver disease (PNALD)/cholestasis (any definition): analysis stratified by low and unclear risk of bias studies versus high risk of bias studies (risk ratios).
We also explored reporting bias for this outcome using a funnel plot, which did not detect any reporting bias for studies comparing F‐LE versus non‐fish oil LE (Figure 5), or for the subgroup restricted to MOFS‐LE versus S‐LE (not shown).
5.
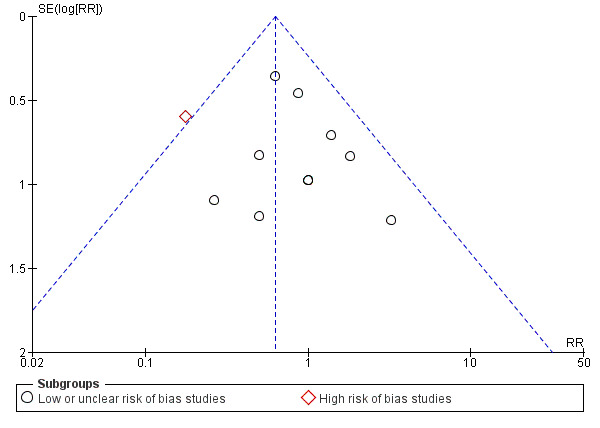
Funnel plot of comparison: 1 Fish oil lipid emulsion (LE) versus non‐fish oil LE, outcome: 1.5 Parenteral nutrition‐associated liver disease (PNALD)/cholestasis (any definition).
Secondary outcome measures
Death before discharge (outcome 1.7)
Thirteen studies reported data in a format that could be used for the meta‐analysis (Beken 2014; D'Ascenzo 2014; Deshpande 2014; Hsiao 2018; Najm 2017; Pawlik 2014; Rayyan 2012; Repa 2018; Savini 2013; Skouroliakou 2016; Techasatid 2017; Uthaya 2016; Vlaardingerbroek 2014) (Analysis 1.7). One was a five‐arm study contributing to multiple comparisons (Savini 2013). No single study showed a statistically significant difference in the groups for death before discharge.
1.7. Analysis.
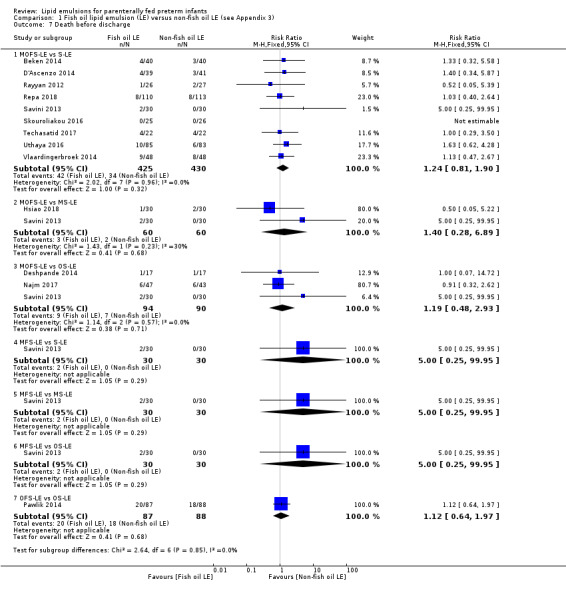
Comparison 1 Fish oil lipid emulsion (LE) versus non‐fish oil LE (see Appendix 3), Outcome 7 Death before discharge.
In the studies comparing MOFS‐LE versus S‐LE, there were nine studies with no statistically significant difference in any individual study (Beken 2014; D'Ascenzo 2014; Rayyan 2012; Repa 2018; Savini 2013; Skouroliakou 2016; Techasatid 2017; Uthaya 2016; Vlaardingerbroek 2014). There was no statistically significant difference between groups in the meta‐analysis (typical RR 1.24, 95% CI 0.81 to 1.90; typical RD 0.02, 95% CI –0.02 to 0.06; n = 855; low‐quality evidence). There was no heterogeneity for RR and RD (I² = 0%).
In the studies comparing MOFS‐LE versus MS‐LE, there were two studies with no statistically significant difference in any individual study (Hsiao 2018; Savini 2013). There was no statistically significant difference between groups in the meta‐analysis (typical RR 1.40, 95% CI 0.28 to 6.89; typical RD 0.02, 95% CI –0.06 to 0.09; n = 120). There was low heterogeneity for RR or RD (I² = 30.2%).
In the studies comparing MOFS‐LE versus OS‐LE, there were three studies with no statistically significant difference in any individual study (Deshpande 2014; Najm 2017; Savini 2013). There was no statistically significant difference between groups in the meta‐analysis (typical RR 1.19,, 95% CI 0.48 to 2.93; typical RD 0.02, 95% CI –0.07 to 0.10; n = 184). There was no heterogeneity for RR or RD (I² = 0%).
One study compared MFS‐LE versus S‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (RR 5.00, 95% CI 0.25 to 99.95; RD 0.07, 95% CI –0.04 to 0.17; n = 60; Savini 2013).
One study compared MFS‐LE versus MS‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (RR 5.00, 95% CI 0.25 to 99.95; RD 0.07, 95% CI –0.04 to 0.17; n = 60; Savini 2013).
One study compared MFS‐LE versus OS‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (RR 5.00, 95% CI 0.25 to 99.95; RD 0.07, 95% CI –0.04 to 0.17; n = 60; Savini 2013).
One study compared OFS‐LE versus OS‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (RR 1.12, 95% CI 0.64 to 1.97; RD 0.03, 95% CI –0.10 to 0.15; n = 175; Pawlik 2014).
Any retinopathy of prematurity (outcome 1.8)
Eight studies (n = 791) reported data in a format that could be used for the meta‐analysis (Analysis 1.8).
1.8. Analysis.
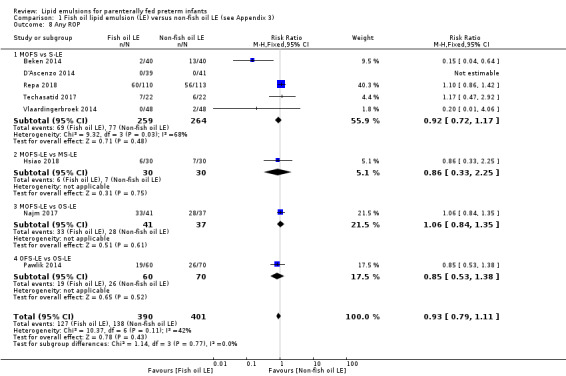
Comparison 1 Fish oil lipid emulsion (LE) versus non‐fish oil LE (see Appendix 3), Outcome 8 Any ROP.
In the studies comparing MOFS versus S‐LE, there were five studies (n = 523) (Beken 2014; D'Ascenzo 2014; Repa 2018; Techasatid 2017; Vlaardingerbroek 2014). One single‐centre study reported significantly lower rates in ROP stage 1 to 2 in the MOFS‐LE group compared with the S‐LE group (1/40 with MOFS‐LE versus 12/40 with S‐LE; P = 0.001; RR 0.08, 95% CI 0.01 to 0.61; RD –0.27, 95% CI –0.43 to –0.12; NNTB 4, 95% CI 2 to 8); however, there was no difference in ROP stage 3 and above (Beken 2014). There was no statistically significant difference between groups in the meta‐analysis (typical RR 0.92, 95% CI 0.72 to 1.17; typical RD –0.02, 95% CI –0.09 to 0.04). There was high heterogeneity for RR (I² = 68%) and RD (67%).
One study compared MOFS‐LE versus MS‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (RR 0.86, 95% CI 0.33 to 2.25; RD –0.03, 95% CI –0.24 to 0.17; n = 60; Hsiao 2018).
One study compared MOFS‐LE versus OS‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (RR 1.06, 95% CI 0.84 to 1.35; RD 0.05, 95% CI –0.14 to 0.23; n = 78; Najm 2017).
One study compared OFS‐LE versus OS‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (RR 0.85, 95% CI 0.53 to 1.38; RD –0.05, 95% CI –0.22 to 0.11; n = 130; Pawlik 2014).
In the meta‐analysis of all subgroups together, there was no statistically significant difference between the F‐LE and non‐fish oil LE groups in the meta‐analysis (typical RR 0.93, 95% CI 0.79 to 1.11; typical RD –0.02, 95% CI –0.08 to 0.03; 8 studies; n = 791). There was no heterogeneity for RR and RD among the subgroups (I² = 0%), though there was low heterogeneity for the whole group for RR (I² = 42%) and RD (46%).
The sensitivity analysis by stratifying for risk of bias did not change the results significantly (not presented).
Retinopathy of prematurity stage 3 or greater or requiring surgery (outcome 1.9)
Seven studies (n = 731) reported data in a format that could be used for the meta‐analysis (Beken 2014; D'Ascenzo 2014; Najm 2017; Pawlik 2014; Repa 2018; Techasatid 2017; Vlaardingerbroek 2014). Most studies appeared to be using the ICROP classification; however, this was only explicitly mentioned in Beken 2014; D'Ascenzo 2014; and Vlaardingerbroek 2014.
In the studies comparing MOFS‐LE versus S‐LE, there were five studies with no statistically significant difference reported in any individual study (Beken 2014; D'Ascenzo 2014; Repa 2018; Techasatid 2017; Vlaardingerbroek 2014) (outcome 1.8; Analysis 1.9). There was no statistically significant difference between groups in the meta‐analysis (typical RR 0.82, 95% CI 0.40 to 1.68; typical RD –0.01, 95% CI –0.05 to 0.03; n = 523). There was no heterogeneity for RR or RD (I² = 0%).
1.9. Analysis.
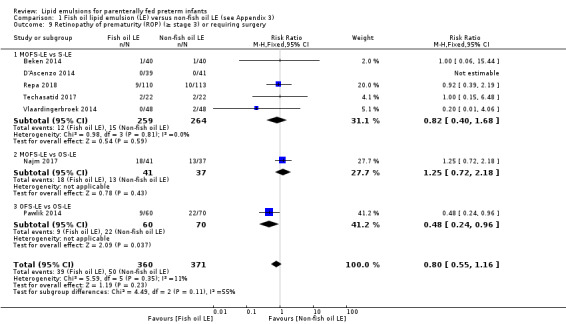
Comparison 1 Fish oil lipid emulsion (LE) versus non‐fish oil LE (see Appendix 3), Outcome 9 Retinopathy of prematurity (ROP) (≥ stage 3) or requiring surgery.
One study compared MOFS‐LE versus OS‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (RR 1.25, 95% CI 0.72 to 2.18; RD 0.09, 95% CI –0.13 to 0.30; n = 78; Najm 2017).
One study compared OFS‐LE versus OS‐LE, with statistically significant effect in favour of F‐LE (RR 0.48, 95% CI 0.24 to 0.96; RD –0.16, 95% CI –0.31 to –0.02; n = 130; Pawlik 2014).
In the meta‐analysis of all subgroups together, there was no statistically significant difference between the F‐LE and non‐fish oil LE groups in the meta‐analysis (typical RR 0.80, 95% CI 0.55 to 1.16; typical RD –0.03, 95% CI –0.07 to 0.02; 7 studies; n = 731; very low‐quality evidence). There was moderate heterogeneity for RR (I² = 55.5%) and RD (61.3%). Heterogeneity was explored in the sensitivity analysis below (outcome 1.10).
Retinopathy of prematurity stage 3 or greater or requiring surgery (sensitivity analysis; outcome 1.10)
As noted above, there was moderate heterogeneity in the outcome of ROP stage 3 or greater or requiring surgery (I² = 55.5% for RR; 61.3% for RD). We performed a sensitivity analysis in the outcome of ROP stage 3 or greater or requiring surgery by separately analysing the studies with low and unclear risk of bias and the study with high risk of bias (Pawlik 2014). There was no statistically significant difference between all the subgroups together in meta‐analysis in sensitivity analysis by pooling effect estimates from the low and unclear risk of bias studies (by removing the study by Pawlik 2014) (typical RR 1.02, 95% CI 0.65 to 1.60; typical RD 0.00, 95% CI –0.04 to 0.05; low‐quality evidence; 6 studies; n = 601; Analysis 1.10). There was no heterogeneity for RR and RD (I² = 0%). There were no statistically significant differences in the subgroup comparisons individually (i.e. MOFS‐LE versus S‐LE and MOFS‐LE versus OS‐LE; Analysis 1.10).
1.10. Analysis.
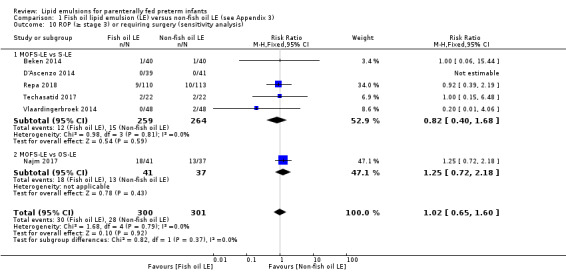
Comparison 1 Fish oil lipid emulsion (LE) versus non‐fish oil LE (see Appendix 3), Outcome 10 ROP (≥ stage 3) or requiring surgery (sensitivity analysis).
We presented the effect estimate from meta‐analysis of all studies as the primary result for severe ROP (outcome 1.8), because the results were not significantly different in the sensitivity analysis. Pawlik 2014 was considered at lesser risk of material bias for ROP (compared to the outcome of cholestasis) (Table 1).
Any bronchopulmonary dysplasia (outcome 1.11)
Eleven studies reported data in a format that could be used for the meta‐analysis (Beken 2014; D'Ascenzo 2014; Deshpande 2009; Hsiao 2018; Najm 2017; Pawlik 2014; Repa 2018; Savini 2013; Skouroliakou 2016; Techasatid 2017; Vlaardingerbroek 2014). One of these was a five‐arm study contributing to multiple comparisons (Savini 2013). Most of the studies described oxygen requirement at 36 weeks as the definition of BPD and one study did not specify the definition (Deshpande 2014).
Beken 2014 defined CLD as oxygen dependency beyond 36 weeks' corrected age with diuretic or steroid use. Two studies used a cut‐off of 36 weeks' (Najm 2017; Techasatid 2017). Hsiao 2018 defined mild, moderate and severe CLD. Three studies defined BPD using the definition provided by Walsh 2004 (D'Ascenzo 2014; Savini 2013; Vlaardingerbroek 2014).
In the studies comparing MOFS‐LE versus S‐LE, there were seven studies with no statistically significant difference in any individual study (Beken 2014; D'Ascenzo 2014; Repa 2018; Savini 2013; Skouroliakou 2016; Techasatid 2017; Vlaardingerbroek 2014). There was no statistically significant difference between groups in the meta‐analysis (typical RR 0.93, 95% CI 0.71 to 1.22; typical RD –0.02, 95% CI –0.08 to 0.05; n = 632; Analysis 1.11). There was no heterogeneity for RR (I² = 10%) or RD (22%).
1.11. Analysis.
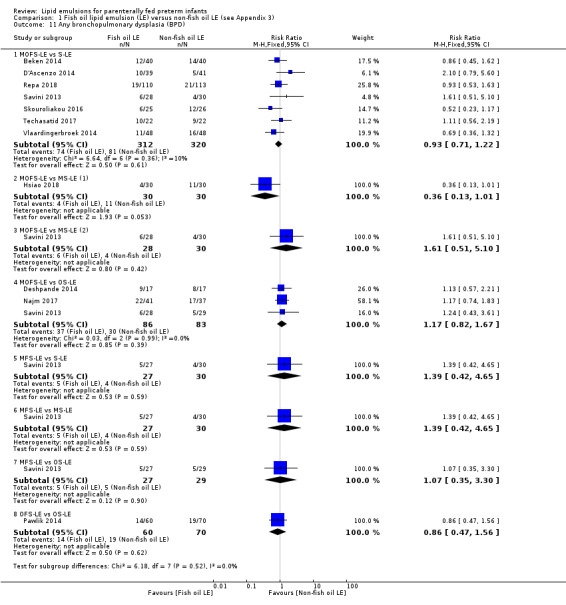
Comparison 1 Fish oil lipid emulsion (LE) versus non‐fish oil LE (see Appendix 3), Outcome 11 Any bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD).
In the studies comparing MOFS‐LE versus MS‐LE, there were two studies (n = 118) with Hsiao 2018 showing statistically significant effect in favour of fish oil LE (RR 0.36, 95% CI 0.13 to 1.01; typical RD –0.23, 95% CI –0.44 to –0.02; n = 60). Hsiao 2018 also had differences in the baseline population relevant to this outcome as only those preterm infants who required ventilation were considered eligible for the study. Savini 2013 reported data with no statistically significant difference between groups (typical RR 1.61, 95% CI 0.51 to 5.10; typical RD 0.08, 95% CI –0.11 to 0.28; n = 58). The results of the two studies were clinically, visually (forest plot) and statistically heterogeneous with differences in population; therefore, we presented the results separately (MOFS‐LE versus MS‐LE (1) Hsiao 2018; MOFS‐LE versus MS‐LE (2) Savini 2013).
In the studies comparing MOFS‐LE versus OS‐LE, there were three studies with no statistically significant difference in any individual study (Deshpande 2014; Najm 2017; Savini 2013). There was no statistically significant difference between groups in the meta‐analysis (typical RR 1.17, 95% CI 0.82 to 1.67; typical RD 0.06, 95% CI –0.08 to 0.20; n = 169). There was no heterogeneity for RR and RD (I² = 0%).
One study compared MFS‐LE versus S‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (RR 1.39, 95% CI 0.42 to 4.65; RD 0.05, 95% CI –0.14 to 0.24; n = 57; Savini 2013).
One study compared MFS‐LE versus MS‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (RR 1.39, 95% CI 0.42 to 4.65; RD 0.05, 95% CI –0.14 to 0.24; n = 57; Savini 2013).
One study compared MFS‐LE versus OS‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (RR 1.07, 95% CI 0.35 to 3.30; RD 0.01, 95% CI –0.19 to 0.21; n = 56; Savini 2013).
One study compared OFS‐LE versus OS‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (RR 0.86, 95% CI 0.47 to 1.56; RD –0.04, 95% CI –0.19 to 0.11; n = 130; Pawlik 2014).
We did not combine all subgroups for this outcome due to the heterogeneous study population (Hsiao 2018), and due to the presence of the multiarm study.
Chronic lung disease (oxygen requirement at 36 weeks' postmenstrual age) (outcome 1.12)
Nine studies reported data in a format that could be used for the meta‐analysis (Analysis 1.12; Beken 2014; D'Ascenzo 2014; Hsiao 2018; Najm 2017; Pawlik 2014; Repa 2018; Savini 2013; Techasatid 2017; Vlaardingerbroek 2014). One was a five‐arm study contributing to multiple comparisons (Savini 2013).
1.12. Analysis.
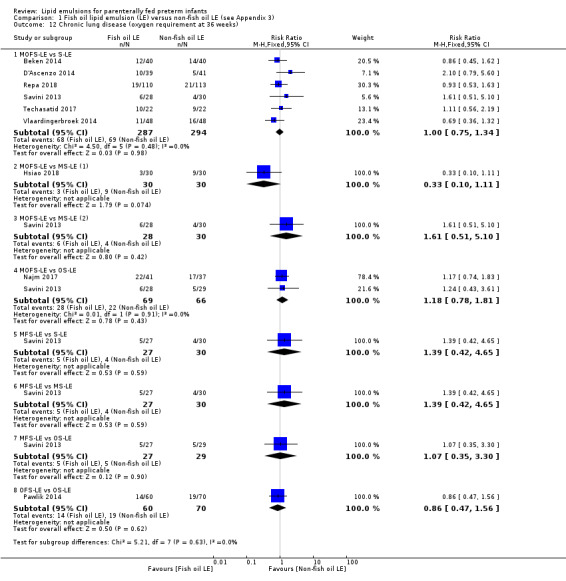
Comparison 1 Fish oil lipid emulsion (LE) versus non‐fish oil LE (see Appendix 3), Outcome 12 Chronic lung disease (oxygen requirement at 36 weeks).
In the studies comparing MOFS‐LE versus S‐LE, there were six studies (n = 581) with no statistically significant difference in any individual study. There was no statistically significant difference between groups in the meta‐analysis (typical RR 1.00, 95% CI 0.75 to 1.34; typical RD –0.00, 95% CI –0.07 to 0.07; n = 581; low‐quality evidence). There was no heterogeneity for RR or RD (I² = 0%).
In the studies comparing MOFS‐LE versus MS‐LE, there were two studies (n = 118) with no individual study showing statistically significant difference between groups (Hsiao 2018; Savini 2013). Hsiao 2018 reported improvement with MOFS‐LE with the upper CI for RD bordering on statistical significance (RR 0.33, 95% CI 0.10 to 1.11; typical RD –0.2, 95% CI –0.4 to –0.00; n = 60). The study by Hsiao 2018 had differences in the baseline population as only those preterm infants who required ventilation were considered eligible for the study.
Savini 2013 reported data with no statistically significant difference between groups (typical RR 1.61, 95% CI 0.51 to 5.10; typical RD 0.08, 95% CI –0.11 to 0.28; n = 58). The results of the two studies were clinically, visually (forest plot) and statistically heterogeneous with differences in population; therefore, we presented the results separately (Hsiao 2018; Savini 2013).
In the studies comparing MOFS‐LE versus OS‐LE, there were two studies with no statistically significant difference in any individual study (Najm 2017; Savini 2013). There was no statistically significant difference between groups in the meta‐analysis (typical RR 1.18, 95% CI 0.78 to 1.81; typical RD 0.06, 95% CI –0.09 to 0.22; n = 135). There was no heterogeneity for RR and RD (I² = 0%).
One study compared MFS‐LE versus S‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (RR 1.39, 95% CI 0.42 to 4.65; RD 0.05, 95% CI –0.14 to 0.24; n = 57; Savini 2013).
One study compared MFS‐LE versus MS‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (RR 1.39, 95% CI 0.42 to 4.65; RD 0.05, 95% CI –0.14 to 0.24; n = 57; Savini 2013).
One study compared MFS‐LE versus OS‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (RR 1.07, 95% CI 0.35 to 3.30; RD 0.01, 95% CI –0.19 to 0.21; n = 56; Savini 2013).
One study compared OFS‐LE versus OS‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (RR 0.86, 95% CI 0.47 to 1.56; RD –0.04, 95% CI –0.19 to 0.11; n = 130; Pawlik 2014).
We did not combine all subgroups for this outcome due to the heterogeneous study population (Hsiao 2018), and due to the presence of the multiarm study.
Duration of ventilation (days) (outcome 1.13)
Six studies reported data for in a format that could be used for the meta‐analysis.
Five studies compared MOFS‐LE versus S‐LE (Beken 2014; Repa 2018; Skouroliakou 2010; Techasatid 2017; Vlaardingerbroek 2014), with Techasatid 2017 showing statistically significant effect in favour of non‐fish oil LE (MD 12.00 days, 95% CI 0.39 to 23.61). There was no statistically significant difference between groups in the meta‐analysis (MD 0.08 days, 95% CI –1.56 to 1.73; n = 475; Analysis 1.13). There was low heterogeneity (I² = 48%).
1.13. Analysis.
Comparison 1 Fish oil lipid emulsion (LE) versus non‐fish oil LE (see Appendix 3), Outcome 13 Duration of ventilation (days).
One study compared MOFS‐LE versus MS‐LE, with statistically significant effect in favour of fish oil LE (MD –7.40 days, 95% CI –10.26 to –4.54; n = 60; Hsiao 2018). This study also had some differences in the baseline population as only those preterm infants who required ventilation were considered eligible for the study. This difference in the population can account for the higher duration of ventilation in the control group of the study.
There were only two subgroups for this outcome. When considering the subgroups together, there was high heterogeneity (I² = 82%; not shown in figure) and even higher heterogeneity for all studies in the whole group considered together (I² = 94.9%). Because of the presence of only two subgroups with high heterogeneity and large effect size in a single small study with baseline population differences (Hsiao 2018), we did not meta‐analyse both subgroups together and presented their results individually.
Duration of supplemental oxygen (days) (outcome 1.14)
Three studies (n = 200) reported data in a format that could be used for the meta‐analysis.
In the studies comparing MOFS‐LE versus S‐LE, there were two studies with no statistically significant difference in any individual study (Beken 2014; Tomsits 2010). There was no statistically significant difference between groups in the meta‐analysis (MD 0.47 days, 95% CI –2.01 to 2.95; n = 140; Analysis 1.14). There was no heterogeneity (I² = 0%).
1.14. Analysis.
Comparison 1 Fish oil lipid emulsion (LE) versus non‐fish oil LE (see Appendix 3), Outcome 14 Duration of supplemental oxygen (days).
One study compared MOFS‐LE versus MS‐LE, with statistically significant effect in favour of fish oil LE (MD –13.80 days, 95% CI –21.18 to –6.42; n = 60; Hsiao 2018). This study also had some differences in the baseline population as only those preterm infants who required ventilation were considered eligible for the study.
There were only two subgroups for this comparison. When considering both the subgroups together there was high heterogeneity (I² = 85%) and even higher heterogeneity for all studies in the group considered together (I² = 92.2%).
Because there were two subgroups with high heterogeneity and large effect size in a single small study which had baseline population differences (Hsiao 2018), we decided not to meta‐analyse the subgroups together and presented their results individually.
Duration of hospital stay (days) (outcome 1.15)
Eight studies (n = 812) reported duration of hospital stay (Beken 2014; Hsiao 2018; Pawlik 2014; Repa 2018; Skouroliakou 2010; Techasatid 2017; Uthaya 2016; Vlaardingerbroek 2014).
Six studies compared MOFS‐LE versus S‐LE, with no statistically significant difference in any individual study (Beken 2014; Repa 2018; Skouroliakou 2010; Techasatid 2017; Uthaya 2016; Vlaardingerbroek 2014). There was no statistically significant difference between groups in the meta‐analysis (MD –0.09 days, 95% CI –3.35 to 3.16; n = 622; Analysis 1.15). There was no heterogeneity for RR or RD (I² = 0%).
1.15. Analysis.
Comparison 1 Fish oil lipid emulsion (LE) versus non‐fish oil LE (see Appendix 3), Outcome 15 Duration of hospital stay (days).
One study compared MOFS‐LE versus MS‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (MD –3.35 days, 95% CI –17.13 to 10.43; n = 60; Hsiao 2018).
One study compared OFS‐LE versus OS‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (MD –1.80 days, 95% CI –9.72 to 6.12; n = 130; Pawlik 2014).
Considering all subgroups together, there was no statistically significant difference between the fish oil LE and non‐fish oil LE in the meta‐analysis (MD –0.48 days, 95% CI –3.42 to 2.46; 8 studies; n = 812). There was no heterogeneity among the subgroups (I² = 0%). The sensitivity analysis comparing evidence from studies with low and unclear risk of bias only versus all studies did not change the results significantly.
Culture‐positive sepsis (outcome 1.16)
Seven studies (n = 774) reported data on culture‐positive sepsis (Analysis 1.16; Beken 2014; Najm 2017; Pawlik 2014; Repa 2018; Skouroliakou 2016; Techasatid 2017; Uthaya 2016). One study reported sepsis as the cause of death in some infants (Najm 2017). These data were not used in the meta‐analysis as it was not clear whether the infants who died of other causes had sepsis during the study period. However, in sensitivity analysis (not shown) including or excluding the data of participants who died in this study did not change the results of the meta‐analysis.
1.16. Analysis.
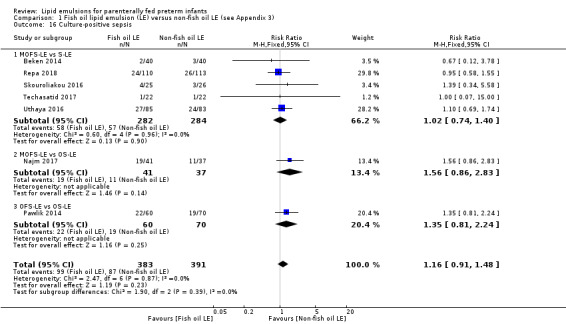
Comparison 1 Fish oil lipid emulsion (LE) versus non‐fish oil LE (see Appendix 3), Outcome 16 Culture‐positive sepsis.
Five studies compared MOFS‐LE versus S‐LE, with no statistically significant difference in any individual study (Beken 2014; Repa 2018; Skouroliakou 2016; Techasatid 2017; Uthaya 2016). There was no statistically significant difference between groups in the meta‐analysis (typical RR 1.02, 95% CI 0.74 to 1.40; typical RD 0.00, 95% CI –0.06 to 0.07; n = 566). There was no heterogeneity for RR or RD (I² = 0%).
One study compared MOFS‐LE versus OS‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (RR 1.56, 95% CI 0.86 to 2.83; RD 0.17, 95% CI –0.05 to 0.38; n = 78; Najm 2017).
One study compared OFS‐LE versus OS‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (RR 1.35, 95% CI 0.81 to 2.24; RD 0.10, 95% CI –0.07 to 0.26; n = 130; Pawlik 2014).
In the meta‐analysis of all subgroups, there was no statistically significant difference between groups (RR 1.16, 95% CI 0.91 to 1.48; RD 0.04, 95% CI –0.02 to 0.09; 7 studies; n = 774; low‐quality evidence). There was no heterogeneity among the subgroups for RR (I² = 0%) and low heterogeneity for RD (I² = 29.2%).
The sensitivity analysis comparing evidence from studies with low and unclear risk of bias only versus all studies did not change the results significantly.
Any sepsis (clinical or culture positive, or both) (outcome 1.17)
Twelve studies reported data in a format that could be used for the meta‐analysis (Analysis 1.17). One was a five‐arm study contributing to multiple comparisons (Savini 2013).
1.17. Analysis.
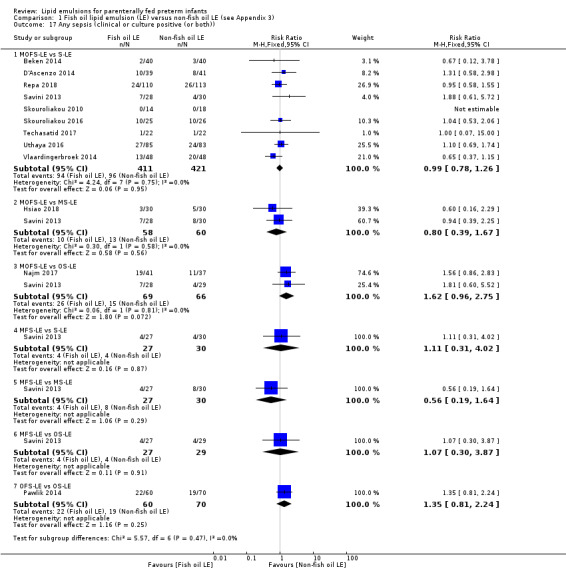
Comparison 1 Fish oil lipid emulsion (LE) versus non‐fish oil LE (see Appendix 3), Outcome 17 Any sepsis (clinical or culture positive (or both)).
Three studies used the criteria described by Stoll 2002, including Vlaardingerbroek 2014 which reported late‐onset septicaemia during the first 28 days, and two other studies reporting neonatal sepsis as positive blood culture or clinical syndrome with systemic signs and symptoms of infection and abnormalities of laboratory findings (D'Ascenzo 2014; Savini 2013). Skouroliakou 2016 provided a definition for clinical sepsis. Two studies reported on infections and infestations as a combined outcome and therefore the data could not be used in the meta‐analysis (Rayyan 2012; Tomsits 2010). Two studies described sepsis as late‐onset sepsis (Hsiao 2018; Techasatid 2017). Seven studies reported data on culture‐positive sepsis (Beken 2014; Najm 2017; Pawlik 2014; Repa 2018; Skouroliakou 2016; Techasatid 2017; Uthaya 2016). One study reported separately sepsis in the cause of death of some infants (Najm 2017). These data were not used in the meta‐analysis as it was not clear whether infants who died of other causes had sepsis (although unlikely). However, in sensitivity analysis (not shown) including or excluding the data of participants who died in this study did not change the results of the meta‐analysis.
Nine studies compared MOFS‐LE versus S‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups in any individual study (Beken 2014; D'Ascenzo 2014; Repa 2018; Savini 2013; Skouroliakou 2010; Skouroliakou 2016; Techasatid 2017; Uthaya 2016; Vlaardingerbroek 2014). There was no statistically significant difference between groups in the meta‐analysis (typical RR 0.99, 95% CI 0.78 to 1.26; typical RD –0.00, 95% CI –0.06 to 0.05; n = 832). There was no heterogeneity for RR or RD (I² = 0%).
Two studies compared MOFS‐LE versus MS‐LE, with no statistically significant difference in any individual study (Hsiao 2018; Savini 2013). There was no statistically significant difference between groups in the meta‐analysis (typical RR 0.80, 95% CI 0.39 to 1.67; typical RD –0.04, 95% CI –0.18 to 0.10; n = 118). There was no heterogeneity for RR or RD (I² = 0%).
Two studies compared MOFS‐LE versus OS‐LE, with no statistically significant difference in any individual study (Najm 2017; Savini 2013). There was no statistically significant difference between groups in the meta‐analysis (typical RR 1.62, 95% CI 0.96 to 2.75; typical RD 0.14, 95% CI –0.01 to 0.29; n = 135). There was no heterogeneity for RR or RD (I² = 0%).
One study compared MFS‐LE versus S‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (RR 1.11, 95% CI 0.31 to 4.02; RD 0.01, 95% CI –0.17 to 0.20; n = 57; Savini 2013).
One study compared MFS‐LE versus MS‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (RR 0.56, 95% CI 0.19 to 1.64; RD –0.12, 95% CI –0.33 to 0.09; n = 57; Savini 2013).
One study compared MFS‐LE versus OS‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (RR 1.07, 95% CI 0.30 to 3.87; RD 0.01, 95% CI –0.17 to 0.19; n = 56; Savini 2013).
One study compared OFS‐LE versus OS‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (RR 1.35, 95% CI 0.81 to 2.24; RD 0.10, 95% CI –0.07 to 0.26; n = 130; Pawlik 2014).
There was no statistically significant difference between groups when all the subgroups were combined and combining all arms of Savini 2013 to account for unit of analysis error (analysis not shown).
Necrotising enterocolitis (stage 2 or greater) (outcome 1.18)
Ten studies reported data in a format that could be used for the meta‐analysis (Analysis 1.18; Beken 2014; D'Ascenzo 2014; Hsiao 2018; Najm 2017; Pawlik 2014; Repa 2018; Savini 2013; Techasatid 2017; Uthaya 2016; Vlaardingerbroek 2014). One was a five‐arm study contributing to multiple comparisons (Savini 2013).
1.18. Analysis.
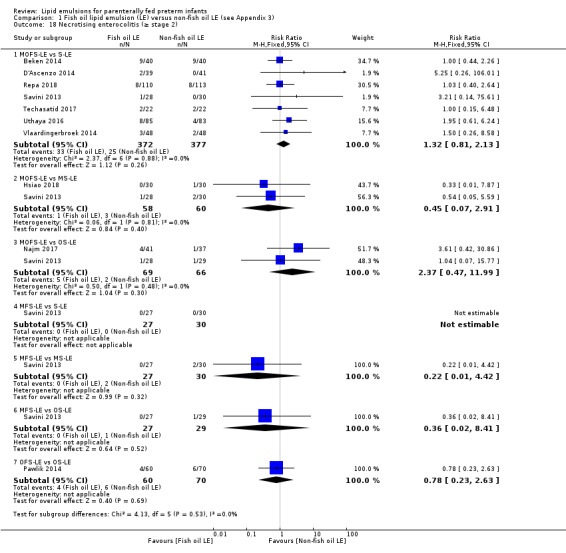
Comparison 1 Fish oil lipid emulsion (LE) versus non‐fish oil LE (see Appendix 3), Outcome 18 Necrotising enterocolitis (≥ stage 2).
Most studies appeared to use the Bell's classification; however, six studies explicitly stated and reported NEC Bell's stage 2 or 3 (D'Ascenzo 2014; Najm 2017; Repa 2018; Savini 2013; Techasatid 2017; Vlaardingerbroek 2014). Beken 2014 reported NEC stage 2 or greater (exact classification not mentioned). Two studies included in the meta‐analysis did not report stage of NEC and excluding them did not make any significant difference to results (Hsiao 2018; Uthaya 2016). One study also reported separately NEC in the cause of death of some infants (Najm 2017). These data were not used in the meta‐analysis as it was not clear whether infants who died of other causes had NEC previously. However in a sensitivity analysis (not shown) including or excluding the data of participants who died in this study did not change the results of the meta‐analysis.
Seven studies compared MOFS‐LE versus S‐LE, with no statistically significant difference in any individual study. There was no statistically significant difference between groups in the meta‐analysis (typical RR 1.32, 95% CI 0.81 to 2.13; typical RD 0.02, 95% CI –0.02 to 0.06; n = 749). There was no heterogeneity for RR or RD (I² = 0%).
Two studies compared MOFS‐LE versus MS‐LE, with no statistically significant difference in any individual study (Hsiao 2018; Savini 2013). There was no statistically significant difference between groups in the meta‐analysis (typical RR 0.45, 95% CI 0.07 to 2.91; typical RD –0.03, 95% CI –0.10 to 0.04; n = 118). There was no heterogeneity for RR or RD (I² = 0%).
Two studies compared MOFS‐LE versus OS‐LE, with no statistically significant difference in any individual study (Najm 2017; Savini 2013). There was no statistically significant difference between groups in the meta‐analysis (typical RR 2.37, 95% CI 0.47 to 11.99; typical RD 0.04, 95% CI –0.03 to 0.11; n = 135). There was no heterogeneity for RR or RD (I² = 0%).
One study compared MFS‐LE versus S‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (RR: not estimable, RD 0.00, 95% CI –0.07 to 0.07; n = 57; Savini 2013).
One study compared MFS‐LE versus MS‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (RR 0.22, 95% CI 0.01 to 4.42; RD –0.07, 95% –0.17 to 0.04; n = 57; Savini 2013).
One study compared MFS‐LE versus OS‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (RR 0.36, 95% CI 0.02 to 8.41; RD –0.03, 95% CI –0.13 to 0.06; n = 56; Savini 2013).
One study compared OFS‐LE versus OS‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (RR 0.78, 95% CI 0.23 to 2.63; RD –0.02, 95% CI –0.11 to 0.07; n = 130; Pawlik 2014).
There was no statistically significant difference between groups when all the subgroups were combined and combining all arms of Savini 2013 to account for unit of analysis error (analysis not shown). The sensitivity analysis comparing evidence with low and unclear risk of bias only versus all studies did not change the results significantly.
Intraventricular haemorrhage (grade III to IV) (outcome 1.19)
Eight studies reported IVH grade III to IV with seven studies reporting data for grade III‐IV intraventricular haemorrhage (Analysis 1.19). One study reported IVH grade II to IV and therefore was not included in this outcome (Pawlik 2014).
1.19. Analysis.
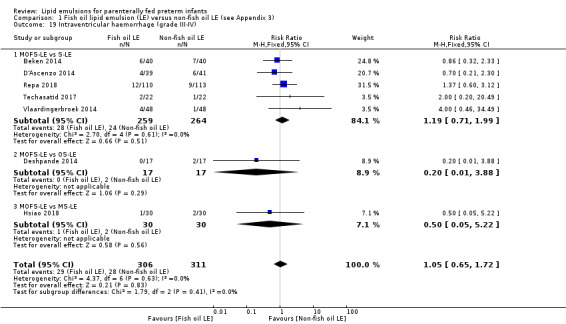
Comparison 1 Fish oil lipid emulsion (LE) versus non‐fish oil LE (see Appendix 3), Outcome 19 Intraventricular haemorrhage (grade III‐IV).
Five studies compared MOFS‐LE versus S‐LE, with no statistically significant difference in any individual study (Beken 2014; D'Ascenzo 2014; Repa 2018; Vlaardingerbroek 2014; Techasatid 2017). There was no statistically significant difference between groups in the meta‐analysis (typical RR 1.19, 95% CI 0.71 to 1.99; typical RD 0.02, 95% CI –0.03 to 0.07; n = 523). There was no heterogeneity for RR or RD (I² = 0%).
One study compared MOFS‐LE versus OS‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (RR 0.20, 95% CI 0.01 to 3.88; RD –0.12, 95% CI –0.29 to 0.06; n = 34; Deshpande 2014).
One study compared MOFS‐LE versus MS‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (RR 0.50, 95% CI 0.05 to 5.22; RD –0.03, 95% CI –0.14 to 0.08; n = 60; Hsiao 2018).
Combining all subgroups together, there was no statistically significant difference between fish oil LE and non‐fish oil LE (typical RR 1.05, 95% CI 0.65 to 1.72; typical RD 0.00, 95% CI –0.04 to 0.05; 7 studies; n = 617). There was no heterogeneity for RR (I² = 0%) or RD (20%).
Periventricular leukomalacia (outcome 1.20)
Three studies compared MOFS‐LE versus S‐LE for PVL (Analysis 1.20). Vlaardingerbroek 2014 mentioned the use of classification described by de Vries 1992, and D'Ascenzo 2014 mentioned the use of "international classification" and Repa 2018 offered no definition.
1.20. Analysis.
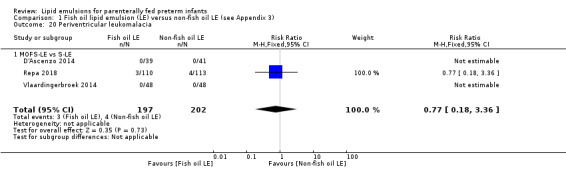
Comparison 1 Fish oil lipid emulsion (LE) versus non‐fish oil LE (see Appendix 3), Outcome 20 Periventricular leukomalacia.
There were no statistically significant difference in any individual study. There was no statistically significant difference between groups in the meta‐analysis (typical RR 0.77, 95% CI 0.18 to 3.36; typical RD 0.00, 95% CI –0.03 to 0.02; n = 399). There was no heterogeneity for RR or RD (I² = 0%).
Any patent ductus arteriosus (outcome 1.21)
Eight studies reported data in a format that could be used for the meta‐analysis (Analysis 1.21). One was a five‐arm study contributing to multiple comparisons (Savini 2013).
1.21. Analysis.
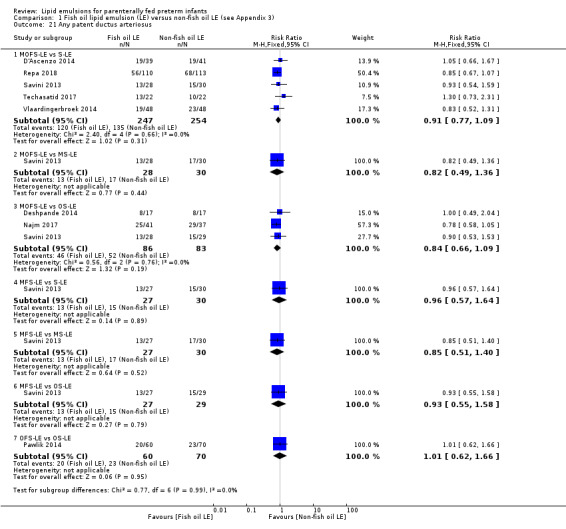
Comparison 1 Fish oil lipid emulsion (LE) versus non‐fish oil LE (see Appendix 3), Outcome 21 Any patent ductus arteriosus.
Three studies reported on significant PDA requiring treatment (Pawlik 2014; Repa 2018; Vlaardingerbroek 2014). Two studies reported the number of infants with PDA in each of the intervention arms but did not report how many of these infants required treatment (D'Ascenzo 2014; Savini 2013).
Five studies compared MOFS‐LE versus S‐LE, with no statistically significant difference in any individual study (D'Ascenzo 2014; Repa 2018; Savini 2013; Techasatid 2017; Vlaardingerbroek 2014). There was no statistically significant difference between groups in the meta‐analysis (typical RR 0.91, 95% CI 0.77 to 1.09; typical RD –0.05, 95% CI –0.13 to 0.04; n = 501). There was no heterogeneity for RR or RD (I² = 0%).
One study compared MOFS‐LE versus MS‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (typical RR 0.82, 95% CI 0.49 to 1.36; typical RD –0.10, 95% –0.36 to 0.15; n = 58; Savini 2013).
Three studies compared MOFS‐LE versus OS‐LE, with no statistically significant difference in any individual study (Deshpande 2014; Najm 2017; Savini 2013). There was no statistically significant difference between groups in the meta‐analysis (typical RR 0.84, 95% CI 0.66 to 1.09; typical RD –0.10, 95% CI –0.24 to 0.05; n = 169). There was no heterogeneity for RR or RD (I² = 0%).
One study compared MFS‐LE versus S‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (RR 0.96, 95% CI 0.57 to 1.64; RD –0.02, 95% CI –0.28 to 0.24; n = 57; Savini 2013).
One study compared MFS‐LE versus MS‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (RR 0.85, 95% CI 0.51 to 1.40; RD –0.09, 95% CI –0.34 to 0.17; n = 57; Savini 2013).
One study compared MFS‐LE versus OS‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (RR 0.93, 95% CI 0.55 to 1.58; RD –0.04, 95% CI –0.30 to 0.23; n = 56; Savini 2013).
One study compared OFS‐LE versus OS‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (RR 1.01, 95% CI 0.62 to 1.66; RD 0.00, 95% CI –0.16 to 0.17; n = 130; Pawlik 2014).
There was no statistically significant difference between groups when all the subgroups were combined (adjusting for Savini 2013 for unit of analysis error) (analysis not shown). The sensitivity analysis comparing evidence from studies with low and unclear risk of bias only versus all studies did not change the results significantly.
Significant patent ductus arteriosus requiring treatment (outcome 1.22)
Six studies (n = 605) reported data in a format that could be used for the meta‐analysis (Analysis 1.22; Deshpande 2009; Najm 2017; Pawlik 2014; Repa 2018; Techasatid 2017; Vlaardingerbroek 2014).
1.22. Analysis.
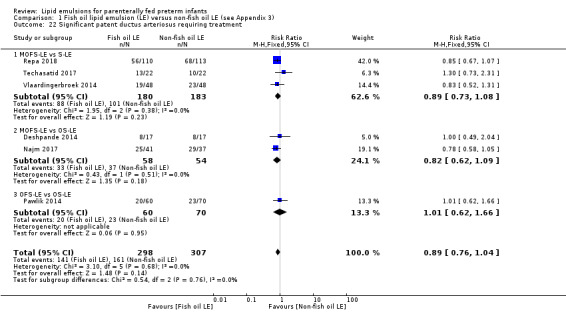
Comparison 1 Fish oil lipid emulsion (LE) versus non‐fish oil LE (see Appendix 3), Outcome 22 Significant patent ductus arteriosus requiring treatment.
Three studies compared MOFS‐LE versus S‐LE, with no statistically significant difference in any individual study (Repa 2018; Techasatid 2017; Vlaardingerbroek 2014). There was no statistically significant difference between groups in the meta‐analysis (typical RR 0.89, 95% CI 0.73 to 1.08; typical RD –0.06, 95% CI –0.16 to 0.04; n = 363). There was no heterogeneity for RR (I² = 0%) or RD (1%).
Two studies compared MOFS‐LE versus OS‐LE, with no statistically significant difference in any individual study (Deshpande 2009; Najm 2017). There was no statistically significant difference between groups in the meta‐analysis (typical RR 0.82, 95% CI 0.62 to 1.09; typical RD –0.12, 95% CI –0.29 to 0.05; n = 112). There was no heterogeneity for RR or RD (I² = 0%).
One study compared OFS‐LE versus OS‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (RR 1.01, 95% CI 0.62 to 1.66; RD 0.00, 95% CI –0.16 to 0.17; n = 130; Pawlik 2014).
In the meta‐analysis of all subgroups, there was no statistically significant difference between the fish oil LE and non‐fish oil LE for the outcome of significant PDA (typical RR 0.89, 95% CI 0.76 to 1.04; typical RD –0.06, 95% CI –0.14 to 0.02; 6 studies; n = 605). There was no heterogeneity among the subgroups (I² = 0%).
The sensitivity analysis comparing evidence from studies with low and unclear risk of bias only versus all studies did not change the results significantly.
Duration of phototherapy (days) (outcome 1.23)
One study compared MOFS‐LE versus S‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (MD 0.00 days, 95% CI –2.57 to 2.57; n = 32; Analysis 1.23; Skouroliakou 2010).
1.23. Analysis.
Comparison 1 Fish oil lipid emulsion (LE) versus non‐fish oil LE (see Appendix 3), Outcome 23 Duration of phototherapy (days).
Hypertriglyceridaemia (outcome 1.24)
The review protocol described hypertriglyceridaemia as TG levels greater than 200 mg/dL (2.25 mmol/L) (Kapoor 2018). However, due to the differential definitions used, we considered all cut‐offs for the meta‐analysis. Five studies (n = 697) reported data in a format that could be used for the meta‐analysis (Analysis 1.24).
1.24. Analysis.
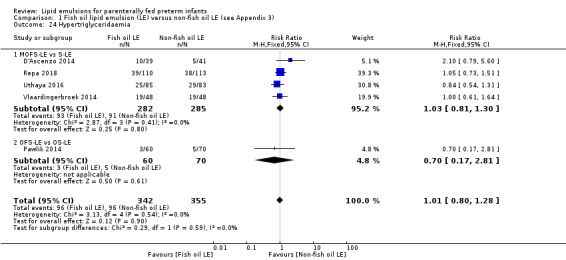
Comparison 1 Fish oil lipid emulsion (LE) versus non‐fish oil LE (see Appendix 3), Outcome 24 Hypertriglyceridaemia.
Two studies defined hypertriglyceridaemia as greater than 250 mg/dL (2.82 mmol/L; D'Ascenzo 2014; Vlaardingerbroek 2014). Two studies only reported the mean TG levels (Rayyan 2012; Tomsits 2010). Two studies reported the percentage of infants with hypertriglyceridaemia (D'Ascenzo 2014; Vlaardingerbroek 2014). One study reported TGs greater than 2.5 mmol/L (Uthaya 2016). No study reported any significant difference in hypertriglyceridaemia between the two groups.
Four studies compared MOFS‐LE versus S‐LE, with no statistically significant difference in any individual study (D'Ascenzo 2014; Repa 2018; Uthaya 2016; Vlaardingerbroek 2014). There was no statistically significant difference between groups in the meta‐analysis (typical RR 1.03, 95% CI 0.81 to 1.30; typical RD 0.01, 95% CI –0.07 to 0.09; n = 567). There was no heterogeneity for RR or RD (I² = 0%).
One study compared OFS‐LE versus OS‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (RR 0.70, 95% CI 0.17 to 2.81; RD –0.02, 95% CI –0.10 to 0.06; n = 130; Pawlik 2014).
In the meta‐analysis of all subgroups, there was no statistically significant difference between groups (typical RR 1.01, 95% CI 0.80 to 1.28; typical RD 0.00, 95% CI –0.06 to 0.07; 5 studies; n = 697). There was no heterogeneity among the subgroups (I² = 0%).
The sensitivity analysis comparing evidence with low and unclear risk of bias only versus all studies did not change the results significantly.
Hyperglycaemia (outcome 1.25)
The review protocol described hyperglycaemia as blood sugar level greater than 8.3 mmol/L (150 mg/dL; Sinclair 2011) (Kapoor 2018). However, due to the different definitions used, we considered all cut‐offs for the meta‐analysis. Three studies contributed data in the subgroup MOFS‐LE versus S‐LE, though this outcome was mentioned in four study reports (Analysis 1.25). Beken 2014 did not mention the cut‐off for hyperglycaemia and Skouroliakou 2010 described the cut‐off as 200 mg/dL (11.1 mmol/L). Rayyan 2012 presented data as a composite outcome with other metabolic problems and therefore could not be included in the meta‐analysis. One study reported infants with high glucose above 15 mmol/L (Uthaya 2016).
1.25. Analysis.
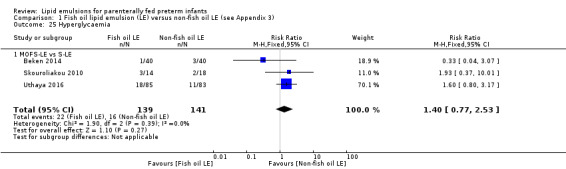
Comparison 1 Fish oil lipid emulsion (LE) versus non‐fish oil LE (see Appendix 3), Outcome 25 Hyperglycaemia.
There were no statistically significant differences in any individual study. There was no statistically significant difference between groups in the meta‐analysis (typical RR 1.40, 95% CI 0.77 to 2.53; typical RD 0.04, 95% CI –0.03 to 0.12; 3 studies; n = 280). There was no heterogeneity among the studies for RR (I² = 0%) and moderate heterogeneity for RD (54%) in the subgroup.
Hypoglycaemia (outcome 1.26)
The review protocol described hypoglycaemia as blood sugar level less than 2.6 mmol/L (Kapoor 2018). We considered all cut‐offs for the meta‐analysis. Two studies reported hypoglycaemia (Analysis 1.26). Uthaya 2016 reported on infants with glucose levels less than 2.6 mmol/L; however, Beken 2014 did not provide the definition or timing of the hypoglycaemia episodes. Both studies compared MOFS‐LE versus S‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups in the meta‐analysis (typical RR 1.14, 95% CI 0.77 to 1.69; typical RD 0.03, 95% CI –0.07 to 0.14; n = 248; Analysis 1.26). There was moderate heterogeneity for RR (I² = 54%) and high heterogeneity for RD (83%).
1.26. Analysis.
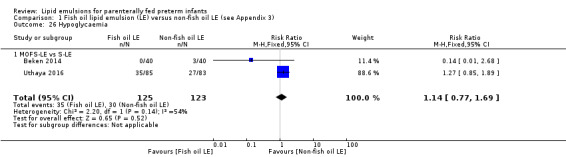
Comparison 1 Fish oil lipid emulsion (LE) versus non‐fish oil LE (see Appendix 3), Outcome 26 Hypoglycaemia.
Head growth velocity (outcome 1.27)
In the subgroup MOFS‐LE versus S‐LE, two studies (n = 140) reported data on |head growth velocity with no statistically significant difference in any individual study (Techasatid 2017; Vlaardingerbroek 2014). Three other studies mentioned no differences in the groups (Deshpande 2009; Deshpande 2014; Skouroliakou 2010), and another study provided z scores that could not be used in meta‐analysis (D'Ascenzo 2011). There was no statistically significant difference between groups in the meta‐analysis (MD 0.00 cm/week, 95% CI –0.08 to 0.08; Analysis 1.27). There was no heterogeneity (I² = 0%).
1.27. Analysis.
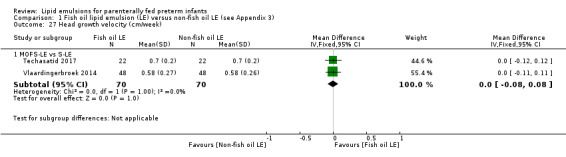
Comparison 1 Fish oil lipid emulsion (LE) versus non‐fish oil LE (see Appendix 3), Outcome 27 Head growth velocity (cm/week).
Length (cm/week) (outcome 1.28)
Several studies reported no group differences in length velocity between groups (Savini 2013; Skouroliakou 2010; Tomsits 2010); however, most studies provide no data or provided data in a format that was not suitable for meta‐analysis (e.g. differences in length at the end of study, z scores (D'Ascenzo 2011) or leg length velocity (Vlaardingerbroek 2014)).
One study compared MOFS‐LE versus S‐LE in terms of length velocity (with no statistically significant difference between groups (MD 0.10 cm/week, 95% CI –0.02 to 0.22; n = 44; Techasatid 2017; Analysis 1.28).
1.28. Analysis.
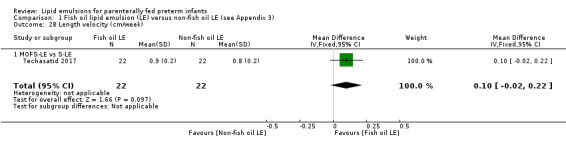
Comparison 1 Fish oil lipid emulsion (LE) versus non‐fish oil LE (see Appendix 3), Outcome 28 Length velocity (cm/week).
Body composition: intrahepatocellular lipid content (outcome 1.29)
One study compared MOFS‐LE versus S‐LE and reported data on IHCL content with no statistically significant difference between groups (MD 0.03, 95% CI –0.17 to 0.23; n = 132; Uthaya 2016; Analysis 1.29).
1.29. Analysis.
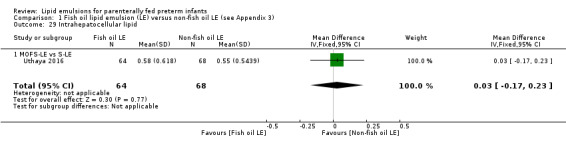
Comparison 1 Fish oil lipid emulsion (LE) versus non‐fish oil LE (see Appendix 3), Outcome 29 Intrahepatocellular lipid.
Body composition: non‐adipose tissue mass (outcome 1.30)
One study compared MOFS‐LE versus S‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (MD 24.2, 95% CI –133.14 to 181.54; n = 133; Uthaya 2016; Analysis 1.30).
1.30. Analysis.
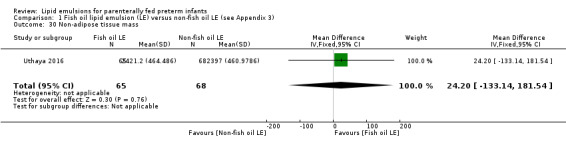
Comparison 1 Fish oil lipid emulsion (LE) versus non‐fish oil LE (see Appendix 3), Outcome 30 Non‐adipose tissue mass.
Conjugated bilirubin levels (outcome 1.31)
Ten studies reported data in a format that could be used for meta‐analysis. One was a five‐arm study contributing to multiple comparisons (Savini 2013). The studies reported the conjugated bilirubin values at different time points.
Eight studies compared MOFS‐LE versus S‐LE, with no statistically significant difference in any individual study (Beken 2014; D'Ascenzo 2014; Rayyan 2012; Repa 2018; Savini 2013; Skouroliakou 2016; Techasatid 2017; Vlaardingerbroek 2014). There was no statistically significant difference between groups in the meta‐analysis (MD –0.48 µmol/L, 95% CI –1.16 to 0.19; n = 673; low‐quality evidence). There was low heterogeneity (I² = 36%).
One study compared MOFS‐LE versus MS‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (MD 0.35 µmol/L, 95% CI –3.65 to 4.35; n = 58; Savini 2013).
Two studies compared MOFS‐LE versus OS‐LE, with no statistically significant difference in any individual study (Deshpande 2014; Savini 2013). There was no statistically significant difference between groups in the meta‐analysis (MD –1.68 µmol/L, 95% CI –4.07 to 0.71; n = 91). There was no heterogeneity (I² = 0%).
One study compared MFS‐LE versus S‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (MD 0.72 µmol/L, 95% CI –3.86 to 5.30; n = 57; Savini 2013).
Two studies compared MFS‐LE versus MS‐LE, with no statistically significant difference in any individual study (D'Ascenzo 2011; Savini 2013). There was no statistically significant difference between groups in the meta‐analysis (MD 2.15 µmol/L, 95% CI –0.67 to 4.98; n = 105). There was no heterogeneity (I² = 0%).
One study compared MFS‐LE versus OS‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (MD –1.16 µmol/L, 95% CI –6.13 to 3.81; n = 56; Savini 2013).
In a meta‐analysis of all fish oil LE versus non‐fish oil LE, there was no statistically significant difference in the levels of conjugated bilirubin levels in the two groups (MD –0.42 µmol/L, 95% CI –1.06 to 0.22; 10 studies; n = 841; low‐quality evidence; Figure 6).
6.
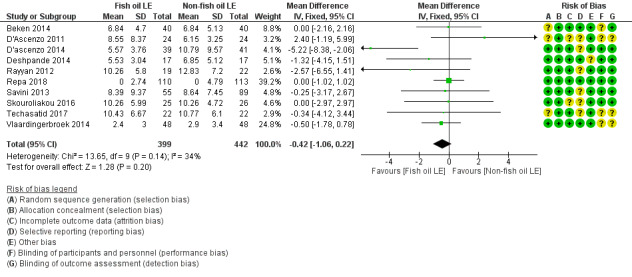
Forest plot of comparison: 1 Fish oil lipid emulsion (LE) versus non‐fish oil LE, outcome: 1.31 Conjugated bilirubin levels (µmol/L): all subgroups combined.
Fish oil LE versus another fish oil LE in preterm infants (Comparison 2)
One study compared a fish oil LE to another fish oil LE (MOFS‐LE versus MFS‐LE) in the population of preterm infants (Savini 2013). This was a five‐arm study contributing to multiple comparisons and all the data refer to the MOFS‐LE and MFS‐LE arms of this study.
Primary outcomes
Days to regain birth weight (outcome 2.1)
There was no statistically significant difference between MOFS‐LE and MFS‐LE for days to regain birth weight (MD 2.00 days, 95% CI –0.64 to 4.64; n = 55; Analysis 2.1).
2.1. Analysis.
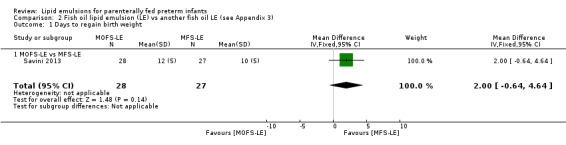
Comparison 2 Fish oil lipid emulsion (LE) vs another fish oil LE (see Appendix 3), Outcome 1 Days to regain birth weight.
Growth rate (outcome 2.2)
There was no statistically significant difference between MOFS‐LE and MFS‐LE for rate of weight gain (MD 4.00 g/kg/day, 95% CI –2.03 to 10.03; n = 55; low‐quality evidence; Analysis 2.2).
2.2. Analysis.
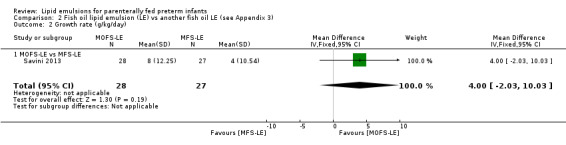
Comparison 2 Fish oil lipid emulsion (LE) vs another fish oil LE (see Appendix 3), Outcome 2 Growth rate (g/kg/day).
PNALD/cholestasis (conjugated bilirubin 2 mg/dL or greater) (outcome 2.3)
There was no statistically significant difference between MOFS‐LE and MFS‐LE for cholestasis (RR 0.96, 95% CI 0.06 to 14.65; RD 0.00, 95% CI –0.10 to 0.10; n = 55; low‐quality evidence; Analysis 2.3).
2.3. Analysis.
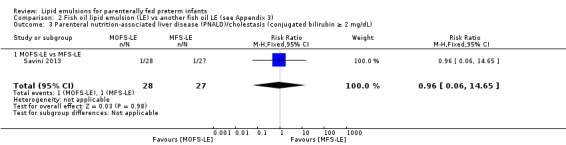
Comparison 2 Fish oil lipid emulsion (LE) vs another fish oil LE (see Appendix 3), Outcome 3 Parenteral nutrition‐associated liver disease (PNALD)/cholestasis (conjugated bilirubin ≥ 2 mg/dL).
PNALD/cholestasis (any definition) (outcome 2.4)
There was no statistically significant difference between MOFS‐LE and MFS‐LE for cholestasis (RR 0.96, 95% CI 0.06 to 14.65; RD 0.00, 95% CI –0.10 to 0.10; n = 55; Analysis 2.4).
2.4. Analysis.
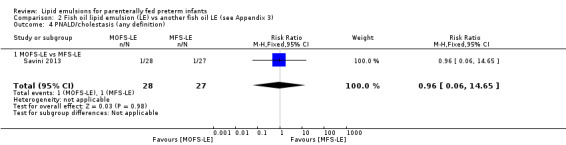
Comparison 2 Fish oil lipid emulsion (LE) vs another fish oil LE (see Appendix 3), Outcome 4 PNALD/cholestasis (any definition).
Secondary outcomes
Death before discharge (outcome 2.5)
There was no statistically significant difference between MOFS‐LE and MFS‐LE for death before discharge (RR 1.00, 95% CI 0.15 to 6.64; RD 0.00, 95% CI –0.13 to 0.13; n = 60; low‐quality evidence; Analysis 2.5).
2.5. Analysis.
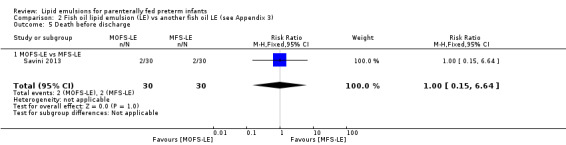
Comparison 2 Fish oil lipid emulsion (LE) vs another fish oil LE (see Appendix 3), Outcome 5 Death before discharge.
Chronic lung disease (oxygen requirement at 36 weeks' postmenstrual age) (outcome 2.6)
There was no statistically significant difference between MOFS‐LE and MFS‐LE for CLD, which was defined in the study as physiological need for oxygen at 36 weeks' postmenstrual age (RR 1.16, 95% CI 0.40 to 3.35; RD 0.03, 95% CI –0.18 to 0.24; n = 55; low‐quality evidence; Analysis 2.6).
2.6. Analysis.
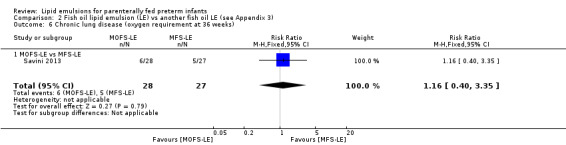
Comparison 2 Fish oil lipid emulsion (LE) vs another fish oil LE (see Appendix 3), Outcome 6 Chronic lung disease (oxygen requirement at 36 weeks).
Any sepsis (clinical or culture positive, or both) (outcome 2.7)
There was no statistically significant difference between MOFS‐LE and MFS‐LE for any sepsis (RR 1.69, 95% CI 0.56 to 5.11; RD 0.10, 95% CI –0.11 to 0.31; n = 55; low‐quality evidence; Analysis 2.7).
2.7. Analysis.
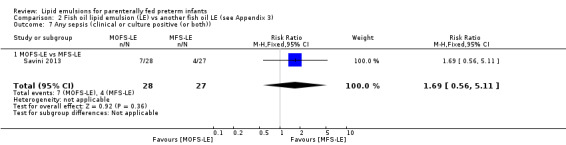
Comparison 2 Fish oil lipid emulsion (LE) vs another fish oil LE (see Appendix 3), Outcome 7 Any sepsis (clinical or culture positive (or both)).
Necrotising enterocolitis stage 2 or greater (outcome 2.8)
There was no statistically significant difference between MOFS‐LE and MFS‐LE for NEC stage 2 or more (RR 2.90, 95% CI 0.12 to 68.15; RD 0.04, 95% CI –0.06 to 0.13; n = 55; low‐quality evidence; Analysis 2.8).
2.8. Analysis.
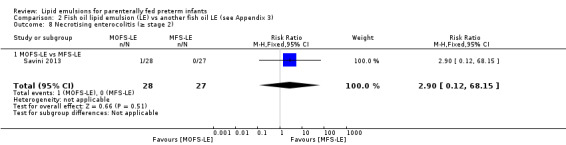
Comparison 2 Fish oil lipid emulsion (LE) vs another fish oil LE (see Appendix 3), Outcome 8 Necrotising enterocolitis (≥ stage 2).
Any patent ductus arteriosus (outcome 2.9)
There was no statistically significant difference between MOFS‐LE and MFS‐LE for any PDA (typical RR 0.96, 95% CI 0.55 to 1.69; typical RD –0.02, 95% CI –0.28 to 0.25; n = 55; low‐quality evidence; Analysis 2.9).
2.9. Analysis.
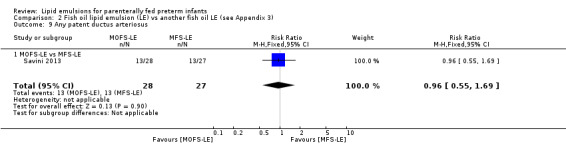
Comparison 2 Fish oil lipid emulsion (LE) vs another fish oil LE (see Appendix 3), Outcome 9 Any patent ductus arteriosus.
Conjugated bilirubin levels (µmol/L) (outcome 2.10)
There was no statistically significant difference between MOFS‐LE and MFS‐LE for mean conjugated bilirubin levels (MD –1.40 µmol/L, 95% CI –6.40 to 3.60; n = 55; low‐quality evidence; Analysis 2.10).
2.10. Analysis.
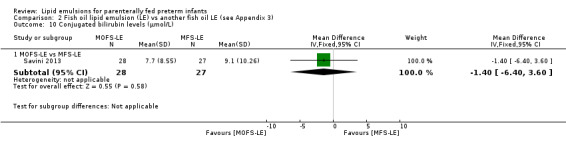
Comparison 2 Fish oil lipid emulsion (LE) vs another fish oil LE (see Appendix 3), Outcome 10 Conjugated bilirubin levels (µmol/L).
Alternative‐LE versus S‐LE in preterm infants (Comparison 3)
Ten studies (n = 536) compared an alternative‐LE versus S‐LE. There were three subgroups: MS‐LE, OS‐LE or BS‐LE to S‐LE in pair‐wise comparisons:
MS‐LE versus S‐LE: four studies (n = 132) (Lehner 2006; Roggero 2010; Rubin 1994; Savini 2013). Three studies did not report data usable for any of the outcomes (Lehner 2006; Roggero 2010; Rubin 1994);
OS‐LE versus S‐LE: eight studies (n = 430) (Demirel 2011; Deshpande 2009; Gawecka 2008b; Göbel 2003; Köksal 2011; Roggero 2010; Savini 2013; Wang 2016);
BS‐LE versus S‐LE: one study (n = 34) (Rubin 1994). This study did not report data on any of the outcomes of the review
Primary outcomes
Days to regain birth weight (outcome 3.1)
Three studies reported data in a format that could be used for the meta‐analysis (Analysis 3.1; Köksal 2011; Savini 2013; Wang 2016). One was a five‐arm study contributing to multiple comparisons (Savini 2013).
3.1. Analysis.
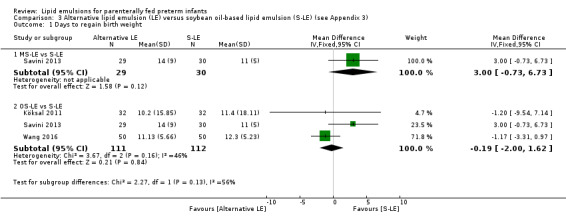
Comparison 3 Alternative lipid emulsion (LE) versus soybean oil‐based lipid emulsion (S‐LE) (see Appendix 3), Outcome 1 Days to regain birth weight.
One study compared MS‐LE versus S‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (MD 3.00 days, 95% CI –0.73 to 6.73; n = 59; Savini 2013).
Three studies compared OS‐LE versus S‐LE, with no statistically significant difference in any individual study (Köksal 2011; Savini 2013; Wang 2016). There was no statistically significant difference between OS‐LE and S‐LE in the meta‐analysis (MD –0.19 days, 95% CI –2.00 to 1.62; n = 223). There was low heterogeneity (I² = 46%).
Growth rate (outcome 3.2)
Two studies reported data in a format that could be used for the meta‐analysis (Analysis 3.2; Savini 2013, unpublished data from Köksal 2011). One was a five‐arm study contributing to multiple comparisons (Savini 2013).
3.2. Analysis.
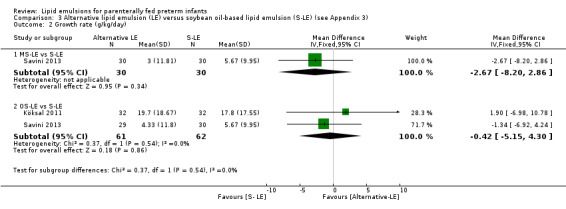
Comparison 3 Alternative lipid emulsion (LE) versus soybean oil‐based lipid emulsion (S‐LE) (see Appendix 3), Outcome 2 Growth rate (g/kg/day).
Savini 2013 provided weekly mean growth rates with SDs for the first three weeks which was pooled by 'lipid type' to give the mean growth rate over three weeks. Demirel 2011 reported mean with SD of the initial weight and the weight on day 14; however, the data on growth rate (g/kg/day) were not available. Wang 2016 provided the mean growth rate in g/day and mean birth weight; however, the SD of the growth rate in g/kg/day could not be imputed due to lack of data on covariance.
One study compared MS‐LE versus S‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (MD –2.67 g/kg/day, 95% CI –8.20 to 2.86; n = 60; low‐quality evidence; Savini 2013).
In the studies comparing OS‐LE versus S‐LE, two studies provided data usable in the meta‐analysis, with no statistically significant difference in any individual study. There was no statistically significant difference between the OS‐LE and S‐LE in the meta‐analysis (MD –0.42 g/kg/day, 95% CI –5.15 to 4.30; n = 123; low‐quality evidence). There was no heterogeneity (I² = 0%).
PNALD/cholestasis (conjugated bilirubin 2 mg/dL or greater) (outcome 3.3)
Two studies used definition of cholestasis as conjugated bilirubin 2 mg/dL or greater and reported data in a format that could be used for the meta‐analysis (Analysis 3.3; Savini 2013; Wang 2016).
3.3. Analysis.
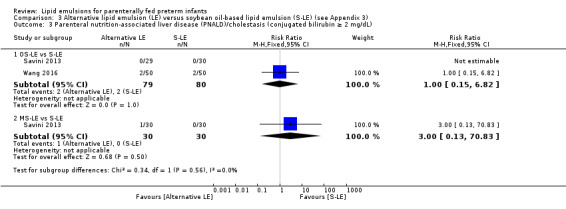
Comparison 3 Alternative lipid emulsion (LE) versus soybean oil‐based lipid emulsion (S‐LE) (see Appendix 3), Outcome 3 Parenteral nutrition‐associated liver disease (PNALD)/cholestasis (conjugated bilirubin ≥ 2 mg/dL).
Two studies compared OS‐LE versus S‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups in the meta‐analysis (typical RR 1.00, 95% CI 0.15 to 6.82; typical RD 0.00, 95% CI –0.05 to 0.05; n = 159; low‐quality evidence; Savini 2013; Wang 2016). There was no heterogeneity for RR or RD (I² = 0%).
One study compared MS‐LE versus S‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (RR 3.00, 95% CI 0.13 to 70.83; RD 0.03, 95% CI –0.05 to 0.12; n = 60; Savini 2013).
PNALD/cholestasis (conjugated bilirubin 2 mg/dL or greater): combined subgroups (outcome 3.4)
Considering both studies together in meta‐analysis and adjusting for the multiarm study (Savini 2013), there was no difference between alternative‐LE and S‐LE (typical RR 1.14, 95% CI 0.22 to 5.84; typical RD 0.01, 95% CI –0.04 to 0.06; Analysis 3.4; Savini 2013; Wang 2016). There was no heterogeneity for RR or RD (I² = 0%).
3.4. Analysis.
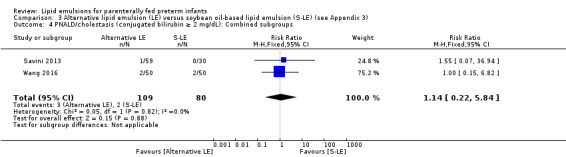
Comparison 3 Alternative lipid emulsion (LE) versus soybean oil‐based lipid emulsion (S‐LE) (see Appendix 3), Outcome 4 PNALD/cholestasis (conjugated bilirubin ≥ 2 mg/dL): Combined subgroups.
PNALD/cholestasis (any definition) (outcome 3.5)
Four studies reported data in a format that could be used for the meta‐analysis (Analysis 3.5; Gawecka 2008b; Köksal 2011; Savini 2013; Wang 2016). One was a five‐arm study contributing to multiple comparisons (Savini 2013).
3.5. Analysis.
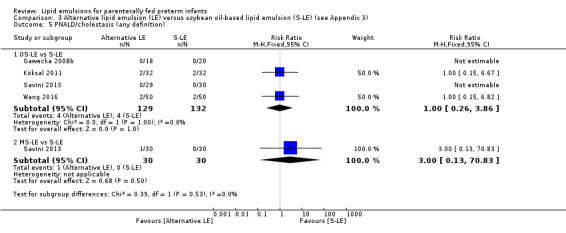
Comparison 3 Alternative lipid emulsion (LE) versus soybean oil‐based lipid emulsion (S‐LE) (see Appendix 3), Outcome 5 PNALD/cholestasis (any definition).
One study defined cholestasis as conjugated bilirubin greater than 2 mg/dL (34.2 mmol/L) at the age of six weeks (Savini 2013). One study defined cholestasis as conjugated bilirubin fraction greater than 20% of the total bilirubin after 14 days of life (Köksal 2011: unpublished data provided by the authors). Two studies did not provide a definition for cholestasis (Gawecka 2008b; Wang 2016). One study only provided mean values for liver functions tests and conjugated bilirubin (Deshpande 2009).
Four studies compared OS‐LE versus S‐LE, with no statistically significant difference in any individual study. There was no statistically significant difference between groups in the meta‐analysis (typical RR 1.00, 95% CI 0.26 to 3.86; typical RD 0.00, 95% CI –0.05 to 0.05; n = 261; low‐quality evidence; Analysis 3.5). There was no heterogeneity for RR or RD (I² = 0%).
One study compared MS‐LE versus S‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (RR 3.00, 95% CI 0.13 to 70.83; RD 0.03, 95% CI –0.05 to 0.12; n = 60; Savini 2013).
PNALD/cholestasis (any definition): combined subgroups (outcome 3.6)
Considering all studies together in meta‐analysis adjusting for the multiarm study (Savini 2013), there was no difference between alternative‐LE and S‐LE (typical RR 1.08, 95% CI 0.31 to 3.72; typical RD 0.00, 95% CI –0.04 to 0.05; Analysis 3.6; Gawecka 2008b; Köksal 2011; Savini 2013; Wang 2016). There was no heterogeneity for RR or RD (I² = 0%) (Figure 7).
3.6. Analysis.
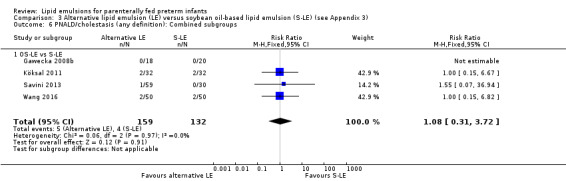
Comparison 3 Alternative lipid emulsion (LE) versus soybean oil‐based lipid emulsion (S‐LE) (see Appendix 3), Outcome 6 PNALD/cholestasis (any definition): Combined subgroups.
7.
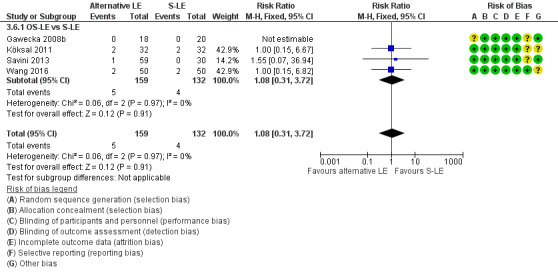
Forest plot of comparison: 3 Alternative lipid emulsion (LE) versus S‐LE, outcome: 3.6 Parenteral nutrition‐associated liver disease (PNALD)/cholestasis (any definition): all subgroups combined.
Secondary outcomes
Death before discharge (outcome 3.7)
Three studies reported data in a format that could be used for the meta‐analysis (Analysis 3.7; Köksal 2011; Savini 2013; Wang 2016). One was a five‐arm study contributing to multiple comparisons (Savini 2013).
3.7. Analysis.
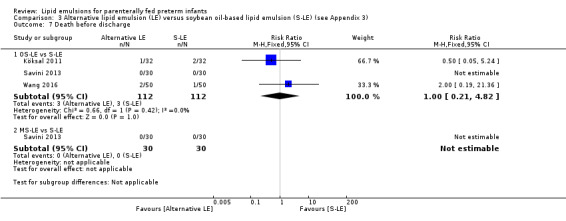
Comparison 3 Alternative lipid emulsion (LE) versus soybean oil‐based lipid emulsion (S‐LE) (see Appendix 3), Outcome 7 Death before discharge.
One study reported two deaths in each of the OS‐LE and S‐LE groups; however, these data could not be used as the authors did not provide the number of infants originally randomised to the two groups (Gawecka 2008b).
Three studies compared OS‐LE versus S‐LE, with no statistically significant difference in any individual study. There was no statistically significant difference between groups in the meta‐analysis (typical RR 1.00, 95% CI 0.21 to 4.82; typical RD 0.00, 95% CI –0.05 to 0.05; n = 224; low‐quality evidence; Analysis 3.7). There was no heterogeneity for RR or RD (I² = 0%).
One study compared MS‐LE versus S‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (RR not estimable; RD 0.00, 95% CI –0.06 to 0.06; n = 60; Savini 2013).
Any retinopathy of prematurity (outcome 3.8)
Three studies (n = 142) all comparing OS‐LE versus S‐LE reported data for ROP (Analysis 3.8). Two studies used the ICROP classification (Gawecka 2008b; Köksal 2011), and one study did not provide the definition used (Demirel 2011). No study reported statistically significant differences between groups.
3.8. Analysis.
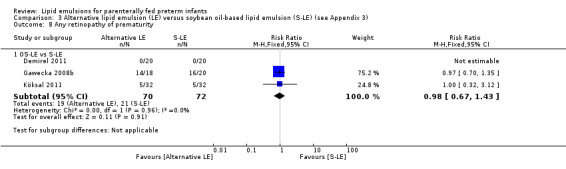
Comparison 3 Alternative lipid emulsion (LE) versus soybean oil‐based lipid emulsion (S‐LE) (see Appendix 3), Outcome 8 Any retinopathy of prematurity.
There was no statistically significant difference between groups in the meta‐analysis (typical RR 0.98, 95% CI 0.67 to 1.43; typical RD –0.01, 95% CI –0.12 to 0.10; n = 142; very low‐quality evidence). There was no heterogeneity for RR or RD (I² = 0%).
Any bronchopulmonary dysplasia (outcome 3.9)
Four studies reported data in a format that could be used for the meta‐analysis (Analysis 3.9). One was a five‐arm study contributing to multiple comparisons (Savini 2013). Two studies defined BPD as oxygen requirement at 36 weeks (Köksal 2011; Savini 2013). One study provided a reference about BPD on the basis of 36 weeks but did not define specific criteria used in their study (Gawecka 2008b). One study did not provide definition of BPD (Wang 2016).
3.9. Analysis.
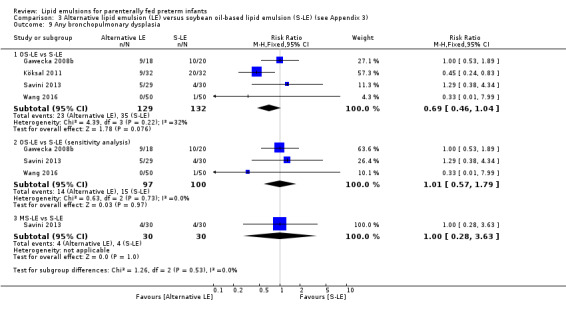
Comparison 3 Alternative lipid emulsion (LE) versus soybean oil‐based lipid emulsion (S‐LE) (see Appendix 3), Outcome 9 Any bronchopulmonary dysplasia.
Four studies compared OS‐LE versus S‐LE, with Köksal 2011 showing statistically significant effect in favour of OS‐LE (typical RR 0.45, 95% CI 0.24 to 0.83; typical RD –0.34, 95% CI –0.57 to –0.11). There was a trend towards statistically significant difference between groups in the meta‐analysis (typical RR 0.69, 95% CI 0.46 to 1.04; typical RD –0.08, 95% CI –0.17 to 0.00; 4 studies; n = 261). There was low heterogeneity for RR (I² = 32%) and RD (76%).
For the subgroup of OS‐LE versus S‐LE, we also performed a sensitivity analysis by removing Köksal 2011 because it was a small study and its results were significantly different from other studies in the group. Three studies compared OS‐LE versus S‐LE (sensitivity analysis), there were three studies with no statistically significant difference in any individual study. There was no clinical or statistically significant difference between groups in the meta‐analysis after removing Köksal 2011 (typical RR 1.01, 95% CI 0.57 to 1.79; typical RD 0.00, 95% CI –0.09 to 0.09; n = 197; low‐quality evidence). There was no heterogeneity among the studies in the sensitivity analysis (I² = 0%).
One study compared MS‐LE versus S‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (RR 1.00, 95% CI 0.28 to 3.63; RD 0.00, 95% CI –0.17 to 0.17; n = 60; Savini 2013).
Chronic lung disease (oxygen requirement at 36 weeks' postmenstrual age) (outcome 3.10)
Two studies (n = 123) reported data in a format that could be used for the meta‐analysis (Analysis 3.10; Köksal 2011; Savini 2013). One was a five‐arm study contributing to multiple comparisons (Savini 2013).
3.10. Analysis.
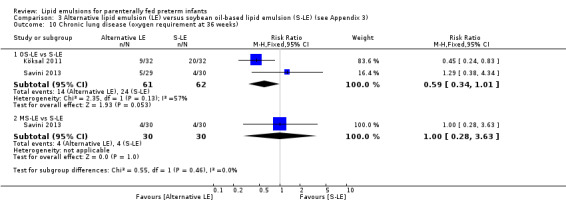
Comparison 3 Alternative lipid emulsion (LE) versus soybean oil‐based lipid emulsion (S‐LE) (see Appendix 3), Outcome 10 Chronic lung disease (oxygen requirement at 36 weeks).
Two studies compared OS‐LE versus S‐LE, there were two studies with Köksal 2011 showing statistically significant effect in favour of OS‐LE (typical RR 0.45, 95% CI 0.24 to 0.83; typical RD –0.34, 95% CI –0.57 to –0.11). There was borderline statistically significant difference between groups in the meta‐analysis (typical RR 0.59, 95% CI 0.34 to 1.01; typical RD –0.16, 95% CI –0.31 to –0.01; 2 studies; n = 123). There was high heterogeneity for RR (I² = 57%) and RD (86%). The baseline rate of BPD was very different in the two studies. It can also be argued that these two studies should not be combined in meta‐analyses.
One study compared MS‐LE versus S‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (RR 1.00, 95% CI 0.28 to 3.63; RD 0.00, 95% CI –0.17 to 0.17; n = 60; Savini 2013).
Duration of ventilation (days) (outcome 3.11)
Three studies (n = 202) provided data for duration of ventilation (Analysis 3.11; Gawecka 2008b; Köksal 2011; Wang 2016). Köksal 2011 reported a statistically significant difference between groups, with longer duration of ventilation in the S‐LE group (mean ± SD: 34.6 ± 29.9 days) compared with the OS‐LE group (mean ± SD: 12.4 ± 26.6 days). Gawecka 2008b found no statistically significant difference between the two groups, with the direction of effect opposite to that seen in Köksal 2011. The largest study in this comparison did not report any significant difference in the median ventilation duration in the two groups (we imputed means and SDs from medians and interquartile ranges; Wang 2016).
3.11. Analysis.
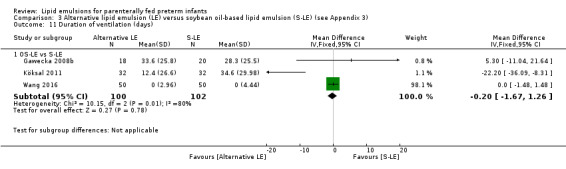
Comparison 3 Alternative lipid emulsion (LE) versus soybean oil‐based lipid emulsion (S‐LE) (see Appendix 3), Outcome 11 Duration of ventilation (days).
The meta‐analysis showed no statistically significant effect with either OS‐LE or S‐LE (MD –0.20 days, 95% CI –1.67 to 1.26; 3 studies; n = 202). There was high heterogeneity (I² = 80%).
Duration of supplemental oxygen (days) (outcome 3.12)
Two studies reported data for duration of supplemental oxygen with no statistically significant difference in any individual study (Analysis 3.12; Gawecka 2008b; Köksal 2011 (unpublished data)). There was no statistically significant difference between groups in the meta‐analysis (MD –0.76 days, 95% CI –16.99 to 15.47; n = 102). There was moderate heterogeneity (I² = 52%).
3.12. Analysis.
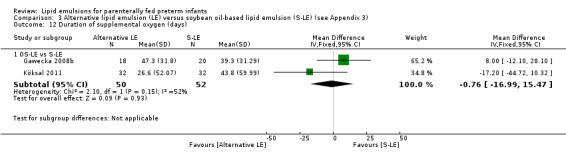
Comparison 3 Alternative lipid emulsion (LE) versus soybean oil‐based lipid emulsion (S‐LE) (see Appendix 3), Outcome 12 Duration of supplemental oxygen (days).
Duration of hospital stay (outcome 3.13)
One study reported on duration of hospital stay (Wang 2016b). Unpublished data from another study was provided by the study author in a personal communication for data request (Köksal 2011). Both studies compared OS‐LE versus S‐LE, with no difference in the individual studies or between the two groups in the meta‐analysis (MD 0.33 days, 95% CI –7.44 to 8.10; Analysis 3.13).
3.13. Analysis.
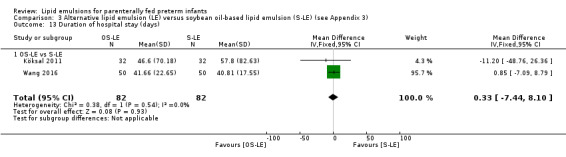
Comparison 3 Alternative lipid emulsion (LE) versus soybean oil‐based lipid emulsion (S‐LE) (see Appendix 3), Outcome 13 Duration of hospital stay (days).
Need for home oxygen therapy (outcome 3.14)
In the subgroup OS‐LE versus S‐LE, only unpublished data for need for home oxygen therapy provided by the authors of one study (n = 64) were available (Köksal 2011). There was no statistically significant difference between groups (RR not estimable; RD 0.00, 95% CI –0.06 to 0.06; Analysis 3.14).
3.14. Analysis.
Comparison 3 Alternative lipid emulsion (LE) versus soybean oil‐based lipid emulsion (S‐LE) (see Appendix 3), Outcome 14 Need for home oxygen therapy.
Any sepsis (clinical or culture positive (or both)) (outcome 3.15)
Five studies reported data on sepsis and nosocomial infections (Analysis 3.15; Demirel 2011; Gawecka 2008b; Köksal 2011; Savini 2013; Wang 2016). Köksal 2011 used the criteria described by Gitto 2001 and categorised sepsis as high probable, probable and possible sepsis. Demirel 2011 described the outcome of sepsis on the basis of clinical and laboratory parameters. Savini 2013 used criteria described by Stoll 2002, reporting neonatal sepsis as positive blood culture or as clinical syndrome with systemic signs and symptoms of infection and abnormalities in laboratory investigations. Wang 2016 defined sepsis as positive blood or cerebrospinal culture in the presence of compatible clinical signs. One study provided data on nosocomial infections (Gawecka 2008b). One was a five‐arm study contributing to multiple comparisons (Savini 2013).
3.15. Analysis.
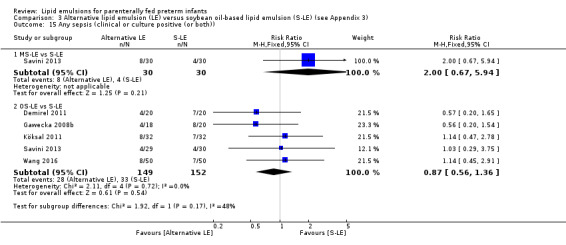
Comparison 3 Alternative lipid emulsion (LE) versus soybean oil‐based lipid emulsion (S‐LE) (see Appendix 3), Outcome 15 Any sepsis (clinical or culture positive (or both)).
Five studies compared OS‐LE versus S‐LE, with no statistically significant difference in any individual study. There was no statistically significant difference between groups in the meta‐analysis (typical RR 0.87, 95% CI 0.56 to 1.36; typical RD –0.03, 95% CI –0.12 to 0.06; n = 301). There was no heterogeneity for RR or RD (I² = 0%).
One study compared MS‐LE versus S‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (RR 2.00, 95% CI 0.67 to 5.94; RD 0.13, 95% CI –0.07 to 0.33; n = 60; Savini 2013).
Culture‐positive sepsis (outcome 3.16)
Two studies compared OS‐LE versus S‐LE, with no statistically significant difference in any either study (Analysis 3.16; Köksal 2011; Wang 2016). There was no statistically significant difference between groups in the meta‐analysis (typical RR 1.22, 95% CI 0.54 to 2.78; typical RD 0.02, 95% CI –0.08 to 0.12; n = 164; low‐quality evidence). There was no heterogeneity for RR or RD (I² = 0%).
3.16. Analysis.
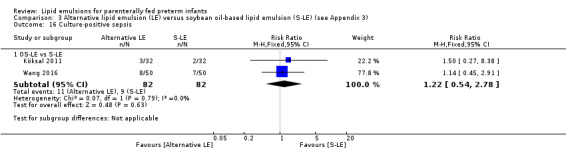
Comparison 3 Alternative lipid emulsion (LE) versus soybean oil‐based lipid emulsion (S‐LE) (see Appendix 3), Outcome 16 Culture‐positive sepsis.
Necrotising enterocolitis (stage 2 or greater) (outcome 3.17)
Four studies mentioned NEC with one study defining the condition as NEC Bell's stage 2 or 3 (Savini 2013), while two studies used the Bell's classification but did not specify the stage of NEC and therefore data from these studies could not be used in the meta‐analysis (Gawecka 2008b; Köksal 2011). One study reported no difference between groups but did not provide data (Demirel 2011). One study did not provide the definition used and did not report the stage of NEC, therefore the data from this study could not be used in meta‐analyses (Wang 2016). None of the studies reported any statistically significant differences in NEC rates between groups.
Only the five‐arm study by Savini 2013 (total enrolled n = 150; infants in relevant comparison arms, n = 89) reported data in a format that could be used for the analysis (Analysis 3.17).
3.17. Analysis.
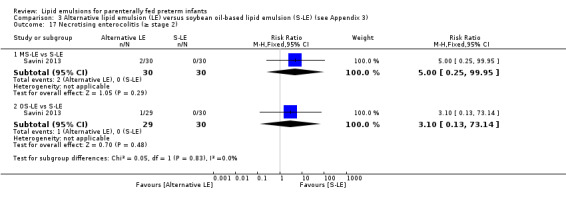
Comparison 3 Alternative lipid emulsion (LE) versus soybean oil‐based lipid emulsion (S‐LE) (see Appendix 3), Outcome 17 Necrotising enterocolitis (≥ stage 2).
One study compared MS‐LE versus S‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (RR 5.00, 95% CI 0.25 to 99.95; RD 0.07, 95% CI –0.04 to 0.17; n = 60; Savini 2013).
One study compared OS‐LE versus S‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (RR 3.10, 95% CI 0.13 to 73.14; RD 0.03, 95% CI –0.06 to 0.12; n = 59; Savini 2013).
Intraventricular haemorrhage (grade III to IV) (outcome 3.18)
Two studies comparing OS‐LE to S‐LE reported data for IVH grade III to IV (Demirel 2011; Köksal 2011 (unpublished data)). Köksal 2011 reported using the Papile classification. Demirel 2011 did not provide information on the classification used. One study reported no difference between groups (grades not mentioned), however provided no data in the study report (Gawecka 2008b). Deshpande 2009 reported that one infant who died in the OS‐LE group had IVH grade IV, however data on IVH in the two groups were not available. There were no statistically significant differences between the OS‐LE and S‐LE groups in the individual studies or in the meta‐analysis (typical RR 0.50, 95% CI 0.10 to 2.61; typical RD –0.04, 95% CI –0.13 to 0.05; n = 104; Analysis 3.18). There was no statistical heterogeneity for RR or RD (I² = 0%).
3.18. Analysis.
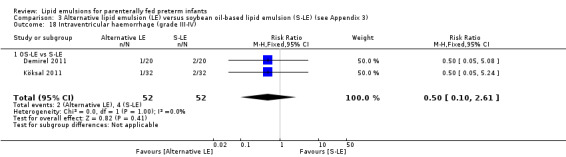
Comparison 3 Alternative lipid emulsion (LE) versus soybean oil‐based lipid emulsion (S‐LE) (see Appendix 3), Outcome 18 Intraventricular haemorrhage (grade III‐IV).
Periventricular leukomalacia (outcome 3.19)
One study compared OS‐LE versus S‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (RR 0.33, 95% CI 0.01 to 7.89; RD –0.03, 95% CI –0.11 to 0.05; n = 64; Analysis 3.19; unpublished data provided by Köksal 2011).
3.19. Analysis.
Comparison 3 Alternative lipid emulsion (LE) versus soybean oil‐based lipid emulsion (S‐LE) (see Appendix 3), Outcome 19 Periventricular leukomalacia.
Any patent ductus arteriosus (outcome 3.20)
One study reported data in a format that could be used for the meta‐analysis (Analysis 3.20). Savini 2013 was a five‐arm study contributing to multiple comparisons.
3.20. Analysis.
Comparison 3 Alternative lipid emulsion (LE) versus soybean oil‐based lipid emulsion (S‐LE) (see Appendix 3), Outcome 20 Any patent ductus arteriosus.
One study compared OS‐LE versus S‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (RR 1.03, 95% CI 0.63 to 1.71; RD 0.02, 95% CI –0.24 to 0.27; n = 59; Savini 2013).
One study compared MS‐LE versus S‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (RR 1.13, 95% CI 0.70 to 1.82; RD 0.07, 95% CI –0.19 to 0.32; n = 60; Savini 2013).
Air leaks (outcome 3.21)
One study compared OS‐LE versus S‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups for air leaks (RR 0.50, 95% CI 0.05 to 5.24; RD –0.03, 95% CI –0.13 to 0.07; n = 64; Analysis 3.21; Köksal 2011 (unpublished data)).
3.21. Analysis.
Comparison 3 Alternative lipid emulsion (LE) versus soybean oil‐based lipid emulsion (S‐LE) (see Appendix 3), Outcome 21 Air leaks.
Significant jaundice requiring treatment (outcome 3.22)
Two studies reported data for significant jaundice requiring treatment (Göbel 2003; Köksal 2011 (unpublished data)). There were no statistically significant differences between the OS‐LE and S‐LE groups in the individual studies or in the meta‐analysis (typical RR 1.04, 95% CI 0.52 to 2.07; typical RD 0.01, 95% CI –0.15 to 0.16; n = 109; Analysis 3.22). There was no statistical heterogeneity for RR or RD (I² = 0%).
3.22. Analysis.
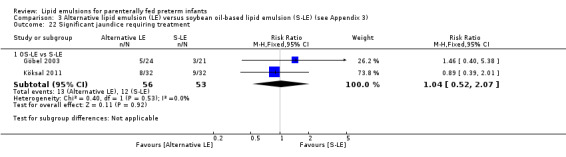
Comparison 3 Alternative lipid emulsion (LE) versus soybean oil‐based lipid emulsion (S‐LE) (see Appendix 3), Outcome 22 Significant jaundice requiring treatment.
Duration of phototherapy (days) (outcome 3.23)
One study compared OS‐LE versus S‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (MD –0.10 days, 95% CI –1.08 to 0.88; n = 38; Analysis 3.23; Gawecka 2008b).
3.23. Analysis.
Comparison 3 Alternative lipid emulsion (LE) versus soybean oil‐based lipid emulsion (S‐LE) (see Appendix 3), Outcome 23 Duration of phototherapy (days).
Hypertriglyceridaemia (outcome 3.24)
Four studies reported data in a format that could be used for the meta‐analysis. Demirel 2011 and Gawecka 2008b used the definition of TG greater than 200 mg/dL (2.25 mmol/L) and Köksal 2011 did not provide any definition. One study mentioned that there was no difference between groups but did not report any numbers (Göbel 2003).
Three studies compared OS‐LE versus S‐LE, with no statistically significant difference in any individual study (Demirel 2011; Gawecka 2008b; Köksal 2011). There was no statistically significant difference between groups in the meta‐analysis (typical RR 0.67, 95% CI 0.12 to 3.73; typical RD –0.01, 95% CI –0.08 to 0.06; n = 142; Analysis 3.24). There was no heterogeneity for RR or RD (I² = 0%).
3.24. Analysis.
Comparison 3 Alternative lipid emulsion (LE) versus soybean oil‐based lipid emulsion (S‐LE) (see Appendix 3), Outcome 24 Hypertriglyceridaemia.
One study compared MS‐LE versus S‐LE, with no hypertriglyceridaemia in either the groups (RR not estimable; RD 0.00, 95% CI –0.27 to 0.27; n = 12; Lehner 2006).
Hyperglycaemia (mmol/L) (outcome 3.25)
One study provided data for hyperglycaemia. There was no statistically significant difference between the OS‐LE and S‐LE groups (RR 1.00, 95% CI 0.22 to 4.59; RD 0.00, 95% CI –0.14 to 0.14; n = 64; Analysis 3.25; Köksal 2011 (unpublished data)).
3.25. Analysis.
Comparison 3 Alternative lipid emulsion (LE) versus soybean oil‐based lipid emulsion (S‐LE) (see Appendix 3), Outcome 25 Hyperglycaemia.
Head growth velocity (cm/week) (outcome 3.26)
One study reported on head growth velocity, with no difference between groups (MD –0.08 cm/week, 95% CI –0.17 to 0.01; n = 100; Analysis 3.26; Wang 2016b).
3.26. Analysis.
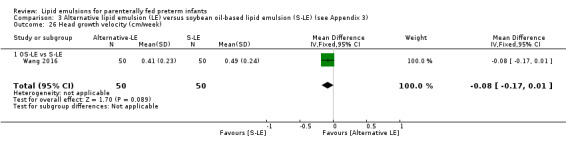
Comparison 3 Alternative lipid emulsion (LE) versus soybean oil‐based lipid emulsion (S‐LE) (see Appendix 3), Outcome 26 Head growth velocity (cm/week).
Conjugated bilirubin levels (outcome 3.27)
Four studies reported data in a format that could be used for the meta‐analysis (Analysis 3.27; Deshpande 2009; Göbel 2003; Savini 2013; Wang 2016b). Another study reported data on total and unconjugated bilirubin with data presented as mean and standard errors (author communication) from which the data on the conjugated bilirubin were imputed (Köksal 2011). The studies reported the conjugated bilirubin values at different time points. One was a five‐arm study contributing to multiple comparisons (Savini 2013).
3.27. Analysis.
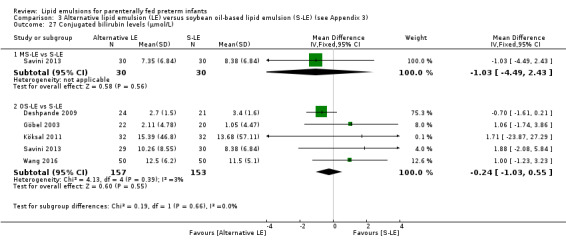
Comparison 3 Alternative lipid emulsion (LE) versus soybean oil‐based lipid emulsion (S‐LE) (see Appendix 3), Outcome 27 Conjugated bilirubin levels (µmol/L).
One study compared MS‐LE versus S‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (MD –1.03 μmol/L, 95% CI –4.49 to 2.43; n = 60; Savini 2013).
In the studies comparing OS‐LE versus S‐LE, there were five studies with no statistically significant difference in any individual study (Deshpande 2009; Göbel 2003; Köksal 2011; Savini 2013; Wang 2016b). There was no statistically significant difference between groups in the meta‐analysis (MD –0.24 μmol/L, 95% CI –1.03 to 0.55; n = 310; low‐quality evidence). There was no heterogeneity (I² = 3%).
Alternative‐LE versus other alternative‐LE in preterm infants (Comparison 4)
The studies under this broad comparison compared:
MS‐LE versus OS‐LE: two studies (n = 84) were in this comparison and only Savini 2013 reported data that could be used for predefined outcomes (Roggero 2010; Savini 2013).
BS‐LE versus MS‐LE: two arms (n = 31) in a multiarm study were in this comparison. The study did not report data for the outcomes of interest in our review (Rubin 1994).
Primary outcomes
Days to regain birth weight (outcome 4.1)
One study compared MS‐LE versus OS‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (MD –2.00 days, 95% CI –5.73 to 1.73; n = 59; Analysis 4.1; Savini 2013).
4.1. Analysis.
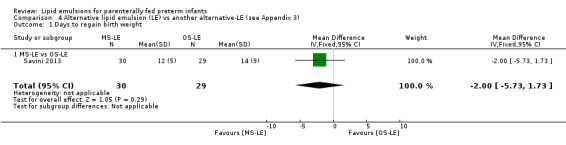
Comparison 4 Alternative lipid emulsion (LE) vs another alternative‐LE (see Appendix 3), Outcome 1 Days to regain birth weight.
Growth rate (outcome 4.2)
One study compared MS‐LE versus OS‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (MD –1.33 g/kg/day, 95% CI –7.36 to 4.70; n = 59; Analysis 4.2; Savini 2013; low‐quality evidence).
4.2. Analysis.
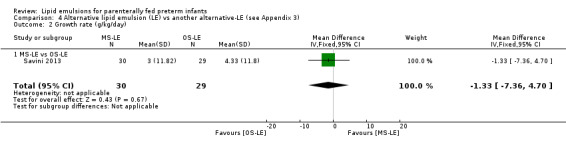
Comparison 4 Alternative lipid emulsion (LE) vs another alternative‐LE (see Appendix 3), Outcome 2 Growth rate (g/kg/day).
PNALD/cholestasis (conjugated bilirubin 2 mg/dL or greater) (outcome 4.3)
One study compared MS‐LE versus OS‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (RR 2.90, 95% CI 0.12 to 68.50; RD 0.03, 95% CI –0.06 to 0.12; n = 59; Analysis 4.3; Savini 2013; low‐quality evidence).
4.3. Analysis.
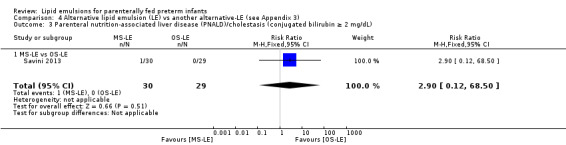
Comparison 4 Alternative lipid emulsion (LE) vs another alternative‐LE (see Appendix 3), Outcome 3 Parenteral nutrition‐associated liver disease (PNALD)/cholestasis (conjugated bilirubin ≥ 2 mg/dL).
PNALD/cholestasis (any definition) (outcome 4.4)
One study compared MS‐LE versus OS‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (RR 2.90, 95% CI 0.12 to 68.50; RD 0.03, 95% CI –0.06 to 0.12; n = 59; Analysis 4.4; Savini 2013).
4.4. Analysis.
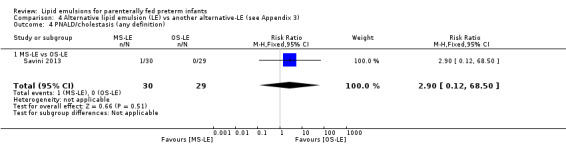
Comparison 4 Alternative lipid emulsion (LE) vs another alternative‐LE (see Appendix 3), Outcome 4 PNALD/cholestasis (any definition).
Secondary outcomes
Death before discharge (outcome 4.5)
One study compared MS‐LE versus OS‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (RR not estimable; RD 0.00, 95% CI –0.06 to 0.06; n = 60; Analysis 4.5; Savini 2013).
4.5. Analysis.
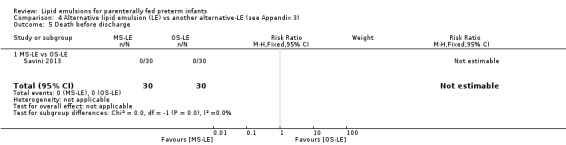
Comparison 4 Alternative lipid emulsion (LE) vs another alternative‐LE (see Appendix 3), Outcome 5 Death before discharge.
Chronic lung disease (oxygen requirement at 36 weeks' postmenstrual age) (outcome 4.6)
One study compared MS‐LE versus OS‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (RR 0.77, 95% CI 0.23 to 2.60; RD –0.04, 95% CI –0.22 to 0.14; n = 59; Analysis 4.6; Savini 2013; low‐quality evidence).
4.6. Analysis.
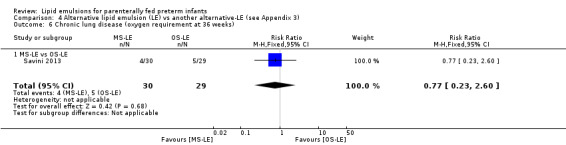
Comparison 4 Alternative lipid emulsion (LE) vs another alternative‐LE (see Appendix 3), Outcome 6 Chronic lung disease (oxygen requirement at 36 weeks).
Any sepsis (clinical or culture positive (or both)) (outcome 4.7)
One study compared MS‐LE versus OS‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (RR 1.93, 95% CI 0.65 to 5.73; RD 0.13, 95% CI –0.07 to 0.33; n = 59; Analysis 4.7; Savini 2013; low‐quality evidence).
4.7. Analysis.
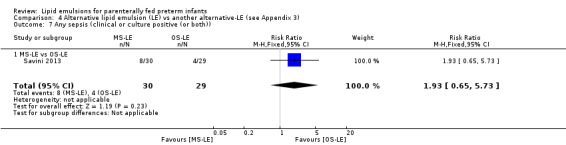
Comparison 4 Alternative lipid emulsion (LE) vs another alternative‐LE (see Appendix 3), Outcome 7 Any sepsis (clinical or culture positive (or both)).
Necrotising enterocolitis (stage 2 or greater) (outcome 4.8)
One study compared MS‐LE versus OS‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (RR 1.93, 95% CI 0.19 to 20.18; RD 0.03, 95% CI –0.08 to 0.14; n = 59; Analysis 4.8; Savini 2013).
4.8. Analysis.
Comparison 4 Alternative lipid emulsion (LE) vs another alternative‐LE (see Appendix 3), Outcome 8 Necrotising enterocolitis (≥ stage 2).
Any patent ductus arteriosus (outcome 4.9)
One study compared MS‐LE versus OS‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (RR 1.10, 95% CI 0.68 to 1.75; RD 0.05, 95% CI –0.20 to 0.30; n = 59; Analysis 4.9; Savini 2013).
4.9. Analysis.
Comparison 4 Alternative lipid emulsion (LE) vs another alternative‐LE (see Appendix 3), Outcome 9 Any patent ductus arteriosus.
Conjugated bilirubin levels (outcome 4.10)
One study compared MS‐LE versus OS‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (MD –2.91 µmol/L, 95% CI –6.87 to 1.05; n = 59; Analysis 4.10; Savini 2013; low‐quality evidence).
4.10. Analysis.
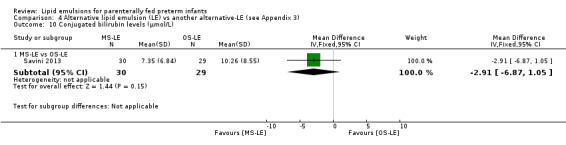
Comparison 4 Alternative lipid emulsion (LE) vs another alternative‐LE (see Appendix 3), Outcome 10 Conjugated bilirubin levels (µmol/L).
Fish oil LE versus non‐fish oil LE in preterm infants with surgical conditions (Comparison 5)
One study (n = 19) compared pure F‐LE (Omegaven) to S‐LE (Intralipid) (Nehra 2014) in infants with surgical conditions.
Primary outcomes
The study described growth parameters in terms of Z scores of weight‐for‐age, length‐for‐age and head circumference‐for‐age (Nehra 2014). The study described a downward trend in the weight‐for‐age scores in the S‐LE group compared to the pure F‐LE group; however, there were no statistically significant differences noted.
PNALD/cholestasis (conjugated bilirubin 2 mg/dL or greater) (outcome 5.1)
One study compared pure F‐LE versus S‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (RR 1.11, 95% CI 0.08 to 15.28; RD 0.01, 95% CI –0.27 to 0.29; n = 19; Analysis 5.1; Nehra 2014; very low‐quality evidence). The study defined cholestasis as conjugated bilirubin greater than 2 mg/dL for two or more consecutive weeks.
5.1. Analysis.
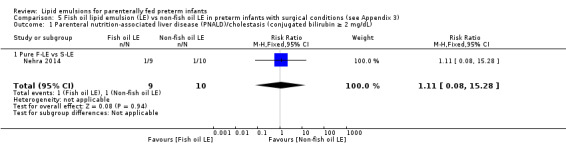
Comparison 5 Fish oil lipid emulsion (LE) vs non‐fish oil LE in preterm infants with surgical conditions (see Appendix 3), Outcome 1 Parenteral nutrition‐associated liver disease (PNALD)/cholestasis (conjugated bilirubin ≥ 2 mg/dL).
Secondary outcomes
Death before discharge (outcome 5.2)
One study compared pure F‐LE versus S‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (RR: not estimable; RD 0.00, 95% CI –0.18 to 0.18; n = 19; Analysis 5.2; Nehra 2014).
5.2. Analysis.
Comparison 5 Fish oil lipid emulsion (LE) vs non‐fish oil LE in preterm infants with surgical conditions (see Appendix 3), Outcome 2 Death before discharge.
Culture‐positive sepsis (outcome 5.3)
One study compared pure F‐LE versus S‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (RR 1.11, 95% CI 0.39 to 3.19; RD 0.04, 95% CI –0.40 to 0.49; n = 19; Analysis 5.3; Nehra 2014; very low‐quality evidence).
5.3. Analysis.
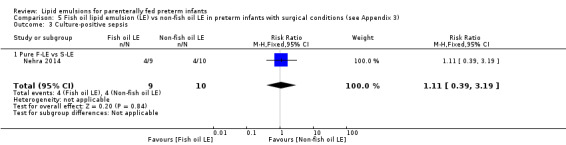
Comparison 5 Fish oil lipid emulsion (LE) vs non‐fish oil LE in preterm infants with surgical conditions (see Appendix 3), Outcome 3 Culture‐positive sepsis.
Hypertriglyceridemia (outcome 5.4)
One study compared pure F‐LE versus S‐LE using a definition of serum TG greater than 300 mg/dL. This study reported no participants with hypertriglyceridaemia in either group. There was no statistically significant difference between groups (RR: not estimable; RD 0.0, 95% CI –0.18 to 0.18; n = 19; Analysis 5.4; Nehra 2014).
5.4. Analysis.
Comparison 5 Fish oil lipid emulsion (LE) vs non‐fish oil LE in preterm infants with surgical conditions (see Appendix 3), Outcome 4 Hypertriglyceridemia.
Conjugated bilirubin levels (outcome 5.5)
One study compared pure F‐LE versus S‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (MD 0.00 µmol/L, 95% CI –11.30 to 11.30; n = 14; Analysis 5.5; Nehra 2014; very low‐quality evidence).
5.5. Analysis.
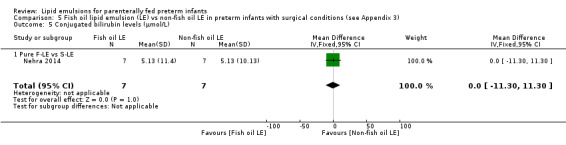
Comparison 5 Fish oil lipid emulsion (LE) vs non‐fish oil LE in preterm infants with surgical conditions (see Appendix 3), Outcome 5 Conjugated bilirubin levels (µmol/L).
Neurodevelopmental outcome (at six and 24 months)
One study compared pure F‐LE versus S‐LE and reported data on the neurodevelopmental outcomes using the BSID, with no statistically significant difference between groups (Nehra 2014). The authors provided medians and interquartile ranges for cognitive, language and motor scores. The reported P values using non‐parametric tests were not significant. We did not impute the mean and SD due to this being the only study in the outcome and given the non‐parametric distribution.
We found no studies in preterm infants with surgical conditions that compared a fish oil‐LE versus another fish oil‐LE, alternative‐LE versus S‐LE or alternative‐LE versus another alternative‐LE.
Fish oil LE versus non‐fish oil LE in preterm infants with established PNALD/cholestasis (Comparison 6)
This comparison included those studies which compared the fish oil‐containing LE with non‐fish oil LEs in preterm infants who had developed cholestasis within the first six months of life. The studies in this comparison also included the infants who had developed cholestasis or PNALD due to surgical conditions.
The studies identified were in the following subgroups:
MOFS‐LE versus S‐LE: one study (n = 24) compared MOFS‐LE (SMOFlipid) to S‐LE (10% Intralipid) (Diamond 2017).
Pure F‐LE versus S‐LE: one study (n = 16) compared Omegaven (a pure fish oil‐LE) to S‐LE (10% Intralipid) (Lam 2014).
Primary outcomes
Growth rate (outcome 6.1)
One study compared pure F‐LE versus S‐LE, with statistically significant effect in favour of pure F‐LE (MD 45.0 g/week, 95% CI 15.0 to 75.0; n = 16; Analysis 6.1; Lam 2014; very low‐quality evidence). Lam 2014 used a 10% Intralipid preparation which is no longer recommended. No study reported weight gain in grams/kg/week.
6.1. Analysis.
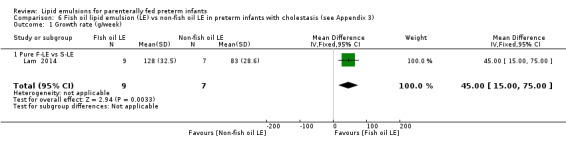
Comparison 6 Fish oil lipid emulsion (LE) vs non‐fish oil LE in preterm infants with cholestasis (see Appendix 3), Outcome 1 Growth rate (g/week).
Resolution of PNALD/cholestasis (conjugated bilirubin less than 2 mg/dL) (outcome 6.2)
One study defined reversal of cholestasis as conjugated bilirubin less than 2 mg/dL (Lam 2014). This study found that the cholestasis had resolved in most of the infants by the trial end point of four months. However, most infants in this study in the S‐LE group improved after they were on full enteral intake. This study also described infants with resolution of cholestasis while on trial PN. There was no statistically significant difference between 10% pure F‐LE and 10% S‐LE (RR 5.60, 95% CI 0.34 to 93.95; typical RD 0.33, 95% CI –0.01 to 0.67; n = 16; Analysis 6.2; very low‐quality evidence).
6.2. Analysis.
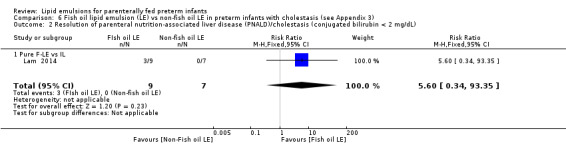
Comparison 6 Fish oil lipid emulsion (LE) vs non‐fish oil LE in preterm infants with cholestasis (see Appendix 3), Outcome 2 Resolution of parenteral nutrition‐associated liver disease (PNALD)/cholestasis (conjugated bilirubin < 2 mg/dL).
PNALD/cholestasis (any definition) (outcome 6.3)
Two studies (n = 40) reported data on cholestasis (Diamond 2017; Lam 2014). Both studies reported on infants with cholestasis at the end of PN or study end, though the primary outcomes in the studies were different. One of the studies included infants with early hepatic dysfunction (conjugated bilirubin 17 µmol/L to 50 µmol/L) on two consecutive readings over seven days (Diamond 2017). This study evaluated progression of PNALD and provided data for infants whose conjugated bilirubin level was greater than 50 µmol/L at the study primary end point (Cbil in the week the infant received the last dose of PN, i.e. at 12 weeks, at full enteral tolerance, or on development of progressive liver disease).
The second study included infants with cholestasis defined as conjugated bilirubin 2 mg/dL (Lam 2014). The primary outcome for this study was the reversal of PNALD defined as conjugated bilirubin level less than 34 µmol/L (2 mg/dL) within four months of the commencement of lipid treatment. However Lam 2014 also described the proportion of infants with/without cholestasis while receiving trial PN which was considered for the meta‐analysis, so that the infants in both groups were in temporal proximity to the end of their trial PN for the outcome for cholestasis.
The number of participants in this outcome did not reach the optimal information size.
One study compared MOFS‐LE versus S‐LE, with statistically significantly lesser cholestasis (conjugated bilirubin greater than 50 µmol/L) in the MOFS‐LE group (typical RR 0.39, 95% CI 0.14 to 1.10; typical RD –0.42, 95% CI –0.78 to –0.06; n = 24; Analysis 6.3; Diamond 2017).
6.3. Analysis.
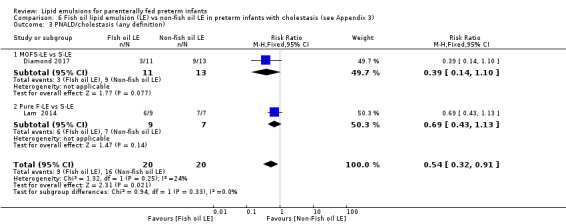
Comparison 6 Fish oil lipid emulsion (LE) vs non‐fish oil LE in preterm infants with cholestasis (see Appendix 3), Outcome 3 PNALD/cholestasis (any definition).
One study compared pure F‐LE versus S‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (RR 0.69, 95% CI 0.43 to 1.13; RD –0.33, 95% CI –0.67 to 0.01; n = 16; Lam 2014). Lam 2014 also reported that in the study period, three out of nine participants improved in the pure F‐LE arm compared to none of the seven participants in the S‐LE arm while infants were receiving the LE. Although this result was not statistically significant, the authors described the rate of increase in the conjugated bilirubin values which was statistically significantly higher in the S‐LE group. However, in Lam 2014, all surviving participants in both arms improved by four months which was the primary outcome of the study.
In the meta‐analysis of both subgroups, there was statistically significant effect in favour of F‐LE compared to S‐LE (typical RR 0.54, 95% CI 0.32 to 0.91; typical RD –0.39, 95% CI –0.65 to –0.12; 2 studies; n = 40; very low‐quality evidence). There was no heterogeneity for RR (0%) and low heterogeneity for RD (24%). There was no heterogeneity in the test for subgroup differences (I² = 0%).
Secondary outcomes
Death before discharge (outcome 6.4)
Two studies (n = 40) reported data with no study individually reporting any significant difference between the two groups (Analysis 6.4). However, all the deaths in both studies were complicated or due to progressive liver disease. The number of participants in this outcome did not reach the optimal information size.
6.4. Analysis.
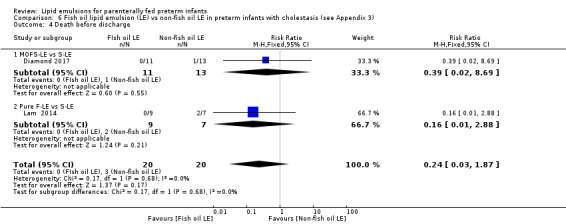
Comparison 6 Fish oil lipid emulsion (LE) vs non‐fish oil LE in preterm infants with cholestasis (see Appendix 3), Outcome 4 Death before discharge.
One study compared MOFS‐LE versus S‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (RR 0.39, 95% CI 0.02 to 8.69; RD –0.08, 95% CI –0.27 to 0.12; n = 24; Diamond 2017).
One study compared pure F‐LE versus S‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (RR 0.16, 95% CI 0.01 to 2.88; RD –0.29, 95% CI –0.63 to 0.06; n = 16; Lam 2014).
In the meta‐analysis of all subgroups (two studies), there was no statistically significant difference between groups (typical RR 0.24, 95% CI 0.03 to 1.87; typical RD –0.16, 95% CI –0.36 to 0.04; n = 40; very low‐quality evidence). There was no heterogeneity among all studies for RR (I² = 0%) or RD (15%) and no heterogeneity for subgroup differences for RR (I² = 0%) or RD (4.2%).
Any sepsis (outcome 6.5)
Two studies (n = 40) reported data in a format that could be used for the meta‐analysis and specific definitions for sepsis were not provided in the study reports (Analysis 6.5).
6.5. Analysis.
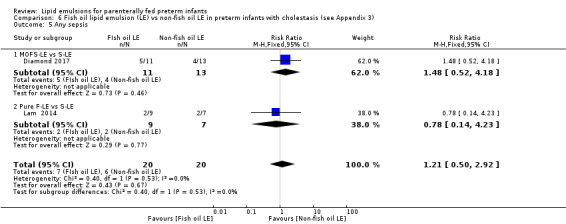
Comparison 6 Fish oil lipid emulsion (LE) vs non‐fish oil LE in preterm infants with cholestasis (see Appendix 3), Outcome 5 Any sepsis.
One study compared MOFS‐LE versus S‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (RR 1.48, 95% CI 0.52 to 4.18; RD 0.15, 95% CI –0.24 to 0.53; n = 24; Diamond 2017).
One study compared pure F‐LE versus S‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (RR 0.78, 95% CI 0.14 to 4.23; RD –0.06, 95% CI –0.49 to 0.37; n = 16; Lam 2014).
In the meta‐analysis of all subgroups, there was no statistically significant difference between groups (typical RR 1.21, 95% CI 0.50 to 2.92; typical RD 0.06, 95% CI –0.23 to 0.35; n = 40; very low‐quality evidence). There was no heterogeneity among the subgroups (I² = 0%).
Hyperglycaemia (outcome 6.6)
One study compared MOFS‐LE versus S‐LE but provided no definition of hyperglycaemia (Diamond 2017). There was no statistically significant difference between groups (RR 1.48, 95% CI 0.52 to 4.18; RD 0.15, 95% CI –0.24 to 0.53; n = 24; Analysis 6.6).
6.6. Analysis.
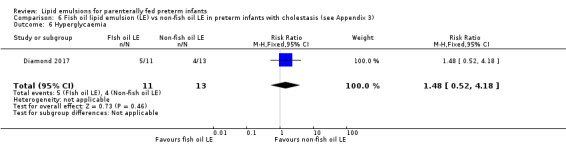
Comparison 6 Fish oil lipid emulsion (LE) vs non‐fish oil LE in preterm infants with cholestasis (see Appendix 3), Outcome 6 Hyperglycaemia.
Head growth velocity (outcome 6.7)
One study compared pure F‐LE versus S‐LE, with no statistically significant difference between groups (MD 0.16 cm/week, 95% CI –0.01 to 0.33; n = 16; Analysis 6.7; Lam 2014; very low‐quality evidence).
6.7. Analysis.
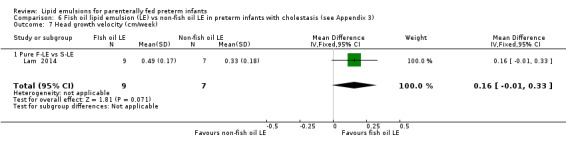
Comparison 6 Fish oil lipid emulsion (LE) vs non‐fish oil LE in preterm infants with cholestasis (see Appendix 3), Outcome 7 Head growth velocity (cm/week).
Conjugated bilirubin levels (outcome 6.8)
One study compared MOFS‐LE versus S‐LE, with statistically significant effect in favour of MOFS‐LE with lower conjugated bilirubin values excluding an outlier in the data who had significant increase in the level of conjugated bilirubin with sepsis (MD –47.00 µmol/L, 95% CI –71.65, –22.35; n = 24; Analysis 6.8; Diamond 2017). The authors reported data in mean, 95% CI (as confirmed from the author) for the distribution excluding the outlier. There was no statistically significant difference between groups when the outlier was included in the analysis. Authors also performed analysis by including the conjugated bilirubin value for the outlying participant when the participant had improved and this analysis showed a statistically significant difference between groups (low‐quality evidence).
6.8. Analysis.
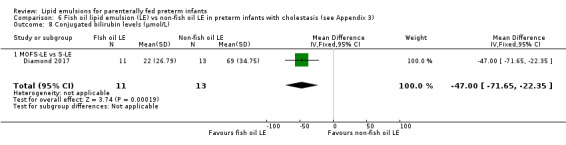
Comparison 6 Fish oil lipid emulsion (LE) vs non‐fish oil LE in preterm infants with cholestasis (see Appendix 3), Outcome 8 Conjugated bilirubin levels (µmol/L).
In their study report, the authors defined cholestasis as increased conjugated bilirubin levels unrelated to sepsis. Therefore, we presented the data without the outlier and also described the analytical aspects reported by the study.
One of the studies described no difference in infants with hyperlipidaemia in MOFS‐LE versus S‐LE (Diamond 2017). No definition was provided.
We found no studies in preterm infants with PNALD/cholestasis that compared a fish oil‐LE versus another fish oil‐LE, alternative‐LE versus S‐LE or alternative‐LE versus another alternative‐LE.
Discussion
The review included 29 studies (total number enrolled 2037 infants). Some studies focusing on biochemical outcomes only contributed to the qualitative synthesis (Biagetti 2016; Roggero 2010; Rubin 1994).
The included studies were conducted in 19 different countries: three studies in Turkey; two studies each in Hungary, Poland, Greece and Australia; five studies in Italy, and one each in Austria, Sweden, the USA, the UK, Canada, Israel, Germany, Belgium, China, Taiwan, Hong Kong, Thailand and the Netherlands.
The type of LE compared in the studies was reflective of the evolution of LEs with the MCT‐LCT emulsions in the earlier studies, olive‐soybean combinations in the later studies and multisource LEs containing fish oil in the more recent years.
In the current review the LE have been classified in three broad categories:
fish oil LE including pure fish oil and multisource LE with fish oil as a constituent: MCT‐olive‐fish‐soybean oil‐LE (MOFS‐LE), MCT‐fish‐soybean oil‐LE (MFS‐LE) and olive‐fish‐soybean oil‐LE (OFS‐LE);
conventional pure soybean oil‐LE (S‐LE);
alternative‐LE including MCT‐soybean oil‐LE (MS‐LE), olive‐soybean oil‐LE (OS‐LE), borage oil‐LE and structured lipids‐based LE.
Summary of main results
In the included studies, the type of participants belonged to three predefined population groups as per the review protocol (Kapoor 2018):
preterm infants less than 37 weeks' gestation (26 studies; n = 1978);
preterm infants less than 37 weeks' with surgical conditions (1 study; n =19);
preterm infants less than 37 weeks' gestation with PNALD (2 studies; n = 40).
There was no restriction on comorbidities including surgery in preterm infants with PNALD. We considered all possible pair‐wise comparisons including studies comparing any LE with another LE in preterm infants.
We performed the following six main comparisons with subgroup comparisons based on the included studies.
Fish oil LE versus non‐fish oil LE in preterm (7 subgroups; 17 studies; n = 1522): MOFS‐LE versus S‐LE (11 studies; n = 973); MOFS‐LE versus OS‐LE (3 studies; n = 184); MOFS‐LE versus MS‐LE (2 studies; n = 120); MFS‐LE versus S‐LE (1 study; n = 60); MFS‐LE versus MS‐LE (3 studies; n = 160); MFS‐LE versus OS‐LE (1 study; n = 60); OFS‐LE versus OS‐LE (1 study; n = 175).
Fish oil LE versus another fish oil LE in preterm infants (1 subgroup; 1 study; n = 60): MOFS‐LE versus MFS‐LE (1 study; n = 60).
Alternative‐LE versus S‐LE in preterm infants (3 subgroups; 10 studies; n = 536): OS‐LE versus S‐LE (8 studies; n = 430); MS‐LE versus S‐LE (4 studies; n = 132); BS‐LE versus S‐LE (1 study; n = 34).
Alternative‐LE versus another alternative‐LE in preterm infants (2 subgroups; 3 studies; n = 115): OS‐LE versus MS‐LE (2 studies; n = 84); borage oil‐LE versus MS‐LE (1 study; n = 31).
Fish oil LE versus non‐fish oil LE in preterm infants with surgical conditions (1 subgroup; 1 study; n = 19): Pure F‐LE versus S‐LE (1 study; n = 19)
Fish oil LE versus non‐fish oil LE in preterm infants with PNALD/cholestasis (2 subgroups; 2 studies; n = 40): MOFS‐LE versus S‐LE (1 study; n = 24); Pure F‐LE versus S‐LE (1 study; n = 16)
The number of subgroups in each comparison depended on the availability of studies. The multiarm studies were represented in more than one comparison.
In infants with cholestasis or surgical conditions there were only a few eligible studies, all of them comparing fish oil‐containing LE versus S‐LE. Most studies in preterm infants used PN for a mean duration of less than four weeks and for longer duration in preterm infants with surgical conditions or cholestasis.
We performed meta‐analyses by pooling the individual studies by subgroups, under a comparison. For the selected important outcomes (e.g. PNALD, severe ROP), we also pooled all the subgroups to compare all fish oil LE versus non‐fish oil LE. This was done to evaluate any potential benefit of the fish oil in LE in specific clinical outcomes (e.g. PNALD or ROP). While pooling the subgroups, we avoided unit of analysis errors by combining relevant arms of a multiarm study as applicable (Savini 2013).
Meta‐analysis could not be performed for MOFS‐LE versus MFS‐LE, MS‐LE versus OS‐LE or BS‐LE versus S‐LE due to a paucity of studies or reported data. There were no eligible studies comparing structured LE (e.g. Structolipid).
Excessive PUFA content exposes preterm infants to the effects of oxidation (Sala‐Vila 2007), and may contribute to adverse outcomes including PNALD, ROP and BPD. Reports and the literature suggests that fish oil may be beneficial in preterm infants due to decreased PUFA content, increased EPA and DHA, and the effect on the nuclear receptors. One systematic review showed improvement in DHA status with fish oil supplementation and its safety in preterm infants (Zhao 2015).
Potential beneficial effects of fish oil LE on PNALD have been evaluated previously in systematic reviews with conflicting results. One systematic review using observational and randomised studies found no evidence of effect of fish oil‐containing LEs in preventing PNALD (odds ratio 0.56, 95% CI 0.28 to 1.10; P = 0.09) (Park 2015). However, more recently, one systematic review and meta‐analysis in newborn infants including randomised studies showed that fish oil LEs were associated with significantly lower incidence of cholestasis compared with S‐LE (RR: 0.31, 95% CI 0.15 to 0.68; 4 studies; n = 386; Vayalthrikkovil 2017).
In the outcome of PNALD/cholestasis, different definitions were used by the included studies ranging from conjugated bilirubin cut‐offs of 17.1 μmol/L (1 mg/dL; Pawlik 2014) to greater than 50 μmol/L (about 3 mg/dL; Najm 2017), which can affect reported cholestasis rates. Some studies used a composite definition for cholestasis (e.g. conjugated bilirubin greater than 1 mg/dL or greater than 20% of total bilirubin if the total bilirubin was greater than 5 mg/dL). In preterm infants, using predefined cut‐off for PNALD/cholestasis of conjugated bilirubin 2 mg/dL or greater as per our review protocol (Kapoor 2018), meta‐analysis showed no difference between the fish oil LE and non‐fish oil LE (typical RR 0.61, 95% CI 0.24 to 1.56; typical RD –0.03, 95% CI –0.08 to 0.02; 4 studies; n = 328; low‐quality evidence). There was no heterogeneity among the studies (I² = 0%) (Figure 3).
We also considered an outcome for PNALD/cholestasis using any definition to evaluate pooled effect of fish oil in LE irrespective of conjugated bilirubin cut‐offs. In meta‐analysis of fish oil LE versus all non‐fish oil LE in preterm infants, using any cholestasis definition, there was evidence of less cholestasis in the fish oil LE group (typical RR 0.63, 95% CI 0.43 to 0.91; typical RD –0.04, 95% CI –0.08 to –0.01; 11 studies; n = 1154; Analysis 1.6; very low‐quality evidence). However, this was likely to be a biased estimate as 28.4% weight was contributed by a single study with high risk of bias (Pawlik 2014), which showed large effect estimate of fish oil LE in reducing cholestasis (3/60 with fish oil LE versus 20/70 with non‐fish oil LE; RR 0.17, 95% CI 0.05 to 0.56; RD –0.24, 95% CI –0.36 to –0.12). This study comparing OFS‐LE (Omegaven and OS‐LE‐ClinOleic 1:1 mix) versus OS‐LE (ClinOleic) reported a high mortality rate in both groups (20/87 (22.9%) with fish oil LE versus 18/88 (20.4%) with non‐fish oil LE). There were seven participant withdrawals, all in the fish oil arm (P = 0.007). Data were not reported for deaths or withdrawals. Pawlik 2014 appeared to be visually an outlier in the forest plot (Analysis 1.5).
When the meta‐analysis for PNALD/cholestasis (any definition) in preterm infants was restricted to low and unclear risk of bias studies (sensitivity analysis), there was no evidence of significant benefit of fish oil LE with decrease in observed effect size (typical RR 0.80, 95% CI 0.53 to 1.21; typical RD –0.02, 95% CI –0.05 to 0.02; 10 studies; n = 1024; low‐quality evidence). The summary estimates from the low risk of bias studies and the unclear risk of bias studies, when analysed separately, also did not show evidence of a significant effect of fish oil LE. The large effect size of the single study with high risk of bias was visually an outlier in the forest plot with moderate between‐study heterogeneity for RD (I² = 54%) and high heterogeneity for the 'risk of bias subgroups' differences (RR: I² =83%; RD: I² =91.6%) (Figure 4; Figure 8; Pawlik 2014). Therefore, we reported the primary results from the low and unclear risk of bias studies to provide effect estimate with higher grade of evidence.
8.
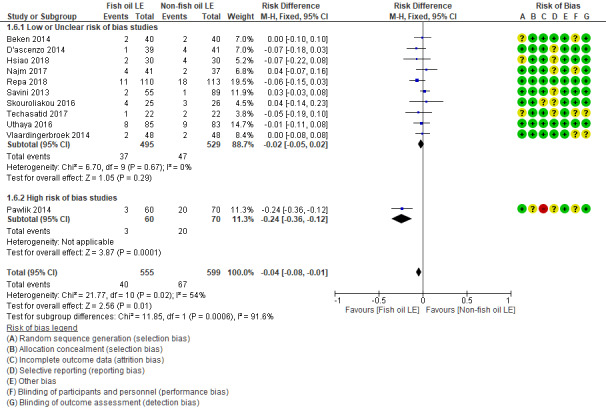
Forest plot of comparison: 1 Fish oil lipid emulsion (LE) versus non‐fish oil LE, outcome: 1.6 Parenteral nutrition‐associated liver disease (PNALD)/cholestasis (any definition): analysis stratified by low and unclear risk of bias studies versus high risk of bias studies (risk differences).
In preterm infants, there was no evidence of difference in PNALD/cholestasis (any definition) in subgroup meta‐analyses of individual LE types in any comparison.
High levels of phytosterols have been thought to contribute to liver failure by affecting the nuclear Farsenoid X receptor (Hojsak 2016). However, one multiarm randomised study showed no association of abnormal liver function with the use of LE with different phytosterol content (Savini 2013). The study by Savini and associates had the lowest incidence of cholestasis in non‐fish oil LE groups (1/89 or 1.1%; Figure 8) and had a low NEC rate (0/30 in S‐LE group) which besides other factors may have contributed to low cholestasis in this study. In addition, the timing of cholestasis detection may affect cholestasis incidence as there can be time dependent resolution of cholestasis once infants are on full enteral nutrition (Lam 2014). The mean duration of PN in Savini 2013 was approximately three weeks. Unlike most other studies that had no time restriction on cholestasis detection, this study looked at cholestasis and liver functions at six weeks, using a conjugated bilirubin cut‐off of greater than 2mg/dL, which may have contributed to the low cholestasis incidence and the lack of association of liver functions with the cumulative phytosterol intake at day 14 of life (Savini 2013).
In preterm infants with surgical conditions, one study (Nehra 2014) compared pure F‐LE (Omegaven) versus S‐LE (Intralipid), with no difference in incidence of cholestasis between groups (RR 1.11, 95% CI 0.08 to 15.28; RD 0.01, 95% CI –0.27 to 0.29; n = 19; very low‐quality evidence).
We also evaluated reversal of PNALD/cholestasis (defined in our review protocol as conjugated bilirubin less than 2 mg/dL) in preterm infants with cholestasis (Kapoor 2018). One previous systematic review and meta‐analysis in newborn infants using randomised and non‐randomised studies showed that fish oil LE were more likely to reverse cholestasis compared to S‐LE (RR 6.14, 95% CI 2.27 to 16.6) (Park 2015). In the current review, in preterm infants with established PNALD/cholestasis, one study (n = 16) showed no evidence of a difference in resolution of cholestasis (conjugated bilirubin less than 2 mg/dL) with a pure fish oil LE versus a 10% S‐LE.
However, in infants with PNALD/cholestasis, meta‐analysis showed significantly less cholestasis (using any Cbil cutoff) with use of fish oil‐LE versus S‐LE (typical RR 0.54, 95% CI 0.32 to 0.91; typical RD –0.39, 95% CI –0.65 to –0.12; NNTB 3, 95% CI 2 to 9; 2 studies; n = 40; very low‐quality evidence). One of the studies in this outcome was stopped after the interim analysis and used 10% LE which is currently not recommended (Lam 2014). There was heterogeneity in the study methodology, definitions and the outcome cut‐offs in the two studies for this outcome. Therefore, though it is possible that in the population of preterm infants with PNALD there is a potential benefit of fish oil LE, very low number of participants from two small studies with early termination of one study, combined with methodological heterogeneity of two studies, increased the uncertainty about the effect estimates. Further research with larger randomised studies is needed to definitively address this aspect.
The primary outcome of weight gain was reported heterogeneously across the studies ranging from z scores at different time points, change in z scores, gram/week, grams/kilogram/day and only subjective mention in some studies. Concerns have been raised about possible impact of decreased arachidonic acid levels in multisource LE and pure fish oil LE on growth outcomes (Biagetti 2016). In the current review, we found no difference in growth between any of the LE types in pair‐wise meta‐analyses in the population of preterm infants. There was paucity of studies in preterm infants with surgical conditions or cholestasis with one small study reporting better growth in infants with PNALD using pure fish oil LE compared to a 10% soybean LE (MD 45 g/week more, 95% CI 15 to 75; n = 16; very low‐quality evidence; Lam 2014).
For the secondary outcomes of the review, we explored the effect of fish oil LE on severe ROP. The rates of severe ROP in the current review varied in studies from 0% in D'Ascenzo 2014 (0/39 SMOFlipid versus 0/41 Intralipid) to 44% in Najm 2017 (18/41 in SMOFlipid arm). Only one study in preterm infants showed any benefit of fish oil LE (Pawlik 2014). This study with 31% incidence of severe ROP in OS‐LE (ClinOleic; control arm) reported a significant decrease in the requirement of laser therapy for ROP in the fish oil arm (OFS‐LE) (RR 0.48, 95% CI 0.24 to 0.96; n = 130).
One systematic review and meta‐analysis which included the Pawlik 2014 study (4 studies; n = 386) showed that there was significant improvement in ROP with fish oil‐containing LE (Vayalthrikkovil 2017). The current meta‐analysis pooled evidence from an additional three RCTs showing no evidence of a significant benefit of fish oil LE for severe ROP in preterm infants (typical RR 0.80, 95% CI 0.55 to 1.16; typical RD –0.03, 95% CI –0.07 to 0.02; 7 studies; n = 731; very low‐quality evidence). One of the studies in this outcome was at high risk of bias (Pawlik 2014). There was moderate heterogeneity among the subgroups which was explored by undertaking sensitivity analysis (I² = 55.5% for RR; 61.3% for RD).
The meta‐analysis for severe ROP (sensitivity analysis) exploring moderate heterogeneity and restricting analysis to low/unclear risk of bias studies, showed no benefit of fish oil LE with effect size approaching one (typical RR 1.02, 95% CI 0.65 to 1.60; typical RD 0.00, 95% CI –0.04 to 0.05; 6 studies; n = 601; low‐quality evidence), with no heterogeneity (I² reduced to = 0%). We presented the estimates from all studies as the primary result for severe ROP as the effect estimates were not significantly different in the sensitivity analysis and the Pawlik 2014 study was at lower risk of material bias for ROP compared to the outcome of cholestasis.
There were no differences in any of the comparison groups in the secondary outcomes of death, BPD, PDA, culture‐positive sepsis, IVH, PVL, jaundice, hyperglycaemia, hypertriglyceridaemia and conjugated bilirubin levels in preterm infants without PNALD or surgical conditions (low‐ to very low‐quality evidence). Only one study evaluated intrahepatic lipid content reporting no significant differences between the MOFS‐LE and S‐LE (Uthaya 2016).
There were no differences in any subgroup meta‐analyses for ventilation and oxygen duration in preterm infants. One small study comparing MOFS‐LE versus MS‐LE reported significantly large differences in the ventilation duration and oxygen duration in the two groups (Hsiao 2018). This study used a population of preterm infants who required ventilation as an entry criteria. The ventilation durations reported by this study were significantly lower in the SMOFlipid group (mean ± SD: 9.2 ± 3.5 days with SMOFlipid versus 16.6 ± 7.2 days with MS‐LE). This study's population, PN duration (greater than four weeks) and results for ventilation were a clinical and statistical outlier with I² = 94.9% for subgroup differences. Hence we did not meta‐analyse the subgroups together for this outcome.
For preterm infants with surgical conditions, one study showed (Nehra 2014; n = 19) no significant differences in secondary outcomes of death, sepsis rates, conjugated bilirubin levels and neurodevelopmental outcomes in comparison between a pure fish oil LE and S‐LE.
In preterm infants with PNALD, there were no evidence of significant differences in death or sepsis rates in meta‐analyses between fish oil LE and S‐LE (2 studies; n = 40; low‐quality evidence). One study in preterm infants with PNALD reported significantly lower conjugated bilirubin levels in the MOFS‐LE group compared with S‐LE (MD –47.00 µmol/L, 95% CI –71.65 to –22.35; n = 24; low‐quality evidence) (Diamond 2017).
Overall completeness and applicability of evidence
This is a comprehensive review of all available LEs in preterm infants using randomised studies. The evidence presented in this review was limited by a paucity of large randomised studies reporting on clinically important outcomes. Study data did not allow for subgroup analysis based on gender or gestational age cut‐offs.
Quality of the evidence
The quality of evidence in this review ranged from low to very low for most of the outcomes (GRADE Working Group recommendations; Schünemann 2013). This was primarily due to the optimal information size not being achieved, with wide CIs for most of the outcomes (Appendix 6). There was no evidence of publication bias for the outcome of PNALD. We could not evaluate publication bias in most other outcomes due to the paucity of studies.
Potential biases in the review process
For some outcomes (e.g. growth rate), we used imputed values for means and SD to be able to use the available data in the meta‐analyses. Investigation of heterogeneity and sensitivity analyses where there are very few studies are unreliable. Another potential source of bias may be the termination of studies prior to trial completion. Importantly, in preterm infants with surgical conditions or cholestasis, two out three studies that contributed data to the outcomes were terminated for various reasons prior to the study completion.
Agreements and disagreements with other studies or reviews
In one previous systematic review using observational and randomised studies the use of fish oil‐containing lipid emulsions was shown to be more likely to reverse PNAC (odds ratio 6.14, 95% CI 2.27 to 16.6; P < 0.01), but the use of fish oil‐containing lipid emulsions had no significant effect on the development of PNAC compared with soybean‐based or olive oil‐based lipid emulsions (odds ratio 0.56, 95% CI 0.28 to 1.10; P = 0.09; Park 2015).
One later systematic review and meta‐analysis in newborn infants showed that fish oil LEs were associated with significantly lower incidence of cholestasis compared with S‐LE (RR 0.50, 95% CI 0.27 to 0.92; P = 0.03; 5 studies; n = 427; Kotiya 2016). However, one of the included studies compared amino acid 3.5 g/kg/day infusion versus amino acid 2.5 g/kg/day infusion and did not report on different lipids in the two groups.
More recently, one systematic review and meta‐analysis in newborn infants including randomised studies showed that fish oil LE were associated with significantly lower incidence of cholestasis compared with soybean‐based lipid emulsions (with or without olive oil) (RR 0.31, 95% CI 0.15 to 0.68; 4 studies; n = 386; Vayalthrikkovil 2017).
The current Cochrane review significantly expands on the current evidence including 11 randomised studies (n = 1154) for the outcome of PNALD and is more exhaustive in its scope looking at all outcomes besides PNALD. Our review suggests that currently there is insufficient evidence from the good‐quality randomised studies that fish oil LEs prevent or reduce the incidence of cholestasis in preterm infants.
The current review expands significantly on the previous version of this review, which only compared different lipid emulsions to S‐LE (Kapoor 2015).
Authors' conclusions
Implications for practice.
In the current review, we found that, in preterm infants without underlying parenteral nutrition‐associated liver disease (PNALD) or surgical conditions, there is insufficient evidence that any particular lipid emulsion (LE) with or without fish oil including any alternative‐LE with olive‐soybean or medium‐chain triglycerides (MCT)‐soybean combination or any multisource LE offers advantage over another LE type for prevention of PNALD/cholestasis. No LE was superior to another for growth, mortality, retinopathy of prematurity (ROP), bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD), metabolic disturbances, or any other important clinical outcome.
In preterm infants with cholestasis or surgical conditions, there is currently insufficient evidence from randomised studies to determine with any certainty that fish oil LEs decrease or improve cholestasis or other outcomes. Further research, with larger well‐designed trials, is warranted to evaluate the ideal composition of LE in preterm infants and the role of fish oil containing and other LEs in prevention and resolution of PNALD/cholestasis.
Implications for research.
At this stage it is not known what is the ideal proportion of lipid constituents from different sources that would maximise the improvement of outcomes in preterm infants.
Also, it is currently not clear whether the beneficial effects of fish oil LE may be more obvious in a setting of high control cholestasis risk, using higher fish oil concentrations in LE and when evaluated with lower conjugated bilirubin thresholds (e.g. 1 mg/dL for cholestasis in Pawlik 2014). The large effect estimates reported in the study by Pawlik and colleagues have not been replicated in the later LE trials, though there were differences in methodology, definitions and dose of fish oil used.
The current status of evidence from randomised studies in preterm populations with established PNALD is very limited. Further research is required to evaluate whether there is a dose‐dependent effect of fish oil on cholestasis and ROP.
Further research with larger well‐designed trials is essential to clarify some of these aspects.
Notes
This review and the companion review of "Lipid emulsions for parenterally fed late preterm and term infants" will replace the published review of "Alternative lipid emulsions versus pure soybean oil‐based lipid emulsions for parenterally fed preterm infants" (Kapoor 2015).
Acknowledgements
The methods section of this review was based on a standard template used by Cochrane Neonatal. Kath Wright created the search strategy; Ms Wright ran and deduplicated the searches. Dr William McGuire, Cochrane Neonatal Nutrition Editor, reviewed the search results at title and abstract screening stage.
Appendices
Appendix 1. Constituents of lipid emulsions used in the studies included in the review.
| Constituents | 20% Intralipid (Fresenius Kabi) | Lipoven (Fresenius Kabi) | Liposyn III (Hospira) | PFE 4501 Pharmacia Sweden* | Lipofundin‐MCT/LCT 20% (B Braun) | Structolipid 20% (Fresenius Kabi) |
Lipovenoes‐MCT (Fresenius Kabi) |
ClinOleic 20% (Baxter) |
Omegaven (Fresenius Kabi) |
Lipodem (B Braun) |
20% SMOFlipid (Fresenius Kabi) |
| Oil source (%) | |||||||||||
| Soybean oil | 100 | 100 | 100 | 85 | 50 | 64 | 50 | 20 | — | 40 | 30 |
| Coconut (MCT) oil | — | — | — | — | 50 | 36 | 50 | — | — | 50 | 30 |
| Olive oil | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 80 | — | — | 25 |
| Fish oil | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 100 | 10 | 15 |
| Borage oil | — | — | — | 15 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
|
Composition of major fatty acids: % by weight of total fatty acids MCTs | |||||||||||
| Caproic acid (6:0) | — | — | — | — | 0.5 | 0.1 | 0.2 | — | — | — | Trace |
| Caprylic acid (8:0) | — | — | — | — | 29 | 26 | 30 | — | — | 30 | 17 |
| Capric acid (10:0) | — | — | — | — | 20 | 10 | 17 | — | — | 19 | 12 |
| Lauric acid (12:0) | — | — | — | — | 1 | 0.2 | 0.2 | — | — | — | 0.2 |
| Long‐chain triacylglycerols | |||||||||||
| Myristic acid (14:0) | 0.2 | — | Trace | — | — | — | Trace | 0.2 | 5 | 0.5 | 1 |
| Palmitic acid (16:0) | 10.8 | 12 | 11 | 11.2 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 12 | 12 | 6 | 9 |
| Palmitoleic acid (16:1 ω‐7) | — | — | Trace | — | — | — | 0.2 | 1.5 | 9 | 0.6 | 2 |
| Stearic acid (18:0) | 4.2 | 5 | 4 | 4.1 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 3 |
| Oleic acid (18:1 ω‐9) | 24 | 24 | 23 | — | 11 | 14 | 13 | 62 | 15 | 8 | 29 |
| ω‐6/ω‐3 ratio | 7:1 | 7:1 | 7:1 | — | 7:1 | 7:1 | 7:1 | 9:1 | 1:8 | 2.7:1 | 2.5:1 |
| ω‐6 long‐chain triacylglycerols | |||||||||||
| Linoleic acid (18:2 ω‐6) | 53 | 53 | 53 | 50.8 | 29 | 35 | 27 | 19 | 4.4 | 24 | 19 |
| Arachidonic acid (20:4 ω‐6) | 0.1 | — | — | — | 0.2 | — | — | 0.5 | 2 | — | 0.5 |
| ω‐3 long‐chain triacylglycerols | |||||||||||
| α‐linolenic acid (18:3 ω‐3) | 7 | 8 | 8.3 | 5.9 | 4 | 5 | 4 | 2 | 1.8 | 3 | 2 |
| EPA (20:5 ω‐3) | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 19 | 3 | 3 |
| DHA (22:6 ω‐3) | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 0.5 | 12 | 2 | 2 |
| α‐tocopherol (mg/L) | 38 | — | — | — | 85 ± 20 | 6.9 | — | 32 | 150–296 | 190 | 200 |
| Other constituents | |||||||||||
| Phytosterols (mg/L)* | 439.1 ± 5.7 | — | — | — | 278.14 ± 5.09 | — | — | 274.4 ± 2.6 | 0 | — | 207 |
| γ‐linolenic acid (GLA; 18:3 ω‐6) | — | — | — | 3.2 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| L‐Carnitine | — | — | — | 0.4 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
Data collated from multiple sources including Vanek 2012; Vlaardingerbroek 2012; Wanten 2007; Xu 2012 and other references in the review.
DHA: docosahexaenoic acid; EPA: eicosapentaenoic acid; MCT: medium‐chain triacylglycerol, NP: not provided.
Lipoven is also known as Lipovenoes; Lipidem is also known as Lipoplus.
*Pharmacia group merged with Pfizer in 2002. No recent trials with PFE 4501 were identified and the current status of manufacturing could not be confirmed at the time of this review.
Appendix 2. Abbreviations for lipid emulsions
Pure soybean oil‐based lipid emulsions (S‐LE): lipid emulsions with 100% lipids derived solely from soybean oil
Intralipid
Ivelip
Liposyn III
Fish oil‐containing lipid emulsions (F‐LE): all fish oil‐containing lipid emulsions (MOFS‐LE, MFS‐LE, and pure F‐LE)
MOFS‐LE (MCT‐olive‐fish‐soybean oil), e.g. SMOFlipid
MFS‐LE (MCT‐fish‐soybean oil), e.g. Lipidem
Pure F‐LE (pure fish oil), e.g. Omegaven
We will also consider any other combination LE that contain fish oil if available at the time of the review.
Alternative lipid emulsions: all alternative lipid emulsions with partial or complete substitution of soybean oil from other sources (but not containing fish oil).
OS‐LE (olive‐soybean oil), e.g. ClinOleic
MS‐LE (MCT‐soybean oil), e.g. Lipovenoes MCT
BS‐LE (borage‐soybean oil), e.g. PFE 4501
Structured lipids (structured MCT‐soybean oil), e.g. Structolipid
We have used the term 'Alternative‐LE' to represent all newer lipid emulsions that decrease the soybean oil content by using lipids from other sources except fish oil. For physiological reasons, any LE including any multisource/combination LE was considered under the group of 'Fish oil‐containing' LE (or also referred to as 'Fish oil LE') if it contained fish oil as a lipid source.
Specific lipid components have been denoted by the following letters: soybean oil by 'S'; MCT (from coconut oil) by 'M'; fish oil by 'F'; olive oil by 'O'; borage oil by 'B'. The abbreviations for the 'alternative lipid emulsion' end in the letter 'S' (if containing soybean oil) for consistency in nomenclature and to indicate the common theme of substitution of soybean oil by lipids from other sources (e.g. olive‐soybean is abbreviated as 'OS‐LE'; MCT‐soybean as 'MS‐LE'; MCT‐olive‐fish‐soybean as 'MOFS‐LE'). Further, except the letter 'S' (which is always the last letter in the lipid emulsion abbreviations), the sequence of letters denoting the other lipid components are in the decreasing order of lipid percentage (as found in commonly available preparations), e.g. in MFS‐LE (e.g. Lipidem), the percentage of MCT > percentage of fish oil; and in MOFS‐LE (e.g. SMOFlipid) the percentage of MCT (30%) > percentage of olive oil (25%) > percentage of fish oil (15%).
Appendix 3. Comparisons of lipid emulsions
We considered newer lipid emulsions with partial or complete substitution of soybean oil by lipids from other sources in the intervention groups.
We considered the following four broad /comparisons with their respective subgroup comparisons.
1. Fish oil‐containing lipid emulsion versus all non‐fish oil lipid emulsion
MOFS‐LE (MCT‐olive‐fish‐soybean oil) versus S‐LE
MFS‐LE (MCT‐fish‐soybean oil) versus S‐LE
Pure F‐LE (pure fish oil) versus S‐LE
MOFS‐LE, e.g. SMOFlipid versus OS‐LE, e.g. ClinOleic
MOFS‐LE, e.g. SMOFlipid versus MS‐LE, e.g. Lipovenoes MCT
MOFS‐LE, e.g. SMOFlipid versus BS‐LE, e.g. PFE 4501
MOFS‐LE, e.g. SMOFlipid versus Structured LE, e.g. Structolipid
MFS‐LE, e.g. Lipidem versus OS‐LE, e.g. ClinOleic
MFS‐LE, e.g. Lipidem versus MS‐LE, e.g. Lipovenoes MCT
MFS‐LE, e.g. Lipidem versus BS‐LE, e.g. PFE 4501
MFS‐LE, e.g. Lipidem versus structured LE, e.g. Structolipid
Pure F‐LE, e.g. Omegaven versus BS‐LE, e.g. PFE 4501
Pure F‐LE, e.g. Omegaven versus structured LE, e.g. Structolipid
Pure F‐LE, e.g. Omegaven versus MS‐LE, e.g. Lipovenoes MCT
Pure F‐LE, e.g. Omegaven versus OS‐LE, e.g. ClinOleic
We also considered any other combination LE containing fish oil in this comparison if available at the time of the review.
2. Fish oil LE versus another fish oil‐containing lipid emulsion
MOFS‐LE, e.g. SMOFlipid versus Pure F‐LE, e.g. Omegaven
MFS‐LE, e.g. Lipidem versus Pure F‐LE, e.g. Omegaven
MOFS‐LE, e.g. SMOFlipid versus MFS‐LE, e.g. Lipidem
3. Alternative lipid emulsion versus pure soybean oil‐based lipid emulsion (S‐LE)
OS‐LE (olive‐soybean oil) versus S‐LE
MS‐LE (MCT‐soybean oil) versus S‐LE
BS‐LE (borage‐soybean oil) versus S‐LE
Structured lipids (structured MCT‐soybean oil) versus S‐LE
4. Alternative lipid emulsion versus another alternative lipid emulsion
OS‐LE, e.g. ClinOleic versus MS‐LE, e.g. Lipovenoes MCT
OS‐LE, e.g. ClinOleic versus BS‐LE, e.g. PFE 4501
OS‐LE, e.g. ClinOleic versus structured LE, e.g. Structolipid
MS‐LE, e.g. Lipovenoes MCT versus BS‐LE, e.g. PFE 4501
MS‐LE, e.g. Lipovenoes MCT versus structured LE, e.g. Structolipid
BS‐LE, e.g. PFE 4501 versus structured LE, e.g. Structolipid
The four broad comparisons were considered in each of the three predefined populations i.e. preterm infants less than 37 weeks', preterm infants with surgical conditions and preterm infants with pre‐existing cholestasis.
Appendix 4. Search strategies
MEDLINE
Database: Ovid MEDLINE(R) Epub Ahead of Print, In‐Process & Other Non‐Indexed Citations, Ovid MEDLINE(R) Daily and Ovid MEDLINE(R) <1946 to Present> Search Strategy: ‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐ 1 exp Parenteral Nutrition/ 2 infusions, intravenous/ 3 Fat Emulsions, Intravenous/ 4 (parenteral$ adj2 (fed or feed$ or nutrition$)).ti,ab. 5 (TPN or PPN or PN).mp. 6 (intravenous adj2 (infus$ or emulsion$)).ti,ab. 7 ("i.v." adj2 (infus$ or emulsion$)).ti,ab. 8 1 or 2 or 3 or 4 or 5 or 6 or 7 9 exp Lipids/ 10 (coconut$ or borage$ or fish$ or olive$ or soy$ or soybean$).mp. 11 ((alternative or conventional or multisource) adj LE).mp. 12 (alternative‐LE or conventional‐LE or multisource‐LE).mp. 13 structured MCT$.mp. 14 (arachidon$ or BS‐LE or clinoleic$ or DHA or docosahexaenoic acid$ or eicosapentaenoic acid$ or EPA or F‐LE).mp. 15 (intralipid$ or ivelip$).mp. 16 (LCT$ or linolenic$ or linoleic$ or lipidem$ or lipoplus$ or liposyn$ or lipovenoes$ or lipofundin$).mp. 17 (MCT‐fish or MCT‐olive or MCT‐soy or MFS‐LE or MOFS$ or MOFSLE$ or MCT$ or MS‐LE or MUFS$ monounsaturated).mp. 18 (omega‐6$ or omega‐3$ or omegaven$ or OS‐LE).mp. 19 (PFE 4501$ or PFE4501$ or polyunsaturated$ or PUFA$).mp. 20 (S‐LE or SMOF$ or structolipid$ or triacylgl$ or triglyc$).mp. 21 9 or 10 or 11 or 12 or 13 or 14 or 15 or 16 or 17 or 18 or 19 or 20 22 8 and 21 23 exp Infant, Newborn/ 24 Premature Birth/ 25 (neonat$ or neo nat$).ti,ab. 26 (newborn$ or new born$ or newly born$).ti,ab. 27 (preterm or preterms or pre term or pre terms).ti,ab. 28 (preemie$ or premie or premies).ti,ab. 29 (prematur$ adj3 (birth$ or born or deliver$)).ti,ab. 30 (low adj3 (birthweight$ or birth weight$)).ti,ab. 31 (lbw or vlbw or elbw).ti,ab. 32 infan$.ti,ab. 33 (baby or babies).ti,ab. 34 23 or 24 or 25 or 26 or 27 or 28 or 29 or 30 or 31 or 32 or 33 35 22 and 34 36 randomised controlled trial.pt. 37 controlled clinical trial.pt. 38 randomised.ab. 39 placebo.ab. 40 drug therapy.fs. 41 randomly.ab. 42 trial.ab. 43 groups.ab. 44 36 or 37 or 38 or 39 or 40 or 41 or 42 or 43 45 exp animals/ not humans.sh. 46 44 not 45 47 35 and 46
Embase
Database: Embase <1974 to 2018 June 15> Search Strategy: ‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐ 1 exp Parenteral Nutrition/ 2 Intravenous Drug Administration/ 3 exp Lipid Emulsion/ 4 (parenteral$ adj2 (fed or feed$ or nutrition$)).ti,ab. 5 (TPN or PPN or PN).mp. 6 (intravenous adj2 (infus$ or emulsion$)).ti,ab. 7 ("i.v." adj2 (infus$ or emulsion$)).ti,ab. 8 1 or 2 or 3 or 4 or 5 or 6 or 7 9 exp Lipid/ 10 (coconut$ or borage$ or fish$ or olive$ or soy$ or soybean$).mp. 11 ((alternative or conventional or multisource) adj LE).mp. 12 (alternative‐LE or conventional‐LE or multisource‐LE).mp. 13 structured MCT$.mp. 14 (arachidon$ or BS‐LE or clinoleic$ or DHA or docosahexaenoic acid$ or eicosapentaenoic acid$ or EPA or F‐LE).mp. 15 (intralipid$ or ivelip$).mp. 16 (LCT$ or linolenic$ or linoleic$ or lipidem$ or lipoplus$ or liposyn$ or lipovenoes$ or lipofundin$).mp. 17 (MCT‐fish or MCT‐olive or MCT‐soy or MFS‐LE or MOFS$ or MOFSLE$ or MCT$ or MS‐LE or MUFS$ monounsaturated).mp. 18 (omega‐6$ or omega‐3$ or omegaven$ or OS‐LE).mp. 19 (PFE 4501$ or PFE4501$ or polyunsaturated$ or PUFA$).mp. 20 (S‐LE or SMOF$ or structolipid$ or triacylgl$ or triglyc$).mp. 21 9 or 10 or 11 or 12 or 13 or 14 or 15 or 16 or 17 or 18 or 19 or 20 22 8 and 21 23 newborn/ 24 prematurity/ 25 (neonat$ or neo nat$).ti,ab. 26 (newborn$ or new born$ or newly born$).ti,ab. 27 (preterm or preterms or pre term or pre terms).ti,ab. 28 (preemie$ or premie or premies).ti,ab. 29 (prematur$ adj3 (birth$ or born or deliver$)).ti,ab. 30 (low adj3 (birthweight$ or birth weight$)).ti,ab. 31 (lbw or vlbw or elbw).ti,ab. 32 infan$.ti,ab. 33 (baby or babies).ti,ab. 34 23 or 24 or 25 or 26 or 27 or 28 or 29 or 30 or 31 or 32 or 33 35 22 and 34 36 (random* or factorial* or placebo* or assign* or allocat* or crossover*).tw. 37 (cross adj over*).tw. 38 (trial* and (control* or comparative)).tw. 39 ((blind* or mask*) and (single or double or triple or treble)).tw. 40 (treatment adj arm*).tw. 41 (control* adj group*).tw. 42 (phase adj (III or three)).tw. 43 (versus or vs).tw. 44 rct.tw. 45 Crossover Procedure/ 46 Double Blind Procedure/ 47 Single Blind Procedure/ 48 Randomization/ 49 Placebo/ 50 exp Clinical Trial/ 51 Parallel Design/ 52 Latin Square Design/ 53 36 or 37 or 38 or 39 or 40 or 41 or 42 or 43 or 44 or 45 or 46 or 47 or 48 or 49 or 50 or 51 or 52 54 exp animal/ or exp nonhuman/ or exp animal experiment/ or exp animal model/ 55 exp human/ 56 54 not 55 57 53 not 56 58 35 and 57
CINAHL
Search Terms S1 (MH "Parenteral Nutrition+") S2 (MH "Infusions, Intravenous") S3 (MH "Fat Emulsions, Intravenous") S4 TX parenteral* N2 (fed or feed* or nutrition*) S5 TX TPN or PPN or PN S6 TX intravenous N2 (infus* or emulsion*) S7 TX "i.v." N2 (infus* or emulsion*) S8 S1 OR S2 OR S3 OR S4 OR S5 OR S6 OR S7 S9 (MH "Lipids+") S10 TX coconut* or borage* or fish* or olive* or soy* or soybean* S11 TX ( (alternative or conventional or multisource) N1 LE ) OR TX ( alternative‐LE or conventional‐LE or multisource‐LE ) S12 TX structured MCT* OR TX ( arachidon* or BS‐LE or clinoleic* or DHA or docosahexaenoic acid* or eicosapentaenoic acid* or EPA or F‐LE ) OR TX ( intralipid* or ivelip* ) S13 TX ( (LCT* or linolenic* or linoleic* or lipidem* or lipoplus* or liposyn* or lipovenoes* or lipofundin*) ) OR TX ( MCT‐fish or MCT‐olive or MCT‐soy or MFS‐LE or MOFS* or MOFSLE* or MCT* or MS‐LE or MUFS* monounsaturated ) S14 TX ( omega‐6* or omega‐3* or omegaven* or OS‐LE ) OR TX ( PFE 4501* or PFE4501* or polyunsaturated* or PUFA* ) OR TX ( S‐LE or SMOF* or structolipid* or triacylgl* or triglyc* ) S15 S9 OR S10 OR S11 OR S12 OR S13 OR S14 S16 S8 AND S15 S17 (MH "Infant, Newborn+") S18 TX ( neonat* or neo nat* ) OR TX ( (newborn* or new born* or newly born*) ) OR TX ( (preterm or preterms or pre term or pre terms) ) OR TX ( (preemie$ or premie or premies) ) OR TX ( (prematur* NEAR/3 (birth* or born or deliver*)) ) OR TX ( (low NEAR/3 (birthweight* or birth weight*)) ) OR TX ( (lbw or vlbw or elbw) ) OR TX infan* OR TX ( (baby or babies) ) S19 S17 OR S18 S20 S16 AND S19 S21 S16 AND S19 S22 (MH "Randomized Controlled Trials") S23 (MH "Clinical Trials+") OR (MH "Preventive Trials") OR (MH "Community Trials") OR (MH "Intervention Trials") S24 S22 OR S23 S25 S21 AND S24
CENTRAL
Description: #1 MeSH descriptor: [Parenteral Nutrition] explode all trees #2 MeSH descriptor: [Infusions, Intravenous] explode all trees #3 MeSH descriptor: [Fat Emulsions, Intravenous] explode all trees #4 parenteral* near/2 (fed or feed* or nutrition*):ti,ab,kw (Word variations have been searched) #5 TPN or PPN or PN:ti,ab,kw (Word variations have been searched) #6 intravenous near/2 (infus* or emulsion*):ti,ab,kw (Word variations have been searched) #7 "i.v." near/2 (infus* or emulsion*):ti,ab,kw (Word variations have been searched) #8 #1 or #2 or #3 or #4 or #5 or #6 or #7 #9 MeSH descriptor: [Lipids] explode all trees #10 coconut* or borage* or fish* or olive* or soy* or soybean*:ti,ab,kw (Word variations have been searched) #11 (alternative or conventional or multisource) near/1 LE:ti,ab,kw or alternative‐LE or conventional‐LE or multisource‐LE:ti,ab,kw (Word variations have been searched) #12 structured MCT*:ti,ab,kw or arachidon* or BS‐LE or clinoleic* or DHA or "docosahexaenoic acid*" or "eicosapentaenoic acid*" or EPA or F‐LE:ti,ab,kw (Word variations have been searched) #13 intralipid* or ivelip*:ti,ab,kw or LCT* or linolenic* or linoleic* or lipidem* or lipoplus* or liposyn* or lipovenoes* or lipofundin*:ti,ab,kw or MCT‐fish or MCT‐olive or MCT‐soy or MFS‐LE or MOFS* or MOFSLE* or MCT* or MS‐LE or "MUFS* monounsaturated":ti,ab,kw (Word variations have been searched) #14 omega‐6* or omega‐3* or omegaven* or OS‐LE:ti,ab,kw or PFE 4501* or PFE4501* or polyunsaturated* or PUFA*:ti,ab,kw or S‐LE or SMOF* or structolipid* or triacylgl* or triglyc*:ti,ab,kw (Word variations have been searched) #15 #9 or #10 or #11 or #12 or #13 or #14 #16 #8 and #15 #17 MeSH descriptor: [Infant, Newborn] explode all trees #18 MeSH descriptor: [Premature Birth] explode all trees #19 neonat*:ti,ab,kw (Word variations have been searched) #20 neo‐nat*:ti,ab,kw (Word variations have been searched) #21 newborn or new born* or newly born*:ti,ab,kw (Word variations have been searched) #22 preterm or preterms or (pre term) or (pre terms):ti,ab,kw (Word variations have been searched) #23 preemie* or premie or premies:ti,ab,kw (Word variations have been searched) #24 prematur* near/3 (birth* or born or deliver*):ti,ab,kw (Word variations have been searched) #25 low near/3 (birthweight* or birth weight*):ti,ab,kw (Word variations have been searched) #26 lbw or vlbw or elbw:ti,ab,kw (Word variations have been searched) #27 infan* or baby or babies:ti,ab,kw (Word variations have been searched) #28 #17 or #18 or #19 or #20 or #21 or #22 or #23 or #24 or #25 or #26 or #27 #29 #16 and #28
Maternity & Infant Care (MIDIRS)
Database: Maternity & Infant Care Database (MIDIRS) <1971 to May 2018>
Search Strategy:
‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐
1 (parenteral$ adj2 (fed or feed$ or nutrition$)).ti,ab.
2 (TPN or PPN or PN).mp.
3 (intravenous adj2 (infus$ or emulsion$)).ti,ab.
4 ("i.v." adj2 (infus$ or emulsion$)).ti,ab.
5 1 or 2 or 3 or 4
6 lipid$.mp.
7 (coconut$ or borage$ or fish$ or olive$ or soy$ or soybean$).mp.
8 ((alternative or conventional or multisource) adj LE).mp.
9 (alternative‐LE or conventional‐LE or multisource‐LE).mp.
10 structured MCT$.mp.
11 (arachidon$ or BS‐LE or clinoleic$ or DHA or docosahexaenoic acid$ or eicosapentaenoic acid$ or EPA or F‐LE).mp.
12 (intralipid$ or ivelip$).mp.
13 (LCT$ or linolenic$ or linoleic$ or lipidem$ or lipoplus$ or liposyn$ or lipovenoes$ or lipofundin$).mp.
14 (MCT‐fish or MCT‐olive or MCT‐soy or MFS‐LE or MOFS$ or MOFSLE$ or MCT$ or MS‐LE or MUFS$ monounsaturated).mp.
15 (omega‐6$ or omega‐3$ or omegaven$ or OS‐LE).mp.
16 (PFE 4501$ or PFE4501$ or polyunsaturated$ or PUFA$).mp.
17 (S‐LE or SMOF$ or structolipid$ or triacylgl$ or triglyc$).mp.
18 5 or 6 or 7 or 8 or 9 or 10 or 11 or 12 or 13 or 14 or 15 or 16 or 17
19 5 and 18
20 (neonat$ or neo nat$).ti,ab.
21 (newborn$ or new born$ or newly born$).ti,ab.
22 (preterm or preterms or pre term or pre terms).ti,ab.
23 (preemie$ or premie or premies).ti,ab.
24 (prematur$ adj3 (birth$ or born or deliver$)).ti,ab.
25 (low adj3 (birthweight$ or birth weight$)).ti,ab.
26 (lbw or vlbw or elbw).ti,ab.
27 infan$.ti,ab.
28 (baby or babies).ti,ab.
29 20 or 21 or 22 or 23 or 24 or 25 or 26 or 27 or 28
30 19 and 29
31 limit 30 to randomised controlled trial
32 limit 31 to yr="1980 ‐Current"
Trials Registers
www.clinicaltrials.gov Search date 19th June 2018 49 Studies found for: lipids | parenteral nutrition | Child WHO ICTRP search date 19th June 2018 40 records for 39 trials found for: parenteral nutrition AND lipids
Appendix 5. Risk of bias tool
We used the standard methods of Cochrane and Cochrane Neonatal to assess the methodological quality of the trials. For each trial, we sought information regarding the method of randomisation, blinding and reporting of all outcomes of all the infants enrolled in the trial. We assessed each criterion as being at a low, high or unclear risk of bias. Two review authors (VK, MM) separately assessed each study. We resolved any disagreements by discussion. We added this information to the Characteristics of included studies table. We evaluated the following issues and entered the findings into the 'Risk of bias' table.
1. Sequence generation (checking for possible selection bias). Was the allocation sequence adequately generated?
For each included study, we categorised the method used to generate the allocation sequence as:
low risk (any truly random process, e.g. random number table; computer random number generator);
high risk (any non‐random process, e.g. odd or even date of birth; hospital or clinic record number) or
unclear risk.
2. Allocation concealment (checking for possible selection bias). Was allocation adequately concealed?
For each included study, we categorised the method used to conceal the allocation sequence as:
low risk (e.g. telephone or central randomisation; consecutively numbered sealed opaque envelopes);
high risk (open random allocation; unsealed or non‐opaque envelopes, alternation; date of birth) or
unclear risk
3. Blinding of participants and personnel (checking for possible performance bias). Was knowledge of the allocated intervention adequately prevented during the study?
For each included study, we categorised the methods used to blind study participants and personnel from knowledge of which intervention a participant received. Blinding was assessed separately for different outcomes or class of outcomes. We categorised the methods as:
low risk, high risk or unclear risk for participants; and
low risk, high risk or unclear risk for personnel.
4. Blinding of outcome assessment (checking for possible detection bias). Was knowledge of the allocated intervention adequately prevented at the time of outcome assessment?
For each included study, we categorised the methods used to blind outcome assessment. Blinding was assessed separately for different outcomes or class of outcomes. We categorised the methods as:
low risk for outcome assessors;
high risk for outcome assessors or
unclear risk for outcome assessors.
5. Incomplete outcome data (checking for possible attrition bias through withdrawals, dropouts, protocol deviations). Were incomplete outcome data adequately addressed?
For each included study and for each outcome, we described the completeness of data including attrition and exclusions from the analysis. We noted whether attrition and exclusions were reported, the numbers included in the analysis at each stage (compared with the total randomised participants), reasons for attrition or exclusion where reported, and whether missing data were balanced across groups or were related to outcomes. Where sufficient information was reported or supplied by the trial authors, we reincluded missing data in the analyses. We categorised the methods as:
low risk (< 20% missing data);
high risk (≥ 20% missing data); or
unclear risk.
6. Selective reporting bias. Are reports of the study free of suggestion of selective outcome reporting?
For each included study, we described how we investigated the possibility of selective outcome reporting bias and what we found. For studies in which study protocols were published in advance, we compared prespecified outcomes versus outcomes eventually reported in the published results. If the study protocol was not published in advance, we contacted study authors to gain access to the study protocol. We assessed the methods as:
low risk (where it was clear that all the study's prespecified outcomes and all expected outcomes of interest to the review were reported);
high risk (where not all the study's prespecified outcomes were reported; one or more reported primary outcomes were not prespecified outcomes of interest and were reported incompletely and so could not be used; study failed to include results of a key outcome that would have been expected to have been reported); or
unclear risk.
7. Other sources of bias. Was the study apparently free of other problems that could put it at a high risk of bias?
For each included study, we described any important concerns we had about other possible sources of bias (e.g. whether there was a potential source of bias related to the specific study design or whether the trial was stopped early due to some data‐dependent process). We assessed whether each study was free of other problems that could put it at risk of bias as:
low risk;
high risk or
unclear risk.
If needed, we explored the impact of the level of bias through undertaking sensitivity analyses.
Appendix 6. Details of GRADE 'Quality of Evidence' decisions in the review and in the 'Summary of findings' tables
Assessment of risk of bias in a study (refer to the 'Risk of bias' tool in Appendix 5)
| No risk of bias | No critical limitation in any criteria* |
| Moderate risk of bias | Critical limitation in 1 criteria or some limitations in > 1 criteria |
| High risk of bias | Critical limitation in > 1 criteria |
*Criteria for assessing risk of bias in a study: lack of allocation concealment, lack of blinding, loss to follow‐up or intention‐to‐treat analysis not performed, selective outcome reporting or other limitations.
Decision matrix to downgrade for 'quality of studies' in an outcome
| Decision to downgrade | Risk of bias across studies for an outcome |
| Do not downgrade | Most information was from studies at low risk of bias |
| Downgrade 1 level | Most information was from studies at moderate risk of bias |
| Downgrade 2 levels | Most information was from studies at high risk of bias |
The evidence was also downgraded for an outcome if there was significant contribution from a study or studies at high risk of bias in one or more key domains, that was sufficient to affect the interpretation of results.
Decision matrix to downgrade for 'imprecision' in an outcome
|
Decision matrix for imprecision |
CIs did not cross null effect |
CIs crossed null effect but not 0.75 or 1.25 |
CIs crossed null effect AND crossed 0.75 or 1.25 |
| OIS adequate | Do not downgrade | Do not downgrade | Downgrade 1 level |
| OIS inadequate | Downgrade 1 level | Downgrade 1 level | Downgrade 2 levels |
Adequate optimal information size (OIS; empirical) for this review:
for categorical variables: "300 or more total events in both groups;"
for continuous variables: "minimum sample size of 400 participants" as a general approximation.
CI: confidence interval.
Decision matrix to downgrade for 'inconsistency' in an outcome
|
Decision matrix for inconsistency |
Heterogeneity I²> 40% (40% to 74%) |
Unexplained high heterogeneity with I²> 75%and very low P value |
| Same direction of effect estimates in the studies | May not downgrade 1 level if most of the studies have similar point estimates and overlapping CI AND all point estimates are pointing in the same direction. | Downgrade 1 level |
| Different direction of effect estimates in the studies | Downgrade 1 level | Downgrade 2 levels |
Adapted from GRADE Working Group recommendations (Schünemann 2013).
If a study was terminated early, we downgraded the level of evidence in the review even if the study was assigned unclear risk of bias for early termination. This was done in outcomes with limited number of participants, or where the terminated study was the only study in the outcome or it was one of the two studies in the outcome with a significant contribution (20% or greater).
Evidence was downgraded by one level for those outcomes where there was only a single small study.
Heterogeneity could not be assessed where there was a single study in an outcome.
CI: confidence interval.
Data and analyses
Comparison 1. Fish oil lipid emulsion (LE) versus non‐fish oil LE (see Appendix 3).
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Days to regain birth weight | 3 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 1.1 MOFS‐LE vs S‐LE | 3 | 234 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.12 [‐0.17, 2.41] |
| 1.2 MOFS‐LE vs OS‐LE | 1 | 57 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐2.0 [‐5.76, 1.76] |
| 1.3 MOFS‐LE vs MS‐LE | 1 | 58 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [‐2.58, 2.58] |
| 1.4 MFS‐LE vs S‐LE | 1 | 57 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐1.0 [‐3.60, 1.60] |
| 1.5 MFS‐LE vs MS‐LE | 1 | 57 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐2.0 [‐4.60, 0.60] |
| 1.6 MFS‐LE vs OS‐LE | 1 | 56 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐4.0 [‐7.78, ‐0.22] |
| 2 Growth rate (g/kg/day) | 5 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 2.1 MOFS‐LE vs S‐LE | 5 | 347 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.71 [‐0.17, 1.60] |
| 2.2 MOFS‐LE vs MS‐LE | 1 | 58 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.33 [‐6.53, 5.87] |
| 2.3 MOFS‐LE vs OS‐LE | 1 | 57 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐1.66 [‐7.91, 4.59] |
| 2.4 MFS‐LE vs S‐LE | 1 | 57 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐1.67 [‐7.01, 3.67] |
| 2.5 MFS‐LE vs MS‐LE | 1 | 57 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.0 [‐4.80, 6.80] |
| 2.6 MFS‐LE vs OS‐LE | 1 | 56 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.33 [‐6.18, 5.52] |
| 3 Parenteral nutrition‐associated liver disease (PNALD)/cholestasis (conjugated bilirubin ≥ 2 mg/dL) | 4 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 3.1 MOFS‐LE vs S‐LE | 3 | 182 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.56 [0.16, 1.99] |
| 3.2 MOFS‐LE vs MS‐LE | 2 | 118 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.61 [0.15, 2.41] |
| 3.3 MOFS‐LE vs OS‐LE | 1 | 57 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 3.10 [0.13, 73.12] |
| 3.4 MFS‐LE vs S‐LE | 1 | 57 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 3.32 [0.14, 78.25] |
| 3.5 MFS‐LE vs MS‐LE | 1 | 57 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.11 [0.07, 16.91] |
| 3.6 MFS‐LE vs OS‐LE | 1 | 56 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 3.21 [0.14, 75.68] |
| 4 PNALD/cholestasis (conjugated bilirubin ≥ 2 mg/dL): combined subgroups | 4 | 328 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.61 [0.24, 1.56] |
| 5 PNALD/cholestasis (any definition) | 11 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 5.1 MOFS‐LE vs S‐LE | 8 | 800 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.76 [0.49, 1.19] |
| 5.2 MOFS‐LE vs MS‐LE | 2 | 118 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.61 [0.15, 2.41] |
| 5.3 MOFS‐LE vs OS‐LE | 2 | 135 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.05 [0.48, 8.72] |
| 5.4 MFS‐LE vs S‐LE | 1 | 57 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 3.32 [0.14, 78.25] |
| 5.5 MFS‐LE vs MS‐LE | 1 | 57 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.11 [0.07, 16.91] |
| 5.6 MFS‐LE vs OS‐LE | 1 | 56 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 3.21 [0.14, 75.68] |
| 5.7 OFS‐LE vs OS‐LE | 1 | 130 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.18 [0.05, 0.56] |
| 6 PNALD/cholestasis (any definition): combined subgroups (all studies) and sensitivity analysis | 11 | 1154 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.63 [0.43, 0.91] |
| 6.1 Low or unclear risk of bias studies | 10 | 1024 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.80 [0.53, 1.21] |
| 6.2 High risk of bias studies | 1 | 130 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.18 [0.05, 0.56] |
| 7 Death before discharge | 13 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 7.1 MOFS‐LE vs S‐LE | 9 | 855 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.24 [0.81, 1.90] |
| 7.2 MOFS‐LE vs MS‐LE | 2 | 120 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.4 [0.28, 6.89] |
| 7.3 MOFS‐LE vs OS‐LE | 3 | 184 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.19 [0.48, 2.93] |
| 7.4 MFS‐LE vs S‐LE | 1 | 60 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 5.0 [0.25, 99.95] |
| 7.5 MFS‐LE vs MS‐LE | 1 | 60 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 5.0 [0.25, 99.95] |
| 7.6 MFS‐LE vs OS‐LE | 1 | 60 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 5.0 [0.25, 99.95] |
| 7.7 OFS‐LE vs OS‐LE | 1 | 175 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.12 [0.64, 1.97] |
| 8 Any ROP | 8 | 791 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.93 [0.79, 1.11] |
| 8.1 MOFS vs S‐LE | 5 | 523 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.92 [0.72, 1.17] |
| 8.2 MOFS‐LE vs MS‐LE | 1 | 60 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.86 [0.33, 2.25] |
| 8.3 MOFS‐LE vs OS‐LE | 1 | 78 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.06 [0.84, 1.35] |
| 8.4 OFS‐LE vs OS‐LE | 1 | 130 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.85 [0.53, 1.38] |
| 9 Retinopathy of prematurity (ROP) (≥ stage 3) or requiring surgery | 7 | 731 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.80 [0.55, 1.16] |
| 9.1 MOFS‐LE vs S‐LE | 5 | 523 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.82 [0.40, 1.68] |
| 9.2 MOFS‐LE vs OS‐LE | 1 | 78 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.25 [0.72, 2.18] |
| 9.3 OFS‐LE vs OS‐LE | 1 | 130 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.48 [0.24, 0.96] |
| 10 ROP (≥ stage 3) or requiring surgery (sensitivity analysis) | 6 | 601 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.02 [0.65, 1.60] |
| 10.1 MOFS‐LE vs S‐LE | 5 | 523 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.82 [0.40, 1.68] |
| 10.2 MOFS‐LE vs OS‐LE | 1 | 78 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.25 [0.72, 2.18] |
| 11 Any bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) | 11 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 11.1 MOFS‐LE vs S‐LE | 7 | 632 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.93 [0.71, 1.22] |
| 11.2 MOFS‐LE vs MS‐LE (1) | 1 | 60 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.36 [0.13, 1.01] |
| 11.3 MOFS‐LE vs MS‐LE (2) | 1 | 58 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.61 [0.51, 5.10] |
| 11.4 MOFS‐LE vs OS‐LE | 3 | 169 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.17 [0.82, 1.67] |
| 11.5 MFS‐LE vs S‐LE | 1 | 57 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.39 [0.42, 4.65] |
| 11.6 MFS‐LE vs MS‐LE | 1 | 57 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.39 [0.42, 4.65] |
| 11.7 MFS‐LE vs OS‐LE | 1 | 56 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.07 [0.35, 3.30] |
| 11.8 OFS‐LE vs OS‐LE | 1 | 130 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.86 [0.47, 1.56] |
| 12 Chronic lung disease (oxygen requirement at 36 weeks) | 9 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 12.1 MOFS‐LE vs S‐LE | 6 | 581 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.00 [0.75, 1.34] |
| 12.2 MOFS‐LE vs MS‐LE (1) | 1 | 60 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.33 [0.10, 1.11] |
| 12.3 MOFS‐LE vs MS‐LE (2) | 1 | 58 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.61 [0.51, 5.10] |
| 12.4 MOFS‐LE vs OS‐LE | 2 | 135 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.18 [0.78, 1.81] |
| 12.5 MFS‐LE vs S‐LE | 1 | 57 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.39 [0.42, 4.65] |
| 12.6 MFS‐LE vs MS‐LE | 1 | 57 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.39 [0.42, 4.65] |
| 12.7 MFS‐LE vs OS‐LE | 1 | 56 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.07 [0.35, 3.30] |
| 12.8 OFS‐LE vs OS‐LE | 1 | 130 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.86 [0.47, 1.56] |
| 13 Duration of ventilation (days) | 6 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 13.1 MOFS‐LE vs S‐LE | 5 | 475 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.08 [‐1.56, 1.73] |
| 13.2 MOFS‐LE vs MS‐LE | 1 | 60 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐7.40 [‐10.26, ‐4.54] |
| 14 Duration of supplemental oxygen (days) | 3 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 14.1 MOFS‐LE vs S‐LE | 2 | 140 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.47 [‐2.01, 2.95] |
| 14.2 MOFS‐LE vs MS‐LE | 1 | 60 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐13.80 [‐21.18, ‐6.42] |
| 15 Duration of hospital stay (days) | 8 | 812 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.48 [‐3.42, 2.46] |
| 15.1 MOFS‐LE vs S‐LE | 6 | 622 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.09 [‐3.35, 3.16] |
| 15.2 MOFS‐LE vs MS‐LE | 1 | 60 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐3.35 [‐17.13, 10.43] |
| 15.3 OFS‐LE vs OS‐LE | 1 | 130 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐1.80 [‐9.72, 6.12] |
| 16 Culture‐positive sepsis | 7 | 774 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.16 [0.91, 1.48] |
| 16.1 MOFS‐LE vs S‐LE | 5 | 566 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.02 [0.74, 1.40] |
| 16.2 MOFS‐LE vs OS‐LE | 1 | 78 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.56 [0.86, 2.83] |
| 16.3 OFS‐LE vs OS‐LE | 1 | 130 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.35 [0.81, 2.24] |
| 17 Any sepsis (clinical or culture positive (or both)) | 12 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 17.1 MOFS‐LE vs S‐LE | 9 | 832 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.99 [0.78, 1.26] |
| 17.2 MOFS‐LE vs MS‐LE | 2 | 118 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.80 [0.39, 1.67] |
| 17.3 MOFS‐LE vs OS‐LE | 2 | 135 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.62 [0.96, 2.75] |
| 17.4 MFS‐LE vs S‐LE | 1 | 57 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.11 [0.31, 4.02] |
| 17.5 MFS‐LE vs MS‐LE | 1 | 57 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.56 [0.19, 1.64] |
| 17.6 MFS‐LE vs OS‐LE | 1 | 56 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.07 [0.30, 3.87] |
| 17.7 OFS‐LE vs OS‐LE | 1 | 130 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.35 [0.81, 2.24] |
| 18 Necrotising enterocolitis (≥ stage 2) | 10 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 18.1 MOFS‐LE vs S‐LE | 7 | 749 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.32 [0.81, 2.13] |
| 18.2 MOFS‐LE vs MS‐LE | 2 | 118 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.45 [0.07, 2.91] |
| 18.3 MOFS‐LE vs OS‐LE | 2 | 135 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.37 [0.47, 11.99] |
| 18.4 MFS‐LE vs S‐LE | 1 | 57 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 18.5 MFS‐LE vs MS‐LE | 1 | 57 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.22 [0.01, 4.42] |
| 18.6 MFS‐LE vs OS‐LE | 1 | 56 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.36 [0.02, 8.41] |
| 18.7 OFS‐LE vs OS‐LE | 1 | 130 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.78 [0.23, 2.63] |
| 19 Intraventricular haemorrhage (grade III‐IV) | 7 | 617 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.05 [0.65, 1.72] |
| 19.1 MOFS‐LE vs S‐LE | 5 | 523 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.19 [0.71, 1.99] |
| 19.2 MOFS‐LE vs OS‐LE | 1 | 34 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.2 [0.01, 3.88] |
| 19.3 MOFS‐LE vs MS‐LE | 1 | 60 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.5 [0.05, 5.22] |
| 20 Periventricular leukomalacia | 3 | 399 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.77 [0.18, 3.36] |
| 20.1 MOFS‐LE vs S‐LE | 3 | 399 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.77 [0.18, 3.36] |
| 21 Any patent ductus arteriosus | 8 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 21.1 MOFS‐LE vs S‐LE | 5 | 501 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.91 [0.77, 1.09] |
| 21.2 MOFS‐LE vs MS‐LE | 1 | 58 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.82 [0.49, 1.36] |
| 21.3 MOFS‐LE vs OS‐LE | 3 | 169 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.84 [0.66, 1.09] |
| 21.4 MFS‐LE vs S‐LE | 1 | 57 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.96 [0.57, 1.64] |
| 21.5 MFS‐LE vs MS‐LE | 1 | 57 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.85 [0.51, 1.40] |
| 21.6 MFS‐LE vs OS‐LE | 1 | 56 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.93 [0.55, 1.58] |
| 21.7 OFS‐LE vs OS‐LE | 1 | 130 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.01 [0.62, 1.66] |
| 22 Significant patent ductus arteriosus requiring treatment | 6 | 605 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.89 [0.76, 1.04] |
| 22.1 MOFS‐LE vs S‐LE | 3 | 363 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.89 [0.73, 1.08] |
| 22.2 MOFS‐LE vs OS‐LE | 2 | 112 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.82 [0.62, 1.09] |
| 22.3 OFS‐LE vs OS‐LE | 1 | 130 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.01 [0.62, 1.66] |
| 23 Duration of phototherapy (days) | 1 | 32 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [‐2.57, 2.57] |
| 23.1 MOFS‐LE vs S‐LE | 1 | 32 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [‐2.57, 2.57] |
| 24 Hypertriglyceridaemia | 5 | 697 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.01 [0.80, 1.28] |
| 24.1 MOFS‐LE vs S‐LE | 4 | 567 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.03 [0.81, 1.30] |
| 24.2 OFS‐LE vs OS‐LE | 1 | 130 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.7 [0.17, 2.81] |
| 25 Hyperglycaemia | 3 | 280 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.40 [0.77, 2.53] |
| 25.1 MOFS‐LE vs S‐LE | 3 | 280 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.40 [0.77, 2.53] |
| 26 Hypoglycaemia | 2 | 248 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.14 [0.77, 1.69] |
| 26.1 MOFS‐LE vs S‐LE | 2 | 248 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.14 [0.77, 1.69] |
| 27 Head growth velocity (cm/week) | 2 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 27.1 MOFS‐LE vs S‐LE | 2 | 140 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [‐0.08, 0.08] |
| 28 Length velocity (cm/week) | 1 | 44 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.10 [‐0.02, 0.22] |
| 28.1 MOFS‐LE vs S‐LE | 1 | 44 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.10 [‐0.02, 0.22] |
| 29 Intrahepatocellular lipid | 1 | 132 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.03 [‐0.17, 0.23] |
| 29.1 MOFS‐LE vs S‐LE | 1 | 132 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.03 [‐0.17, 0.23] |
| 30 Non‐adipose tissue mass | 1 | 133 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 24.20 [‐133.14, 181.54] |
| 31 Conjugated bilirubin levels (µmol/L) | 10 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 31.1 MOFS‐LE vs S‐LE | 8 | 673 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.48 [‐1.16, 0.19] |
| 31.2 MOFS‐LE vs MS‐LE | 1 | 58 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.35 [‐3.65, 4.35] |
| 31.3 MOFS‐LE vs OS‐LE | 2 | 91 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐1.68 [‐4.07, 0.71] |
| 31.4 MFS‐LE vs S‐LE | 1 | 57 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.72 [‐3.86, 5.30] |
| 31.5 MFS‐LE vs MS‐LE | 2 | 105 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.15 [‐0.67, 4.98] |
| 31.6 MFS‐LE vs OS‐LE | 1 | 56 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐1.16 [‐6.13, 3.81] |
1.31. Analysis.
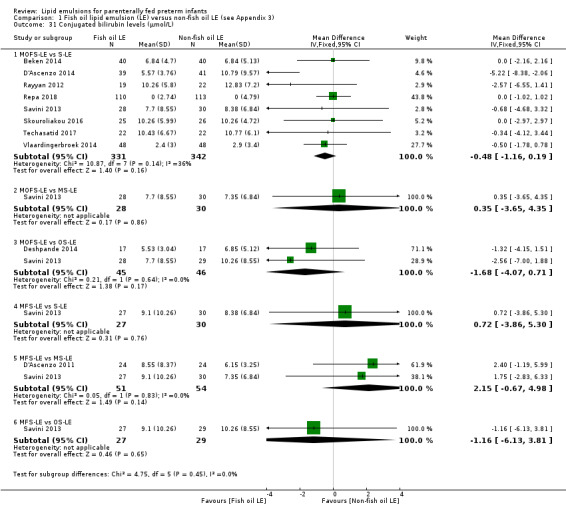
Comparison 1 Fish oil lipid emulsion (LE) versus non‐fish oil LE (see Appendix 3), Outcome 31 Conjugated bilirubin levels (µmol/L).
Comparison 2. Fish oil lipid emulsion (LE) vs another fish oil LE (see Appendix 3).
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Days to regain birth weight | 1 | 55 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.0 [‐0.64, 4.64] |
| 1.1 MOFS‐LE vs MFS‐LE | 1 | 55 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.0 [‐0.64, 4.64] |
| 2 Growth rate (g/kg/day) | 1 | 55 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 4.0 [‐2.03, 10.03] |
| 2.1 MOFS‐LE vs MFS‐LE | 1 | 55 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 4.0 [‐2.03, 10.03] |
| 3 Parenteral nutrition‐associated liver disease (PNALD)/cholestasis (conjugated bilirubin ≥ 2 mg/dL) | 1 | 55 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.96 [0.06, 14.65] |
| 3.1 MOFS‐LE vs MFS‐LE | 1 | 55 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.96 [0.06, 14.65] |
| 4 PNALD/cholestasis (any definition) | 1 | 55 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.96 [0.06, 14.65] |
| 4.1 MOFS‐LE vs MFS‐LE | 1 | 55 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.96 [0.06, 14.65] |
| 5 Death before discharge | 1 | 60 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.0 [0.15, 6.64] |
| 5.1 MOFS‐LE vs MFS‐LE | 1 | 60 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.0 [0.15, 6.64] |
| 6 Chronic lung disease (oxygen requirement at 36 weeks) | 1 | 55 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.16 [0.40, 3.35] |
| 6.1 MOFS‐LE vs MFS‐LE | 1 | 55 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.16 [0.40, 3.35] |
| 7 Any sepsis (clinical or culture positive (or both)) | 1 | 55 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.69 [0.56, 5.11] |
| 7.1 MOFS‐LE vs MFS‐LE | 1 | 55 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.69 [0.56, 5.11] |
| 8 Necrotising enterocolitis (≥ stage 2) | 1 | 55 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.90 [0.12, 68.15] |
| 8.1 MOFS‐LE vs MFS‐LE | 1 | 55 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.90 [0.12, 68.15] |
| 9 Any patent ductus arteriosus | 1 | 55 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.96 [0.55, 1.69] |
| 9.1 MOFS‐LE vs MFS‐LE | 1 | 55 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.96 [0.55, 1.69] |
| 10 Conjugated bilirubin levels (µmol/L) | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 10.1 MOFS‐LE vs MFS‐LE | 1 | 55 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐1.40 [‐6.40, 3.60] |
Comparison 3. Alternative lipid emulsion (LE) versus soybean oil‐based lipid emulsion (S‐LE) (see Appendix 3).
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Days to regain birth weight | 3 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 1.1 MS‐LE vs S‐LE | 1 | 59 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 3.0 [‐0.73, 6.73] |
| 1.2 OS‐LE vs S‐LE | 3 | 223 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.19 [‐2.00, 1.62] |
| 2 Growth rate (g/kg/day) | 2 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 2.1 MS‐LE vs S‐LE | 1 | 60 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐2.67 [‐8.20, 2.86] |
| 2.2 OS‐LE vs S‐LE | 2 | 123 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.42 [‐5.15, 4.30] |
| 3 Parenteral nutrition‐associated liver disease (PNALD)/cholestasis (conjugated bilirubin ≥ 2 mg/dL) | 2 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 3.1 OS‐LE vs S‐LE | 2 | 159 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.0 [0.15, 6.82] |
| 3.2 MS‐LE vs S‐LE | 1 | 60 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 3.0 [0.13, 70.83] |
| 4 PNALD/cholestasis (conjugated bilirubin ≥ 2 mg/dL): Combined subgroups | 2 | 189 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.14 [0.22, 5.84] |
| 5 PNALD/cholestasis (any definition) | 4 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 5.1 OS‐LE vs S‐LE | 4 | 261 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.0 [0.26, 3.86] |
| 5.2 MS‐LE vs S‐LE | 1 | 60 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 3.0 [0.13, 70.83] |
| 6 PNALD/cholestasis (any definition): Combined subgroups | 4 | 291 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.08 [0.31, 3.72] |
| 6.1 OS‐LE vs S‐LE | 4 | 291 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.08 [0.31, 3.72] |
| 7 Death before discharge | 3 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 7.1 OS‐LE vs S‐LE | 3 | 224 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.0 [0.21, 4.82] |
| 7.2 MS‐LE vs S‐LE | 1 | 60 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 8 Any retinopathy of prematurity | 3 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 8.1 OS‐LE vs S‐LE | 3 | 142 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.98 [0.67, 1.43] |
| 9 Any bronchopulmonary dysplasia | 4 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 9.1 OS‐LE vs S‐LE | 4 | 261 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.69 [0.46, 1.04] |
| 9.2 OS‐LE vs S‐LE (sensitivity analysis) | 3 | 197 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.01 [0.57, 1.79] |
| 9.3 MS‐LE vs S‐LE | 1 | 60 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.0 [0.28, 3.63] |
| 10 Chronic lung disease (oxygen requirement at 36 weeks) | 2 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 10.1 OS‐LE vs S‐LE | 2 | 123 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.59 [0.34, 1.01] |
| 10.2 MS‐LE vs S‐LE | 1 | 60 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.0 [0.28, 3.63] |
| 11 Duration of ventilation (days) | 3 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 11.1 OS‐LE vs S‐LE | 3 | 202 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.20 [‐1.67, 1.26] |
| 12 Duration of supplemental oxygen (days) | 2 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 12.1 OS‐LE vs S‐LE | 2 | 102 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.76 [‐16.99, 15.47] |
| 13 Duration of hospital stay (days) | 2 | 164 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.33 [‐7.44, 8.10] |
| 13.1 OS‐LE vs S‐LE | 2 | 164 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.33 [‐7.44, 8.10] |
| 14 Need for home oxygen therapy | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 14.1 OS‐LE vs S‐LE | 1 | 64 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 15 Any sepsis (clinical or culture positive (or both)) | 5 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 15.1 MS‐LE vs S‐LE | 1 | 60 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.0 [0.67, 5.94] |
| 15.2 OS‐LE vs S‐LE | 5 | 301 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.87 [0.56, 1.36] |
| 16 Culture‐positive sepsis | 2 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 16.1 OS‐LE vs S‐LE | 2 | 164 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.22 [0.54, 2.78] |
| 17 Necrotising enterocolitis (≥ stage 2) | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 17.1 MS‐LE vs S‐LE | 1 | 60 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 5.0 [0.25, 99.95] |
| 17.2 OS‐LE vs S‐LE | 1 | 59 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 3.1 [0.13, 73.14] |
| 18 Intraventricular haemorrhage (grade III‐IV) | 2 | 104 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.5 [0.10, 2.61] |
| 18.1 OS‐LE vs S‐LE | 2 | 104 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.5 [0.10, 2.61] |
| 19 Periventricular leukomalacia | 1 | 64 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.33 [0.01, 7.89] |
| 19.1 OS‐LE vs S‐LE | 1 | 64 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.33 [0.01, 7.89] |
| 20 Any patent ductus arteriosus | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 20.1 OS‐LE vs S‐LE | 1 | 59 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.03 [0.63, 1.71] |
| 20.2 MS‐LE vs S‐LE | 1 | 60 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.13 [0.70, 1.82] |
| 21 Air leaks | 1 | 64 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.5 [0.05, 5.24] |
| 21.1 OS‐LE vs S‐LE | 1 | 64 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.5 [0.05, 5.24] |
| 22 Significant jaundice requiring treatment | 2 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 22.1 OS‐LE vs S‐LE | 2 | 109 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.04 [0.52, 2.07] |
| 23 Duration of phototherapy (days) | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 23.1 OS‐LE vs S‐LE | 1 | 38 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.10 [‐1.08, 0.88] |
| 24 Hypertriglyceridaemia | 4 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 24.1 OS‐LE vs S‐LE | 3 | 142 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.67 [0.12, 3.73] |
| 24.2 MS‐LE vs S‐LE | 1 | 12 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 25 Hyperglycaemia | 1 | 64 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.0 [0.22, 4.59] |
| 25.1 OS‐LE vs S‐LE | 1 | 64 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.0 [0.22, 4.59] |
| 26 Head growth velocity (cm/week) | 1 | 100 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.08 [‐0.17, 0.01] |
| 26.1 OS‐LE vs S‐LE | 1 | 100 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.08 [‐0.17, 0.01] |
| 27 Conjugated bilirubin levels (µmol/L) | 5 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 27.1 MS‐LE vs S‐LE | 1 | 60 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐1.03 [‐4.49, 2.43] |
| 27.2 OS‐LE vs S‐LE | 5 | 310 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.24 [‐1.03, 0.55] |
Comparison 4. Alternative lipid emulsion (LE) vs another alternative‐LE (see Appendix 3).
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Days to regain birth weight | 1 | 59 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐2.0 [‐5.73, 1.73] |
| 1.1 MS‐LE vs OS‐LE | 1 | 59 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐2.0 [‐5.73, 1.73] |
| 2 Growth rate (g/kg/day) | 1 | 59 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐1.33 [‐7.36, 4.70] |
| 2.1 MS‐LE vs OS‐LE | 1 | 59 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐1.33 [‐7.36, 4.70] |
| 3 Parenteral nutrition‐associated liver disease (PNALD)/cholestasis (conjugated bilirubin ≥ 2 mg/dL) | 1 | 59 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.90 [0.12, 68.50] |
| 3.1 MS‐LE vs OS‐LE | 1 | 59 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.90 [0.12, 68.50] |
| 4 PNALD/cholestasis (any definition) | 1 | 59 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.90 [0.12, 68.50] |
| 4.1 MS‐LE vs OS‐LE | 1 | 59 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.90 [0.12, 68.50] |
| 5 Death before discharge | 1 | 60 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 5.1 MS‐LE vs OS‐LE | 1 | 60 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 6 Chronic lung disease (oxygen requirement at 36 weeks) | 1 | 59 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.77 [0.23, 2.60] |
| 6.1 MS‐LE vs OS‐LE | 1 | 59 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.77 [0.23, 2.60] |
| 7 Any sepsis (clinical or culture positive (or both)) | 1 | 59 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.93 [0.65, 5.73] |
| 7.1 MS‐LE vs OS‐LE | 1 | 59 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.93 [0.65, 5.73] |
| 8 Necrotising enterocolitis (≥ stage 2) | 1 | 59 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.93 [0.19, 20.18] |
| 8.1 MS‐LE vs OS‐LE | 1 | 59 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.93 [0.19, 20.18] |
| 9 Any patent ductus arteriosus | 1 | 59 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.10 [0.68, 1.75] |
| 9.1 MS‐LE vs OS‐LE | 1 | 59 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.10 [0.68, 1.75] |
| 10 Conjugated bilirubin levels (µmol/L) | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 10.1 MS‐LE vs OS‐LE | 1 | 59 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐2.91 [‐6.87, 1.05] |
Comparison 5. Fish oil lipid emulsion (LE) vs non‐fish oil LE in preterm infants with surgical conditions (see Appendix 3).
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Parenteral nutrition‐associated liver disease (PNALD)/cholestasis (conjugated bilirubin ≥ 2 mg/dL) | 1 | 19 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.11 [0.08, 15.28] |
| 1.1 Pure F‐LE vs S‐LE | 1 | 19 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.11 [0.08, 15.28] |
| 2 Death before discharge | 1 | 19 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 2.1 Pure F‐LE vs S‐LE | 1 | 19 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 3 Culture‐positive sepsis | 1 | 19 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.11 [0.39, 3.19] |
| 3.1 Pure F‐LE vs S‐LE | 1 | 19 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.11 [0.39, 3.19] |
| 4 Hypertriglyceridemia | 1 | 19 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 4.1 Pure F‐LE vs S‐LE | 1 | 19 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 5 Conjugated bilirubin levels (µmol/L) | 1 | 14 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [‐11.30, 11.30] |
| 5.1 Pure F‐LE vs S‐LE | 1 | 14 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [‐11.30, 11.30] |
Comparison 6. Fish oil lipid emulsion (LE) vs non‐fish oil LE in preterm infants with cholestasis (see Appendix 3).
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Growth rate (g/week) | 1 | 16 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 45.0 [15.00, 75.00] |
| 1.1 Pure F‐LE vs S‐LE | 1 | 16 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 45.0 [15.00, 75.00] |
| 2 Resolution of parenteral nutrition‐associated liver disease (PNALD)/cholestasis (conjugated bilirubin < 2 mg/dL) | 1 | 16 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 5.6 [0.34, 93.35] |
| 2.1 Pure F‐LE vs IL | 1 | 16 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 5.6 [0.34, 93.35] |
| 3 PNALD/cholestasis (any definition) | 2 | 40 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.54 [0.32, 0.91] |
| 3.1 MOFS‐LE vs S‐LE | 1 | 24 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.39 [0.14, 1.10] |
| 3.2 Pure F‐LE vs S‐LE | 1 | 16 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.69 [0.43, 1.13] |
| 4 Death before discharge | 2 | 40 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.24 [0.03, 1.87] |
| 4.1 MOFS‐LE vs S‐LE | 1 | 24 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.39 [0.02, 8.69] |
| 4.2 Pure F‐LE vs S‐LE | 1 | 16 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.16 [0.01, 2.88] |
| 5 Any sepsis | 2 | 40 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.21 [0.50, 2.92] |
| 5.1 MOFS‐LE vs S‐LE | 1 | 24 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.48 [0.52, 4.18] |
| 5.2 Pure F‐LE vs S‐LE | 1 | 16 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.78 [0.14, 4.23] |
| 6 Hyperglycaemia | 1 | 24 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.48 [0.52, 4.18] |
| 7 Head growth velocity (cm/week) | 1 | 16 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.16 [‐0.01, 0.33] |
| 7.1 Pure F‐LE vs S‐LE | 1 | 16 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.16 [‐0.01, 0.33] |
| 8 Conjugated bilirubin levels (µmol/L) | 1 | 24 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐47.0 [‐71.65, ‐22.35] |
| 8.1 MOFS‐LE vs S‐LE | 1 | 24 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐47.0 [‐71.65, ‐22.35] |
Characteristics of studies
Characteristics of included studies [ordered by study ID]
Beken 2014.
| Methods | Design: RCT Setting: single‐centre NICU of Dr Sami Ulus Maternity and Children Research Centre in Ankara, Turkey Study enrolment: 1 January 2013 to 31 July 2013 I. Allocation concealment: yes II. Blinding of intervention: could not determine III. Blinding of outcome measurement(s): yes (for ROP) IV. Complete follow‐up: yes |
|
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: < 1500 g and < 32 weeks' gestation Exclusion criteria: major congenital abnormalities, congenital infections and metabolic errors |
|
| Interventions | 80 infants were randomly assigned. Group 1 (n = 40): MOFS‐LE; 20% SMOFlipid Group 2 (n = 40): S‐LE; 20% Intralipid TPN was started with intravenous glucose and amino acid solution 1 g/kg on first day of life. The LEs were administered from day 1 as a continuous infusion for 24 hour/day. Initial lipid daily dose 0.5 g/kg/day if birth weight < 1000 g and 1 g/kg/day if birth weight > 1000 g. Lipids were increased by 0.5–1.0 g/kg every 24 hours to a maximum of 3 g/kg/day. Infants in both arms also received trace elements, water and lipid‐soluble vitamins as a standard part of the TPN protocol. Both groups were started on enteral feeds with DHA‐enriched preterm formula or breast milk. |
|
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: ROP Secondary outcomes: cholestasis, nosocomial infections, NEC, CLD and mortality Laboratory data including complete blood count, TG levels, and liver and kidney function tests were recorded. |
|
| Notes | Funding: none revealed. DHA levels were not recorded in the 2 groups. |
|
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "Randomly assigned to one of the two groups by balanced blocks using sealed envelopes. Stratification was not included in the block design." Comment: method of random sequence generation not described. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "Randomly assigned to one of the two groups by balanced blocks using sealed envelopes. Group assignment was made by the investigator (last author) who was not involved in the care of the infants." "A member of the TPN team who was blinded and not involved in the care of infants followed orders from the sealed envelope prepared by the investigators." Comment: review authors decided by consensus that the risk was low. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | Quote: "Nurses and doctors responsible for the infants were also blinded to the group assignment." Comment: how the blinding was achieved was not described, therefore the risk was unclear. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Quote: "All fundus examinations were performed by the same pediatric ophthalmologist who was blinded to the group assignment." Comment: probably done (decision by consensus between review author (VK and MM)). |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Comment: follow‐up complete |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Comment: trial registered with ClinicalTrials.gov under identifier: NCT01875510 and there appeared to be no deviation from the protocol. Study started on 1 January 2013; however, protocol was registered on 31 May 2013. Review authors decided by consensus that the risk was probably low for selective reporting. |
| Other bias | Low risk | Comment: none identified |
Biagetti 2016.
| Methods | Design: 2‐arm, parallel group, pilot RCT Setting: single‐centre NICU of "G. Salesi" Children's Hospital, Ancona, Italy Study enrolment: January 2007 to June2012 I. Allocation concealment: yes II. Blinding of intervention: yes III. Blinding of outcome measurement(s): yes IV. Complete follow‐up: no |
|
| Participants | Population: neonates with a birth weight of 500–1249 g, who routinely received PN from the first hour of life and not participating to other trials, were enrolled. At birth, the caring neonatologist randomised the study infants by a simple randomisation method (sealed envelope system). Exclusion criteria: severe malformations, inborn errors of metabolism and severe sepsis. In addition, infants without a catheter suitable for blood sampling on day of life 7 were excluded because of the impossibility of blood drawing. |
|
| Interventions | Interventions: newborn infants were randomly assigned in a 1:1 ratio. Group 1 (n = 26): MFS‐LE: LE consisting of a physical mixture of 50% MCT, 40% soybean oil, and 10% fish oil, MSF (Lipidem; B Braun, Milan, Italy) Group 2 (n = 26): MS‐LE; standard product containing 50:50 MCT:SO, MS (Lipofundin MCT; B. Braun) PN was an all‐in‐one mixture for the study groups and the PN bags containing the study LE were of the same size and identical appearance. PN with glucose, amino acids and lipids was started at about 1 hour after birth, according to the NICU protocol. LE were infused at dose of 1 g/kg/day, 1.5 g/kg/day, 2 g/kg/day, 2.5 g/kg/day and 3 g/kg/day from postnatal day 0 to day 5, and were then kept constant from day 5 to day 7. Fat intake on postnatal day 7 was 2.5–3.0 g/kg/day. Minimal enteral feeding with human milk was provided from days 0–7, the maximum amount supplied being 8 mL/kg/day from day 1 to day 4, and 16 mL/kg/day from day 5 to day 7. |
|
| Outcomes | Primary outcomes: plasma PL palmitate biosynthesis (for de novo lipogenesis) and FC biosynthesis (for cholesterol synthesis) on day 7. Secondary outcomes: PL, FC and CE and TG plasma concentrations, measured from 0.4 mL EDTA‐blood collected on day 7. Lipogenesis of stearate and oleate in plasma PL, TG and CE and lipogenesis of palmitate in plasma TG and CE were measured on day 7. CE biosynthesis was also measured on day 7. |
|
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: at birth, the caring neonatologist randomised the study infants by a simple randomisation method (sealed envelope system)." Comment: the random element was not described. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "At birth, the caring neonatologist randomised the study infants by a simple randomisation method (sealed envelope system)." Comment: probably done. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Quote: "Both the caregivers involved with data collection and the laboratory personnel were blinded to group assignment." Comment: probably done. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Quote: "Both the caregivers involved with data collection and the laboratory personnel were blinded to group assignment." Probably done (by author consensus). |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | High risk | Quote: "5 out of 20 in Lipidem arm and 4 out of 20 in Lipofundin arm were excluded from analysis because of difficult blood sampling." Comment: this amounts to close to 20% of participants in both arms. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "Since this trial started in 2007, trial registration was not required." Comment: selective reporting could not be assessed as we did not have access to the protocol. |
| Other bias | Low risk | None detected |
D'Ascenzo 2011.
| Methods | Design: pilot study Setting: single‐centre NICU of "G. Salesi" Children's Hospital, Ancona, Italy Study enrolment: September 2007 to May 2008 7‐day study primarily looking at the plasma lipids in preterm infants given a new LE containing 10% fish oil, 50% MCTs. Study enrolment: 1 January 2013 to 31 July 2013 I. Allocation concealment: yes II. Blinding of intervention: could not determine III. Blinding of outcome measurement(s): could not determine IV. Complete follow‐up: yes (as per the study design) |
|
| Participants | Preterm infants bodyweight 500–1249 g, who routinely receive PN from the first hour of life. Exclusion criteria were severe malformations, inborn errors of metabolism and severe sepsis. | |
| Interventions | 48 infants < 1250 g were randomly assigned Group 1 (n = 24): MFS‐LE (10:50:40) Group 2 (n = 24): MS‐LE (50:50) LE started at 0.5 g/kg/day, increased by increments of 0.5 g/kg/day to reach 2.5 g/kg/day with 8 mL/kg/day EBM or formula for days 1–4, and then 16 mL/kg/day for days 5–8. Oral feeding was gradually increased from day 9 to reach full oral feeds by day 18, when the TPN was completely tapered. |
|
| Outcomes | Plasma and RBC FA composition was evaluated on days 7 and 14. Daily weight and weekly head circumference, length were measured with z scores calculated using the Italian reference data. The z scores could not be used to give gram/kg/day for the study as: we had no access to the normative growth charts for Italian children; even with using the growth charts we would not get the correct decimal value by back conversion; we did not have the data on covariance for conversion of growth parameters to rate of growth. |
|
| Notes | No other clinical outcomes reported. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "random assignment was performed by sealed envelope system in the first minutes of life." Comment: random component not adequately described. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "random assignment was performed by sealed envelope system in the first minutes of life." Comment: though the envelopes were not described as opaque, guided by the previous studies of the research group, we did not increase the risk. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | Comment: not mentioned. Though blinding was not mentioned, the outcomes (blood parameters, growth parameters) were objective outcomes and may not have been significantly impacted. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | Comment: not mentioned. Though blinding was not mentioned, the outcomes (blood parameters, growth parameters) were objective outcomes and may not have been significantly impacted. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Comment: adequate reporting of the outcome data. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: trial protocol not available. Comment: we could not estimate the risk. |
| Other bias | Low risk | Comment: none detected. |
D'Ascenzo 2014.
| Methods | Setting: NICU of Salesi Children's Hospital, Rome, Italy Study enrolment: January 2008 to December 2012 I. Allocation concealment: yes II. Blinding of intervention: yes III. Blinding of outcome measurement(s): yes IV. Complete follow‐up: yes |
|
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: preterm infants, birth weight 500–1249 g Exclusion criteria: severe congenital malformations or no consent |
|
| Interventions | 80 preterm infants were randomised in 1:1:1:1 ratio to receive either SMOFlipid or Intralipid at rate of either 3.5 g/kg/day or 2.5 g/kg/day in 4 groups: Group 1 (n = 21): MOFS‐LE 2.5: MOFS‐LE (30% soybean oil, 30% MCT, 25% olive oil, 15% fish oil), SMOFlipid Fresenius Kabi. Group 2 (n = 18): MOFS‐LE 3.5: MOFS‐LE (30% soybean oil, 30% MCT, 25% olive oil, 15% fish oil), SMOFlipid Fresenius Kabi. Group 3 (n = 22): S‐LE 2.5: S‐LE (100% soybean oil), Intralipid Fresenius Kabi. Group 4 (n = 19): S‐LE 3.5: S‐LE (100% soybean oil), Intralipid Fresenius Kabi. |
|
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: plasma PL and DHA (mol%) on postnatal day 7. Secondary outcomes: on postnatal day 7 and 14, levels of plasma FAs and plasma lipid concentration, TG levels, FC and CEs. Other outcomes reported: death and clinical outcomes. |
|
| Notes | Funding source: none revealed. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "At birth, the caring neonatologist randomised the study infants by a simple randomisation method (sealed envelope system)." Comment: probably done as the previous reports involving the same team has mentioned it in their previous report: "Randomization was obtained with sealed envelopes using a random permuted blocks within strata protocol" (decision by consensus between the review authors). |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "sealed envelope system." Comment: low risk of bias. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Quote: "The PN bags containing the study lipid emulsion were of the same size and of identical appearance. Both the caregivers involved with data collection and the laboratory personnel were blind to group assignment." Comment: probably done. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Quote: "The PN bags containing the study lipid emulsion were of the same size and of identical appearance. Both the caregivers involved with data collection and the laboratory personnel were blind to group assignment." Comment: probably done. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Comment: follow‐up was complete. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "The trial was conducted between January 2008 and December 2012 so we had not registered it in a public trials registry as it is now required for trials that started after July 2008." Comment: study protocol was not available so we could not ascertain any deviation from the protocol. |
| Other bias | Low risk | Comment: none identified. |
Demirel 2011.
| Methods | Design: prospective RCT Setting: single‐centre NICU of Zekai Tahir Burak Maternity Teaching Hospital in Turkey Study enrolment: January 2010 to October 2010 I. Allocation concealment: could not determine II. Blinding of intervention: no III. Blinding of outcome measurement(s): no IV. Complete follow‐up: yes (however, deaths were excluded) |
|
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: VLBW preterm infants ≤ 32 weeks' gestation and receiving ≥ 40% parenteral calories at 14th day of life. Exclusion criteria: metabolic disorders, congenital anomalies, severe unconjugated hyperbilirubinaemia, using medications in competition with bilirubin, birth asphyxia and death within 14 days of life. |
|
| Interventions | Group 1 (n = 20): OS‐LE; ClinOleic Group 2 (n = 20): S‐LE; Intralipid TPN protocol: LE was started on day 2 of life at 1 g/kg/day and increased daily by 1g/kg/day to 3 g/kg/day (24‐hour infusion). Amino acids were given as Primene 10% besides glucose, electrolytes and vitamins. Enteral feeding started on day 2, lipids started on day 2. |
|
| Outcomes | Main outcome measures: plasma lipid concentrations and acyl carnitine profile Other outcomes: gestational age, birth weight, sex, APGAR scores, day 14 weight, RDS, ROP and sepsis. No data provided for NEC and BPD Liver function tests (ALT, AST, GGT), lipid profile and carnitine levels were recorded. |
|
| Notes | Authors postulated that higher levels of hexanoyl carnitine reflecting defective mitochondrial transport of hexanoyl may lead to immunosuppression which may be the cause of higher sepsis risk in the Intralipid group (hexanoyl carnitine levels 0.38 ± 0.12 μM in Group 1 and 2.18 ± 2.10 μM in group 2 (P = 0.005). | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "Using computer‐generated randomisation sequence." Comment: probably done. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: the details of allocation concealment have not been mentioned. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | High risk | Comment: not a blinded study. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | High risk | Comment: not a blinded study. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Comment: outcomes were reported for all included participants. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: study protocol was not available so we could not ascertain any deviation from the protocol. Also, data were not provided for outcomes of NEC and BPD which were reported as "statistically insignificant between the groups" (data for these outcomes could not be used in meta‐analyses). |
| Other bias | High risk | Quote: "The major limitation of our study was based on the randomisation method based on per protocol. We analyzed the patients that fulfil the inclusion criteria at the 14th day of life." "Only patients who were receiving 40% of calories parenterally at Day 14 were included in the study. Those who died were also excluded from the study. This methodology can introduce problems with randomisation design and serious bias." Comment: possibly high risk. |
Deshpande 2009.
| Methods | Design: double‐blind RCT Setting: Department of Neonatal Paediatrics at KEM Hospital in Perth, Western Australia. Study enrolment: November 2006 to August 2007 I. Allocation concealment: yes II. Blinding of intervention: yes III. Blinding of outcome measurement(s): yes IV. Complete follow‐up: yes |
|
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: preterm infants < 28 weeks' gestation aged < 7 days at recruitment with PN accounting for > 75% of energy intake. Exclusion criteria: major congenital malformations, inborn errors of metabolism, transfusion before baseline bloods could be taken, exchange transfusion for hyperbilirubinaemia or LE given before enrolment. Withdrawal: enteral nutrition > 25% at any time. |
|
| Interventions | 50 infants were randomised; the detailed results were available for 45 infants (24 infants in ClinOleic group; 21 in Intralipid group) Group 1 (n = 25): OS‐LE; ClinOleic Group 2 (n = 25): S‐LE; Intralipid TPN protocol: the amino acids were added on day 1 and lipids added on day 2 in increments of 0.5 g/kg/day, 1 g/kg/day, 2 g/kg/day, 3 g/kg/day every day for 4 consecutive days. LE was in coded amber‐coloured syringes. The lipid infusion was given for 20 hours/day. Bloods was taken 2 hours after stopping the lipid infusion. |
|
| Outcomes | Primary outcomes: plasma F2‐isoprostane levels as indicators of lipid peroxidation; levels of LC‐PUFAs in plasma and RBC membrane. Secondary outcomes: safety outcomes: liver and renal function tests, blood culture positive sepsis, blood cell counts; total enteral nutrition and PN; anthropometry |
|
| Notes | Funding: study partly funded by research grant from Baxter Healthcare Australia and this funding was used for cost of laboratory assays and fat emulsions. Baxter Healthcare had no involvement in study design, data analysis or manuscript preparation. 1 death on day 3 due to IVH in the olive oil group and shown in study diagram. 2 more deaths occurred due to respiratory failure during the study period, however, information regarding which group these participants belonged to was not available. |
|
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "The coordinating pharmacist who was not directly involved in the management of patients performed block randomisation using a computer‐generated code." Comment: probably done. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "The coordinating pharmacist who was not directly involved in the management of patients performed block randomisation using computer‐generated code." "lipid emulsions were dispensed in coded and amber‐coloured (light protected) syringes." Comment: probably done. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Quote: "The lipid emulsions were dispensed in coded and amber‐coloured (light protected) syringes." Comment: blinding of participants and personnel was acceptable in this study. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Quote: "The data were analyzed without breaking the code to ensure masking of statistical analysers." Comment: probably done. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Quote: "One participant in the OL group died on day 2 (grade IV IVH) but was included in the analysis on intention to treat basis; however, there was no blood sample on day 6 for the patient." Comment: 2 more deaths occurred due to respiratory failure during the study period, however, information regarding which group these participants belonged to was not available. There was 1 participant in the ClinOleic group and 4 participants in the Intralipid group who were withdrawn from the study due to enteral energy intake > 25%. Their data were not available. Probably low risk. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: protocol for the study was not available to us so we could not ascertain any deviation from the protocol. The data on outcomes of sepsis and weight were not available (could not be used in meta‐analysis). |
| Other bias | Low risk | Comment: no other biases identified. |
Deshpande 2014.
| Methods | Design: single‐centre double‐blind RCT Setting: regional tertiary NICU of King Edward Memorial Hospital for Women, Perth, Australia Study enrolment: January 2010 to June 2011 I. Allocation concealment: yes II. Blinding of intervention: yes III. Blinding of outcome measurement(s): yes IV. Complete follow‐up: yes |
|
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: preterm neonates, < 30 weeks' gestation admitted to NICU requiring PN providing > 75% of energy expenditure requirements for 7 days and postnatal age < 7 days. Exclusion criteria: blood culture‐positive sepsis; thrombocytopenia (platelet count < 150 × 109 cells/L); unconjugated hyperbilirubinaemia (requiring exchange transfusion); metabolic disorders including lactic or uncompensated acidosis (or both); no parenteral consent; administration of intravenous lipid infusion before study; postnatal age > 7 days; bleeding disorder. | |
| Interventions | 34 infants were randomised, 30 initially and then 2 more in each arm Group 1 (n = 17): OS‐LE; 20% ClinOleic Group 2 (n = 17): MOFS‐LE; 20% SMOFlipid TPN protocol: dose protocol was day 1, 1 g/kg; day 2, 2 g/kg; day 3, 3 g/kg and days 4 to 7, 3 g/kg. Duration of study was 7 days, after which all of the participants received ClinOleic LE, which was the standard of practice in the nursery. Intravenous lipids were continued as long as PN support was deemed necessary by the attending neonatologist. The emulsions were dispensed in amber‐coloured coded syringes and amber‐coloured infusion lines suitable for infusion pumps and infused intravenously through a central or peripheral line. |
|
| Outcomes | Primary outcomes: levels of LC‐PUFA (mean and SD) in red cell membrane and lipid peroxidation status measured by plasma F2‐isoprostane levels (mean and SD) as picomole per litre. Secondary outcomes: weight, head circumference and length at birth at study entry, exit and at discharge; enteral vs PN proportion; number of episodes of blood culture‐positive sepsis; IVH; duration of hospital stay, mechanical ventilation and PN support; mortality and vitamin E levels. | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "The coordinating pharmacist who was not directly involved in patient care randomised neonates (by using a computer‐generated randomisation list)." |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "Pharmacist prepared coded ready‐to‐use syringes of either OO (20% ClinOleic Baxter, S.A. Belgium) or FO [fish oil] (20% SMOFlipid Fresenius Kabi, Pymble, Australia) lipid emulsion. Given this strategy and the identical appearance of the coded, ready‐to‐use identical syringes, the researcher and other team members were blinded to the allocation status and the content of syringes." |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Quote: "similar appearance of lipid emulsions with code broken after analysis;" "amber colored coded syringes." Comment: done |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Quote: "The data were analyzed without breaking the code to ensure masking of statistical analysers" and "similar appearance of lipid emulsions with code broken after analysis" " amber colored coded syringes." Comment: done |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Outcomes described for the whole group and ITT analysis performed. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Quote: "Clinical trial registration number: ACTRN 12609001017213" Comment: not identified. |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | 55 participants could not be approached on weekends due to resource limitations in the study. Funding: partial funding from Fresenius Kabi and Baxter Health Care for 2 similar studies. Though author mentions that both the companies had no influence on any aspect of the study. |
Diamond 2017.
| Methods | Design: multicentre blinded RCT Setting: NICUs at multiple sites including Hospital for Sick Children, Toronto, ON, Canada; McMaster Children's Hospital, Hamilton, ON, Canada; Alberta Children's Hospital, Calgary; Stollery Children's Hospital, Edmonton, AB, Canada; and CHU Sainte‐Justine, Montreal, QC, Canada. Study enrolment: January 2009 to September 2011 I. Allocation concealment: yes II. Blinding of intervention: yes III. Blinding of outcome measurement(s): yes IV. Complete follow‐up: yes |
|
| Participants | Population: 26 preterm infants with hepatic dysfunction due to surgical conditions Inclusion criteria: infants aged < 24 months with short bowel syndrome or intestinal failure who received substantial PN support (> 40% total calories) and was demonstrating early hepatic dysfunction (Cbil: 17–50 µmol/L (1–3 mg/dL)) in the absence of sepsis. Although the age of inclusion was < 24 months, all the included infants were in preterm or borderline preterm range with the outer range of the ages being < 6 months and therefore met the current review's inclusion criteria. Age, mean (range): 6.5 (4.3 to 8.7) weeks in SMOFlipid group; 5.3 (3.5 to 7.2) weeks in Intralipid group Gestational age, mean (range): 34.5 (32.4 to 36.7) weeks in SMOFlipid group; 35.2 (33.2 to 37.1) weeks in Intralipid group Exclusion criteria: sepsis or haemodynamic instability of any cause; coagulopathy (platelets ≤ 150 000 cells/μL, or INR ≥ 1.4); hypersensitivity to fish‐, egg‐ or soybean protein or to any of the active substances or excipients; current enrolment in another clinical trial involving a surgical or pharmacological intervention; serum Cbil > 50 μmol/L; hyperlipidaemia; treatment with intravenous N‐acetylcysteine or oral ursodeoxycholic acid; renal insufficiency; disorders of fluid balance; unstable medical conditions. |
|
| Interventions | 26 infants randomised; results available for 24 infants (11 infants in SMOFLipid group; 13 in Intralipid group) MPFS‐LE vs S‐LE Group 1 (n = 11): MOFS‐LE; SMOFlipid Group 2 (n = 13): S‐LE; Intralipid TPN protocol: participants received trial lipid for up to 12 weeks. Participants also ended the trial if they achieved full enteral tolerance (autonomy from PN) prior to this time point or if they developed progressive liver disease defined by a serum Cbil > 100 µmol/L for > 14 days. Lipid dosing was according to a nomogram which adjusted the amount of the lipids proportional to the enteral intake. All type of enteral formulas were allowed except the enteral fish oil solution. |
|
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: last value of the Cbil the week the infant received the last dose of the trial lipid (i.e. at 12 weeks, at full enteral tolerance or on the development of the progressive liver disease). Secondary outcomes: liver markers other than Cbil in the blood, weight, length and head circumference were assessed at baseline, week 6 and post‐trial. A full blood count at weeks 0, 4 and 8 and post‐trial. INR, C‐reactive protein, immunological markers (IL‐1, IL‐6, IL‐8, IL‐10 and IL‐12; tumour necrosis factor‐α), nephelometry, serum cholesterol and serum TGs assessed at baseline, week 6 and post‐trial. RBC PL composition assessed at baseline, week 6 and post‐trial. |
|
| Notes | The investigators also had a provision of replacement of the study participants who discontinued PN prior to second week of study due to achievement of full enteral tolerance. Mean duration on trial was 8 weeks and did not differ according to treatment (P = 0.99). Infants who received SMOFlipid were more likely to have a decrease in serum Cbil to 0 µmol/L than those in the Intralipid group over the entire observation period (hazard ratio 10.6, 95% CI 1.3 to 86.9; P = 0.006). At the time the primary end point was achieved, 3 (27%) infants in the SMOFlipid group had a serum Cbil exceeding 50 μmol/L, while 9 (69%) infants in the Intralipid group had Cbil above this level (P = 0.04). The authors did not provide a specific definition for some adverse outcomes, e.g. sepsis. Beginning and end weights were described and growth rates could not be imputed due to lack of data on covariance. |
|
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "The randomisation sequence was developed by the research support pharmacy using a random number table prior to enrolment of the first patient. The sequence was developed in blocks of variable size without investigator input or knowledge." Comment: done |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "Allocation concealment was achieved by the randomisation sequence only being known to the research support pharmacy at the Hospital for Sick Children. The group assignment was relayed to the dispensing pharmacist at the patient's institution only after enrolment had occurred." Comment: done |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Quote: "All participants, treating clinicians, and investigators were blinded to the treatment assignment. Only the research support pharmacist at the Hospital for Sick Children and the dispensing pharmacist at the patient's institution were aware of the group assignment." Comment: possibly done (by author consensus (VK, MM)). |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Quote: "All participants, treating clinicians, and investigators were blinded to the treatment assignment. Only the research support pharmacist at the Hospital for Sick Children and the dispensing pharmacist at the patient's institution were aware of the group assignment." Comment: possibly done |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Quote: "complete outcomes reported." Comment: done |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Quote: "This trial was registered at clinicaltrials.gov as NCT00793195." Comment: no significant concerns as per the outcome reporting. |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Quote: "The investigators also had a provision of replacement of the study participants who discontinued the PN prior to second week of the study due to achievement of full enteral tolerance. Comment: The study investigators performed an per protocol analysis as two patients in the SMOFlipid arm were not analyzed as they reached PN within 14 days. However as this is < 20% of the data it may not make a significant difference. For this reason we have assigned unclear risk of bias. |
Gawecka 2008b.
| Methods | Setting: single‐centre NICU of Medical Academy Neonatology Department in Warsaw, Poland Study enrolment: March 2004 to September 2005 I. Allocation concealment: yes II. Blinding of intervention: yes III. Blinding of outcome measurement(s): yes IV. Complete follow‐up: yes |
|
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: preterm infants < 32 weeks' gestation with birth weight < 1500 g, admitted to NICU on day 1 and requiring PN Exclusion criteria: severe malformations, metabolic disease, congenital infection with positive blood culture, enteral calories > 25% |
|
| Interventions | Initially 44 infants at the enrolment stage Group 1 (n = 18): OS‐LE; 20% ClinOleic Group 2 (n = 20): S‐LE; 20% Ivelip PN protocol: PN started on day 1 with amino acids. LE started within 72 hours of life from 1 g/kg/day and was increased to the maximal dose of 3–3.5 g/kg/day. Lipids were infused continuously over 24 hours. Blood sampling was done at baseline and after 14 days of lipid infusion. Follow‐up: all infants were followed up to discharge. |
|
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: tumour necrosis factor‐α, IL‐6 and IL‐10 synthesis in unstimulated and anti‐CD3‐induced peripheral blood mononuclear cells of parenterally fed preterm infants. Secondary outcomes: incidence of BPD, ROP, NEC, IVH and nosocomial infections | |
| Notes | Study showed no difference in the inflammatory cytokines or clinical parameters between groups. Low‐density lipoprotein cholesterol was significantly higher in OS‐LE group. No funding source reported. |
|
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "The randomisation was done by a hospital pharmacist." Comment: details of random sequence generation not reported. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "Investigators, parents, and nursing staff were unaware of the treatment allocation," "The randomisation was done by a hospital pharmacist." Comments: probably done |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Quote: "randomised with double‐blind method;" "randomisation code was broken after the data analysis was performed." "The parenteral lipid emulsion was prepared by the pharmacist;" "fat emulsion was administered in a syringe with 'lipids'." (from the article in Polish). Comment: probably done |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Quote: "randomisation code was broken after the data analysis was performed." Comment: probably done |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Comment: of the 44 recruited infants, 38 (87%) completed the study, 18 in OS‐LE group and 20 in S‐LE group. 2 deaths occurred in each group due to pulmonary complications. 2 more infants were excluded but the group allocation was not mentioned. ITT analysis was not performed. Authors' consensus was that material risk of bias was probably low. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: the protocol for the study was not available so we could not ascertain any deviation from the protocol. The study report did not provide data on IVH (mentioned as not significantly different between groups). |
| Other bias | Low risk | None identified |
Göbel 2003.
| Methods | Design: double‐blind RCT Setting: 2 NICUs in Munich Randomisation was stratified for study centre and birth weight (< 1250 g and > 1250 g). I. Allocation concealment: could not determine II. Blinding of intervention: could not determine III. Blinding of outcome measurement(s): could not determine IV. Complete follow‐up: no Safety analysis performed on the ITT population (42 treated infants including dropouts), efficacy analysis performed on the per‐protocol population (33 infants treated for 7 days). |
|
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: preterm infants with gestation range of 28 weeks to < 37 weeks with admission to NICU within 24 hours of birth and PN providing ≥ 80% calories during the study. Exclusion criteria: severe malformations, inborn error of metabolism, jaundice before randomisation, hyperlipidaemia, bacterial infection, and transfusion of packed RBCs or fresh frozen plasma (or both) of more than 15 mL/kg (cumulative volume) before baseline blood sampling. |
|
| Interventions | Randomised 45 infants within 72 hours of life Group 1 (n = 24): OS‐LE; 20% ClinOleic Group 2 (n = 21): S‐LE; 20% Intralipid LE started within 72 hours of birth, given as 24‐hour infusions at doses of 0.5 g/kg/day, 1.0 g/kg/day and 2.0 g/kg/day on the first 3 consecutive study days and 2 g/kg/day for the next 4 days. The remainder of the TPN cointerventions were the same in the 2 groups. Vitamin E was not given, minimal enteral nutrition was provided and infants were excluded if the enteral calories exceeded 20% at any time. |
|
| Outcomes | Outcomes included levels of TGs, cholesterol and PLs. Clinical outcomes included hyperbilirubinaemia, bradycardia, apnoea and gastro‐oesophageal reflux. The study reported no serious adverse events in either group. Efficacy outcomes were evaluated in per protocol infants on days 0 and 8, which included proportions of plasma PL FAs, alpha‐tocopherol levels and urine malondialdehyde excretion. |
|
| Notes | Supported by Baxter Healthcare Some of authors were affiliated with Baxter research and development centre. |
|
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: method of random sequence generation not described. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: details of allocation concealment not provided. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | Quote: "After the study was completed and the database locked, the blind code was opened." Comment: authors did not mention how blinding was achieved. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | Quote: "After the study was completed and the database locked, the blind code was opened." Comment: authors did not mention how blinding was achieved. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Comment: initially 45 infants randomised; 3 infants did not fit inclusion criteria and 9 were excluded as enteral intake exceeded 20%. ITT analysis was done for safety outcomes (including the excluded infants) for initially randomised infants. For this review, the only outcome of interest was hyperbilirubinaemia, which was a safety variable. Taking all these factors into account, the study was graded at low risk of bias. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: the protocol for the study was not available so we could not ascertain any deviation from the protocol. |
| Other bias | Low risk | Comment: none identified |
Hsiao 2018.
| Methods | Design: double‐blind RCT Setting: single‐centre NICU in Changhua, Taiwan Study enrolment: 1 March 2012 to 28 February 2014 I. Allocation concealment: yes II. Blinding of intervention: yes III. Blinding of outcome measurement(s): yes IV. Complete follow‐up: yes (outcomes mentioned till discharge including length of stay) |
|
| Participants | VLBW infants who were ventilated, recruited within 24 hours of birth | |
| Interventions | Group 1: MOFS‐LE; SMOF Group 2: MS‐LE; Lipovenoes Both emulsions by Fresenius‐Kabi, Bad Homburg vor der Höhe, Germany |
|
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: IL‐1b and IL‐6 in serum and BALF. Secondary outcomes: mortality, length of hospital stay, ventilator use days, oxygen‐dependent days, weight gain rate, liver function, PNAC, BPD, ROP, NEC, IVH and late sepsis | |
| Notes | Dramatic differences in BPD between groups compared to any other study in the cohort. This could be due to baseline incidence of BPD was high with all ventilated children and study reported complete follow‐up of infants to discharge. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "Simple randomisation was done by a hospital pharmacist opening a sealed opaque envelope containing cards." Comment: study authors did not describe method of random sequence generation. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "pharmacist prepared lipid emulsion syringes (without labels describing their contents) and which were identical in appearance and color." Comment: acceptable |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Quote: "lipid emulsion syringes (without labels describing their contents) and which were identical in appearance and colour," "The physicians and nurses did not know to which group the patients had been allocated." Comment: acceptable blinding as per the description |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Quote: "lipid emulsion syringes (without labels describing their contents) and which were identical in appearance and colour," "The physicians and nurses did not know to which group the patients had been allocated." Comment: acceptable blinding of outcome assessment for the healthcare providers |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Comment: low risk of attrition with near complete outcome data |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "Study was retrospectively registered at Current Controlled Trials: ISRCTN11427103 after the study had finished." Comment: we could not find any deviation from the protocol due to retrospective registration. |
| Other bias | Low risk | Comment: none |
Köksal 2011.
| Methods | Design: single‐centre blinded RCT Setting: NICU of Division of Neonatology, Görükle, Bursa, Turkey Study enrolment: September 2005 to December 2009 I. Allocation concealment: yes II. Blinding of intervention: yes III. Blinding of outcome measurement(s): yes IV. Complete follow‐up: yes |
|
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: ≤ 34 weeks' gestation, admission to NICU within 24 hours after birth and TPN requirement expected to be ≥ 80% of the total energy intake during the study. Exclusion criteria: severe malformations, hyperlipidaemia, metabolic disease, enteral nutrition > 20 mL/kg/day and transfusion > 15 mL/kg/day |
|
| Interventions | Group 1 (n = 32): OS‐LE; 20% ClinOleic Group 2 (n = 32): S‐LE; 20% Intralipid LE was started within 72 hours after the baseline blood sample was obtained. LE was infused at 1 g/kg/day, 2 g/kg/day and 3 g/kg/day on first 3 days and 3 g/kg/day over the next 4 days in both groups. After 7 days of LE, infusion was stopped and blood samples taken after 6 hours. Study end point was day 7 for total antioxidant capacity (primary outcome). The secondary clinical outcomes have been reported until discharge. |
|
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: total anti‐oxidant capacity in both LEs at day 7 (not significantly different between groups) Secondary outcomes: neonatal morbidity and the biochemical indices after LE administration. Biochemical indices were also compared at day 7. The neonatal morbidities have been reported to discharge (including ROP, BPD, IVH, NEC, RDS and sepsis). |
|
| Notes | No source of funding stated. No growth outcomes provided in the study report; however, these were provided by the study authors on request. Unpublished data provided by the authors. |
|
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "Block randomisation was performed using a computer‐generated code." Comment: probably done |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "The coded emulsion was prepared and labelled by the blinded clinical pharmacist." Comment: probably done |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Quote: "Parents, trial physicians and clinical staff were blinded to the lipid content of the TPN." "The coded emulsion was prepared and labelled by the blinded clinical pharmacist." Comment: probably done (by author consensus (VK, MM)) |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Quote: "Parents, trial physicians and clinical staff were blinded to the lipid content of the TPN." "The coded emulsion was prepared and labelled by the blinded clinical pharmacist." Comment: probably done |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Comment: outcomes were reported for all participants. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: protocol for study was not available so we could not ascertain any deviation from the protocol. |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Comment: study contributed to high heterogeneity in the outcomes of ventilation duration and duration of oxygen therapy (SD data confirmed by authors). The level of sickness of patients has not been described between the two groups. |
Lam 2014.
| Methods | Design: single‐centre study Setting: Departments of Paediatrics, Paediatric Surgery and Pharmacy at the Prince of Wales Hospital, Sha Tin, Hong Kong Study enrolment: September 2005 to December 2009 I. Allocation concealment: yes II. Blinding of intervention: yes III. Blinding of outcome measurement(s): yes IV. Complete follow‐up: yes |
|
| Participants | Infants who developed the PNAC and fulfilled the inclusion criteria: Cbil ≥ 34 μmol/L (2 mg/dL), expected to continue requiring PN for > 2 weeks and informed parental consent. Exclusion criteria: major congenital or lethal chromosomal abnormalities; multiorgan failure or imminent death; and cholestatic jaundice secondary to other known causes, e.g. congenital or acquired TORCH (acronym for a group of diseases that cause congenital conditions; Toxoplasmosis, Other (such as syphilis, varicella, mumps, parvovirus and HIV), Rubella, Cytomegalovirus, Herpes simplex), syphilis, hepatitis B or C infection, biliary atresia, or other intra‐ or extrahepatic diseases obstructing bile flow. |
|
| Interventions | Group 1 (n = 9): pure F‐LE; 10% Omegaven; Fresenius Kabi AG, Bad Homburg vor der Höhe, Germany Group 2 (n = 7): S‐LE; 10% Intralipid; Fresenius Kabi AG, Uppsala, Sweden |
|
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: reversal of PNAC, defined as Cbil level < 34 μmol/L within 4 months after commencement of lipid treatment. Secondary outcomes: rate of change of weekly liver function tests, infant growth parameters (head circumference and bodyweight), blood lipid profile and number of episodes of late‐onset infection |
|
| Notes | Pharmacists not involved in the care of the infants prepared the lipids and the clinical and research teams were unaware of the randomisation during the study period. 2 deaths in the S‐LE group with both infants dying of hepatic and multiorgan failure secondary to septicaemia. |
|
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "Pharmacists not involved in the care of the infants prepared the lipids and the clinical and research teams were unaware of the randomisation during the study period." From appendix: "Randomisation was performed by the computer minimising three predetermined clinical parameters with equal weighting that could potentially influence the outcome measures." Comment: done with details in appendix. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "Pharmacists not involved in the care of the infants prepared the lipids and the clinical and research teams were unaware of the randomisation during the study period." Comment: done with details in appendix. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Quote: "Pharmacists not involved in the care of the infants prepared the lipids and the clinical and research teams were unaware of the randomisation during the study period." From appendix: "For infants randomised to the soy‐based parenteral lipid preparation (SLP) arm, the preparation used was not only identical to FOLP in appearance, but also volume prescribed and delivered." Comment: probably done with details in appendix. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Quote: "Pharmacists not involved in the care of the infants prepared the lipids and the clinical and research teams were unaware of the randomisation during the study period." Comment: probably done with details in appendix. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Comment: low risk |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Quote: "Chinese Clinical Trial Registry: ChiCTR‐TRC‐09000718." On the registry trial number was ChiCTR‐TRC‐08000717 at Chinese Trial Registry Number. Comment: low risk |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Quote: "parents became unwilling for randomisation"; "in view of the interim results, we decided to terminate the study" Comment: unclear risk as the trial was stopped mid‐way due to limitations as described in the study. |
Lehner 2006.
| Methods | Design: single‐centre RCT Setting: Division of Neonatology at the University of Pécs, Hungary I. Allocation concealment: could not determine II. Blinding of intervention: could not determine III. Blinding of outcome measurement(s): could not determine IV. Complete follow‐up: no |
|
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: 25 to 37 week preterm infants bodyweight < 3 kg with requirement of LE within 48 hours with expected enteral calorie intake < 20% Exclusion criteria: known metabolic diseases |
|
| Interventions | 15 infants enrolled, 3 withdrawals (all from the MS‐LE group) leaving 6 infants in each group. Group 1 (n = 6): S‐LE; 20% Lipofundin N Group 2 (n = 6): MS‐LE emulsion; 20% Lipofundin MCT Cointerventions with 10% glucose, amino acids, electrolytes (sodium chloride, potassium chloride, calcium gluconate), trace elements (Pedel; Pharmacia, Budapest, Hungary) and water‐soluble vitamins (Soluvit; Baxter) were the same in both groups. |
|
| Outcomes | Intended outcomes: plasma FA profile, plasma cholesterol level and hypertriglyceridaemia. However the study reported some clinical outcomes, i.e. weight on day 8. The study reported faster regain of birth weight in the MS‐LE group, but no data were available. | |
| Notes | No episodes of hypertriglyceridaemia in either group. Outcomes are reported for 8 days. Funding: B Braun and Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft and Child Health Foundation (Munich, Germany) The study was primarily a biochemical study with some clinical outcomes reported. |
|
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "randomised double blind trial." Comment: method of random sequence generation not mentioned. Initially there were 9 infants in the MS‐LE group and 6 infants in the S‐LE group. 1 infant was reported to have the wrong randomisation. Details regarding the wrong randomisation were not provided. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: method of allocation concealment not mentioned. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | Quote: "randomised double blind trial." Comment: no details provided regarding how blinding was achieved. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | Mentioned "randomised double blind trial." Comment: no details provided regarding how blinding was achieved. Study did not report whether there was blinding of the outcomes. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | High risk | Comment: initially 15 infants were randomised with 3 infants excluded (all from the MS‐LE group; unbalanced exclusions; 33% in 1 group), giving 6 infants in each arm. Reasons for exclusion were provided (wrong randomisation, breaching of the study conditions and contraindication to the feeding protocol: 1 infant each). |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: the protocol for the study was not available to us so we could not ascertain any deviation from the protocol. |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Comment: none identified |
Najm 2017.
| Methods | Design: single‐centre blinded RCT in infants < 28 weeks' gestation Setting: NICU of Sahlgrenska University Hospital in Gothenburg, Sweden Study enrolment: 4 April 2013 to 22 September 2015 I. Allocation concealment: yes II. Blinding of intervention: no III. Blinding of outcome measurement(s): yes (for data analysts and screening ophthalmologists) IV. Complete follow‐up: yes |
|
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: 90 infants < 28 weeks' gestation admitted to NICU Exclusion criteria: major congenital malformations |
|
| Interventions | Group 1 (n = 41): MOFS‐LE; 20% SMOFlipid Group 2 (n = 37): OS‐LE; 20% ClinOleic PN was initiated as soon as possible after birth with a standard solution containing Vaminolac and 10% glucose (total protein content 2 g/100 mL) aiming at 80–90 mL/kg/day of the resulting solution during the first 24 hours. Lipid solution (ClinOleic or SMOFLipid) was normally started 6–12 hours after birth at a rate of 1 g/kg/day with daily increases up to 2 g/kg/day. Enteral nutrition used either maternal or donor breast milk with individualised fortification based on results from breast milk analysis using a commercial bovine milk fortifier. Daily intakes of FAs arachidonic acid, EPA and DHA (mg/kg/day) were prospectively registered from birth during the first 2 weeks of life. The parenteral lipid dosing strategy was to deliver 2 to 3 g/kg bodyweight every 24 hours. The FA compositions of SMOFlipid and ClinOleic were analysed by gas chromatography |
|
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: ROP classified as no ROP or ROP stage 1, 2, 3, or 3+. Other outcomes: serum LC‐PUFA (DHA, EPA and arachidonic acid) profiles, ROP, BPD, NEC, PDA, sepsis and growth between birth and 36 weeks. Cbil blood level of > 50 μmol/L for ≥ 2 weeks at any time during the follow‐up, unrelated to sepsis was consider significant. Data presented for 78 infants. 12 infants died. The cause of death (and thereby partial outcomes) were presented for the deceased infants in the supplementary table. |
|
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "Randomization was in blocks of 20 infants, adjusting for gestational age." Comment: low risk (by author consensus (VK, MM)) |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "The treating nurse/doctor received the randomisation online." Comment: possibly done. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | Quote: "The type of lipid emulsion given was not blinded." However, blinding was done for the analysts and the screening ophthalmologists. Comment: the LE were not blinded, which could potentially introduce possibility of performance bias. However, most of the outcomes were objective based on study methodology for blood sampling at predefined time points. The review authors (by consensus; MM, VK) considered that the risk of performance bias affecting the study was unclear. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Quote: "Type of lipid emulsion was blinded for data analysis and the screening ophthalmologists." Comment: blinding was reported for ROP. We did not consider that there would be risk of material bias for most objective outcomes including cholestasis, sepsis, etc. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Comment: data were only presented for 78 infants who survived the study period with the gestation. Cause and the day of death of deceased infants (6 in each arm) was presented in the supplementary table from which additional data were extracted but not used for primary meta‐analysis. A sensitivity analysis was performed including and excluding the data of sepsis and NEC from the reported causes of death which did not change the results of these outcomes. The deceased infants would have died prior to the ROP screening (primary outcome) could be done. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "The study was approved by the Regional Ethical Board, Gothenburg (Dnr 303‐11) (Clinical trial NCT02760472)." Comments: the protocol was published on the ClinicalTrials.gov website after the trial had stopped recruiting according to the information from the ClinicalTrials.gov website. The first record on the ClinicalTrials.gov was on 30 March 2016 whereas the trial stopped on 22 September 2015 as per the authors. The fact that the protocol was published on clinicaltrials.gov after the study completed makes assessment for the selective reporting difficult. |
| Other bias | Low risk | None detected. |
Nehra 2014.
| Methods | Design: double‐blind RCT Setting: Boston Children's Hospital, Boston, USA Study enrolment: July 2007 to June 2009 I. Allocation concealment: yes II. Blinding of intervention: yes III. Blinding of outcome measurement(s): yes IV. Complete follow‐up: 2/10 in S‐LE and 3/9 F‐LE (33%) lost to follow‐up All analyses were performed on an ITT basis |
|
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: neonates and infants (< 3 months' age) with baseline conjugated bilirubin < 1.0 mg/dL and a gastrointestinal disease requiring surgical intervention who were expected to be PN dependent for ≥ 21 days Exclusion criteria: INR > 1.5 (> 2 if ≤ 1 week of age) or TG level > 400 mg/dL and those with a haemolytic disorder, liver disease or shock requiring vasopressor support, extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, nitric oxide treatment or a combination of these. Infants who had undergone an intestinal lengthening procedure were not eligible. |
|
| Interventions | Group 1 (n = 10): S‐LE; Intralipid Group 2 (n = 9): Pure F‐LE; Omegaven |
|
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: incidence of cholestasis, defined as a serum conjugated bilirubin > 2 mg/dL for ≥ 2 consecutive weeks Secondary outcomes: neurodevelopmental outcome assessed by BSID‐III (series of motor, cognitive and language scales) at 6 and 24 months' corrected age |
|
| Notes | Financial disclosures: supported by the March of Dimes, the Food and Drug Administration Orphan Drugs Division (grant 1 R01FD003436), Children's Hospital Boston Surgical Foundation and The Vascular Biology Program (Boston, MA). C.D. was supported in part by K24HD058795. Trial registered at ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT 00512629). |
|
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "Following informed consent, patients were randomly assigned by a computer‐generated list of random numbers to the control (SIFE) or experimental (FIFE) group in a 1:1 ratio." Comment: done |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "Patients, parents, physicians, dieticians, and nurses were blinded to the treatment allocation for the duration of the study. Members of the department of pharmacy were aware of the randomisation and identically packaged the IFEs." Comment: probably done |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Quote: "Patients, parents, physicians, dieticians, and nurses were blinded to the treatment allocation for the duration of the study. Members of the department of pharmacy were aware of the randomisation and identically packaged the IFEs." Comment: probably done |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Quote: "Patients, parents, physicians, dieticians, and nurses were blinded to the treatment allocation for the duration of the study. Members of the department of pharmacy were aware of the randomisation and identically packaged the IFEs." Comment: probably done |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Comment: clinical outcomes were reported for most infants. Secondary outcome: neurodevelopment outcome had 26% loss to follow‐up. By consensus the review authors considered that the overall risk was low. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Quote: "This trial is registered at clinicaltrials.gov (NCT 00512629)." Comment: protocol was registered at the time of trial initiation and trial was reported in line with the published protocol. |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Trial stopped early. |
Pawlik 2014.
| Methods | Setting: single‐centre in Krakow, Poland Study enrolment: 1 August 2010 to 31 May 2012 I. Allocation concealment: could not determine II. Blinding of intervention: could not determine III. Blinding of outcome measurement(s): yes (for ROP) IV. Complete follow‐up: no; details of infants who died (about 20% in both groups) not available. |
|
| Participants | Preterm infants < 32 weeks' gestation and < 1250 g bodyweight | |
| Interventions | Group 1 (n = 60): OFS‐LE; 20% ClinOleic IV (50% volume of soybean and olive oil; Baxter SA, Norfolk, UK) + 10% Omegaven (50% volume of fish oil; Fresenius Kabi, Bad Hamburg, Germany) Group 2 (n = 70): OS‐LE; 20% ClinOleic (20% soybean and olive oil emulsion; Baxter SA, Norfolk, UK; control group) |
|
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: ROP Secondary outcome: cholestasis. The study also reported BPD, NEC, death and sepsis. |
|
| Notes | The study had high mortality in both the groups (close to 20% in both the groups). The data on infants who died were not available. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "Participants were allocated to groups using a computer‐based random number generator." Comment: random component described |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: "Participants were allocated to groups using a computer‐based random number generator." Comment: no description of how allocation concealment was performed. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | Quote: "Physicians and nurses caring for the infants were blind to the type of lipid emulsion." Comment: no description of how blinding was performed. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Quote: "Retinal examinations were performed by a single ophthalmologist who was blinded." Comment: probably done (by author consensus(VK, MM)) |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | High risk | Quote: "Of the 38 patients who died, 36 deaths occurred before the first screening and eye examination;" "Moreover, 7 infants excluded on the 2nd, 4th, 7th, or 10th day because of withdrawal of parental consent differed significantly with respect to the total intravenous intake of the fish‐oil lipid emulsion. Therefore, we decided not to include them in our analysis." Comment: there was statistically significant differential participant consent withdrawals (0/88 (0%) from ClinOleic group vs 7/87 (about 10%) withdrawals from OFS‐LE group (P = 0.007). The withdrawals were excluded from analysis. There was a high proportion of deaths (greater than 20%) where the outcome data were not provided for any outcome (ROP examination was not applicable in 36 infants). Though the deaths were balanced across groups, both the rate and actual numbers of infants with cholestasis were low, i.e. 3/60 (5%) in OFS‐LE group compared to ClinOleic group. The impact of missing data can vary depending on the rate (differential rates) of cholestasis in missing data in the two groups. The data for 2 deceased infants who had eye examinations for ROP were not included. Overall, the review authors considered that there may be higher risk of material bias for cholestasis compared to ROP. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "The protocol was approved by the ethics committee." Comment: the protocol was not available. |
| Other bias | Low risk | None detected |
Rayyan 2012.
| Methods | Design: double‐blind RCT Setting: single‐centre at Department of Neonatology, University Hospitals, Leuven, Belgium Enrolment period: November 2004 to February 2006. I. Allocation concealment: yes II. Blinding of intervention: yes III. Blinding of outcome measurement(s): yes IV. Complete follow‐up: yes Study duration: 15 days or until last intravenous infusion. Main study period was until day 7 of treatment; all infants were followed up until discharge. For statistical analysis, the last value was carried forward. Adverse events were reported until 6 days after the end of last infusion. |
|
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: < 34 weeks' gestation preterm infants with bodyweight 500–2000 g, who received PN for ≥ 7 days. Exclusion criteria: extremely preterm infants, severe congenital malformations, heart failure, organ damage, anuria, haemolytic disease, thrombocytopenia, oxygen saturations < 80% for > 2 hours, severe acidosis, use of catecholamines, hypoxic‐ischaemic encephalopathy and multiorgan failure. |
|
| Interventions | Group 1 (n = 26): MOFS‐LE; 20% SMOFlipid Group 2 (n = 27): S‐LE; 20% Intralipid LE were given for ≥ 7 days and up to 14 days, peripherally or centrally. Enteral intake was allowed as per protocol, i.e. < 30% of the total lipid intake on days 1–3, < 50% on days 4–7 and < 70% on days 8–14 of the total energy intake. Daily target dosage of fat started at 1.0 g/kg/day on days 1–3 and was increased to 2 g/kg/day on day 4, 3 g/kg/day on day 5, and 3.5 g/kg/day from day 6 onwards. Other components of PN were given as standardised solutions at the discretion of the investigator. |
|
| Outcomes | Primary safety outcome: TG levels Primary efficacy outcome: change in bodyweight at day 8 from baseline Secondary outcomes: blood counts and biochemical parameters Clinical assessments (heart rate, temperature, blood pressure, bodyweight, oxygen therapy) were performed daily from day 0 (prestudy visit) to study termination, either on day 15 or following the last infusion of study treatment (post‐treatment). |
|
| Notes | Financial disclosure: supported by the Fund for Scientific Research, Flanders (Belgium) J a Fundamental Clinical Investigatorship (1 800209 N) and a research grant (1506409 N). Sponsored by Fresenius Kabi, Bad Homburg vor der Höhe, Germany. Authors: Hugo Devlieger and Frank Jochum received speaking honoraria and consulting fees from Fresenius Kabi. The publication of the supplement in which this article appeared was sponsored by Nestlé Nutrition Institute. |
|
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "using the software RANCODE," "The randomisation was stratified by weight‐ 500 to 1000, 1000 to 1500, 1501 to 2000 g." Comment: probably done |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "Randomization list was prepared prior to the study and lipid emulsion dispensed by pharmacy." Comment: probably done |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Quote: "Double blind controlled," "… the study and control infusions were of the same size and identical appearance," "Infusions were prepared in the hospital pharmacy identified only by the patient number on the outside of packaging." Comment: probably done. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Comment: probably done. The review authors agreed that the risk was low. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Comment: protocol violations/preterm discontinuation occurred only in 3 participants in the SMOFlipid group and in 4 participants in the Intralipid group (balanced in both groups). The trial profile and participant flow was well described. All outcome data are provided. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: the protocol for the study was not available so we could not ascertain any deviation from the protocol. Data could not be used for sepsis (it was reported as a combined outcome of infection and infestations). |
| Other bias | Low risk | Comment: none identified. |
Repa 2018.
| Methods | Design: prospective, double‐blind RCT in ELBW infants Setting: level IV NICU of University Children's Hospital Vienna, Medical University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria Study enrolment: July 2012 to July 2015. Last follow‐up October 2015 I. Allocation concealment: yes II. Blinding of intervention: yes III. Blinding of outcome measurement(s): yes IV. Complete follow‐up: yes Both ITT and per‐protocol analyses were performed. |
|
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: ELBW < 1000 g admitted before 24 hours Exclusion criteria: cholestasis (Cbil > 1.5 mg/dL (25 mol/L)) before intervention, and higher‐order multiples infants with conditions associated with cholestasis independent of PN (i.e. infection with cytomegalovirus, HIV, hepatitis B or C, rhesus‐mediated haemolysis, cystic fibrosis, inborn errors of metabolism or primary liver diseases) were not eligible or excluded post‐randomisation. |
|
| Interventions | Group 1 (n = 110): MOFS‐LE; 20% SMOFlipid Group 2 (n = 113): S‐LE; 20% Intralipid Participants received full PN from birth using S‐LE (1 g/kg/day) were switched to study lipids after enrolment. Lipids were dosed up to 3 g/kg/day at the discretion of the attending physicians and reduced in relation to enteral nutrition (increased up to 20 mL/kg/day). Serum TG were measured at least weekly. Lipids were halted for 24 hours at TG levels > 400 mg/dL (4.5 mmol/ L) or downtitrated > 250 mg/dL (2.8 mmol/L). PN was stopped at 140–160 mL/kg/day of enteral feeds. Therapy adherence was calculated as the percentage study lipids were correctly provided; > 80% was considered highly adherent. Urodeoxycholic acid was administered to infants who developed cholestasis. Parenteral fish oil (Omegaven; Fresenius Kabi, Bad Homburg vor der Höhe, Germany) was permitted as rescue therapy (1 g/ kg/day) if Cbil was > 6 mg/dL (100 mol/L). Infants were followed until their 44th week' postmenstrual age, discharge or transfer to another hospital. All infants received probiotics and lactoferrin. Enteral feeds were provided every 3 hours; the median volume of a single feed per kg in the first week of life was calculated. For growth analysis (anthropometry with z score difference from birth to discharge), only survivors were analysed to avoid distortion of measurements by perimortal oedema. |
|
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: PNAC (Cbil > 1.5 mg/dL (25 mol/L) at 2 consecutive measurements). Peak levels of liver enzymes (ALT, AST,GGT, ALP during hospitalisation were identified. Blood sampling was performed weekly as long as PN was required and then every 7 to 14 days. Secondary outcomes: neonatal morbidities (death, duration of hospitalisation, ROP (any), and highest stage requiring treatment (severe ROP), culture‐confirmed sepsis, IVH III/IV, cystic PLVL, NEC ≥ IIa, focal intestinal perforation, abdominal surgery, days on mechanical ventilation, CLD, PDA requiring treatment, number of ibuprofen cycles or requiring surgical ligation, pulmonary hypertension, iNO/sildenafil treatment. |
|
| Notes | PNAC incidence of only 15.9% in the current trial, attributable to an accelerated weaning from PN compared with the planning phase (10 days). This shorter time on PN was an important study limitation and possibly related to the implementation of probiotics at the NICU before the start of the trial in 2010 and their preventive effect against NEC. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "… Participants were randomised using permuted blocks (ratio 1:1, block size of 4) and stratified according to sex and birth weight (< 750 vs ≥ 750 g) using a software, prepared by an independent statistician." Comment: done. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "… an independent statistician, who kept the randomisation sequence concealed until the end of the study Comment: probably done, with author consensus |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Quote: "… Participants, healthcare providers, data collectors, and outcome adjudicators were blinded. A blinding team uninvolved in clinical decisions established the blinding code and masked the glass containers using opaque labels designated "Lipid A" or "Lipid B." Labels were resistant to detachment, in particular by 70% alcohol used during aseptic preparation. Neonatal nurses who prepared the study lipids for PN were part of the blinding team. Discarded containers were controlled for blinding integrity." Comment: well described |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Quote: "… Participants, healthcare providers, data collectors, and outcome adjudicators were blinded." Comment: well described in the study report |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Clinical outcomes were reported for all infants. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | The study protocol was available: NCT1585935: the review of the protocol indicated that the authors had not published the details of the secondary outcome measures of amplitude integrated amplitude integrated electroencephalography and visual evoked potentials at this stage. The review authors (VK, MM) were in consensus that risk of bias for selective reporting is low, as these secondary study outcomes were not a part of the current review's outcomes. |
| Other bias | Low risk | Not identified |
Roggero 2010.
| Methods | Design: single‐centre study with 3 arms Setting: Università degli Studi di Milano, Italy I. Allocation concealment: could not determine II. Blinding of intervention: could not determine III. Blinding of outcome measurement(s): could not determine IV. Complete follow‐up: yes |
|
| Participants | 36 consecutive preterm infants, gestational age 28–33 weeks | |
| Interventions | Group 1 (n = 12): S‐LE Group 2 (n = 12): OS‐LE Group 3 (n = 12): MS‐LE |
|
| Outcomes | Isoprostane and TRAP level evaluated at day 87 | |
| Notes | This study did not contribute data to any outcome in the current review. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "All preterm infants were randomised into three groups matched for birth weight and gestational age, to receive one of the following different parenteral lipid emulsions." Random element not described. Matching aspects not elaborated. Comment: could not determine. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "in a double‐blind study performed according to good clinical practice guidelines" Comment: could not determine |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | Quote: "the bags containing the PN solution were prepared by the hospital pharmacy using an automatic compounding system (Siframix, SIFRA, Verona,. Italy)." Comment: possibly low risk although the authors did not mention how blinding was achieved. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | Quote: "the bags containing the PN solution were prepared by the hospital pharmacy using an automatic compounding system (Siframix, SIFRA, Verona, Italy)." Comment: possibly low risk although the authors did not mention how blinding was achieved. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Comment: no concerns |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: protocol not available; could not determine |
| Other bias | Low risk | Comment: none |
Rubin 1994.
| Methods | Design: double‐blind RCT Setting: Beilinson Medical Center, Petach‐Tiqva, Israel Enrolment period: not mentioned. I. Allocation concealment: could not determine II. Blinding of intervention: could not determine III. Blinding of outcome measurement(s): could not determine IV. Complete follow‐up: no |
|
| Participants | Preterm infants < 35 weeks' gestation who received TPN for ≥ 6 days. 59 infants enrolled, 10 withdrawals | |
| Interventions | Group 1 (n = 16): 20% PFE 4501 (soybean + borage oil in 8.5:1.5 ratio to increase GLA + added carnitine); Group 2 (n = 18): S‐LE; 20% Intralipid Group 3 (n = 15): MS‐LE; 20% Lipofundin MCT (LCT from soybean: MCT from coconut in 1:1 weight ratio) LE: day 1: 0.5 g/kg/day, day 2: 1.5 g/kg/day to a maximum of 2.5 g/kg/day on day 3, and this dose was maintained until the end of the study period. Cointerventions with amino acid solution (Vamin) and electrolytes were similar in the 2 groups. |
|
| Outcomes | Weight gain, clinical variables, acid–base, blood counts, glucose levels (remained normal) mentioned for all the groups. AST decreased significantly in groups 2 and 3 from baseline, however the values were only provided for TG levels. The FA profile was reported in detail from the same study in Rubin 1995. | |
| Notes | TG levels (mean ± SD) were reported but authors did not report the proportion of infants with hypertriglyceridaemia. Therefore, we were unable to include data in the quantitative synthesis for the clinical outcomes. Short study of 6 days. Authors demonstrated the safety of LE in jaundiced infants as the bilirubin levels fell in both groups despite the rise in free FAs as reported in Rubin 1995. Results regarding FA profile from this study were published in 1995 (Rubin 1995). |
|
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "The infant were randomly assigned to …" Comment: no information on random sequence generation provided. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: no information on allocation concealment provided. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | Quote: "randomly assigned in a double blind manner." Comment: blinding not described. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | Quote: "randomly assigned in a double blind manner." Comment: blinding not described. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | High risk | Comment: 10 withdrawals in the study equivalent to 16% of the study sample. Withdrawals were for varying reasons including sepsis (5), hyperbilirubinaemia (1) and thrombocytopenia (2). It is not reported which intervention arm these infants belonged to. Data from these infants is not available. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: the protocol for the study was not available so we could not ascertain any deviation from the protocol. |
| Other bias | Low risk | Comment: none identified. |
Savini 2013.
| Methods | Design: double‐blind single‐centre 5‐arm RCT Setting: NICU of "G. Salesi" Children's Hospital, Ancona, Italy Study enrolment period: January 2007 to October 2011 I. Allocation concealment: yes II. Blinding of intervention: yes III. Blinding of outcome measurement(s): yes IV. Complete follow‐up: yes Study duration: primary study criteria including phytosterol to day 21, but clinical outcomes were reported beyond that period (e.g. liver enzymes and cholestasis at 6 weeks). Follow‐up: all study participants appeared to have been followed until discharge. |
|
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: preterm infants bodyweight 500–1249 g who received PN from 1st hour of life Exclusion criteria: severe malformations, metabolic disease and severe congenital sepsis |
|
| Interventions | 150 consecutive admitted preterm infants were randomly assigned to receive five different LE Group 1 (n = 30): S‐LE: Intralipid (100% S‐LE) Group 2 (n = 30): MS‐LE: Lipofundin (MCT 50%/soybean LCT 50%) Group 3 (n = 30): MFS‐LE: Lipidem (MCT 50%/soybean 40%/fish oil 10%) Group 4 (n = 30): OS‐LE: ClinOleic (olive oil 80%/soybean oil 20%) Group 5 (n = 30): MOFS‐LE: SMOFlipid (MCT 30%/soybean oil 30%/olive oil 25%/fish oil 15%) |
|
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: plasma phytosterol concentrations (campesterol and β‐sitosterol levels) day 0 (cord), day 7 (full TPN), day 14 (50% enteral calories) Secondary outcomes: clinical outcomes including mortality, growth outcomes, BPD, NEC, PDA, sepsis and cholestasis |
|
| Notes | No funding source mentioned. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "randomly assigned in a 1:1:1:1:1 ratio to 1 of the 5 LEs studied following a simple randomisation procedure." Comment: how random sequence was generated is not mentioned. Quote: "pharmacy received the enveloped randomisation list with the patient codes and provided the allocated interventions." Comment: probably done. Previous reports involving the same team mentioned: "Randomization was obtained with sealed envelopes using a random permuted blocks within strata protocol." |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "The pharmacy received the enveloped randomisation list with the patient codes and provided the allocated interventions. (sealed envelope system);" "They were identified only by the patient number according to the randomisation schedule." Comment: probably done |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Quote: "5 different LEs prepared in the hospital pharmacy were of the same size and identical appearance." Comment: probably done |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Quote: "5 different LEs prepared in the hospital pharmacy were of the same size and identical in appearance;" "The clinicians, the patient's parents, and the individuals who assessed the study endpoints were blinded to the LEs." Comment: probably done |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Comment: outcome data complete, attrition well explained and less than 10%. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: the protocol for the study was not available so we could not ascertain any deviation from the protocol. |
| Other bias | Low risk | Comment: none identified |
Skouroliakou 2010.
| Methods | Design: RCT in preterm infants Setting: single‐centre NICU of 'IASO' Maternity Hospital in Athens, Greece Study enrolment: Nov 2008 to April 2009 I. Allocation concealment: yes II. Blinding of intervention: yes III. Blinding of outcome measurement(s): yes IV. Complete follow‐up: no |
|
| Participants | 38 infants enrolled Inclusion criteria: preterm infants < 32 weeks' gestation with birth weight < 1500 g requiring admission to NICU within 12 hours of birth and expected to receive > 80% of the energy intake by parenteral route in the first 8 days of life and requiring PN for at least 7 days. Exclusion criteria: inherited metabolic disorders, congenital malformations, transfusion of blood/fresh frozen plasma > 15 mL/kg and participation in another study |
|
| Interventions | Group 1 (n = 19): MOFS‐LE; SMOFlipid Group 2 (n = 19): S‐LE; Intralipid 4 different TPN protocols were created based on gestational age, weight and clinical condition. Lipids were started on day 1 or 2 of life (based on gestational age) with a maximum of 3 g/kg/day in both the groups. Enteral feeds were allowed at ≤ 20% of total energy intake and started as soon as feasible. Oral feeds were started after at least 14 days of PN for all infants in the study group. |
|
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: oxidation potential (vitamins A and E, and total anti‐oxidant potential) Hypothesis: a reduction in oxidative stress in the SMOFlipid group? Secondary outcomes: growth parameters, blood count, clinical condition and length of stay (parameters noted on day 0, day 14 and at discharge). |
|
| Notes | SMOFlipid was supplied by Fresenius Kabi. Vitamin A and E levels were not affected by the intervention, however TAP level was increased in the SMOFlipid group, indicating possible reduction in the oxidant stress. Authors mentioned: "none of the children in each group had any side effects related to parenteral nutrition or sepsis." |
|
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "Computer generated randomisation." Comment: probably done. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "the pharmacist, who was responsible for the placement of each infant in a group (intervention vs control) …" Comment: statistician and pharmacist not involved in the trial. Probably done. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Quote: "PN were in identical bags." Comment: probably done |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Quote: "PN were in identical bags;" " All medical personnel and participants were blinded to treatment assignment during the whole course of the study." Comment: probably done |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | High risk | Comment: out of 38 randomised infants there were 6 exclusions (16%) with 5 from the SMOFlipid group (n = 2 transfusion > 15 mL/kg, n = 1 PN < 7 days, n = 1 transfer to another centre) and 1 from the 20% Intralipid group (PN < 7 days) (unbalanced exclusions) |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: protocol for the study was not available so we could not ascertain any deviation from the protocol. |
| Other bias | Low risk | None identified. |
Skouroliakou 2016.
| Methods | Design: single‐centre RCT in preterm neonates Setting: NICU of "IASO" Maternity Hospital Thessaloniki, Greece Study enrolment: September 2012 to September 2013 |
|
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: infants with 26–32 weeks' gestational age, anticipated need for PN > 60% of total energy requirements for ≥ 15 days, parental consent for participation to the study | |
| Interventions | 51 infants enrolled Group 1 (n = 26): MOFS‐LE; 20% SMOFlipid (Fresenius Kabi HELLAS; contained MCTs (30%), lipids from soybean oil (30%), olive oil (25%), fish oil (15%) and α‐tocopherol (200 mg/L)) Group 2 (n = 25): S‐LE; 20% Intralipid (Fresenius Kabi HELLAS; conventional soybean oil‐based 20% Intralipid that contained α‐tocopherol 38 mg/L) Infant followed up 30 days of life or until the PN‐derived energy decreased to < 40% of total daily energy requirements. |
|
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: tumour necrosis factor‐α, IL‐6 and IL‐8 Secondary outcomes: plasma α‐tocopherol and FA profiles Clinical outcomes: death, RDS requiring treatment, BPD, clinical and culture‐confirmed sepsis, liver enzymes and cholestasis |
|
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "Simple randomisation was based on a computer‐generated randomisation list." Comment: done |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "The list was given to the pharmacist, who prepared the different PN formulations in identical bags and assigned neonates in 1 of 2 groups. The pharmacist was not involved in neonates' care." Comment: done |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Quote: "All medical personnel and participants were blinded to treatment assignment during the whole study period." Comment: probably done |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Quote: "All medical personnel and participants were blinded to treatment assignment during the whole study period." Comment: probably done |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | Quote: "Of the 60 recruited neonates, 51 completed the study. Nine neonates (4 and 5 from the IG [intervention group] and CG [control group], respectively) were excluded after randomisation." Comment: this is similar to a per‐protocol study flow and analysis rather than ITT with concerns regarding incomplete outcome data from both arms. However as the exclusions were equally distributed in both arms, we assigned 'unclear risk' of bias (by author consensus). |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "The trial has not been included in a Clinical Trials database because the relevant database in Greece is reserved for phase III trials for novel treatments." Comment: selective reporting could not be ascertained as we did not have access to the trial protocol. |
| Other bias | Low risk | None detected |
Techasatid 2017.
| Methods | Design: double‐blind RCT Setting: NICU of Thammasat Hospital and Nopparat Rajathanee Hospital, both in Bangkok. Study enrolment: December 2013 and December 2015 I. Allocation concealment: yes II. Blinding of intervention: yes III. Blinding of outcome measurement(s): yes IV. Complete follow‐up: yes |
|
| Participants | 44 infants enrolled Inclusion criteria: < 30 weeks' gestational age and birth weight < 1250 g who required PN for ≥ 7 days Exclusion criteria: evidence of congenital infection, perinatal asphyxia, congenital anomalies, IVH grade > 2, thrombocytopenia, shock or circulation failure, and renal or hepatic disorders. |
|
| Interventions | Group 1 (n = 22): MOFS‐LE; 20% SMOFlipid Group 2 (n = 22): S‐LE; 20% Intralipid Lipids were first administered at 1 g/kg/day within 24 hours after birth for both groups; lipid dosage was increased by an increment of 0.5 g/kg/day until the maximal dose of 3.5 g/kg/day was reached. The other macronutrients and micronutrients were provided using the same products and protocol in both groups. Parenteral lipid and amino acid administration were temporarily stopped when either plasma TG concentrations exceeded 250 mg/dL or when urea concentrations exceeded 35 mg/dL respectively. |
|
| Outcomes | Primary outcomes: incidence of cholestasis, defined as a conjugated bilirubin level > 2 mg/dL on 2 consecutive measurements and biochemical signs of hepatic dysfunction including ALT, AST, ALP and GGT Secondary outcomes: clinical outcomes death; BPD defined as the need for supplementary oxygen or any form of respiratory support at 36 weeks' postmenstrual age; duration of ventilator support (days); NEC stage > 1 on Bell's staging system; ROP as defined by the International Classification of ROP; haemodynamically significant PDA diagnosed by echocardiography as needing treatment by medication or surgery; sepsis defined as a positive blood culture; IVH, all grades, and severe IVH (grade 3 and 4) of Papile classification; duration of hospital stay (days) and growth parameters assessed using in‐hospital growth rates, the gain in head circumference and height from birth until discharge. |
|
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "Enrolled infants were randomly assigned to a multi component emulsion (study group) or to a pure soybean oil (control group) within 48 hours after birth. Blocks of four stratified randomisations by treatment centres were used." Comment: how random element was generated was not described clearly, but given statements in the study report it was probably done (by author consensus (VK, MM)). |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "The allocations were kept in sequentially numbered, opaque, sealed envelopes." Comment: done |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Quote: "The investigators and the patient care teams were blinded to the treatment allocation and remained throughout the study and the analysis." Comment: possibly done (author consensus (VK, MM)). |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Quote: "The investigators and the patient care teams were blinded to the treatment allocation and remained throughout the study and the analysis." Comment: possibly done. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Clinical outcomes reported for most infants. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "trial was registered in Clinical Trials.gov (Clinical Trials.gov Identifier: NCT02663453)." Comments: trial registration was done, with first submission on 11 January 2016 which is well past the trial completion. Comments: selective reporting risk could not be assessed. We do not know if the protocol was published elsewhere. |
| Other bias | Low risk | Not identified |
Tomsits 2010.
| Methods | Design: single‐centre RCT Setting: Department of Paediatrics at Semmelweis University, Budapest, Hungary Study enrolment: April 2004 to January 2006 I. Allocation concealment: could not determine II. Blinding of intervention: could not determine III. Blinding of outcome measurement(s): could not determine IV. Complete follow‐up: yes Both ITT and per‐protocol analysis were performed: both with the last observation carried forward. Stratified study with the following strata: 1000 to 1499 g, 1500 to 1999 g and 2000 to 2500 g |
|
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: preterm infants < 34 weeks' gestation aged 3 to 7 days expected to receive TPN for ≥ 7 days Exclusion criteria: none mentioned |
|
| Interventions | 60 infants Group 1 (n = 30): MOFS‐LE; 20% SMOF Group 2 (n = 30): S‐LE; 20% Intralipid LE was started at 0.5 g/kg/day on day 1 and was increased by increments of 0.5 g/kg/day daily up to a maximum of 2 g/kg/day on days 4 to 14. Additional oral/enteral intake comprising < 20% at baseline, < 30% on days 1 to 3, and < 50% on days 4 to 14 of the total energy intake was permitted if appropriate. Other components of PN were given at the discretion of the investigator. |
|
| Outcomes | Outcomes were evaluated on day 0, 8 and 15 Primary efficacy outcome: change in weight from day 1 to day 8 Secondary efficacy outcomes: mechanical ventilation/oxygen therapy and RBC FA profile Primary safety outcome: serum TG Secondary safety outcomes: vital signs, haematology, coagulation profile and liver enzymes Study also reported growth rate and sepsis. |
|
| Notes | No funding source mentioned. 57 adverse events: all mild, some outcomes grouped into composite groups, sepsis was reported as infections and infestations. Decreased GGT in the SMOFlipid group (and increased GGT in the Intralipid group, P < 0.05). The SMOFlipid group had lower GGT, and higher ω‐3, RBC, EPA levels and α‐tocopherol levels. |
|
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "… randomised to receive PN …" Comment: method of random sequence generation not mentioned. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: details not provided |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | Quote: "were randomised to receive in a double blind manner …" Comment: details of how blinding was achieved were not mentioned. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | Quote: "were randomised to receive in a double blind manner …" Comment: details of blinding were not mentioned. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | 9 infants (15% participants; 4 in the study group) terminated the study early and were included in the ITT analysis with last observation carried forward. Out of 9, in 7 "oral feeding reached exclusion criteria" and in 2 consent was withdrawn. Missing participants were balanced in numbers across groups; however, it was not mentioned to which group the 2 infants where consent was withdrawn belonged. As the data is provided for the ITT set (all participants), the review authors agreed to give a low risk rating. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | The study protocol was not available. Some adverse effects were grouped (infections and infestations) and could not be used in the meta‐analysis for sepsis. Ventilation and oxygen duration appeared to be a combined outcome. In the absence of the study protocol, we have assigned the risk category as 'unknown.' |
| Other bias | Low risk | None identified. |
Uthaya 2016.
| Methods | Design: NEON (Nutritional Evaluation and Optimisation in Neonates), a 2 × 2 factorial, double‐blind, multicentre RCT Setting: 4 National Health Service NICUs in London and southeast England I. Allocation concealment: yes II. Blinding of intervention: yes III. Blinding of outcome measurement(s): yes IV. Complete follow‐up: yes |
|
| Participants | Inclusion: preterm infants < 31 weeks' gestation Exclusion: life‐threatening abnormalities and those for whom study authors were unable to administer trial PN within 24 hours of birth. When possible, the trial was discussed with parents antenatally, and written informed consent was sought within 24 hours of birth |
|
| Interventions | The infants were randomised to one of four groups: Group 1: Inc‐AA/S‐LE (20% Intralipid); n = 42; Group 2: Inc‐AA/SMOF (20% SMOFLipid); n = 42; Group 3: Imm‐RDI/S‐LE (20% Intralipid); n = 41; Group 4: Imm‐RDI/SMOF; (20% SMOFLipid) n = 43; Inc‐AA infants received 1.7 g/kg amino acids on day 1, 2.1 g/kg on day 2, and a maximum of 2.7 g/kg/d from day 3; Imm‐RDI infants received 3.6 g/kg/d amino acids from day 1. PN within 24 hours of birth to trial PN ceased when an infant had received and tolerated 150 mL milk/kg/d21 for at least 24 hours. |
|
| Outcomes | Primary outcomes: non‐adipose mass for the amino acid intervention and intrahepatocellular lipid for the lipid intervention using MRI and MR spectroscopy. Study evaluated prespecified safety measures (serum lipids, cholesterol, creatinine, urea, bilirubin, liver function tests, blood glucose, and base deficit) from routine clinical tests. | |
| Notes | Well‐designed trial with collaboration from various trial units in London and overseen by the Imperial College London Clinical Trials Unit. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "incorporated minimization with a random element." The trial was managed by the Imperial College London Clinical Trials Unit. This may also add to validity of the trial procedures. Comment: done |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "use of an interactive voice recognition telephone system to 1 of 4 groups (Inc‐AA/SO, Inc‐AA/SMOF, Imm‐RDI/SO, and Imm‐RDI/SMOF) and incorporated minimization with a random element and stratification by gestational age (23 to 26 or 27 to 31 completed weeks), birth weight (< 500, 500 to 1000, or > 1000 g), and centre." Comment: done |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Quote: "Trial formulations were investigational medicinal products prepared by a licensed facility (Bath ASU). Other PN components were identical across randomized groups." "Hospital pharmacy staff dispensed trial PN between 0900 and 1700; attending clinicians were blinded to trial allocation." Comment: done |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Comment: "Image analysis with the use of Slice‐O‐Matic (version 4.2; Tomovision) was undertaken independently by the Vardis Group and was blinded to participant identity and group allocation." Quote: review authors agreed that the risk was low. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Quote: The primary and most other clinical outcomes are available for most participants. The authors also provided detailed information about outcomes for all participants and for those infants completing magnetic resonance assessment. Comment: done |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Quote: "ISRCTN29665319; EudraCT 2009‐016731‐34" Comment: no concerns regarding reporting bias. |
| Other bias | Low risk | Comment: none. |
Vlaardingerbroek 2014.
| Methods | Design: prospective single‐centre RCT in VLBW preterm infants Setting: NICU of Erasmus MC‐Sophia Children's Hospital, Rotterdam, The Netherlands Study enrolment: December 2008 to January 2012. I. Allocation concealment: yes II. Blinding of intervention: could not determine III. Blinding of outcome measurement(s): could not determine IV. Complete follow‐up: yes (per protocol only) |
|
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: VLBW infants (birth weight < 1500 g) with central venous catheter for clinical purposes Exclusion criteria: congenital anomalies; chromosome defects; metabolic diseases; and endocrine, renal or hepatic disorders. |
|
| Interventions | 98 preterm infants Group 1 (n = 49): MOFS‐LE; 20% SMOFlipid (Fresenius Kabi, Germany) Group 2 (n = 49): S‐LE; Intralipid 20% (Fresenius Kabi, Germany) 1 withdrawal from each arm (leaving 48 infants in each arm). |
|
| Outcomes | Primary outcomes: FA concentration in plasma TG and PLs. Secondary outcomes: haematological biochemical parameters; phytosterol concentrations; and clinical outcomes including survival, duration of hospital stay, symptomatic PDA, RDS, BPD, NEC, late‐onset sepsis, IVH, PVL, ROP and cholestasis. Growth outcomes were reported as a part of efficacy parameters. |
|
| Notes | Funding source: none disclosed. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "computer generated block randomisation list with variable block sizes generated by a statistician." |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "sealed opaque randomisation envelope that was stratified by weight (< 1000 g and 1000 to 1499 g) and sex. The envelopes were made by a research pharmacist who was not involved in clinical care." |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | Quote: "randomisation to the lipid group remained double‐blinded throughout the study and the analyses;" "double‐blind randomised controlled trial." Comment: details of how blinding was achieved not described. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | Quote: "randomisation to the lipid group remained double‐blinded throughout the study and the analyses;" "double‐blind randomised controlled trial." Comment: details of how blinding was achieved not described. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Comment: clinical outcomes were reported for most infants. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Comment: study protocol was available at www.trialregister.nl.com, registration no. NTR1445. |
| Other bias | Low risk | Comment: none identified. |
Wang 2016.
| Methods | Design: double‐blind RCT Setting: NICU of Xin Hua Hospital and Shanghai Children's Medical Center in Shanghai, China Study enrolment from February 2012 to July 2013 I. Allocation concealment: yes II. Blinding of intervention: yes III. Blinding of outcome measurement(s): yes IV. Complete follow‐up: yes (per protocol only) |
|
| Participants | 118 preterm infants (< 37 weeks); 103 infants (12 refused consent and 3 died in < 72 hours before randomisation) randomised | |
| Interventions | Group 1 (n = 51): S‐LE; Intralipid Group 2 (n = 52): OS‐LE; ClinOleic |
|
| Outcomes | Primary end point: liver chemistry Secondary end point: plasma bile acid composition. Serum conjugated bilirubin was reported to be higher after 7 days in the S‐LE group. The study reported on weight gain, days to regain birth weight, duration of ventilation, BPD, NEC and culture‐positive sepsis. There were 3 deaths before randomisation and 3 deaths during the study (2 in OS‐LE group and 1 in S‐LE group). ROP, IVH and PVL were not reported. |
|
| Notes | Funding disclosure: supported in part by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81100631) and Shanghai Key Laboratory of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition (No. 11DZ2260500). | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "cards were created with a unique randomisation code." Comment: though the authors did not mention how the unique randomisation code was generated, the review authors agreed that the risk was low; it was probably done. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "… unique randomisation code and placed in sequentially numbered opaque envelopes." |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Quote: "Investigators, parents, and all the physicians and nurses involved in patient care were blinded to the group assignment," "The 2 solutions looked identical to the clinicians." Comment: blinding strategy was not clearly described (by current consensus between review authors). |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Quote: "Investigators, parents, and all the physicians and nurses involved in patient care were blinded to the group assignment," "The 2 solutions looked identical to the clinicians." Comment: blinding strategy was not clearly described (by current consensus between review authors). |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Comment: clinical outcomes were reported for most infants. 2 infants in the OS‐LE arm and 2 infant in the S‐LE arm were excluded from analysis as they had < 14 days of PN. ITT analysis was done. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Comment: the study protocol was available: NCT01786759. |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Comment: another publication with duplicate data with data irregularities was published in Clinical Nutrition by the same author. At the time of writing this review, the clarifications regarding the duplicate publication and data irregularity were still awaited. We have included those data which were consistently reported across the 2 study reports. |
ALP: alkaline phosphatase; ALT: alanine aminotransferase; AST: aspartate transaminase; BALF: bronchoalveolar lavage fluid; BPD: bronchopulmonary dysplasia; BSID‐III: Bayley Scales of Infant and Toddler Development, 3rd edition; Cbil: conjugated bilirubin; CE: cholesterol ester; CI: confidence interval; CLD: chronic lung disease; DHA: docosahexaenoic acid; EBM: expressed breast milk; EDTA: ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid; ELBW: extremely low birthweight; EPA: eicosapentaenoic acid; F‐LE: fish oil‐containing lipid emulsion; FA: fatty acid; FC: free cholesterol; GGT: gamma‐glutamyltransferase; IL: interleukin; iNO: inhaled nitric oxide; INR: international normalised ratio; ITT: intention to treat; IVH: intraventricular haemorrhage; LC‐PUFA: long‐chain polyunsaturated fatty acid; LE: lipid emulsion; n: number of participants; MCT: medium‐chain triglyceride; MFS: medium‐chain triglyceride‐fish‐soybean oil lipid emulsion; MFS‐LE: medium‐chain triglyceride‐fish‐soybean oil lipid emulsion; MOFS‐LE: medium‐chain triglyceride‐olive‐fish‐soybean oil lipid emulsion; MS‐LE: medium‐chain triglyceride‐soybean oil lipid emulsion; NEC: necrotising enterocolitis; NICU: neonatal intensive care unit; PDA: patent ductus arteriosus; PL: phospholipid; PN: parenteral nutrition; PNAC: parenteral nutrition‐associated cholestasis; RBC: red blood cell; RCT: randomised controlled trial; RDS: respiratory distress syndrome; ROP: retinopathy of prematurity; S‐LE: soybean oil‐based lipid emulsions; SD: standard deviation; TAP: tocopherol‐associated protein; TG: triglyceride; TPN: total parenteral nutrition; TRAP: total radical‐trapping antioxidant potential; VLBW: very low birthweight.
Characteristics of excluded studies [ordered by study ID]
| Study | Reason for exclusion |
|---|---|
| Angsten 2002 | Included term infants. Population included 36‐ to 41‐week newborn infants ≤ 4 days of age needing surgery and expected to require total PN for ≥ 5 days. |
| Ariyawangso 2014 | Included newborn infants requiring surgery and term infants. Infants were randomised to receive SMOFlipid 20% (experimental group, n = 21) or Intralipid 20% (control group, n = 21). |
| Lima 1988 | Included term infants up to 38 weeks' gestation. |
| Magnusson 1997 | Included newborn infants requiring surgery and term infants. |
| Webb 2008 | Included term infants with mean gestation of infants 37.0 (SD 3.6) weeks and 36.7 (SD 3.0) weeks in the 2 arms of the study. |
| Wilson 1997 | Compare "aggressive parenteral nutrition" in preterm infants vs "conventional parenteral nutrition." The "aggressive nutrition group" received a higher rate of lipids, proteins, dextrose and 33% of participants in this group received insulin besides getting medium chain and long chain triglyceride‐based LE (Lipofundin). The conventional nutrition group received a lesser percentage of dextrose, lesser rate of lipids (S‐LE) and no insulin. The duration of LE was a median of 20 days (interquartile range 12 to 28 days) in the aggressive nutrition (MS‐LE) group vs a median of 6 days (interquartile range 2–15 days) in the conventional nutrition (S‐LE group). This study, done in 1997, reported advantages of the aggressive PN regimen vs conventional PN. |
MS‐LE: medium‐chain triglyceride‐soybean oil lipid emulsion; n: number of participants; PN: parenteral nutrition; S‐LE: soybean oil‐based lipid emulsions; SD: standard deviation.
Characteristics of studies awaiting assessment [ordered by study ID]
Karagiozoglou‐Lampoudi 2012.
| Methods | Double‐blind RCT of MCT/ω‐3‐PUFA‐enriched LEs compared to S‐LEs for preterm infants receiving PN. 127 infants in the intervention group; 122 infants in the control group. |
| Participants | Preterm infants 23 to 36 weeks |
| Interventions | Intervention LEs included MCTs/ω‐3‐PUFAs‐enriched (MCTs/ ω‐3‐LE) and soybean‐based, on the incidence of TPNAC and lipid profile of preterm infants (as per abstract). |
| Outcomes | Cholestasis was observed in 6.4% infants (3.9% in the intervention group and 9% in the control group). |
| Notes | Only preliminary data were presented in conference proceedings. We contacted the author to request the full publication. |
NCT00497289.
| Methods | Double‐blind RCT of an MCT/LCT/FO containing 20% LE with a MCT/LCT emulsion (20%) for PN in preterm infants. 34 infants were estimated for enrolment. |
| Participants | Preterm infants 500 to 1500 g |
| Interventions | Lipofundin MCT/LCT 20% vs Lipidem 20% |
| Outcomes | Safety parameters as per the study protocol: bilirubin, ALT, PTT, platelet count on study days 1 and 6 |
| Notes | Study was completed in February 2008, but no published data available. Authors have been contacted. |
NCT03275090.
| Methods | RCT conducted in a NICU in Egypt. 40 preterm infants. 20 preterm infants received PN containing 20% MOFS‐LE (SMOFlipid). 20 preterm infants with sepsis received the usual PN containing S‐LE (20% Intralipid) at daily increasing doses guided by serum triglycerides. |
| Participants | Preterm infants |
| Interventions | SMOFlipid vs 20% Intralipid |
| Outcomes | Soluble intercellular adhesion molecule‐1 (sICAM‐1) and leukocyte integrin levels Secondary outcomes: length of hospital stay and mechanical ventilation |
| Notes | Only preliminary data presented in conference proceedings. |
Wang 2016b.
| Methods | Randomised study which appears to have 3 intervention arms. |
| Participants | Preterm infants < 37 weeks' gestation |
| Interventions | 156 infants randomised to either OS‐LE or MS‐LE or S‐LE. |
| Outcomes | Fatty acid profile, anthropometry and several clinical parameters |
| Notes | Published in Clinical Nutrition and appeared to have 2 out of 3 arms common with an earlier report of a randomised study (Wang 2016) in Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition, which was included in the previous version of this review. Several baseline participant characteristics were common between the 2 reports and there were some data irregularities which were brought to the notice of the editors of the journals. At the time of writing this review, we are awaiting clarifications and some changes expected to the study reports as per the editors of the 2 journals. We included the data from the earlier report of the study published in Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition for the consistently reported data between the 2 study reports (Wang 2016). |
ALT: alanine aminotransferase; LCT: long‐chain triglyceride; LE: lipid emulsion; MCT: medium‐chain triglyceride; MOFS‐LE: medium‐chain triglyceride‐olive‐fish‐soybean oil lipid emulsion; MS‐LE: medium‐chain triglyceride‐soybean oil lipid emulsion; NICU: neonatal intensive care unit; OS‐LE: olive oil‐soybean oil‐based lipid emulsion; PN: parenteral nutrition; PTT: prothrombin time; PUFA: polyunsaturated fatty acid; RCT: randomised controlled trial; S‐LE: soybean oil‐based lipid emulsion; TPNAC: total parenteral nutrition‐associated cholestasis.
Differences between protocol and review
Outcomes: we added an outcome of cholestasis including all definitions given the heterogeneity in the definitions used in the studies and the guidelines. We also added the following: outcome for any BPD (to include differential definitions); combined outcome of ROP stage 3 or greater and ROP requiring surgery to avoid bias due to incomplete information in either of outcomes as some studies reported on ROP requiring surgery and others on ROP stage 3 or greater. Both ROP outcomes are similar on the scale of severity. We added an outcome of any sepsis to include all reports of sepsis in included studies. We added conjugated bilirubin levels (µmol/L) as a secondary outcome and as an outcome for the 'Summary of findings' table.
The method of dealing with the unit of analysis error was finalised at the review stage.
Contributions of authors
For the original review (Kapoor 2015), all review authors were involved in conceiving and designing the protocol.
RS, VK and MM performed the update of the protocol (2018) to address the requests of UK guideline developers of the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR).
VK and MM selected studies, extracted data and assessed risk of bias, relying upon RS as a third assessor when necessary. VK and MM prepared the manuscript, conferring and collaborating with RS.
Sources of support
Internal sources
No sources of support supplied
External sources
-
National Institute for Health Research, UK.
Editorial support for Cochrane Neonatal has been funded by a UK National Institute of Health Research (NIHR) Cochrane Programme Grant (16/114/03). The views expressed in this publication are those of the authors and not necessarily those of the National Health Service, the NIHR or the UK Department of Health.
-
Vermont Oxford Network, USA.
Cochrane Neonatal Reviews are produced with support from Vermont Oxford Network, a worldwide collaboration of health professionals dedicated to providing evidence‐based care of the highest quality for newborn infants and their families.
-
National Institute for Health Research, UK.
The review has received support through the Cochrane Review Incentive Scheme, reference number 17/62/30.
Declarations of interest
VK: none.
MM: none.
RS: none.
New
References
References to studies included in this review
Beken 2014 {published data only}
- Beken S, Dilli D, Fettah ND, Kabatas EU, Zenciroqlu A, Okumus N. The influence of fish‐oil lipid emulsions on retinopathy of prematurity in very low birth weight infants: a randomised controlled trial. Early Human Development 2014;90(1):27‐31. [DOI: 10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2013.11.002; PUBMED: 24314586] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Biagetti 2016 {published data only}
- Biagetti C, Vedovelli L, Savini, S, Simonato M, D'Ascenzo R, Pompilio A, et al. Double blind exploratory study on de novo lipogenesis in preterm infants on parenteral nutrition with a lipid emulsion containing 10% fish oil. Clinical Nutrition 2016;35(2):337‐43. [DOI: 10.1016/j.clnu.2015.04.005; PUBMED: 25912232] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
D'Ascenzo 2011 {published data only}
- D'Ascenzo R, D'Egidio S, Angelini L, Bellagamba MP, Manna M, Pompilio A, et al. Parenteral nutrition of preterm infants with a lipid emulsion containing 10% fish oil: effect on plasma lipids and long‐chain polyunsaturated fatty acids. Journal of Pediatrics 2011;159(1):33‐8.e1. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2010.12.052; PUBMED: 21362575] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
D'Ascenzo 2014 {published data only}
- D'Ascenzo R, Savini S, Biagetti C, Bellagamba MP, Marchionni P, Pompilio A, et al. Higher docosahexaenoic acid, lower arachidonic acid and reduced lipid tolerance with high doses of a lipid emulsion containing 15% fish oil: a randomised clinical trial. Clinical Nutrition 2014;33(6):1002‐9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Demirel 2011 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
- Demirel G, Oguz SS, Celik IH, Erdeve O, Uras N, Dilmen U. The metabolic effects of two different lipid emulsions used in parenterally fed premature infants – a randomised comparative study. Early Human Development 2012;88(7):499‐501. [DOI: 10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2011.12.008; PUBMED: 22245235] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Deshpande 2009 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
- Deshpande GC, Simmer K, Mori T, Croft K. Parenteral lipid emulsions based on olive oil compared with soybean oil in preterm (≤ 28 weeks' gestation) neonates: a randomised controlled trial. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition 2009;49(5):619‐25. [DOI: 10.1097/MPG.0b013e31819ca1b8; PUBMED: 19644398] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Deshpande 2014 {published data only}
- Deshpande G, Simmer K, Deshmukh M, Mori T, Croft K, Kristensen J. Fish oil (SMOFlipid) and olive oil lipid (ClinOleic) in very preterm neonates. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology & Nutrition 2014;58(2):177‐82. [DOI: 10.1097/MPG.0000000000000174; PUBMED: 24048161] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Diamond 2017 {published data only}
- Diamond IR, Grant RC, Pencharz PB, Silva N, Feldman BM, Fitzgerald P, et al. Preventing the progression of intestinal failure‐associated liver disease in infants using a composite lipid emulsion: a pilot randomized controlled trial of SMOFlipid. JPEN. Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition 2017; Vol. 41, issue 5:866‐77. [DOI: 10.1177/0148607115626921; PUBMED: 26838529] [DOI] [PubMed]
Gawecka 2008b {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
- Gawecka A, Michalkiewicz J, Kornacka MK, Luckiewicz B, Kubiszewska I. Immunologic properties differ in preterm infants fed olive oil vs soy‐based lipid emulsions during parenteral nutrition. JPEN. Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition 2008;32(4):448‐53. [DOI: 10.1177/0148607108319802; PUBMED: 18596318] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Göbel 2003 {published data only}
- Göbel Y, Koletzko B, Böhles HJ, Engelsberger I, Forget D, Brun A, et al. Parenteral fat emulsions based on olive and soybean oils: a randomised clinical trial in preterm infants. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition 2003;37(2):161‐7. [PUBMED: 12883303] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Hsiao 2018 {published data only}
- Hsiao CC, Lin HC, Chang YJ, Yang SP, Tsao LY, Lee CH, et al. Intravenous fish oil containing lipid emulsion attenuates inflammatory cytokines and the development of bronchopulmonary dysplasia in very premature infants: a double‐blind, randomised controlled trial. Clinical Nutrition 2018, (18):31148‐8. [DOI: 10.1016/j.clnu.2018.06.929; PUBMED: 29941233] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Köksal 2011 {published and unpublished data}
- Köksal N, Kavurt AV, Cetinkaya M, Ozarda Y, Ozkan H. Comparison of lipid emulsions on antioxidant capacity in preterm infants receiving parenteral nutrition. Pediatrics International 2011;53(4):562‐6. [DOI: 10.1111/j.1442-200X.2011.03335.x; PUBMED: 21342355] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Lam 2014 {published data only}
- Lam HS, Tam YH, Poon TC, Cheung HM, Yu X, Chan BP, et al. A double‐blind randomised controlled trial of fish oil‐based versus soy‐based lipid preparations in the treatment of infants with parenteral nutrition‐associated cholestasis. Neonatology 2014;4(105):290‐6. [DOI: 10.1159/000358267; PUBMED: 24576844] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Lehner 2006 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
- Lehner F, Demmelmair H, Röschinger W, Decsi T, Szász M, Adamovich K, et al. Metabolic effects of intravenous LCT or MCT/LCT lipid emulsions in preterm infants. Journal of Lipid Research 2006;47(2):404‐11. [DOI: 10.1194/jlr.M500423-JLR200; PUBMED: 16299352] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Najm 2017 {published data only}
- Najm S, Löfqvist C, Hellgren G, Engström E, Lundgrenb P, Hård AL, et al. Effects of a lipid emulsion containing fish oil on polyunsaturated fatty acid profiles, growth and morbidities in extremely premature infants: a randomised controlled trial. Clinical Nutrition ESPEN 2017;20:17‐23. [DOI: 10.1016/j.clnesp.2017.04.004; PUBMED: 29072164] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Nehra 2014 {published data only}
- Nehra D, Fallon EM, Potemkin AK, Voss SD, Mitchell PD, Valim C, et al. A comparison of 2 intravenous lipid emulsions: interim analysis of a randomised controlled trial. JPEN. Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition 2014;38(6):693‐701. [DOI: 10.1177/0148607113492549; PUBMED: 23770843] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Pawlik 2014 {published data only}
- Pawlik D, Lauterbach R, Walczak M, Hurkala J, Sherman MP. Fish‐oil fat emulsion supplementation reduces the risk of retinopathy in very low birth weight infants: a prospective, randomised study. JPEN. Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition 2014;38(6):711‐6. [DOI: 10.1177/0148607113499373; PUBMED: 23963690] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Rayyan 2012 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
- Rayyan M, Devlieger H, Jochum F, Allegaert K. Short‐term use of parenteral nutrition with a lipid emulsion containing a mixture of soybean oil, olive oil, medium‐chain triglycerides, and fish oil: a randomised double‐blind study in preterm infants. Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition 2012;36(1 Suppl):81S‐94S. [DOI: 10.1177/0148607111424411; PUBMED: 22237883] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Repa 2018 {published data only}
- Repa A, Binder C, Thanhaeuser M, Kreissl A, Pablik E, Huber‐Dangl M, et al. A mixed lipid emulsion for prevention of parenteral nutrition associated cholestasis in extremely low birth weight infants: a randomized clinical trial. Journal of Pediatrics 2018;194:87‐93. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2017.11.012; PUBMED: 29269199] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Roggero 2010 {published data only}
- Roggero P, Mosca F, Gianni ML, Orsi A, Amato O, Migliorisi E, et al. F2‐isoprostanes and total radical‐trapping antioxidant potential in preterm infants receiving parenteral lipid emulsions. Nutrition 2010;26(5):551‐5. [DOI: 10.1016/j.nut.2009.06.018; PUBMED: 19880291] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Rubin 1994 {published data only}
- Rubin M, Moser A, Naor N, Merlob P, Pakula R, Sirota L. Effect of three intravenously administered fat emulsions containing different concentrations of fatty acids on the plasma fatty acid composition of premature infants. Journal of Pediatrics 1994;125(4):596‐602. [PUBMED: 7931881] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Savini 2013 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
- Savini S, D'Ascenzo R, Biagetti C, Serpentini G, Pompilio A, Bartoli A, et al. The effect of 5 intravenous lipid emulsions on plasma phytosterols in preterm infants receiving parenteral nutrition: a randomised clinical trial. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2013;98(2):312‐8. [DOI: 10.3945/ajcn.112.056556; PUBMED: 23761482] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Skouroliakou 2010 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
- Skouroliakou M, Konstantinou D, Koutri K, Kakavelaki C, Stathopoulou M, Antoniadi M, et al. A double‐blind, randomised clinical trial of the effect of omega‐3 fatty acids on the oxidative stress of preterm neonates fed through parenteral nutrition. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2010;64(9):940‐7. [DOI: 10.1038/ejcn.2010.98; PUBMED: 20551967] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Skouroliakou 2016 {published data only}
- Skouroliakou M, Konstantinou D, Agakidis C, Kaliora A, Kalogeropoulos N, Massara P, et al. Parenteral MCT/omega‐3 polyunsaturated fatty acid‐enriched intravenous fat emulsion is associated with cytokine and fatty acid profiles consistent with attenuated inflammatory response in preterm neonates: a randomized, double‐blind clinical trial. Nutrition in Clinical Practice 2016;31(2):235‐44. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Techasatid 2017 {published data only}
- Techasatid W, Sapsaprang S, Tantiyavarong P, Luvira A. Effectiveness of multicomponent lipid emulsion in preterm infants requiring parenteral nutrition: a two‐center, double‐blind randomized clinical trial. Journal of the Medical Association of Thai 2017;100(9):972‐9. [Google Scholar]
Tomsits 2010 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
- Tomsits E, Pataki M, Tölgyesi A, Fekete G, Rischak K, Szollár L. Safety and efficacy of a lipid emulsion containing a mixture of soybean oil, medium‐chain triglycerides, olive oil, and fish oil: a randomised, double‐blind clinical trial in premature infants requiring parenteral nutrition. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition 2010;51(4):514‐21. [DOI: 10.1097/MPG.0b013e3181de210c; PUBMED: 20531018] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Uthaya 2016 {published data only}
- Uthaya S, Liu X, Babalis D, Dore C, Warwick J, Bell J, et al. Nutritional evaluation and optimisation in neonates: a randomised, double‐blind controlled trial of amino acid regimen and intravenous lipid composition in preterm parenteral nutrition. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2016;103:1443‐52. [PUBMED: 27030860] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Vlaardingerbroek 2014 {published data only}
- Vlaardingerbroek H, Vermeulen MJ, Carnielli VP, Vaz FM, Akker CH, Goudoever JB. Growth and fatty acid profiles of VLBW infants receiving a multicomponent lipid emulsion from birth. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition 2014;58(4):417‐27. [DOI: 10.1097/MPG.0000000000000280; PUBMED: 24667866] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlaardingerbroek H, Vermeulen MJ, Rook D, Akker CH, Dorst K, Wattimena JL, et al. Safety and efficacy of early parenteral lipid and high‐dose amino acid administration to very low birth weight infants. The Journal of Pediatrics 2013;163(3):638‐44.e1‐5. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2013.03.059] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Wang 2016 {published data only}
- Wang Y, Zhou KJ, Tang QY, Hong L, Feng Y, Lu LN, et al. Effect of an olive oil‐based lipid emulsion compared with a soybean oil‐based lipid emulsion on liver chemistry and bile acid composition in preterm infants receiving parenteral nutrition: a double‐blind, randomized trial. Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition 2016;40(6):842‐50. [DOI: 10.1177/0148607114566853; PUBMED: 25560678] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
References to studies excluded from this review
Angsten 2002 {published data only}
- Angsten G, Boberg M, Cederblad G, Meurling S, Stiernström H. Metabolic effects in neonates receiving intravenous medium‐chain triglycerides. Acta Paediatrica 2002;91(2):188‐97. [PUBMED: 11952008] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Ariyawangso 2014 {published data only}
- Ariyawangso U, Puttilerpong C, Ratanachuek S, Anuntkosol M. Short‐term safety and efficacy of fish‐oil emulsions on the prevention of parenteral nutrition‐associated liver disease in surgical neonates: a randomised controlled trial. Thai Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 2014;38(4):202‐9. [Google Scholar]
Lima 1988 {published data only}
- Lima LA, Murphy JF, Stansbie D, Rowlandson P, Gray OP. Neonatal parenteral nutrition with a fat emulsion containing medium chain triglycerides. Acta Paediatrica Scandinavica 1988;77(3):332‐9. [PUBMED: 3133924] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Magnusson 1997 {published data only}
- Magnusson G, Boberg M, Cederblad G, Meurling S. Plasma and tissue levels of lipids, fatty acids and plasma carnitine in neonates receiving a new fat emulsion. Acta Paediatrica 1997;86(6):638‐44. [PUBMED: 9202801] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Webb 2008 {published data only}
- Webb AN, Hardy P, Peterkin M, Lee O, Shalley H, Croft KD, et al. Tolerability and safety of olive oil‐based lipid emulsion in critically ill neonates: a blinded randomised trial. Nutrition 2008;24(11‐2):1057‐64. [DOI: 10.1016/j.nut.2008.05.004; PUBMED: 18619813] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Wilson 1997 {published data only}
- Wilson DC, Cairns P, Halliday HL, Reid M, McClure G, Dodge JA. Randomised controlled trial of an aggressive nutritional regimen in sick very low birthweight infants. Archives of Disease in Childhood. Fetal and Neonatal Edition 1997;77(1):F4‐11. [PUBMED: 9279175] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
References to studies awaiting assessment
Karagiozoglou‐Lampoudi 2012 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
- Karagiozoglou‐Lampoudi T, Skouroliakou M, Konstantinou D, Agakidis C, Delikou N, Koutri K, et al. Omega‐3‐polyunsaturated fatty acid – enriched parenteral lipid emulsion and prevention of cholestasis in preterm infants. Comparison with soybean‐based lipid emulsion. European Journal of Hospital Pharmacy: Science and Practice 2012;19(2):221‐2. [DOI: ] [Google Scholar]
NCT00497289 {unpublished data only}
NCT03275090 {unpublished data only}
- Wahba Y, Abdelkareem M, Shouman B, Mesbah A. The effects of two different intravenous lipid emulsions on the outcomes of preterm infants with sepsis: a randomised controlled trial. Journal of Pediatric Care 2018;4. [DOI: 10.21767/2471-805X-C2-009] [DOI] [Google Scholar]
Wang 2016b {published data only}
- Wang Y, Feng Y, Lu LN, Wang WP, He ZJ, Xie LJ, et al. The effects of different lipid emulsions on the lipid profile, fatty acid composition, and antioxidant capacity of preterm infants: a double‐blind, randomised clinical trial. Clinical Nutrition 2016;35(5):1023‐31. [DOI: 10.1016/j.clnu.2015.10.011; PUBMED: 26561301] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Additional references
AAP 1985
- American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Nutrition. Nutritional needs of low‐birth‐weight infants. Pediatrics 1985;75(5):976‐86. [PUBMED: 3921937] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Ahmad 2010
- Ahmad I, Nemet D, Eliakim A, Koeppel R, Grochow D, Coussens M, et al. Body composition and its components in preterm and term newborns: a cross‐sectional, multimodal investigation. American Journal of Human Biology 2010;22(1):69‐75. [DOI: 10.1002/ajhb.20955; PUBMED: 19533616] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Beauchamp 2005
- Beauchamp GK, Keast RS, Morel D, Lin J, Pika J, Han Q, et al. Phytochemistry: ibuprofen‐like activity in extra‐virgin olive oil. Nature 2005;437(7055):45‐6. [DOI: 10.1038/437045a; PUBMED: 16136122] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Bell 1978
- Bell MJ, Ternberg JL, Feigin RD, Keating JP, Marshall R, Barton L, et al. Neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis. Therapeutic decisions based upon clinical staging. Annals of Surgery 1978;187(1):1‐7. [PUBMED: 413500] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Buenestado 2006
- Buenestado A, Cortijo J, Sanz MJ, Naim‐Abu‐Nabah Y, Martinez‐Losa M, Mata M, et al. Olive oil‐based lipid emulsion's neutral effects on neutrophil functions and leukocyte–endothelial cell interactions. Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition 2006;30(4):286‐96. [DOI: 10.1177/0148607106030004286; PUBMED: 16804125] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Christensen 2007
- Christensen RD, Henry E, Wiedmeier SE, Burnett J, Lambert DK. Identifying patients, on the first day of life, at high‐risk of developing parenteral nutrition‐associated liver disease. Journal of Perinatology 2007;27(5):284‐90. [DOI: 10.1038/sj.jp.7211686; PUBMED: 17344923] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Cober 2010
- Cober MP, Teitelbaum DH. Prevention of parenteral nutrition‐associated liver disease: lipid minimization. Current Opinion in Organ Transplantation 2010;15(3):330‐3. [DOI: 10.1097/MOT.0b013e328338c2da; PUBMED: 20386446] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
de Meijer 2009
- Meijer VE, Gura KM, Le HD, Meisel JA, Puder M. Fish oil‐based lipid emulsions prevent and reverse parenteral nutrition‐associated liver disease: the Boston experience. Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition 2009;33(5):541‐7. [DOI: 10.1177/0148607109332773; PUBMED: 19571170] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
de Vries 1992
- Vries LS, Eken P, Dubowitz LM. The spectrum of leukomalacia using cranial ultrasound. Behavioural Brain Research 1992;49(1):1‐6. [PUBMED: 1388792] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Deeks 2017
- Deeks JJ, Higgins JP, Altman DG, editor(s), Cochrane Statistical Methods Group. Chapter 9: Analysing data and undertaking meta‐analyses. In: Higgins JP, Green S editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Chichester (UK): John Wiley & Sons, 2017. [Google Scholar]
Driscoll 2008
- Driscoll DF, Bistrian BR, Demmelmair H, Koletzko B. Pharmaceutical and clinical aspects of parenteral lipid emulsions in neonatology. Clinical Nutrition 2008;27(4):497‐503. [DOI: 10.1016/j.clnu.2008.05.003; PUBMED: 18582994] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Ehrenkranz 2000
- Ehrenkranz RA. Growth outcomes of very low‐birth weight infants in the newborn intensive care unit. Clinics in Perinatology 2000;27(2):325‐45. [PUBMED: 10863653] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Fenton 2017
- Fenton TR, Chan HT, Madhu A, Griffin IJ, Hoyos A, Ziegler EE, et al. Preterm infant growth velocity calculations: a systematic review. Pediatrics 2017;139(3):e20162045. [DOI: 10.1542/peds.2016-2045; PUBMED: 28246339] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Furukawa 2006
- Furukawa TA, Barbui C, Cipriani A, Brambilla P, Watanabe N. Imputing missing standard deviations in meta‐analyses can provide accurate results. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2006;59(1):7‐10. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2005.06.006; PUBMED: 16360555] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Fürst 2000
- Fürst P, Kuhn KS. Fish oil emulsions: what benefits can they bring?. Clinical Nutrition 2000;19(1):7‐14. [DOI: 10.1054/clnu.1999.0072; PUBMED: 10700528] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Gawecka 2008a
- Gawecka A, Kornacka MK, Luckiewicz B, Rudzinska I. Tolerance of two lipid emulsions used in parenterally‐fed premature infants – a comparative study. Medycyna Wieku Rozwojowego 2008;12(3):782‐8. [PUBMED: 19305031] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Gawecka 2008c
- Gawecka A, Michalkiewicz J, Kornacka MK, Luckiewicz B, Kubiszewska I. Immunologic properties differ in preterm infants fed olive oil vs soy‐based lipid emulsions during parenteral nutrition. Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition 2008;32(4):448‐53. [DOI: 10.1177/0148607108319802; PUBMED: 18596318] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Gitto 2001
- Gitto E, Karbownik M, Reiter RJ, Tan DX, Cuzzocrea S, Chiurazzi P, et al. Effects of melatonin treatment in septic newborns. Pediatric Research 2001;50(6):756‐60. [PUBMED: 11726736] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Gogos 1995
- Gogos CA, Kalfarentzos F. Total parenteral nutrition and immune system activity: a review. Nutrition 1995;11(4):339‐44. [PUBMED: 8580573] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Goulet 1999
- Goulet O, Potter S, Antebi H, Driss F, Colomb V, Bereziat G, et al. Long‐term efficacy and safety of a new olive oil‐based intravenous fat emulsion in pediatric patients: a double‐blind randomised study. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1999;70(3):338‐45. [DOI: 10.1093/ajcn/70.3.338; PUBMED: 10479195] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
GRADEpro GDT [Computer program]
- McMaster University (developed by Evidence Prime). GRADEpro GDT. Version accessed 22 January 2018. Hamilton (ON): McMaster University (developed by Evidence Prime), 2015.
Granato 2000
- Granato D, Blum S, Rossle C, Boucher J, Malnoe A, Dutot G. Effects of parenteral lipid emulsions with different fatty acid composition on immune cell functions in vitro. Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition 2000;24(2):113‐8. [DOI: 10.1177/0148607100024002113; PUBMED: 10772192] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Grimm 2005
- Grimm H. A balanced lipid emulsion – a new concept in parenteral nutrition. Clinical Nutrition Supplements 2005;1(3):25‐30. [DOI: ] [Google Scholar]
Gura 2005
- Gura KM, Parsons SK, Bechard LJ, Henderson T, Dorsey M, Phipatanakul W, et al. Use of a fish oil‐based lipid emulsion to treat essential fatty acid deficiency in a soy allergic patient receiving parenteral nutrition. Clinical Nutrition 2005;24(5):839‐47. [DOI: 10.1016/j.clnu.2005.05.020; PUBMED: 16029913] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Hay 2008
- Hay WW. Strategies for feeding the preterm infant. Neonatology 2008;94(4):245‐54. [DOI: 10.1159/000151643; PUBMED: 18836284] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Heird 2005
- Heird WC, Lapillonne A. The role of essential fatty acids in development. Annual Review of Nutrition 2005;25:549‐71. [DOI: 10.1146/annurev.nutr.24.012003.132254; PUBMED: 16011478] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Higgins 2017
- Higgins JP, Altman DG, Sterne JA, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.2.0 (updated June 2017). Cochrane, 2017. Available from training.cochrane.org/handbook.
Hojsak 2016
- Hojsak I, Colomb V, Braegger C, Bronsky J, Campoy C, Domellof M, et al. ESPGHAN Committee on Nutrition Position Paper. Intravenous lipid emulsions and risk of hepatotoxicity in infants and children: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition 2016;62(5):776‐92. [PUBMED: 26825766] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Hozo 2005
- Hozo SP, Djulbegovic B, Hozo I. Estimating the mean and variance from the median, range, and the size of a sample. BMC Medical Research Methodology 2005;5:13. [DOI: 10.1186/1471-2288-5-13; PUBMED: 15840177] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
ICROP 2005
- International Committee for the Classification of Retinopathy of Prematurity. The International Classification of Retinopathy of Prematurity revisited. Archives of Ophthalmology 2005;123(7):991‐9. [DOI: 10.1001/archopht.123.7.991; PUBMED: 16009843] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Koletzko 2001
- Koletzko B, Agostoni C, Carlson SE, Clandinin T, Hornstra G, Neuringer M, et al. Long chain polyunsaturated fatty acids (LC‐PUFA) and perinatal development. Acta Paediatrica 2001;90(4):460‐4. [PUBMED: 11332943] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Koletzko 2005
- Koletzko B, Goulet O, Hunt J, Krohn K, Shamir R. Guidelines on Paediatric Parenteral Nutrition of the European Society of Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition (ESPGHAN) and the European Society for Clinical Nutrition and Metabolism (ESPEN), supported by the European Society of Paediatric Research (ESPR). Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition 2005;41 Suppl 2:1‐87. [PUBMED: 16254497] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Kotiya 2016
- Kotiya P, Zhao X, Cheng P, Zhu X, Xiao Z, Wang J. Fish oil‐ and soy oil‐based lipid emulsions in neonatal parenteral nutrition: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2016;70(10):1106‐15. [DOI: 10.1038/ejcn.2016.69; PUBMED: 27142348] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Krohn 2006
- Krohn K, Koletzko B. Parenteral lipid emulsions in paediatrics. Current Opinion in Clinical Nutrition and Metabolic Care 2006;9(3):319‐23. [DOI: 10.1097/01.mco.0000222118.76536.ad; PUBMED: 16607135] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Lam 2014
- Lam HS, Tam YH, Poon TC, Cheung HM, Yu X, Chan BP, et al. A double‐blind randomised controlled trial of fish oil‐based versus soy‐based lipid preparations in the treatment of infants with parenteral nutrition‐associated cholestasis. Neonatology 2014;105(4):290‐6. [DOI: 10.1159/000358267; PUBMED: 24576844] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Lapillonne 2013
- Lapillonne A, Groh‐Wargo S, Gonzalez CH, Uauy R. Lipid needs of preterm infants: updated recommendations. Journal of Pediatrics 2013;162 Suppl 3:S37‐47. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2012.11.052; PUBMED: 23445847] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Lee 1993
- Lee EJ, Simmer K, Gibson, RA. Essential fatty acid deficiency in parenterally fed preterm infants. Journal of Paediatrics and Child Health 1993;29(1):51‐5. [PUBMED: 8461181] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Lekka 2004
- Lekka ME, Liokatis S, Nathanail C, Galani V, Nakos G. The impact of intravenous fat emulsion administration in acute lung injury. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2004;169(5):638‐44. [DOI: 10.1164/rccm.200305-620OC; PUBMED: 14656749] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
McNaught 1997
- McNaught AD, Wilkinson A. IUPAC. Compendium of Chemical Terminology (the "Gold Book"). 2nd Edition. Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Publications, 1997. [Google Scholar]
Moher 2009
- Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta‐analyses: the PRISMA statement. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2009;62(10):1006‐12. [DOI: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1000097; PUBMED: 19631508] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Mylonas 1999
- Mylonas C, Kouretas D. Lipid peroxidation and tissue damage. In Vivo 1999;13(3):295‐309. [PUBMED: 10459507] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Palmblad 1991
- Palmblad J. Intravenous lipid emulsions and host defense – a critical review. Clinical Nutrition 1991;10(6):303‐8. [DOI: ; PUBMED: 16839936] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Papile 1978
- Papile LA, Burstein J, Burstein R, Koffler H. Incidence and evolution of subependymal and intraventricular hemorrhage: a study of infants with birth weights less than 1,500 gm. Journal of Pediatrics 1978;92(4):529‐34. [PUBMED: 305471] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Park 2015
- Park HW, Lee NM, Kim JH, Kim KS, Kim SN. Parenteral fish oil‐containing lipid emulsions may reverse parenteral nutrition‐associated cholestasis in neonates: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Journal of Nutrition 2015;145(2):277‐83. [DOI: 10.3945/jn.114.204974; PUBMED: 25644348] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Pawlik 2011
- Pawlik D, Lauterbach R, Turyk E. Fish‐oil fat emulsion supplementation may reduce the risk of severe retinopathy in VLBW infants. Pediatrics 2011;127(2):223‐8. [DOI: 10.1542/peds.2010-2427; PUBMED: 21199856] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Pereira‐da‐Silva 2017
- Pereira‐da‐Silva L, Nobrega S, Rosa ML, Alves M, Pita A, Virella D, et al. Parenteral nutrition‐associated cholestasis and triglyceridemia in surgical term and near‐term neonates: a pilot randomized controlled trial of two mixed intravenous lipid emulsions. Clinical Nutrition ESPEN 2017;22:7‐12. [PUBMED: 29415837] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Pitkanen 1991
- Pitkanen O, Hallman M, Andersson S. Generation of free radicals in lipid emulsion used in parenteral nutrition. Pediatric Research 1991;29(1):56‐9. [DOI: 10.1203/00006450-199101000-00011; PUBMED: 1900362] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Puder 2009
- Puder M, Valim C, Meisel JA, Le HD, Meijer VE, Robinson EM, et al. Parenteral fish oil improves outcomes in patients with parenteral nutrition‐associated liver injury. Annals of Surgery 2009;250(3):395‐402. [DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e3181b36657; PUBMED: 19661785] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Putet 2000
- Putet G. Lipid metabolism of the micropremie. Clinics in Perinatology 2000;27(1):57‐69. [PUBMED: 10690564] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Reimund 2004
- Reimund JM, Scheer O, Muller CD, Pinna G, Duclos B, Baumann R. In vitro modulation of inflammatory cytokine production by three lipid emulsions with different fatty acid compositions. Clinical Nutrition 2004;23(6):1324‐32. [DOI: 10.1016/j.clnu.2004.04.007; PUBMED: 15556254] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Review Manager 2014 [Computer program]
- Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager 5 (RevMan 5). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Robinson 2008
- Robinson DT, Ehrenkranz RA. Parenteral nutrition‐associated cholestasis in small for gestational age infants. Journal of Pediatrics 2008;152(1):59‐62. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2007.06.002; PUBMED: 18154901] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Roggero 2007
- Roggero P, Giannì ML, Amato O, Agosti M, Fumagalli M, Mosca F. Measuring the body composition of preterm and term neonates: from research to clinical applications. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition 2007;45 Suppl 3:S159–62. Erratum in: Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition. 2009;48(1):121‐2. [DOI: 10.1097/01.mpg.0000302964.85922.1a; PUBMED: 18185084] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Rubin 1995
- Rubin M, Naor N, Sirota L, Moser A, Pakula R, Harell D, et al. Are bilirubin and plasma lipid profiles of premature infants dependent on the lipid emulsion infused?. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition 1995;21(1):25‐30. [PUBMED: 8576810] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Sala‐Vila 2007
- Sala‐Vila A, Barbosa VM, Calder PC. Olive oil in parenteral nutrition. Current Opinion in Clinical Nutrition and Metabolic Care 2007;10(2):165‐74. [DOI: 10.1097/MCO.0b013e32802bf787; PUBMED: 17285004] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
SanGiovanni 2000
- SanGiovanni JP, Berkey CS, Dwyer JT, Colditz GA. Dietary essential fatty acids, long‐chain polyunsaturated fatty acids, and visual resolution acuity in healthy full term infants: a systematic review. Early Human Development 2000;57(3):165‐88. [PUBMED: 10742608] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Schock 2001
- Schock BC, Sweet DG, Halliday HL, Young IS, Ennis M. Oxidative stress in lavage fluid of preterm infants at risk of chronic lung disease. American Journal of Physiology. Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology 2001;281(6):L1386‐91. [DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.2001.281.6.L1386; PUBMED: 11704534] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Scholtens 2009
- Scholtens S, Wijga AH, Smit HA, Brunekreef B, Jongste JC, Gerritsen J, et al. Long‐chain polyunsaturated fatty acids in breast milk and early weight gain in breast‐fed infants. British Journal of Nutrition 2009;101(1):116‐21. [PUBMED: 18492299] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Schünemann 2013
- Schünemann H, Brożek J, Guyatt G, Oxman A, editor(s). Handbook for grading the quality of evidence and the strength of recommendations using the GRADE approach (updated October 2013). GRADE Working Group, 2013. Available from gdt.guidelinedevelopment.org/app/handbook/handbook.html.
Sinclair 2011
- Sinclair JC, Bottino M, Cowett RM. Interventions for prevention of neonatal hyperglycemia in very low birth weight infants. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2011, Issue 10. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD007615.pub3; PUBMED: 21975772] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Skouroliakou 2012
- Skouroliakou M, Konstantinou D, Agakidis C, Delikou N, Koutri K, Antoniadi M, et al. Cholestasis, bronchopulmonary dysplasia, and lipid profile in preterm infants receiving MCT/ω‐3‐PUFA‐containing or soybean‐based lipid emulsions. Nutrition in Clinical Practice 2012;27(6):817‐24. [DOI: 10.1177/0884533612454547; PUBMED: 22878361] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Sterne 2017
- Sterne JA, Egger M, Moher D, Boutron I. Chapter 10: Addressing reporting biases. In: Higgins JP, Churchill R, Chandler J, Cumpston MS editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.2.0 (updated June 2017). Cochrane, 2017. Available from www.training.cochrane.org/handbook.
Stoll 2002
- Stoll BJ, Hansen N, Fanaroff AA, Wright LL, Carlo WA, Ehrenkranz RA, et al. Late‐onset sepsis in very low birth weight neonates: the experience of the NICHD Neonatal Research Network. Pediatrics 2002;110(2 PT 1):285‐91. [PUBMED: 12165580] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Van Kempen 2006
- Kempen AA, Crabben SN, Ackermans MT, Endert E, Kok JH, Sauerwein HP. Stimulation of gluconeogenesis by intravenous lipids in preterm infants: response depends on fatty acid profile. American Journal of Physiology. Endocrinology and Metabolism 2006;290(4):E723‐30. [DOI: 10.1152/ajpendo.00303.2005; PUBMED: 16291574] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Vanek 2012
- Vanek VW, Seidner DL, Allen P, Bistrian B, Collier S, Gura K, et al. A.S.P.E.N. position paper: clinical role for alternative intravenous fat emulsions. Nutrition in Clinical Practice 2012;27(2):150‐92. [DOI: 10.1177/0884533612439896; PUBMED: 22378798] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Vayalthrikkovil 2017
- Vayalthrikkovil S, Bashir RA, Rabi Y, Amin H, Spence JM, Robertson HL, et al. Parenteral fish‐oil lipid emulsions in the prevention of severe retinopathy of prematurity: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. American Journal of Perinatology 2017;34(7):705‐15. [DOI: 10.1055/s-0036-1597131; PUBMED: 27992937] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Vlaardingerbroek 2012
- Vlaardingerbroek H, Veldhorst M, Spronk S, Akker CH, Goudoever JB. Parenteral lipid administration to very‐low‐birth‐weight infants – early introduction of lipids and use of new lipid emulsions: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2012;96(2):255‐68. [DOI: 10.3945/ajcn.112.040717; PUBMED: 22743312] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Waitzberg 2006
- Waitzberg DL, Torrinhas RS, Jacintho TM. New parenteral lipid emulsions for clinical use. JPEN. Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition 2006;30(4):351‐67. [DOI: 10.1177/0148607106030004351; PUBMED: 16804134] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Walsh 2004
- Walsh MC, Yao Q, Gettner P, Hale E, Collins M, Hensman A, et al. Impact of a physiologic definition on bronchopulmonary dysplasia rates. Pediatrics 2004;114(5):1305‐11. [PUBMED: 15520112] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Wanten 2007
- Wanten GJ, Calder PC. Immune modulation by parenteral lipid emulsions. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2007;85(5):1171‐84. [DOI: 10.1093/ajcn/85.5.1171; PUBMED: 17490951] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Xu 2012
- Xu ZW, Li YS. Pathogenesis and treatment of parenteral nutrition‐associated liver disease. Hepatobiliary & Pancreatic Diseases International 2012;11(6):586‐93. [PUBMED: 23232629] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Zhao 2015
- Zhao Y, Wu Y, Pei J, Chen Z, Wang Q, Xiang B. Safety and efficacy of parenteral fish oil‐containing lipid emulsions in premature neonates. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition 2015;60(6):708‐16. [DOI: 10.1097/MPG.0000000000000665; PUBMED: 25514619] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
References to other published versions of this review
Kapoor 2015
- Kapoor V, Glover R, Malviya MN. Alternative lipid emulsions versus pure soy oil based lipid emulsions for parenterally fed preterm infants. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2015, Issue 12. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD009172.pub2; PUBMED: 26630252] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Kapoor 2018
- Kapoor V, Malviya MN, Soll R. Lipid emulsions for parenterally fed preterm infants. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2018, Issue 11. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD013163] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


