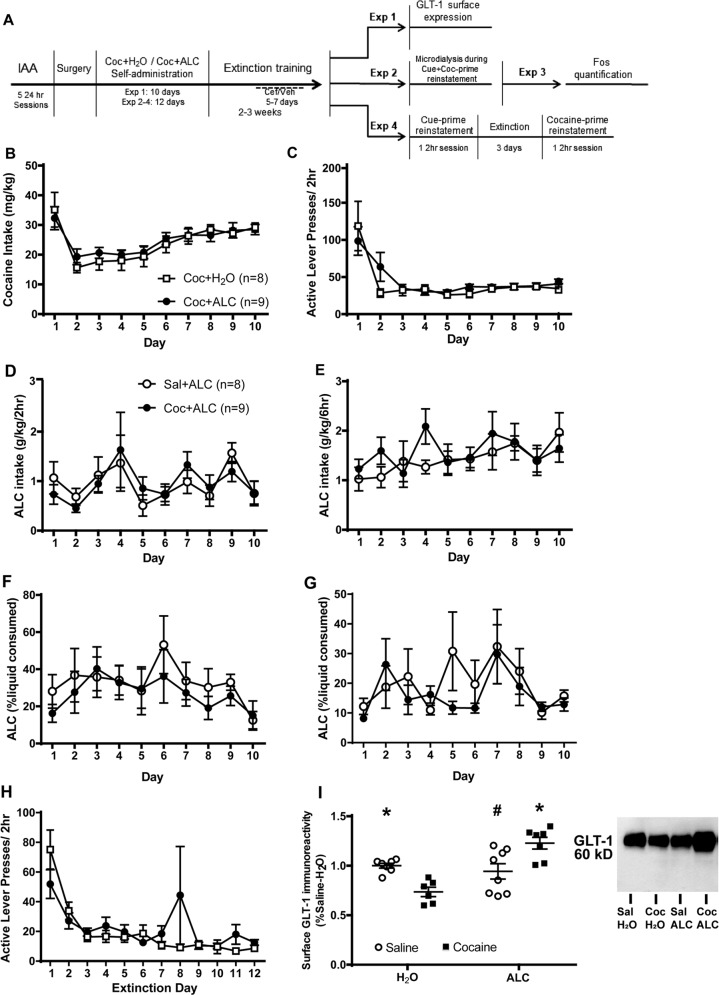
Fig. 1.
Access to alcohol immediately following cocaine or saline self-administration sessions did not alter intake of either cocaine or alcohol. a Timeline of methods for all experiments. b Mean cocaine intake (mg/kg) attained during 2 h intravenous cocaine self-administration sessions did not differ between rats afforded 2-bottle choice between water and alcohol (ALC) and those given only water. c Mean number of active lever presses during self-administration also did not differ between groups. d, e The amount of alcohol intake during the 2 and 6 h access to alcohol did not differ between groups that self-administered cocaine or saline. f, g The percent liquid consumed that was alcohol did not differ between groups when assessed at 2 and 6 h after presentation of bottles. h Active lever presses during extinction did not differ between groups. i Surface GLT-1 expression was reduced in the NA core of Coc-H2O rats relative to SAL-H2O rats. Coc-ALC rats displayed greater expression relative to Coc-H2O and Sal-ALC rats. * = p < 0.05 vs. Coc-H2O; # = p < 0.05 vs. Coc-ALC