Abstract
The importance of prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) PET/CT for primary staging of treatment-naïve prostate cancer patients is still under debate. Therefore, the present study aimed to evaluate the role of PSMA PET/CT in detecting nodal metastases in a large cohort of men and compare imaging results with the risk of lymph node involvement based on the Roach formula. Methods: In total, 280 men with newly diagnosed prostate carcinoma were included in the present study. For all patients, PSMA PET/CT was performed for primary staging. Median age was 67 y (range, 38–84 y), and 84% of all patients were classified as high-risk according to the d’Amico criteria. The risk of lymph node involvement was calculated using the Roach formula and compared with the PSMA PET/CT results. Results: PSMA-positive nodes were detected in 90 of 280 men (32.1%). Although most nodal metastases occurred within the pelvis, 36.0% were in extrapelvic sites. In 9 patients (3.2%), nodal metastases occurred in the Virchow node. After comparison of PSMA data with the results of the Roach formula, an area under the curve of 0.781 was obtained for the Roach predictions. Conclusion: For treatment-naïve prostate cancer patients, PSMA PET/CT is well suited for the detection of nodal metastases. However, the original Roach formula can still be used for a quick assessment of potential lymphatic spread in daily clinical routine.
Keywords: prostate cancer, PSMA, PET/CT, Roach formula, Virchow
Definitive treatment for patients with nonmetastatic prostate cancer includes surgery or radiotherapy with or without androgen deprivation therapy. The risk of lymphatic spread is minimal for low-risk disease according to the d’Amico criteria (1); however, up to 33% of patients with intermediate- or high-risk disease are diagnosed with lymph node metastases (2). Unfortunately, pretreatment conventional staging such as CT and MRI are insensitive for the detection of lymph node metastases. For instance, in a cohort of 130 patients with prostate carcinoma, Maurer et al. reported a sensitivity and accuracy of morphologic imaging of only 43.9% and 72.3%, respectively (3). Although for most patients undergoing prostatectomy, histopathologic correlation can be performed because of pelvic lymph node dissection, there is no such comparison for men undergoing definitive radiotherapy.
By 1994, Roach et al. had derived a simple equation from the Partin nomogram estimating the risk of lymph node metastases (4). This so-called Roach formula includes the prostate-specific antigen (PSA) level and Gleason score (GS) and provides an assessment of risk of lymph node involvement (LNI) (4). This formula is widely used in the field of radiation oncology for a quick estimation of whether an elective node irradiation should be performed for patients with a high risk for nodal involvement. However, several studies suggest that the Roach formula overpredicts the risk of nodal metastases (5,6). Rahman et al. found that the Roach formula overestimated risk by 2.5- to 4.5-fold in a retrospective analysis of 1,022 men with T1c–T3 prostate cancer (6). Moreover, new diagnostic imaging such as multiparametric MRI and prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) PET/CT increases the accuracy of staging before irradiation. In particular, PSMA PET/CT imaging has reported sensitivity and specificity of up to 80% and 95%, respectively, for prostate cancer and is well suited for assessing the detection of nodal metastases—even compared with 18F-fluorocholine PET/CT (7–11). For detection of nodal metastases, a sensitivity of 84% and a specificity of 82% were observed for PSMA imaging (12). The present study evaluated the role of PSMA PET/CT in localizing nodal metastases in a large cohort of treatment-naïve patients with prostate cancer. The results are correlated with the risk of LNI according to the Roach formula.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Patient Cohort
This retrospective study was approved by the local institutional review board. PSMA PET/CT was performed on more than 2,000 men with prostate carcinoma at the Department of Nuclear Medicine, Heidelberg University Hospital, between July 2011 and July 2018. Most patients underwent PSMA-imaging because of PSA relapse after surgery or definitive radiotherapy. From the remaining cohort, 280 patients with treatment-naïve prostate cancer and sufficient clinical data were included in the present study.
PSMA PET/CT Imaging and Calculation of the Roach Formula
PSMA imaging was performed with 3 different scanners: a Biograph mCT Flow (Siemens) was used for 192 patients (69%), a Biograph 6 PET/CT (Siemens) for 85 (30%), and a Biograph 20mT (Siemens) for 3 (1.1%). All scans were performed according to previously published protocols (2). For 254 patients (91%), 68Ga-PSMA-11 PET/CT was used, whereas 26 patients (9.3%) were imaged with 18F-PSMA-1007 PET/CT. Synthesis of 68Ga-PSMA-11 and 18F-PSMA-1007 followed the methods described by Eder et al. (13) and Cardinale et al. (14), respectively.
PSMA PET/CT scans were interpreted by 2 board-certified nuclear medicine physicians and 1 board-certified radiation oncologist with regard to lymph node metastases. For image evaluation, tracer accumulation was considered positive if PSMA uptake in a node had a relevant difference from the background. Evaluation was done using Syngo TrueD (Siemens) and a dedicated workstation. All PSMA PET/CT scans were evaluated in consensus. A consensus reading was performed for 12 patients because of PSMA uptake within the ureter.
The risk for LNI was calculated according to the Roach formula {2/3 PSA + [(GS – 6) × 10]} (4) for every patient included in this study. We compared the probability derived from the Roach formula with the results of PSMA PET/CT imaging.
Statistical Analysis
For statistical analysis, IBM SPSS Statistics 23 was used. In 280 patients with prostate cancer who underwent PSMA PET/CT, PSA and GS were collected. Using these values, binary logistic regression was applied in various combinations of either PSA or ln(PSA) combined with either GS or International Society of Urological Pathology (ISUP) classification, to obtain a new formula for the calculation of regional lymph node metastases. The different formulas were compared in terms of the area under the receiver-operating curves. In addition, the distribution of lymph node metastases was characterized descriptively under different conditions and tested for significance (P < 0.05) using Mann–Whitney U tests. Because of the large number of tests, the resulting P values for lymph node metastasis comparisons were adjusted for multiple testing using the Bonferroni–Holm method. Further comparisons, especially of the separate logistic regression models, were considered as exploratory variants and no additional corrections for multiple testing were done.
RESULTS
The median age of our cohort was 67 y (range, 38–84 y). According to the d’Amico risk classification (1), 235 men (84%) were diagnosed with high-risk disease and 39 (14%) had intermediate-risk prostate cancer; 97 men (35%) underwent surgery after PSMA imaging, whereas 52 (19%) were irradiated. Because of newly diagnosed bone or visceral metastases, 20 men (7.1%) directly received androgen deprivation therapy or chemotherapy (Table 1).
TABLE 1.
Patient Characteristics
| Characteristic | Data |
| Total patients | 280 |
| Age (y) | 66.8 (38–84) |
| T-stage | |
| T1 | 0 (0.0%) |
| T2 | 238 (85.0%) |
| T3 | 33 (11.8%) |
| T4 | 9 (3.2%) |
| Unknown | 0 (0%) |
| GS | |
| ≤6 (ISUP grade 1) | 35 (12.5%) |
| 7 (ISUP grade 2/3) | 102 (36.4%) |
| 8 (ISUP grade 4) | 52 (18.6%) |
| ≥9 (ISUP grade 5) | 83 (29.6%) |
| Unknown | 8 (2.9%) |
| iPSA (ng/mL) | 11.8 (1.4–511) |
| Risk-group according to d’Amico (1) | |
| Low | 6 (2.2%) |
| Intermediate | 39 (13.9%) |
| High | 235 (83.9%) |
| Unknown | 0 (0%) |
| Further treatment | |
| Surgery | 97 (34.6%) |
| Radiotherapy | 52 (18.6%) |
| Systemic therapy | 20 (7.1%) |
| Unknown | 111 (39.7%) |
Qualitative data are expressed as numbers followed by percentages in parentheses; continuous data are expressed as median followed by range in parentheses.
The risk for LNI according to the Roach formula was 31% (median; range, 2.1%–100%) among all patients. Risk varied from low (≤10%) for 26 men (9.3%) to very high (>50%) for 13.6% of our cohort. Because of high GS or PSA values, 10 patients (3.6%) had a calculated probability for nodal metastases of more than 90% (Table 2).
TABLE 2.
Risk for LNI According to Roach Formula
| Characteristic | Data |
| Total patients (n) | 280 |
| Median (%) | 31.1 |
| Range (%) | 2.1–100 |
| Subgroup | |
| ≤10% | 26 (9.3%) |
| 10.1%–20% | 60 (21.4%) |
| 20.1%–30% | 72 (25.7%) |
| 30.1%–40% | 61 (21.8%) |
| 40.1%–50% | 23 (8.2%) |
| 50.1%–60% | 14 (5.0%) |
| 60.1%–70% | 7 (2.5%) |
| 70.1%–80% | 5 (1.8%) |
| 80.1%–90% | 2 (0.7%) |
| >90% | 10 (3.6%) |
| Unknown | 0 (0%) |
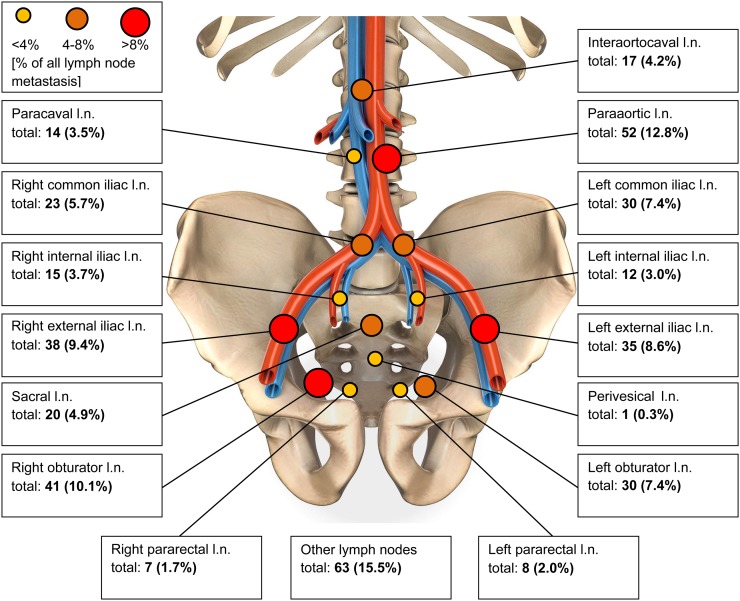
PSMA imaging found 90 of 280 men in our cohort to have LNI (32%), almost exactly corresponding to the prediction for the group by the Roach formula. In total, 406 PSMA-positive nodal metastases were observed in these 90 patients (mean, 4.6 nodes per patient; range, 0–31 positive nodes per patient). Most PSMA-avid lesions occurred in intrapelvic regions (64.0%), with the highest intrapelvic detection rate being noted in the external iliac lymph node basin (18.0%) and the obturator region (17.5%). The distribution of left-sided versus right-sided nodal metastases showed no statistically significant difference. Outside the pelvis, most lesions were diagnosed in the paraaortic (12.8%), mediastinal (6.2%), and interaortocaval (4.2%) node groups. A group of 9 patients (8.9%) had pathologic PSMA enhancement in a supraclavicular Virchow node (Fig. 1; Table 3) (15). For 65 men (23.2%), PSMA-positive metastases in 164 bones were observed, whereas visceral metastases occurred in 11 men (3.9%) in 14 organs.
FIGURE 1.
Anatomic distribution of PSMA-avid nodes. l.n. = lymph nodes.
TABLE 3.
Overview of Extrapelvic Node Distribution
| Node | ∑ (n) |
| Left supraclavicular | 13 (3.2%) |
| Right supraclavicular | 1 (0.3%) |
| Left infraclavicular | 4 (1.0%) |
| Right infraclavicular | 0 (0%) |
| Cervical | 7 (1.7%) |
| Paraesophageal | 1 (0.3%) |
| Left axillary | 1 (0.3%) |
| Right axillary | 1 (0.3%) |
| Hilar | 8 (2.0%) |
| Mediastinal | 25 (6.2%) |
| Left paradiaphragmatic | 1 (0.3%) |
| Right paradiaphragmatic | 0 (0%) |
| Infracarinal | 1 (0.3%) |
The Mann–Whitney U test revealed a significantly higher incidence of lymph node metastases with a PSA of more than 10 ng/mL versus a PSA of 10 ng/mL or less for right-sided external iliac (P = 0.026) left-sided external iliac (P = 0.032), right-sided obturator (P = 0.001), left-sided obturator (P = 0.009), left-sided pararectal (P = 0.020), paraaortic (P = 0.049), and hilar (P = 0.049) nodes. In addition, in primary tumors with a GS of 8 or higher compared with 7b or lower, the occurrence of abnormal uptake was higher in the following nodes: right internal iliac (P = 0.002), left internal iliac (P = 0.013), left external iliac (P = 0.016), right obturator (P < 0.001), left obturator (P < 0.001), sacral (P = 0.001), right common iliac (P = 0.005), left common iliac (P = 0.014), left pararectal (P = 0.044), paraaortic (P = 0.005), paracaval (P = 0.002), and left supraclavicular (P = 0.002). After the P values were adjusted according to Bonferroni–Holm, there were less significant differences. A significantly higher incidence was seen with a PSA of more than 10 ng/mL compared with a PSA of 10 ng/mL or less only in the right obturator lymph nodes (P = 0.028), and a significantly higher incidence was seen with a GSC of 8 or more compared with a GSC of less than 8 in the right (P < 0.001) and left (P < 0.001) obturator lymph nodes and the sacral lymph nodes (P = 0.026).
The area under the curve for the Roach formula, with regard to predicting the PSMA PET/CT classification, was 0.781. When the ISUP scoring was used instead of GS in a modified Roach formula {2/3 PSA + [(ISUP – 1) × 10]}, the area under the curve was 0.774. When the 4 combinations of PSA, ln(PSA), GS, and ISUP score were compared in a logistic regression model, only the binary logistic regression formula with ln(PSA) and GS showed a slightly better area under the curve (0.789) than the original Roach formula (Table 4).
TABLE 4.
Results of Receiver-Operating-Curve Analyses for Classic Roach Formula and Various Combinations
| Characteristic | Area under curve |
| Original Roach formula | 0.781 |
| Modified Roach formula with ISUP scoring | 0.774 |
| Binary logistic regression with PSA and ISUP score | 0.764 |
| Binary logistic regression with ln(PSA) and ISUP score | 0.781 |
| Binary logistic regression with PSA and GS | 0.768 |
| Binary logistic regression with ln(PSA) and GS | 0.789 |
DISCUSSION
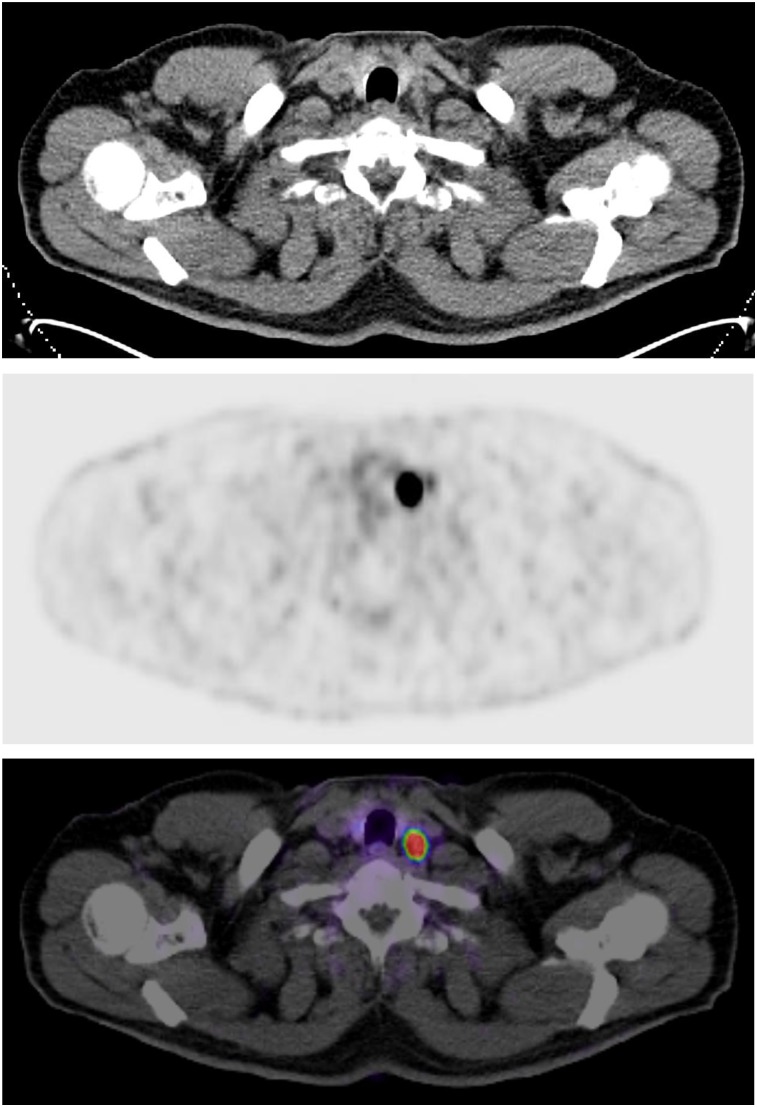
Our study demonstrated that PSMA PET/CT is able to detect a large number of nodal metastases with a high sensitivity and specificity in treatment-naïve prostate cancer patients. Most of them were within the pelvis, as is in accordance with several reports from surgery. For instance, Briganti et al. observed nodal involvement most commonly in iliac and obturator sites, followed by hypogastric and presacral nodes (16). In our cohort, external iliac and obturator nodes were also diagnosed frequently. Interestingly, extrapelvic nodal sites occurred in almost 36% of our patients, which is a significantly higher proportion than in other trials using PSMA imaging. In comparison, Gupta et al. reported that 24% of their treatment-naïve patients had extrapelvic, nodal disease (17). The large number of high-risk cancers in this study likely explains this difference. Over 3% of our study population (9/280) had uptake in the left supraclavicular node, also known as the Virchow node (Fig. 2), a surprisingly high rate for this site. Thus, PSMA PET/CT now reveals involvement of the left supraclavicular node in a substantial fraction of patients, as has been previously documented (18). We found that metastases in the Virchow lymph nodes were significantly more frequent (0.002) for primary tumors with a GS of 8 or higher than for those with a GS of 7b or lower. There is a need for further studies to understand the frequency and implications of Virchow node involvement for prostate cancer patients.
FIGURE 2.
CT (top), PET (middle), and PET/CT (bottom) scan of 54-y-old patient with 18F-PSMA-1007 uptake at Virchow position (PSA, 4.6 ng/mL; GS, 10; cT2c cN1 cM1b).
For men with prostate carcinoma, the presence of LNI has important implications. Knowing the location of involved nodes enables targeted radiotherapy wherein radiation dose can be directed to positive nodes using intensity-modulated radiotherapy or image-guided radiotherapy. Nomograms have been developed to avoid or extend pelvic lymph node dissection (6,19–22). Gandaglia et al. reported on a novel model including PSA, clinical stage biopsy GS group, percentage of cores with highest-grade prostate cancer, and percentage of cores with lower-grade disease. This nomogram was helpful in identifying candidates for extended pelvic lymph node dissection (21). For patients undergoing irradiation after primary diagnosis of prostate carcinoma, there is ongoing debate over whether the risk of LNI is high enough to consider radiotherapy. Although several retrospective or small prospective studies observed an excellent clinical outcome when also irradiating pelvic nodes for specific high-risk groups (23–27), the latest updates of 2 large phase III trials were not able to verify a survival benefit for whole-pelvis radiotherapy in general (28,29). Pommier et al. concluded, after a median follow-up of 11.4 y, that pelvic node irradiation failed to improve event-free survival or overall survival in a cohort of 446 men (28). Most of these trials used the Roach formula for calculating the risk of LNI even if the cutoffs were slightly different. The present study confirmed that the Roach formula provides an overall accurate estimate for LNI. Although the area under the curve of the Roach formula was 0.781, implying some inaccuracies and a tendency toward overestimation (5,6), the Roach formula is still useful for radiooncologic treatment planning even in the era of PSMA PET imaging. PSMA PET/CT, however, provides anatomic localization of LNI, permitting tailored treatment planning. Because PSMA PET/CT does not have 100% sensitivity either, there will continue to be a need for a priori risk assessment in combination with the results of PSMA PET/CT.
Major limitations of our study include its retrospective nature and its being performed at only 1 center, leading to somewhat optimistic results as the performance was checked using the same dataset on which the model was fitted. Moreover, the number of patients undergoing post-PSMA surgery was relatively low, preventing histopathologic validation in most patients. A minor subgroup was imaged with 18F-PSMA-1007 instead of 68Ga-PSMA-11, leading to a potential impact on the patient evaluation. Nevertheless, to our knowledge this retrospective study evaluating treatment-naïve prostate cancer patients after PSMA PET/CT staging is one of the largest worldwide. Further research is required to understand the correlation of PSMA PET/CT–defined volumes and radiooncologic target volume delineation. It is possible that this approach will provide more individualized treatment approaches for men with prostate carcinoma undergoing definitive radiotherapy.
CONCLUSION
The present study demonstrated that nodal metastases derived from prostate cancer could be detected reliably by PSMA PET/CT in a large cohort of treatment-naïve patients. After we correlated imaging data with the results of the Roach formula, our findings tended to validate this fast and useful estimate of LNI risk. Even when considering that PSMA imaging helps to specifically localize PSMA-positive metastases, which can support intensity-modulated radiotherapy and image-guided radiotherapy planning, the Roach formula is well suited for a quick assessment of LNI in daily clinical routine.
DISCLOSURE
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
KEY POINTS
QUESTION: The importance of PSMA PET/CT for primary staging of treatment-naïve patients with prostate carcinoma is still under debate.
PERTINENT FINDINGS: Our study demonstrated in a large cohort of 280 men that PSMA PET/CT is well suited for the detection of nodal metastases.
IMPLICATIONS FOR PATIENT CARE: Even when considering that PSMA imaging helps to specifically localize PSMA-positive metastases, which can support IMRT and IGRT planning, the Roach formula can be used for a quick assessment of LNI in daily clinical routine.
REFERENCES
- 1.D’Amico AV, Whittington R, Malkowicz SB, et al. Biochemical outcome after radical prostatectomy, external beam radiation therapy, or interstitial radiation therapy for clinically localized prostate cancer. JAMA. 1998;280:969–974. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Koerber SA, Will L, Kratochwil C, et al. 68Ga-PSMA-11 PET/CT in primary and recurrent prostate carcinoma: implications for radiotherapeutic management in 121 patients. J Nucl Med. July 5, 2018 [Epub ahead of print]. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Maurer T, Gschwend JE, Rauscher I, et al. Diagnostic efficacy of 68gallium-PSMA positron emission tomography compared to conventional imaging for lymph node staging of 130 consecutive patients with intermediate to high risk prostate cancer. J Urol. 2016;195:1436–1443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Roach M, III, Marquez C, Yuo HS, et al. Predicting the risk of lymph node involvement using the pre-treatment prostate specific antigen and Gleason score in men with clinically localized prostate cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1994;28:33–37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Nguyen PL, Chen MH, Hoffman KE, et al. Predicting the risk of pelvic node involvement among men with prostate cancer in the contemporary era. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2009;74:104–109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Rahman S, Cosmatos H, Dave G, et al. Predicting pelvic lymph node involvement in current-era prostate cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012;82:906–910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Bluemel C, Krebs M, Polat B, et al. 68Ga-PSMA-PET/CT in patients with biochemical prostate cancer recurrence and negative 18F-choline-PET/CT. Clin Nucl Med. 2016;41:515–521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Eiber M, Fendler WP, Rowe SP, et al. Prostate-specific membrane antigen ligands for imaging and therapy. J Nucl Med. 2017;58(suppl 2):67S–76S. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Kesch C, Vinsensia M, Radtke JP, et al. Intraindividual comparison of 18F-PSMA-1007 PET/CT, multiparametric MRI, and radical prostatectomy specimens in patients with primary prostate cancer: a retrospective, proof-of-concept study. J Nucl Med. 2017;58:1805–1810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Schwarzenboeck SM, Rauscher I, Bluemel C, et al. PSMA ligands for PET imaging of prostate cancer. J Nucl Med. 2017;58:1545–1552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Vinsensia M, Chyoke PL, Hadaschik B, et al. 68Ga-PSMA PET/CT and volumetric morphology of PET-positive lymph nodes stratified by tumor differentiation of prostate cancer. J Nucl Med. 2017;58:1949–1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Herlemann A, Wenter V, Kretschmer A, et al. 68Ga-PSMA positron emission tomography/computed tomography provides accurate staging of lymph node regions prior to lymph node dissection in patients with prostate cancer. Eur Urol. 2016;70:553–557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Eder M, Neels O, Müller M, et al. Novel preclinical and radiopharmaceutical aspects of [68Ga]Ga-PSMA-HBED-CC: a new PET tracer for imaging of prostate cancer. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2014;7:779–796. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Cardinale J, Martin R, Remde Y, et al. Procedures for the GMP-compliant production and quality control of [18F]PSMA-1007: a next generation radiofluorinated tracer for the detection of prostate cancer. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2017;10:E77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Virchow RLK. Zur diagnose der krebse im unterleibe. https://www.researchgate.net/figure/A-Original-German-article-Zur-Diagnose-der-Krebse-im-Unterleibe-by-Rudolf-Karl_fig1_324241604. Accessed November 20, 2019.
- 16.Briganti A, Suardi N, Capogrosso P, et al. Lymphatic spread of nodal metastases in high-risk prostate cancer: the ascending pathway from the pelvis to the retroperitoneum. Prostate. 2012;72:186–192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Gupta SK, Watson T, Denham J, et al. Prostate-specific membrane antigen positron emission tomography-computed tomography for prostate cancer: distribution of disease and implications for radiation therapy planning. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2017;99:701–709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Werner RA, Andree C, Javadi MS, et al. A voice from the past: rediscovering the Virchow node with prostate-specific membrane antigen-targeted 18F-DCFPyL positron emission tomography imaging. Urology. 2018;117:18–21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Briganti A, Larcher A, Abdollah F, et al. Updated nomogram predicting lymph node invasion in patients with prostate cancer undergoing extended pelvic lymph node dissection: the essential importance of percentage of positive cores. Eur Urol. 2012;61:480–487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Eifler JB, Feng Z, Lin BM, et al. An updated prostate cancer staging nomogram (Partin tables) based on cases from 2006 to 2011. BJU Int. 2013;111:22–29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Gandaglia G, Fossati N, Zaffuto E, et al. Development and internal validation of a novel model to identify the candidates for extended pelvic lymph node dissection in prostate cancer. Eur Urol. 2017;72:632–640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Turo R, Forster JA, West RM, et al. Do prostate cancer nomograms give accurate information when applied to European patients? Scand J Urol. 2015;49:16–24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Adkison JB, McHaffie DR, Bentzen SM, et al. Phase I trial of pelvic nodal dose escalation with hypofractionated IMRT for high-risk prostate cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012;82:184–190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Di Muzio NG, Fodor A, Noris Chiorda B, et al. Moderate hypofractionation with simultaneous integrated boost in prostate cancer: long-term results of a phase I-II study. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2016;28:490–500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Magli A, Moretti E, Tullio A, et al. Hypofractionated simultaneous integrated boost (IMRT-SIB) with pelvic nodal irradiation and concurrent androgen deprivation therapy for high-risk prostate cancer: results of a prospective phase II trial. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2018;21:269–276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Mantini G, Tagliaferri L, Mattiucci GC, et al. Effect of whole pelvic radiotherapy for patients with locally advanced prostate cancer treated with radiotherapy and long-term androgen deprivation therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2011;81:e721–e726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Pervez N, Small C, MacKenzie M, et al. Acute toxicity in high-risk prostate cancer patients treated with androgen suppression and hypofractionated intensity-modulated radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2010;76:57–64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Pommier P, Chabaud S, Lagrange JL, et al. Is there a role for pelvic irradiation in localized prostate adenocarcinoma? Update of the long-term survival results of the GETUG-01 randomized study. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2016;96:759–769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Roach M, Moughan J, Lawton CAF, et al. Sequence of hormonal therapy and radiotherapy field size in unfavourable, localised prostate cancer (NRG/RTOG 9413): long-term results of a randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2018;19:1504–1515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]