Abstract
Background: Endometrial cancer (EC) is the fourth most common malignancy among women. Epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) and invasion have been identified as central cellular processes in tumor progression and malignant transformation. The function and molecular basis of microRNA-20a-5p (miR-20a-5p) in the development of EC are poorly defined. Methods: RT-qPCR assay was used to detect the levels of miR-20a-5p and signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) mRNA. Western blot assay was conducted to determine protein expression of STAT3, N-cadherin, Vimentin and E-cadherin. Cell invasive capacity was examined by transwell invasion assay. Bioinformatics analysis, luciferase reporter assay and RIP assay were performed to investigate the interaction between miR-20a-5p and STAT3 3’UTR. Results: miR-20a-5p expression was strikingly reduced in EC tissues and cells. Functional analysis revealed that miR-20a-5p overexpression inhibited EMT and invasion of EC cells. Further exploration showed that miR-20a-5p inhibited STAT3 expression by direct interaction. Moreover, the knockdown of STAT3 suppressed EMT and invasion of EC cells. Additionally, the depletion of STAT3 weakened miR-20a-5p downregulation-induced cell EMT and invasion in EC. Conclusion: miR-20a-5p inhibited EMT and invasion of EC cells by targeting STAT3, highlighting the vital roles of miR-20a-5p and STAT3 in the metastasis and malignant transformation of EC.
Keywords: microRNA-20a-5p, endometrial cancer, epithelial to mesenchymal transition, invasion, STAT3
Introduction
Endometrial cancer (EC), also called uterine corpus cancer, is the fourth most prevalent malignancy among women with an estimated 63230 new cases in the USA alone in 2018 [1,2]. Moreover, EC mortality ranks the seventh in cancer-related deaths in the USA with an estimated 11350 deaths in 2018 [1]. Although the prognosis for patients with early stage EC is relatively good, the 5-year relative survival rate for patients with distant EC is only 10-30% [1,3,4]. Hence, it is imperative to get a better understanding on the pathogenesis of EC so as to identify new strategies to manage this disease.
Epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT), a vital process in tumor progression and malignant transformation, is characterized by a switch from polarized immotile epithelial phenotype to motile mesenchymal phenotype and accompanied by the progressive decrease of epithelial markers and increase of mesenchymal markers [5,6]. It has been well documented that EMT plays critical roles in the invasive process of multiple tumors including EC [5,7]. However, the regulatory mechanisms of EMT and invasion signals have not been fully elucidated in EC.
MicroRNAs (miRNAs), a class of small evolutionarily conserved single-strand RNAs without protein coding potential, have been reported to be implicated in tumor initiation, progression, and metastasis [8,9]. Also, miRNAs play vital roles in the regulation of cell EMT and invasion in EC [6,10]. For example, microRNA-106b inhibited EMT and invasion of EC cells by targeting twist family bHLH transcription factor 1 [11]. MicroRNA-93 facilitated EMT, migration and invasion by downregulating forkhead box A1 expression in EC cells [12]. MicroRNA-20a (miR-20a) is a member of miR-17-92 cluster, which also contains miR-17, miR-18a, miR-19a, miR-19b-1 and miR-92a [13,14]. The upregulation of miR-17-92 cluster has been widely reported as an essential oncogenic event in multiple cancers [14-16]. However, some findings showed that miR-17-92 cluster could inhibit the development of cancers in certain settings [15,16]. For instance, miR-17-5p suppressed the metastasis of breast cancer cells and orthotopic xenografts [17], whereas Torres et al. pointed out that the inhibition of miR-92a curbed EC cell proliferation in vitro and xenograft growth in vivo [18]. Prior studies showed that miR-20a expression was markedly upregulated in endometriotic stromal cells and increased miR-20a facilitated the expression of elk-related tyrosine kinase (ERK)-related genes, which play vital roles in angiogenesis and endometrial proliferation [19], indicating a correlation between miR-20a and EC progression.
In the present study, we aimed to further investigate the roles and molecular mechanisms of miR-20a-5p in the EMT and invasion in EC cells.
Materials and methods
Clinical samples and cell culture
Forty-one pairs of EC tissues and adjacent normal tissues were collected from EC patients underwent hysterectomy at our hospital during August 2016 and October 2017. All patients did not receive any therapy prior to recruitment to the project. Our study was conducted with the written informed consents from all EC patients and the approval of Ethics Committee of Sichuan Academy of Medical Sciences, Sichuan Provincial People’s Hospital.
Human uterine epithelial cell line HES was obtained from Dr. Doug Kniss (Ohio State University, Columbus, OH). EC cell lines ECC-1 and Ishikawa were purchased from Cell Bank of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Shanghai, China). HES cells were cultured in DMEM medium(Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) containing 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS, Thermo Fisher Scientific) and 100 μM sodium pyruvate (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA). Ishikawa cells were maintained in MEM medium (Thermo Fisher Scientific) containing 5% FBS (Thermo Fisher Scientific), 300 mM L-glutamine (Sigma-Aldrich), and 5 μg/ml bovine insulin (Sigma-Aldrich). ECC-1 cells were grown in RPMI 1640 medium (Thermo Fisher Scientific) supplemented with 5% FBS (Thermo Fisher Scientific), 300 mM L-glutamine (Sigma-Aldrich), and 5 μg/ml bovine insulin (Sigma-Aldrich). All cells were maintained in an incubator containing 5% CO2 at 37°C.
Reagents and cell transfection
miR-20a-5p mimic and its negative control (miR-NC), miR-20a-5p inhibitor (anti-miR-20a-5p), its negative control (anti-miR-NC), small interference RNA targeting signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) (siSTAT3) and its scramble control (siNC) were purchased from GenePharma Co., Ltd (Shanghai, China). All these oligonucleotides were transfected into ECC-1 and Ishikawa cells by Lipofectamine 2000 reagent (Thermo Fisher Scientific) following the protocols of manufacturer.
Reverse transcription-quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) assay
Total RNA was extracted from EC tissues and cells using Trizol reagent (Thermo Fisher Scientific) according the instructions of manufacturer. For the expression determination of miR-20a-5p, RNA was converted into cDNA using TaqMan miRNA Reverse Transcription Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific) and real time-qPCR assay was performed using TaqMan MiRNA Assay Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific) with specific quantitative primer for miR-20a-5p and U6 snRNA. For STAT3 expression analysis, cDNA was synthesized by M-MLV reverse transcriptase (Thermo Fisher Scientific) and then quantified using Fast SYBR™ Green Master Mix (Thermo Fisher Scientific). The primer sequences of real-time PCR were presented as below: STAT3, 5’-ATCACGCCTTCTACAGACTGC-3’ (forward) and 5’-CATCCTGGAGATTCTCTACCACT-3’ (reverse); GAPDH, 5’-TCAACGACCACTTTGTCAAGCTCA-3’ (forward) and 5’-GCTGGTGGTCCAGGGGTCTTACT-3’ (reverse). U6 snRNA and GAPDH functioned as the internal controls of miR-20a-5p and STAT3, respectively.
Western blot assay
EC cells were collected using ice-cold PBS at 48 h post transfection and lysed using ice-cold RIPA buffer (Cell Signaling Technology, Danvers, MA, USA) supplemented with protease inhibitor cocktail (Thermo Fisher Scientific). Protein concentration was measured using a Pierce BCA Protein Assay Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific). Then, equal amounts of protein (40 μg/sample) were separated by SDS-PAGE and electro-blotted onto polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membranes (Millipore, Bedford, MA, USA). Next, the membranes were blocked with 5% skim milk for 1 h at room temperature and then probed overnight at 4°C with primary antibodies against N-cadherin (ab76011, 1:5000 dilution, Abcam, Cambridge, UK), Vimentin (ab92547, 1:2000 dilution, Abcam), E-cadherin (ab133597, 1:2000 dilution, Abcam), STAT3 (ab119352, 1:5000 dilution, Abcam) and β-actin (ab8227, 1:2000 dilution, Abcam). Subsequently, the membranes were incubated with horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-conjugated goat-anti-mouse (ab6789, 1:5000 dilution, Abcam) or goat-anti-rabbit (ab6721, 1:5000 dilution, Abcam) secondary antibody for 1 h at room temperature. Finally, HRP activity was detected using Pierce™ ECL Western Blotting Substrate (Thermo Fisher Scientific) and the relative intensity of protein bands were analyzed by Image J software (National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, USA).
Transwell invasion assay
EC cell invasive ability was assessed by transwell invasion assay. Briefly, cells were transfected with miRNA or siRNA for 24 h. Then, transfected cells (1×105 cells/well) in serum-free medium were plated in invasion chambers pre-coated with matrigel (8 μm pore size; BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA, USA) and medium containing 20% FBS was introduced into the 24-well plates. After 24 h of incubation, non-filtered cells were erased with a cotton swab. Cells in the bottom side of the membranes were fixed with methanol, stained with 0.1% crystal violet, and photographed using a light microscope. Invasive cell number was counted in 10 random fields.
Luciferase reporter assay
The partial segment of STAT3 3’UTR containing predicted miR-20a-5p binding sites was constructed into psiCHECK-2 luciferase reporter vector (Promega) to obtain wild type (WT) STAT3 reporter. Also, mutant type (MUT) STAT3 reporter containing mutant miR-20a-5p binding sites was generated using GeneArt™ Site-Directed Mutagenesis System (Thermo Fisher Scientific). Luciferase activities were measured using a dual luciferase reporter assay kit (Promega, Madison, WI, USA) referring to manufacturer’s protocols at 48 h after transfection.
RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP) assay
ECC-1 and Ishikawa cells were transfected with miR-NC or miR-20a-5p mimic. At 48 h after transfection, RIP assay was conducted with Magna RIP™ RNA-Binding Protein Immunoprecipitation Kit (Millipore) and primary antibodies against IgG (Millipore) and Argonaute 2 (Ago 2, Millipore) following the instructions of manufacturer. Then, STAT3 level in IgG or Ago 2 immunoprecipitation complex was quantified by RT-qPCR assay.
Statistical analysis
All experiments were repeated more than 3 times with the results expressed as mean ± standard deviation. Data analysis was conducted using GraphPad Prism 5 (GraphPad Sof-tware, San Diego, CA, USA). Difference analysis was performed using Student’s t-test (for the comparison between two group data) or one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) (for the comparison among multiple group data) with P<0.05 as statistically significant.
Results
miR-20a-5p expression was strikingly reduced in EC tissues and cells
First, RT-qPCR assay was carried out the measure miR-20a-5p level in 41 pairs of EC tissues and adjacent normal tissues. Results showed that miR-20a-5p level was remarkably reduced in 41 cases of EC tissues as compared to that in adjacent normal tissues (Figure 1A). Also, a notable downregulation of miR-20a-5p level was observed in EC cell lines (ECC-1 and Ishikawa) compared with human normal uterine epithelial cell line (HES) (Figure 1B). In a word, these data indicated a close correlation of miR-20a-5p with the pathogenesis of EC.
Figure 1.
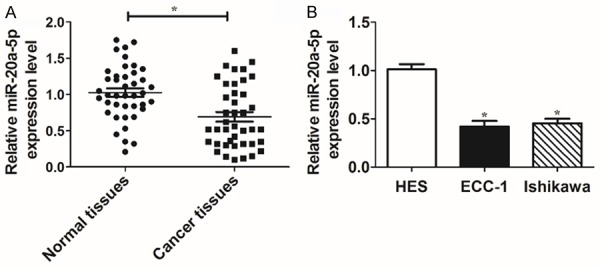
miR-20a-5p expression was strikingly reduced in EC tissues and cells. A and B: RT-qPCR assay was conducted to detect miR-20a-5p level in 41 pairs of EC tissues and adjacent normal tissues, HES cells, ECC-1 cells, and Ishikawa cells. *P<0.05. A: Student’s t test, B: One-way ANOVA and Student’s t test.
miR-20a-5p overexpression inhibited EMT and invasion of EC cells
To further explore the function of miR-20a-5p in the development of EC, miR-20a-5p mimics were transfected into ECC-1 and Ishikawa cells. Firstly, RT-qPCR assay revealed that the introduction of miR-20a-5p mimic resulted in the marked upregulation of miR-20a-5p level in ECC-1 and Ishikawa cells (Figure 2A), hinting that miR-20a-5p mimic could be used for the subsequent gain-of-function experiments. Next, the effect of miR-20a-5p overexpression on EMT and invasion was tested in ECC-1 and Ishikawa cells. As presented in Figure 2B-E, enforced expression of miR-20a-5p resulted in the conspicuous reduction of N-cadherin (a mesenchymal cell marker) and vimentin (a mesenchymal cell marker) protein levels and obvious increase of E-cadherin (an epithelial cell marker) protein level in ECC-1 (Figure 2B and 2C) and Ishikawa cells (Figure 2D and 2E), indicating that miR-20a-5p inhibited the EMT of EC cells. Moreover, transwell invasion assay showed that miR-20a-5p overexpression resulted in the notable reduction of invasive ability of ECC-1 and Ishikawa cells compared with control cells (Figure 2F and 2G). In sum, these data showed that ectopic expression of miR-20a-5p suppressed EMT and invasion of EC cells.
Figure 2.
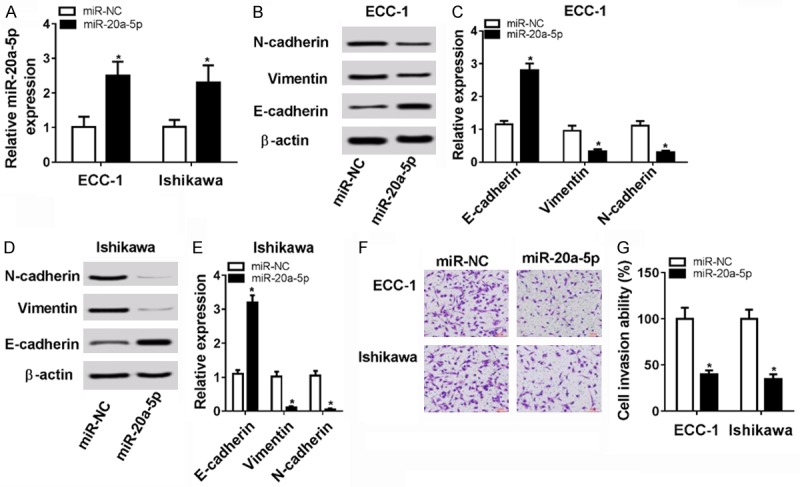
miR-20a-5p overexpression inhibited cell EMT and invasion in EC. A-F: ECC-1 and Ishikawa cells were transfected with miR-20a-5p mimic or miR-NC. A: The level of miR-20a-5p was determined by RT-qPCR assay at 48 h after transfection. B-E: Protein levels of N-cadherin, vimentin, and E-cadherin were measured by western blot assay at 48 h post transfection. F, G: Cell invasive capacity was assessed by transwell invasion assay at 48 h upon transfection. *P<0.05. A-F: Student’s t test.
STAT3 was a target of miR-20a-5p
Bioinformatics test by TargetScan online analysis website showed that there existed some complementary sites between miR-20a-5p and STAT3 3’UTR (Figure 3A). To further confirm this prediction, a dual luciferase reporter assay was performed in ECC-1 and Ishikawa cells. Results showed that the transfection of miR-20a-5p mimic triggered a marked downregulation of luciferase activity of wild type STAT3 reporter in ECC-1 and Ishikawa cells (Figure 3B and 3C). On the contrary, the luciferase activity of wild type STAT3 reporter was significantly elevated in ECC-1 and Ishikawa cells transfected with anti-miR-20a-5p (Figure 3D and 3E). However, the upregulation or downregulation of miR-20a-5p had no influence on luciferase activity of mutant type STAT3 reporter in ECC-1 and Ishikawa cells (Figure 3B-E), indicating that miR-20a-5p could interact with STAT3 3’UTR by predicted binding sites. Next, western blot assay further disclosed that ectopic expression of miR-20a-5p resulted in an obvious reduction of STAT3 protein level, whereas miR-20a-5p silencing induced STAT3 expression in ECC-1 and Ishikawa cells (Figure 3F). Moreover, RIP assay evinced that miR-20a-5p overexpression resulted in the increase of STAT3 enrichment level in Ago2 immunoprecipitation complex in ECC-1 and Ishikawa cells, further implying the potential interaction between miR-20a-5p and STAT3 (Figure 3G). Taken together, these data showed that miR-20a-5p inhibited STAT3 expression by direct interaction in ECC-1 and Ishikawa cells.
Figure 3.
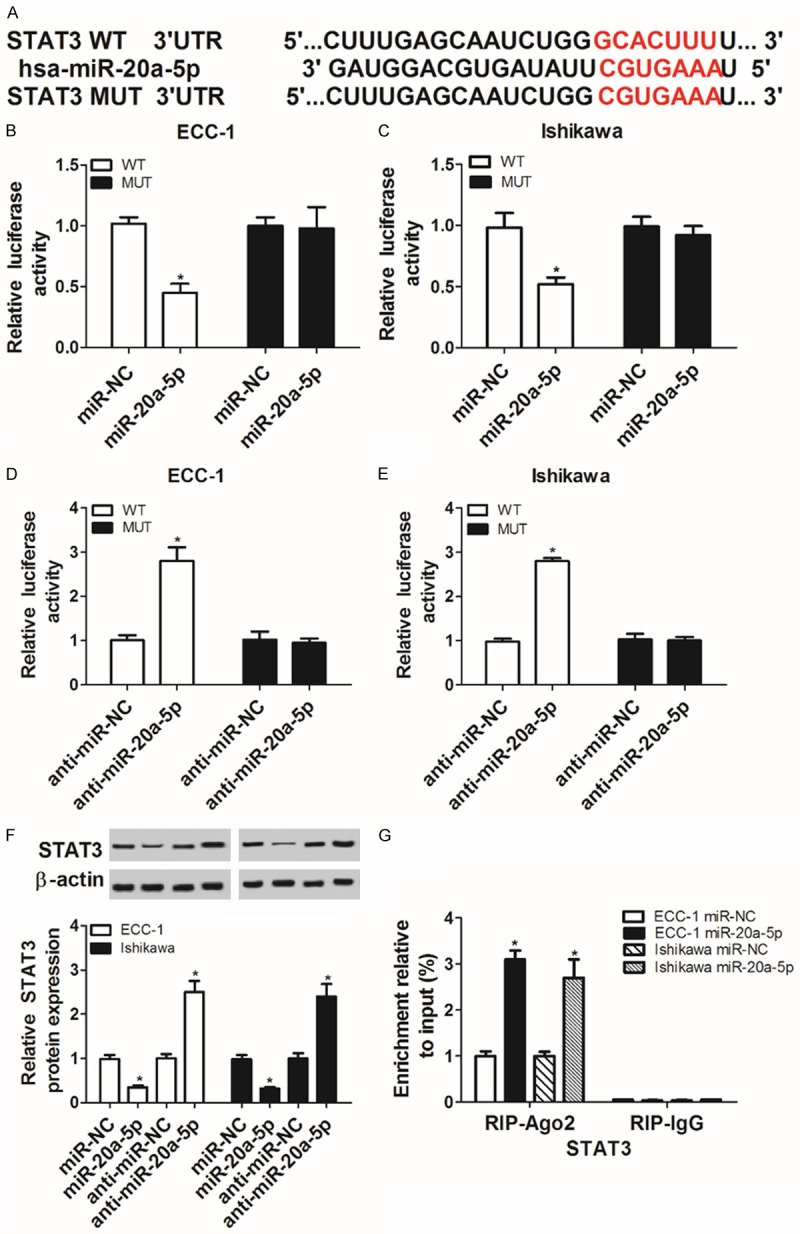
STAT3 is a target of miR-20a-5p. A: The complementary sites between miR-20a-5p and STAT3 3’UTR and the mutant sites in mutant type STAT3 reporter. B-E: The effect of miR-20a-5p overexpression or depletion on luciferase activity of wild type or mutant type STAT3 reporter was measured by dual luciferase reporter assay in ECC-1 and Ishikawa cells at 48 h after transfection. F: ECC-1 and Ishikawa cells were transfected with miR-NC, miR-20a-5p mimic, anti-miR-NC or anti-miR-20a-5p, followed by the detection of STAT3 protein level at 48 h following transfection. G: ECC-1 and Ishikawa cells were transfected with miR-20a-5p mimic or miR-NC. Then, RIP assay was conducted using IgG or Ago2 antibody at 48 h after transfection. Next, STAT3 mRNA level in IgG or Ago2 immunoprecipitation complex was determined by RT-qPCR assay. *P<0.05. A-G: Student’s t test.
The knockdown of STAT3 suppressed EMT and invasion of EC cells
Next, we further demonstrated that the transfection of siSTAT3 resulted in the marked reduction of STAT3 mRNA (Figure 4A) and protein (Figure 4B) levels in ECC-1 and Ishikawa cells, meaning that siSTAT3 had potential applied values in the exploration of STAT3 functions. Moreover, protein levels of N-cadherin and vimentin were strikingly reduced and E-cadherin protein level was noticeably increased in STAT3-depleted ECC-1 and Is-hikawa cells (Figure 4C-F). Additionally, a prominent reduction in cell invasive ability was observed in ECC-1 and Ishikawa cells following the knockdown of STAT3 (Figure 4G). In summary, these data manifested that STAT3 silencing inhibited EMT and invasion of EC cells.
Figure 4.
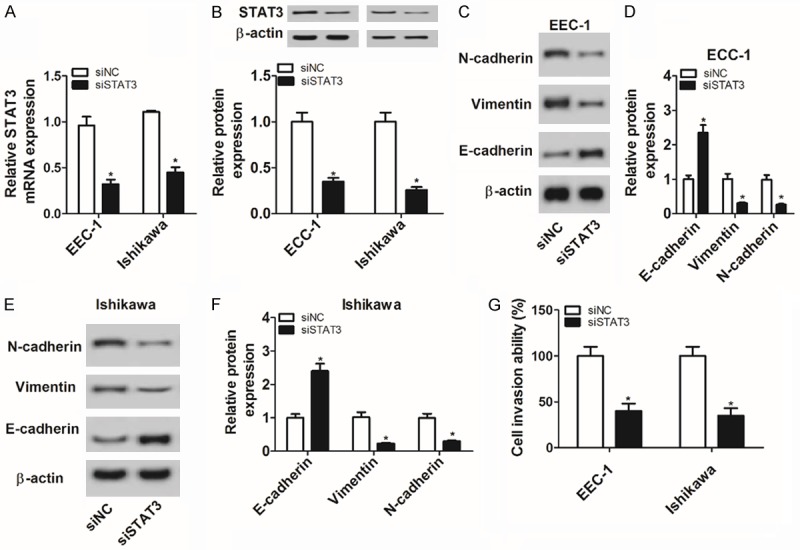
The knockdown of STAT3 suppressed cell EMT and invasion in EC. A-G: ECC-1 and Ishikawa cells were transfected with siSTAT3 or siNC. A: At 48 h after transfection, STAT3 mRNA level was measured by RT-qPCR assay. B-F: Protein levels of STAT3, N-cadherin, vimentin and E-cadherin were determined by western blot assay at 48 h following transfection. G: Cell invasive capacity was evaluated by transwell invasion assay at 48 h upon transfection. *P<0.05. A-G: Student’s t test.
The depletion of STAT3 weakened the promotive effect of miR-20a-5p loss on cell EMT and invasion in EC
Next, we further demonstrated that the depletion of miR-20a-5p induced EMT and invasion of ECC-1 and Ishikawa cells, as evidenced by increased N-cadherin and vimentin expression, reduced E-cadherin expression and elevated cell invasive capacity in anti-miR-20a-5p-transfected cells compared with anti-miR-NC-transfected cells (Figure 5A-E). Moreover, the silencing of STAT3 resulted in the downregulation of N-cadherin and vimentin protein levels and the upregulation of E-cadherin protein level in ECC-1 and Ishikawa cells transfected with anti-miR-20a-5p (Figure 5A-D). Also, cell invasive ability was strikingly reduced in miR-20a-5p-depleted ECC-1 and Ishikawa cells following the knockdown of STAT3 (Figure 5E). In other words, these data showed that the knockdown of STAT3 abrogated miR-20a-5p loss-induced cell EMT and invasion in EC.
Figure 5.
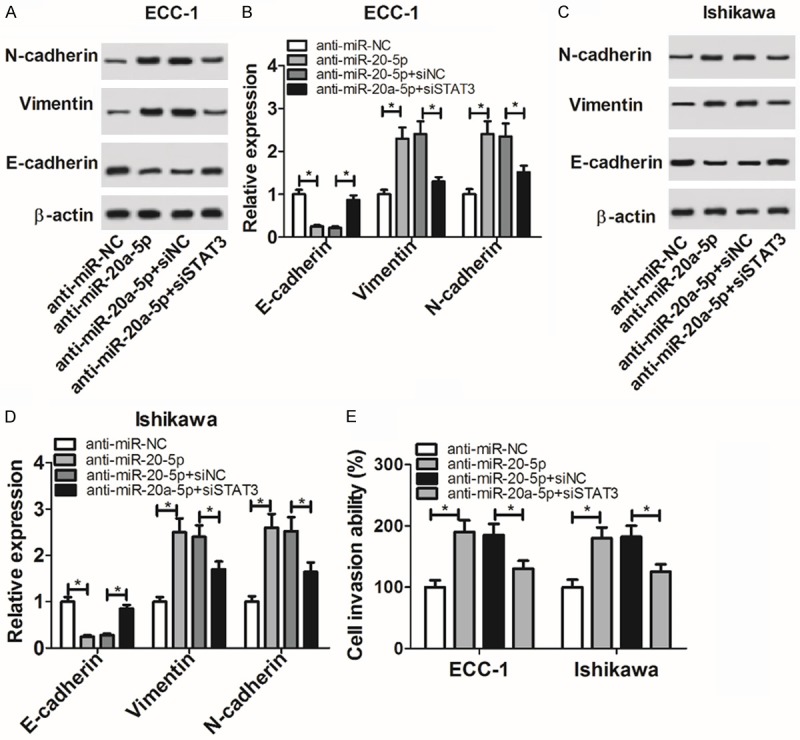
The depletion of STAT3 weakened the promotive effect of miR-20a-5p loss on EC cell EMT and invasion. A-E: ECC-1 and Ishikawa cells were transfected with anti-miR-NC, anti-miR-20a-5p, anti-miR-20a-5p + siNC or anti-miR-20a-5p + siSTAT3. A-D: At 48 h after transfection, protein levels of N-cadherin, vimentin, and E-cadherin were detected by western blot assay. E: Cell invasive capacity was evaluated by transwell invasion assay at 48 h upon transfection. *P<0.05. A-E: Student’s t test.
Discussion
EC is responsible for 4.8% of new-diagnosed cancer cases and 2.1% of cancer deaths in women globally with higher incidence, mortality and disease burden in developed areas and countries [3,20,21]. Moreover, women with EC have a higher risk to die from cardiovascular diseases [22]. Over the past decades, mounting miRNAs have been identified as vital players in the pathogenesis of EC with potential values of diagnosis, screening, detection, or therapy [23,24].
Prior studies showed that miR-20a could exert oncogenic or tumor suppressive roles in cancers. For example, miR-20a-5p overexpression facilitated cell proliferation and migration by downregulating runt related transcription factor 3 (RUNX3) expression in hepatocellular cancer [25]. The depletion of miR-20a hampered the migration and invasion of prostate cancer cells in vitro and suppressed tumor growth in vivo by targeting ABL2 tyrosine kinase [26]. Conversely, Zhou et al. showed that miR-20a inhibited cell metastasis and proliferation by targeting LIM kinase-1 (LIMK1) in cutaneous squamous cell cancer [27]. Zhao et al. pointed out that enforced expression of miR-20a-5p inhibited cell proliferation, migration and invasion, and induced cell apoptosis by targeting high mobility group AT-hook 2 (HMGA2) in breast cancer [28]. In the present study, we demonstrated that miR-20a-5p expression was strikingly downregulated in EC tissues and cells. Functional analysis showed that enforced expression of miR-20a-5p inhibited EMT and invasion of EC cells.
It is well known to us that miRNAs can exert their functions by regulating expression or translation of target mRNAs. Hence, bioinformatics analysis by TargetScan online website was used to seek for potential targets of miR-20a-5p. Results showed that miR-20a-5p had a chance to interact with STAT3 3’UTR, which was further confirmed by subsequent luciferase reporter assay and RIP assay.
Transcription factor STAT3, a member of STAT family, has been widely reported to be constitutively activated with potential oncogenic effect in multiple cancers [29,30]. For instance, Saini et al. showed that the knockdown or inhibition of STAT3 curbed tumor growth and metastasis in mouse xenograft models of ovarian cancer [31]. However, some evidences showed that STAT3 could act as a tumor suppressor in some circumstances. For example, the knockdown of STAT3 promoted cancer progression in a PTEN-deficient prostate cancer (PCa) mouse model and the loss of STAT3 expression was associated with poor prognosis and advanced pathological status in PCa [32]. Moreover, a prior study pointed out that STAT3 phosphorylation level was markedly elevated and positively associated with the expression of downstream antiapoptotic genes (e.g. Bcl-xL, survivin, and Mcl-1) in human EC tissues [33]. Additionally, the silence of STAT3 weakened the promotive effect of adipose-derived stem cell medium on proliferation and invasion of EC cells [34]. Li et al. showed that the knockdown of STAT3 suppressed cell proliferation, migration and invasion and induced cell apoptosis in EC [35].
Our study further demonstrated that the silence of STAT3 hampered cell EMT progression and induced the reduction of invasive ability in EC, which was in line with a prior study [35]. Additionally, restoration experiments further showed that the knockdown of STAT3 abrogated miR-20a-5p downregulation-induced cell EMT and invasion in EC.
Taken together, our data showed that miR-20a-5p suppressed cell EMT and invasion by targeting STAT3 in EC, further elucidating the critical roles and molecular mechanism of miR-20a-5p in development of EC cells and providing some candidate targets for the diagnosis and therapy of EC. However, our study only tested the roles of miR-20a-5p and STAT3 on EC cell EMT and invasion in vitro. It is indispensable to further confirm our conclusion by in vivo experiments.
Disclosure of conflict of interest
None.
References
- 1.Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:11. doi: 10.3322/caac.21442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Buhtoiarova TN, Brenner CA, Singh M. Endometrial carcinoma: role of current and emerging biomarkers in resolving persistent clinical dilemmas. Am J Clin Pathol. 2016;145:8–21. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/aqv014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Mcalpine JN, Temkin SM, Mackay HJ. Endometrial cancer: not your grandmother’s cancer. Cancer. 2016;122:2787–2798. doi: 10.1002/cncr.30094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Morice P, Leary A, Creutzberg C, Abu-Rustum N, Darai E. Endometrial cancer. Lancet. 2016;387:1094–1108. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)00130-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Zaravinos A. The regulatory role of MicroRNAs in EMT and cancer. J Oncol. 2015;2015:865816. doi: 10.1155/2015/865816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Kent CN, Guttilla Reed IK. Regulation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in endometrial cancer: connecting PI3K, estrogen signaling, and microRNAs. Clin Transl Oncol. 2016;18:1056–1061. doi: 10.1007/s12094-016-1492-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Makker A, Goel MM. Tumor progression, metastasis and modulators of EMT in endometrioid endometrial carcinoma: an update. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2016;23:R85–R111. doi: 10.1530/ERC-15-0218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Shah MY, Ferrajoli A, Sood AK, Lopezberestein G, Calin GA. MicroRNA therapeutics in cancer-an emerging concept. Ebiomedicine. 2016;12:34–42. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2016.09.017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Oliveto S, Mancino M, Manfrini N, Biffo S. Role of microRNAs in translation regulation and cancer. World J Biol Chem. 2017;8:45–56. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v8.i1.45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Stope MB, Koensgen D, Weimer J, Paditz M, Burchardt M, Bauerschlag D, Mustea A. The future therapy of endometrial cancer: microRNA’s functionality, capability, and putative clinical application. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2016;294:889–895. doi: 10.1007/s00404-016-4194-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Dong P, Kaneuchi M, Watari H, Sudo S, Sakuragi N. MicroRNA-106b modulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition by targeting TWIST1 in invasive endometrial cancer cell lines. Mol Carcinog. 2014;53:349–359. doi: 10.1002/mc.21983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Chen S, Chen X, Sun KX, Xiu YL, Liu BL, Feng MX, Sang XB, Zhao Y. MicroRNA-93 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition of endometrial carcinoma cells. PLoS One. 2016;11:e0165776. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0165776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.van Haaften G, Agami R. Tumorigenicity of the miR-17-92 cluster distilled. Genes Dev. 2010;24:1–4. doi: 10.1101/gad.1887110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Fuziwara CS, Kimura ET. Insights into regulation of the miR-17-92 cluster of mirnas in cancer. Front Med (Lausanne) 2015;2:64. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2015.00064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Xiang J, Wu J. Feud or friend? The role of the mir-17-92 cluster in tumorigenesis. Curr Genomics. 2010;11:129–135. doi: 10.2174/138920210790886853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Mendell JT. miRiad roles for the miR-17-92 cluster in development and disease. Cell. 2008;133:217–222. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.04.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Fan M, Sethuraman A, Brown M, Sun W, Pfeffer LM. Systematic analysis of metastasis-associated genes identifies miR-17-5p as a metastatic suppressor of basal-like breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2014;146:487–502. doi: 10.1007/s10549-014-3040-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Torres A, Kozak J, Korolczuk A, Wdowiak P, Domańska-Glonek E, Maciejewski R, Torres K. In vitro and in vivo activity of miR-92a-locked nucleic acid (LNA)-inhibitor against endometrial cancer. BMC Cancer. 2016;16:822. doi: 10.1186/s12885-016-2867-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Lin SC, Wang CC, Wu MH, Yang SH, Li YH, Tsai SJ. Hypoxia-induced microRNA-20a expression increases ERK phosphorylation and angiogenic gene expression in endometriotic stromal cells. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012;97:E1515–1523. doi: 10.1210/jc.2012-1450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortettieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65:87–108. doi: 10.3322/caac.21262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D, Bray F. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 2015;136:E359–E386. doi: 10.1002/ijc.29210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Felix AS, Bower JK, Pfeiffer RM, Raman SV, Cohn DE, Sherman ME. High cardiovascular disease mortality after endometrial cancer diagnosis: results from the surveillance, epidemiology, and end results (SEER) database. Int J Cancer. 2017;140:555–564. doi: 10.1002/ijc.30470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Yanokura M, Banno K, Iida M, Irie H, Umene K, Masuda K, Kobayashi Y, Tominaga E, Aoki D. MicroRNAS in endometrial cancer: recent advances and potential clinical applications. EXCLI J. 2015;14:190–198. doi: 10.17179/excli2014-590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Sianou A, Galyfos G, Moragianni D, Andromidas P, Kaparos G, Baka S, Kouskouni E. The role of microRNAs in the pathogenesis of endometrial cancer: a systematic review. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2015;292:271–282. doi: 10.1007/s00404-015-3660-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Chen Y, Wang X, Cheng J, Wang Z, Jiang T, Hou N, Liu N, Song T, Huang C. MicroRNA-20a-5p targets RUNX3 to regulate proliferation and migration of human hepatocellular cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 2016;36:3379. doi: 10.3892/or.2016.5144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Qiang XF, Zhang ZW, Liu Q, Sun N, Pan LL, Shen J, Li T, Yun C, Li H, Shi LH. miR-20a promotes prostate cancer invasion and migration through targeting ABL2. J Cell Biochem. 2014;115:1269–1276. doi: 10.1002/jcb.24778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Zhou J, Liu R, Luo C, Zhou X, Xia K, Chen X, Zhou M, Zou Q, Cao P, Cao K. MiR-20a inhibits cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma metastasis and proliferation by directly targeting LIMK1. Cancer Biol Ther. 2014;15:1340–1349. doi: 10.4161/cbt.29821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Zhao W, Geng D, Li S, Chen Z, Sun M. LncRNA HOTAIRinfluences cell growth, migration, invasion, and apoptosis via the miR-20a-5p/HMGA2axis in breast cancer. Cancer Med. 2018;7:842–855. doi: 10.1002/cam4.1353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- 29.Gkouveris I, Nikitakis N, Sauk J. STAT3 signaling in cancer. J Cancer Ther. 2015;6:709–726. [Google Scholar]
- 30.Zhang HF, Lai R. STAT3 in cancer-friend or foe? Cancers. 2014;6:1408–1440. doi: 10.3390/cancers6031408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Saini U, Naidu S, Elnaggar AC, Bid HK, Wallbillich JJ, Bixel K, Bolyard C, Suarez AA, Kaur B, Kuppusamy P. Elevated STAT3 expression in ovarian cancer ascites promotes invasion and metastasis: a potential therapeutic target. Oncogene. 2017;36:168–181. doi: 10.1038/onc.2016.197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Pencik J, Schlederer M, Gruber W, Unger C, Walker SM, Chalaris A, Marié IJ, Hassler MR, Javaheri T, Aksoy O, Blayney JK, Prutsch N, Skucha A, Herac M, Krämer OH, Mazal P, Grebien F, Egger G, Poli V, Mikulits W, Eferl R, Esterbauer H, Kennedy R, Fend F, Scharpf M, Braun M, Perner S, Levy DE, Malcolm T, Turner SD, Haitel A, Susani M, Moazzami A, Rose-John S, Aberger F, Merkel O, Moriggl R, Culig Z, Dolznig H, Kenner L. STAT3 regulated ARF expression suppresses prostate cancer metastasis. Nat Commun. 2015;6:7736. doi: 10.1038/ncomms8736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Chen CL, Hsieh FC, Lieblein JC, Brown J, Chan C, Wallace JA, Cheng G, Hall BM, Lin J. Stat3 activation in human endometrial and cervical cancers. Br J Cancer. 2007;96:591. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6603597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Chu Y, Wang Y, Peng W, Xu L, Liu M, Li J, Hu X, Li Y, Zuo J, Ye Y. STAT3 activation by IL-6 from adipose-derived stem cells promotes endometrial carcinoma proliferation and metastasis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;500:626–631. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.04.121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Li Y, Zhang Z, Liu X, Huang T, He W, Shen Y, Liu X, Hong K, Cao Q. miR-124 functions as a tumor suppressor in the endometrial carcinoma cell line HEC-1B partly by suppressing STAT3. Mol Cell Biochem. 2014;388:219–231. doi: 10.1007/s11010-013-1913-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


