Abstract
Background
Francisella noatunensis subsp. orientalis (Fno) is the etiological agent of francisellosis in cultured warm water fish, such as tilapia. Antibiotics are administered to treat the disease but a better understanding of Fno infection biology will inform improved treatment and prevention measures. However, studies with native hosts are costly and considerable benefits would derive from access to a practical alternative host. Here, larvae of Galleria mellonella were assessed for suitability to study Fno virulence.
Results
Larvae were killed by Fno in a dose-dependent manner but the insects could be rescued from lethal doses of bacteria by antibiotic therapy. Infection progression was assessed by histopathology (haematoxylin and eosin staining, Gram Twort and immunohistochemistry) and enumeration of bacteria recovered from the larval haemolymph on selective agar. Fno was phagocytosed and could survive intracellularly, which is consistent with observations in fish. Virulence of five Fno isolates showed strong agreement between G. mellonella and red Nile tilapia hosts.
Conclusions
This study shows that an alternative host, G. mellonella, can be applied to understand Fno infections, which will assist efforts to identify solutions to piscine francisellosis thus securing the livelihoods of tilapia farmers worldwide and ensuring the production of this important food source.
Keywords: Alternative model, Aquaculture, Piscine francisellosis, Oreochromis niloticus, Red Nile tilapia
Background
Piscine francisellosis is a global disease caused by the bacterium Francisella noatunensis, with F. noatunensis subsp. orientalis (Fno) infecting warm water fish and F. noatunensis subsp. noatunensis (Fnn) affecting cold water species [1]. Once inside a host, like other Francisella spp. pathogens, F. noatunensis survives and replicates in host cells, particularly phagocytes such as monocytes, macrophages, neutrophils and phagocytic B-cells [2–11]. Fno is a particular concern for tilapia producers as it can cause up to 95% mortality [12, 13] and diagnosis of francisellosis is challenging, especially due to difficulties isolating this fastidious bacterium and the presence of other pathogens, which may have led to underreporting of the problem [1]. Current therapy relies on antibiotics and no safe and effective commercial vaccine is available, though there is progress towards its development [14].
Relatively little is known of the infection biology of Fno and a deeper fundamental understanding of virulence and pathogenicity may inform new and improved treatments, prevention measures and farm management practices. To this end, experimental studies have been performed in the native fish hosts and, though these trials have extended our knowledge of francisellosis, such an approach is costly, requires specialist infrastructure such as aquaria, raises ethical questions and can be constrained by legal statutes. Moreover, a lack of access to animals of the right age and size can also impact on these experiments. Hence, more practical alternative hosts that offer insights into the biology of F. noatunensis infections have been explored including zebrafish and their embryos [6, 15]; however, this fish model suffers similar drawbacks to native hosts and best practice in research seeks adherence to the principles of the 3Rs, i.e. the replacement, reduction and refinement of the use of animals in experiments [16, 17].
As a result, non-vertebrate alternative hosts have been pursued as a way to study bacterial pathogens of fish, and this has led to investigations in the slime mould amoeba Dictyostelium discoideum [18, 19], the freshwater ciliate Tetrahymena thermophile [20], the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans [21], the crustacean Artemia franciscana [22], and the insect Galleria mellonella [23]. Of these, the larva of G. mellonella has considerable practical and biological benefits [24, 25], which has seen it used widely to study human pathogens, including the relatively low costs associated with sourcing, storage and disposal; ease of acquiring the skills needed to perform experiments; ability to deliver precise doses of a pathogen, examine pathology and perform studies at different temperatures; and the strong correlation in the virulence of pathogens in G. mellonella and vertebrate hosts [26, 27]. Indeed, an earlier study demonstrated the virulence of 11 Vibrio anguillarum isolates correlated strongly between the native Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) host and the G. mellonella alternative host [23]. The insect immune system shares structural and functional characteristics with vertebrates but lacks the adaptive response; however, this still permits valuable insight into pathogen interactions with innate defences [28, 29]. Fish rely on the innate arm of immunity to defend against pathogens and similar humoral and cellular processes are present in fish and insects with respect to pathogen recognition; inducible production of lysozyme, antimicrobial peptides, reactive intermediates of oxygen and nitrogen species; phagocytosis of invading microbes; and signalling cascades that regulate coagulation and melanisation [28–35]. More recently, the G. mellonella genome has been sequenced which allows for even better understanding of host-pathogen interactions at the molecular level and can further the interpretation of findings with greater biological relevance [36]. Importantly, pathogens respond similarly to conditions in vivo when evading host defences and exploiting host tissues through conserved mechanisms of virulence, including cell adhesion and invasion, antioxidant protection measures, metal ion uptake, secretion systems, and toxin and enzyme production [23, 26, 27, 37–39]. Of note, G. mellonella has been used as an alternative host to understand infections by other Francisella spp., including the human pathogens Francisella hispaniensis [40], Francisella novicida [40], Francisella philomiragia [41] and Francisella tularensis [42, 43].
Therefore, G. mellonella may prove suitable for studying the virulence and pathogenicity of Fno; however, first it is necessary to confirm that an infection occurs and virulence reflects that observed in the native host, including with respect to conserved mechanisms of virulence. Thus, the aim of the present study was to assess the suitability of G. mellonella as an alternative model for studying the virulence and pathogenicity of Fno.
Results
Effect of temperature on G. mellonella survival after injection with Fno
In the initial experiment to determine the effect of temperature on survival of G. mellonella larvae after injection with ca. 1 × 109 colony-forming units (CFU)/mL of Fno STIR-GUS-F2f7 (isolated from Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus [10]), the group of larvae incubated at 28 °C appeared to have lowest survival while the group kept at 15 °C had greatest survival (Fig. 1), so in all subsequent experiments larvae were incubated at 28 °C. Larvae injected with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) only showed little change during the experiment from the usual cream body colour, but those injected with bacteria typically started to darken within hours due to melanisation, particularly along the dorsal midline, and the body became increasingly darkened up to death or the end of the experiment.
Fig. 1.
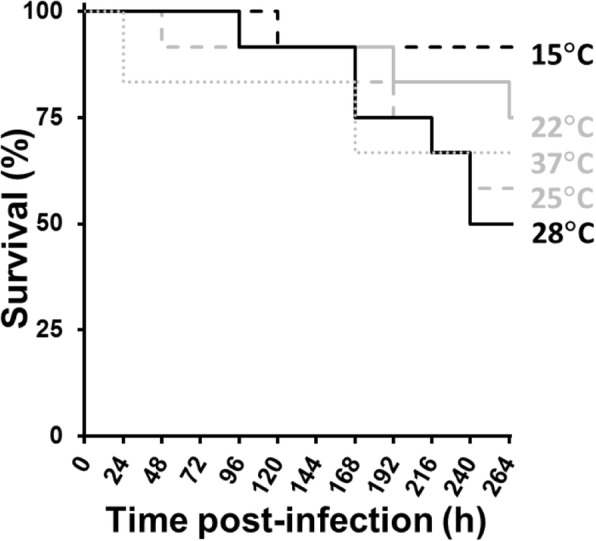
Effect of temperature on Galleria mellonella larva survival after injection with Fno. Kaplan-Meier plot of G. mellonella larva survival during 264 h after injection with Fno STIR-GUS-F2f7 at 1 × 109 CFU/mL and incubated at 15, 22, 25, 28 and 37 °C, showing that the group of larvae incubated at 28 °C had lowest survival; survival was 100% in the unmanipulated and PBS only control groups at all temperatures (data not shown). n = 12
Virulence of five isolates of Fno in G. mellonella
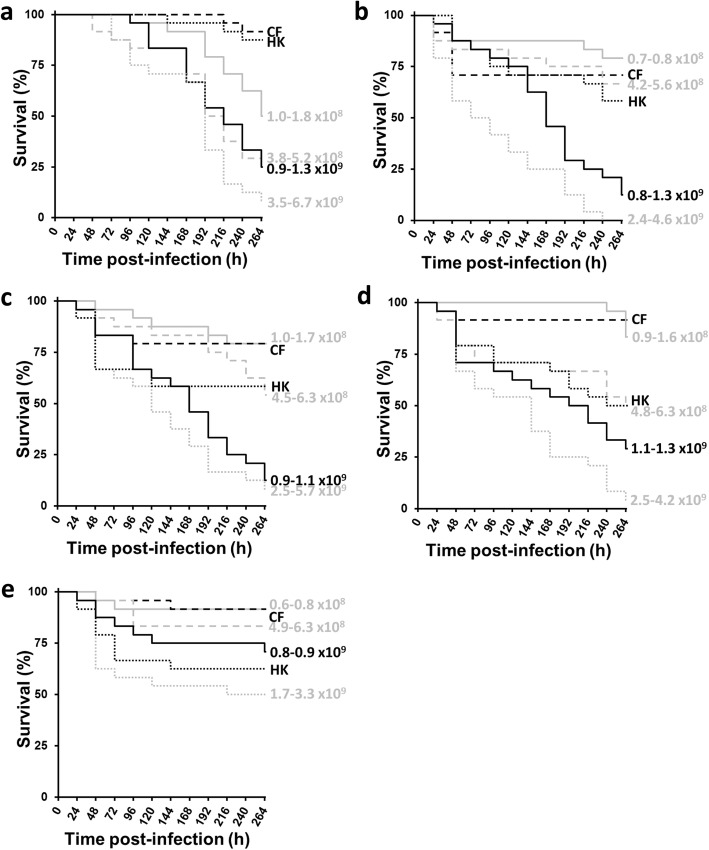
Having established that Fno STIR-GUS-F2f7 could cause mortality in G. mellonella larvae, the next experiment aimed to determine the virulence of five isolates of Fno obtained from separate disease outbreaks in fish. After injection into the larvae of different doses of each isolate (ca. 1 × 108, 5 × 108, 1 × 109 or 5 × 109 CFU/mL), in each case there was a dose-dependent reduction in larval survival, with injection of greater CFU/mL causing greater reductions in larval survival (Fig. 2). For each Fno isolate, the area under each curve was determined for each dose of CFU/mL and a cumulative value calculated. Accordingly, the most to least virulent Fno isolate in the larvae was of the order: Austria > PQ1104 > Franc-COS1 > STIR-GUS-F2f7 > Ehime-1. Heat-killed cells of each Fno isolate caused some mortality in the larval groups, but typically survival was reduced to an extent similar to injection with 10 to 50 times fewer live cells (Fig. 2), indicating live bacteria to be far more capable of exploiting the larval host, probably through the production of virulence factors, and larvae were not dying solely due to toxicity associated with injection with a large abundance of Fno cells. Larvae injected with heat-killed cells darkened almost immediately after injection, suggesting rapid immune recognition of pathogen-associated molecular patterns and possible masking and evasion of recognition by living Fno cells. Melanisation of larvae occurred more quickly and extensively with increasing doses of each Fno isolate, though injection of culture filtrate led to minimal changes in body colour. Interestingly, in the case of Fno Austria and Fno PQ1104 (the two most virulent isolates), survival of larvae injected with sterile culture filtrate led to reductions in survival similar to injection with ca. 1 × 108 CFU/mL of live bacteria (Fig. 2), perhaps indicating the production of extracellular virulence factors by these isolates in vitro.
Fig. 2.
Effect of different doses of five Fno isolates on Galleria mellonella larva survival. Kaplan-Meier plots of G. mellonella larva survival during 264 h at 28 °C after injection of ca. 1 × 108, 5 × 108, 1 × 109 and 5 × 109 CFU/mL of (a) Fno STIR-GUS-F2f7, (b) Fno Austria, (c) Fno PQ1104, (d) Fno Franc-COS1, and (e) Fno Ehime-1, showing dose-dependent reductions in larval survival. Heat-killed (HK) cells (equal dose to group injected with ca. 5 × 109 CFU/mL; killed by 30 min at 90 °C) and sterile culture filtrates (CF) of each Fno isolate were also injected. Actual CFU/mL after plating bacterial suspensions of each Fno isolate on CHAH presented beside each line on the plots. Survival was 100% in the unmanipulated and PBS only control groups for each replicate (data not shown). n = 24
Enumeration of Fno in G. mellonella after injection
Abundance of Fno in the haemolymph of G. mellonella larvae was assessed after injection with 1 × 109 CFU/mL of Fno STIR-GUS-F2f7 or Fno Ehime-1 isolate by collecting the haemolymph and plating on cysteine heart agar (Melford Laboratories Ltd., Ipswich, UK) supplemented to 10% bovine haemoglobin solution (Becton Dickenson BBL, Sparks, MD, USA) to give CHAH medium and containing for this experiment 1 mg/L penicillin and 1 mg/L amphotericin B. While Fno CFU in the haemolymph reduced during the 264 h incubation for both isolates, it was the less virulent Fno Ehime-1 isolate that reduced in abundance more quickly than the Fno STIR-GUS-F2f7 isolate; indeed, Fno Ehime-1 was not detected at or after 192 h (Fig. 3). No Fno colonies were recovered from PBS only or unmanipulated groups of G. mellonella larvae.
Fig. 3.

Enumeration of Fno in Galleria mellonella larva after injection. Abundance of Fno STIR-GUS-F2f7 (black line) and Fno Ehime-1 (grey line) in the haemolymph of G. mellonella larvae during 264 h at 28 °C after injection with ca. 1 × 109 CFU/mL. Actual CFU/mL after plating bacterial suspensions of each Fno isolate on CHAH were: 5.7 × 109 for Fno STIR-GUS-F2f7 and 1.6 × 109 for Fno Ehime-1. Unmanipulated and PBS only larvae were sampled at the start, middle (144 h) and end of the experiment and no Fno colonies were recovered (data not shown). Bars are means of log10 transformations of (CFU/mL + 1) data + one standard deviation (n = 5)
Rescue of G. mellonella from lethal dose of Fno by antibiotic therapy
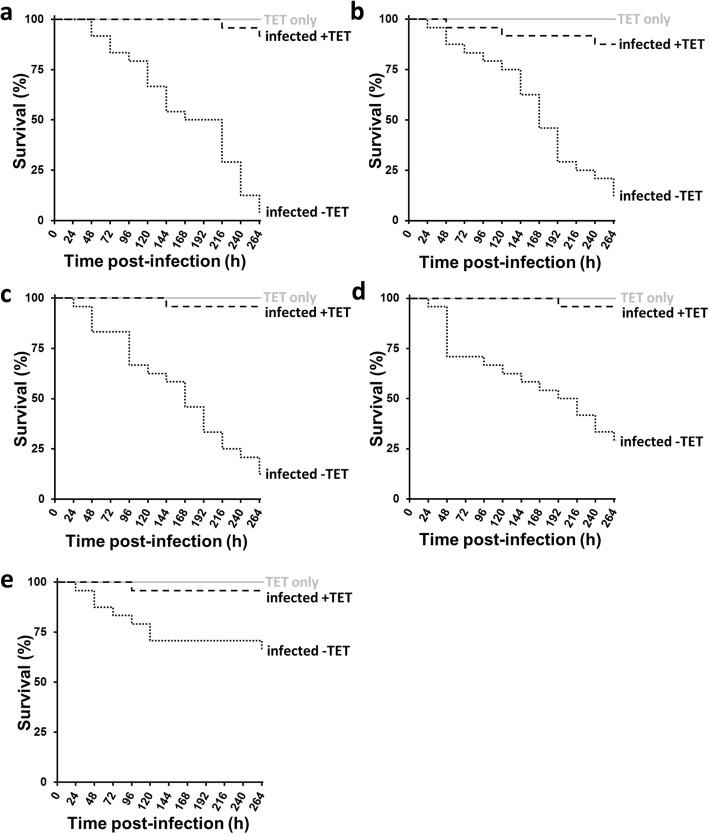
Larvae injected with lethal doses of each of the five Fno isolates (ca. 1 × 109 CFU/mL) were treated with three doses of tetracycline (10 mg/g body weight at 2, 24 and 48 h post-infection) and in each case antibiotic treatment led to significant (p < 0.05) increases in larval survival, indicating that infections leading to mortalities could be prevented through antimicrobial therapy (Fig. 4).
Fig. 4.
Effect of antibiotic therapy on Galleria mellonella larva survival after injection with Fno. Kaplan-Meier plots of G. mellonella larva survival during 264 h at 28 °C after injection of ca. 1 × 109 CFU/mL of (a) Fno STIR-GUS-F2f7, (b) Fno Austria, (c) Fno PQ1104, (d) Fno Franc-COS1, and (e) Fno Ehime-1, and treatment with tetracycline at 10 mg/g body weight at 2, 24 and 48 h (infected +TET), showing that the antibiotic treatment increased larval survival compared to groups treated with PBS (infected -TET). Actual CFU/mL after plating bacterial suspensions of each Fno isolate on CHAH were: 0.81–1.33 × 109 for Fno STIR-GUS-F2f7, 0.81–1.25 × 109 for Fno Austria, 0.90–1.10 × 109 for Fno PQ1104, 1.32–1.35 × 109 for Fno Franc-COS1, and 0.87–0.90 × 109 for Fno Ehime-1. One control group of larvae was injected with PBS instead of bacteria and treated with the tetracycline (TET only) to assess the toxicity of the antibiotic alone, while survival was 100% in the unmanipulated and PBS only control groups for each replicate (data not shown). n = 24
Histology of Fno infection of G. mellonella
Histological analyses revealed the progression of infection in the larval tissues and the larva immune response (Fig. 5). In control larvae, a few scattered haemocytes were located in and around the normal fat body (Fig. 5a-c), around the muscle fibres and tracheal walls, circulating in the haemolymph, in the subcuticular area (Fig. 5d) and in small clusters surrounding the gastrointestinal tract (Fig. 5b). There was no evidence for Fno in any control tissues by immunohistochemistry (IHC) when performed with polyclonal anti-Fnn NCIMB 14265 antibodies that cross-react with Fno (Fig. 5e). In larvae injected with 1 × 109 CFU/mL of Fno, at 48 h haemocytes had infiltrated the fat body (Fig. 5f), while the presence of eosinophilic fluid in the coelomic cavity suggested vascular leakage and the mounting of an inflammatory response (Fig. 5f). Enlarged haemocytes containing Gram-negative bacteria (Fig. 5g) and melanised haemocytes were observed in tissues, particularly within the fat body where necrosis was also evident (Fig. 5h), and this was consistent with the timing of the darkening of the larval body observed in earlier experiments. Larger clusters of haemocytes formed distinct nodules, often surrounded by flattened cells exhibiting the spindle morphology (Fig. 5i). Fno was detected by IHC in the subcuticular area, the gastrointestinal tract and at the tracheal walls (Fig. 5j).
Fig. 5.
Progression of infection in Galleria mellonella larva tissues after injection with Fno. Visualisation of G. mellonella larva tissues during 96 h after injection of Fno STIR-GUS-F2f7 in 10 μL phosphate-buffered saline at 1 × 109 CFU/mL and incubation at 28 °C. Tissues were stained by haematoxylin and eosin (a, b, f, k, n, o), Gram Twort (c, d, g, h, i, l) or immunohistochemistry (IHC) with anti-Fnn primary antibodies that cross-react with Fno (e, j, m, p) in unmanipulated control larvae at 0 h (a-e) or larvae injected with Fno and sampled at 48 h (f-j), 72 h (k-h) and 96 h (n-p). Control larvae at 0 h showed scattered haemocytes in and around the fat body (a-c), subcuticular area (d) and in clusters surrounding the gastrointestinal tract (b); Fno was not detected by IHC (e). At 48 h, larvae injected with Fno showed infiltration of haemocytes into the fat body, eosinophilic fluid in the coelomic cavity (f) and enlarged haemocytes containing bacteria (g, h); melanised haemocytes were also observed (h). Clusters of haemocytes formed nodules, often surrounded by flattened cells (i), and Fno was detectable by IHC (j). At 72 h, large nodules had formed (k), and enlarged and melanised haemocytes were observed (l); great abundances of Fno cells were detected by IHC (m, p). At 96 h, large and increasingly melanised nodules were observed, while haemocytes at the periphery were flat in appearance (n); there was evidence for the recruitment of new, round haemocytes (n). Large protein lakes and severe tissue necrosis were observed (o) and great abundances of Fno cells were detected by IHC (p). Ct, cuticle; FB, fat body; GI, gastrointestinal tract; MF, muscle fibres; Me, melanin; Ne, necrosis; PL, protein lake; T, trachea. Scale bars: a, i = 20 μm; b, k, o = 100 μm; c, d, g, h, l = 10 μm; e, f, j, n, p = 50 μm
At 72 h, greater abundances of haemocytes and the formation of large nodules were observed in the subcuticular area, muscle fibres, fat body and tracheal walls (Fig. 5k). Enlarged and melanised haemocytes were observed in various tissues, including around the trachea (Fig. 5l). Great abundances of Fno cells were detected by IHC in the fat body, muscle fibres, subcuticular areas and trachea (Fig. 5m). At 96 h, multiple large and increasingly melanised nodules were observed (Fig. 5n), which was consistent with progressive darkening of larval body observed macroscopically. Haemocytes at the periphery of nodules were flat in appearance and there was evidence for recruitment of new, round haemocytes to the nodules (Fig. 5n). Large protein lakes and severe tissue necrosis were evident, especially around the tracheal walls and gastrointestinal tract, where necrosis was extensive (Fig. 5o). Fno was detected by IHC in great abundance inside and around the gastrointestinal tract, tracheal walls and fat body (Fig. 5p).
Virulence of Fno isolates in O. niloticus
In a final experiment, the virulence of each of four Fno isolates in O. niloticus was assessed by intraperitoneal injection of 100 μL of ca. 1 × 104, 1 × 105, 1 × 106, 1 × 107 or 1 × 108 CFU/mL and monitoring the fish for 20 d at 23 ± 2 °C. Fno was detected in each dead/moribund fish. Consistent with the G. mellonella larva findings, for each Fno isolate there was dose-dependent reductions in fish survival, with injection of greater CFU/mL causing greater group mortalities (Fig. 6). For each Fno isolate, the area under each curve was determined for each dose of CFU and a cumulative value calculated. Accordingly, the most to least virulent Fno isolate in the tilapia was of the order: STIR-GUS-F2f7 > Austria > PQ1104 > Franc-COS1. Fno Ehime-1 was not tested in the fish as this isolate was non-virulent in the pre-challenge test (data not shown).
Fig. 6.
Effect of different doses of Fno on Oreochromis niloticus survival. Kaplan-Meier plots of O. niloticus survival during 20 d at 23 ± 2 °C after intraperitoneal injection of 100 μL of Fno suspensions at ca. 1 × 104, 1 × 105, 1 × 106, 1 × 107 and 1 × 108 CFU/mL: (a) Fno STIR-GUS-F2f7, (b) Fno Austria, (c) Fno PQ1104, and (d) Fno Franc-COS1, showing dose-dependent reductions in fish survival. No mortalities were observed in the PBS only control group. n = 20
Discussion
Francisellosis is an emerging bacterial disease in tilapia farming caused by Fno and relatively little is known of the infection biology of this bacterium, with efforts towards improved understanding hampered by difficulties associated with performing fish trials, including cost, legislative burden and ethical acceptability. Non-vertebrate alternative hosts offer solutions to many of these problems and can deliver valuable insights in host-pathogen interactions given the similarities in host innate immunity due to the universal ancestry of all organisms. G. mellonella is an alternative host used widely for understanding virulence and pathogenicity of bacterial pathogens, including those causing disease in fish [23], due to a range of benefits around ease of use, ability to examine pathology and availability of the genome sequence [36, 44]. Hence, this present study aimed to assess whether G. mellonella would be suitable for studying Fno infections.
Direct injection of Fno into the G. mellonella larva appeared to cause infection, as evidenced by the far greater mortalities caused by living bacteria compared to heat-killed counterparts; the dose-dependent increase in mortalities caused by greater doses of Fno; and significant improvement in larval survival after treatment with an antibiotic to which Fno was susceptible. Antibiotic therapy kills or inhibits the replication of the bacterium and allows the host immune system to counter successfully this microbial invasion. Importantly, there was good correlation in the relative virulence of four Fno isolates between G. mellonella and O. niloticus hosts, although Fno STIR-GUS-F2f7 did differ in virulence between the two hosts. This finding suggests similar virulence factors are involved in insect and fish infections, though this needs to be confirmed by further approaches such as testing of knockout strains, and these investigations might uncover the reason for the discrepancy between hosts in the virulence of Fno STIR-GUS-F2f7. Still, Fno STIR-GUS-F2f7 was detected intracellularly in G. mellonella, as observed with other Francisella spp. in this insect model [43], and this pathogen is known to survive intracellularly in fish host cells [7–9, 11, 45], which further supports G. mellonella to be a suitable alternative host for studying Fno infections. The progression of Fno infection in G. mellonella is similar in nature to previous findings where these larvae have been inoculated with other pathogens, with evidence of non-host recognition, an inflammatory response, the formation of melanised nodules and tissue necrosis [46–49]. Heat-killed Fno were recognised by the insect and mounted an immune response, as evidenced by the darkening of the larval colour shortly after injection due to activation of prophenoloxidase pathway leading to melanisation [28]. Mortalities did occur in the heat-killed bacteria groups, which is probably due to the presence of a large abundance of elicitors being recognised as foreign by the host and the stress associated with the host mounting a massive immune response.
Fno appeared to cause greatest mortality in G. mellonella at 28 °C, which is close to the optimum for replication of this bacterium in vitro [8, 50, 51]. In farm conditions, Fno typically causes infections in tilapia when the water temperature reduces and this becomes more prevalent below 25 °C, probably due to increased host stress [1, 52], which may explain the disparity between the models because G. mellonella typically lives around 28 °C in its natural environment and thus is probably in better physiological condition [53]. Nevertheless, the G. mellonella model provides an opportunity to investigate the temperature-regulation of virulence factor expression in Fno more ethically, as it can be incubated at a range of temperatures [24, 25] and quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR) can be performed to quantify bacterial gene expression in vivo [54].
Relatively little is known of the key virulence factors involved in Fno infection, though oxidative stress response proteins (e.g., Hsp60, Hsp90), type-4 pili, iron sequestration mechanisms and a type-VI secretion system have been detected in the Fno genome, all of which are key virulence factors for other pathogenic Francisella spp. [7, 55–57]. Even so, there is much to be done to uncover the suite of virulence factors important for Fno infection and certainly G. mellonella lends itself to high-throughput screens, which are often necessary for these types of studies. Moreover, the detection of lethal activity in sterile culture filtrates in this present study suggests the presence of extracellular virulence factors, such as toxins or degradative enzymes, and fish-pathogenic Francisella spp. do produce outer-membrane vesicles embedded with virulence factors [45, 58]. Beyond virulence factor discovery and probing of host-pathogen interactions, the G. mellonella system would be useful for determining the relative virulence of isolates, as such information is useful for identifying particularly problematic (i.e., virulent) strains.
Interestingly, when haemolymph was collected from inoculated larvae and plated on to agar, Fno did not appear to replicate, which is in contrast to a previous study on V. anguillarum where more virulent isolates replicated inside the haemolymph to a far greater extent than less virulent isolates [23]. However, unlike McMillan et al. [23], where V. anguillarum was confirmed to be mostly in the haemolymph compared to the rest of the body, it was not possible to obtain Fno CFU counts for whole-larva homogenate, due to the difficulty of selecting for this fastidious bacterium against the abundant bacteria found on the larva surface and in the gastrointestinal tract (data not shown). Nevertheless, the histopathological analyses appeared to support replication of Fno inside the G. mellonella as the bacteria appeared to become more abundant during the progression of the infection, though the Fno were increasingly detected inside haemocytes, in tissues including the fat body, or in aggregates in the haemolymph, all of which might explain the lower than expected Fno CFU counts in the haemolymph when plated on agar. Indeed, the protocol in this present study was refined to lyse the host cells in the haemolymph because this increased Fno CFU abundance (data not shown), likely by releasing the bacterium from the confines of host cells. Hence, agar counts are probably not a true representation of Fno replication in the larvae and quantification of Fno abundance during infection from pathology preparations, or by molecular methods such as quantitative PCR, likely offer more accurate estimates.
Conclusion
In conclusion, this present study demonstrates G. mellonella to be a useful model for studying infections caused by Fno and thus can be applied to increase our understanding of the virulence and pathogenicity of this pathogen. Such an approach will support efforts towards solutions that prevent and reduce outbreaks of francisellosis in tilapia and improve production in this important industry.
Methods
Reagents
Unless stated, all reagents were sourced from Sigma Aldrich Ltd. (Poole, United Kingdom [UK]), while solvents were purchased from Thermo Fisher Scientific (Loughborough, UK). One-litre of PBS (0.02 M, pH 7.2) consisted 0.876 g NaH2PO4.2H2O (VWR International Ltd., Lutterworth, UK), 2.56 g Na2HPO4.2H2O (VWR International Ltd) and 8.77 g NaCl. Culture media, PBS and water were sterilised by autoclaving at 121 °C for at least 15 min. Antibiotic solutions were sterilised by passing through a sterile polyethersulfone 0.22-μm filter (Millipore, Watford, Herts, UK).
Bacteria and culture conditions
Five isolates of Fno were collected from separate outbreaks of francisellosis: Austria (isolated from ornamental Malawi cichlids [59]), Ehime-1 (DSM 21254, type strain; isolated from three-lined grunt, Parapristipoma trilineatum, in Japan in 2001 [51]), Franc-COS1 (isolated from Oreochromis sp. in Mexico in 2012 [60]), PQ1104 (isolated from Oreochromis sp. in Costa Rica in 2007), and STIR-GUS-F2f7 (isolated from O. niloticus in UK in 2012 [10]). Routinely, Fno was cultured at 28 °C on CHAH medium or in cation-adjusted Mueller-Hinton II broth (MHB; Becton Dickinson BBL, Sparks, MD, USA) supplemented with 0.1% glucose and 2% IsoVitaleX (Becton Dickinson BBL). Glycerol stocks (20%) were prepared for long-term storage at − 70 °C. The bacterial isolates were confirmed as Fno according to the methods described by Frerichs and Millar [61], including primary identification tests (Gram-staining, catalase, oxidase, oxidation/fermentation of glucose, and motility) and biochemical profiles determined with API20E and ZYM kits (BioMerieux; Marcy L’étoile, France) according to the manufacturer guidelines except the inoculated strips were incubated at 28 °C and read at 72 h and 24 h, respectively.
G. mellonella
Final instar stage G. mellonella larvae were purchased from UK Waxworms Ltd. (Sheffield, UK). Moribund, discoloured and dead larvae were removed and only those with uniform cream colouration and of 250–350 mg were used for experiments. Routinely, larvae were kept in the dark in Petri dishes at 4 °C and used within one week of receipt.
Inoculum preparation
A few colonies of Fno were inoculated into 15 mL supplemented MHB and cultured for 20 h at 150 rpm to mid-logarithmic phase of growth. Bacterial cells were harvested by centrifugation (3000×g, 15 min, 4 °C) and then washed twice by resuspension in 10 mL PBS, before finally re-suspending in 15 mL PBS. Cell density was determined by measuring absorbance at 600 nm (A600) using a spectrophotometer (Cecil CE-2014; Buck Scientific, Inc., East Norwalk, CT, USA) and then adjusted by dilution with PBS to the desired CFU/mL according to a standard curve (data not shown). Typically, serial 10-fold dilutions of bacterial suspensions in PBS were plated on CHAH (6× 20 μL of each dilution) to determine accurate CFU/mL after incubation (48 h, 28 °C), or for fish trials by the drop plate method as described by Chen et al. [62].
Injection of G. mellonella larvae
G. mellonella larvae experiments were performed in a bacteriological laboratory according to the methods described by McMillan et al. [23]. Briefly, larvae were injected with 10 μL of solution (bacterial suspension, antibiotic or PBS) using a 50-μL Hamilton syringe (Sigma Aldrich Ltd) into the haemocoel via the last left pro-leg, after the larvae had been cooled on ice for 5 min. Consecutive washes of 1% (w/v) sodium hypochlorite solution, 70% ethanol and sterile water were used to clean the syringe in between experimental groups. After injection, each group of larvae was kept in a disposable 90-mm diameter plastic Petri dish and incubated in the dark for 264 h at 28 °C, unless stated. The larvae were assessed each 24 h for survival and were considered dead (and removed from the Petri dish) if displaying no response to the tactile stimulus given by brushing with a sterile inoculation loop. Each experimental group consisted 12 larvae selected at random and each experiment was repeated using larvae from a different batch to give n = 24, with mean percentage group survival calculated prior to preparing Kaplan-Meier plots. Two control groups were included in each experiment: one group of G. mellonella larvae received injections of ‘PBS only’ to assess the impact of physical trauma, while a second ‘unmanipulated’ group received no injections and was used to assess background larval mortality.
Effect of temperature on G. mellonella larvae survival after injection with Fno
Groups of G. mellonella larvae were injected with a ca. 1 × 109 CFU/mL suspension of Fno STIR-GUS-F2f7 and incubated at 15, 22, 25, 28 or 37 °C for 264 h to determine the effect of temperature on larval survival after injection with live Fno. This experiment was performed only once.
Virulence of different Fno isolates in G. mellonella
Groups of G. mellonella larvae were injected separately with ca. 1 × 108, 5 × 108, 1 × 109 or 5 × 109 CFU/mL suspensions of each of the Fno isolates. In addition, the supernatant from the first centrifugation step to harvest the Fno cells (see ‘Inoculum preparation’) was passed through a sterile polyethersulfone 0.22-μm filter to give sterile culture filtrates. Sterile culture filtrates were also injected into groups of G. mellonella larvae, as this can indicate the presence of extracellular virulence factors such as toxins and enzymes. Finally, PBS-washed suspensions of each Fno isolate at ca. 5 × 109 CFU/mL were heat-killed for 30 min at 90 °C and administered to further groups of G. mellonella larvae. Heat-killing was confirmed by the absence of colonies on CHAH inoculated with 100 μL of bacterial suspension and incubated for 48 h at 28 °C.
Enumeration of Fno in G. mellonella larvae haemolymph
To assess the abundance of Fno in the haemolymph of G. mellonella larvae after injection, groups of 175 G. mellonella larvae were injected with ca. 5 × 108 CFU/mL of Fno STIR-GUS-F2f7 or Fno Ehime-1 and incubated as above; more larvae were injected than would be required to ensure there would be sufficient surviving larvae to sample at each intended time point. Five surviving larvae in each group were selected at random for determination of bacterial load at 2, 4, 8 and 24 h, and then every 24 h up to 264 h. Prior to sampling, larvae were cooled on ice for 30 min and then the body surface was sterilized by spraying with 70% ethanol and wiping with sterile tissue paper. The last abdominal segment (final 2 mm of the body) was removed aseptically with sterile scissors and harvesting the haemolymph according to McMillan et al. [23]. The haemolymph (ca. 5–10 μL) was drained from each larva into a sterile 0.5-mL micro-centrifuge tube, and then pipetted up and down 30 times before briefly agitated on a vortex to lyse the cells (modified from Senior et al. [63]). Ten-fold serial dilutions were performed in PBS in sterile 96-well microtitre plates, before 10 μL of each dilution was plated on CHAH supplemented with 1 mg/L penicillin and 1 mg/L amphotericin B to select for Fno and against other bacteria. Still, primary identification tests (see ‘Bacteria and culture conditions’) were performed on a subset of colonies to confirm that those recovered from infected larvae were indeed Fno. Haemolymph was also collected from PBS only and unmanipulated control groups at the start, middle (144 h) and end of the experiment.
Antibiotic treatment of G. mellonella larvae injected with Fno
To assess whether antibiotic therapy would rescue G. mellonella larvae from lethal doses of each of the Fno isolates (ca. 1 × 109 CFU/mL), sterile-filtered tetracycline in PBS (ca. 10 mg/g body weight) was administered by injection at 2, 24, and 48 h post-infection. Each Fno isolate had been shown to be highly susceptible to the action of tetracycline by disk diffusion (data not shown). In addition to the PBS injected and unmanipulated controls, two extra control groups were prepared: one group of G. mellonella larvae was injected with PBS instead of bacteria and then with tetracycline (to assess the toxicity of the antibiotic), and another group was injected with bacteria and then with PBS instead of tetracycline (to confirm the virulence of the Fno). The multiple injections were administered to different prolegs, as described in Desbois and Coote [64].
Histopathology and localisation of Fno in G. mellonella larvae cells
To observe the progression of infection and localise Fno STIR-GUS-F2f7 in the G. mellonella larvae tissues, 20 G. mellonella larvae were injected with 1 × 109 CFU/mL and incubated as above. Three larva were sampled at 48, 72 and 96 h for histopathological analyses by haematoxylin and eosin (H & E) staining, Gram Twort staining and IHC. Each larva was anesthetized on ice for at least 30 min, injected with ca. 100 μL of 10% (v/v) neutral-buffered formalin and then kept in this solution for 24 h at 4 °C to fix the internal organs and block melanisation [65]; unmanipulated larvae at 0 h were sampled as controls.
Tissue sectioning
Tissue sections were prepared from whole larvae that were dissected transverse to the median plane of the body into six equal sections using a scalpel (i.e., one distal, four middle and one proximal), and then each section was wrapped in biopsy tissue paper prior to placing into standard tissue cassettes for processing overnight on a processor (Shandon Citadel 2000; Thermo Fisher Scientific) and subsequent embedding in paraffin wax (EG1160 Histoembedder; Leica Biosystems, Nussloch, Germany). The procedure was performed carefully to avoid squeezing the larval tissues. Each wax block was trimmed with a microtome (RM 2255; Leica Biosystems) to expose the tissue and soaked in water for 30 min prior to cutting. Four micrometer-thick sections were mounted onto glass slides (Solmedia Supplying Science, Shrewsbury, UK) and dried in an oven overnight at 60 °C. Then the sections were deparaffinised in xylene for 3 min then 2 min (twice), rehydrated in absolute ethanol (2 min) and methylated spirit (1 min), before rinsing in tap water (1 min).
H & E staining
Sections were stained with Mayer’s haematoxylin ‘Z’ stain (CellPath Ltd., Newtown, UK) for 5 min and then rinsed in tap water. Next, the sections were dipped three times in 1% acid alcohol (methylated spirit:hydrochloric acid; 100:1), rinsed in tap water, counterstained with eosin solution (1% [w/w] eosin Y:Putt’s eosin [Cellpath, Newton, UK]; 8:1) before rinsing again in tap water. The slides were dehydrated in absolute ethanol for 2 min then 1 min (twice), before being cleared with xylene (5 min) and mounted with Pertex medium (HistoLab Products Ab, Gothenburg, Sweden). Once dry, the slides were examined using an upright light microscope (BX53M; Olympus, Southend-on-Sea, UK) and images were collected with a digital camera (SC100; Media Cybernetics, Abingdon, UK) and cellSens 1.17 software (Olympus).
Gram Twort staining
Sections were stained with 2% Lillie’s crystal violet solution (500 mL consists 10 g crystal violet [Merck Chemical, Darmstadt, Germany] and 4 g ammonium oxalate in 20% ethanol) for 1 min and then rinsed in running tap water. The slides were treated with 0.4% Lugol’s iodine solution (100 mL consists 1 g iodine [Thermo Fisher Scientific] and 2 g potassium iodide [VWR International Ltd] in water) for 1 min, before being rinsed in tap water, and flooded with acetone (Thermo Fisher Scientific) for 2–5 s. The slides were rinsed again in running water and counterstained with Twort’s stain in a closed Wheaton Coplin staining jar (S5516-6EA; Sigma Aldrich Ltd) for 5 min. Five hundred millilitres of Twort’s stain consisted 100 mg of neutral red and 900 mg of 0.2% fast green (Thermo Fisher Scientific) in 95% ethanol, with a working solution prepared by diluting this stock solution in distilled water (1:3). After staining, the slide was rinsed in tap water. Finally, each section was rapidly dehydrated by dipping twice in absolute ethanol for 5 s each time, and then cleared, mounted and examined as described in Section 5.10.2.
IHC
IHC was performed to localise Fno in larvae tissues using polyclonal anti-Fnn NCIMB 14265 antibodies that cross-react with Fno. First, sections were pre-treated with 3% (v/v) hydrogen peroxide in methanol for 10 min to block endogenous peroxidase activity and then washed thrice in PBS. All incubations were performed in a humidified chamber at room temperature (ca. 22 °C). Non-specific binding of the secondary antibody was blocked by incubation with normal goat serum (Sigma Aldrich Ltd., UK) diluted 1:10 in PBS for 15 min. The serum was discarded, slides tapped dry and then rabbit antisera containing the primary antibodies (diluted 1:300 in PBS) was added to the slides and incubated for 1 h (PBS was added in place of antisera in a negative control). The slides were washed with PBS and then goat anti-rabbit immunoglobulin G conjugated to horseradish peroxidase conjugate (1:200; Sigma Aldrich Ltd) was added for 30 min. Slides were washed in PBS and incubated with the Immpact DAB peroxidase substrate (Vector Laboratories, Peterborough, UK) for 10 min, before the reaction was stopped by immersion in tap water. The slides were counterstained with Mayer’s haematoxylin for 4 min, rinsed in tap water, dehydrated in a graded series of ethanol (70% followed by 100% for 5 min each) and cleared in xylene (5 mins twice) prior to adding a coverslip with Pertex mounting media. Slides were examined by light microscopy.
Virulence of different Fno isolates in tilapia
Fish and rearing conditions
Red Nile tilapia (O. niloticus) of 10 ± 0.5 g and 7.0 ± 0.19 cm were purchased from a private farm in Prachinburi, Thailand and transported to the research aquarium of Fish Vet Group Asia Ltd. (FVGAL), Chonburi, Thailand. Upon arrival, the fish were transferred to 100-L circular tanks in a recirculation system for acclimation. Water conditions were maintained as follows: 28 ± 1 °C; 6.5–7 mg/L dissolved oxygen; pH 7–7.5; ≤0.1 mg/L free ammonia; ≤0.25 mg/L nitrite; and ≤ 0.2 mg/L nitrate. Fish were acclimated for 2 weeks and fed at 3% body weight per day with a commercial tilapia feed (Charoen Pokphand Foods Public Company Ltd., Bangkok, Thailand). The Fno-free status of the fish was determined prior to challenge using samples of spleen and head kidney from four fish by bacteriological analyses and a Francisella genus-specific PCR performed as described previously [8, 66].
Fish challenge
First, each Fno isolate was passaged two times in three fish (each fish was ca. 20 g) by intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection of 1010 CFU/fish in PBS after being anaesthetised (stock of 10% benzocaine [w/w] prepared in 70% ethanol and used at 50 mL/L; Thermo Fisher Scientific), and then incubated for 4 d at 23 ± 2 °C. As Fno Ehime-1 did not cause any mortalities in either passage it was not included in the subsequent challenge trial (data not shown). Ten fish were allocated randomly into each of 40 3-L tanks containing 2.5 L of dechlorinated water and fish were not fed for 48 h prior to the Fno challenge. Tanks were divided into four main groups (one for each Fno isolate) and five sub-groups of duplicate tanks. Then the fish in each sub-group (n = 20) were i.p. injected separately with 100 μL of ca. 1 × 104, 1 × 105, 1 × 106, 1 × 107 or 1 × 108 CFU/mL in PBS of each of the Fno isolates, with the bacterial inoculums prepared according to Section 5.4. A further two tanks with 10 fish in each contained the controls that received an injection of PBS only. Fish were maintained for 20 d at 23 ± 2 °C, fed ad libitum and examined four times per day for mortalities. To confirm recovery of Fno from dead and moribund fish, these animals were removed and tissues collected (including the head kidney and spleen) for: i) direct PCR with Francisella genus-specific primers (see ‘Fish and rearing conditions’); ii) isolation of bacteria on CHAH agar, followed phenotypic testing and PCR of colonies. Fish surviving to 20 d post-challenge were euthanised by overdose of anaesthetic (prepared and used as above) followed by a lethal blow to the head according to Schedule 1 technique of the UK Animals (Scientific Procedures) Act 1986.
Data analyses
Where required, survival differences between groups were compared with the logrank test in Prism (GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA, USA) and a p-value of < 0.05 was considered to indicate a significant difference. Relative virulence of the Fno isolates in O. niloticus and G. mellonella models of infection were calculated using area under the curve of cumulative survival of each group of injected larvae and fish (as described in McMillan et al. [23]). For CFU over time data, means of log10 transformations of (CFU/mL + 1) were calculated and standard deviations determined.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to express our gratitude to Dr. Jose Gustavo Ramírez-Paredes (Ridgeway Biologicals, Compton, UK) for providing Fno Franc-COS1 and Fno STIR-GUS-F2f7, Dr. Duncan Colquhoun (Norwegian Veterinary Institute, Oslo, Norway) for providing Fno PQ1104 and the anti-Fnn serum, and Professor Mansour El-Matbouli (University of Veterinary Medicine, Vienna, Austria) for providing Fno Austria. We gratefully acknowledge Dr. Andy Shinn (Fish Vet Group Asia Ltd., Thailand) for technical assistance during the fish trials, and Mrs. Debbie Faichney and Dr. Johanna Baily for help with histology.
Abbreviations
- CFU
Colony-forming units
- CHAH
Cysteine heart agar supplemented with 10% bovine haemoglobin solution
- Fnn
Francisella noatunensis subsp. noatunensis
- Fno
Francisella noatunensis subsp. orientalis
- H & E
Haematoxylin and eosin
- MHB
Mueller-Hinton II broth
- PBS
Phosphate-buffered saline
- UK
United Kingdom
Authors’ contributions
APD conceived the study; WASD and KS performed the experiments; APD, WASD, KS, MM and AA designed the experiments, and analysed and interpreted the data; WASD and APD wrote the first draft of the manuscript; KS, MM and AA provided critical revisions; and APD, WASD, KS, MM and AA have approved the final manuscript.
Funding
WASD was funded by a PhD scholarship received from the Director General of Higher Education, Ministry of Research, Technology and Higher Education (Kemenristek Dikti), Republik of Indonesia. The fish challenge experiment was funded by the Egyptian Ministry of Higher Education and Scientific Research (Grant Number 1582014) and Benchmark Animal Health Ltd. through a PhD scholarship awarded to KS. The funders played no role in the conception or design of this study; however, MM is an employee of Benchmark Animal Health Ltd. and was involved in the collection, analysis and interpretation of data and provided critical revisions during manuscript preparation.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The experiments were approved by the Institute of Aquaculture Ethics Committee and the University of Stirling Animal Welfare and Ethical Review Body. Procedures were performed in accordance with the UK Animals (Scientific Procedures) Act 1986, European Union (2010) guidelines [17] and National Research Council of Thailand regulations.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests. Benchmark Animal Health Ltd. provided bacterial isolates and trials facilities for the tilapia study, but this project is not part of the core development program and there are no financial or non-financial competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Winarti Achmad Sarmin Djainal, Email: wie2n_angelfish@yahoo.com.
Khalid Shahin, Email: kshahin@ucdavis.edu.
Matthijs Metselaar, Email: matthijs.metselaar@bmkanimalhealth.com.
Alexandra Adams, Email: alexandra.adams@stir.ac.uk.
Andrew P. Desbois, Email: ad54@stir.ac.uk
References
- 1.Colquhoun DJ, Duodu S. Francisella infections in farmed and wild aquatic organisms. Vet Res. 2011;42:47. doi: 10.1186/1297-9716-42-47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Bakkemo KR, Mikkelsen H, Bordevik M, Torgersen J, Winther-Larsen HC, Vanberg C, Olsen R, Johansen LH, Seppola M. Intracellular localisation and innate immune responses following Francisella noatunensis infection of Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) macrophages. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2011;31:993–1004. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2011.08.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Bakkemo KR, Mikkelsen H, Johansen A, Robertsen B, Seppola M. Francisella noatunensis subsp. noatunensis invades, survives and replicates in Atlantic cod cells. Dis Aquat Org. 2016;121:149–159. doi: 10.3354/dao03043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Vestvik N, Rønneseth A, Kalgraff CA, Winther-Larsen HC, Wergeland HI, Haugland GT. Francisella noatunensis subsp. noatunensis replicates within Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua L.) leukocytes and inhibits respiratory burst activity. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013;35:725–733. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2013.06.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Furevik A, Pettersen EF, Colquhoun D, Wergeland HI. The intracellular lifestyle of Francisella noatunensis in Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua L.) leucocytes. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2011;30:488–494. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2010.11.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Brudal E, Ulanova LS, Lampe EO, Rishovd AL, Griffiths G, Winther-Larsen HC. Establishment of three Francisella infections in zebrafish embryos at different temperatures. Infect Immun. 2014;82:2180–2194. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00077-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Soto E, Fernandez D, Hawke JP. Attenuation of the fish pathogen Francisella sp. by mutation of the iglC* gene. J Aquat Anim Health. 2009;21:140–149. doi: 10.1577/H08-056.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Soto E, Hawke JP, Fernandez D, Morales JA. Francisella sp., an emerging pathogen of tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus (L.), in Costa Rica. J Fish Dis. 2009;32:713–722. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2761.2009.01070.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Soto E, Fernandez D, Thune R, Hawke JP. Interaction of Francisella asiatica with tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) innate immunity. Infect Immun. 2010;78:2070–2078. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01308-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Ramírez-Paredes JG, Larsson PE, Wehner S, Bekaert M, Öhrman C, Metselaar M, Thompson KD, Richards RH, Penman DJ, Adams A. Draft genome sequence of Francisella noatunensis subsp. orientalis STIRGUS- F2f7, a highly virulent strain recovered from diseased red Nile tilapia farmed in Europe. Genome Announc. 2017;5:16–17. doi: 10.1128/genomeA.01555-16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Soto E, Yun S, Lewis J, Kearney MT, Hansen J. Interaction of Francisella noatunensis subsp. orientalis with Oreochromis mossambicus bulbus arteriosus cell line. Microb Pathog. 2017;105:326–333. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2017.03.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Chern R, Chao C. Outbreaks of a disease caused by rickettsia-like organism in cultured tilapias in Taiwan. Fish Pathol. 1994;29:61–71. doi: 10.3147/jsfp.29.61. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Soto E, Abrams SB, Revan F. Effects of temperature and salt concentration on Francisella noatunensis subsp. orientalis infections in Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus. Dis Aquat Org. 2012;101:217–223. doi: 10.3354/dao02533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Shahin K, Shinn AP, Metselaar M, Ramirez-Paredes JG, Monaghan SJ, Thompson KD, Hoare R, Adams A. Efficacy of an inactivated whole-cell injection vaccine for Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus (L), against multiple isolates of Francisella noatunensis subsp. orientalis from diverse geographical regions. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019;89:217–227. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2019.03.071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Vojtech LN, Sanders GE, Conway C, Ostland V, Hansen JD. Host immune response and acute disease in a zebrafish model of Francisella pathogenesis. Infect Immun. 2009;77:914–925. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01201-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Hartung T. Comparative analysis of the revised directive 2010/63/EU for the protection of laboratory animals with its predecessor 86/609/EEC - a t4 report. ALTEX. 2010;27:285–303. doi: 10.14573/altex.2010.4.285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Union E. Directive 2010/63/EU of the European Parliament and of the council of 22 September 2010 on the protection of animals used for scientific purposes. Off J Eur Union. 2010;276:33–79. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Froquet R, Cherix N, Burr SE, Frey J, Vilches S, Tomas JM, Cosson P. Alternative host model to evaluate Aeromonas virulence. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2007;73:5657–5659. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00908-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Lampe EO, Brenz Y, Herrmann L, Repnik U, Griffiths G, Zingmark C, Winther-Larsen HC, Hagedorn M. Dissection of Francisella-host cell interactions in Dictyostelium discoideum. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2016;82:1586–1598. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02950-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Pang M-D, Lin X-Q, Hu M, Li J, Lu C-P, Liu Y-J. Tetrahymena: an alternative model host for evaluating virulence of Aeromonas strains. PLoS One. 2012;7:e48922. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0048922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Brackman G, Celen S, Hillaert U, van Calenbergh S, Cos P, Maes L, Nelis HJ, Coenye T. Structure-activity relationship of cinnamaldehyde analogs as inhibitors of AI-2 based quorum sensing and their effect on virulence of Vibrio spp. PLoS One. 2011;6:e16084. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0016084. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Defoirdt T, Bossier P, Sorgeloos P, Verstraete W. The impact of mutations in the quorum sensing systems of Aeromonas hydrophila, Vibrio anguillarum and Vibrio harveyi on their virulence towards gnotobiotically cultured Artemia franciscana. Environ Microbiol. 2005;7:1239–1247. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2005.00807.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.McMillan S, Verner-Jeffreys D, Weeks J, Austin B, Desbois AP. Larva of the greater wax moth, Galleria mellonella, is a suitable alternative host for studying virulence of fish pathogenic Vibrio anguillarum. BMC Microbiol. 2015;15:127. doi: 10.1186/s12866-015-0466-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Desbois AP, Coote PJ. Utility of greater wax moth larva (Galleria mellonella) for evaluating the toxicity and efficacy of new antimicrobial agents. Adv Appl Microbiol. 2012;78:25–53. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-394805-2.00002-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Jorjão AL, Oliveira LD, Scorzoni L, Figueiredo-Godoi LMA, Cristina A, Prata M, Jorge AOC, Junqueira JC. From moths to caterpillars: ideal conditions for Galleria mellonella rearing for in vivo microbiological studies. Virulence. 2018;9:383–389. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2017.1397871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Jander G, Rahme LG, Ausubel FM. Positive correlation between virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa mutants in mice and insects. J Bacteriol. 2000;182:3843–3845. doi: 10.1128/JB.182.13.3843-3845.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Olsen RJ, Watkins ME, Cantu CC, Beres SB, Musser JM. Virulence of serotype M3 group a Streptococcus strains in wax worms (Galleria mellonella) larvae. Virulence. 2011;2:111–119. doi: 10.4161/viru.2.2.14338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Jiang H, Vilcinskas A, Kanost MR. Immunity in lepidopteran insects. In: Söderhäll K, editor. Invertebrate immunity. New York: Springer US; 2010. pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Browne N, Heelan M, Kavanagh K. An analysis of the structural and functional similarities of insect hemocytes and mammalian phagocytes. Virulence. 2013;4:597–603. doi: 10.4161/viru.25906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Neumann NF, Stafford JL, Barreda D, Ainsworth AJ, Belosevic M. Antimicrobial mechanisms of fish phagocytes and their role in host defense. Dev Comp Immunol. 2001;25:807–825. doi: 10.1016/S0145-305X(01)00037-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Lavine MD, Strand MR. Insect hemocytes and their role in immunity. Insect Biochem Molec. 2002;32:1295–1309. doi: 10.1016/S0965-1748(02)00092-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Agius C, Roberts RJ. Melano-macrophage centres and their role in fish pathology. J Fish Dis. 2003;26:499–509. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2761.2003.00485.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Magnadóttir B. Innate immunity of fish (overview) Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2006;20:137–151. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2004.09.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Cytryńska M, Mak P, Zdybicka-Barabas A, Suder P, Jakubowicz T. Purification and characterization of eight peptides from Galleria mellonella immune hemolymph. Peptides. 2007;28:533–546. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2006.11.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Vogel H, Altincicek B, Glockner G, Vilcinskas A. A comprehensive transcriptome and immune-gene repertoire of the lepidopteran model host Galleria mellonella. BMC Genomics. 2011;12:308. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-12-308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Lange A, Beier S, Huson DH, Parusel R, Iglauer F, Frick J-S. Genome sequence of Galleria mellonella (greater wax moth) Genome Announc. 2018;6:e01220–e01217. doi: 10.1128/genomeA.01220-17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Salamitou S, Ramisse F, Brehélin M, Bourguet D, Gilois N, Gominet M, Hernandez E, Lereclus D. The plcR regulon is involved in the opportunistic properties of Bacillus thuringiensis and Bacillus cereus in mice and insects. Microbiology. 2000;146:2825–2832. doi: 10.1099/00221287-146-11-2825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Miyata S, Casey M, Frank DW, Ausubel FM, Drenkard E. Use of the Galleria mellonella caterpillar as a model host to study the role of the type III secretion system in Pseudomonas aeruginosa pathogenesis. Infect Immun. 2003;71:2404–2413. doi: 10.1128/IAI.71.5.2404-2413.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Champion OL, Cooper IAM, James SL, Ford D, Karlyshev A, Wren BW, Duffield M, Oyston PCF, Titball RW. Galleria mellonella as an alternative infection model for Yersinia pseudotuberculosis. Microbiology. 2009;155:1516–1522. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.026823-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Thelaus J, Lundmark E, Lindgren P, Sjödin A, Forsman M. Galleria mellonella reveals niche differences between highly pathogenic and closely related strains of Francisella spp. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2018;8:188. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2018.00188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Propst CN, Pylypko SL, Blower RJ, Ahmad S, Mansoor M, van Hoek ML. Francisella philomiragia infection and lethality in mammalian tissue culture cell models, Galleria mellonella, and BALB/c mice. Front Microbiol. 2016;7:1–10. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.00696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Aperis G, Fuchs BB, Anderson CA, Warner JE, Calderwood SB, Mylonakis E. Galleria mellonella as a model host to study infection by the Francisella tularensis live vaccine strain. Microbes Infect. 2007;9:729–734. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2007.02.016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Ahmad S, Hunter L, Qin A, Mann BJ, van Hoek ML. Azithromycin effectiveness against intracellular infections of Francisella. BMC Microbiol. 2010;10:123. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-10-123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Desbois AP, McMillan S. Paving the way to acceptance of Galleria mellonella as a new model insect. Virulence. 2015;6:410–411. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2015.1036218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Lagos L, Tandberg JI, Repnik U, Boysen P, Ropstad E, Varkey D, Paulsen IT, Winther-Larsen HC. Characterization and vaccine potential of membrane vesicles produced by Francisella noatunensis subsp. orientalis in an adult zebrafish model. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2017;24:e00557–e00516. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00557-16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Sherry L, Rajendran R, Lappin DF, Borghi E, Perdoni F, Falleni M, Tosi D, Smith K, Williams C, Jones B, Nile CJ, Ramage G. Biofilms formed by Candida albicans bloodstream isolates display phenotypic and transcriptional heterogeneity that are associated with resistance and pathogenicity. BMC Microbiol. 2014;14:182. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-14-182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Trevijano-Contador N, Herrero-Fernández I, García-Barbazán I, Scorzoni L, Rueda C, Rossi SA, García-Rodas R, Zaragoza O. Cryptococcus neoformans induces antimicrobial responses and behaves as a facultative intracellular pathogen in the non mammalian model Galleria mellonella. Virulence. 2015;6:66–74. doi: 10.4161/21505594.2014.986412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Rajendran R, Borghi E, Falleni M, Perdoni F, Tosi D, Lappin DF, O’Donnell L, Greetham D, Ramage G, Nile C. Acetylcholine protects against Candida albicans infection by inhibiting biofilm formation and promoting hemocyte function in a Galleria mellonella infection model. Eukaryot Cell. 2015;14:834–844. doi: 10.1128/EC.00067-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Barnoy S, Gancz H, Zhu Y, Honnold CL, Zurawski DV, Venkatesan MM. The Galleria mellonella larvae as an in vivo model for evaluation of Shigella virulence. Gut Microbes. 2017;8:335–350. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2017.1293225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Baker CN, Hollis DG, Thornsberry C. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing of Francisella tularensis with a modified Mueller-Hinton broth. J Clin Microbiol. 1985;22:212–215. doi: 10.1128/JCM.22.2.212-215.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Kamaishi T, Fukuda Y, Nishiyama M, Kawakami H, Matsuyama T, Yoshinaga T, Oseko N. Identification and pathogenicity of intracellular Francisella bacterium in three-line grunt Parapristipoma trilineatum. Fish Pathol. 2005;40:67–71. doi: 10.3147/jsfp.40.67. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Mauel MJ, Miller DL, Styer E, Pouder DB, Yanong RPE, Goodwin AE, Schwedler TE. Occurrence of piscirickettsiosis-like syndrome in tilapia in the continental United States. J Vet Diagn Investig. 2005;17:601–605. doi: 10.1177/104063870501700616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Kwadha CA, Ong'amo GO, Ndegwa PN, Raina SK, Fombong AT. The biology and control of the greater wax moth. Galleria mellonella Insects. 2017;8:61. doi: 10.3390/insects8020061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Mukherjee K, Hain T, Fischer R, Chakraborty T, Vilcinskas A. Brain infection and activation of neuronal repair mechanisms by the human pathogen Listeria monocytogenes in the lepidopteran model host Galleria mellonella. Virulence. 2013;4:324–332. doi: 10.4161/viru.23629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Shahin K, Thompson KD, Inglis NF, Mclean K, Ramirez-Paredes JG, Monaghan SJ, Hoare R, Fontaine M, Metselaar M, Adams A. Characterisation of the outer membrane proteome of Francisella noatunensis subsp. orientalis. J Appl Microbiol. 2018;125:686–699. doi: 10.1111/jam.13918. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Sridhar S, Sharma A, Kongshaug H, Nilsen F, Jonassen I. Whole genome sequencing of the fish pathogen Francisella noatunensis subsp. orientalis Toba04 gives novel insights into Francisella evolution and pathogenicity. BMC Genomics. 2012;13:598. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Lewis J, Soto E. Gene expression of putative type VI secretion system (T6SS) genes in the emergent fish pathogen Francisella noatunensis subsp. orientalis in different physiochemical conditions. BMC Microbiol. 2019;19:21. doi: 10.1186/s12866-019-1389-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Brudal E, Lampe EO, Reubsaet L, Roos N, Hegna IK, Thrane IM, Koppang EO, Winther-Larsen HC. Vaccination with outer membrane vesicles from Francisella noatunensis reduces development of francisellosis in a zebrafish model. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015;42:50–57. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2014.10.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Lewisch E, Dressler A, Menanteau-Ledouble S, Saleh M, El-Matbouli M. Francisellosis in ornamental African cichlids in Austria. Bull Eur Assoc Fish Pathol. 2014;34:63–70. [Google Scholar]
- 60.Ortega C, Mancera G, Enríquez R, Vargas A, Martínez S, Fajardo R, Avendaño-Herrera R, Navarrete M, Romero A. First identification of Francisella noatunensis subsp. orientalis causing mortality in Mexican tilapia Oreochromis spp. Dis Aquat Org. 2016;120:205–215. doi: 10.3354/dao02999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Frerichs GN, Millar SD. Manual for the isolation and identification of fish bacterial pathogens. Stirling: Pisces Press; 1993. [Google Scholar]
- 62.Chen CY, Nace GW, Irwin PL. A 6×6 drop plate method for simultaneous colony counting and MPN enumeration of Campylobacter jejuni, Listeria monocytogenes, and Escherichia coli. J Microbiol Methods. 2003;55:475–479. doi: 10.1016/S0167-7012(03)00194-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Senior NJ, Bagnall MC, Champion OL, Reynolds SE, La Ragione RM, Woodward MJ, Salguero FJ, Titball RW. Galleria mellonella as an infection model for Campylobacter jejuni virulence. J Med Microbiol. 2011;60:661–669. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.026658-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Desbois AP, Coote PJ. Wax moth larva (Galleria mellonella): an in vivo model for assessing the efficacy of antistaphylococcal agents. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2011;66:1785–1790. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkr198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Perdoni F, Falleni M, Tosi D, Cirasola D, Romagnoli S, Braidotti P, Clementi E, Bulfamante G, Borghi E. A histological procedure to study fungal infection in the wax moth Galleria mellonella. Eur J Histochem. 2014;58:258–262. doi: 10.4081/ejh.2014.2428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Forsman M, Sandström G, Sjostedt A. Analysis of 16S ribosomal DNA sequences of Francisella strains and utilization for determination of the phylogeny of the genus and for identification of strains by PCR. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1994;44:38–46. doi: 10.1099/00207713-44-1-38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.