Abstract
Cardiovascular diseases are the main cause of death in the industrialized world, with the main risk factors being elevated blood pressure and blood lipid levels, leading to arterial stiffness and arteriosclerosis. In this study, we examined the effect of aged garlic extract (AGE) on arterial elasticity, using the EndoPAT™ technology in subjects with slightly elevated blood pressure. This randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial examined 57 subjects over a period of 12 weeks, with EndoPAT™ measurements taken at 0 and 12 weeks; in addition, changes in blood pressure were analyzed. The positive effect of AGE on blood pressure values previously reported was confirmed. The results revealed a significant decrease in blood pressure in the AGE group, and in particular diastolic blood pressure. Using the EndoPAT™ technology, the augmentation index (AI) was analyzed, which measures arterial stiffness calculated via pulse waveform analysis of the PAT signal; lower AI values reflect better arterial elasticity. The AGE group exhibited a significant improvement in arterial elasticity, measured as AI75, by 21.6%. The result of this well-controlled clinical trial confirmed the positive effect of AGE on blood pressure. To the best of our knowledge, for the first time, the effect of AGE on arterial elasticity could be proven using the EndoPAT™ methodology. These results not only demonstrate the positive effects of AGE on the relevant risk factors of cardiovascular diseases, but also the direct effect on arterial elasticity. These data clearly indicate that AGE may exert several positive direct effects on the development and progression of cardiovascular diseases.
Keywords: clinical trial, arterial elasticity, blood pressure, cardiovascular disease, aged garlic extract
Introduction
According to the WHO data (1), cardiovascular diseases (CVD), such as coronary heart disease (CHD) and stroke are globally the most frequent causes of death. Hypertension, dyslipidemia, and atherosclerosis are considered as key risk factors for CVD (2,3).
The augmentation index (AI) is a parameter measured by EndoPAT™ that characterizes arterial elasticity/stiffness (4). As a pressure wave moves through the arterial tree, it encounters impedance, resulting in a reflected wave that moves back toward the heart and may augment peak systolic pressure. Arterial stiffness increases pulse wave velocity, causing early reflection of this waveform. Thus, lower AI values reflect better arterial elasticity and a low peripheral resistance of the arterial wall. Conversely, increased arterial stiffness results in an altered AI, associated with high peripheral resistance of the arterial wall (4).
AI in the Endo PAT™ is calculated from the PAT™ pulses at the baseline period of the occluded arm, by averaging multiple valid pulses and finding the systolic peak (P1) and the backward reflected peak (P2) and then using the following formula: (P2-P1)/P1 (4). AI75 is standardized to a heart rate of 75 beats per minute.
In 2008, a total of approximately 40% of adults age 25 and older were diagnosed with hypertension (5). However, the early stages of increased blood pressure (BP) rarely cause symptoms, and thus remain undiagnosed in many cases (2).
The classification for different levels of BP should be based upon ≥2 readings at ≥2 separate occasions, separated by at least 1 week. In individuals >50 years of age, a systolic blood pressure (SBP) >140 mmHg is a much more important risk factor of CVD than diastolic blood pressure (DBP) (6). The risk of CVD, beginning at 115/75 mmHg, doubles with each increment of 20/10 mmHg. Subjects who have a normal BP at 55 years of age have a 90% lifetime risk of developing hypertension (6). If an individual's BP rises above the normal level, lifestyle modifications without drug treatment are recommended in the first line to prevent CVD, at least in the absence of <3 additional risk factors (7). In The Seventh Report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation and Treatment of High Blood Pressure, Chobanian et al (6) defined normal blood pressure as a SBP <120 mmHg and DBP <80 mmHg, pre-hypertension as a SBP 120–139 mmHg and DBP 80–89 mmHg, and stage 1 hypertension as a SPB 140–159 mmHg and DBP 90–99 mmHg.
Various forms of dyslipidemia lead to an increased risk of CVD, independently of e.g., known genetic variations or lifestyle (8,9). Lipid parameters with known association to CVD include elevated low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) or triglyceride (TG) concentrations or high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) below the lower limit of the normal range.
The determination of total cholesterol (TC) has been established for decades in routine laboratory work as a first screening step, with fractioning into HDL-C and LDL-C in the case of elevated levels. Furthermore, a causal association between increased circulating TG levels and CHD has now been established (10).
Non-HDL-C is a parameter first proposed by Di Angelantonio et al (11) following the analysis of >300,000 individuals with lipid assessments in vascular disease. The authors revealed that hazard ratios (HR) were almost identical to those observed with Apo-B and Apo-AI. Non-HDL-C levels are easier to assess than LDL-C levels, which are calculated indirectly by subtracting HDL-C and fasting TG levels from TC levels. Instead, non-HDL-C is calculated by the subtraction of HDL-C from non-fasting TC levels, i.e. it does not require a fasting state, but is also valid in fasted subjects (12). As it also provides better estimates of a treatment effect and of CVD risk reduction than LDL-C, it is recommended in the most recent British NICE guidance of July 2014 (13).
Garlic (Allium sativum L.) has been used in traditional medicine for centuries. Aged garlic extract (AGE) is an odorless garlic preparation that has been shown to contain various water-soluble organic sulfur compounds, such as S-allylcysteine (SAC) and S-1-propenylcysteine, which are formed during its unique manufacturing process (14). AGE and its components have been shown to display various health benefits that have been described in >820 publications of in vitro and animal studies, as well as in clinical trials, reporting the cardiovascular protective effects against cholesterol levels (15), hypertension (16,17), homocysteine levels (18), LDL oxidation (18), anti-platelet aggregation and adhesion (15,19), blood circulation (20), etc. It can be concluded that the safety and beneficial effects of AGE in the area of cardiovascular health have been well-established.
The aim of this randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group nutritional study was to evaluate the benefit of AGE on arterial elasticity, as well as its tolerability in overweight subjects with high normal and hypertension grade 1 blood pressure. In addition, changes in blood pressure and lipid profiles were explored.
Materials and methods
Participants
A total of 57 generally healthy male and female subjects were randomised into the study (26 verum, 29 placebo) according to the inclusion and exclusion criteria presented in Table I. In total, 28 participiants were administered the AGE, hereinafter referred to as verum, and 29 were administered a placebo. Following randomization, 2 subjects completed the study before visit 3 (v3) without any measurement values post baseline visit. These subjects were excluded from the full analysis set (FAS) and valid case analysis set (VCAS), but were be kept in the safety population. All subjects voluntarily gave their written informed consent. The clinical trial was approved by the Ethics Committee of Charité - Universitaetsmedizin Berlin, Germany.
Table I.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria.
| Inclusion criteria | Exclusion criteria |
|---|---|
| Age, 40–75 years | Known allergy or hypersensitivity to the components of the investigational product, genetic hyperlipidemia, secondary hypertension, white-coat hypertension, type-1-diabetes or type-2-diabetes that was uncontrolled or diagnosed within the last 6 months prior to first visit, untreated or non-stabilized thyroid disorder |
| Body mass index (BMI): 25–34,9 kg/m2 | History and/or presence of clinically significant cardiovascular disease as per investigator's judgement such as known congenital heart defects, myocardial infarction, heart failure, angina pectoris, life-threatening arrhythmia or stroke within the last 6 months prior to first visit, existing thrombosis or disposition to thrombosis, or any other known significant or serious conditions/diseases that might render subjects ineligible, e.g., a history of malignancy within the past 5 years prior to the first visit, bleeding disorders and/or need for anticoagulants, current psychiatric care and/or use of neuroleptics, bariatric surgery in the last 12 months prior to the first visit, any known metabolic disease, gastrointestinal disorder or other clinically significant disease/disorder which in the investigator's opinion could interfere with the results of the study or the safety of the subject |
| High normal or hypertension grade 1 blood pressure levels (130–159/85–99 mmHg) | Arm lymphedema (e.g., due to mastectomy) |
| EndoPAT™ reactive hyperemia index (RHI) score of <2.2 at first visit | Deviations of laboratory parameter(s) at the first visit that were clinically significant or 2× the upper limit of normal (ULN), unless the deviation was justified by a previously known not clinically relevant condition, e.g., Gilbert's syndrome) |
| Readiness to comply with the study procedures, in particular with consumption of the investigational product (IP) as instructed during the treatment period | Dietary habits that may interfere with the study objectives, such as eating disorders, dietary restrictions that may affect the study outcome, participation in a weight loss program or use of weight loss treatment |
| Adhering to their respective former diets (except consumption of max. 2 garlic cloves per week) and physical activity, requirements for blood pressure/EndoPAT™ measurements, and accepting blood draws | Making use of the following medication/supplementation within the last 4 weeks prior to first visit and during the study, according to investigator's judgement: |
| • Drugs or supplements that can influence SBP or DBP (e.g., ACE (angiotensin- converting-enzyme) inhibitors, diuretics, calcium channel or β-blockers, grape seed extract, coenzyme Q10 etc.) | |
| • Lipid-lowering drugs (affecting lipid metabolism, platelet function or antioxidant status, etc.) | |
| • Dietary or health supplements (e.g., omega-3 fatty acids, green tea extract, calcium, red yeast rice, phytosterols (incl. enriched products such as, Becel), oat fiber, niacin, soy protein, psyllium seed husk, glucomannan, chitosan or probiotics/prebiotics) | |
| • Drugs that can significantly influence cholesterol levels (e.g., corticosteroids, amiodarone, anabolic steroids) | |
| • Medications (e.g., statins, renin angiotensin system inhibitors, nebivolol, carvedilol, calcium channel blockers) | |
| • Supplements (e.g., cocoa) that can influence vascular endothelial function and/or blood flow within the last 4 weeks prior to first visit and during the study | |
| • Antiplatelet agents and/or anticoagulants (e.g., warfarin, acetylsalicylic acid) | |
| Non-smokers or, respectively, smoking cessation in the last ≥12 months prior to the first visit | Drug abuse or alcohol abuse (males, ≥21 U/week; females, ≥14 U/week; 1 unit equals approximately 250 ml of beer, 100 ml of wine or 35 ml of spirits) |
| Stable body weight over the past 3 months prior to the first visit (<3 kg self-reported change) | Reported participation in night-shift work 2 weeks prior to first visit and/or during the study |
| If any allowed concomitant medications stable at least during the last month prior to the first visit | Participation in another study or blood donation during the last 30 days prior to the first visit and any other reason deemed suitable for exclusion as per the investigator's judgment were taken as further exclusion criteria |
| Negative pregnancy testing (β human chorionic gonadotropin test in urine) at first visit (women of childbearing potential) | For women of child-bearing potential: being pregnant or breast-feeding |
Interventions
AGE is manufactured under ISO 9001 quality control and Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) under a license issued by the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare of Japan and according to the following steps: Organically grown raw garlic (Allium sativum L.) was cut into slices, immersed in aqueous ethanol, and aged over a period of 10 months at room temperature. The procedure and specifications are described in the US Pharmacopeia/National Formulary (USP/NF) monograph (21).
AGE was stored according to the manufacturer's recommendations. The placebo was a liquid identical in color and flavor to the verum. In order to maintain the ‘blind’ factor with respect to the odour, the placebo contained 3% concentrated AGE (drug-extract-ratio: 0.9–1.2:1), which is considered as inactive with respect to any potential beneficial effect. The daily uptake amount was 2 ml (with 1 ml taken twice per day at mealtimes) for a duration of 84±3 days.
EndoPAT™
In this study, EndoPAT™ parameters AI75 and the reactive hyperemia index (RHI) were assessed as per Endo-PAT 2000 according to standardized procedures provided by the manufacturer (Itamar Medical Ltd.), at visits 1 (RHI only), 2 and 4.
Blood pressure measurements
Seated BP measurements were taken in a quiet environment after the subjects had been seated for at least 15 min upon arrival. The subjects were positioned in a comfortable manner with their feet located on the floor, legs not crossed and back placed against the back of a chair. The measurements were carried out in triplicate according to a standardized method (22). The three BP measurements were performed with 2- to 5-min intervals inbetween. The first measurement was disregarded and the mean of the latter two was calculated. If blood pressure varied in these determinations by ≥5 mmHg, 2 additional measurements were performed to measure SBP and DBP. The final two measurements were then averaged to determine the overall SBP and DBP for each subject.
The time of day the measurements were taken was also documented. A trained medical professional using a standardized calibrated oscillometric device with a universal 22–42 cm cuff performed the measurements. At visit 1, BP measurements were performed on both arms; in the case of difference, the dominant arm (with the higher BP) was used. The specification of which arm was used for the BP measurements was documented. The measurements were performed using the same method and equipment, the same arm (with the arm supported at heart level and slightly flexed at the elbow) at similar times of day per subject, preferably by the same medical professional for individual subjects. The subject and the medical professional were required to remain silent and not talk while the measurements were being taken. The subjects were instructed and had to comply with the following restrictions prior to any BP assessment: i) To avoid any strenuous exercise and stimulants (alcohol and caffeine) for at least last 24 h prior to the assessment; ii) to refrain from extreme heat and cold exposure and fluid and food intake for at least 1 h prior to the assessment; iii) to empty their bladder and bowel prior to the assessment.
Determination of lipid parameters
Fasting blood samples were obtained for the assessment of the serum TC, LDL-C, HDL-C and TG concentrations at visits 1 through 4, with the results obtained from visit 1 considered as safety/eligibility assessments. Values from samples at visit 2 were used as baseline. Measurements were performed in a central laboratory using standard procedures.
SCORE value assessment
The SCORE value was assessed as described by the European Society of Cardiology (23).
Global assessment
Both the subjects and investigator(s) evaluated independently the benefit and the tolerability of the Investigational Product (IP) by means of a global scaled evaluation with ‘very good’, ‘good’, ‘moderate’ and ‘poor’.
Visit schedule
Visit 1 was conducted at day 0. Visit 2 (baseline) was conducted 10–14 days after visit 1. Visit 3 (control) was conducted 6 weeks ± 3 days after visit 2. Visit 4 (final) was conducted 6 weeks ± 3 days after visit 3 (for the visit schedule, please refer to Table II).
Table II.
Visit schedule.
| Procedure/assessment | Visit 1 screening | Visit 2 baseline 10+4 days after visit 1 | Visit 3 control 6 weeks ± 3 days after visit 2 | Visit 4 final 6 weeks ± 3 days after visit 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subject information | X | |||
| Written informed consent | X | |||
| Anamnestic, demographic data | X | |||
| Inclusion and exclusion criteria | X | Xa | ||
| Check eligibility criteria | X | |||
| Randomization | X | |||
| Medical history/concurrent diseases | X | |||
| Concurrent treatment (incl. supplementation) | X | X | X | X |
| Physical examination (incl. an electrocardiogram) | X | |||
| Blood pressure and pulse rate | X | X | X | X |
| BMI, body weight and heightb | X | X | X | X |
| Urine analysisc | X | X | ||
| Blood draw safety parameters (including glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c), thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)d | X | X | ||
| Blood draws (fasted) for lipids (TC, LDL-C, HDL-C, TG) | X | X | X | X |
| Changes in dietary habits | X | X | X | |
| Changes in physical activity | X | X | X | |
| EndoPAT™ measurements | X | X | X | |
| Issue of investigational product (IP) | X | X | ||
| Issue of IP instructions | X | |||
| Collection of IP and check of compliance | X | X | ||
| Adverse events | X | X | X | X |
| Global evaluation of benefit and tolerability by subject and investigator | X |
BMI, body mass index; TC, total cholesterol; LDL-C, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; HDL-C, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; TG, triglyceride.
Control of inclusion criterion no. 3 (blood pressure) at visit 2 before randomization
height and BMI only at visit 1
including pregnancy test for women of childbearing potential at visit 1
HbA1c, TSH only at visit 1.
Outcome measures
To characterize the benefits of AGE, the following endpoints were analysed in comparison between the verum and placebo: EndoPAT™ AI75 and RHI at visit 4 vs. visit 2: i) SBP at visits 3 and 4 vs. visit 2, respectively; ii) DBP at visits 3 and 4 vs. visit 2, respectively; iii) fasting LDL-C concentrations and non-HDL-C at visits 3 and 4 vs. visit 2, respectively; iv) fasting TC concentrations at visits 3 and 4 vs. visit 2, respectively; v) fasting HDL-C concentrations at visits 3 and 4 vs. visit 2, respectively; vi) fasting TG concentrations at visits 3 and 4 vs. visit 2, respectively; vii) fasting LDL-C/HDL-C and TC/HDL-C ratio at visits 3 and 4 vs. visit 2, respectively; viii) SCORE value at visits 3 and 4 vs. visit 2, respectively; ix) global evaluation of benefit by the subjects/investigator at visit 4.
Statistical analysis
The benefit endpoints, as well as the safety and tolerability and other concomitant variables received an explorative examination and were descriptively assessed. For the metric data (continuous data), the statistical characteristics are given (number, mean, standard deviation, median, extremes, quartiles). For ordinal data (discrete data), the frequency distribution was performed. If suitable, ordinal data was supplementary considered as metric data. All nominal data (categorical data) was summarized using frequency tables. The values of metric data could be merged in ordinal classes according to clinical criteria to determine their frequency distribution. Performing the explorative estimation the structural consistency of the verum and placebo groups at baseline was proven in detail. If there were differences or distinctive individual values (‘outliers’), their possible influences on the study results was considered.
All secondary, safety and tolerability, and concomitant variables were evaluated primarily by exact non-parametrics procedures as follows: i) The Mann-Whitney U test for independent groups (comparison of groups or subgroups); ii) the Wilcoxon test for dependent groups (comparison pre-post within groups or subgroups); and iii) Fisher's exact test for the comparison of percentages. Parametric procedures (t-tests) supplemented the analysis if the scale of the observed values justified this type of test.
The influence of baseline values was investigated using analysis of variance with baseline value as covariate. Changes in variables over time (repeated measurements) were analyzed using analysis of variance (one-way ANOVA) with respect to differences in groups and systematic changes over time within each group, respectively. All tests were performed with a significance level (type I error) of 5.0% (two-tailed test). The 95% confidence interval was performed. Multiple tests were performed without correction of significance level in the explorative analysis. All P-values of statistical tests in the exploratory analysis, which go beyond the examination of the primary endpoint, were also understood only exploratory, meaning they did not serve to confirm in advance proposed theses. A value of P<0.05 was considered to indicate a statistically significant difference.
Analysis of datasets
The statistical analysis was carried out in the full analysis set (FAS) population, which is defined as all subjects enrolled in the study who have at least once taken the investigational product and for whom benefit parameters can be demonstrated. The primary endpoints were also evaluated in the valid case analysis set (VCAS) population composed of all subjects in the FAS population, for which there are no major protocol violations. Secondary endpoints and other parameters can also be evaluated in the VCAS population as a sensitivity analysis. The evaluation of the safety endpoints is performed in the safety population, for all the subjects who have at least once taken the investigational product. No interim analysis was performed.
Results
Population characteristics
There were no differences in age or body mass index (BMI) between the participants in the verum and placebo groups (Table III). In addition, there were no differences in sex between the participants in the verum and placebo groups (Table IV).
Table III.
Population characteristics.
| Characteristic | N | Mean | SD |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | |||
| V group | 26 | 57.0 | 7.6 |
| P group | 29 | 57.9 | 10.5 |
| P-value | 0.479 | ||
| BMI (kg/m2) visit 1 | |||
| V group | 26 | 28.07 | 2.63 |
| P group | 29 | 27.69 | 2.03 |
| P-value | 0.870 | ||
N, number of subjects; SD, standard deviation; V, verum; P, placebo; BMI, body mass index.
Table IV.
Sex distribution in the verum and placebo groups.
| V group (n=26) | P group (n=29) | |
|---|---|---|
| Sex | No. (%) | No. (%) |
| Male | 12 (46.2) | 9 (31.0) |
| Female | 14 (53.8) | 20 (69.0) |
| P-value | 0.279 | |
N, number of subjects; SD, standard deviation; V, verum; P, placebo.
EndoPAT™: Arterial stiffness reduction
Quantitative changes in arterial stiffness (measured as AI75) from a mean of 12.86 to 10.08 were found from baseline to the study end in the verum group, showing a statistically significant result (P=0.028). The change in arterial stiffness in the placebo group ranged from 8.10 to 5.59 during the same time period (P=0.171) (Tables V and VI). Satistically significant qualitative changes in AI75 were observed from baseline to study end in the verum group (P=0.041), with 69.2% of the subjects responding to the AGE with an AI75 reduction (Table VII).
Table V.
Arterial stiffness reduction from visit2 to visit 4.
| Visit 2 | Visit 4 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AI75 (%) | N | Mean | SD | Mean | SD |
| V group | 26 | 12.86 | 10.94 | 10.08 | 11.34 |
| P group | 29 | 8.10 | 18.26 | 5.59 | 15.11 |
N, number of subjects; SD, standard deviation; V, verum; P, placebo; AI75, augmentation index (EndoPAT™).
Table VI.
Arterial stiffness reduction: Quantitative change.
| Change in AI75 (%) Visit 2-visit 4 | N | Mean | SD | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V group | 26 | 2.78 | 6.08 | 0.028 |
| P group | 29 | 2.51 | 9.62 | 0.171 |
N, number of subjects; SD, standard deviation; V, verum; P, placebo; AI75, augmentation index (EndoPAT™).
Table VII.
Arterial stiffness reduction: Responders.
| V group (n=26) | P group (n=29) | |
|---|---|---|
| Changes in AI75 Visit 2-visit 4 | No. (%) | No. (%) |
| Decreased | 18 (69.2) | 15 (51.7) |
| Unaltered | 0 (0.0) | 1 (3.4) |
| Increased | 8 (30.8) | 13 (44.8) |
| P-value | 0.041 | 0.295 |
N, number of subjects; SD, standard deviation; V, verum; P, placebo; AI75, augmentation index (EndoPAT™).
EndoPAT™: RHI
No statistically significant differences were observed in the RHI score between the study groups at the end of the study (data not shown).
Changes in SBP
A strong trend towards differences in the quantitative change of SBP from baseline to study end was observed between the groups in favor of verum. The mean SBP decreased from 142.9 mmHg at visit 2 to 134.0 mmHg at visit 4 in the verum group, corresponding to a mean change of 8.9 mmHg (Tables VIII and IX). This differed from the placebo group (strong trend, P=0.056). In the verum group, 21 of the 26 subjects (80.8%) responded to AGE with a decrease in SBP (data not shown).
Table VIII.
Systolic blood pressure.
| Visit 2 | Visit 4 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SBP (mmHg) | N | Mean | SD | Mean | SD |
| V group | 26 | 142.9 | 8.4 | 134.0 | 10.7 |
| P group | 29 | 141.9 | 7.5 | 138.1 | 11.5 |
SBP, systolic blood pressure; N, number of subjects; SD, standard deviation; V, verum; P, placebo.
Table IX.
Reduction in systolic blood pressure.
| Reduction in SBP (mmHg) v2 - v4 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Group | N | Mean | SD |
| V group | 26 | 8.9 | 8.2 |
| P group | 29 | 3.8 | 12.3 |
| P-value | 0.056 | ||
SBP, systolic blood pressure, N, number of subjects; SD, standard deviation; V, verum; P, placebo; v, visit; P-values were derived from the Mann-Whitney test.
Changes in DBP
Similar to the SBP, a difference in quantitative changes (P=0.038) in DBP was observed from baseline to study end between the groups in favor of verum. The mean DBP decreased in the verum group from 91.0 to 85.3 mmHg, corresponding to a mean change of 5.6 mmHg (Tables X and XI). In the verum group, 22 of the 26 participants (85%) responded to the AGE with a DBP reduction.
Table X.
Diastolic blood pressure.
| Visit 2 | Visit 4 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DBP (mmHg) | N | Mean | SD | Mean | SD |
| V group | 26 | 91.0 | 3.8 | 85.3 | 6.8 |
| P group | 29 | 89.2 | 3.8 | 86.6 | 7.0 |
DBP, systolic blood pressure; N, number of subjects; SD, standard deviation; V, verum; P, placebo.
Table XI.
Reduction in diastolic blood pressure.
| Reduction in DBP (mmHg) v2 - v4 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Group | N | Mean | SD |
| V group | 26 | 5.6 | 5.1 |
| P group | 29 | 2.6 | 6.5 |
| P-value | 0.038 | ||
DBP, diastolic blood pressure; N, number of subjects; SD, standard deviation; V, verum; P, placebo; v, visit; P-values were derived from the Mann-Whitney test.
Decrease in the TG level
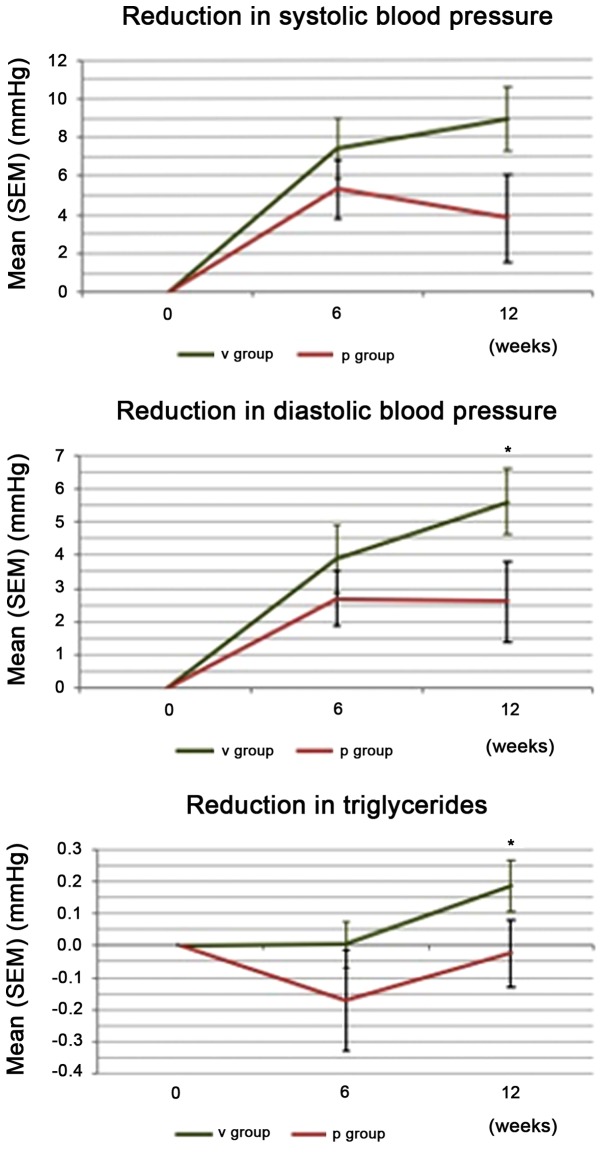
A statistically significant difference in quantitative changes was found for the TG levels from baseline to study end between the groups in favor of verum (1.33 mmol/l at visit 2 to 1.15 mmol/l at visit 4, P=0.022). Qualitative changes in the TG levels were statistically significant (P=0.022), with 77% of the responders observed with decreased values in the verum group (Table XII). Changes in CVD parameters SBP, DBP, and TG are summarized in Fig. 1.
Table XII.
Changes in observed CVD parameters.
| Parameter | Group | N decreased (%) | N unaltered (%) | N increased (%) | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SBP | Verum | 21 (80.8) | 0 (0.0) | 5 (19.2) | <0.001 |
| Placebo | 18 (62.1) | 0 (0.0) | 11 (37.0) | 0.091 | |
| DBP | Verum | 22 (84.6) | 0 (0.0) | 4 (15.4) | <0.001 |
| Placebo | 17 (58.6) | 2 (6.9) | 10 (34.5) | 0.051 | |
| TG | Verum | 20 (76.9) | 0 (0.0) | 6 (23.1) | 0.022 |
| Placebo | 12 (41.4) | 0 (0.0) | 17 (58.6) | 0.408 | |
| SCORE | Verum | 8 (30,8) | 17 (65.4) | 1 (3.8) | 0.039 |
| Placebo | 4 (13.8) | 23 (79.3) | 2 (6.9) | 0.688 |
CVD, cardiovascular disease; N, number of participants; SBP, systolic blood pressure; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; TG, triglycerides.
Figure 1.
Differences in cardiovascular disease parameters (visit 2 to visit 4). V, verum; P, placebo; SEM, standard error of the mean; *P<0.05, statistically significant compared to the placebo.
SCORE value of CVD risk
The SCORE value indicating a risk of developing CVD from baseline to study end showed stastistically significant qualitative changes in the verum group (31% responders with reduction) (Table XII).
Global assessments of benefit and tolerability
Differences between the study groups in the global assessment of benefit were in favor of the verum both in the rating by subjects (P=0.006) and by the investigator (P=0.007); close comparability between verum and placebo was observed in the global assessment of tolerability (data not shown).
Adverse events
In total, 9% of the subjects reported an adverse event (AE; there were 6 AEs in 5 subjects (5/57; 8.8%) (Table XIII). No differences in the percentage of subjects with AE was observed between the groups. In all cases, there was an ‘unlikely’ causal association to the investigational product. None of the AEs were considered serious.
Table XIII.
Adverse events.
| Group | N | Adverse event | Intensity |
|---|---|---|---|
| V | 1 | Back pain | Moderate |
| V | 1 | Common cold | Light |
| P | 1 | Common cold | Moderate |
| V | 1 | Alanine transaminase increased | Light |
| Pa | 1 | Knee joint mobilization | Moderate |
| Pa | 1 | Vomiting | Light |
V, verum group; P, placebo group; N, number of subjects.
Both adverse events occured in the same test subject.
No differences were observed between the groups with regards to the examined safety laboratory parameters. Pulse rate and body weight exhibited no changes. In addition, no changes in dietary habits or level of physical activity were observed during the study (data not shown).
Discussion
The present placebo-controlled, randomized, double-blind, parallel-group nutritional study in subjects with a high BMI and elevated blood pressure provides further clinical evidence for the cardiovascular benefits of AGE, a specialized garlic extract. As well as showing, for the first time, at least to the best of our knowledge, indications of improved arterial elasticity (measured by EndoPAT™ as AI), this study also supports efficacy regarding common cardiovascular targets (TG levels, and SBP and DBP), which all exhibited significant changes from baseline to study end in favor of verum.
Arterial stiffness reduction. In spite of the small sample size, the present study demonstrated a significant improvement in arterial elasticity, as measured by AI75 using EndoPAT™ technology. The majority of the subjects in the verum group (69,2%) exhibited decreased values of arterial stiffness from baseline to study end; furthermore, significant quantitative changes were observed (reduction by 21.6%). This direct significant effect of AGE on arterial elasticity has not previously been reported, at least to the best of our knowledge, further cementing its benefits in the area of CVD prevention. Ried et al (24) measured arterial stiffness using the Mobil-O-Graph device (Millar Instruments) and found non-significant tendencies towards a decrease of arterial stiffness as measured by the AI, which are supported by the first significant results of the present study.
The results of the present study indicate that EndoPAT™ AI measurements may be a valuable method for measuring AGE-mediated improvements of arterial elasticity. Further studies on larger sample sizes are required to substantiate these results. The results obtained in the present study support the numerous published studies on AGE that have previously shown improvements in cardiovascular targets (15–17).
Reduction of hypertension. In a pre-clinical trial, Harauma and Moriguchi (25) compared the effects of AGE and raw garlic (RG) in spontaneaously hypertensive rats. Their findings indicated an improvement of the pliability of the artery for AGE and a reduction in SBP compared to the controls for both AGE and RG. These findings are in line with the results of the present study on human subjects.
Ried et al (24) observed a reduction in peripheral and central blood pressure in patients with uncontrolled hypertension by 11.5±1.9 mmHg systolic and by 6.3±1.1 mmHg diastolic BP in responders, compared to the placebo. This is in line with the results found in the present study (8.9 mean SBP reduction and 5.6 mean DPB reduction). Ried et al (24) also reported a percentage of garlic non-responders (30%), comparable to the 20% of non-responders in the present study. The authors speculated the incidence of these non-responders among their study population as being linked to underlying vitamin B6, vitamin B12, or folate deficiency, or to genetic polymorphisms. Further investigation into this phenomenon is warranted.
Nitric oxide (NO) production may play a role in the observed BP reduction. Morihara et al (26) observed an increase of NO of 30–40% in mice from 15 to 60 min following the administration of AGE, leading to a possible vasorelaxant effect, supporting the findings of an ex vivo trial conducted by Takashima et al (27), who found that AGE induced a concentration-dependant vasorelaxation in isolated, precontracted rat aortic rings with their endotheliums intact. This NO-dependent effect may account for the short-term BP-lowering effects of AGE.
Another indication of the possible mode of action of AGE on hypertension was discovered by Ushijima et al (28). The authors found a significant and dose-dependent reduction in SBP in hypertensive rats treated with S-1-propenylcysteine, one of the key compounds of AGE. Other AGE compounds did not exert the same effect. The authors concluded that S-1-propenylcysteine was responsible for the anti-hypertensive effects of AGE.
Reduction of TG levels. The reduction in the TG levels observed in the present study is also in line with the results from previous studies. Lau et al (29) observed a decrease in cholesterol, TG, low density and very low density lipoprotein levels, together with an increase in HDL levels in the majority of subjects after 6 months of taking AGE. The authors observed an initial significant increase in cholesterol and TG levels after 1 month and attributed this to a mobilization of lipids from the tissue deposits, pointing out previous studies that had observed the same phenomenon. The present study with a duration of 12 weeks demonstrated a significant decrease in TG levels by study end, supporting the findings of the study by Lau et al (29) with a duration of 24 weeks, that also showed the first significant decrease in TG levels after 12 weeks.
The observed reduction in arterial stiffness due to the consumption of AGE, together with lowered blood pressure, as well as improved TG values, leads to a significant reduction in CVD risk in subjects with elevated BMI and blood pressure, as shown by the SCORE value (31% of subjects with decreased values).
To evaluate the mechanisms of the long-term effects of AGE on cardiovascular targets observed in numerous studies, Ried et al (17) investigated changes in gut microbial diversity in subjects receiving AGE over a period of 12 weeks, observing a small, yet significant increase in diversity, with the increase in numbers of Clostridia and Lactobacillus species and the decrease in numbers of Firmicutes prausnitzii being significantly associated with a concommittant decrease in BP. While the present study did not monitor the gut microbiota composition of the study participants, this effect of AGE may still be one of the mechanisms responsible for its cardioprotective effects. Further investigation into this matter is warranted.
Tolerability of AGE. AGE was generally very well tolerated. While some AEs were reported, none of them involved gastrointestinal (GI) disturbances, which are the expected AEs linked to garlic products. Nakagawa et al (30) observed that raw garlic juice (5 ml/kg) administered to Wistar rats led to stomach injury, swelling of the liver, hypertrophy of the spleen and adrenal glands, and to the decrease of erythrocytes with various morphological changes. Harauma and Moriguchi (25) reported that animals in the RG group exhibited several harmful effects that were not present in the AGE group, indicating that RG contains compounds that exert a harmful effect, which are not present in AGE. In contrast to these findings, Sumiyoshi et al (31) reported no toxic symptoms in Wistar rats due to AGE even at dose levels of 2,000 mg/kg for 5 times a week over a period of 6 months.
This is in line with the fact that AGE does not contain the harsh organosulfur constituents present in fresh garlic that can lead to GI disturbances in humans (32). This generally high tolerability of AGE is frequently reported in other studies. For example, Ried et al (24) reported a compliance of 96.6% of participants, with minor side-effects that abated after the first week of the trial and were considered bothersome by few participants.
As regards the study limitations, it should be noted that the main limitation of this study was the small sample size.
In conclusion, the present study supports the cardiovascular benefits of AGE that have been previously reported. In addition, at least to the best of our knowledge, for the first time, an effect on arterial stiffness as measured by EndoPAT™ AI75 in healthy subjects was observed. AGE was well-tolerated, further cementing its usefulness as a long-term preventative measure against cardiovascular conditions.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dr Norman Bitterlich and Irene Wohlfahrt for their valuable assistance in this study.
Funding
This clinical study was funded by Wakunaga of America Co., Ltd. and conducted by Analyze & Realize GmbH.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Authors' contributions
JG was responsible for the study initiation and conception, and scientific supervision, UB was the study investigator, GB contributed to the study planning and design, and RU was the study medical expert and principal investigator.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All subjects voluntarily gave their written informed consent. The clinical trial was approved by the Ethics Committee of Charité - Universitaetsmedizin Berlin, Germany. Participation was based upon written informed consent by the participant following written and oral information by the investigator regarding nature, purpose, consequences, and possible risks of the clinical study.
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
Wakunaga of America Co., Ltd. was not involved in the conduct of this clinical study. The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
References
- 1.World Health Organization (WHO), corp-author Vol. 317. WHO; Geneva: 2013. Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs): Fact sheet No. [Google Scholar]
- 2.World Health Organization (WHO), corp-author WHO; Geneva: 2013. World Health Day 2013: Control your blood pressure. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Dieterle T. Blood pressure measurement - an overview. Swiss Med Wkly. 2012;142:w13517. doi: 10.4414/smw.2012.13517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Itamar Medical: PAT® Technology. Itamar Medical Ltd., Caesarea, corp-author. https://www.itamar-medical.com/pat_technology/ [Mar;2019 ];2019
- 5.World Health Organization (WHO), corp-author WHO; Geneva: 2010. [Mar;2019 ]. Global status report on noncommunicable diseases. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Chobanian AV, Bakris GL, Black HR, Cushman WC, Green LA, Izzo JL, Jr, Jones DW, Materson BJ, Oparil S, Wright JT, Jr, et al. Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure. National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; National High Blood Pressure Education Program Coordinating Committee Seventh report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure. Hypertension. 2003;42:1206–1252. doi: 10.1161/01.HYP.0000107251.49515.c2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Mancia G, Fagard R, Narkiewicz K, Redon J, Zanchetti A, Böhm M, Christiaens T, Cifkova R, De Backer G, Dominiczak A, et al. 2013 ESH/ESC guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: The Task Force for the Management of Arterial Hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH) and of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Eur Heart J. 2013;34:2159–2219. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/eht151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Conroy RM, Pyörälä K, Fitzgerald AP, Sans S, Menotti A, De Backer G, De Bacquer D, Ducimetière P, Jousilahti P, Keil U, et al. SCORE project group Estimation of ten-year risk of fatal cardiovascular disease in Europe: The SCORE project. Eur Heart J. 2003;24:987–1003. doi: 10.1016/S0195-668X(03)00114-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Jacobson TA, Ito MK, Maki KC, Orringer CE, Bays HE, Jones PH, McKenney JM, Grundy SM, Gill EA, Wild RA, et al. National Lipid Association recommendations for patient-centered management of dyslipidemia: Part 1 - executive summary. J Clin Lipidol. 2014;8:473–488. doi: 10.1016/j.jacl.2014.07.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Sarwar N, Sandhu MS, Ricketts SL, Butterworth AS, Di Angelantonio E, Boekholdt SM, Ouwehand W, Watkins H, Samani NJ, Saleheen D, et al. Triglyceride Coronary Disease Genetics Consortium and Emerging Risk Factors Collaboration Triglyceride-mediated pathways and coronary disease: Collaborative analysis of 101 studies. Lancet. 2010;375:1634–1639. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60545-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Di Angelantonio E, Sarwar N, Perry P, Kaptoge S, Ray KK, Thompson A, Wood AM, Lewington S, Sattar N, Packard CJ, et al. Emerging Risk Factors Collaboration Major lipids, apolipoproteins, and risk of vascular disease. JAMA. 2009;302:1993–2000. doi: 10.1001/jama.2009.1619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Virani SS. Non-HDL cholesterol as a metric of good quality of care: Opportunities and challenges. Tex Heart Inst J. 2011;38:160–162. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Duerden M, O'Flynn N, Qureshi N. Cardiovascular risk assessment and lipid modification: NICE guideline. Br J Gen Pract. 2015;65:378–380. doi: 10.3399/bjgp15X685933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kodera Y, Ushijima M, Amano H, Suzuki JI, Matsutomo T. Chemical and Biological Properties of S-1-Propenyl-l-Cysteine in Aged Garlic Extract. Molecules. 2017;22:22. doi: 10.3390/molecules22040570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Budoff MJ, Takasu J, Flores FR, Niihara Y, Lu B, Lau BH, Rosen RT, Amagase H. Inhibiting progression of coronary calcification using Aged Garlic Extract in patients receiving statin therapy: A preliminary study. Prev Med. 2004;39:985–991. doi: 10.1016/j.ypmed.2004.04.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Ried K, Frank OR, Stocks NP. Aged garlic extract lowers blood pressure in patients with treated but uncontrolled hypertension: A randomised controlled trial. Maturitas. 2010;67:144–150. doi: 10.1016/j.maturitas.2010.06.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Ried K, Travica N, Sali A. The Effect of Kyolic Aged Garlic Extract on Gut Microbiota, Inflammation, and Cardiovascular Markers in Hypertensives: The GarGIC Trial. Front Nutr. 2018;5:122. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2018.00122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Budoff MJ, Ahmadi N, Gul KM, Liu ST, Flores FR, Tiano J, Takasu J, Miller E, Tsimikas S. Aged garlic extract supplemented with B vitamins, folic acid and L-arginine retards the progression of subclinical atherosclerosis: A randomized clinical trial. Prev Med. 2009;49:101–107. doi: 10.1016/j.ypmed.2009.06.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Steiner M, Lin RS. Changes in platelet function and susceptibility of lipoproteins to oxidation associated with administration of aged garlic extract. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1998;31:904–908. doi: 10.1097/00005344-199806000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Kikuchi N, Nishimura Y, Tsukamoto C, Kawashima Y, Ochiai H, Hayashi Y, Fujisaki I. Shinyaku to Rinsho. Jpn J New Remedies Clin. 1994;43:146–158. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Pharmacopoeia US, corp-author. US Pharmacopeial Conv I. 2015;38:6052–6055. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Pickering TG, Hall JE, Appel LJ, Falkner BE, Graves J, Hill MN, Jones DW, Kurtz T, Sheps SG, Roccella EJ. Recommendations for blood pressure measurement in humans and experimental animals: part 1: blood pressure measurement in humans: a statement for professionals from the Subcommittee of Professional and Public Education of the American Heart Association Council on High Blood Pressure Research. Circulation. 2005;111:697–716. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000154900.76284.F6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Perk J, De Backer G, Gohlke H, Graham I, Reiner Z, Verschuren WM, Albus C, Benlian P, Boysen G, Cifkova R, et al. European Association for Cardiovascular Prevention & Rehabilitation (EACPR) European guidelines on cardiovascular disease prevention in clinical practice (version 2012): The fifth joint task force of the European society of cardiology and other societies on cardiovascular disease prevention in clinical practice (constituted by representatives of nine societies and by invited experts) Int J Behav Med. 2012;19:403–488. doi: 10.1007/s12529-012-9242-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Ried K, Travica N, Sali A. The effect of aged garlic extract on blood pressure and other cardiovascular risk factors in uncontrolled hypertensives: The AGE at Heart trial. Integr Blood Press Control. 2016;9:9–21. doi: 10.2147/IBPC.S93335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Harauma A, Moriguchi T. Aged garlic extract improves blood pressure in spontaneously hypertensive rats more safely than raw garlic. J Nutr. 2006;136(Suppl):769S–773S. doi: 10.1093/jn/136.3.769S. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Morihara N, Sumioka I, Moriguchi T, Uda N, Kyo E. Aged garlic extract enhances production of nitric oxide. Life Sci. 2002;71:509–517. doi: 10.1016/S0024-3205(02)01706-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Takashima M, Kanamori Y, Kodera Y, Morihara N, Tamura K. Aged garlic extract exerts endothelium-dependent vasorelaxant effect on rat aorta by increasing nitric oxide production. Phytomedicine. 2017;24:56–61. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2016.11.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Ushijima M, Takashima M, Kunimura K, Kodera Y, Morihara N, Tamura K. Effects of S-1-propenylcysteine, a sulfur compound in aged garlic extract, on blood pressure and peripheral circulation in spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2018;70:559–565. doi: 10.1111/jphp.12865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Lau BH, Lam F, Wang-Cheng R. Effect of an odor-modified garlic preparation on blood lipids. Nutr Res. 1987;7:139–149. doi: 10.1016/S0271-5317(87)80026-X. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Nakagawa S, Masamoto K, Sumiyoshi H, Kunihiro K, Fuwa T. Effect of raw and extracted-aged garlic juice on growth of young rats and their organs after peroral administration (author's transl) J Toxicol Sci. 1980;5:91–112. doi: 10.2131/jts.5.91. (In Japanese) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Sumiyoshi H, Kanezawa A, Masamoto K, Harada H, Nakagami S, Yokota A, Nishikawa M, Nakagawa S. Chronic toxicity test of garlic extract in rats. J Toxicol Sci. 1984;9:61–75. doi: 10.2131/jts.9.61. (In Japanese) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Aged Garlic Extract™, corp-author. Wakunaga of America Co., Ltd.; Mission Viejo, CA: 2015. [Mar;2019 ]. Research Excerpts from Peer Reviewed Scientific Journals & Scientific Meetings. [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.