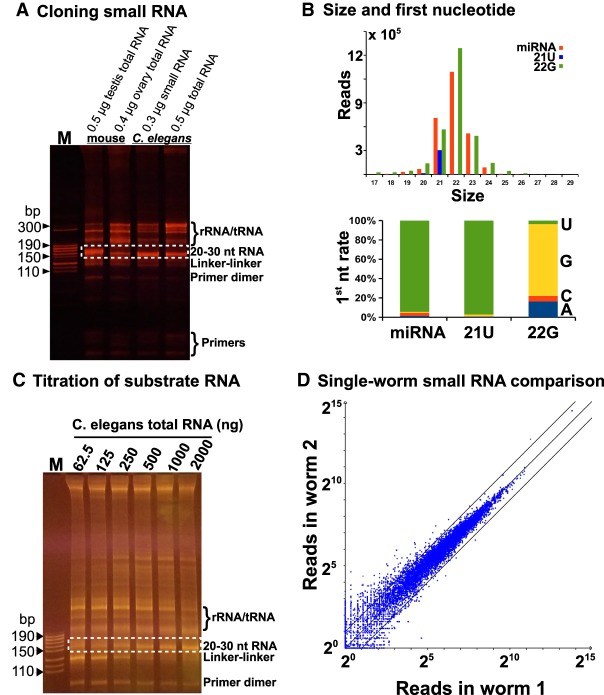
FIGURE 3.
Analysis of sensitivity and reliability of the cloning strategy. (A) 0.5 µg mouse testis total RNA, 0.4 µg mouse ovary total RNA, 0.3 µg C. elegans small RNA of size less than 200 nt, and 0.5 µg C. elegans total RNA were used to clone small RNA, and 5 µL of each PCR product was resolved on an 8% native PAGE gel. The inserted RNA in the PCR product is labeled on the right as well as the linker–linker ligation product, primer dimers, and free primers, as compared to the DNA size marker (M); the dotted box represents the 20–30 nt RNA inserts. (B) The size and first nucleotide analyses of miRNA, 21U, and 22G cloned using 0.5 µg C. elegans total RNA treated with PIR-1. (C) A twofold serial titration of C. elegans total RNA (62.5–2000 ng) was used to examine the cloning sensitivity threshold with the dot-boxed area representing the desired amplicon and “M” representing the DNA size marker. (D) The comparison of 22G derived from two single worms with each blue dot representing one gene, with “X” mapped to 22G reads in worm 1 and “Y” reads in worm 2.