Abstract
Background: UBE2T, a human E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme, is overexpressed in some human cancers, suggesting the biological significance of UBE2T in cancer progression. However, its role in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) progression is still unclear. This study was aimed to investigate the critical roles of UBE2T in NSCLC progression. Methods: QRT-PCR and Western blot were performed to explore the expression levels of UBE2T in NSCLC tissues and cell lines. Cell proliferation was detected using MTT assay and EdU assay. Cell invasion and migration were evaluated using transwell assay. Results: Our data showed that UBE2T expression was upregulated in NSCLC tissues and cell lines. Functionally, UBE2T knockdown suppressed NSCLC cell proliferation, migration and invasion in vitro. Mechanistic investigations revealed that UBE2T downregulation suppressed the activity of Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Conclusion: These results suggested that UBE2T play critical roles in the progression of NSCLC and could be a potential therapeutic target for the treatment of NSCLC patients.
Keywords: UBE2T, NSCLC, progression, Wnt/β-catenin
Introduction
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) accounts for approximately 85% of all lung cancers, which are the primary cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide [1,2]. Actually, lung carcinogenesis is a complicated biological process due to mutual dysregulation of different tumor-related genes [3]. Although the treatment including surgery, radiotherapy, and platinum-based combination chemotherapy for NSCLC has improved a lot in recent years, the prognosis of NSCLC remains poor and the five-year survival rate is less than 15% [4]. Therefore, it is still urgent to explore precise and special markers for improving the survival of NSCLC patients.
Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2T (UBE2T; also known as HSPC150) is a member of E2 the family in the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway, a complex protein degradation system that serves crucial roles in extensive biological processes, including cell cycle control, signal transduction and tumorigenesis [5,6]. For example, Wen et al showed that elevated expression of UBE2T exhibited oncogenic properties in human prostate cancer [7]. Gong et al showed that UBE2T silencing suppressed proliferation and induced cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in bladder cancer cells [8]. Hu et al found that UBE2T promoted nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell proliferation, invasion, and metastasis by activating the AKT/GSK3β/β-catenin pathway [9]. But reports about UBE2T in NSCLC are rare and the potential role of UBE2T in NSCLC progression is still unclear.
The current study showed that the expression of UBE2T was upregulated in human NSCLC tissues and cell lines. Decreased expression UBE2T suppressed NSCLC cells proliferation, migration and invasion in vitro. Moreover, our data showed that UBE2T downregulation could suppress the activity of the wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in NSCLC cells. These findings revealed a potential oncogenic role of UBE2T in NSCLC, and suggested that it might serve as a therapeutic target for the treatment of lung cancer.
Materials and methods
Patients and samples
A total of 10 NSCLC tissue samples and matched non-tumor adjacent tissues specimens were obtained from patients who had pathologically confirmed as NSCLC in Huaihe Hospital of Henan University. None of the patients had undergone adjuvant treatments including radiotherapy, chemotherapy or immunotherapy before surgical resection. After resection, all tissues were immediately snap-frozen in liquid nitrogen, and then stored at -80°C until use. The protocol of this study was approved by the Ethical Committee of Huaihe Hospital of Henan University, and all patients signed the informed consent.
Cell lines and cell culture
The human NSCLC cell lines (A549, H1299, and Calu-3) and the immortalized human bronchial epithelial cell line (BEAS-2B) were purchased from Cell Bank of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Shanghai, China). All cell lines were cultured with RPMI1640 medium, 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) and 1× penicillin/streptomycin at 37°C and 5% CO2 incubator according to the instructions recommended by American Type Culture Collection.
SiRNA transfection
UBE2T siRNA (si-UBE2T) and scrambled siRNA (si-NC) were purchased from Life Technologies. The sequences of si-UBE2T and si-NC were GCUGACAUAUCCUCAGAAUTT and UUCUCCGAACGUGUCACGUTT, respectively. A549 and Calu-3 cells were transfected with si-UBE2T or si-NC using Lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen) in accordance with the manufacturer’s instruction. After 24 h of transfection, the cells were collected for the following studies. QRT-PCR assays were performed to determine the transfection efficiency.
Quantitative real-time PCR
Total RNA was isolated from cells using TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen) according to the manufacturer’s protocol, and then the first cDNA was synthesized using a Reverse Transcription Kit (Takara). QRT-PCR was performed with the Applied Biosystems 7900 Fast Real-Time PCR system (Applied Biosystems) to quantify UBE2T. GAPDH was taken as the endogenous control and the sequences of primers were as follows: UBE2T, forward 5’-CAAATATTAGGTGGAGCCAACAC-3’ and reverse 5’-TAGATCACCTTGGCAAAGAACC-3’, GAPDH, forward 5’-GCCGCATCTTCTTTTGCGTCGC-3’ and reverse 5’-TCCCGTTCTCAGCCTTGACGGT’. The relative expression levels of UBE2T were calculated by 2-ΔΔCt method and all experiments were presented in triplicate.
Western blot
Cells were lysed and proteins were separated by 10% SDS polyacrylamide gel. After electrotransferred to polyvinylidene fluoride membranes (Millipore), the membranes were probed with primary antibody (1:200) (Cell signaling) overnight at 4°C. Then the membranes were incubated with horseradish peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibody (1:1000; Cell signaling) for 1 h at 37°C. GAPDH was used as an internal control. The bands were obtained with enhanced chemiluminescence detection system (Pierce, USA).
MTT assay
24 h after transfection, cells were plated into 96 well plate at a density of 3000 cells/well and cultured with 200 ul RPMI1640 medium containing 10% FBS at 37°C and 5% CO2. Each group had 6 replicates and meanwhile a blank group was set up containing RPMI1640 medium only and no added cells. 10 ul MTT was added at 80% density and the 96 well plate was incubated for 4 hours followed by the supernatant carefully removed and replaced with 150 μl DMSO. The optical density (OD) was measured using a plate reader at 570 nm after oscillated for 10 min.
EdU proliferation assay
48 h after transfection, cell proliferation was detected using the incorporation of 5-ethynyl-29-deoxyuridine (EdU) with the EdU Cell Proliferation Assay Kit (Ribobio). Briefly, the cells were incubated with 50 mM EdU for 3 h before fixation, permeabilization and EdU staining, which were performed according to the manufacturer’s protocol. The cell nuclei were stained with DAPI (Sigma) at a concentration of 1 mg/mL for 10 min. The proportion of cells that incorporated EdU was determined by fluorescence microscopy.
Cell cycle assay
Cell cycle was investigated by flow cytometry analysis. Cells were harvested and fixed in 70% ethanol overnight. Then, cells were added with RNase (50 μg/mL) and PI (50 μg/mL) (BD). After incubation for 30 min, samples were subjected to flow cytometer (FACScan, BD) for analysis. Data were analyzed using CELL Quest 3.0 software.
Cell migration and invasion assay
Cell migration assay was carried out using transwell insert chambers (8 μm pore size, Corning). Approximate 5×104 cells in 200 μl serum-free RPMI-1640 medium were seeded into the upper chamber of the transwell chamber. 600 μl RPMI-1640 medium containing 10% FBS as chemoattractant was added to the lower chamber. After incubation for 48 h, non-migrating cells were removed by cotton swab, and the migrating cells on the lower side of the insert filter were fixed using methanol and stained with 0.1% crystal violet for 20 min. The number of migrating cells was counted in five random visual fields and imaged using the light microscope (Olympus). Invasion assay was performed using transwell insert chambers coated with Matrigel (BD Biosciences).
Statistical analysis
The data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD) and analyzed by SPSS14.0 (IBM). Differences between groups were analyzed using Student’s t test. P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
UBE2T was upregulated in NSCLC
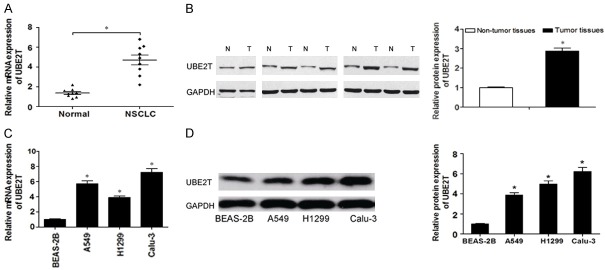
To determine whether UBE2T was dysregulated in NSCLC, we analyzed UBE2T expression in NSCLC tissues and adjacent non-tumor tissues by using qRT-PCR and western blot. As shown in Figure 1A and 1B, UBE2T was significantly increased in NSCLC tissues compared with the adjacent normal tissues. Aberrant expression of UBE2T in cancer tissues indicated that UBE2T might play an important role in the progression of NSCLC. Furthermore, the expression of UBE2T was assessed in NSCLC cell lines (A549, H1299 and Calu-3) and the immortalized human bronchial epithelial cell line (BEAS-2B). Our result demonstrated that the expression of UBE2T was significantly higher in NSCLC cells than that in BEAS-2B cells (Figure 1C and 1D). These data indicated that UBE2T might contribute to the development and progress of NSCLC.
Figure 1.
UBE2T is upregulated in NSCLC tissues and cell lines. A. The relative expression of UBE2T in NSCLC tissues and adjacent non-cancer tissues was determined by qRT-PCR. B. The protein expression of UBE2T in NSCLC tissues and adjacent non-cancer tissues was determined by western blot (n=5). C. UBE2T expression was analyzed by qRT-PCR in NSCLC cell lines (A549, H1299, SK-MES-1 and Calu-3) and BEAS-2B cells. D. UBE2T expression was analyzed by western blot in NSCLC cell lines (A549, H1299, and Calu-3) and BEAS-2B cells. N, non-cancer tissues; T: tumor tissues. *P<0.05.
UBE2T promoted NSCLC cells proliferation
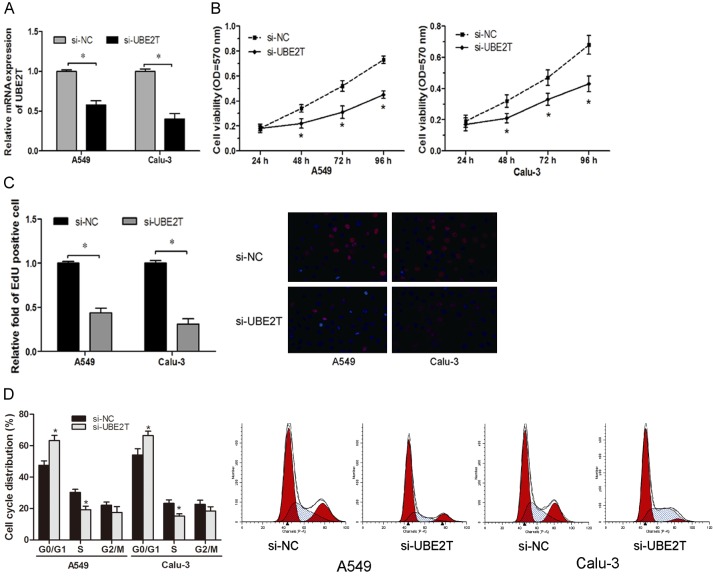
Since UBE2T might act as an oncogene in NSCLC, we explored the biological function of UBE2T by employing specific siRNAs and confirmed knockdown efficiency using qRT-PCR (Figure 2A). MTT assay showed that UBE2T inhibition significantly decreased the proliferation ability of NSCLC cells compared with control cells (Figure 2B). EdU proliferation assay showed that the percentage of EdU positive cells was significantly decreased cells transfected with si-UBET2 (Figure 2C). Furthermore, flow cytometry analysis was used to further determine whether the function of UBE2T on NSCLC cell proliferation was by altering cell-cycle progression. We found that the percentage of cells in G0/G1 phase significantly increased with UBE2T silencing in NSCLC cell lines (Figure 2D). These data indicated that UBE2T regulated NSCLC cells proliferation by mediating cell cycle.
Figure 2.
UBE2T promotes NSCLC cell proliferation. A. qRT-PCR analysis was performed to detect the expression of UBE2T in A549 and Calu-3 cells transfected with si-UBE2T or si-NC. B. Cell proliferation was measured by MTT assay in A549 and Calu-3 cells transfected with si-UBE2T or si-NC. C. EdU proliferation assay was used to detect the proliferation of cells transfected with si-UBE2T or si-NC. D. Flow cytometry assay showed that UBE2T depletion significantly increased the percentage of G0/G1 stage in A549 and Calu-3 cells. *P<0.05.
UBE2T promoted NSCLC cells migration and invasion
The crucial process of cancer progression was that cancer cells could degrade extracellular matrix and penetrate the basement membrane to adjacent and/or distant tissues [10]. To assess whether UBE2T regulated the migratory and invasive ability of NSCLC cells, transwell assays were performed. Migration and invasion assays revealed that knocked-down of UBE2T markedly inhibited NSCLC cell migration and invasiveness compared to control cells (Figure 3A and 3B). Thus, our findings suggested that UBE2T depletion might decrease malignant NSCLC cell mobility.
Figure 3.
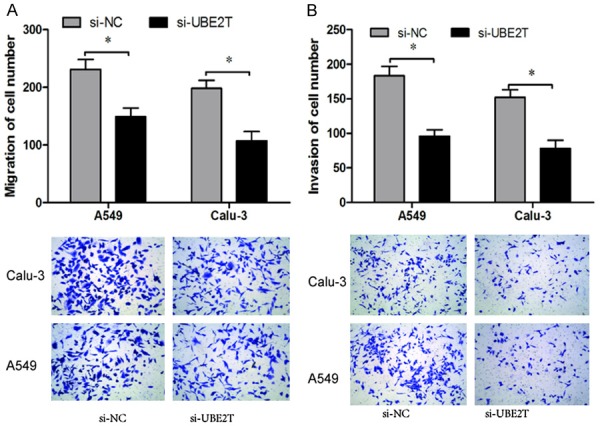
UBE2T promotes NSCLC cells migration and invasion. A. Transwell migration assay showed that UBE2T silencing significantly decreased the number of migrated cells. B. Transwell invasion assay showed that UBE2T suppression significantly decreased the number of invaded cells. *P<0.05.
UBE2T knockdown suppressed the activity of Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
As previously revealed, Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway plays important roles in the regulation of cell growth and migration. Thus, we determine the effect of UBE2T on β-catenin expression and a few of the downstream genes of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, such as, cyclin D1, c-myc and E-cadherin in NSCLC cells. As indicated by the Western blot assay, the protein levels of β-catenin, c-myc and cyclin D1 was significantly decreased in NSCLC cells transfected with si-UBE2T, while E-cadherin expression was obviously augmented (Figure 4). Thus, these data indicated that UBE2T knockdown might suppress NSCLC progression by regulating Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.
Figure 4.
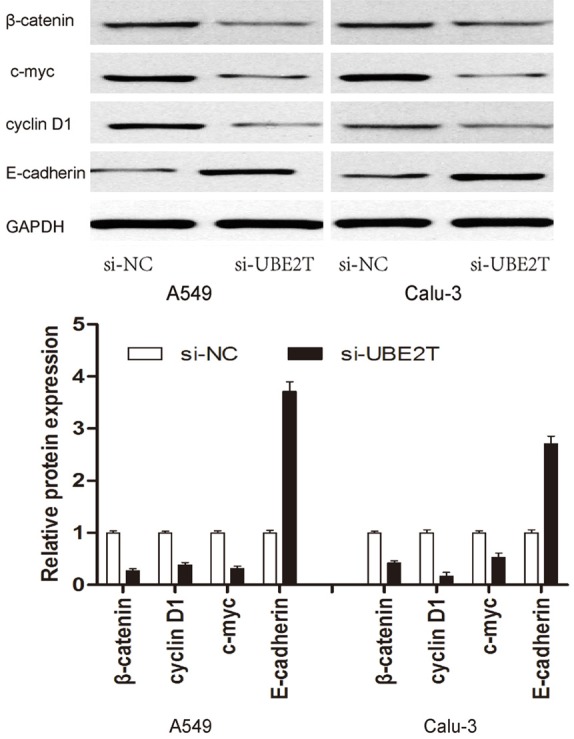
UBE2T promotes the activity of Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Western blot assays were used to detect the protein levels of β-catenin, cmyc, cyclin D1 and E-cadherin, with GAPDH as the control.
Discussion
As the most common malignant disease in the world, lung cancer is the leading cause of mortality in China [11]. According to the past researches, several therapeutic targets for NS-CLC have been identified [12-14], which have improved the outcome of the NSCLC patients. However, the 5-year survival rate for the NSCLC is still unsatisfactory. Therefore, it is still urgent to identify novel and reliable therapeutic targets to improve the prognosis of NSCLC patients.
UBE2T, a new member of ubiquitin conjugating enzymes, is involved in DNA damage repair in Fanconi pathway [15]. Recent studies have shown that disruption of UBE2T expression could directly lead to Fanconi anemia as wellas an increase in tumor cell sensitivity to crossing-link agents, by interfering with the DNA damage-repair response [16]. Recent studies showed that UBE2T was overexpressed in prostate cancer, bladder cancer and nasopharyngeal carcinoma [8-10]. In addition, Hao et al showed that UBE2T was significantly upregulated in lung cancer tissue and cell lines [17]. However, the function of UBE2T in NSCLC is still unclear.
In our study, we found that UBE2T was over-expressed in human NSCLC tissues and cell lines. In vitro assays showed that UBE2T inhibition significantly decreased the proliferation of NSCLC cells compared to control cells. Flow cytometry analysis revealed that the percentage of cells in G0/G1 phase significantly increased with UBE2T silencing in NSCLC cell lines. These data indicate that UBE2T regulates cell proliferation by mediated cell cycle progression. Furthermore, migration and invasion assays revealed that knocked-down of UBE2T markedly inhibited NSCLC cell migration and invasion ability compared to control cells. Those data indicated that UBE2T might act as an oncogene in NSCLC progression. However, the underlying mechanisms of UBE2T in NSCLC remain unclear.
The Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway is of great importance in the malignant development of NSCLC. For example, Rong et al showed that highly expressed long non-coding RNA FOXD2-AS1 promoted NSCLC progression via Wnt/β-catenin signaling [18]. He et al found that Sox2 inhibited Wnt/β-catenin signaling and metastatic potency of cisplatin-resistant lung adenocarcinoma cells [19]. Zhang et al showed that MicroRNA-410 acted as oncogene in NSCLC through downregulating SLC34A2 via activating Wnt/β-catenin pathway [20]. To shed light on the precise mechanism underlying in UBE2T promoted NSCLC cell growth and invasion, effects of UBE2T on Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway was determined. Our data showed that a significant decrease in the protein levels of β-catenin, c-myc and cyclin D1 was observed in NSCLC transfected with si-UBE2T, while E-cadherin expression was obviously augmented when UBE2T was decreased in NSCLC cells. These findings suggested that UBE2T suppression might inhibit NSCLC cells proliferation and invasion by suppressing Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.
In conclusion, our results indicated that UBE2T could act as an oncogene in NSCLC progression. Decreased UBE2T expression suppressed NSCLC cells proliferation and invasion via the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Consequently, we indicated that UBE2T could be a potential target for the treatment of NSCLC patients.
Acknowledgements
We thank the great help and funding from Huaihe Hospital of Henan University.
Disclosure of conflict of interest
None.
References
- 1.Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90. doi: 10.3322/caac.20107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Ettinger DS, Akerley W, Bepler G, Blum MG, Chang A, Cheney RT, Chirieac LR, D’Amico TA, Demmy TL, Ganti AK, Govindan R, Grannis FW Jr, Jahan T, Jahanzeb M, Johnson DH, Kessinger A, Komaki R, Kong FM, Kris MG, Krug LM, Le QT, Lennes IT, Martins R, O’Malley J, Osarogiagbon RU, Otterson GA, Patel JD, Pisters KM, Reckamp K, Riely GJ, Rohren E, Simon GR, Swanson SJ, Wood DE, Yang SC NCCN Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Panel Members. Non-small cell lung cancer. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2010;8:740–801. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2010.0056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R, Gurubhagavatula S, Okimoto RA, Brannigan BW, Harris PL, Haserlat SM, Supko JG, Haluska FG, Louis DN, Christiani DC, Settleman J, Haber DA. Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of nonsmall-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:2129–2139. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa040938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Scagliotti GV, Parikh P, von Pawel J, Biesma B, Vansteenkiste J, Manegold C, Serwatowski P, Gatzemeier U, Digumarti R, Zukin M, Lee JS, Mellemgaard A, Park K, Patil S, Rolski J, Goksel T, de Marinis F, Simms L, Sugarman KP, Gandara D. Phase III study comparing cisplatin plus gemcitabine with cisplatin plus pemetrexed in chemotherapy-naive patients with advanced-stage non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008;26:3543–3551. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2007.15.0375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Machida YJ, Machida Y, Chen Y, Gurtan AM, Kupfer GM, D’Andrea AD, Dutta A. UBE2T is the E2 in the Fanconi anemia pathway and undergoes negative autoregulation. Mol Cell. 2006;23:589–596. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2006.06.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Kelsall IR, Langenick J, MacKay C, Patel KJ, Alpi AF. The Fanconi anaemia components UBE2T and FANCM are functionally linked to nucleotide excision repair. PLoS One. 2012;7:e36970. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0036970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Wen M, Kwon Y, Wang Y, Mao JH, Wei G. Elevated expression of UBE2T exhibits oncogenic properties in human prostate cancer. Oncotarget. 2015;6:25226–25239. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.4712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Gong YQ, Peng D, Ning XH, Yang XY, Li XS, Zhou LQ, Guo YL. UBE2T silencing suppresses proliferation and induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in bladder cancer cells. Oncol Lett. 2016;12:4485–4492. doi: 10.3892/ol.2016.5237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Hu W, Xiao L, Cao C, Hua S, Wu D. UBE2T promotes nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell proliferation, invasion, and metastasis by activating the AKT GSK3beta/beta-catenin pathway. Oncotarget. 2016;7:15161–15172. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.7805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Stetler-Stevenson WG, Aznavoorian S, Liotta LA. Tumor cell interactions with the extracellular matrix during invasion and metastasis. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1993;9:541–573. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.09.110193.002545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.She J, Yang P, Hong Q, Bai C. Lung cancer in China: challenges and interventions. Chest. 2013;143:1117–1126. doi: 10.1378/chest.11-2948. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Gutschner T, Hämmerle M, Eißmann M, Hsu J, Kim Y, Hung G, Revenko A, Arun G, Stentrup M, Groß M. The noncoding RNA MALAT1 is a critical regulator of the metastasis phenotype of lung cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2013;73:1180–1189. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-2850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Kasinski AL, Kelnar K, Stahlhut C, Orellana E, Zhao J, Shimer E, Dysart S, Chen X, Bader AG, Slack FJ. A combinatorial microRNA therapeutics approach to suppressing non-small cell lung cancer. Oncogene. 2015;34:3547–3555. doi: 10.1038/onc.2014.282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Tay Y, Karreth FA, Pandolfi PP. Aberrant ceRNA activity drives lung cancer. Cell Res. 2014;24:259–260. doi: 10.1038/cr.2014.21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Hira A, Yoshida K, Sato K, Okuno Y, Shiraishi Y, Chiba K, Tanaka H, Miyano S, Shimamoto A, Tahara H, Ito E, Kojima S, Kurumizaka H, Ogawa S, Takata M, Yabe H, Yabe M. Mutations in the gene encoding the E2 conjugating enzyme UBE2T cause Fanconi anemia. Am J Hum Genet. 2015;96:1001–1007. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2015.04.022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Morreale FE, Bortoluzzi A, Chaugule VK, Arkinson C, Walden H, Ciulli A. Allosteric targeting of the fanconi anemia ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme Ube2T by fragment screening. J Med Chem. 2017;60:4093–4098. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.7b00147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Hao J, Xu A, Xie X, Hao J, Tian T, Gao S, Xiao X, He D. Elevated expression of UBE2T in lung cancer tumors and cell lines. Tumor Biol. 2008;29:195–203. doi: 10.1159/000148187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Rong L, Zhao R, Lu J. Highly expressed long non-coding RNA FOXD2-AS1 promotes nonsmall cell lung cancer progression via Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017;484:586–591. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.01.141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.He J, Shi J, Zhang K, Xue J, Li J, Yang J, Chen J, Wei J, Ren H, Liu X. Sox2 inhibits Wnt-betacatenin signaling and metastatic potency of cisplatin-resistant lung adenocarcinoma cells. Mol Med Rep. 2017;15:1693–1701. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.6170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Zhang X, Ke X, Pu Q, Yuan Y, Yang W, Luo X, Jiang Q, Hu X, Gong Y, Tang K. MicroRNA-410 acts as oncogene in NSCLC through downregulating SLC34A2 via activating Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Oncotarget. 2016;7:14569. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.7538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]