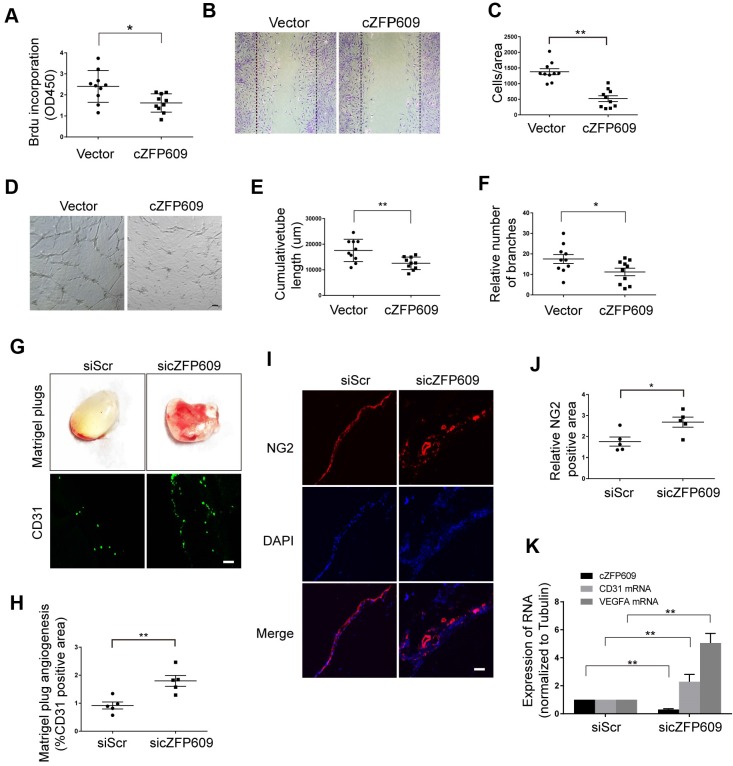
Figure 5.
cZFP609 inhibits the endothelial angiogenic functions. (A-F) The mouse ECs were transfected with vector or cZFP609 for 24 h, and then treated by hypoxia for 24 h. (A) Proliferation of ECs was determined by BrdU incorporation. Bar graphs show the relative activity of proliferation. (B and C) The migration of cells was evaluated by a cell-wounding assay. The number of cells in the wounded area shows the relative activity of migration. (D-F) Representative images of tube formation. Relative tube length and number of branches were quantified by measuring the cumulative tube length and branches. Scale bars = 200 μm. (G-K) The matrigel was premixed with siScr or sicZFP609, and was injected subcutaneously into SIRT1-Tg mice. (G) Bright field image of angiogenesis (upper lane) and representative images of CD31 (lower lane) and NG2 (I) immunostaining in matrigel plugs. Nuclei were stained with DAPI in blue. Scale bars = 100 μm. Angiogenesis in matrigel plugs was quantified by measuring CD31 (H) and NG2 positive area (J). (K) qRT-PCRs of CD31 mRNA, VEGFA mRNA and cZFP609 expression in matrigel plugs (n=5 mice per group). (A, C, E, F, H, J and K) Bar graphs show mean±SEM. Student's t-test: *P<0.05, **P<0.01 versus the corresponding control.