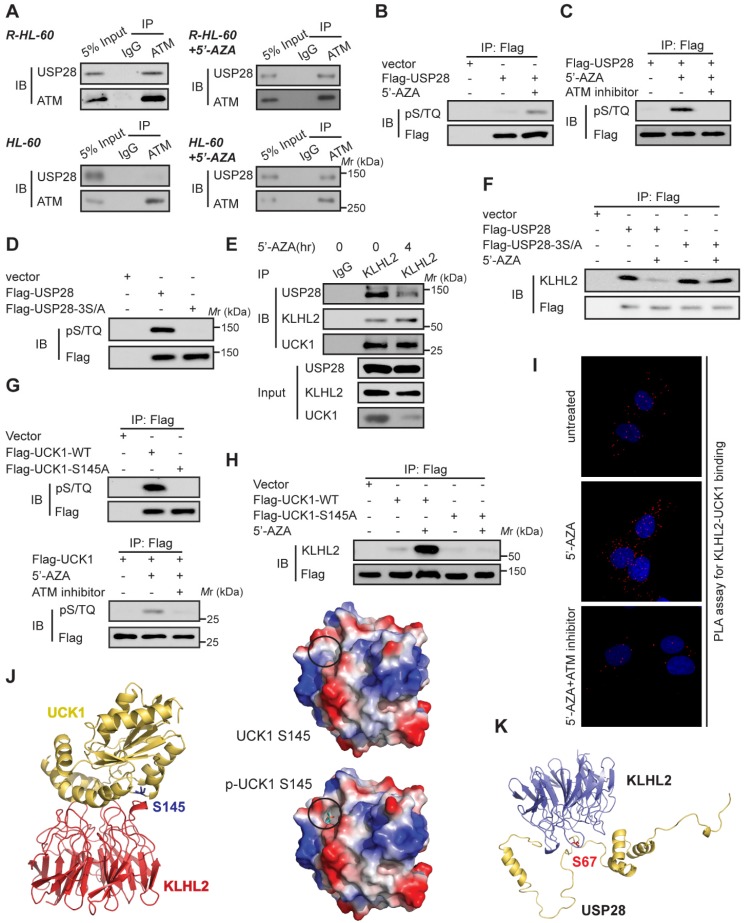
Figure 5.
ATM-mediated phosphorylation of USP28 and UCK1 and its physiological significance. (A) ATM interacted with USP28. Cell lysates were collected from 5'-AZA resistant R-HL-60 cells with or without 5'-AZA treatment (upper panel), or HL-60 cells with or without 5'-AZA treatment (lower panel) respectively. Then immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting were performed. (B and C) ATM phosphorylated USP28 in response to 5'-AZA treatment. HL-60 cells expressing Flag-USP28 were treated with or without 5'-AZA for 6 h (B), or pre-treated with the ATM inhibitor KU-55933 for 1 h before 5'-AZA treatment (C), cell lysates were collected, and immunoprecipitation followed by immunoblotting. (D) USP28 was phosphorylated on its S/TQ motifs. HL-60 cells were transfected with vector, Flag-USP28-WT or Flag-USP28-3S/A, in which all the three S/TQ sites within the USP28 polypeptide were mutated to A (USP28-3S/A). 48 h later, immunoblotting was performed. (E) The interaction between KLHL2 and USP28 significantly decreased under 5'-AZA treatment. Cell lysates were collected from HL-60 cells with or without 5'-AZA treatment for 4 h and immunoprecipitated with an anti-KLHL2 antibody. (F) Phosphorylation-deficient USP28-3S/A stably bind to KLHL2 after 5'-AZA treatment. HL-60 cells expressing Flag-USP28 or Flag-USP28-3S/A were treated with 5'-AZA for 4 h, cell lysates were harvested. (G) UCK1 was phosphorylated by ATM in response to 5'-AZA treatment. HL-60 cells expressing Flag-UCK1-WT or Flag-UCK1-S145A were treated with or without 5'-AZA for 6 h (upper panel), or pre-treated with KU-55933 for 1 h before 5'-AZA treatment (lower panel), cells were harvested and subjected to immunoprecipitation followed by immunoblotting. (H) UCK1 was phosphorylated on its S/TQ motifs. HL-60 cells were transfected with vector, Flag-UCK1-WT or Flag-UCK1-S145A. 2 days later, these cells were treated with or without 5'-AZA for 6 h, then lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation followed by immunoblotting. (I) PLA of the interaction between UCK1 and KLHL2 in HL-60 cells with indicated treatment. (J) Based on the prediction in ZDOCK and pymol software, Ser145 of UCK1 lays in the interface between KLHL2 and UCK1, and Ser145 phosphorylation greatly enhances the binding affinity of UCK1 to KLHL2 by increasing hydrophilicity. (K) Structural docking modeling predicted in ZDOCK and pymol software reveals that Ser67 of USP28 lays in the interface between KLHL2 and USP28.