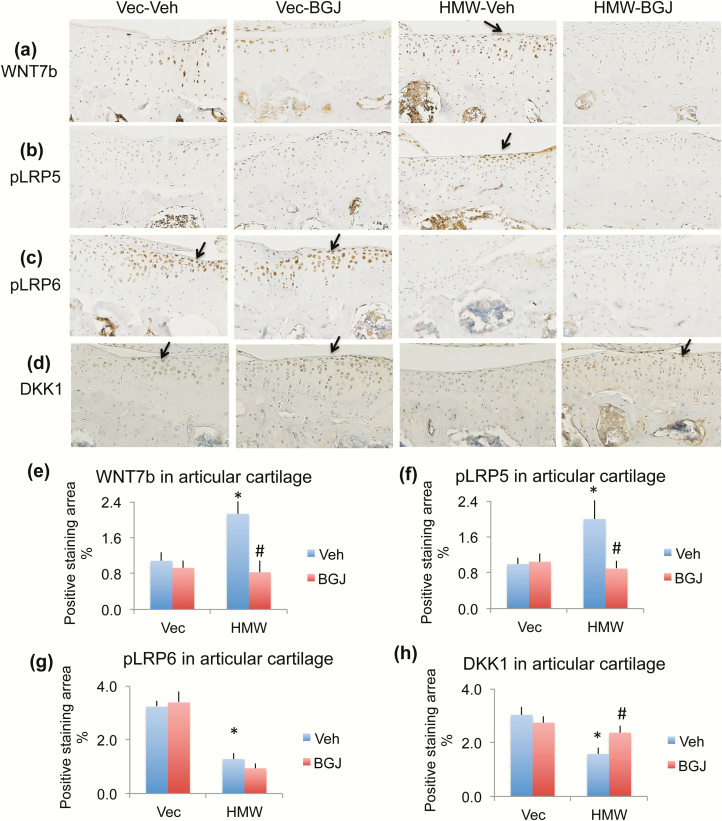
Figure 7.
Effect of BGJ on Wnt signaling component proteins in knees of VectorTg and HMWTg mice. Representative immunohistochemical staining images for (a) WNT7b, (b) phosphorylated LRP5 (pLRP5), (c) pLRP6, and (d) DKK1. Quantitative analysis of percentage of positive staining area for (e) WNT7b, (f) pLRP5, (g) pLRP6, and (h) DKK1 in articular cartilage. (a and e) WNT7b was greatly increased in HMWTg vehicle-treated cartilage compared with VectorTg vehicle-treated group, which was rescued with BGJ treatment, n = 7–9 males/group. (b and f) pLRP5 was strongly expressed in HMWTg vehicle-treated cartilage compared with VectorTg vehicle-treated group, which was rescued with BGJ treatment, n = 7–9 males/group. (c and g) pLRP6 protein was decreased in HMWTg vehicle-treated and HMWTg BGJ-treated articular cartilage, compared with VectorTg cartilage, n = 7–9 males/group. (d and h) DKK1 was significantly decreased in chondrocytes of articular cartilage of HMWTg-vehicle knees compared with VectorTg vehicle-treated mice, which was rescued with BGJ treatment, n = 4–5 males/group. *compared with VectorTg-vehicle group P < 0.05; #compared with corresponding vehicle group P < 0.05 by 2-way ANOVA.